Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2718-2725.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.19
Xuan GUO1,2( ), Yang LIU1, Yan XIONG1, Biaoshui LIU1, Ting SONG2, Yunfei LI1(
), Yang LIU1, Yan XIONG1, Biaoshui LIU1, Ting SONG2, Yunfei LI1( )
)
Received:2025-05-13
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Yunfei LI
E-mail:guoxuan@sysucc.org.cn;liyf1@syusucc.org.cn
Supported by:Xuan GUO, Yang LIU, Yan XIONG, Biaoshui LIU, Ting SONG, Yunfei LI. Analysis of setup errors and their correlation with clinical factors in image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer using different immobilization devices[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2718-2725.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.19
| Metric | 1.2 m vacuum bag | 1.8 m vacuum bag | Orfit board | Individualized prone | χ²/F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 64.2±7.8 | 65.1±8.2 | 63.8±6.9 | 65.5±7.5 | 0.78 | 0.505 |
| BMI (kg/m², Mean±SD) | 24.1±2.8 | 23.8±3.1 | 24.3±2.9 | 23.9±3.0 | 0.38 | 0.769 |
| Clinical stage [n (%)] | 2.15 | 0.542 | ||||
| T3 | 36 (60.0) | 33 (55.0) | 35 (58.3) | 35 (58.3) | ||
| T4 | 24 (40.0) | 27 (45.0) | 25 (41.7) | 25 (41.7) | ||
| Risk stratification [n (%)] | 1.08 | 0.782 | ||||
| Intermediate risk | 22 (36.7) | 20 (33.3) | 19 (31.7) | 23 (38.3) | ||
| High risk | 38 (63.3) | 40 (66.7) | 41 (68.3) | 37 (61.7) | ||
| Lymph node irradiation [n (%)] | 32 (53.3) | 30 (50.0) | 28 (46.7) | 30 (50.0) | 0.74 | 0.864 |
Tab.1 Comparison of baseline characteristics of the patients in the 4 groups (n=60)
| Metric | 1.2 m vacuum bag | 1.8 m vacuum bag | Orfit board | Individualized prone | χ²/F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 64.2±7.8 | 65.1±8.2 | 63.8±6.9 | 65.5±7.5 | 0.78 | 0.505 |
| BMI (kg/m², Mean±SD) | 24.1±2.8 | 23.8±3.1 | 24.3±2.9 | 23.9±3.0 | 0.38 | 0.769 |
| Clinical stage [n (%)] | 2.15 | 0.542 | ||||
| T3 | 36 (60.0) | 33 (55.0) | 35 (58.3) | 35 (58.3) | ||
| T4 | 24 (40.0) | 27 (45.0) | 25 (41.7) | 25 (41.7) | ||
| Risk stratification [n (%)] | 1.08 | 0.782 | ||||
| Intermediate risk | 22 (36.7) | 20 (33.3) | 19 (31.7) | 23 (38.3) | ||
| High risk | 38 (63.3) | 40 (66.7) | 41 (68.3) | 37 (61.7) | ||
| Lymph node irradiation [n (%)] | 32 (53.3) | 30 (50.0) | 28 (46.7) | 30 (50.0) | 0.74 | 0.864 |
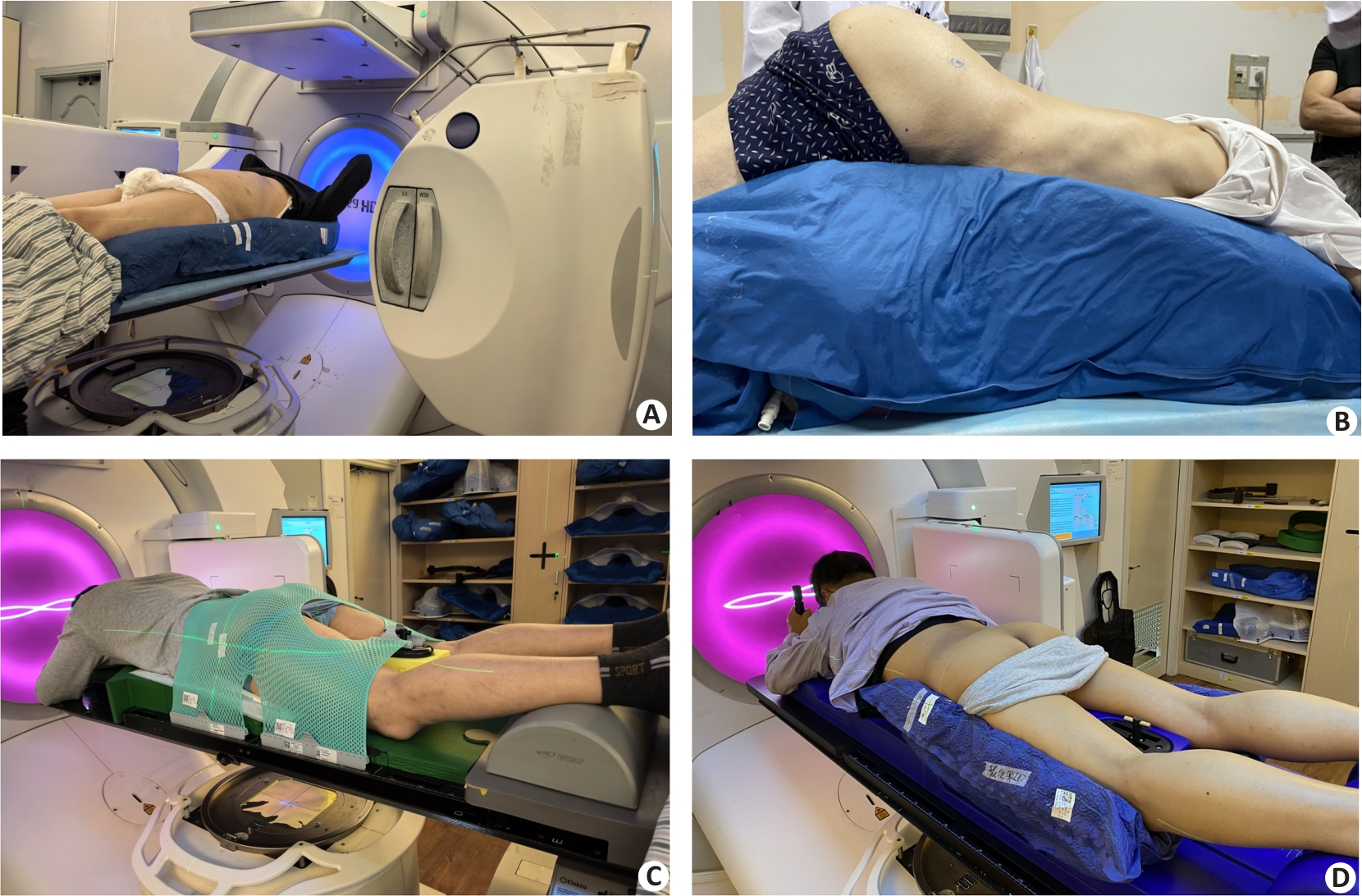
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the 4 types of fixation device. A: 1.2 m vacuum bag immobilization. B: 1.8 m vacuum bag immobilization. C: Orfit board immobilization. D: Individualized prone panel immobilization.
| Direction/devices | 1.2 m vacuum bag | 1.8 m vacuum bag | Orfit board | Individualized prone panel | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Ldirection | 0.05±0.28 | 0.05±0.23 | -0.05±0.28*ΔΟ | 0.02±0.25 | <0.001 |
| S-Idirection | -0.06±0.36*▲ | 0.03±0.30 | -0.13±0.45*▲ | 0.01±0.32 | <0.001 |
| A-Pdirection | 0.03±0.24∆* | -0.10±0.42▲ | -0.02±0.21*▲ | -0.28±0.36Ο | <0.001 |
| ≥0.5 cm (%) | 15.0% | 11.67% | 13.33% | 18.33% | - |
Tab.2 Positioning errors of the 4 fixing devices in 3-dimensional directions and pairwise comparisons (cm, Mean±SD)
| Direction/devices | 1.2 m vacuum bag | 1.8 m vacuum bag | Orfit board | Individualized prone panel | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Ldirection | 0.05±0.28 | 0.05±0.23 | -0.05±0.28*ΔΟ | 0.02±0.25 | <0.001 |
| S-Idirection | -0.06±0.36*▲ | 0.03±0.30 | -0.13±0.45*▲ | 0.01±0.32 | <0.001 |
| A-Pdirection | 0.03±0.24∆* | -0.10±0.42▲ | -0.02±0.21*▲ | -0.28±0.36Ο | <0.001 |
| ≥0.5 cm (%) | 15.0% | 11.67% | 13.33% | 18.33% | - |
| Direction | R-L | S-I | A-P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Have lymph nodes | -0.04±0.30 | 0.003±0.35 | -0.22±0.36 |
| No lymph nodes | 0.002±0.29 | -0.075±0.47 | -0.01±0.43 |
| t | 2.14 | 3.46 | 4.27 |
| P | 0.033 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
Tab.3 Positioning errors in 3 directions in patients with or without lymph node irradiations (cm, Mean±SD)
| Direction | R-L | S-I | A-P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Have lymph nodes | -0.04±0.30 | 0.003±0.35 | -0.22±0.36 |
| No lymph nodes | 0.002±0.29 | -0.075±0.47 | -0.01±0.43 |
| t | 2.14 | 3.46 | 4.27 |
| P | 0.033 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| Direction/devices | R-L | S-I | A-P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 m vacuum bag | ∑ | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.18 |
| σ | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.17 | |
| MPTV | 0.64 | 0.9 | 0.57 | |
| 1.8 mvacuum bag | ∑ | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.35 |
| σ | 0.08 | 0.91 | 0.14 | |
| MPTV | 0.81 | 1.11 | 0.97 | |
| Orfit board | ∑ | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.19 |
| σ | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.27 | |
| MPTV | 0.71 | 1.07 | 0.66 | |
| Individualized prone panel | ∑ | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.26 |
| σ | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| MPTV | 0.41 | 0.58 | 0.69 | |
| Individualized prone panel | ||||
| With lymph nodes | ∑ | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.28 |
| σ | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | |
| MPTV | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.77 | |
| Withoutlymph nodes | ∑ | 0.18 | 0.37 | 0.32 |
| σ | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.13 | |
| MPTV | 0.51 | 0.97 | 0.88 | |
Tab.4 Comparison of MPTV among the 4 fixation methods
| Direction/devices | R-L | S-I | A-P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 m vacuum bag | ∑ | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.18 |
| σ | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.17 | |
| MPTV | 0.64 | 0.9 | 0.57 | |
| 1.8 mvacuum bag | ∑ | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.35 |
| σ | 0.08 | 0.91 | 0.14 | |
| MPTV | 0.81 | 1.11 | 0.97 | |
| Orfit board | ∑ | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.19 |
| σ | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.27 | |
| MPTV | 0.71 | 1.07 | 0.66 | |
| Individualized prone panel | ∑ | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.26 |
| σ | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| MPTV | 0.41 | 0.58 | 0.69 | |
| Individualized prone panel | ||||
| With lymph nodes | ∑ | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.28 |
| σ | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | |
| MPTV | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.77 | |
| Withoutlymph nodes | ∑ | 0.18 | 0.37 | 0.32 |
| σ | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.13 | |
| MPTV | 0.51 | 0.97 | 0.88 | |
| Variable | Group | n | RLError | SIError | APError | Statistical method | Statistic | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | <65 | 80 | 0.02±0.23 | -0.01±0.30 | -0.14±0.32 | Independent t-test | t=1.02 | 0.310 |
| ≥65 | 160 | 0.01±0.25 | 0.03±0.33 | -0.17±0.35 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | <24 | 120 | -0.01±0.21 | -0.13±0.31 | -0.09±0.32 | Independent t-test | t=4.18 | <0.001* |
| ≥24 | 120 | -0.03±0.22 | 0.02±0.27 | -0.20±0.29 | ||||
| Correlation analysis | Age | r=0.03 | r=0.02 | r=-0.04 | Pearson correlation | >0.05 | ||
| BMI | R=-0.12 | r=-0.45 | r=-0.10 | Pearson correlation | <0.001* |
Tab.5 Correlation analysis of age, BMI with setup errors (cm, Mean±SD)
| Variable | Group | n | RLError | SIError | APError | Statistical method | Statistic | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | <65 | 80 | 0.02±0.23 | -0.01±0.30 | -0.14±0.32 | Independent t-test | t=1.02 | 0.310 |
| ≥65 | 160 | 0.01±0.25 | 0.03±0.33 | -0.17±0.35 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | <24 | 120 | -0.01±0.21 | -0.13±0.31 | -0.09±0.32 | Independent t-test | t=4.18 | <0.001* |
| ≥24 | 120 | -0.03±0.22 | 0.02±0.27 | -0.20±0.29 | ||||
| Correlation analysis | Age | r=0.03 | r=0.02 | r=-0.04 | Pearson correlation | >0.05 | ||
| BMI | R=-0.12 | r=-0.45 | r=-0.10 | Pearson correlation | <0.001* |
| [1] | Raychaudhuri R, Lin DW, Montgomery RB. Prostate cancer: areview[J]. JAMA, 2025, 333(16): 1433-46. doi:10.1001/jama.2025.0228 |
| [2] | 李 星, 曾晓勇. 中国前列腺癌流行病学研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(1): 98-102. |
| [3] | Zhai Z, Zheng Y, Li N, et al. Incidence and disease burden of prostate cancer from 1990 to 2017: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Cancer, 2020, 126(9): 1969-78. doi:10.1002/cncr.32733 |
| [4] | Tan EH, Burn E, Barclay NL, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and survival of prostate cancer in the UK[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2024, 7(9): e2434622. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34622 |
| [5] | Moll M, Nechvile E, Kirisits C, et al. Radiotherapy in localized prostate cancer: a multicenter analysis evaluating tumor control and late toxicity after brachytherapy and external beam radiotherapy in 1293 patients[J]. Strahlenther Onkol, 2024, 200(8): 698-705. doi:10.1007/s00066-024-02222-w |
| [6] | Inui S, Ueda Y, Ohira S, et al. Comparison of interfractional setup reproducibility between two types of patient immobilization devices in image-guided radiation therapy for prostate cancer[J]. J Med Phys, 2018, 43(4): 230-5. doi:10.4103/jmp.jmp_20_18 |
| [7] | 曹 飞, 赵永亮, 李 明, 等. 宫颈癌放疗仰、俯卧位固定下的摆位误差及剂量学差异探讨[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(21): 3862-5. |
| [8] | 赵丰雨, 杜德成. 锥形束CT用于盆腔肿瘤放射治疗摆位中的效果分析[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2021, 5(4): 225-6. |
| [9] | Chen H, Liu YD, Qin SB, et al. Optical surface management system and BladderScan for patient setup during radiotherapy of postoperative prostate cancer[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2024, 2024: 3573796. doi:10.1155/2024/3573796 |
| [10] | 丘敏敏, 钟嘉健, 李 敏, 等. 鼻咽癌调强放疗摆位不同配准方式对实际剂量学的影响[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2020(11): 94-7, 101. |
| [11] | Anand M, Parikh A, Shah SP. Comparison of thermoplastic masks and knee wedge as immobilization devices for image-guided pelvic radiation therapy using Cone Beam Computed Tomography[J]. Indian J Cancer, 2020, 57(2): 182-6. doi:10.4103/ijc.ijc_602_18 |
| [12] | Wang L, Chen Z, Li X, et al.Setup errors in radiotherapy for prostate cancer: A retrospective analysis of Chinese patients with different immobilization techniques[J].Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:12439-12447. |
| [13] | Inui S, Ueda Y, Ohira S, et al.Impact of body mass index on setup reproducibility in image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer[J]. J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2021, 22(3): 214-21. |
| [14] | Stroom JC, Heijmen BJ. Geometrical uncertainties, radiotherapy planning margins, and the ICRU-62 report[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2002, 64(1): 75-83. doi:10.1016/s0167-8140(02)00140-8 |
| [15] | Van HM, Remeijer P, Lebesque JV. Errors and margins in radiotherapy[J]. Semin Radiat Oncol, 2004, 14(1): 52-64. doi:10.1053/j.semradonc.2003.10.003 |
| [16] | Serizawa I, Kozuka T, Soyano T, et al. Clinical and dosimetric comparison between non-image guided radiation therapy and fiducial-based image guided radiation therapy with or without reduced margin in intensity modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer[J]. Adv Radiat Oncol, 2024, 9(10): 101612. doi:10.1016/j.adro.2024.101612 |
| [17] | Mirzaei M, Gill S, Sabet M, et al. Treatment efficiency and quality improvement via double imaging modality (DIM) versus single imaging modality (SIM) image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer[J]. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol, 2025, 33: 100307. doi:10.1016/j.tipsro.2025.100307 |
| [18] | Duffton A, McNee S, Muirhead R, et al. Clinical commissioning of online seed matching protocol for prostate radiotherapy[J]. Br J Radiol, 2012, 85(1020): e1273-81. doi:10.1259/bjr/72368557 |
| [19] | Greer PB, Dahl K, Ebert MA, et al. Comparison of prostate set-up accuracy and margins with off-line bony anatomy corrections and online implanted fiducial-based corrections[J]. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol, 2008, 52(5): 511-6. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1673.2008.02005.x |
| [20] | 彭庆国, 尹 勇, 余宁莎,等. 三种体位固定技术在盆腔肿瘤放疗中的应用比较[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2015, 22(12): 974-7, 983. |
| [21] | Guckenberger M, Meyer J, Wilbert J, et al. Cone-beam CT based image-guidance for extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy of intrapulmonary tumors[J]. Acta Oncol, 2006, 45(7): 897-906. doi:10.1080/02841860600904839 |
| [22] | Foster R, Meyer J, Iyengar P, et al. Localization accuracy and immobilization effectiveness of a stereotactic body frame for a variety of treatment sites[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2013, 87(5): 911-6. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.09.020 |
| [23] | Fonteyne V, Villeirs G, Speleers B, et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy as primary therapy for prostate cancer: report on acute toxicity after dose escalation with simultaneous integrated boost to intraprostatic lesion[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2008, 72(3): 799-807. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.01.040 |
| [24] | De Crevoisier R, Tucker SL, Dong L, et al. Increased risk of biochemical and local failure in patients with distended rectum on the planning CT for prostate cancer radiotherapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2005, 62(4): 965-73. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.11.032 |
| [25] | 黄伯天, 张丹丹, 彭应林, 等. 图像配准条件对头颈部CBCT引导放疗精度影响[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2016, 25(4): 391-4. |
| [26] | 彭清河, 彭应林, 朱金汉, 等. 图像配准方式对宫颈癌后装自适应放射治疗图像配准精度的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1344-8. |
| [27] | Shinde P, Jadhav A, Shankar V, et al. Assessment of dosimetric impact of interfractional 6D setup error in tongue cancer treated with IMRT and VMAT using daily kV-CBCT[J]. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2023, 28(2): 224-40. doi:10.5603/rpor.a2023.0020 |
| [28] | Dekker J, Essers M, Verheij M, et al. Dose coverage and breath-hold analysis of breast cancer patients treated with surface-guided radiotherapy[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2023, 18(1): 72. doi:10.1186/s13014-023-02261-0 |
| [29] | 李雅宁, 林承光, 杨 鑫. 体质量指数对宫颈癌调强放疗摆位误差影响[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2021, 30(2): 186-90. |
| [30] | Price RG, Lloyd S, Wang XC, et al. Adipose tissue distribution and body mass index (BMI) correlation with daily image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) shifts of abdominal radiation therapy patients[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15(6): e40979. |
| [31] | Mulla Z, Hashem R, AlMohamad A, et al. Effect of body mass factors on setup displacement in gynecologic tumors and subsequent effect on PTV margins[J]. Adv Radiat Oncol, 2022, 8(1): 101108. doi:10.1016/j.adro.2022.101108 |
| [32] | 李 军. 不同年龄前列腺癌患者的临床病理特征与生存状况分析[J]. 新乡医学院学报, 2020, 37(9): 862-4. |
| [33] | 潘启勇, 丁秋娥, 姜仁伟, 等. 盆腔肿瘤常规放疗摆位误差分析[J]. 中国实用医药, 2010, 5(24): 47-8. |
| [34] | 丁伟杰, 孙 菁, 陈一兴. 肝肿瘤螺旋断层放疗中患者年龄对摆位误差的影响[J]. 肿瘤, 2016, 36(7): 810-3. |
| [35] | Bossuyt E, Nevens D, Weytjens R, et al. Assessing the impact of adaptations to the clinical workflow in radiotherapy using transit in vivo dosimetry[J]. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023,25:100420. doi:10.1016/j.phro.2023.100420 |
| [36] | 王春霞, 宋 真, 李红燕, 等. 不同年龄前列腺癌患者疾病不确定感与生活质量[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2019, 39(1): 200-3. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||