Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 150-161.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.18
Previous Articles Next Articles
Qiao CHU1( ), Xiaona WANG2, Jiaying XU3, Huilin PENG3, Yulin ZHAO3, Jing ZHANG3, Guoyu LU1, Kai WANG3(
), Xiaona WANG2, Jiaying XU3, Huilin PENG3, Yulin ZHAO3, Jing ZHANG3, Guoyu LU1, Kai WANG3( )
)
Received:2024-08-29
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Kai WANG
E-mail:chuqiao670906094@163.com;wangkai@swmu.edu.cn
Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.18
| Compound | Target genes | Number of targets |
|---|---|---|
| PSD | BLM, PTPN1, GPR6, APEX1, KDM1A, GPR55, PTGS1, KLF5, TOP2A, TRIM24, NFKB1, SLC6A5, CLK4, ADAM10, CTSD, PDGFRA, NTRK3, NR3C2, CSNK2B, SCN2A, PTPN2, MTOR, TFPI, TLR4, SCN3A, PIK3R1, DUSP3, CYP3A4, PDE3A, GLRA1ITK, HSP90AB1, GRIA2, GRIN1, C5AR1, HSP90AA1, MMP1, FPR2, CFTR, ACACB, HDAC2, TLR8, S1PR5, SLC9A1, PSMB1, AURKB, NTSR2, HDAC7, LTA4H, F13A1, SOAT1, ATG4B, NFE2L2, CACNA1B, CHUK, NR2E3, CDK1, ADORA1, CYSLTR2, AR, CDC25B, MDM4, NR4A1, SLC40A1, SLC1A3, SCN4A, AKR1C3, CAPN1, KIF11, WDR5, TERT, PRCP, HDAC5, MAP3K14, CHRM1, TACR2, QRFPR, NR1I2, GABRA1, PSMB9, ABL1, PTGER2, CBX4, PRMT1, ABCB1, CACNA1H, DCUN1D1, FAAH, FPR1, ACACA, MC4R, RXFP1, ADK, CDK5, PDGFRB, SLC1A2, METAP2, NOX1, PROC, PRSS1, PLA2G2A, MME, PTK2B, RECQ2, PTP1B, APE, AOF2, COX1, BTEB2, TOP2, RNF82, GLYT2, KUZ, CPSD, PDGFR2, TRKC, MCR, CK2N, HBA, PTPT, FRAP, LACI, KIAA1356, GRB1, VHR, CYP3A3, EMT, HSP90B, GLUR2, NMDAR1, C5AR, HSP90A, CLG, FPRH1, ABCC7, ACC2, UNQ249/PRO286, EDG8, APNH1, PSC5, AIK2, HDAC7A, LTA4, F13A, ACACT, APG4B, NRF2, CACH5, IKKA, PNR, CDC2, CYSLT2, DHTR, CDC25HU2, MDMX, GFRP1, FPN, EAAT1, DDH1, CANPL1, EG5, BIG3, EST2, PCP, KIAA0600, NIK, NK2R, GPR103, PXR, LMP2, ABL, HMT2, MDR1, DCN1, FAAH1, ACAC, LGR7, CDKN5, PDGFR, EAAT2, MNPEP, MOX1, TRP1, PLA2B, EPN, FAK2, RECQL3, APE1, KDM1, CKLF, TIF1, NET1, MADM, RHEPDGFRA, MLR, G5A, NAC2, FRAP1, TFPI1, NAC3, LYK, HSPC2, C5R1, HSPC1, FPRL1, ACCB, NHE1, AIM1, ACACT1, AUTL1, CACNL1A5, TCF16, RNR, CDC28A, CYSLT2R, NR3C4, HMR, FPN1, GLAST, HSD17B5, PIG30, KNSL1, TCS1, NKNAR, PSMB6i, JTK7, HRMT1L2, PGY1, DCUN1L1, ACC1, PSSALRE, PDGFR1, GLT1, P67EIF2, NOH1, TRY1, PLA2L, PYK2, APEX, KIAA0601, IKLF, TIF1A, SCN2A1, FRAP2, HSPCB, HSPCA, LXA4R, AIRK2, ACAT, KIAA0943, CDKN1, PSEC0146, NAK1, IREG1, GLAST1, KIAA0119, TRIP5, TRT, TAC2R, RING12, IR1B4, RP42, ACCA, TRYP1, RASF-A, RAFTK, SCCRO, APX, LSD1, HAP1, REF1, RAPT1, SCN2A2, RAFT1, STK12, STK5, ARK2, STAT, ACAT1, P34CDC2, MSTP079, SLC11A3, PGFS, STK1, SOAT | 285 |
Tab.1 Potential targets of Pulsatilla saponin D (PSD)
| Compound | Target genes | Number of targets |
|---|---|---|
| PSD | BLM, PTPN1, GPR6, APEX1, KDM1A, GPR55, PTGS1, KLF5, TOP2A, TRIM24, NFKB1, SLC6A5, CLK4, ADAM10, CTSD, PDGFRA, NTRK3, NR3C2, CSNK2B, SCN2A, PTPN2, MTOR, TFPI, TLR4, SCN3A, PIK3R1, DUSP3, CYP3A4, PDE3A, GLRA1ITK, HSP90AB1, GRIA2, GRIN1, C5AR1, HSP90AA1, MMP1, FPR2, CFTR, ACACB, HDAC2, TLR8, S1PR5, SLC9A1, PSMB1, AURKB, NTSR2, HDAC7, LTA4H, F13A1, SOAT1, ATG4B, NFE2L2, CACNA1B, CHUK, NR2E3, CDK1, ADORA1, CYSLTR2, AR, CDC25B, MDM4, NR4A1, SLC40A1, SLC1A3, SCN4A, AKR1C3, CAPN1, KIF11, WDR5, TERT, PRCP, HDAC5, MAP3K14, CHRM1, TACR2, QRFPR, NR1I2, GABRA1, PSMB9, ABL1, PTGER2, CBX4, PRMT1, ABCB1, CACNA1H, DCUN1D1, FAAH, FPR1, ACACA, MC4R, RXFP1, ADK, CDK5, PDGFRB, SLC1A2, METAP2, NOX1, PROC, PRSS1, PLA2G2A, MME, PTK2B, RECQ2, PTP1B, APE, AOF2, COX1, BTEB2, TOP2, RNF82, GLYT2, KUZ, CPSD, PDGFR2, TRKC, MCR, CK2N, HBA, PTPT, FRAP, LACI, KIAA1356, GRB1, VHR, CYP3A3, EMT, HSP90B, GLUR2, NMDAR1, C5AR, HSP90A, CLG, FPRH1, ABCC7, ACC2, UNQ249/PRO286, EDG8, APNH1, PSC5, AIK2, HDAC7A, LTA4, F13A, ACACT, APG4B, NRF2, CACH5, IKKA, PNR, CDC2, CYSLT2, DHTR, CDC25HU2, MDMX, GFRP1, FPN, EAAT1, DDH1, CANPL1, EG5, BIG3, EST2, PCP, KIAA0600, NIK, NK2R, GPR103, PXR, LMP2, ABL, HMT2, MDR1, DCN1, FAAH1, ACAC, LGR7, CDKN5, PDGFR, EAAT2, MNPEP, MOX1, TRP1, PLA2B, EPN, FAK2, RECQL3, APE1, KDM1, CKLF, TIF1, NET1, MADM, RHEPDGFRA, MLR, G5A, NAC2, FRAP1, TFPI1, NAC3, LYK, HSPC2, C5R1, HSPC1, FPRL1, ACCB, NHE1, AIM1, ACACT1, AUTL1, CACNL1A5, TCF16, RNR, CDC28A, CYSLT2R, NR3C4, HMR, FPN1, GLAST, HSD17B5, PIG30, KNSL1, TCS1, NKNAR, PSMB6i, JTK7, HRMT1L2, PGY1, DCUN1L1, ACC1, PSSALRE, PDGFR1, GLT1, P67EIF2, NOH1, TRY1, PLA2L, PYK2, APEX, KIAA0601, IKLF, TIF1A, SCN2A1, FRAP2, HSPCB, HSPCA, LXA4R, AIRK2, ACAT, KIAA0943, CDKN1, PSEC0146, NAK1, IREG1, GLAST1, KIAA0119, TRIP5, TRT, TAC2R, RING12, IR1B4, RP42, ACCA, TRYP1, RASF-A, RAFTK, SCCRO, APX, LSD1, HAP1, REF1, RAPT1, SCN2A2, RAFT1, STK12, STK5, ARK2, STAT, ACAT1, P34CDC2, MSTP079, SLC11A3, PGFS, STK1, SOAT | 285 |
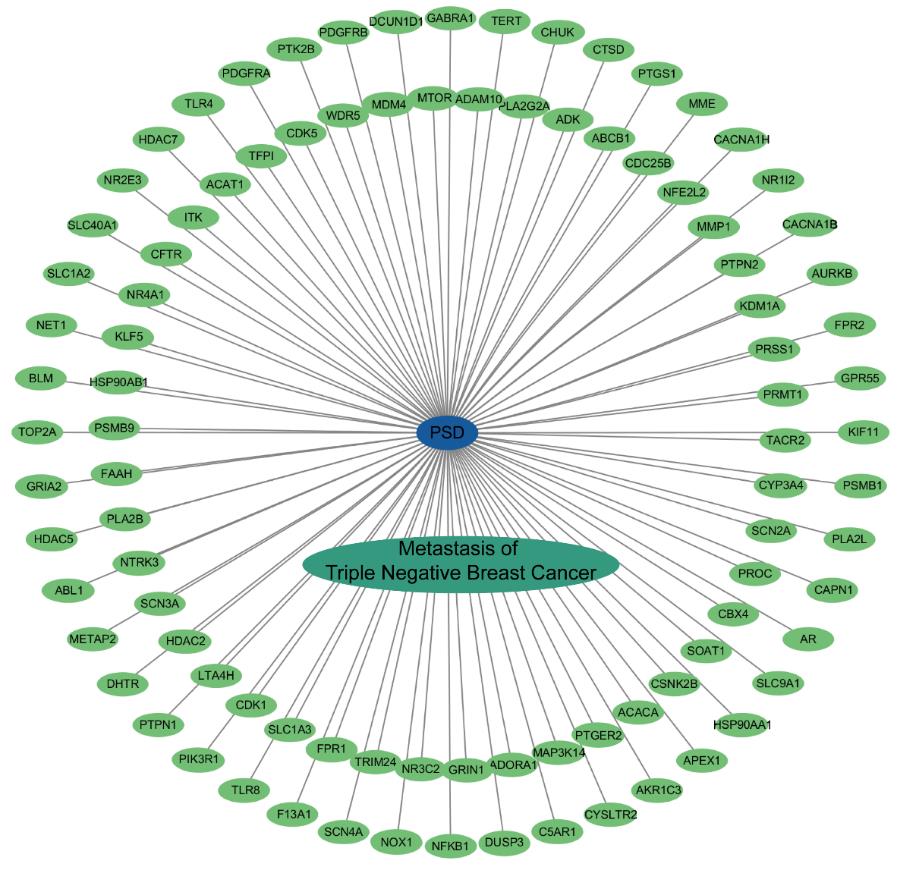
Fig.2 "PSD-target-disease" interaction network. Blue oval nodes represent compound PSD, green oval nodes represent crossover genes, cyan oval nodes denote triple-negative breast cancer metastasis (disease), and gray lines stand for interactions.
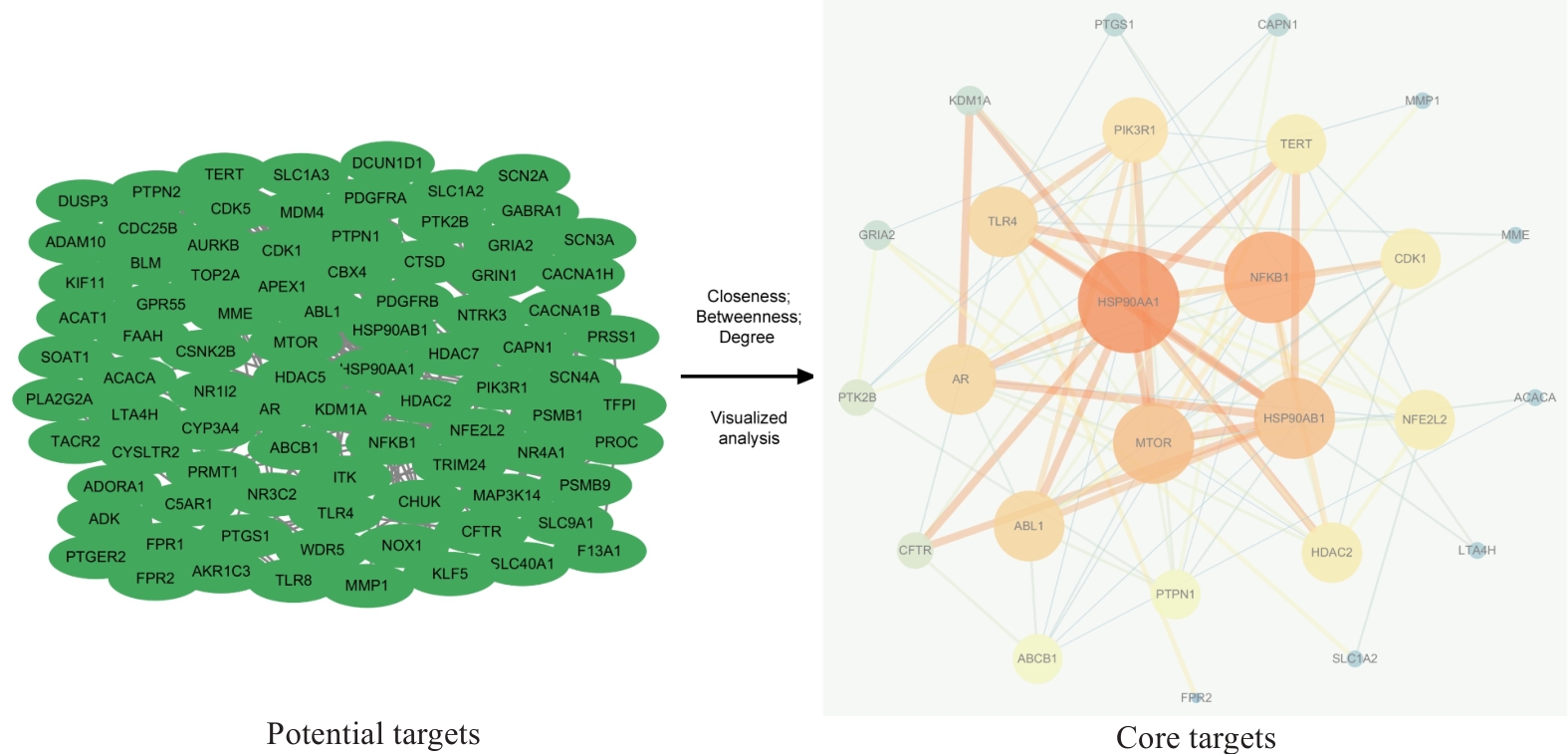
Fig.3 Visualization of PPI network for PSD treatment of TNBC invasion and metastasis. Green oval nodes on the left side represent 94 potential targets and the circular nodes on the right side represent 26 core targets. The size and color shades of the nodes are proportional to their importance, and the thickness and color shades of the lines are proportional to the importance between nodes.
| Core targets | Degree unDir | PDB ID |
|---|---|---|
| HSP90AA1 | 39 | 6GR5 |
| HSP90AB1 | 33 | 6N8Y |
| NFKB1 | 27 | 1SVC |
| MTOR | 24 | 4JSN |
| HDAC2 | 23 | 7JS8 |
| ABL1 | 20 | 5HU9 |
| CDK1 | 19 | 6GU2 |
| TLR4 | 18 | 2Z62 |
| TERT | 17 | 5UGW |
| AR | 17 | 8E1A |
| PIK3R1 | 17 | 7PG5 |
| NFE2L2 | 16 | 7X5G |
| ABCB1 | 12 | 7A69 |
| KDM1A | 12 | 7E0G |
| CFTR | 11 | 5TFJ |
| PTPN1 | 11 | 7MN9 |
| PTGS1 | 10 | 6Y3C |
| GRIA2 | 9 | 7F3O |
| MME | 8 | 6SUK |
| PTK2B | 7 | 3CC6 |
| ACACA | 6 | 2YL2 |
| FPR2 | 6 | 6LW5 |
| CAPN1 | 6 | 7W7O |
| SLC1A2 | 5 | 7VR7 |
| LTA4H | 4 | 3U9W |
| MMP1 | 4 | 966C |
Tab.2 Core targets of PSD for the treatment of TNBC invasion and metastasis
| Core targets | Degree unDir | PDB ID |
|---|---|---|
| HSP90AA1 | 39 | 6GR5 |
| HSP90AB1 | 33 | 6N8Y |
| NFKB1 | 27 | 1SVC |
| MTOR | 24 | 4JSN |
| HDAC2 | 23 | 7JS8 |
| ABL1 | 20 | 5HU9 |
| CDK1 | 19 | 6GU2 |
| TLR4 | 18 | 2Z62 |
| TERT | 17 | 5UGW |
| AR | 17 | 8E1A |
| PIK3R1 | 17 | 7PG5 |
| NFE2L2 | 16 | 7X5G |
| ABCB1 | 12 | 7A69 |
| KDM1A | 12 | 7E0G |
| CFTR | 11 | 5TFJ |
| PTPN1 | 11 | 7MN9 |
| PTGS1 | 10 | 6Y3C |
| GRIA2 | 9 | 7F3O |
| MME | 8 | 6SUK |
| PTK2B | 7 | 3CC6 |
| ACACA | 6 | 2YL2 |
| FPR2 | 6 | 6LW5 |
| CAPN1 | 6 | 7W7O |
| SLC1A2 | 5 | 7VR7 |
| LTA4H | 4 | 3U9W |
| MMP1 | 4 | 966C |
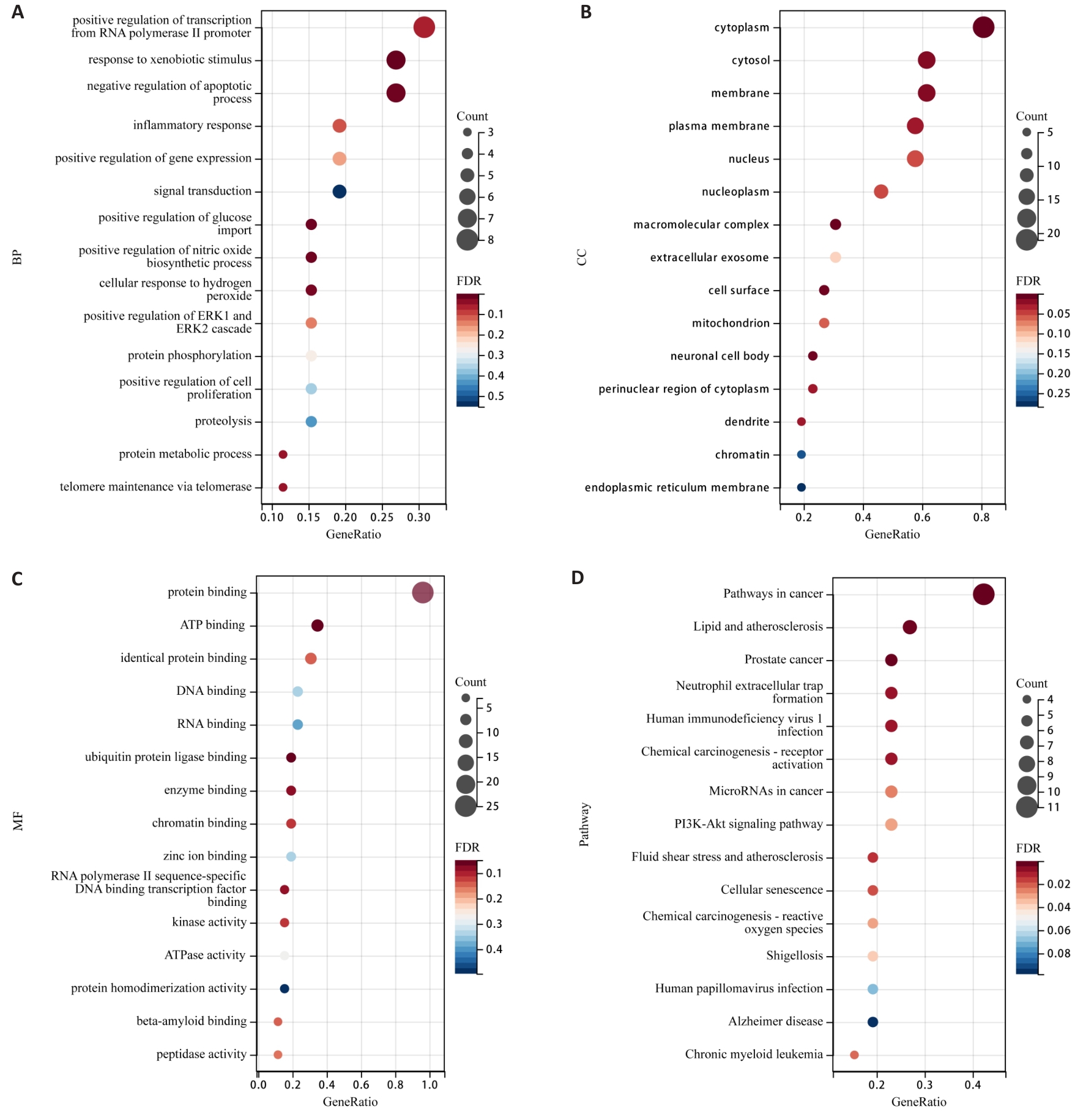
Fig.4 Bubble plots of GO function and KEGG pathway enrichment for PSD inhibition of TNBC invasion and metastasis. A: Enrichment analysis of BP. B: Enrichment analysis of CC. C: Enrichment analysis of MF. D: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
| ID | Pathways | P | Number of related genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 0.000000974 | 11 |
| hsa05417 | Lipid and atherosclerosis | 0.000026000 | 7 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 0.000007060 | 6 |
| hsa04613 | Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | 0.000184000 | 6 |
| hsa05170 | Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05207 | Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05206 | MicroRNAs in cancer | 0.001673574 | 6 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 0.003182088 | 6 |
| hsa05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 0.000618000 | 5 |
| hsa04218 | Cellular senescence | 0.000953000 | 5 |
| hsa05208 | Chemical carcinogenesis-reactive oxygen species | 0.003535389 | 5 |
| hsa05131 | Shigellosis | 0.005091764 | 5 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 0.014031422 | 5 |
| hsa05010 | Alzheimer disease | 0.022984313 | 5 |
| hsa05220 | Chronic myeloid leukemia | 0.001299397 | 4 |
| hsa05235 | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | 0.002047819 | 4 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 0.002394257 | 4 |
| hsa04914 | Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | 0.003020588 | 4 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 0.003644426 | 4 |
| hsa04152 | AMPK signaling pathway | 0.004886673 | 4 |
| hsa04910 | Insulin signaling pathway | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05135 | Yersinia infection | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05226 | Gastric cancer | 0.008693554 | 4 |
| hsa04217 | Necroptosis | 0.010557294 | 4 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 0.010919274 | 4 |
| hsa05225 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.012048446 | 4 |
| hsa04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | 0.012439336 | 4 |
| hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.015830764 | 4 |
| hsa05203 | Viral carcinogenesis | 0.020215918 | 4 |
| hsa05163 | Human cytomegalovirus infection | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa04024 | cAMP signaling pathway | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa05171 | Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 | 0.028568364 | 4 |
| hsa05132 | Salmonella infection | 0.033858771 | 4 |
| hsa05016 | Huntington disease | 0.056576135 | 4 |
| hsa04213 | Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | 0.013188318 | 3 |
| hsa05221 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 0.015766996 | 3 |
| hsa05212 | Pancreatic cancer | 0.020005321 | 3 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 0.02466712 | 3 |
| hsa04211 | Longevity regulating pathway | 0.026868984 | 3 |
| hsa05146 | Amoebiasis | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa05142 | Chagas disease | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.038349814 | 3 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 0.045714487 | 3 |
| hsa04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 0.047106228 | 3 |
Tab.3 KEGG pathway enrichment
| ID | Pathways | P | Number of related genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 0.000000974 | 11 |
| hsa05417 | Lipid and atherosclerosis | 0.000026000 | 7 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 0.000007060 | 6 |
| hsa04613 | Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | 0.000184000 | 6 |
| hsa05170 | Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05207 | Chemical carcinogenesis - receptor activation | 0.000298000 | 6 |
| hsa05206 | MicroRNAs in cancer | 0.001673574 | 6 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 0.003182088 | 6 |
| hsa05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 0.000618000 | 5 |
| hsa04218 | Cellular senescence | 0.000953000 | 5 |
| hsa05208 | Chemical carcinogenesis-reactive oxygen species | 0.003535389 | 5 |
| hsa05131 | Shigellosis | 0.005091764 | 5 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 0.014031422 | 5 |
| hsa05010 | Alzheimer disease | 0.022984313 | 5 |
| hsa05220 | Chronic myeloid leukemia | 0.001299397 | 4 |
| hsa05235 | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | 0.002047819 | 4 |
| hsa04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | 0.002394257 | 4 |
| hsa04914 | Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | 0.003020588 | 4 |
| hsa04931 | Insulin resistance | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 0.003550859 | 4 |
| hsa04066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 0.003644426 | 4 |
| hsa04152 | AMPK signaling pathway | 0.004886673 | 4 |
| hsa04910 | Insulin signaling pathway | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05135 | Yersinia infection | 0.006900929 | 4 |
| hsa05226 | Gastric cancer | 0.008693554 | 4 |
| hsa04217 | Necroptosis | 0.010557294 | 4 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 0.010919274 | 4 |
| hsa05225 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 0.012048446 | 4 |
| hsa04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | 0.012439336 | 4 |
| hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.015830764 | 4 |
| hsa05203 | Viral carcinogenesis | 0.020215918 | 4 |
| hsa05163 | Human cytomegalovirus infection | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa04024 | cAMP signaling pathway | 0.026104939 | 4 |
| hsa05171 | Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 | 0.028568364 | 4 |
| hsa05132 | Salmonella infection | 0.033858771 | 4 |
| hsa05016 | Huntington disease | 0.056576135 | 4 |
| hsa04213 | Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | 0.013188318 | 3 |
| hsa05221 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 0.015766996 | 3 |
| hsa05212 | Pancreatic cancer | 0.020005321 | 3 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 0.02466712 | 3 |
| hsa04211 | Longevity regulating pathway | 0.026868984 | 3 |
| hsa05146 | Amoebiasis | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa05142 | Chagas disease | 0.034548353 | 3 |
| hsa04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.038349814 | 3 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 0.045714487 | 3 |
| hsa04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 0.047106228 | 3 |
| Compound | Targets | PDB ID | MM-GBSA dG Bind (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSD | MTOR | 4JSN | -32.00 |
| HDAC2 | 7JS8 | -17.49 | |
| ABL1 | 5HU9 | -30.56 | |
| CDK1 | 6GU2 | -32.77 | |
| TLR4 | 2Z62 | -19.87 | |
| TERT | 5UGW | -39.09 | |
| PIK3R1 | 7PG5 | -31.43 | |
| NFE2L2 | 7X5G | -43.75 | |
| KDM1A | 7E0G | -43.68 | |
| PTPN1 | 7MN9 | -20.59 |
Tab.4 Free energy of PSD binding to the core target proteins
| Compound | Targets | PDB ID | MM-GBSA dG Bind (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSD | MTOR | 4JSN | -32.00 |
| HDAC2 | 7JS8 | -17.49 | |
| ABL1 | 5HU9 | -30.56 | |
| CDK1 | 6GU2 | -32.77 | |
| TLR4 | 2Z62 | -19.87 | |
| TERT | 5UGW | -39.09 | |
| PIK3R1 | 7PG5 | -31.43 | |
| NFE2L2 | 7X5G | -43.75 | |
| KDM1A | 7E0G | -43.68 | |
| PTPN1 | 7MN9 | -20.59 |
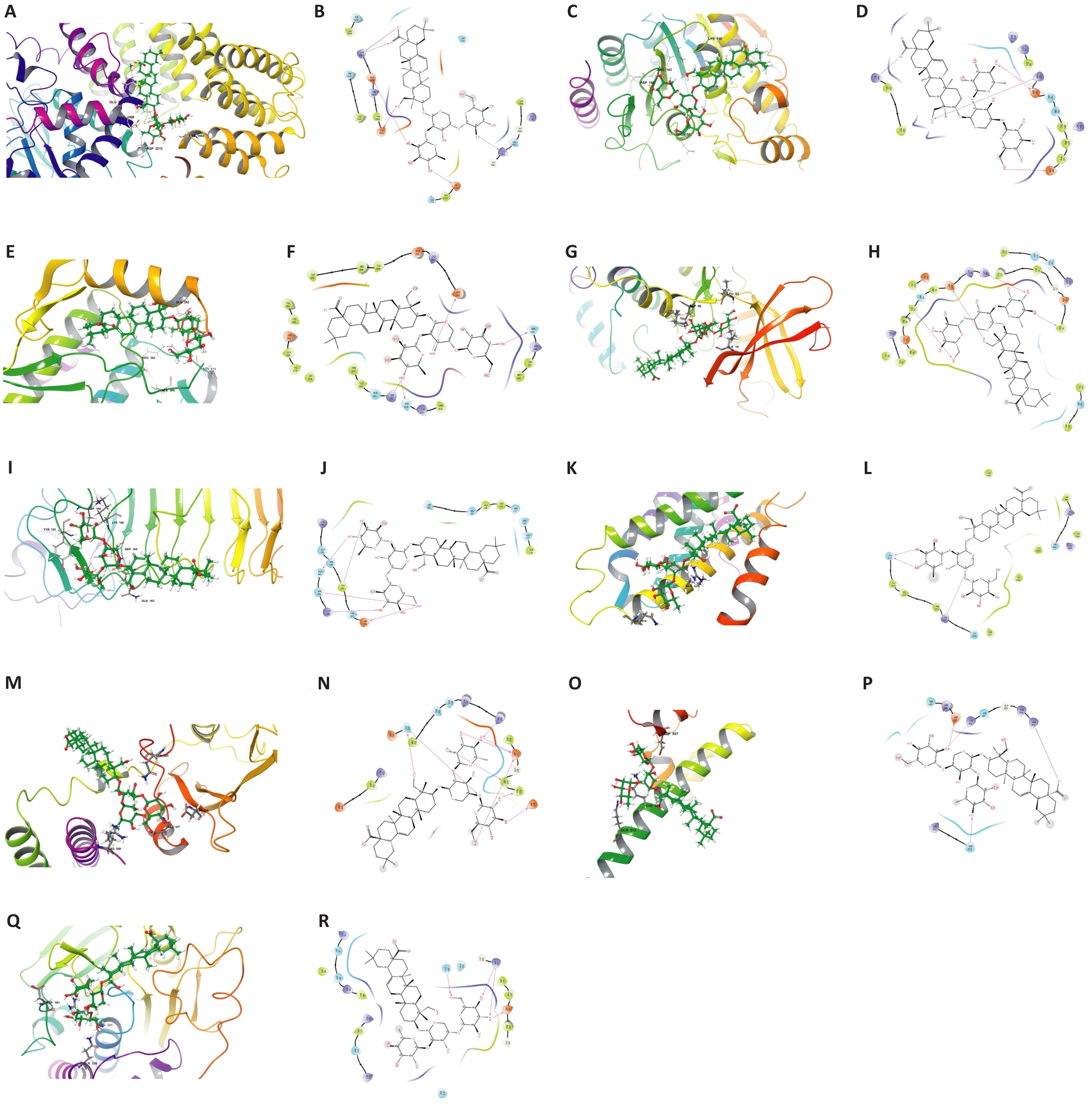
Fig.5 2D and 3D binding pattern maps of PSD to the core target proteins. A: 3D binding model of PSD and MTOR. B: 2D binding model of PSD and MTOR. C: 3D binding model of PSD and HDAC2. D: 2D binding model of PSD and HDAC2. E: 3D binding model of PSD and ABL1. F: 2D binding model of PSD and ABL1. G: 3D binding model of PSD and CDK1. H: 2D binding model of PSD and CDK1. I: 3D binding model of PSD and TLR4. J: 2D binding model of PSD and TLR4. K: 3D binding model of PSD and TERT. L: 2D binding model of PSD and TERT. M: 3D binding model of PSD and PIK3R1. N: 2D binding model of PSD and PIK3R1. O: 3D binding model of PSD and NFE2L2. P: 2D binding model of PSD and NFE2L2. Q: 3D binding model of PSD and PTPN1. R: 2D binding model of PSD and PTPN1.
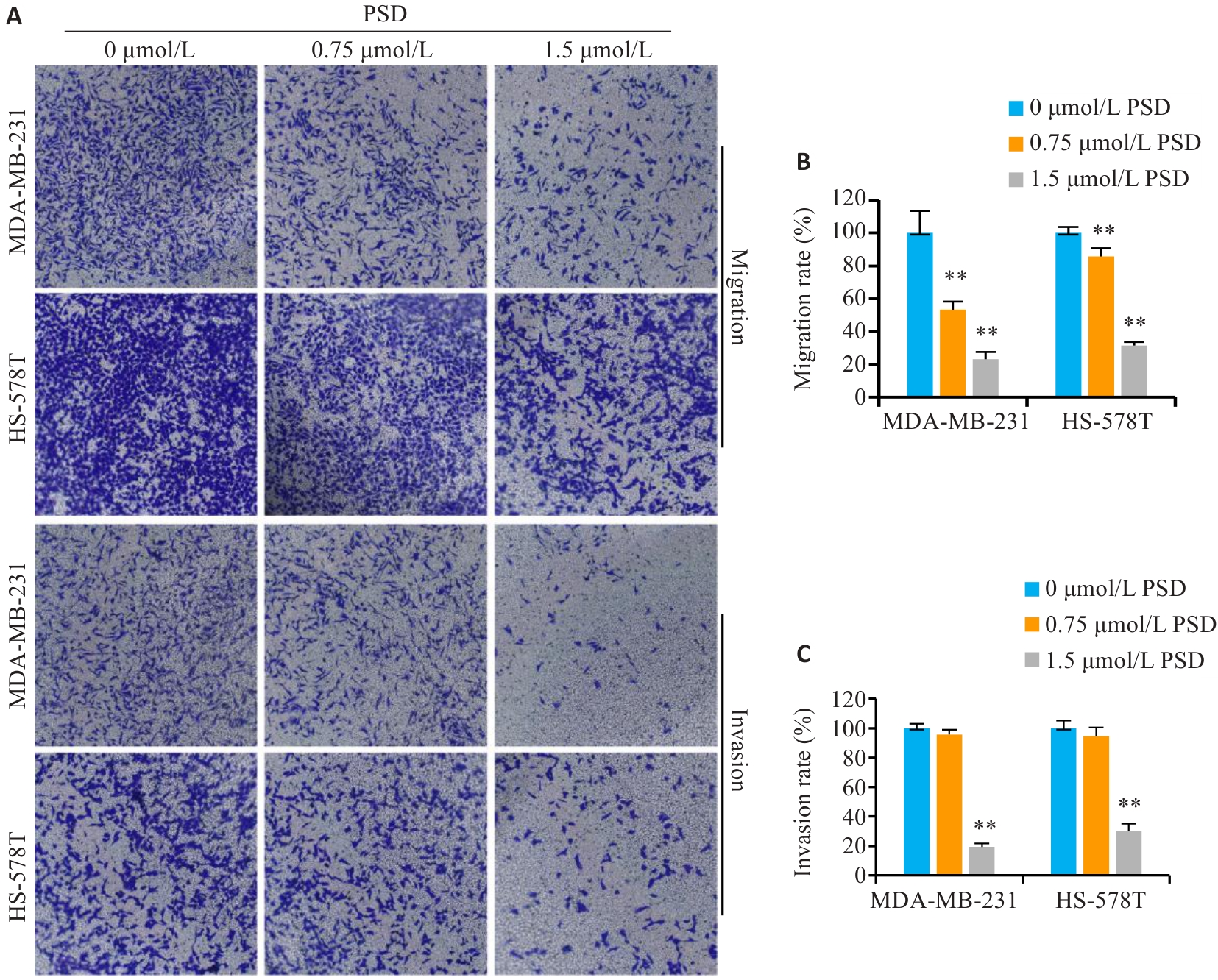
Fig.6 PSD inhibits invasion and migration of TNBC cells. A: Crystal violet staining for detecting migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 and HS-578T cells (Original magnification: ×200). B, C: Quantitative analysis of the results. **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L PSD group.
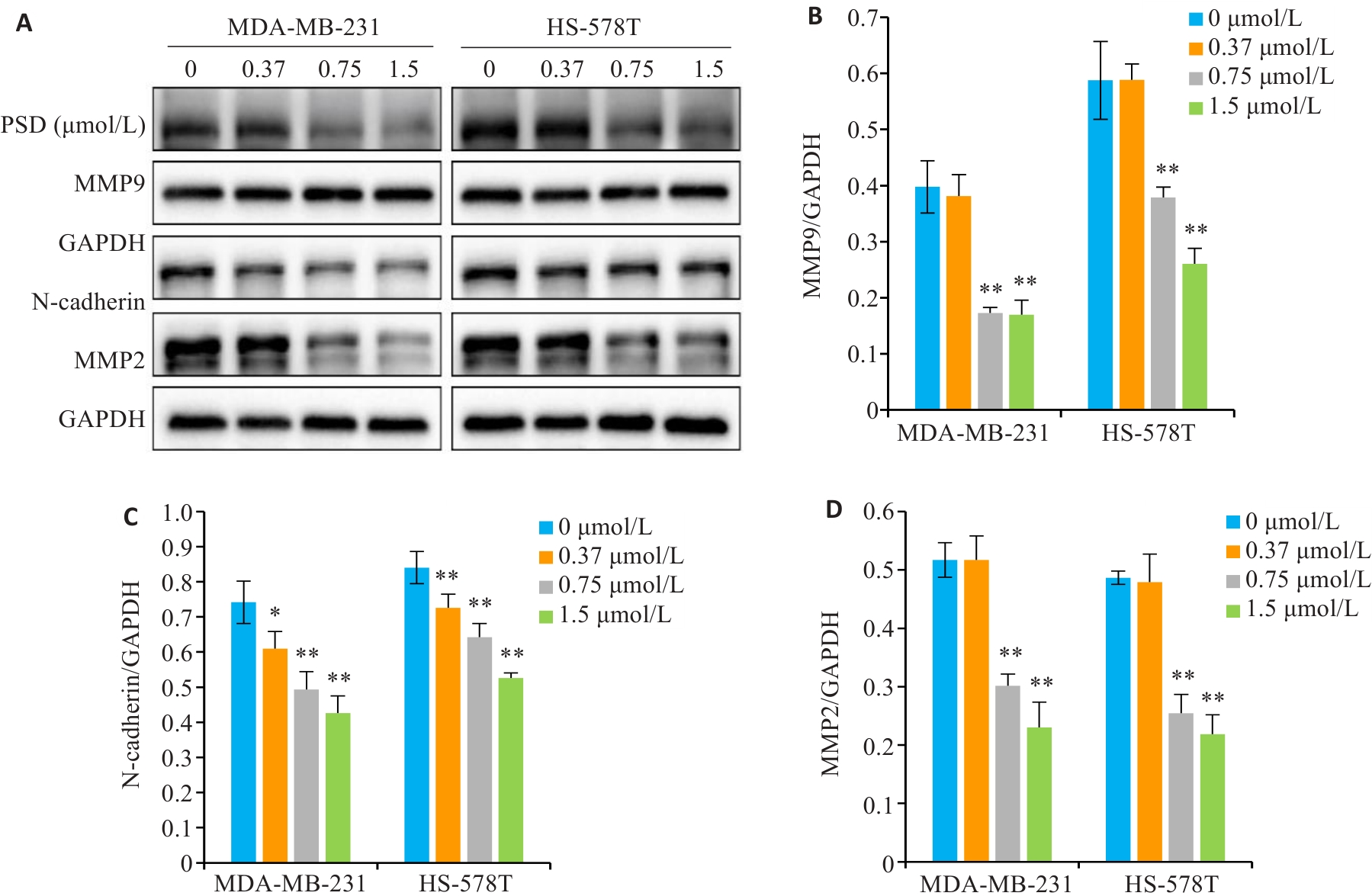
Fig.7 PSD inhibits the expression of invasion and migration related proteins. A: MMP9, N-cadherin, and MMP2 protein levels were detected by Western blotting. B-D: Quantitative analysis of the results. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L group.

Fig.8 PSD inhibits the expression of 9 core target proteins in TNBC cells. A: p-mTOR, mTOR, CDK1, ABL1, TERT, PTPN1, HDAC2, PIK3R1, TLR4 and nuclear NRF2 protein levels detected by Western blotting. B-J: Quantitative analysis of the results. NRF2: NFE2L2. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs 0 μmol/L PSD group.
| 1 | Adrada BE, Moseley TW, Kapoor MM, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: histopathologic features, genomics, and treatment[J]. Radiographics, 2023, 43(10): e230034. |
| 2 | Lin SY, Mo HN, Li YQ, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and survival outcomes in patients with synchronous lung metastases upon initial metastatic breast cancer diagnosis in Han population[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 1330. |
| 3 | 尹海庆, 苏 莉, 陈万贞, 等. 术后首发肺转移的三阴性乳腺癌临床病理特点及预后因素分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(16): 2872-6. |
| 4 | Yang R, Shi YY, Han XH, et al. The impact of platinum-containing chemotherapies in advanced triple-negative breast cancer: meta-analytical approach to evaluating its efficacy and safety[J]. Oncol Res Treat, 2021, 44(6): 333-43. |
| 5 | Mason SR, Willson ML, Egger SJ, et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy for early triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2023, 9(9): CD014805. |
| 6 | McGuinness JE, Kalinsky K. Antibody-drug conjugates in metastatic triple negative breast cancer: a spotlight on sacituzumab govitecan, ladiratuzumab vedotin, and trastuzumab deruxtecan[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2021, 21(7): 903-13. |
| 7 | Mediratta K, El-Sahli S, D’Costa V, et al. Current progresses and challenges of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(12): 3529. |
| 8 | Li LY, Zhang F, Liu ZY, et al. Immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: combination strategies to improve outcome[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(1): 321. |
| 9 | Ye F, Dewanjee S, Li YH, et al. Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 105. |
| 10 | Lev S. Targeted therapy and drug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer: the EGFR axis[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2020, 48(2): 657-65. |
| 11 | Li YH, Zou M, Han Q, et al. Therapeutic potential of triterpenoid saponin anemoside B4 from Pulsatilla chinensis [J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 160: 105079. |
| 12 | Fang YY, Hu DY, Li HL, et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and mode of action of Pulsatilla saponin D derivatives as promising anticancer agents[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 1208. |
| 13 | Zhang YL, Bao JL, Wang K, et al. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits autophagic flux and synergistically enhances the anticancer activity of chemotherapeutic agents against HeLa cells[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2015, 43(8): 1657-70. |
| 14 | Hong SW, Jung KH, Lee HS, et al. SB365, Pulsatilla saponin D, targets c-Met and exerts antiangiogenic and antitumor activities[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2013, 34(9): 2156-69. |
| 15 | Lu YY, He WB, Huang XX, et al. Pulsatilla saponin D regulates ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 3 (RAC3) to overcome resistance to paclitaxel in lung adenocarcinoma cells[J]. BMC Cancer, 2024, 24(1): 55. |
| 16 | Lim JH, Jung KH, Kim MS, et al. SB365 induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation of glioblastoma cells[J]. Indian J Pharmacol, 2020, 52(2): 102-7. |
| 17 | Wang K, Tu YB, Wan JB, et al. Synergistic anti-breast cancer effect of pulsatilla saponin D and camptothecin through interrupting autophagic-lysosomal function and promoting p62-mediated ubiquitinated protein aggregation[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2020, 41(6): 804-16. |
| 18 | Zhong JM, Tan LH, Chen MW, et al. Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms of Pulsatilla saponins[J]. Chin Med, 2022, 17(1): 59. |
| 19 | Bryan S, Witzel I, Borgmann K, et al. Molecular mechanisms associated with brain metastases in HER2-positive and triple negative breast cancers[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(16): 4137. |
| 20 | 江远玲, 冯 楠, 邵欣宇, 等. 黄芪的现代药理作用研究进展[J]. 西南医科大学学报, 2023, 46(5): 456-60, 封3. |
| 21 | Tewari D, Patni P, Bishayee A, et al. Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: a novel therapeutic strategy[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 80: 1-17. |
| 22 | Zheng YY, Dai MR, Dong Y, et al. ZEB2/TWIST1/PRMT5/NuRD Multi complex Contributes to the Epigenetic Regulation of EMT and Metastasis in Colorectal Carcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(14): 3426. |
| 23 | Bradley WD, Koleske AJ. Regulation of cell migration and morphogenesis by Abl-family kinases: emerging mechanisms and physiological contexts[J]. J Cell Sci, 2009, 122(Pt 19): 3441-54. |
| 24 | Ren LW, Yang YH, Li W, et al. CDK1 serves as a therapeutic target of adrenocortical carcinoma via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition, G2/M phase transition, and PANoptosis[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 444. |
| 25 | Kashani B, Zandi Z, Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi A, et al. The role of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in cancer progression: a possible therapeutic target[J]? J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(6): 4121-37. |
| 26 | Zhou Q, Xue CQ, Man JW, et al. Correlation of tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in glioblastoma with magnetic resonance imaging characteristics: a retrospective cross-sectional study[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2023, 13(9): 5958-73. |
| 27 | Lin L, Wu Q, Lu FF, et al. Nrf2 signaling pathway: current status and potential therapeutic targetable role in human cancers[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1184079. |
| 28 | Sivaganesh V, Sivaganesh V, Scanlon C, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: mechanisms in cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(23): 12865. |
| 29 | Liu Q, Guan CC, Liu C, et al. Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha: a new strategy for triple-negative breast cancer therapy[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 156: 113861. |
| 30 | Xu ZW, Goel HL, Burkart C, et al. Inhibition of VEGF binding to neuropilin-2 enhances chemosensitivity and inhibits metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2023, 15(694): eadf1128. |
| 31 | Wu TQ, Song HM, Xie D, et al. Silencing of ASPP2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2018, 52(6): 2001-10. |
| 32 | Liu X, Adorno-Cruz V, Chang YF, et al. EGFR inhibition blocks cancer stem cell clustering and lung metastasis of triple negative breast cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(13): 6632-43. |
| 33 | Liu T, Li KD, Zhang ZX, et al. Tetrandrine inhibits cancer stem cell characteristics and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer via SOD1/ROS signaling pathway[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2023, 51(2): 425-44. |
| 34 | Fang H, Xie JP, Zhang M, et al. miRNA-21 promotes proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting PTEN[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2017, 9(3): 953-61. |
| 35 | Xu JH, Zhao JX, Jiang MY, et al. MiR-193 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by ING5/PI3K/AKT pathway of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(6): 3122-9. |
| 36 | Chen CH, Li SH, Xue JL, et al. PD-L1 tumor-intrinsic signaling and its therapeutic implication in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. JCI Insight, 2021, 6(8): e131458. |
| 37 | Bacci M, Lorito N, Ippolito L, et al. Reprogramming of amino acid transporters to support aspartate and glutamate dependency sustains endocrine resistance in breast cancer[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 28(1): 104-18.e8. |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Xiuying GONG, Shunfu HOU, Miaomiao ZHAO, Xiaona WANG, Zhihan ZHANG, Qinghua LIU, Chonggao YIN, Hongli LI. LncRNA SNHG15 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating COX6B1 through sponge adsorption of miR-30b-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1498-1505. |
| [5] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [6] | Jiahao LI, Ruiting XIAN, Rong LI. Down-regulation of ACADM-mediated lipotoxicity inhibits invasion and metastasis of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1163-1173. |
| [7] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [8] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [9] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [10] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [11] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [12] | Shunjie QING, Zhiyong SHEN. High expression of hexokinase 2 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by activating the JAK/STAT pathway and regulating tumor immune microenvironment [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [13] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [14] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [15] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||