Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2412-2420.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.18
Caolin LIU1( ), Qingqing ZOU2, Menghong WANG1, Qinmei YANG1, Liwen SONG1, Zixiao LU1, Qianjin FENG2, Yinghua ZHAO1(
), Qingqing ZOU2, Menghong WANG1, Qinmei YANG1, Liwen SONG1, Zixiao LU1, Qianjin FENG2, Yinghua ZHAO1( )
)
Received:2024-08-06
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Yinghua ZHAO
E-mail:liucaolun08@smu.edu.cn;zyh7258957@163.com
Supported by:Caolin LIU, Qingqing ZOU, Menghong WANG, Qinmei YANG, Liwen SONG, Zixiao LU, Qianjin FENG, Yinghua ZHAO. Identification of osteoid and chondroid matrix mineralization in primary bone tumors using a deep learning fusion model based on CT and clinical features: a multi-center retrospective study[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2412-2420.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.18
| Characteristics | Osteogenic bone tumors (n=123) | Chondrogenic bone tumors (n=99) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender [n (%)] | 0.078 | ||
| Male | 79 (64.23%) | 52 (52.53%) | |
| Female | 44 (35.77%) | 47 (47.47%) | |
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 22.10±14.71 | 39.49±17.87 | <0.001 |
| Pathological fracture [n (%)] | 31 (25.20%) | 26 (26.26%) | 0.857 |
| Mineralization location [n (%)] | <0.001 | ||
| Femur | 45 (36.58%) | 18 (18.18%) | |
| Tibia and fibula | 26 (21.14%) | 7 (7.071%) | |
| Humerus | 7 (5.69%) | 12 (12.12%) | |
| Pelvis | 9 (7.32%) | 21 (21.21%) | |
| Others | 36 (29.67%) | 41 (41.41%) | |
Tab.1 Clinical characteristics of the patients
| Characteristics | Osteogenic bone tumors (n=123) | Chondrogenic bone tumors (n=99) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender [n (%)] | 0.078 | ||
| Male | 79 (64.23%) | 52 (52.53%) | |
| Female | 44 (35.77%) | 47 (47.47%) | |
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 22.10±14.71 | 39.49±17.87 | <0.001 |
| Pathological fracture [n (%)] | 31 (25.20%) | 26 (26.26%) | 0.857 |
| Mineralization location [n (%)] | <0.001 | ||
| Femur | 45 (36.58%) | 18 (18.18%) | |
| Tibia and fibula | 26 (21.14%) | 7 (7.071%) | |
| Humerus | 7 (5.69%) | 12 (12.12%) | |
| Pelvis | 9 (7.32%) | 21 (21.21%) | |
| Others | 36 (29.67%) | 41 (41.41%) | |
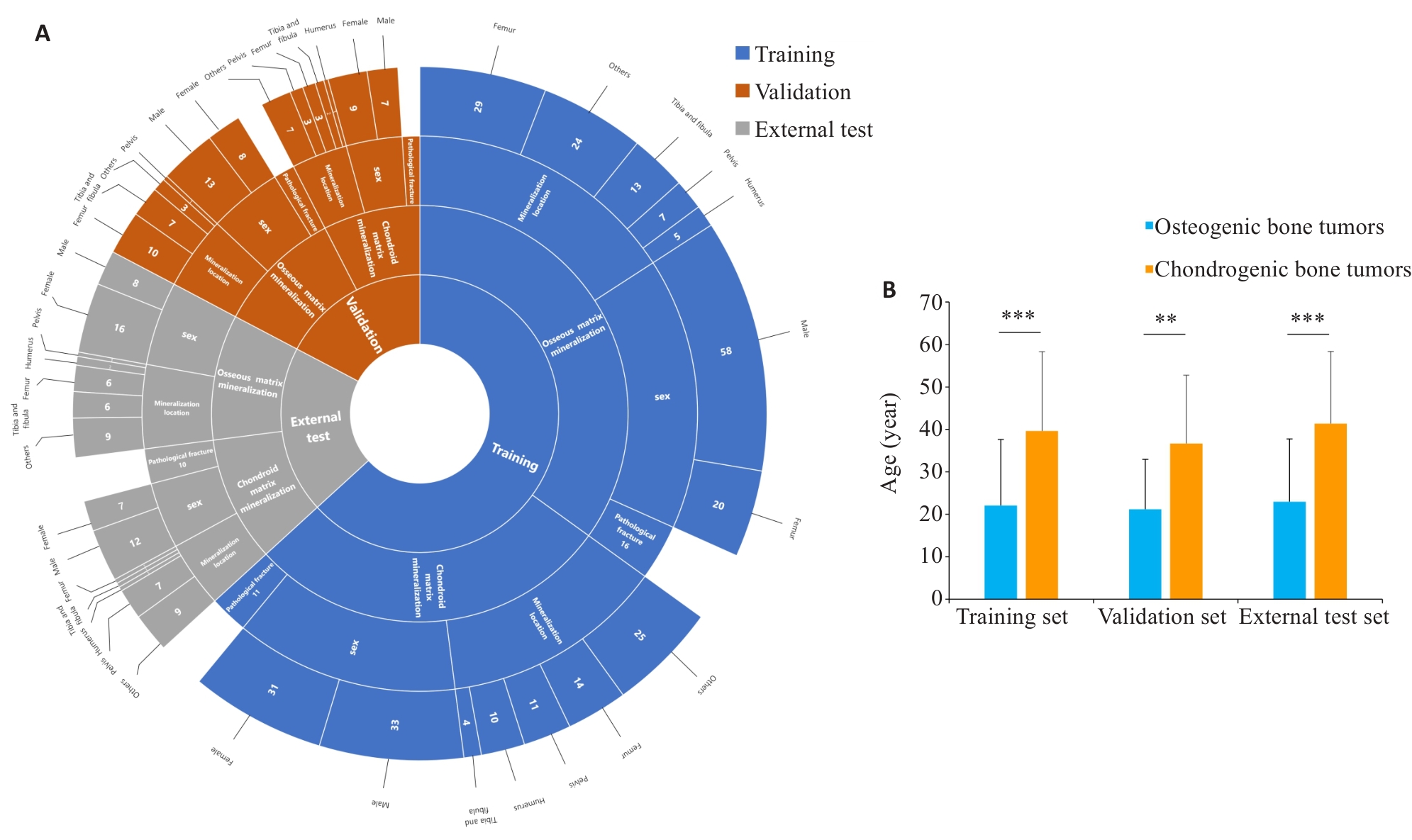
Fig. 2 Distribution of clinical features across training, validation, and external test sets. A: Sunburst chart showing the distribution of patient characteristics, including matrix mineralization pattern(osseous matrix mineralization, chondroid matrix mineralization), gender (male, female), mineralization location(femur, tibia and fibula, humerus, pelvis, others), and pathological fracture presence, across the training (blue), validation (red), and external test sets (gray). B: Histogram of patient age statistics, showing statistically significant differences in age distribution among the three groups. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Precision (95% CI) | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL model(R-Net) | 0.830 (0.700-0.961) | 0.730 (0.559-0.862) | 0.952 (0.762-0.999) | 0.438 (0.198-0.701) | 0.690 (0.492-0.847) | 0.800 |
| DL model (S-Net) | 0.774 (0.620-0.927) | 0.730 (0.559-0.862) | 0.810 (0.581-0.946) | 0.625 (0.354-0.848) | 0.739 (0.516-0.898) | 0.773 |
| DL model (RC-Net) | 0.857 (0.724-0.990) | 0.838 (0.680-0.938) | 0.810 (0.581-0.946) | 0.875 (0.617-0.984) | 0.895 (0.669-0.987) | 0.850 |
| DL model (SC-Net) | 0.869 (0.748-0.990) | 0.757 (0.588-0.882) | 0.905 (0.696-0.988) | 0.563 (0.299-0.802) | 0.731 (0.522-0.884) | 0.809 |
| ML model | 0.702 (0.531-0.874) | 0.676 (0.502-0.820) | 0.524 (0.298-0.743) | 0.875 (0.617-0.984) | 0.846 (0.546-0.981) | 0.647 |
| ML combined model | 0.830 (0.690-0.971) | 0.757 (0.588-0.882) | 0.762 (0.528-0.918) | 0.750 (0.476-0.927) | 0.800 (0.563-0.943) | 0.780 |
| DL: Deep learning; ML: Machine learning; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval. | ||||||
Tab.2 Classification performance of deep learning models, machine learning models and combined models in the internal validation set
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Precision (95% CI) | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL model(R-Net) | 0.830 (0.700-0.961) | 0.730 (0.559-0.862) | 0.952 (0.762-0.999) | 0.438 (0.198-0.701) | 0.690 (0.492-0.847) | 0.800 |
| DL model (S-Net) | 0.774 (0.620-0.927) | 0.730 (0.559-0.862) | 0.810 (0.581-0.946) | 0.625 (0.354-0.848) | 0.739 (0.516-0.898) | 0.773 |
| DL model (RC-Net) | 0.857 (0.724-0.990) | 0.838 (0.680-0.938) | 0.810 (0.581-0.946) | 0.875 (0.617-0.984) | 0.895 (0.669-0.987) | 0.850 |
| DL model (SC-Net) | 0.869 (0.748-0.990) | 0.757 (0.588-0.882) | 0.905 (0.696-0.988) | 0.563 (0.299-0.802) | 0.731 (0.522-0.884) | 0.809 |
| ML model | 0.702 (0.531-0.874) | 0.676 (0.502-0.820) | 0.524 (0.298-0.743) | 0.875 (0.617-0.984) | 0.846 (0.546-0.981) | 0.647 |
| ML combined model | 0.830 (0.690-0.971) | 0.757 (0.588-0.882) | 0.762 (0.528-0.918) | 0.750 (0.476-0.927) | 0.800 (0.563-0.943) | 0.780 |
| DL: Deep learning; ML: Machine learning; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval. | ||||||
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Precision (95% CI) | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL model(R-Net) | 0.768 (0.620-0.915) | 0.698 (0.539-0.828) | 0.833 (0.626-0.953) | 0.526 (0.289-0.756) | 0.690 (0.492-0.847) | 0.755 |
| DL model (S-Net) | 0.818 (0.694-0.942) | 0.767 (0.614-0.882) | 1.000 (0.858-1.000) | 0.474 (0.244-0.711) | 0.706 (0.525,0.849) | 0.828 |
| DL model (RC-Net) | 0.890 (0.802-0.988) | 0.791 (0.640-0.900) | 0.833 (0.626-0.953) | 0.737 (0.488-0.909) | 0.800 (0.593-0.932) | 0.816 |
| DL model (SC-Net) | 0.901 (0.803-1.00) | 0.837 (0.693-0.932) | 0.875 (0.676-0.973) | 0.789 (0.544-0.939) | 0.840 (0.639-0.955) | 0.857 |
| ML model | 0.761 (0.619-0.903) | 0.721 (0.563-0.847) | 0.583 (0.366-0.779) | 0.895 (0.669-0.987) | 0.875 (0.617-0.984) | 0.700 |
| ML combined model | 0.791 (0.655-0.926) | 0.744 (0.588-0.865) | 0.625 (0.406-0.812) | 0.895 (0.669-0.987) | 0.882 (0.636-0.985) | 0.732 |
| Radiologist 3 | - | 0.744 (0.588-0.865) | 0.792 (0.578-0.929) | 0.684 (0.475-0.874) | 0.760 (0.549-0.906) | 0.776 |
| Radiologist 4 | - | 0.814 (0.666-0.916) | 0.875 (0.676-0.973) | 0.737 (0.488-0.909) | 0.808 (0.606-0.934) | 0.840 |
| DL: Deep learning; ML: Machine learning; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval; Radiologist 3: Junior radiologist; Radiologist 4: Senior radiologist. | ||||||
Tab.3 Classification performance of deep learning models, machine learning models and combined models on the external test set
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Precision (95% CI) | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL model(R-Net) | 0.768 (0.620-0.915) | 0.698 (0.539-0.828) | 0.833 (0.626-0.953) | 0.526 (0.289-0.756) | 0.690 (0.492-0.847) | 0.755 |
| DL model (S-Net) | 0.818 (0.694-0.942) | 0.767 (0.614-0.882) | 1.000 (0.858-1.000) | 0.474 (0.244-0.711) | 0.706 (0.525,0.849) | 0.828 |
| DL model (RC-Net) | 0.890 (0.802-0.988) | 0.791 (0.640-0.900) | 0.833 (0.626-0.953) | 0.737 (0.488-0.909) | 0.800 (0.593-0.932) | 0.816 |
| DL model (SC-Net) | 0.901 (0.803-1.00) | 0.837 (0.693-0.932) | 0.875 (0.676-0.973) | 0.789 (0.544-0.939) | 0.840 (0.639-0.955) | 0.857 |
| ML model | 0.761 (0.619-0.903) | 0.721 (0.563-0.847) | 0.583 (0.366-0.779) | 0.895 (0.669-0.987) | 0.875 (0.617-0.984) | 0.700 |
| ML combined model | 0.791 (0.655-0.926) | 0.744 (0.588-0.865) | 0.625 (0.406-0.812) | 0.895 (0.669-0.987) | 0.882 (0.636-0.985) | 0.732 |
| Radiologist 3 | - | 0.744 (0.588-0.865) | 0.792 (0.578-0.929) | 0.684 (0.475-0.874) | 0.760 (0.549-0.906) | 0.776 |
| Radiologist 4 | - | 0.814 (0.666-0.916) | 0.875 (0.676-0.973) | 0.737 (0.488-0.909) | 0.808 (0.606-0.934) | 0.840 |
| DL: Deep learning; ML: Machine learning; AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval; Radiologist 3: Junior radiologist; Radiologist 4: Senior radiologist. | ||||||
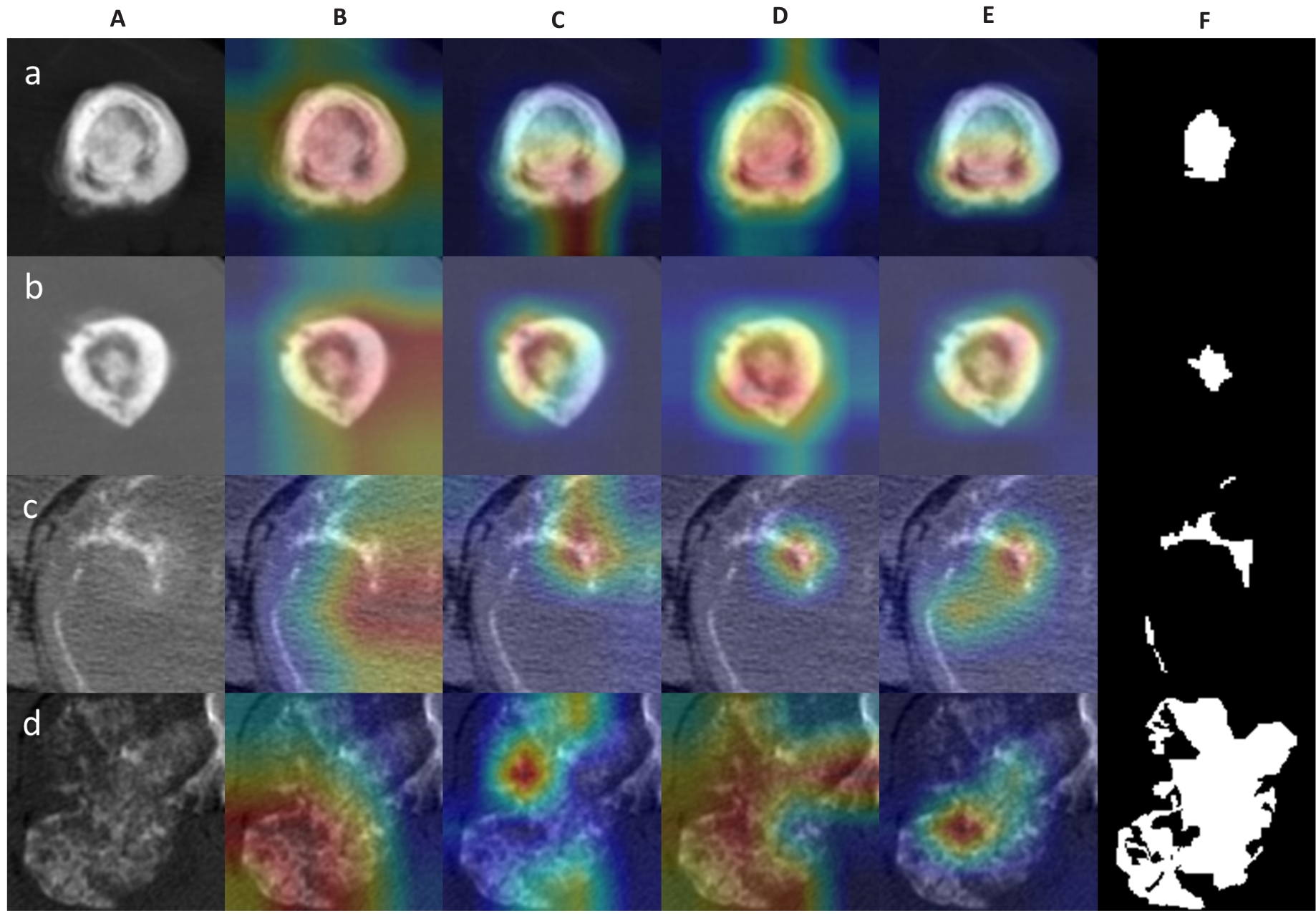
Fig. 3 Examples of activation heatmaps of the deep learning models. A: Original CT images. B-E: Regions of interest (ROIs) focused on by the deep learning models (red color indicates areas of primary concern for the model). F: Manually outlined ROIs. The rows a, b, c, and d show the original and processed images of osteosarcoma of the femur (osteoid matrix mineralization) in a 18-year-old patient, osteosarcoma of the humerus (osteoid matrix mineralization) in a 15-year-old female patient, chondrosarcoma of the rib (chondroid matrix mineralization) in a 53-year-old male patient, and chondrosarcoma of the rib near the thoracic vertebrae (chondroid matrix mineralization) in a 36-year-old male patient, respectively.
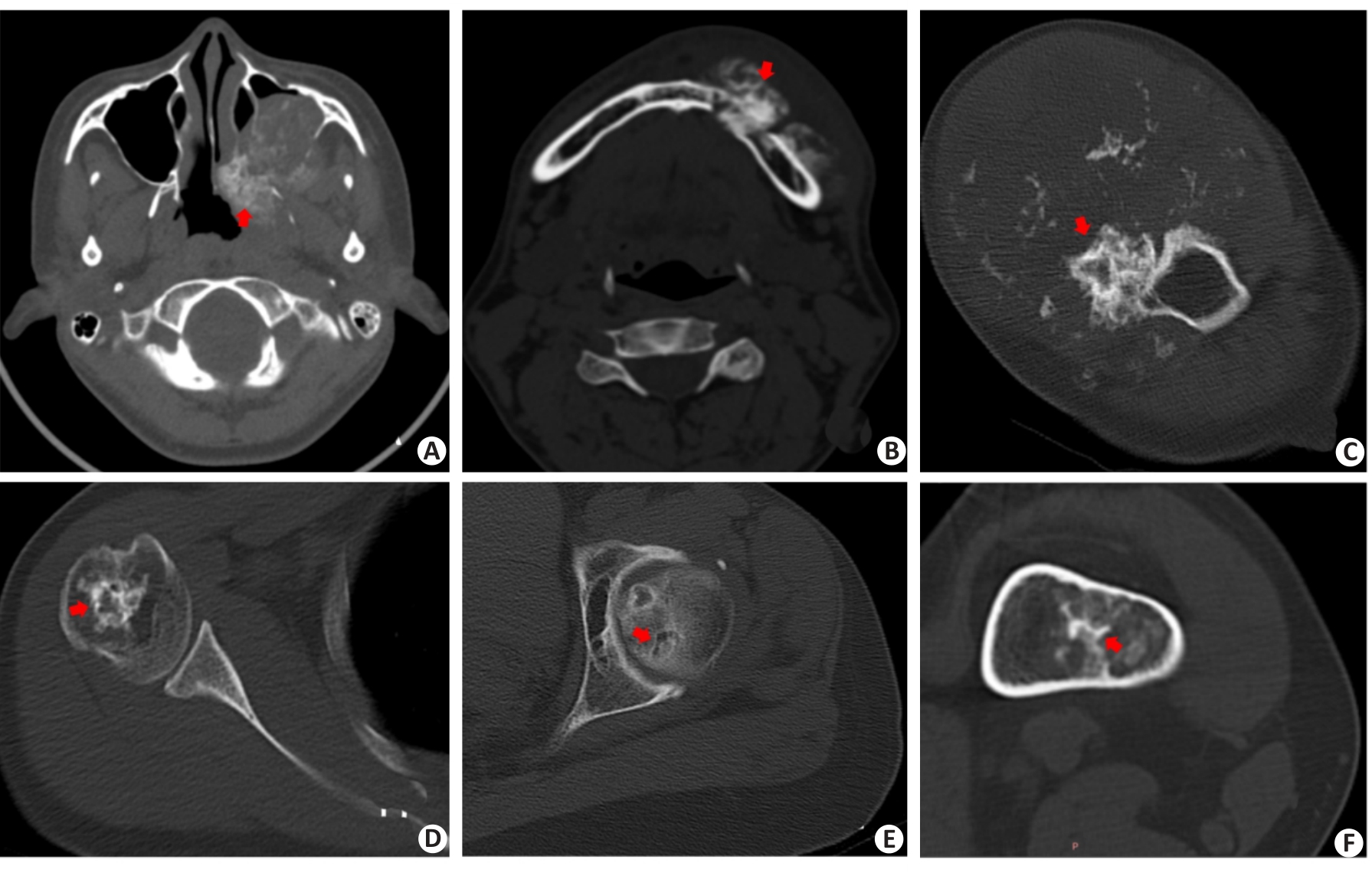
Fig.5 Cases of misclassification by deep learning model or machine learning model or Radiologist. DL: deep learning; ML: machine learning.A: Female,16 years; Pathological result: Osteosarcoma of the jawbone; Matrix mineralization pattern: Osteoid matrix (red arrow); Accurate classification: Senior radiologist; Inaccurate classification: Junior radiologist, DL model R-Net; B: Male, 37 years; Pathological result: Osteosarcoma of the jawbone; Matrix mineralization pattern: Osteoid matrix (red arrow); Accurate classification: Senior radiologist; Inaccurate classification: Junior radiologist, DL model R-Net;C: Male, 34 years; Pathological result; Chondrosarcoma of proximal humerus; Matrix mineralization pattern: Chondroid matrix (red arrow); Accurate Classification: Senior radiologist, DL model SC-Net; Inaccurate classification: Junior radiologist,ML model;D: Female, 44 years; Pathological result: Chondrosarcoma of proximal humerus; Matrix mineralization pattern: Chondroid matrix (red arrow); Accurate Classification: Senior radiologist, DL model SC-Net; Inaccurate classification: Junior radiologist, ML model; E: Female, 63 years; Pathological result: Intrafemoral chondroma; Matrix mineralization pattern: Chondroid matrix(red arrow); Accurate Classification: Junior, Senior Radiologist; Inaccurate classification: ML model,ML combined model, DL model R-Net;F: Female, 42 years; Pathological result: Intrafemoral chondroma; Matrix mineralization pattern: Chondroid matrix(red arrow); Accurate Classification: Junior,Senior Radiologist; Inaccurate classification: ML model, ML combined model, DL model R-Net.
| 1 | 崔久法. 双能量CT多参数成像技术对骨肿瘤瘤骨与瘤软骨钙化的鉴别诊断价值研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2018. |
| 2 | Sweet DE, Madewell JE, Ragsdale BD. Radiologic and pathologic analysis of solitary bone lesions. Part III: matrix patterns[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 1981, 19(4): 785-814. |
| 3 | 陈冠宇, 王仁法. 典型皮质旁骨肉瘤一例[J]. 放射学实践, 2016, 31(5): 466-7. |
| 4 | Erlemann R. Imaging and differential diagnosis of primary bone tumors and tumor-like lesions of the spine[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2006, 58(1): 48-67. |
| 5 | 张立华, 袁慧书. 脊柱软骨源性肿瘤的影像分析及鉴别[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2020, 39(7): 1379-83. |
| 6 | 吴杰芳, 秦耿耿, 童 凯, 等. 肩胛骨肿瘤的临床及影像学分析[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2021, 31(2): 317-21. |
| 7 | Abd-el-Naby W, Hammond T, Court-Brown CM. Atypical osteochondroma of the distal femur[J]. Orthopedics, 2000, 23(7): 725-6. |
| 8 | Berberat J, Grobholz R, Boxheimer L, et al. Differentiation between calcification and hemorrhage in brain tumors using susceptibility-weighted imaging: a pilot study[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2014, 202(4): 847-50. |
| 9 | Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48(4): 441-6. |
| 10 | Tomaszewski MR, Gillies RJ. The biological meaning of radiomic features[J]. Radiology, 2021, 298(3): 505-16. |
| 11 | Napel S, Mu W, Jardim-Perassi BV, et al. Quantitative imaging of cancer in the postgenomic era: radio(geno)mics, deep learning, and habitats[J]. Cancer, 2018, 124(24): 4633-49. |
| 12 | Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis[J]. Med Image Anal, 2017, 42: 60-88. |
| 13 | 袁 源, 王晨曦, 叶 凯, 等. 基于CT的影像组学在鉴别脊柱骨肉瘤与软骨肉瘤中的价值[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2024, 43(8): 1384-7. |
| 14 | 潘洁琳, 姜云萍, 占颖莺, 等. 基于MRI平扫的影像组学模型鉴别软骨肉瘤与内生软骨瘤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(4): 483-90. |
| 15 | Archer L, Snell KIE, Ensor J, et al. Minimum sample size for external validation of a clinical prediction model with a continuous outcome[J]. Stat Med, 2021, 40(1): 133-46. |
| 16 | Lafata KJ, Wang YQ, Konkel B, et al. Radiomics: a primer on high-throughput image phenotyping[J]. Abdom Radiol, 2022, 47(9): 2986-3002. |
| 17 | Guiot J, Vaidyanathan A, Deprez L, et al. A review in radiomics: making personalized medicine a reality via routine imaging[J]. Med Res Rev, 2022, 42(1): 426-40. |
| 18 | Zhou ZJ. Artificial intelligence on MRI for molecular subtyping of diffuse gliomas: feature comparison, visualization, and correlation between radiomics and deep learning[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(2): 745-6. |
| 19 | Pak M, Kim S. A review of deep learning in image recognition [C]. Proc 2017 4th Int Conf Comput Appl Inf Process Technol (CAIPT), Kuta Bali, Indonesia: IEEE, 2017: 1-3. |
| 20 | He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 27-30, 2016. Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 770-8. |
| 21 | Toseef M, Olayemi Petinrin O, Wang FZ, et al. Deep transfer learning for clinical decision-making based on high-throughput data: comprehensive survey with benchmark results[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2023, 24(4): bbad254. |
| 22 | Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, et al. How transferable are features in deep neural networks?[C]//Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 27 (NIPS 2014. PressMIT, 2014: 3320-8. |
| 23 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention Is All You Need [C]//Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 30 (NIPS 2017. Associates Curran, Inc., 2017: 5998-6008. |
| 24 | Wang Y, Wang H, Li YM, et al. High-accuracy, direct aberration determination using self-attention-armed deep convolutional neural networks[J]. J Microsc, 2022, 286(1): 13-21. |
| 25 | Naraghi AM, Mohankumar R, Linda D, et al. Bone tumors: imaging features of common and rare benign entities[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 2022, 60(2): 205-19. |
| 26 | Park S, Lee IS, Song YS, et al. Diagnostic performance of tomosynthesis for evaluation of bone tumors and tumor-like lesions: a comparison with radiography[J]. Acta Radiol, 2022, 63(8): 1086-92. |
| 27 | Deventer N, Deventer N, Gosheger G, et al. Chondroblastoma: is intralesional curettage with the use of adjuvants a sufficient way of therapy[J]? J Bone Oncol, 2021, 26: 100342. |
| 28 | Tepelenis K, Skandalakis GP, Papathanakos G, et al. Osteoid osteoma: an updated review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, radiological features, and treatment option[J]. In Vivo, 2021, 35(4): 1929-38. |
| 29 | Limaiem F, Byerly D W, Singh R. Osteoblastoma [M]. StatPearls (Internet). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2023:3-4. |
| 30 | Fu P, Shi Y, Chen G, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with osteosarcoma with the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2020, 19: 1533033820947701. |
| 31 | Zamora T. Enchondroma[M]// Bone Tumors. London: Springer, 2021: 57-62. |
| 32 | Biondi NL, Varacallo M. Enchondroma [M]//StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2024:5-7. |
| 33 | Bhure U, Roos JE, Strobel K. Osteoid osteoma: multimodality imaging with focus on hybrid imaging[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2019, 46(4): 1019-36. |
| 34 | Czarnecka AM, Synoradzki K, Firlej W, et al. Molecular biology of osteosarcoma[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(8): 2130. |
| 35 | Pan JL, Zhang K, Le HB, et al. Radiomics nomograms based on non-enhanced MRI and clinical risk factors for the differentiation of chondrosarcoma from enchondroma[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2021, 54(4): 1314-23. |
| 36 | Weinschenk RC, Wang WL, Lewis VO. Chondrosarcoma[J]. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2021, 29(13): 553-62. |
| 37 | Jia Q, Liu C, Yang J, et al. Clinical features, treatments and long-term follow-up outcomes of spinal chondroblastoma: report of 13 clinical cases in a single center[J]. J Neurooncol, 2018, 140(1): 99-106. |
| 38 | Zoccali C, Novello M, Arrigoni F, et al. Osteoblastoma: when the treatment is not minimally invasive, an overview[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(20): 4645. |
| 39 | Kumar N, Gupta B. Global incidence of primary malignant bone tumors[J]. Curr Orthop Pract, 2016, 27(5): 530-4. |
| 40 | Chlap P, Min H, Vandenberg N, et al. A review of medical image data augmentation techniques for deep learning applications[J]. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol, 2021, 65(5): 545-63. |
| 41 | Cheung TH, Yeung DY. A survey of automated data augmentation for image classification: learning to compose, mix, and generate[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2024, 35(10): 13185-205. |
| 42 | Garcea F, Serra A, Lamberti F, et al. Data augmentation for medical imaging: a systematic literature review[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2023, 152: 106391. |
| [1] | Weiyang FANG, Hui XIAO, Shuang WANG, Xiaoming LIN, Chaomin CHEN. A deep learning model based on magnetic resonance imaging and clinical feature fusion for predicting preoperative cytokeratin 19 status in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1738-1751. |
| [2] | Jiazhi OU, Chang'an ZHAN, Feng YANG. An autoencoder model based on one-dimensional neural network for epileptic EEG anomaly detection [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1796-1804. |
| [3] | Shengwang PENG, Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA, Jing HUANG. A dual-domain cone beam computed tomography reconstruction framework with improved differentiable domain transform for cone-angle artifact correction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1188-1197. |
| [4] | Zongyue LIN, Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA. A deep blur learning-based motion artifact reduction algorithm for dental cone-beam computed tomography images [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1198-1208. |
| [5] | Chen WANG, Mingqiang MENG, Mingqiang LI, Yongbo WANG, Dong ZENG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA. Reconstruction from CT truncated data based on dual-domain transformer coupled feature learning [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 950-959. |
| [6] | LONG Kaixing, WENG Danyi, GENG Jian, LU Yanmeng, ZHOU Zhitao, CAO Lei. Automatic classification of immune-mediated glomerular diseases based on multi-modal multi-instance learning [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 585-593. |
| [7] | CHEN Shixuan, ZENG Dong, BIAN Zhaoying, MA Jianhua. A low-dose CT reconstruction algorithm across different scanners based on federated feature learning [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 333-343. |
| [8] | XIAO Hui, FANG Weiyang, LIN Mingjun, ZHOU Zhenzhong, FEI Hongwen, CHEN Chaomin. A multiscale carotid plaque detection method based on two-stage analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 387-396. |
| [9] | ZHONG Weixiong, LIANG Fangrong, YANG Ruimeng, ZHEN Xin. Prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma based on multi-phase dynamic enhanced CT radiomics feature and multi-classifier hierarchical fusion model [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 260-269. |
| [10] | Jingyi LIAO, Shengwang PENG, Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN. A dual-domain cone beam computed tomography sparse-view reconstruction method based on generative projection interpolation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 2044-2054. |
| [11] | MI Jia, ZHOU Yujia, FENG Qianjin. A 3D/2D registration method based on reconstruction of orthogonal-view Xray images [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1636-1643. |
| [12] | CHU Zhiqin, QU Yaoming, ZHONG Tao, LIANG Shujun, WEN Zhibo, ZHANG Yu. A Dual-Aware deep learning framework for identification of glioma isocitrate dehydrogenase genotype using magnetic resonance amide proton transfer modalities [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1379-1387. |
| [13] | YU Jiahong, ZHANG Kunpeng, JIN Shuang, SU Zhe, XU Xiaotong, ZHANG Hua. Sinogram interpolation combined with unsupervised image-to-image translation network for CT metal artifact correction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1214-1223. |
| [14] | TENG Lin, WANG Bin, FENG Qianjin. Deep learning-based dose prediction in radiotherapy planning for head and neck cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 1010-1016. |
| [15] | ZHOU Hao, ZENG Dong, BIAN Zhaoying, MA Jianhua. A semi-supervised network-based tissue-aware contrast enhancement method for CT images [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 985-993. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||