Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 110-117.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.14
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenjuan DUO1,2,4( ), Yixiang WANG1,2(
), Yixiang WANG1,2( ), Jiaxing WANG1, Xinlong XU1, Linxian LI1, Dongchen YANG1, Qili SHEN3, Lichun YANG3, Xiaojing LIU1, Qiwang JING1,2, Liang CHU3(
), Jiaxing WANG1, Xinlong XU1, Linxian LI1, Dongchen YANG1, Qili SHEN3, Lichun YANG3, Xiaojing LIU1, Qiwang JING1,2, Liang CHU3( ), Xiaodi YANG1,2(
), Xiaodi YANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-09-15
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Liang CHU, Xiaodi YANG
E-mail:18332762023@163.com;1506214487@qq.com;chew8151@163.com;yxd_qf@bbmc.edu.cn
Wenjuan DUO, Yixiang WANG, Jiaxing WANG, Xinlong XU, Linxian LI, Dongchen YANG, Qili SHEN, Lichun YANG, Xiaojing LIU, Qiwang JING, Liang CHU, Xiaodi YANG. Schistosoma japonicum cystatin has protective effects against "two-hit" sepsis in mice by regulating the inflammatory microenvironment[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 110-117.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.14
| Hepatocyte edema, congestion, inflammatory cell infiltration | Index |
|---|---|
| None | 0 |
| 0%-25% | 1 |
| 25%-50% | 2 |
| 50%-70% | 3 |
| 75%-100% | 4 |
Tab. 1 Liver injury scoring criteria
| Hepatocyte edema, congestion, inflammatory cell infiltration | Index |
|---|---|
| None | 0 |
| 0%-25% | 1 |
| 25%-50% | 2 |
| 50%-70% | 3 |
| 75%-100% | 4 |
| Index | |
|---|---|
| None | 0 |
| 0%-25% | 1 |
| 25%-50% | 2 |
| 50%-70% | 3 |
| 75%-100% | 4 |
Tab. 2 Lung injury scoring criteria
| Index | |
|---|---|
| None | 0 |
| 0%-25% | 1 |
| 25%-50% | 2 |
| 50%-70% | 3 |
| 75%-100% | 4 |
| Injured renal tubules and shrunk glomerulu | Index |
|---|---|
| None | 0 |
| 0%-25% | 1 |
| 25%-50% | 2 |
| 50%-70% | 3 |
| 75%-100% | 4 |
Tab. 3 Kidney injury scoring criteria
| Injured renal tubules and shrunk glomerulu | Index |
|---|---|
| None | 0 |
| 0%-25% | 1 |
| 25%-50% | 2 |
| 50%-70% | 3 |
| 75%-100% | 4 |
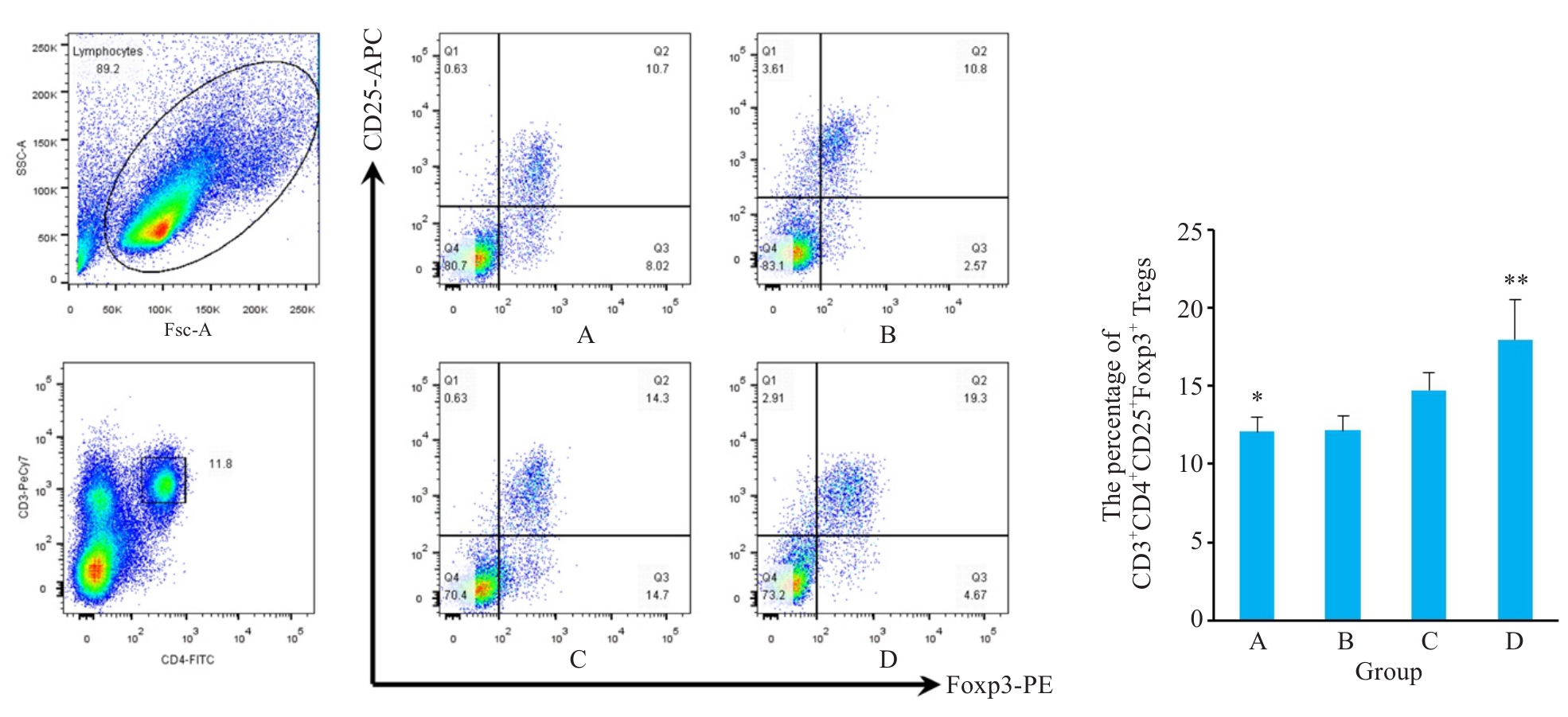
Fig.3 Proportion of CD3+CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells in the spleen of mice in each experimental group. Representative three-dimension scatter diagrams of CD3+CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells in the spleen of mice in each group. The percentage of CD3+CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells in the splenocytes of mice in each group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Group C.
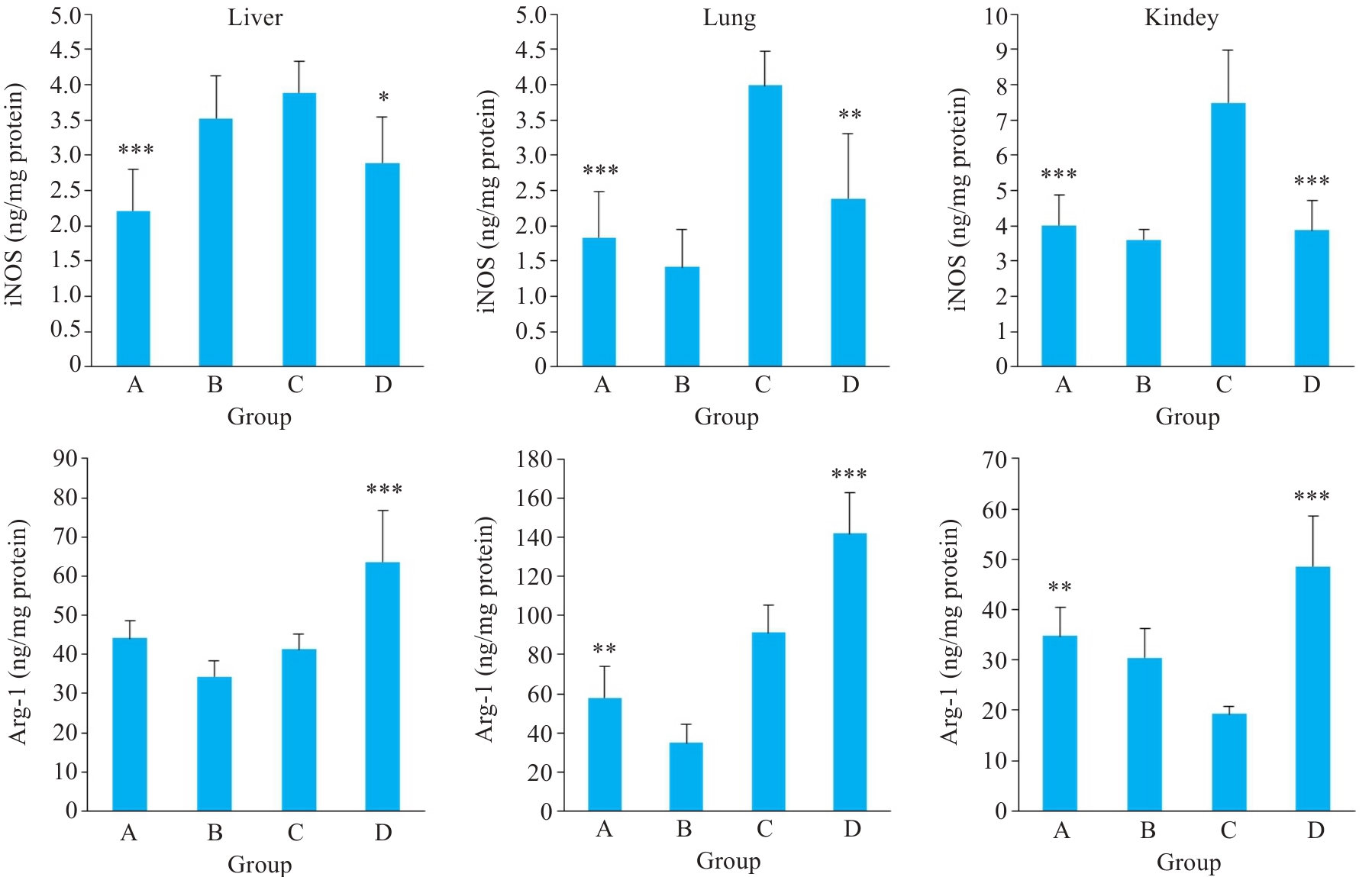
Fig.6 Expression of M1 and M2 type biomarkers iNOS and Arg-1 in the liver, lungs, and kidney tissues in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Group C.
| 1 | Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 801-10. |
| 2 | Iba T, Helms J, Neal MD, et al. Mechanisms and management of the coagulopathy of trauma and sepsis: trauma-induced coagulopathy, sepsis-induced coagulopathy, and disseminated intravascular coagulation[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2023, 21(12): 3360-70. |
| 3 | Kang R, Zeng L, Xie YC, et al. A novel PINK1- and PARK2-dependent protective neuroimmune pathway in lethal sepsis[J]. Autophagy, 2016, 12(12): 2374-85. |
| 4 | Negrin LL, Jahn A, van Griensven M. Leptin protects against mortality and organ dysfunction in A two-hit trauma/sepsis model and is IL-6-dependent[J]. Shock, 2017, 48(1): 130-7. |
| 5 | Jiang YX, Xia MZ, Huang Q, et al. Protective effect of dexmedetomidine against organ dysfunction in a two-hit model of hemorrhage/resuscitation and endotoxemia in rats[J]. Rev Bras De Pesquisas Med E Biol, 2019, 52(3): e7905. |
| 6 | 吴海荣, 孙月雯, 吴锡平. 单味黄芩煎剂对内毒素"二次打击"脓毒症大 鼠体内Fn及肺组织EPCR、AMPK表达的影响[J]. 中国中医急症, 2023, 32(4): 581-5. |
| 7 | Murphy TJ, Paterson HM, Kriynovich S, et al. Linking the "two-hit" response following injury to enhanced TLR4 reactivity[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2005, 77(1): 16-23. |
| 8 | Venet F, Monneret G. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2018, 14(2): 121-37. |
| 9 | Wammes LJ, Mpairwe H, Elliott AM, et al. Helminth therapy or elimination: epidemiological, immunological, and clinical consi-derations[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2014, 14(11): 1150-62. |
| 10 | Mu Y, McManus DP, Hou N, et al. Schistosome infection and schistosome-derived products as modulators for the prevention and alleviation of immunological disorders[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 619776. |
| 11 | Wang M, Wu LX, Weng RN, et al. Therapeutic potential of helminths in autoimmune diseases: helminth-derived immune-regulators and immune balance[J]. Parasitol Res, 2017, 116(8): 2065-74. |
| 12 | Stachyra A, Zawistowska-Deniziak A, Basałaj K, et al. The immunological properties of recombinant multi-cystatin-like domain protein from Trichinella britovi produced in yeast[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2420. |
| 13 | Li HH, Qiu DP, Yuan Y, et al. Trichinella spiralis cystatin alleviates polymicrobial sepsis through activating regulatory macrophages[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 109: 108907. |
| 14 | Coronado S, Zakzuk J, Regino R, et al. Ascaris lumbricoides cystatin prevents development of allergic airway inflammation in a mouse model[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2280. |
| 15 | 褚 亮, 李徽徽, 王书书, 等. 源自日本血吸虫的半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎的影响[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2018, 30(3): 269-72, 338. |
| 16 | Liu F, Cheng WS, Pappoe F, et al. Schistosoma japonicum cystatin attenuates murine collagen-induced arthritis[J]. Parasitol Res, 2016, 115(10): 3795-806. |
| 17 | Yang HJ, Li HQ, Chen WD, et al. Therapeutic effect of Schistosoma japonicum cystatin on atherosclerotic renal damage[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 760980. |
| 18 | 陈道刚, 芦灵军.脓毒症患者肠道微生态的研究进展[J].现代医药卫生, 2024, 40(3): 477-81. |
| 19 | Tran DT, Jeong YY, Kim JM, et al. The anti-inflammatory role of bilirubin on "two-hit" sepsis animal model[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(22): 8650. |
| 20 | Efron PA, Mohr AM, Bihorac A, et al. Persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism and the development of chronic critical illness after surgery[J]. Surgery, 2018, 164(2): 178-84. |
| 21 | Bone RC. Immunologic dissonance: a continuing evolution in our understanding of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)[J]. Ann Intern Med, 1996, 125(8): 680-7. |
| 22 | Li HH, Wang SS, Zhan B, et al. Therapeutic effect of Schistosoma japonicum cystatin on bacterial sepsis in mice[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2017, 10(1): 222. |
| 23 | Cui Z, Wang L, Li H, et al. Study on immune status alterations in patients with sepsis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 118:110048. |
| 24 | Chiu C, Legrand M. Epidemiology of sepsis and septic shock[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol, 2021, 34(2): 71-6. |
| 25 | Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, et al. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. current estimates and limitations[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2016, 193(3): 259-72. |
| 26 | 中国医师协会急诊医师分会, 中国研究型医院学会休克与脓毒症专业委员会. 中国脓毒症/脓毒性休克急诊治疗指南(2018)[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2018, 19(9): 567-88. |
| 27 | Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D. Sepsis-induced immuno-suppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2013, 13(12): 862-74. |
| 28 | Kellum JA, Ronco C. The role of endotoxin in septic shock[J]. Crit Care, 2023, 27(1): 400. |
| 29 | 杨小迪, 贺文欣, 方 强, 等. 旋毛虫成虫排泄分泌蛋白抗CLP诱导的小鼠脓毒症的观察[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2016, 28(3): 293-6, 322. |
| 30 | Jiang J, Yin HL, Sun Y, et al. Clonorchis sinensis cyclophilin A immunization protected mice from CLP-induced sepsis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 59: 347-53. |
| 31 | Puneet P, McGrath MA, Tay HK, et al. The helminth product ES-62 protects against septic shock via Toll-like receptor 4-dependent autophagosomal degradation of the adaptor MyD88[J]. Nat Immunol, 2011, 12(4): 344-51. |
| 32 | 李燕楠, 杨小迪, 陈思宇, 等. 日本血吸虫重组半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对小鼠心肌梗死预后的影响及其免疫调节机制[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志, 2022, 35(1): 55-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5503.2022.1.zgswzpxzz202201011 |
| 33 | Xie H, Wu LQ, Chen XZ, et al. Schistosoma japonicum cystatin alleviates sepsis through activating regulatory macrophages[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 617461. |
| 34 | Acharya S, Da’dara AA, Skelly PJ. Schistosome immunomodulators[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2021, 17(12): e1010064. |
| 35 | Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeos-tasis and disease[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 445-55. |
| [1] | Kai CHEN, Zhaofei MENG, Jingting MIN, Jiahui WANG, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO, Junfeng HU. Curcumin alleviates septic lung injury in mice by inhibiting TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1805-1813. |
| [2] | Jing ZENG, Rong CHEN, Xiangyi REN, Lei HUA, Yong YANG, Jiangping WEI, Xiaomei ZHANG. Yigong San improves cognitive decline in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease by regulating intestinal microorganisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1297-1305. |
| [3] | FANG Shangping, SUN Renke, SU Hui, ZHAI Kecheng, XIANG Yu, GAO Yangmengna, GUO Wenjun. Chlorogenic acid alleviates acute kidney injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes and the caspase-1 canonical pyroptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 317-323. |
| [4] | LING Xuguang, XU Wenwen, PANG Guanlai, HONG Xuxing, LIU Fengqin, LI Yang. Tea polyphenols ameliorates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| [5] | Xiaofei SU, Lin LI, Jingrong DAI, Bao XIAO, Ziqi JIN, Bin LIU. GSK484, a PAD4 inhibitor, improves endothelial dysfunction in mice with sepsis-induced lung injury by inhibiting H3Cit expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2396-2403. |
| [6] | Ruoli DU, Qi YUN, Yiren WANG, Xinyu DOU, Hongwei YE, Jiahui WANG, Qin GAO. Plumbagin protect against sepsis-induced myocardial injury in mice by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway to reduce cardiomyocyte pyroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2209-2219. |
| [7] | YU Jiachi, LI Ruibing, XIA Tian, WANG Jianan, JIN Jiacheng, YUAN Manqiu, LI Mianyang. PDCD4 knockdown ameliorates lipopolysaccharide- induced endothelial cell damage by improving mitochondrial dynamics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 25-35. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xiaohong, ZHAO Pin, KUAI Jianke, CHANG Chao, YUAN Qing. Spermidine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury in mice by suppressing apoptosis, ROS production and ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 166-172. |
| [9] | WANG Liya, TIAN Meihui, LI Rong, WU Yue, WANG Shasha, LÜ Heng, LIU Zhongyi, YU Ying. Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 ameliorates lung endothelial barrier and balances mitochondrial dynamics in mice with acute lung injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1388-1395. |
| [10] | GUO Jingjing, ZHANG Wenlong, LIANG Piao, ZHANG Longjun, PENG Lingyin, MIN Yuqi, PAN Xiaozhen, YANG Zhiying, DENG Huafei. Puerarin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in mice by modulating the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1248-1253. |
| [11] | LIN Jiayi, LOU Anni, LI Xu. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates macrophages to secrete exosomes containing miR-155-5p to promote activation and migration of hepatic stellate cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 994-1001. |
| [12] | WU Songlin, LI Xuexin, GUAN Fasheng, FENG Jianguo, JIA Jing, LI Jing, LIU Li. Enhanced endoplasmic reticulum RyR1 receptor phosphorylation leads to diaphragmatic dysfunction in septic rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(4): 631-636. |
| [13] | TANG Wentao, DENG Juan, HE Sicheng, LI Junfen, ZHOU Yiqing, WANG Yan. Inhibitory effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on apoptosis of splenic lymphocytes in septic rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1789-1795. |
| [14] | KANG Huiwen, JIANG Shoufang, SONG Qian, ZHANG Yili. Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 alleviates acute lung injury in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(9): 1374-1380. |
| [15] | YUAN Yuan, NIAN Feng, LI Huihui, YANG Huijuan, WU Yuzhi, MA Mengxi, WANG Kaigui, CHEN Xueling, ZHANG Ziqiang, LI Gen, YANG Xiaodi, WU Qiang. Protective effect of excretory-secretory proteins from Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae against myocardial injury in septic mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(6): 824-831. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||