Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 1297-1305.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.09
Jing ZENG1,2( ), Rong CHEN1,2, Xiangyi REN3, Lei HUA1,2, Yong YANG1,2,5, Jiangping WEI1,2,4(
), Rong CHEN1,2, Xiangyi REN3, Lei HUA1,2, Yong YANG1,2,5, Jiangping WEI1,2,4( ), Xiaomei ZHANG1,2,5(
), Xiaomei ZHANG1,2,5( )
)
Received:2024-04-11
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-25
Contact:
Jiangping WEI, Xiaomei ZHANG
E-mail:1589905936@qq.com;sichuanwjp@163.com;ZXM761@163.com
Jing ZENG, Rong CHEN, Xiangyi REN, Lei HUA, Yong YANG, Jiangping WEI, Xiaomei ZHANG. Yigong San improves cognitive decline in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease by regulating intestinal microorganisms[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1297-1305.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.09
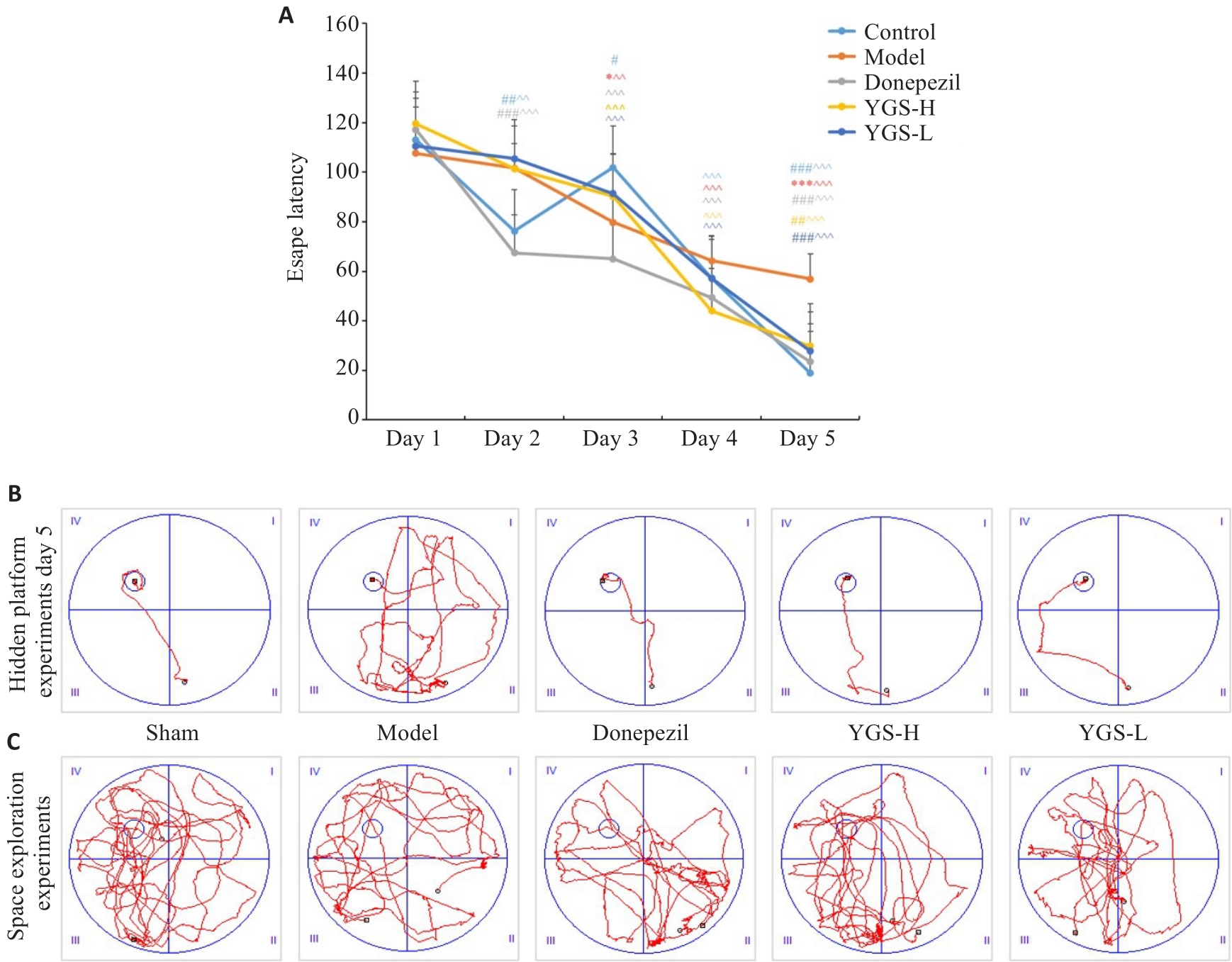
Fig.1 Effect of Yigong San on learning and memory ability of rats with LPS-induced Alzheimer's disease (AD). A: Escape latency in hidden platform test (n=8). B: Representative trajectory map of hidden platform test on day 5 after modeling. C: Representative trajectory map of spatial probe test. ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.01, ^^^P<0.001 vs the escape latency on the first day in each group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs Model.
| Group | Dosage | Times of platform crossing time (s) | Platform quadrant cumulative time (s) | Average swimming speed(cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 3.85±1.77## | 34.53±10.21# | 14.43±1.77 |
| Model | - | 1.43±0.98** | 21.49±2.92* | 12.71±2.75 |
| Donepezil | 1.3 mg/kg | 2.00±0.89 | 24.45±8.71 | 9.72±2.60 |
| YGS-H | 5.25 g/kg | 4.14±2.97# | 26.19±6.33 | 14.32±1.62 |
| YGS-L | 2.63 g/kg | 3.29±0.95## | 28.81±5.83 | 14.60±3.27 |
Tab.1 Number of platform crossings, platform quadrant accumulation time and average swimming speed (Mean±SD)
| Group | Dosage | Times of platform crossing time (s) | Platform quadrant cumulative time (s) | Average swimming speed(cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 3.85±1.77## | 34.53±10.21# | 14.43±1.77 |
| Model | - | 1.43±0.98** | 21.49±2.92* | 12.71±2.75 |
| Donepezil | 1.3 mg/kg | 2.00±0.89 | 24.45±8.71 | 9.72±2.60 |
| YGS-H | 5.25 g/kg | 4.14±2.97# | 26.19±6.33 | 14.32±1.62 |
| YGS-L | 2.63 g/kg | 3.29±0.95## | 28.81±5.83 | 14.60±3.27 |

Fig.2 Effect of Yigong San on pathomorphology of the hippocampus in rats with LPS-induced AD. A: Control. B: Model. C: YGS-H. D: YGS-L. n=8, *P<0.05 vs Control; ##P<0.01 vs Model.
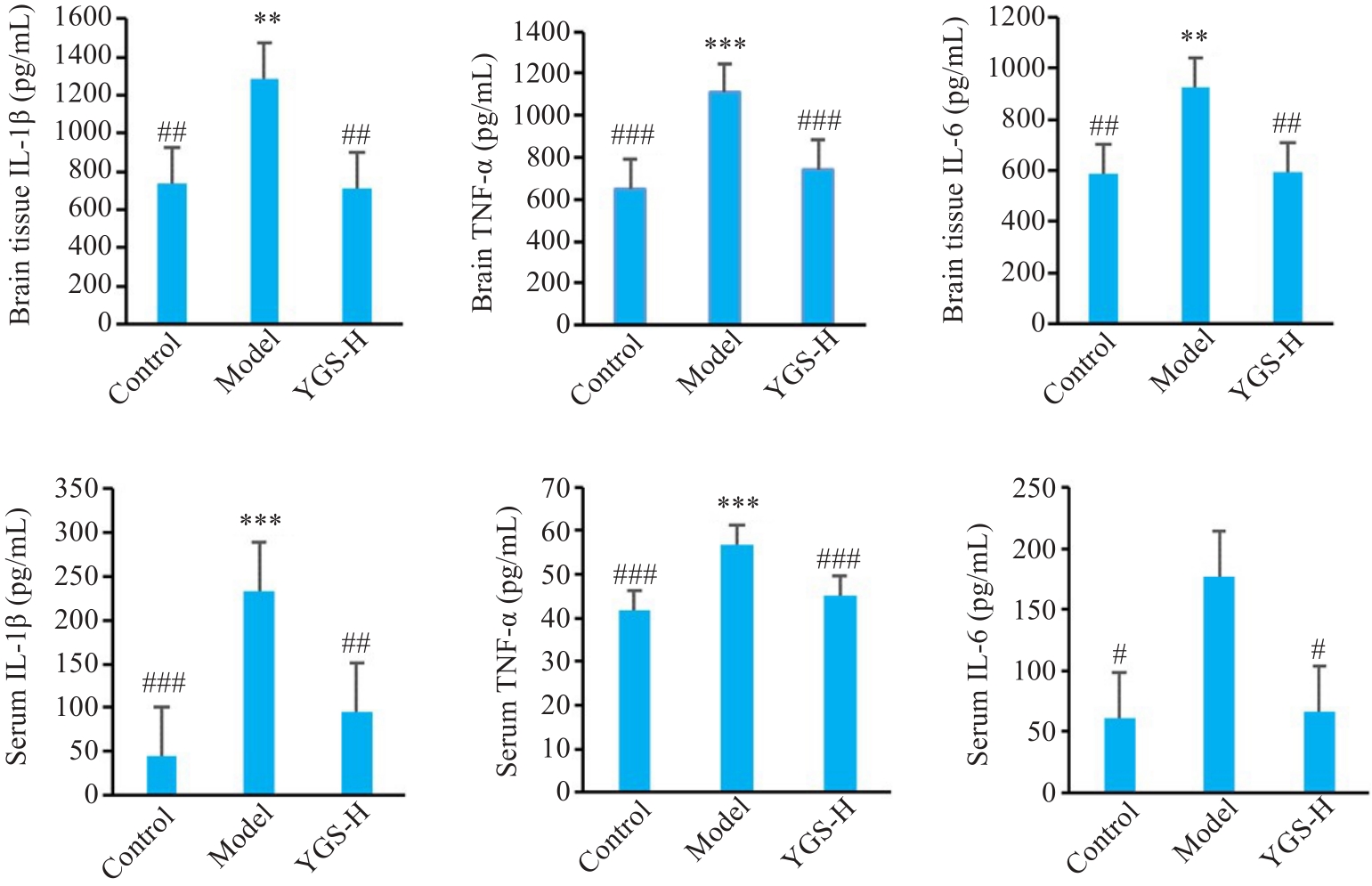
Fig.3 Effect of Yigong San on brain tissue and serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in rats with LPS-induced AD. n=6, **P<0.01, ***P<0.01 vs Control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs Model.

Fig.4 Diversity analysis of intestinal microbiota of the rats. A: Statistical analysis of alpha diversity index (n=6). B: β-diversity analysis-principal coordinates analysis (PCoA). C: β-diversity analysis-non-metricmulti-dimensional scaling (NMDS). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs Model.
| 1 | 陈路军, 孙智玲, 陈文静, 等. 从“津液代谢” 探讨变通小青龙汤在慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性期的应用[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2022, 34(10): 1811-4. |
| 2 | Angelucci F, Cechova K, Amlerova J, et al. Antibiotics, gut microbiota, and Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 108. |
| 3 | Luo YX, Yang LL, Yao XQ. Gut microbiota-host lipid crosstalk in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for disease progression and therapeutics[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2024, 19(1): 35. |
| 4 | Zhang T, Gao GQ, Kwok LY, et al. Gut microbiome-targeted therapies for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Gut Microbes, 2023, 15(2): 2271613. |
| 5 | 魏江平, 赵子瑄, 曾 静, 等. 异功散调控CXCL12/CXCR4信号减少谷氨酸释放改善衰老模型小鼠认知下降[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(23): 6483-91. |
| 6 | Shi ZS, Zhu LH, Li TT, et al. Neuroprotective mechanisms of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides against ischemic insults by regulating NR2B and NR2A containing NMDA receptor signaling pathways[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2017, 11(9): 288. |
| 7 | Parks DH, Tyson GW, Hugenholtz P, et al. STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(21): 3123-34. |
| 8 | 徐世军, 赵宜军, 张文生, 等. 从中医脑络功能演变谈轻度认知障碍的病机[J]. 中医杂志, 2011, 52(19): 1627-9. DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2010.68 |
| 9 | 田 恺, 张向宇, 牛博真, 等. 基于“毒损脑络” 理论中医脑病病因病机和辨证施治的研究进展[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2021, 19(8): 1308-10. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2021.08.014 |
| 10 | Ho L, Ono K, Tsuji M, et al. Protective roles of intestinal microbiota derived short chain fatty acids in Alzheimer’s disease-type beta-amyloid neuropathological mechanisms[J]. Expert Rev Neurother, 2018, 18(1): 83-90. |
| 11 | Yang YH, Lu MM, Xu YC, et al. Dietary methionine via dose-dependent inhibition of short-chain fatty acid production capacity contributed to a potential risk of cognitive dysfunction in mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(48): 15225-43. |
| 12 | Yuan SL, Yang JL, Jian Y, et al. Treadmill exercise modulates intestinal microbes and suppresses LPS displacement to alleviate neuroinflammation in the brains of APP/PS1 mice[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(19): 4134. |
| 13 | Aboulhoda BE, Rashed LA, Ahmed H, et al. Hydrogen sulfide and mesenchymal stem cells-extracted microvesicles attenuate LPS-induced Alzheimer’s disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(8): 5994-6010. |
| 14 | Decandia D, Gelfo F, Landolfo E, et al. Dietary protection against cognitive impairment, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease animal models of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(6): 5921-33. |
| 15 | Mao XS, Kelty TJ, Kerr NR, et al. Creatine supplementation upregulates mTORC1 signaling and markers of synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus while ameliorating LPS-induced cognitive impairment in female rats[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(8): 2758. |
| 16 | Schirmbeck GH, Seady M, Fróes FT, et al. Long-term LPS systemic administration leads to memory impairment and disturbance in astrocytic homeostasis[J]. Neurotoxicology, 2023, 99: 322-31. |
| 17 | Chen YY, Cui WW, Li X, et al. Interaction between commensal bacteria, immune response and the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12(11): 761981. |
| 18 | Martens EC, Neumann M, Desai MS. Interactions of commensal and pathogenic microorganisms with the intestinal mucosal barrier[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2018, 16(8): 457-70. |
| 19 | Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson's disease[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(6): 1469-80. |
| 20 | 杨 澜, 刘明飞, 孙成宏, 等. 基于肠道菌群与肠道代谢探究脉络舒通丸对大鼠股骨骨折引起的后肢肿胀的治疗作用及机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(17): 4711-21. |
| 21 | Cui YT, Zhang FY, Xu WM, et al. Effects of Si-Miao-Yong-An Decoction on myocardial I/R rats by regulating gut microbiota to inhibit LPS-induced TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2023, 23(1): 180. |
| 22 | Shen L, Liu L, Ji HF. Alzheimer's disease histological andBehavioral manifestations inTransgenic mice correlate with Specific Gut microbiome state[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2017, 56(1): 385-90. |
| 23 | Wang M, Amakye WK, Gong C, et al. Effect of oral and intraperitoneal administration of walnut-derived pentapeptide PW5 on cognitive impairments in APPSWE/PS1ΔE9 mice[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 180(1): 191-7. |
| 24 | He YS, Luo RL, Xia MY, et al. Orally administered diosgenin alleviates colitis in mice induced by dextran sulfate sodium through gut microbiota modulation and short-chain fatty acid generation[J]. J Med Food, 2022, 25(3): 261-71. |
| 25 | Hiippala K, Barreto G, Burrello C, et al. Novel Odoribacter splanchnicus strain and its outer membrane vesicles exert immunoregulatory effects in vitro [J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11(11): 575455. |
| 26 | Yang WY, Gao BM, Qin L, et al. Puerarin improves skeletal muscle strength by regulating gut microbiota in young adult rats[J]. J Orthop Translat, 2022(9), 35: 87-98. |
| 27 | García-Belenguer S, Grasa L, Valero O, et al. Gut microbiota in canine idiopathic epilepsy: effects of disease and treatment[J]. Animals, 2021, 11(11): 3121. |
| 28 | Tran TTT, Corsini S, Kellingray L, et al. APOE genotype influences the gut microbiome structure and function in humans and mice: relevance for Alzheimer's disease pathophysiology[J]. FASEB J, 2019, 33(7): 8221-31. |
| 29 | Scheperjans F, Aho V, Pereira PA, et al. Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson's disease and clinical phenotype[J]. Mov Disord, 2015, 30(3): 350-8. |
| 30 | Forsyth CB, Shannon KM, Kordower JH, et al. Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson's disease[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(12): e28032. |
| 31 | Holmqvist S, Chutna O, Bousset L, et al. Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2014, 128(6): 805-20. |
| 32 | Zhang D, Fu X, Dai XH, et al. A new biological process for short-chain fatty acid generation from waste activated sludge improved by Clostridiales enhancement[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2016, 23(23): 23972-82. |
| 33 | Li H, Christman LM, Yagiz Y, et al. Dealcoholized muscadine wine was partially effective in preventing and treating dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and restoring gut dysbiosis in mice[J]. Food Funct, 2023, 14(13): 5994-6011. |
| 34 | Li J, Liao XJ, Yin XD, et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome profiles of capsaicin with cognitive benefits in APP/PS1 mice[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 15(1): 118. |
| 35 | Hung CC, Chang CC, Huang CW, et al. Gut microbiota in patients with Alzheimer’s disease spectrum: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Aging, 2022, 14(1): 477-96. |
| 36 | Murray ER, Kemp M, Nguyen TT. The microbiota-gut-brain axis in Alzheimer's disease: a review of taxonomic alterations and potential avenues for interventions[J]. Arch Clin Neuropsychol, 2022, 37(3): 595-607. |
| 37 | Hou YJ, Dan XL, Babbar M, et al. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2019(10), 15: 565-81. |
| 38 | Czapski GA, Strosznajder JB. Glutamate and GABA in microglia-neuron cross-talk in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(21): 11677. |
| 39 | Andersen JV, Schousboe A, Verkhratsky A. Astrocyte energy and neurotransmitter metabolism in Alzheimer's disease: integration of the glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2022(7), 217: 102331. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||