Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1284-1296.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.08
Jinguang LUO1,2( ), Huaixiang TAO1,2, Zhiyuan WEN1, Long CHEN1,2, Hao HU1,2, Han GUAN1(
), Huaixiang TAO1,2, Zhiyuan WEN1, Long CHEN1,2, Hao HU1,2, Han GUAN1( )
)
Received:2024-02-18
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-25
Contact:
Han GUAN
E-mail:2895664010@qq.com;gh668689@126.com
Jinguang LUO, Huaixiang TAO, Zhiyuan WEN, Long CHEN, Hao HU, Han GUAN. Tumor-associated fibroblasts promotes proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells by suppressing FBXL3 via upregulating hsa-miR-18b-5p[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1284-1296.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.08
| Gene | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| hsa-miR-18b-5p | F: AGGCGCATTAAGGTGCATCTAGT |
| R: ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| has-miR-148a | F: TCTGAGACACTCCGACTCTG |
| R: AGTTCTGTAGTGCACTGACTTCT | |
| has-miR-17 | F: AAGTGCTTACAGTGCAGGTAGT |
| R: GTCACCATAATGCTACAAGTGC | |
| has-miR-770 | F: CCTCCAGTACCACGTGTCAG |
| R: CCCCAGCACCACATCAGG | |
| has-miR-297-3p | F: AGTGCTTACAGTGCAGGTAGT |
| R: TCACCATAATGCTACAAGTGCC | |
| U6 | F: GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT |
| R: CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT | |
| FBXL3 | F: ATGCTTCACAAGTTTGCCGC |
| R: CACGGCCAAGCACATCTTTG | |
| GAPDH | F: TCATGACCACAGTCCATGCC |
| R: TTCTAGACGGCAGGTCAGGT |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| hsa-miR-18b-5p | F: AGGCGCATTAAGGTGCATCTAGT |
| R: ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| has-miR-148a | F: TCTGAGACACTCCGACTCTG |
| R: AGTTCTGTAGTGCACTGACTTCT | |
| has-miR-17 | F: AAGTGCTTACAGTGCAGGTAGT |
| R: GTCACCATAATGCTACAAGTGC | |
| has-miR-770 | F: CCTCCAGTACCACGTGTCAG |
| R: CCCCAGCACCACATCAGG | |
| has-miR-297-3p | F: AGTGCTTACAGTGCAGGTAGT |
| R: TCACCATAATGCTACAAGTGCC | |
| U6 | F: GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT |
| R: CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT | |
| FBXL3 | F: ATGCTTCACAAGTTTGCCGC |
| R: CACGGCCAAGCACATCTTTG | |
| GAPDH | F: TCATGACCACAGTCCATGCC |
| R: TTCTAGACGGCAGGTCAGGT |
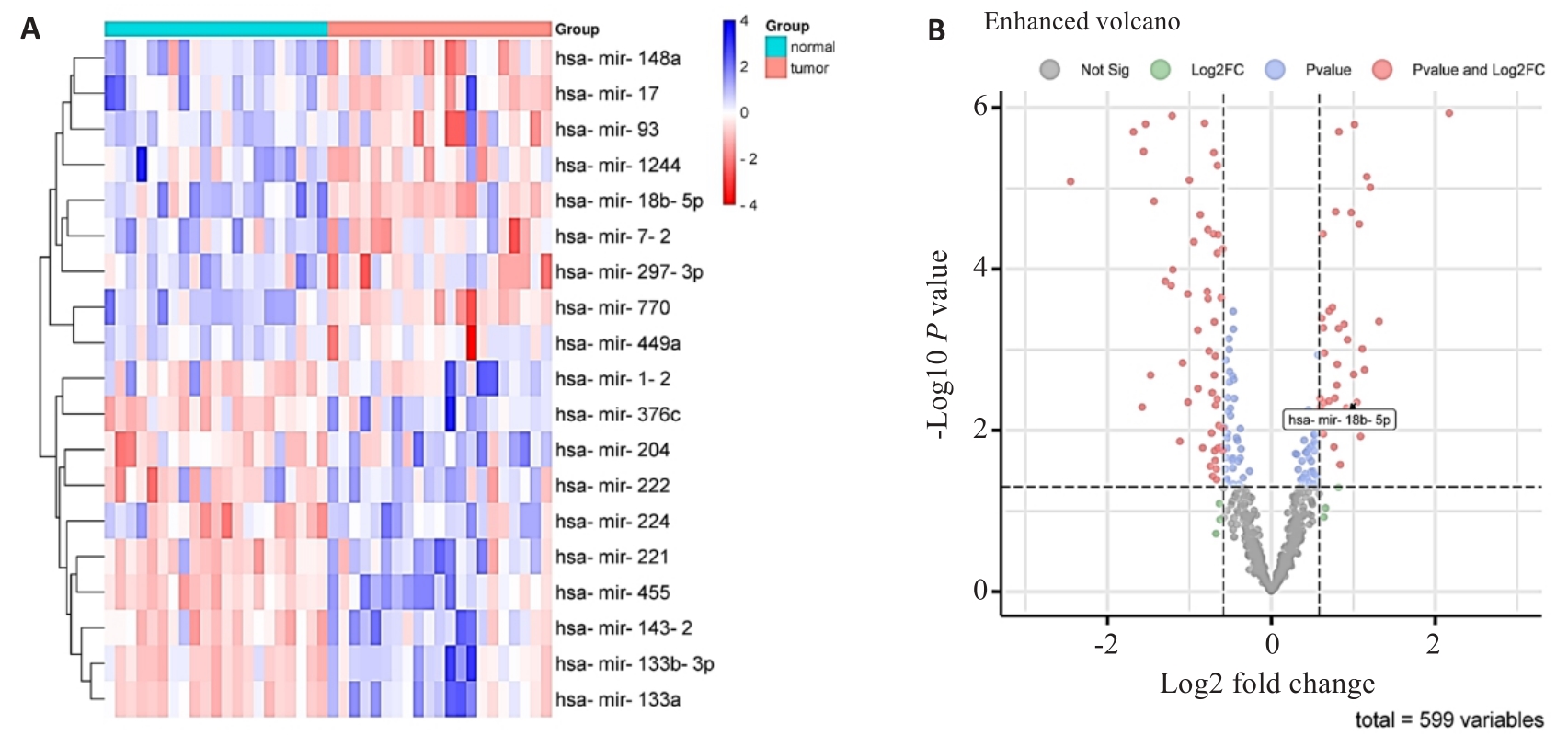
Fig.1 Volcano plot and heat map of the differential miRNAs in prostate cancer. A: Differential miRNA heat map in prostate cancer. B: Volcano plot of differential miRNA in prostate cancer.

Fig.2 Identification of CAFs and NFs and co-cultured prostate cancer C4-2 cells. A: Morphology of CAFs and NFs were observed under light microscope. B, C: Expression of vimentin and α-SMA in CAFs and NFs detected by Western blotting. D: RT-qPCR for detecting vimentin and α-SMA mRNAs in co-cultures of C4-2 cells with CAFs or NFs. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.3 Effect of CAFs on proliferation and migration of PCa cells. A, B: Colony formation assays of C4-2 cells co-cultured with CAFs. C, D: Transwell migration assay of C4-2 cells co-cultured with CAFs. **P<0.01.

Fig.4 Knocking down has-miR-18b-5p attenuates the effect of CAFs on proliferation and migration of PCa cells. A, B: Colony formation assays of CAFs co-cultured with C4-2 cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. C, D: Transwell migration assays of CAFs co-cultured with C4-2 cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. **P<0.01.

Fig.5 Expression of hsa-miR-18b-5p in prostate cancer cell lines and clinical tumor tissues. A: Expression of hsa-miR-18b-5p in clinical tumor tissues. B: Expression of hsa-miR-18b-5p in prostate cancer cell lines. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs BPH-1 group.

Fig.6 Effect of Has-miR-18b-5p on proliferation of prostate cancer cells. A: CCK-8 assay of C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. B, C: Colony formation assay of C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.7 Effect of hsa-miR-18b-5p on migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells. A,B: Wound-healing assay of C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. C, E: Transwell migration assay of C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. D, F: Transwell invasion assay of in C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.9 Effect of hsa-miR-18b-5p on apoptosis and cell cycle of prostate cancer cells. A,B: Apoptosis assays of C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. C-F: Cell cycle assays of C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.10 Effect of hsa-miR-18b-5p on tumor load in nude mice. A,B: Tumor weight in mice. C: Tumor volume in mice. D: Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of survival of the mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
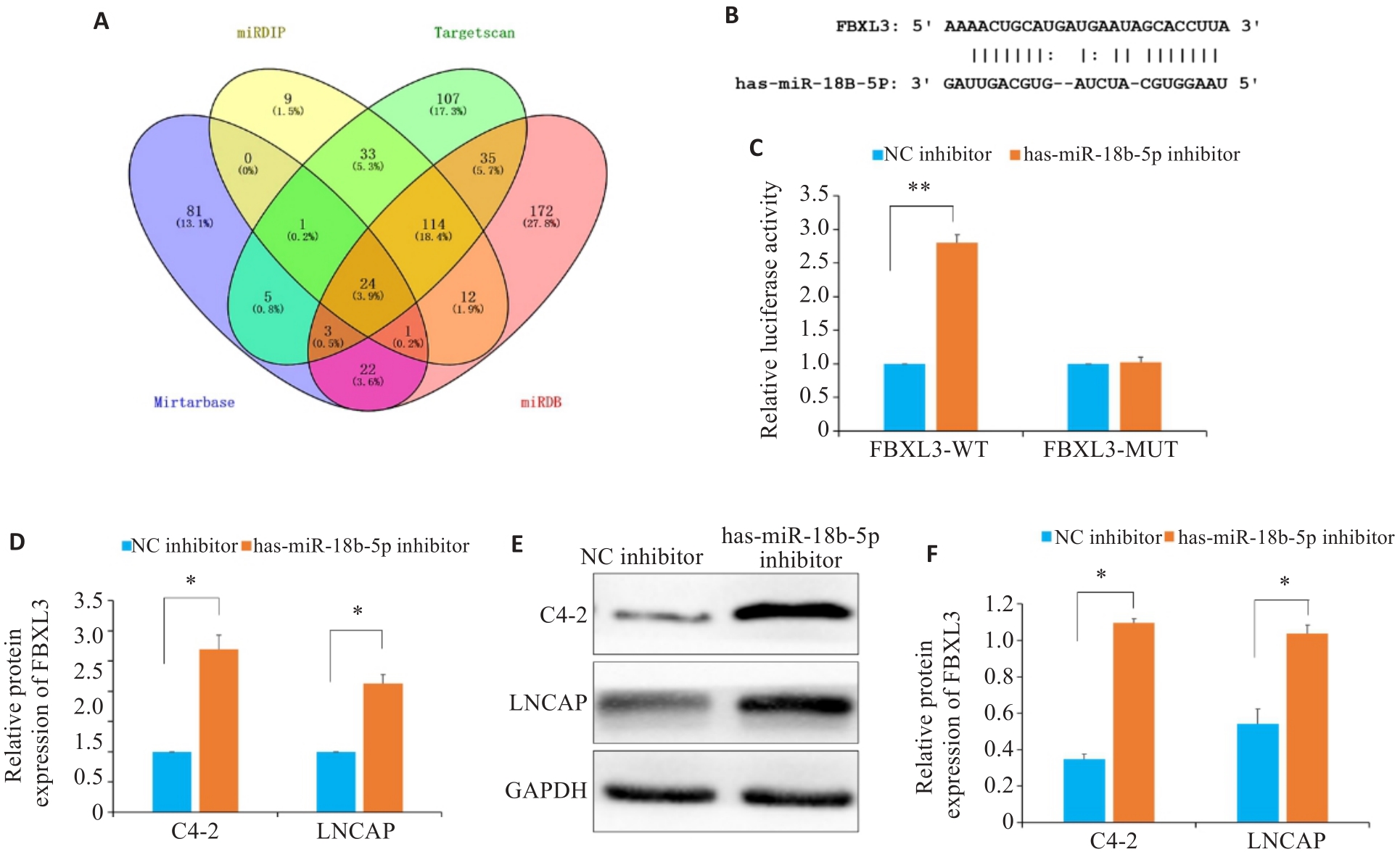
Fig.11 Targeting relationship between hsa-miR-18b-5p and FBXL3 in prostate cancer. A: Wayne diagram of hsa-miR-18b-5p target gene. B: Binding sites of hsa-miR-18b-5p and FBXL3. C: Results of dual luciferase reporter assay. D: RT-qPCR of FBXL3 in C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. E,F: Western blotting of FBXL3 in C4-2 and LNCAP cells transfected with NC inhibitor and hsa-miR-18b-5p inhibitor. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.12 Overexpression of FBXL3 reverses the effects of hsa-miR-18b-5p knockdown in prostate cancer cell line. A: CCK8 assay of the two co-transfected PCa cell lines. B: Transwell assay of the two co-transfected PCa cell lines. C: Wound healing assay of the two co-transfected PCa cell lines. *P<0.05.
| 1 | Sehn JK. Prostate cancer pathology: recent updates and controversies[J]. Mo Med, 2018, 115(2): 151-5. |
| 2 | Kimura T, Egawa S. Epidemiology of prostate cancer in Asian countries[J]. Int J Urol, 2018, 25(6): 524-31. |
| 3 | Zelic R, Garmo H, Zugna D, et al. Predicting prostate cancer death with different pretreatment risk stratification tools: a head-to-head comparison in a nationwide cohort study[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 77(2): 180-8. |
| 4 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. |
| 5 | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. |
| 6 | Taylor LG, Canfield SE, Du XL. Review of major adverse effects of androgen-deprivation therapy in men with prostate cancer[J]. Cancer, 2009, 115(11): 2388-99. |
| 7 | Zarour L, Alumkal J. Emerging therapies in castrate-resistant prostate cancer[J]. Curr Urol Rep, 2010, 11(3): 152-8. |
| 8 | Boulos S, Mazhar D. The evolving role of chemotherapy in prostate cancer[J]. Future Oncol, 2017, 13(12): 1091-5. |
| 9 | Sebesta EM, Anderson CB. The surgical management of prostate cancer[J]. Semin Oncol, 2017, 44(5): 347-57. |
| 10 | Shevach J, Chaudhuri P, Morgans AK. Adjuvant therapy in high-risk prostate cancer[J]. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol, 2019, 17(1): 45-53. |
| 11 | Chistiakov DA, Myasoedova VA, Grechko AV, et al. New biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of localized prostate cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018, 52(Pt 1): 9-16. |
| 12 | Michlewski G, Cáceres JF. Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis[J]. RNA, 2019, 25(1): 1-16. |
| 13 | Liu T, Zhang Q, Zhang JK, et al. EVmiRNA: a database of miRNA profiling in extracellular vesicles[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D89-93. |
| 14 | Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, et al. Regulatory mechanism of microRNA expression in cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(5): 1723-9. |
| 15 | Friedman RC, Farh KKH, Burge CB, et al. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs[J]. Genome Res, 2009, 19(1): 92-105. |
| 16 | Cocks A, Del Vecchio F, Martinez-Rodriguez V, et al. Pro-tumoral functions of tumor-associated macrophage EV-miRNA[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86(Pt 1): 58-63. |
| 17 | Del Valle-Morales D, Le P, Saviana M, et al. The epitranscriptome in miRNAs: crosstalk, detection, and function in cancer[J]. Genes, 2022, 13(7): 1289-95. |
| 18 | Smolarz B, Durczyński A, Romanowicz H, et al. miRNAs in cancer (review of literature)[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(5): 2805-13. |
| 19 | Iqbal MA, Arora S, Prakasam G, et al. MicroRNA in lung cancer: role, mechanisms, pathways and therapeutic relevance[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019, 70: 3-20. |
| 20 | Kt RD, Karthick D, Saravanaraj KS, et al. The roles of microRNA in pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Cancer Invest, 2022, 40(8): 700-9. |
| 21 | Ismail A, Abulsoud AI, Fathi D, et al. The role of miRNAs in ovarian cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic resistance-A focus on signaling pathways interplay[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2022, 240: 154222. |
| 22 | Hwang GR, Yuen JG, Ju JF. Roles of microRNAs in gastrointestinal cancer stem cell resistance and therapeutic development[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4): 1624-36. |
| 23 | Doghish AS, Ismail A, El-Mahdy HA, et al. A review of the biological role of miRNAs in prostate cancer suppression and progression[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2022, 197: 141-56. |
| 24 | Mao XQ, Xu J, Wang W, et al. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 131-8. |
| 25 | Tsoumakidou M. The advent of immune stimulating CAFs in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2023, 23(4): 258-69. |
| 26 | Wang YF, Liang HY, Zheng J. Exosomal microRNAs mediating crosstalk between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2022, 239: 154159. |
| 27 | Bullock MD, Pickard KM, Nielsen BS, et al. Pleiotropic actions of miR-21 highlight the critical role of deregulated stromal microRNAs during colorectal cancer progression[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2013, 4(6): e684-92. |
| 28 | Gandellini P, Giannoni E, Casamichele A, et al. MiR-205 hinders the malignant interplay between prostate cancer cells and associated fibroblasts[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2014, 20(7): 1045-59. |
| 29 | Yan ZQ, Sheng ZM, Zheng YH, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-18b promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis by regulating TCEAL7[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(12): 1120-32. |
| 30 | Xue F, Xu YH, Shen CC, et al. Non-coding RNA LOXL1-AS1 exhibits oncogenic activity in ovarian cancer via regulation of miR-18b-5p/VMA21 axis[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2020, 125: 109568. |
| 31 | Wang YY, Yan L, Yang S, et al. Long noncoding RNA AC073284.4 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-18b-5p in paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer cells[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(12): 23202-15. |
| 32 | Komura K, Sweeney CJ, Inamoto T, et al. Current treatment strategies for advanced prostate cancer[J]. Int J Urol, 2018, 25(3): 220-31. |
| 33 | Swarbrick S, Wragg N, Ghosh S, et al. Systematic review of miRNA as biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2019, 56(9): 6156-67. |
| 34 | Pottoo FH, Iqubal A, Iqubal MK, et al. miRNAs in the regulation of cancer immune response: effect of miRNAs on cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(23): 6145-56. |
| 35 | Khan AQ, Ahmed EI, Elareer NR, et al. Role of miRNA-regulated cancer stem cells in the pathogenesis of human malignancies[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(8): 840-8. |
| 36 | Hussen BM, Hidayat HJ, Salihi A, et al. MicroRNA: a signature for cancer progression[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2021, 138: 111528. |
| 37 | Liang Y, Lu Q, Li W, et al. Reactivation of tumour suppressor in breast cancer by enhancer switching through NamiRNA network[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(15): 8556-72. |
| 38 | Hu HH, Cheng RJ, Wang YB, et al. Oncogenic KRAS signaling drives evasion of innate immune surveillance in lung adenocarcinoma by activating CD47[J]. J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(2): e153470. |
| 39 | Liu LN, Zhang Y, Hu X, et al. MiR-138-5p inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance by targeting APOBEC3B[J]. Transl Oncol, 2023, 35: 101723-36. |
| 40 | Li WJ, Liu XZ, Dougherty EM, et al. MicroRNA-34a, prostate cancer stem cells, and therapeutic development[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(18): 4538-50. |
| 41 | Angel CZ, Stafford MYC, McNally CJ, et al. MiR-21 is induced by hypoxia and down-regulates RHOB in prostate cancer[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(4): 1291-309. |
| 42 | Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-74. |
| 43 | Cirri P, Chiarugi P. Cancer-associated-fibroblasts and tumour cells: a diabolic liaison driving cancer progression[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2012, 31(1/2): 195-208. |
| 44 | Aprelikova O, Yu X, Palla J, et al. The role of miR-31 and its target gene SATB2 in cancer-associated fibroblasts[J]. Cell Cycle, 2010, 9(21): 4387-98. |
| 45 | Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Wallace JA, et al. Reprogramming of the tumour microenvironment by stromal PTEN-regulated miR-320[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2011, 14(2): 159-67. |
| 46 | Yao Q, Cao SY, Li C, et al. Micro-RNA-21 regulates TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting PDCD4 in tumor-stroma interaction[J]. Int J Cancer, 2011, 128(8): 1783-92. |
| 47 | Wang DZ, Han X, Li C, et al. FBXL3 is regulated by miRNA-4735-3p and suppresses cell proliferation and migration in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2019, 215(2): 358-65. |
| 48 | Huber AL, Papp SJ, Chan AB, et al. CRY2 and FBXL3 cooperatively degrade c-MYC[J]. Mol Cell, 2016, 64(4): 774-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||