Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2082-2091.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.04
Xiaohui QIU1( ), Meng WANG2, Jiangjie TANG3, Jianda ZHOU4, Chen JIN5(
), Meng WANG2, Jiangjie TANG3, Jianda ZHOU4, Chen JIN5( )
)
Received:2024-12-05
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Chen JIN
E-mail:keyi0540658@163.com;oyqn845ifgi265@163.com
Xiaohui QIU, Meng WANG, Jiangjie TANG, Jianda ZHOU, Chen JIN. Chitosan hydrogel loaded with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes healing of chronic diabetic wounds in rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2082-2091.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.04
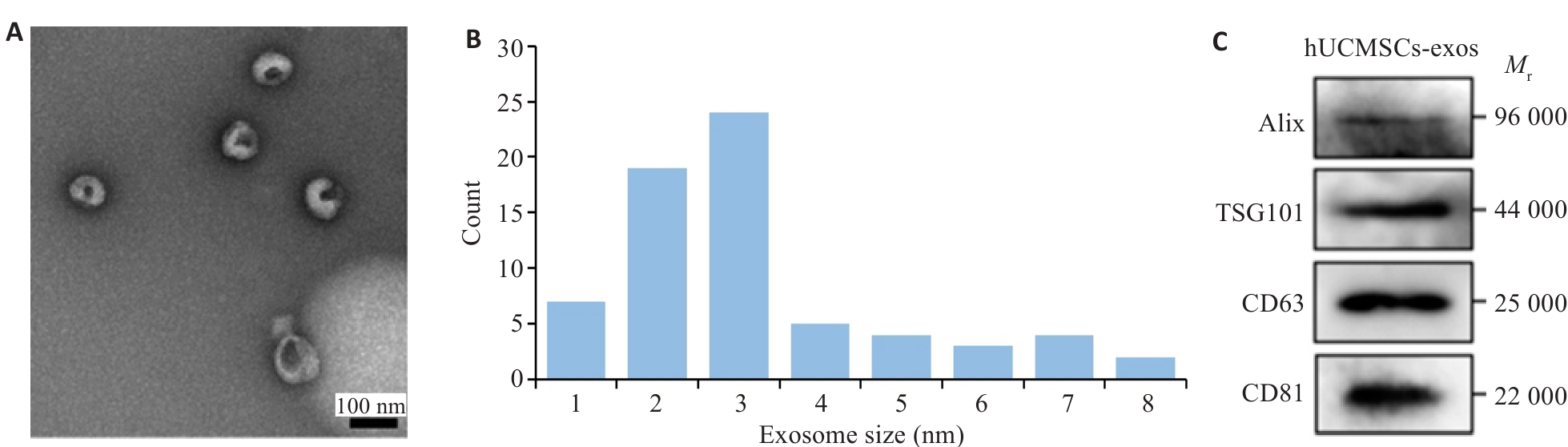
Fig.1 Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUVECs)-derived exosomes (hUCMSC-exos). A: Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of hUCMSC-exos. B: Histogram showing the diameter and concentration distribution of hUCMSC-exos. C: Western blotting of exosomal markers (Alix, TSG101, CD63, and CD81) in hUCMSC-exos.
| Concentration | IGT (℃) | Gelation time at 37 ℃ (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 20% | 17.2±1.4 | 92.7±6.3 |
| 22% | 16.3±1.2 | 78.5±5.2 |
| 24% | 14.2±1.5 | 66.3±3.4 |
| 26% | 12.9±1.1 | 51.2±2.7 |
| 28% | 11.8±0.9 | 46.9±2.9 |
Tab.1 Initial gelation temperature (IGT) of different concentrations of Exos@CS-Gel and their gelation time at 37 ℃ (Mean±SD)
| Concentration | IGT (℃) | Gelation time at 37 ℃ (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 20% | 17.2±1.4 | 92.7±6.3 |
| 22% | 16.3±1.2 | 78.5±5.2 |
| 24% | 14.2±1.5 | 66.3±3.4 |
| 26% | 12.9±1.1 | 51.2±2.7 |
| 28% | 11.8±0.9 | 46.9±2.9 |
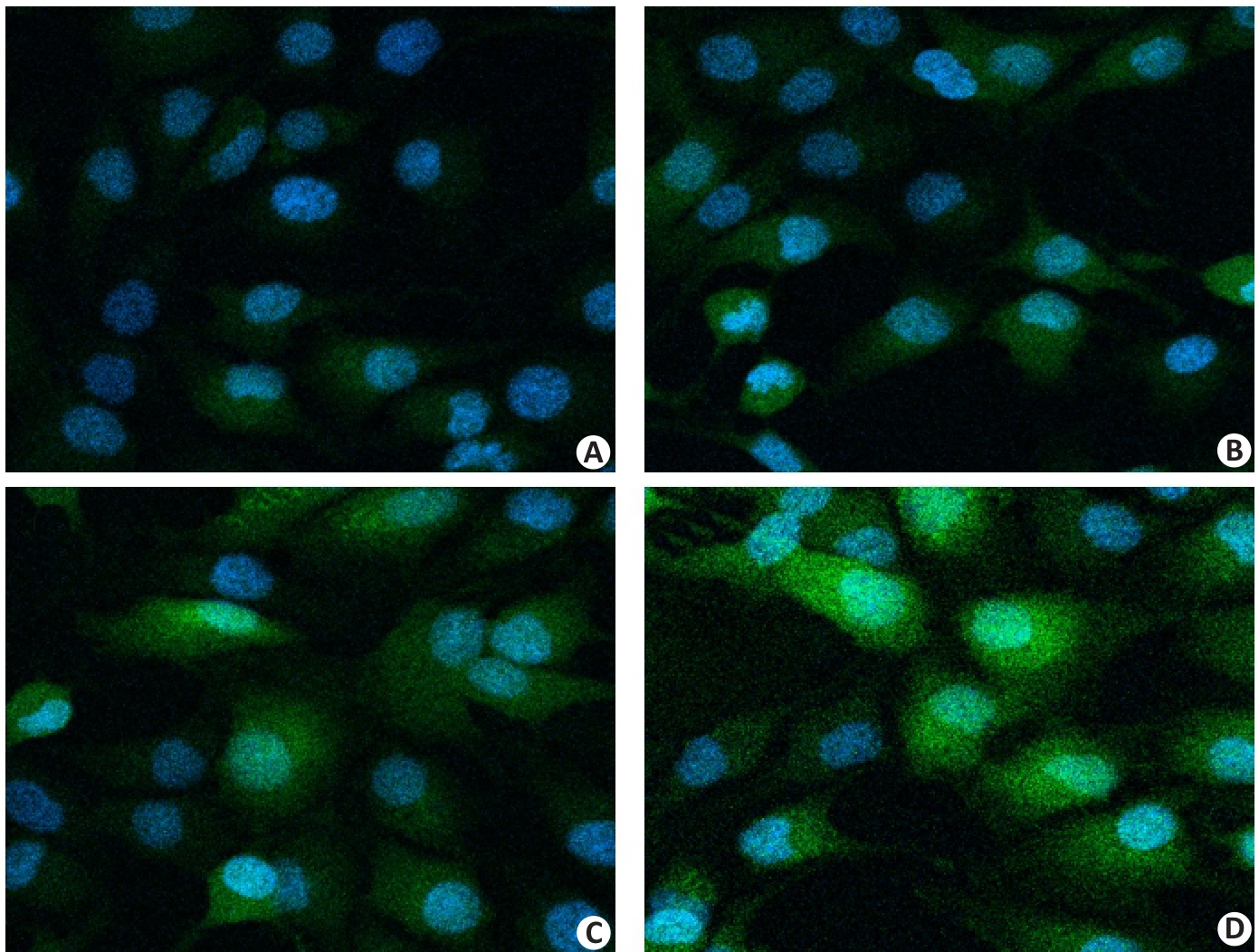
Fig.2 Cellular localization of exosomes tracked by PKH67 staining (Original magnification: ×400). A: PBS group. B: CS group. C: hUCMSCs-exos group. D: Exos@CS-Gel group. Green indicates PKH67 (exosome staining dye), and blue indicates DAPI (nuclear staining dye).
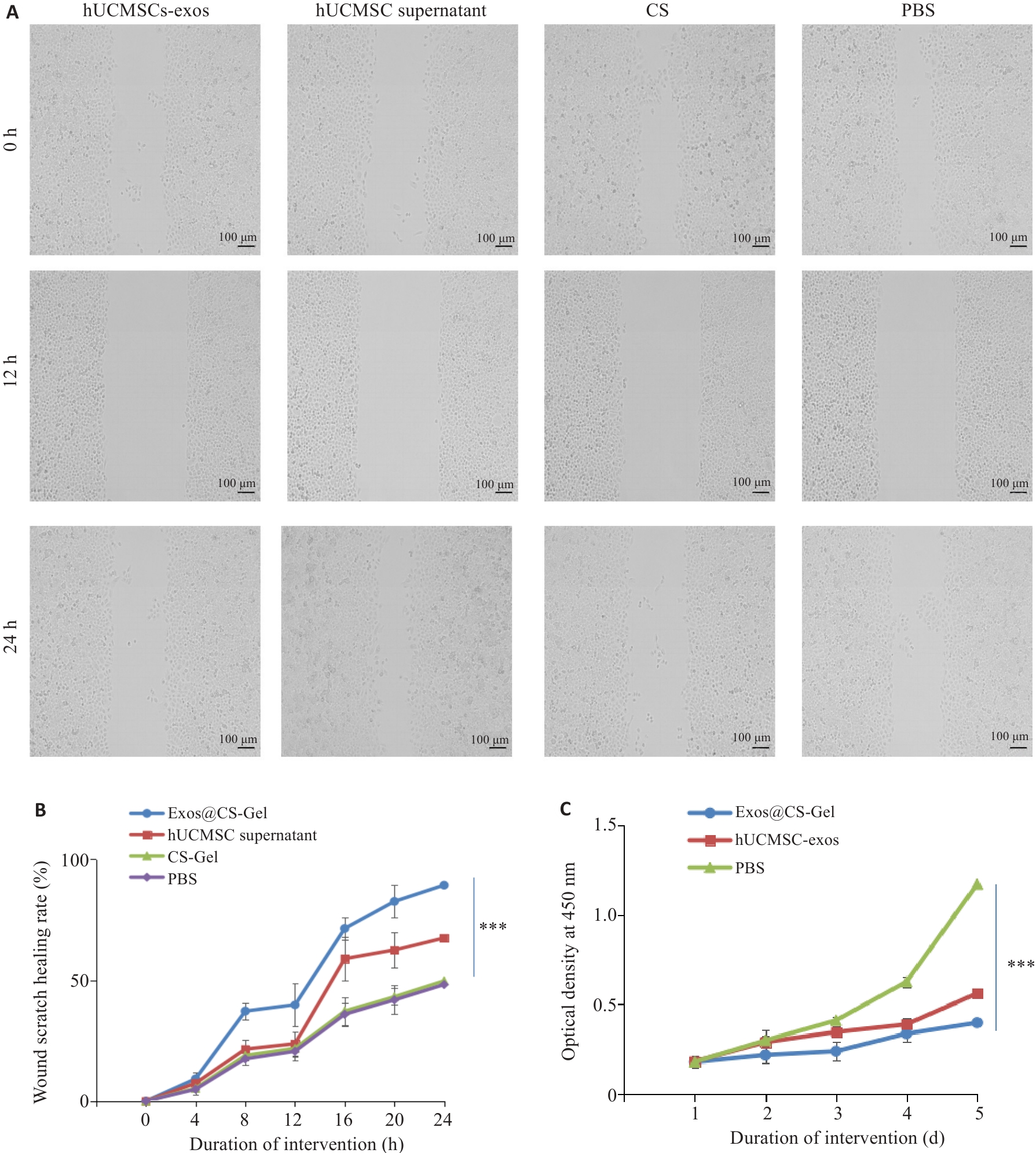
Fig.3 Effect of Exos@CS-Gel on HUVEC migration and proliferation. A: Wound healing assay showing the effect of Exos@CS-Gel on HUVEC cell migration ability. B: Comparison of wound healing rates among different groups. C: CCK-8 assay evaluating the effect of Exos@CS-Gel on HUVEC proliferation ability. ***P<0.001.
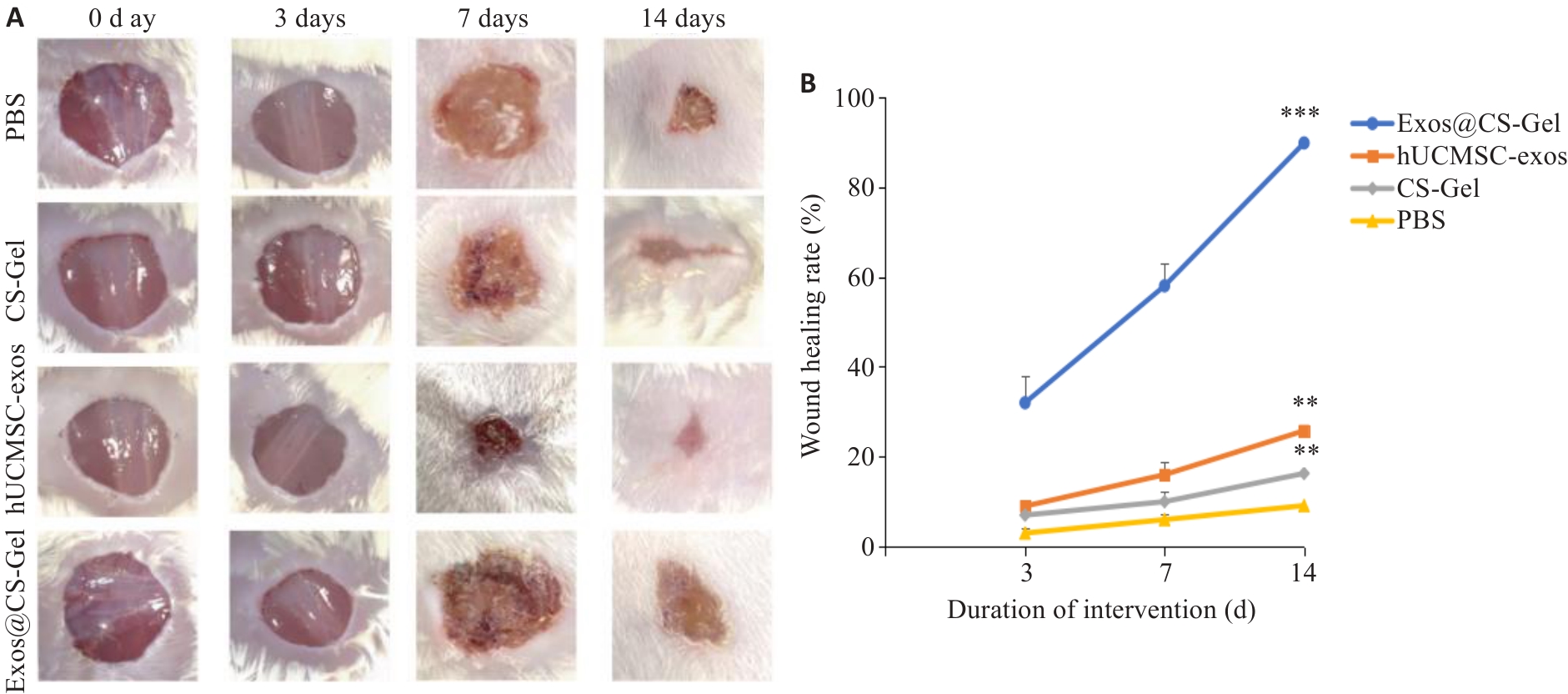
Fig.4 Wound healing c in each group of rats. A: Representative wound images of each group on days 0, 3, 7, 14. B: Comparison of wound area changes over time among the groups. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs PBS group.
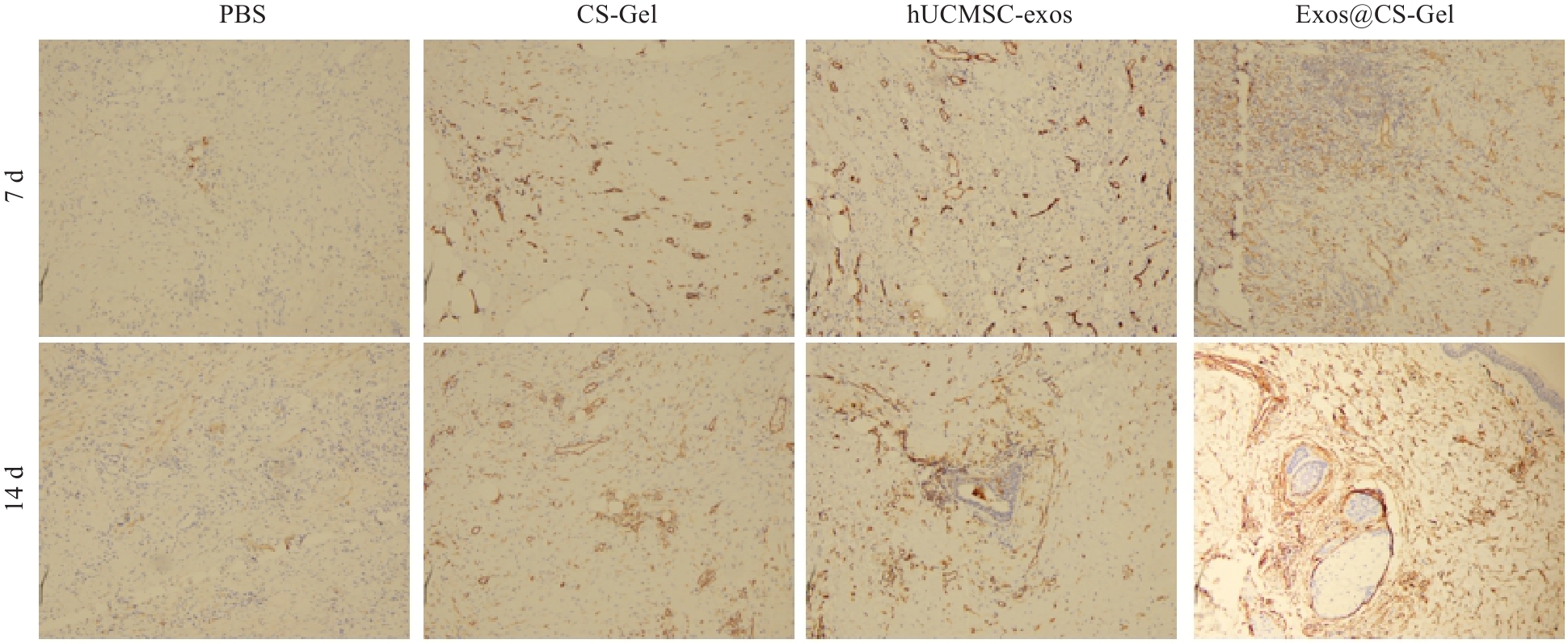
Fig.6 Effect of Exos@CS-Gel on angiogenesis in rat wound tissues assess by immunohistochemical detection of CD31 expression (vascular endothelial cell marker) in the wound tissues from each group on day 7 and 14 after the treatments (immunohistochemical staining, ×100).
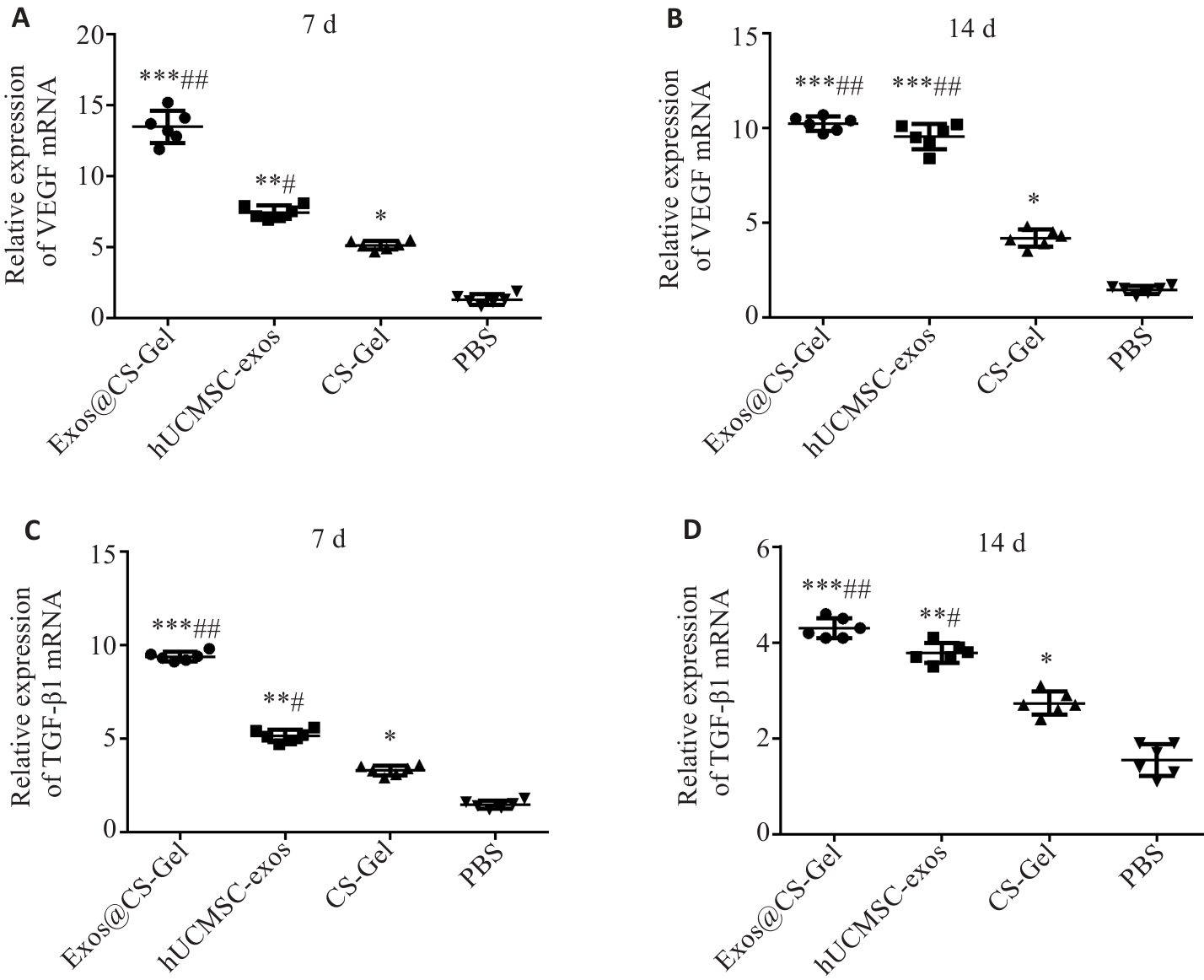
Fig.8 Effect of Exos@CS-Gel on VEGF and TGF-β1 expression levels in rat wound tissues, assessed by qRT-PCR of mRNA expression levels of VEGF (A, B) and TGF-β1 (C, D) in the wound granulation tissues on day 7 and day 14 after treatments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs PBS group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CS-Gel group.
| [1] | McGuire J, Thomson A, Kennedy PG. The biomechanics of diabetic foot amputation[J]. Wounds, 2021: WNDS20210414-2. doi:10.25270/wnds/041421.01 |
| [2] | Jiang PN, Li QH, Luo YH, et al. Current status and progress in research on dressing management for diabetic foot ulcer[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1221705. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1221705 |
| [3] | Ferreira G, Faria S, Carvalho A, et al. Relaxation intervention to improve diabetic foot ulcer healing: Results from a pilot randomized controlled study[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2023, 31(4): 528-41. doi:10.1111/wrr.13085 |
| [4] | Pereira MG, Vilaça M, Pedras S, et al. Wound healing and healing process in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: a survival analysis study[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2023, 198: 110623. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110623 |
| [5] | Rehman ZU, Khan J, Noordin S. Diabetic foot ulcers: contemporary assessment and management[J]. J Pak Med Assoc, 2023, 73(7): 1480-7. doi:10.47391/jpma.6634 |
| [6] | Deng HB, Li BH, Shen Q, et al. Mechanisms of diabetic foot ulceration: a review[J]. J Diabetes, 2023, 15(4): 299-312. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13372 |
| [7] | Ju YK, Hu Y, Yang P, et al. Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration[J]. Mater Today Bio, 2022, 18: 100522. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100522 |
| [8] | Zou JX, Yang WN, Cui WS, et al. Therapeutic potential and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioactive materials in tendon-bone healing[J]. J Nanobio-technology, 2023, 21(1): 14. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-01778-6 |
| [9] | Wang T, Gao HQ, Wang DZ, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes in the treatment of Melasma and its percutaneous penetration[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2023, 55(2): 178-89. doi:10.1002/lsm.23628 |
| [10] | Liu YY, Zhang MW, Liao Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote murine skin wound healing by neutrophil and macrophage modulations revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1142088. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142088 |
| [11] | Zhang KY, Zhao XN, Chen XN, et al. Enhanced therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes with an injectable hydrogel for hindlimb ischemia treatment[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10(36): 30081-91. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b08449 |
| [12] | Li ZT, Xing XL, Zhao CR, et al. A rapid interactive chitosan-based medium with antioxidant and pro-vascularization properties for infected burn wound healing[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2024, 333: 121991. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.121991 |
| [13] | 陈金妙, 朱灵颖, 廖米荣, 等. 糖尿病慢性伤口感染患者的临床特点及伤口愈合的危险因素分析[J]. 中国现代医生, 2022, 60(27): 50-4. |
| [14] | Bi HS, Li H, Zhang C, et al. Stromal vascular fraction promotes migration of fibroblasts and angiogenesis through regulation of extracellular matrix in the skin wound healing process[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10(1): 302. doi:10.1186/s13287-019-1415-6 |
| [15] | Kim J, Lee CB, Shin Y, et al. sEVs from tonsil-derived mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis through miR-486-5p[J]. Mol Ther, 2021, 29(4): 1471-86. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.12.025 |
| [16] | Keramaris NC, Kaptanis S, Moss HL, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in bone healing[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2012, 7(4): 293-301. doi:10.2174/157488812800793081 |
| [17] | Wang LM, Chen J, Song J, et al. Activation of the Wnt/β‑catenin signalling pathway enhances exosome production by hucMSCs and improves their capability to promote diabetic wound healing[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 373. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02650-x |
| [18] | Teng LP, Maqsood M, Zhu M, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells accelerate diabetic wound healing via promoting M2 macrophage polarization, angiogenesis, and collagen deposition[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(18): 10421. doi:10.3390/ijms231810421 |
| [19] | Yan CC, Xv Y, Lin Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerate diabetic wound healing via ameliorating oxidative stress and promoting angiogenesis[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2022, 10: 829868. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.829868 |
| [20] | 蒋 杨, 陈 博, 王贤君, 等. 人脐带间充质干细胞治疗肺部疾病的研究与应用进展[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2022, 27(1): 124-9. |
| [21] | He SH, Hou TY, Zhou JL, et al. Endothelial cells promote migration of mesenchymal stem cells via PDGF-BB/PDGFR β-src-Akt in the context of inflammatory microenvironment upon bone defect[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2022, 2022: 2401693. doi:10.1155/2022/2401693 |
| [22] | Song YL, You YC, Xu XY, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes biopotentiated extracellular matrix hydrogels accelerate diabetic wound healing and skin regeneration[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(30): e2304023. doi:10.1002/advs.202304023 |
| [23] | 张丁丁, 郭 荣, 赵松峰, 等. 载锰单原子纳米酶和驱蛔素的壳聚糖水凝胶制备及其抗幽门螺杆菌活性[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(6): 1925-34. |
| [24] | 由子樱, 伍彦霖, 孙一民, 等. 搭载米诺环素-壳聚糖纳米粒复合水凝胶用于牙周炎治疗的初步研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(1): 11-20. |
| [25] | Kwon SK, Song JJ, Cho CG, et al. Polycaprolactone spheres and theromosensitive Pluronic F127 hydrogel for vocal fold augmen-tation: in vivo animal study for the treatment of unilateral vocal fold palsy[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(7): 1694-703. doi:10.1002/lary.23879 |
| [26] | Wang CG, Wang M, Xu TZ, et al. Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(1): 65-76. doi:10.7150/thno.29766 |
| [27] | Yang MY, Li JP, Gu P, et al. The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment[J]. Bioact Mater, 2021, 6(7): 1973-87. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.010 |
| [28] | Amiri Z, Molavi AM, Amani A, et al. Fabrication, characterization and wound-healing properties of core-shell SF@chitosan/ZnO/Astragalus arbusculinus gum nanofibers[J]. Nanomedicine (Lond), 2024, 19(6): 499-518. doi:10.2217/nnm-2023-0311 |
| [29] | le Noble F, Kupatt C. Interdependence of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis in development and disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(7): 3879. doi:10.3390/ijms23073879 |
| [30] | Idrovo JP, Yang WL, Jacob A, et al. Combination of adrenomedullin with its binding protein accelerates cutaneous wound healing[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0120225. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120225 |
| [31] | Oviedo-Socarrás T, Vasconcelos AC, Barbosa IX, et al. Diabetes alters inflammation, angiogenesis, and fibrogenesis in intra-peritoneal implants in rats[J]. Microvasc Res, 2014, 93: 23-9. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2014.02.011 |
| [32] | Chuar PF, Ng YT, Phang SCW, et al. Tocotrienol-rich vitamin E (tocovid) improved nerve conduction velocity in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a phase II double-blind, randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(11): 3770. doi:10.3390/nu13113770 |
| [1] | Haimei BO, Xinying CAO, Pingchuan XING, Zhijun WANG. Exosome-derived miR-1275 mediates IL-38 upregulation in lymphocytes to suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of myocardial cells in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1608-1615. |
| [2] | Changlong FU, Lu XU, Ruolan CHEN, Jinghang YANG, Yan LUO, Yanfeng HUANG. Tougu Xiaotong Capsule promotes repair of osteoarthritis cartilage damage in mice by activating the CXCL12/GDF5 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1122-1130. |
| [3] | Shuyu TU, Xiangyu CHEN, Chenghui LI, Danping HUANG, Li ZHANG. Buyang Huanwu Decoction delays vascular aging in rats through exosomal miR-590-5p signal-mediated macrophage polarization [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [4] | Wei SU, Houhua LAI, Xin TANG, Qun ZHOU, Yachun TANG, Hao FU, Xuancai CHEN. Apelin promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in bladder cancer by activating the FGF2/FGFR1 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1289-1296. |
| [5] | Yanpeng PU, Zhen WANG, Haoran CHU. Eye acupuncture improves neural function in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting angiogenesis via upregulating METTL3-mediated m6A methylation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 921-928. |
| [6] | Zhiliang CHEN, Yonggang YANG, Xia HUANG, Yan CHENG, Yuan QU, Qiqi HENG, Yujia FU, Kewei LI, Ning GU. Differential expressions of exosomal miRNAs in patients with chronic heart failure and hyperuricemia: diagnostic values of miR-27a-5p and miR-139-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 43-51. |
| [7] | Siqi HE, Nan WEN, Xun CHEN, Yue WANG, Tin ZHANG, Yandong MU. Lycium barbarum glycopeptide reduces bone loss caused by exosomes derived from human gingival fibroblasts with radiation exposure [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1752-1759. |
| [8] | Rong DAI, Zeping CAO, Chuanjiao LIU, Yong GE, Meng CHENG, Weili WANG, Yizhen CHEN, Lei ZHANG, Yiping WANG. Qingshen Granules alleviates renal fibrosis in mice by regulating exosomes, miR-330-3p, and CREBBP expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1431-1440. |
| [9] | Zhiyong KE, Zicheng HUANG, Ruolin HE, Qian ZHANG, Sixu CHEN, Zhong-Kai CUI, Jing DING. Hmga2 knockdown enhances osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and accelerates bone defect healing in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1227-1235. |
| [10] | Guangya CHEN, Xingliang XIANG, Zhaoxiang ZENG, Rongzeng HUANG, Shuna JIN, Mingzhong XIAO, Chengwu SONG. Regulatory effect of Diwu Yanggan Decoction on lysoglycerophospholipids in circulating exosomes in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1382-1388. |
| [11] | Tong YUAN, Yuying GUO, Junling ZHANG, Saijun FAN. Normal mouse serum alleviates radiation pneumonitis in mice by inhibiting the focal adhesion signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 801-809. |
| [12] | RONG Shengwei, LI Hongfang, WEI Yiran, FENG Zihang, GAN Lu, DENG Zhonghao, ZHAO Liang. Zinc finger protein-36 deficiency inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and preosteoblasts by activating the ERK/MAPK pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 697-705. |
| [13] | Kun WANG, Haoxiang FANG, Xiaomei CAO, Ziheng ZHU. MiR-139-5p regulates the Notch/RBP-J/Hes1 axis to promote homing of bone mesenchymal stem cells in bronchial asthma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2283-2290. |
| [14] | Fenxia LI, Haosheng LIN, Yilin LI, Wenqian ZHU, Yuanjie SUN, Yuan HUANG, Yuwen QIU, Xia QIN, Qingxian CHANG. Differential expression profile of miRNAs in maternal amniotic fluid exosomes in fetuses with isolated ventriculomegaly [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2256-2264. |
| [15] | LUO Rui, TIAN Longhai, YANG Yongyao. Galangin inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced angiogenic activity in human aortic endothelial cells by downregulating lncRNA H19 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 52-59. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||