Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 2044-2054.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.23
Jingyi LIAO1,2( ), Shengwang PENG1,2, Yongbo WANG1,2, Zhaoying BIAN1,2(
), Shengwang PENG1,2, Yongbo WANG1,2, Zhaoying BIAN1,2( )
)
Received:2024-05-31
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Zhaoying BIAN
E-mail:1jy@smu.edu.cn;zybian@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:Jingyi LIAO, Shengwang PENG, Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN. A dual-domain cone beam computed tomography sparse-view reconstruction method based on generative projection interpolation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 2044-2054.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.23
| Sparse views | Methods | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 (4×) | DSI | 25.9465±2.2533 | 0.7529±0.0283 | 13.9843±2.3840 |
| PDCNN | 27.8746±2.8157 | 0.8278±0.0252 | 12.0208±1.9469 | |
| SPINet | 28.6782±2.2693 | 0.8509±0.0172 | 10.5398±1.3201 | |
| 180 (2×) | DSI | 26.6960±2.4689 | 0.8713±0.0241 | 12.9739±2.4037 |
| PDCNN | 28.9448±2.5004 | 0.9118±0.0287 | 10.3867±1.9012 | |
| SPINet | 30.0966±2.7070 | 0.9785±0.0207 | 8.3688±1.6338 |
Tab.1 Interpolated projection quantitative comparison results (Mean±SD)
| Sparse views | Methods | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 (4×) | DSI | 25.9465±2.2533 | 0.7529±0.0283 | 13.9843±2.3840 |
| PDCNN | 27.8746±2.8157 | 0.8278±0.0252 | 12.0208±1.9469 | |
| SPINet | 28.6782±2.2693 | 0.8509±0.0172 | 10.5398±1.3201 | |
| 180 (2×) | DSI | 26.6960±2.4689 | 0.8713±0.0241 | 12.9739±2.4037 |
| PDCNN | 28.9448±2.5004 | 0.9118±0.0287 | 10.3867±1.9012 | |
| SPINet | 30.0966±2.7070 | 0.9785±0.0207 | 8.3688±1.6338 |
| Sparse views | Methods | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 (4×) | FDK | 31.0643±0.6153 | 0.7633±0.0134 | 7.1513±0.5106 |
| SART | 33.4367±0.6592 | 0.9239±0.008 | 5.4443±0.4266 | |
| TV | 33.5211±0.4835 | 0.9348±0.0039 | 5.3844±0.3017 | |
| DSI | 33.6291±0.8131 | 0.9231±0.0079 | 5.3328±0.5112 | |
| FBPConvNet | 38.8857±0.8032 | 0.9710±0.0037 | 3.2664±0.3069 | |
| DualCNN | 39.5630±0.7447 | 0.9654±0.0032 | 2.6912±0.2324 | |
| DualSFR-Net | 40.3288±0.7870 | 0.9788±0.0024 | 2.4652±0.2273 | |
| 180 (2×) | FDK | 37.3787±1.0431 | 0.8622±0.0171 | 3.4725±0.4186 |
| SART | 38.9154±1.1361 | 0.9617±0.0073 | 2.9132±0.3806 | |
| TV | 38.3474±0.8411 | 0.9657±0.0051 | 3.0984±0.2983 | |
| DSI | 38.6474±1.5467 | 0.9436±0.0109 | 3.0261±0.5438 | |
| FBPConvNet | 42.8195±1.1914 | 0.9740±0.0058 | 1.8601±0.2566 | |
| DualCNN | 43.9429±1.1090 | 0.9769±0.0052 | 1.6324±0.2075 | |
| DualSFR-Net | 44.6044±1.1207 | 0.9822±0.0038 | 1.5129±0.1939 |
Tab.2 Quantitative comparison results for different methods under sparse 2× and 4× condition (Mean±SD)
| Sparse views | Methods | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 (4×) | FDK | 31.0643±0.6153 | 0.7633±0.0134 | 7.1513±0.5106 |
| SART | 33.4367±0.6592 | 0.9239±0.008 | 5.4443±0.4266 | |
| TV | 33.5211±0.4835 | 0.9348±0.0039 | 5.3844±0.3017 | |
| DSI | 33.6291±0.8131 | 0.9231±0.0079 | 5.3328±0.5112 | |
| FBPConvNet | 38.8857±0.8032 | 0.9710±0.0037 | 3.2664±0.3069 | |
| DualCNN | 39.5630±0.7447 | 0.9654±0.0032 | 2.6912±0.2324 | |
| DualSFR-Net | 40.3288±0.7870 | 0.9788±0.0024 | 2.4652±0.2273 | |
| 180 (2×) | FDK | 37.3787±1.0431 | 0.8622±0.0171 | 3.4725±0.4186 |
| SART | 38.9154±1.1361 | 0.9617±0.0073 | 2.9132±0.3806 | |
| TV | 38.3474±0.8411 | 0.9657±0.0051 | 3.0984±0.2983 | |
| DSI | 38.6474±1.5467 | 0.9436±0.0109 | 3.0261±0.5438 | |
| FBPConvNet | 42.8195±1.1914 | 0.9740±0.0058 | 1.8601±0.2566 | |
| DualCNN | 43.9429±1.1090 | 0.9769±0.0052 | 1.6324±0.2075 | |
| DualSFR-Net | 44.6044±1.1207 | 0.9822±0.0038 | 1.5129±0.1939 |
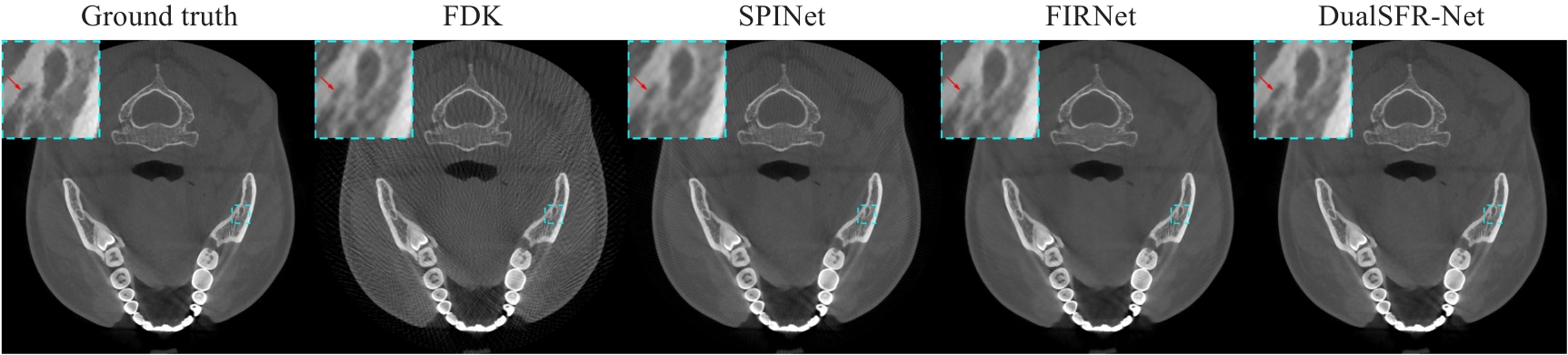
Fig.8 Validation of the effect of projection interpolation and image restoration modules on performance of the model. The image display window is [-1000,2300] HU.
| Methods | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDK | 37.3787±1.0431 | 0.8622±0.0171 | 3.4725±0.4186 |
| SPINet | 39.4331±1.0367 | 0.9461±0.0113 | 2.7409±0.3280 |
| FIRNet | 43.9257±1.2024 | 0.9721±0.0038 | 1.6210±0.2244 |
| DualSFR-Net ( | 44.0192±1.0474 | 0.9808±0.0031 | 1.6164±0.1855 |
| DualSFR-Net | 44.6044±1.1207 | 0.9822±0.0038 | 1.5129±0.1939 |
Tab.3 Quantitative comparison results of the ablation experiments (Mean±SD)
| Methods | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDK | 37.3787±1.0431 | 0.8622±0.0171 | 3.4725±0.4186 |
| SPINet | 39.4331±1.0367 | 0.9461±0.0113 | 2.7409±0.3280 |
| FIRNet | 43.9257±1.2024 | 0.9721±0.0038 | 1.6210±0.2244 |
| DualSFR-Net ( | 44.0192±1.0474 | 0.9808±0.0031 | 1.6164±0.1855 |
| DualSFR-Net | 44.6044±1.1207 | 0.9822±0.0038 | 1.5129±0.1939 |
| 1 | Pauwels R, Araki K, Siewerdsen JH, et al. Technical aspects of dental CBCT: state of the art[J]. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2015, 44(1): 20140224. |
| 2 | Jaffray DA, Siewerdsen JH, Wong JW, et al. Flat-panel cone-beam computed tomography for image-guided radiation therapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2002, 53(5): 1337-49. |
| 3 | Wang G, Zhao SY, Heuscher D. A knowledge-based cone-beam X-ray CT algorithm for dynamic volumetric cardiac imaging[J]. Med Phys, 2002, 29(8): 1807-22. |
| 4 | Hall EJ, Brenner DJ. Cancer risks from diagnostic radiology[J]. Br J Radiol, 2008, 81(965): 362-78. |
| 5 | Feldkamp LA, Davis LC, Kress JW. Practical cone-beam algorithm[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 1984, 1(6): 612. |
| 6 | Li S, Cao Q, Chen Y, et al. Dictionary learning based sinogram inpainting for CT sparse reconstruction[J]. Optik, 2014, 125(12): 2862-7. |
| 7 | Zhang H, Sonke JJ. Directional sinogram interpolation for sparse angular acquisition in cone-beam computed tomography[J]. J Xray Sci Technol, 2013, 21(4): 481-96. |
| 8 | Han Y, Ye JC. Framing U-net via deep convolutional framelets: application to sparse-view CT[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1418-29. |
| 9 | Jiang ZR, Chen YX, Zhang YW, et al. Augmentation of CBCT reconstructed from under-sampled projections using deep learning[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2019, 38(11): 2705-15. |
| 10 | Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou TH, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA. IEEE, 2017: 5967-76. |
| 11 | Zhang ZC, Liang XK, Dong X, et al. A sparse-view CT reconstruction method based on combination of DenseNet and deconvolution[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1407-17. |
| 12 | Xie SP, Yang T. Artifact removal in sparse-angle CT based on feature fusion residual network[J]. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci, 2021, 5(2): 261-71. |
| 13 | Ma JH, Zhang H, Gao Y, et al. Iterative image reconstruction for cerebral perfusion CT using a pre-contrast scan induced edge-preserving prior[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2012, 57(22): 7519-42. |
| 14 | Liu Y, Ma JH, Fan Y, et al. Adaptive-weighted total variation minimization for sparse data toward low-dose X-ray computed tomography image reconstruction[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2012, 57(23): 7923-56. |
| 15 | He J, Yang Y, Wang YB, et al. Optimizing a parameterized plug-and-play ADMM for iterative low-dose CT reconstruction[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2019, 38(2): 371-82. |
| 16 | Lee D, Choi S, Kim HJ. High quality imaging from sparsely sampled computed tomography data with deep learning and wavelet transform in various domains[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(1): 104-15. |
| 17 | Zhou B, Chen XC, Zhou SK, et al. DuDoDR-Net: dual-domain data consistent recurrent network for simultaneous sparse view and metal artifact reduction in computed tomography[J]. Med Image Anal, 2022, 75: 102289. |
| 18 | Shi CR, Xiao YS, Chen ZQ. Dual-domain sparse-view CT reconstruction with Transformers[J]. Phys Med, 2022, 101: 1-7. |
| 19 | Li RR, Li Q, Wang HX, et al. DDPTransformer: dual-domain with parallel transformer network for sparse view CT image reconstruction[J]. IEEE Trans Comput Imag, 2022, 8: 1101-16. |
| 20 | He J, Wang YB, Ma JH. Radon inversion via deep learning[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39(6): 2076-87. |
| 21 | He J, Chen SL, Zhang H, et al. Downsampled imaging geometric modeling for accurate CT reconstruction via deep learning[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2021, 40(11): 2976-85. |
| 22 | Chao LY, Wang ZW, Zhang HB, et al. Sparse-view cone beam CT reconstruction using dual CNNs in projection domain and image domain[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 493: 536-47. |
| 23 | Zhao XZ, Liu X, Wang XY, et al. Dual-domain neural networks for clinical and low-dose CBCT reconstruction[C]//2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Workshops (ICASSPW). Seoul, Korea, Republic of. IEEE, 2024: 17-8. |
| 24 | 彭声旺, 王永波, 边兆英, 等. 基于改进可微分域转换的双域锥束计算机断层扫描重建网络用于锥角伪影校正[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1188. |
| 25 | Wu JY, Li Y, Wang Z, et al. Dual-domain fusion network for metal artifact reduction in CT[C]//Medical Imaging 2024: Physics of Medical Imaging. February 18-23, 2024. San Diego, USA. SPIE, 2024: 378-384. |
| 26 | Wurfl T, Hoffmann M, Christlein V, et al. Deep learning computed tomography: learning projection-domain weights from image domain in limited angle problems[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1454-63. |
| 27 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III. |
| 28 | Chen H, Zhang Y, Kalra MK, et al. Low-dose CT with a residual encoder-decoder convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2017, 36(12): 2524-35. |
| 29 | Yamanaka J, Kuwashima S, Kurita T. Fast and accurate image super resolution by deep CNN with skip connection and network in network[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Cham: Springer, 2017: 217-25. |
| 30 | Yang QS, Yan PK, Zhang YB, et al. Low-dose CT image denoising using a generative adversarial network with Wasserstein distance and perceptual loss[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1348-57. |
| 31 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. 2014: arXiv: 1409.1556. |
| 32 | Bera S, Biswas PK. Noise conscious training of non local neural network powered by self attentive spectral normalized Markovian patch GAN for low dose CT denoising[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2021, 40(12): 3663-73. |
| 33 | Kingma DP, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. 2014: arXiv: 1412.6980. . |
| 34 | JinKyong Hwan, McCann MT, Froustey E, et al. Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2017, 26(9): 4509-22. |
| 35 | Wang S, Gao J, Li Z, et al. A closer look at self-supervised lightweight vision transformers[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2023: 35624-41. |
| 36 | Wang A, Chen H, Lin ZJ, et al. Rep ViT: revisiting mobile CNN from ViT perspective[C]//2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, WA, USA. IEEE, 2024: 15909-20. |
| [1] | Shengwang PENG, Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA, Jing HUANG. A dual-domain cone beam computed tomography reconstruction framework with improved differentiable domain transform for cone-angle artifact correction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1188-1197. |
| [2] | . Design and optimization of a cone-beam CT system for extremity imaging [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(11): 1331-. |
| [3] | . Cone-beam computed tomography for determination of mesial root canal curvatures of human mandibular first molars [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(07): 824-. |
| [4] | . Motion-compensated compressed sensing four-dimensional cone-beam CT reconstruction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(07): 969-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||