南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1535-1542.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.21
收稿日期:2025-01-17
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
金齐力
E-mail:wuxuan2019@aliyun.com;1316281065@qq.com
作者简介:吴 璇,主管技师,硕士,E-mail: wuxuan2019@aliyun.com
基金资助:
Xuan WU( ), Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN(
), Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN( )
)
Received:2025-01-17
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Qili JIN
E-mail:wuxuan2019@aliyun.com;1316281065@qq.com
摘要:
目的 探究含PRELI域1(PRELID1)在胃癌组织中的表达水平及对患者预后和癌细胞上皮间质转化的影响与可能的调控机制。 方法 纳入115例我院在2018年2月~2023年3月接受胃癌根治术的患者,探究PRELID1在胃癌组织中的表达水平与肿瘤进展和预后的关系。使用慢病毒转染干预MGC803和AGS胃癌细胞PRELID1的表达水平,将细胞分为3组:对照组(NC)、PRELID1过表达组(LV组)和干扰组(siRNA组),分析其对细胞迁移、侵袭和上皮间质转化的影响,以及相关的分子机制。 结果 免疫组化结果显示,PRELID1在胃癌组织中的表达水平高于癌旁组织(P<0.05),且和患者的恶性进展临床参数[CEA≥5 ng/mL(P=0.007)、CA199≥37 U/mL(P=0.007)、G3~4(P=0.001)、T3~4(P=0.001)和N2~3期(P=0.020)]呈正相关。依据单因素分析和Cox多因素分析的结果提示PRELID1高表达是影响胃癌5年生存期的独立危险因素(P=0.001)。CCK-8实验结果显示,过表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞的增殖(P<0.05),而干扰PRELID1则抑制(P<0.05);Transwell迁移和侵袭实验数据提示,过表达PRELID1上调胃癌细胞的迁移与侵袭数量(P<0.05),而干扰PRELID1则结果相反(P<0.05);免疫印迹检测发现,过表达PRELID1增强胃癌细胞中基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)的表达(P<0.05),而干扰PRELID1则反之(P<0.05)。过表达PRELID1上调胃癌细胞中N-cadherin和vimentin的表达(P<0.05),以及下调E-cadherin的表达(P<0.05);而干扰PRELID1则结果相反(P<0.05)。过表达胃癌细胞中PRELID1增加了p-PI3K、p-AKT和p-mTOR的表达(P<0.05),而干扰则抑制(P<0.05);相对干扰PRELID1组的细胞,PI3K/AKT通路激活剂(740 Y-P)增加了细胞迁移和侵袭的数量(P<0.05),以及上调了N-cadherin和vimentin的表达与下调E-cadherin的表达(P<0.05)。 结论 PRELID1高表达于胃癌中且影响患者预后,其可能通过激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路,进而增强胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭及上皮间质转化。
吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542.
Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542.
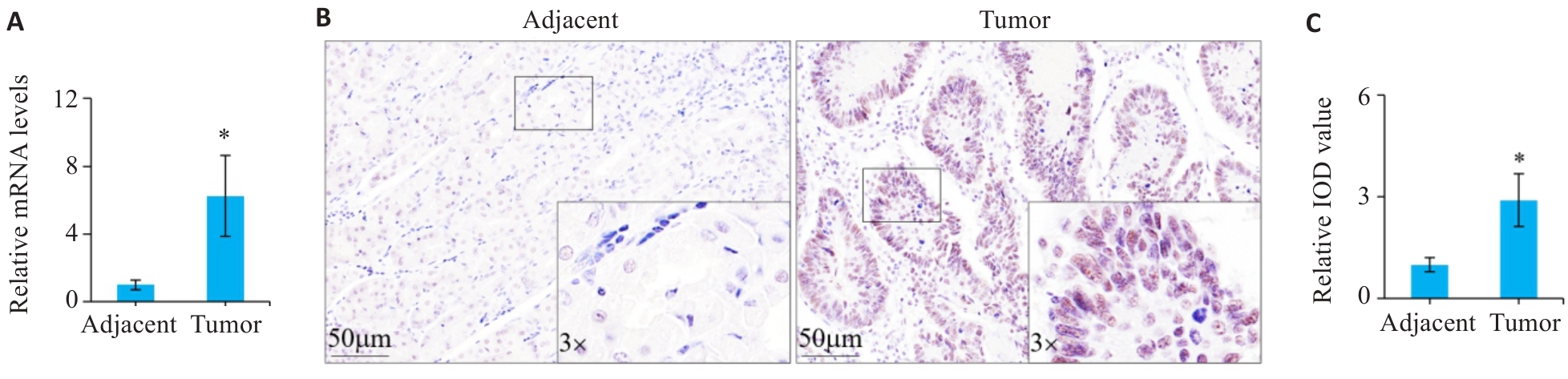
图1 胃癌组织中的PRELID1表达情况
Fig 1 PRELID1 expression in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues. A: mRNA level of PRELID1 detected by qRT-PCR (n=10). B: Immunohistochemistry of PRELID1 expression in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues. C: Relative integrated optical density value of PRELID1 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues (Mean±SD, n=52). *P<0.05 vs Adjacent.
| Characteristic | n | PRELID1 expression (n, %) | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low expression (n=58) | High expression (n=57) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 55 | 32 (58.2%) | 23 (41.8%) | 2.531 | 0.112 |
| Male | 60 | 26 (43.3%) | 34 (56.7%) | ||
| Age(year) | |||||
| <60 | 45 | 24 (53.3%) | 21 (46.7%) | 0.248 | 0.618 |
| ≥60 | 70 | 34 (48.6%) | 36 (51.4%) | ||
| CEA (ng/mL) | |||||
| <5 | 61 | 38 (62.3%) | 23 (37.7%) | 7.31 | 0.007 |
| ≥5 | 54 | 20 (37.0%) | 34 (63.0%) | ||
| CA199 (U/mL) | |||||
| <37 | 59 | 37 (62.7%) | 22 (37.3%) | 7.305 | 0.007 |
| ≥37 | 56 | 21 (37.5%) | 35 (62.5%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| <5 | 57 | 31 (54.4%) | 26 (45.6%) | 0.706 | 0.401 |
| ≥5 | 58 | 27 (46.6%) | 31 (53.4%) | ||
| Pathological type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 93 | 49 (52.7%) | 44 (47.3%) | 0.987 | 0.32 |
| Other | 22 | 9 (40.9%) | 13 (59.1%) | ||
| Pathological grading | |||||
| G1-G2 | 62 | 40 (64.5%) | 22 (35.5%) | 10.671 | 0.001 |
| G3-G4 | 53 | 18 (34.0%) | 35 (66.0%) | ||
| T Stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 57 | 38 (66.7%) | 19 (33.3%) | 11.912 | 0.001 |
| T3-T4 | 58 | 20 (34.5%) | 38 (65.5%) | ||
| N Stage | |||||
| N0-N1 | 63 | 38 (60.3%) | 25 (39.7%) | 5.443 | 0.02 |
| N2-N3 | 52 | 20 (38.5%) | 32 (61.5%) | ||
表1 PRELID1在胃癌中表达水平与患者临床病理参数间的关系
Tab.1 Correlation of PRELID1 expression levels in gastric cancer with clinicopathological parameters of patients
| Characteristic | n | PRELID1 expression (n, %) | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low expression (n=58) | High expression (n=57) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 55 | 32 (58.2%) | 23 (41.8%) | 2.531 | 0.112 |
| Male | 60 | 26 (43.3%) | 34 (56.7%) | ||
| Age(year) | |||||
| <60 | 45 | 24 (53.3%) | 21 (46.7%) | 0.248 | 0.618 |
| ≥60 | 70 | 34 (48.6%) | 36 (51.4%) | ||
| CEA (ng/mL) | |||||
| <5 | 61 | 38 (62.3%) | 23 (37.7%) | 7.31 | 0.007 |
| ≥5 | 54 | 20 (37.0%) | 34 (63.0%) | ||
| CA199 (U/mL) | |||||
| <37 | 59 | 37 (62.7%) | 22 (37.3%) | 7.305 | 0.007 |
| ≥37 | 56 | 21 (37.5%) | 35 (62.5%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| <5 | 57 | 31 (54.4%) | 26 (45.6%) | 0.706 | 0.401 |
| ≥5 | 58 | 27 (46.6%) | 31 (53.4%) | ||
| Pathological type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 93 | 49 (52.7%) | 44 (47.3%) | 0.987 | 0.32 |
| Other | 22 | 9 (40.9%) | 13 (59.1%) | ||
| Pathological grading | |||||
| G1-G2 | 62 | 40 (64.5%) | 22 (35.5%) | 10.671 | 0.001 |
| G3-G4 | 53 | 18 (34.0%) | 35 (66.0%) | ||
| T Stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 57 | 38 (66.7%) | 19 (33.3%) | 11.912 | 0.001 |
| T3-T4 | 58 | 20 (34.5%) | 38 (65.5%) | ||
| N Stage | |||||
| N0-N1 | 63 | 38 (60.3%) | 25 (39.7%) | 5.443 | 0.02 |
| N2-N3 | 52 | 20 (38.5%) | 32 (61.5%) | ||
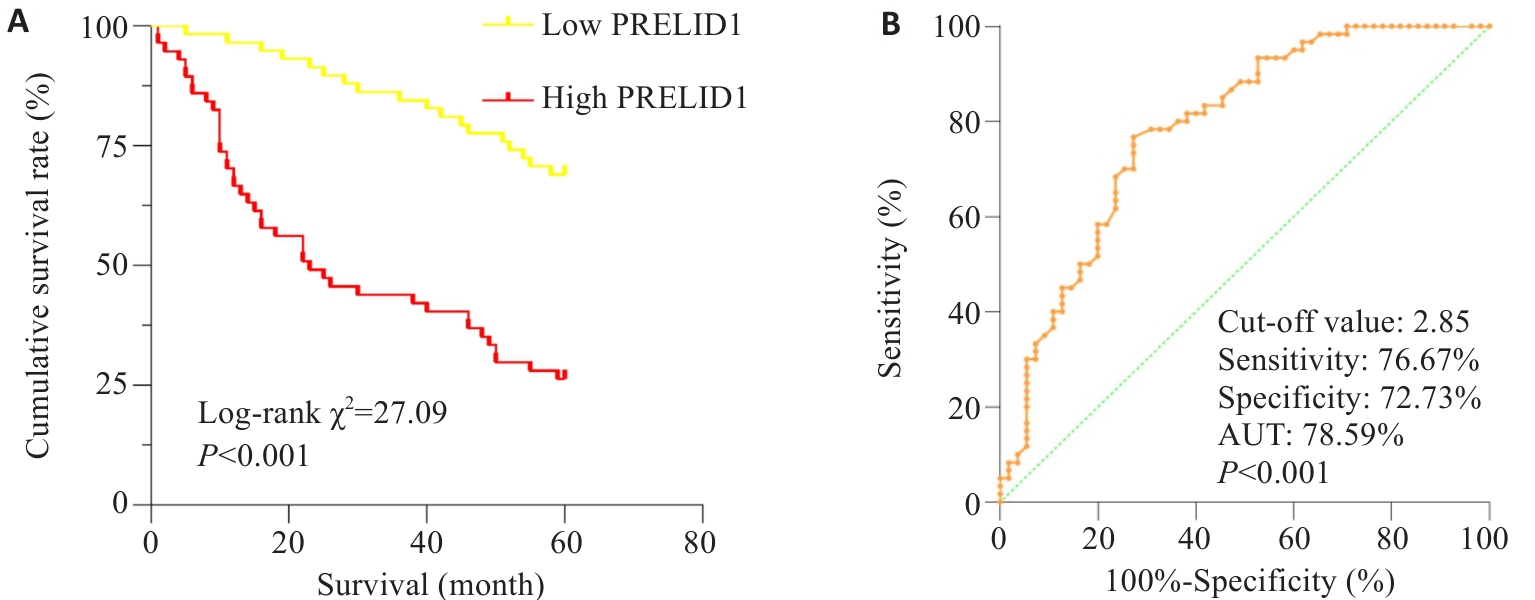
图2 PRELID1表达水平对患者术后5年生存期的影响
Fig.2 Effect of PRELID1 expression level on 5-year postoperative survival of gastric cancer patients. A: Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis. B: ROC analysis.
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | |
| Gender (male vs female) | 2.758 | 0.097 | |||
| Age (<60 year vs ≥60 year) | 0.063 | 0.801 | |||
| PRELID1 expression (high vs low) | 27.093 | <0.001 | 2.776 | 1.518-5.075 | 0.001 |
| CEA level (<5 ng/mL vs ≥5 ng/mL) | 32.566 | <0.001 | 2.297 | 1.188-4.440 | 0.013 |
| CA199 level (<37 U/mLvs ≥37 U/mL) | 42.932 | <0.001 | 2.570 | 1.254-5.268 | 0.010 |
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 2.490 | 0.115 | |||
| Pathological grading (G1-G2 vs G3-G4) | 30.733 | <0.001 | 2.512 | 1.377-4.584 | 0.003 |
| Tumor size (<5 cm vs ≥5 cm) | 1.250 | 0.264 | |||
| T stage (T1~T2 vs T3~T4) | 47.055 | <0.001 | 2.959 | 1.394-6.281 | 0.005 |
| N stage (N0~N1 vs N2~N3) | 44.963 | <0.001 | 2.375 | 1.201-4.697 | 0.013 |
表2 影响115例胃癌根治术后5年生存期的单因素及多因素分析
Tab.2 Univariate and multivariate analyses of factors affecting 5-year survival of the patients after radical gastrectomy (n=115)
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | |
| Gender (male vs female) | 2.758 | 0.097 | |||
| Age (<60 year vs ≥60 year) | 0.063 | 0.801 | |||
| PRELID1 expression (high vs low) | 27.093 | <0.001 | 2.776 | 1.518-5.075 | 0.001 |
| CEA level (<5 ng/mL vs ≥5 ng/mL) | 32.566 | <0.001 | 2.297 | 1.188-4.440 | 0.013 |
| CA199 level (<37 U/mLvs ≥37 U/mL) | 42.932 | <0.001 | 2.570 | 1.254-5.268 | 0.010 |
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 2.490 | 0.115 | |||
| Pathological grading (G1-G2 vs G3-G4) | 30.733 | <0.001 | 2.512 | 1.377-4.584 | 0.003 |
| Tumor size (<5 cm vs ≥5 cm) | 1.250 | 0.264 | |||
| T stage (T1~T2 vs T3~T4) | 47.055 | <0.001 | 2.959 | 1.394-6.281 | 0.005 |
| N stage (N0~N1 vs N2~N3) | 44.963 | <0.001 | 2.375 | 1.201-4.697 | 0.013 |
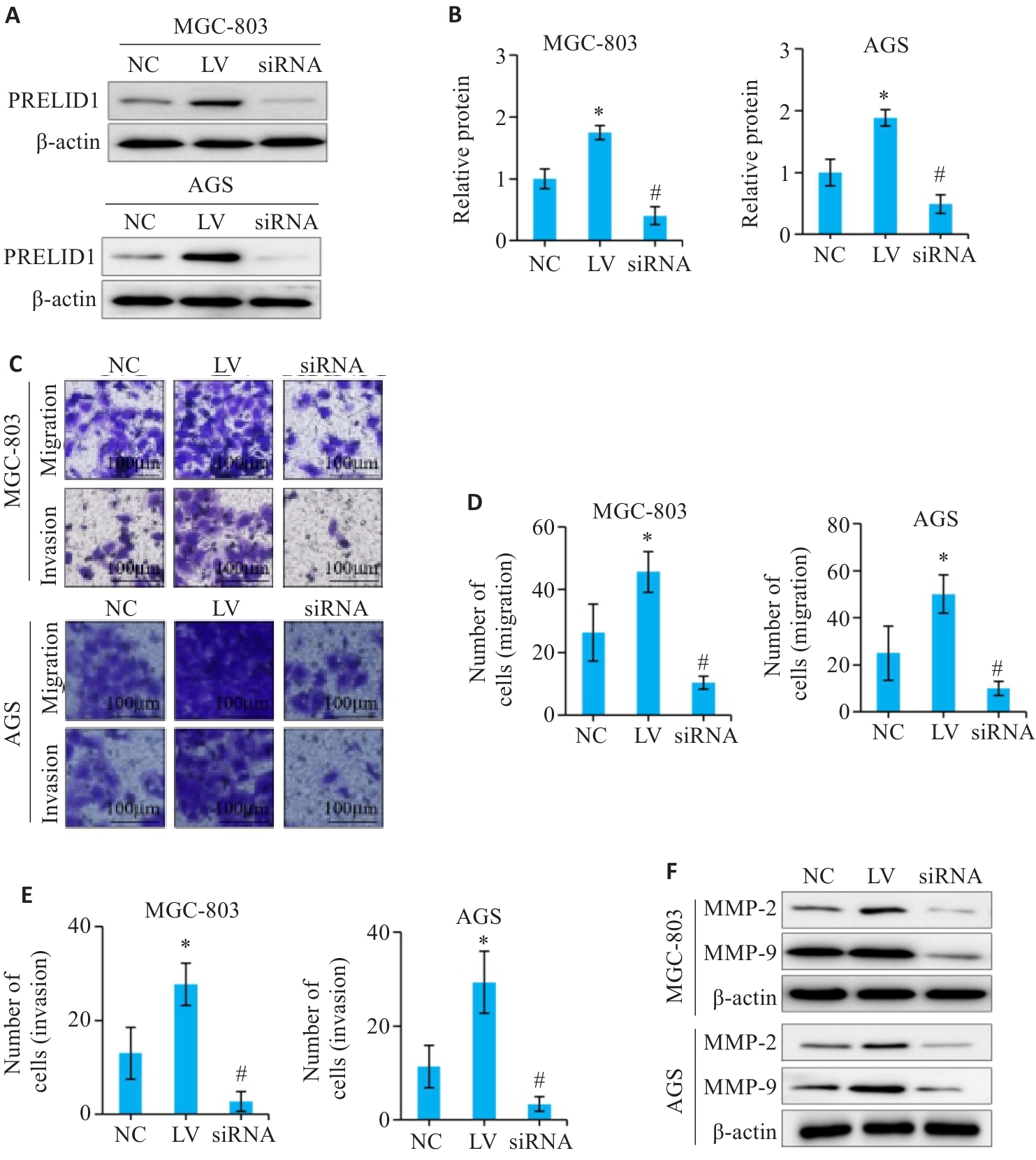
图3 调控胃癌细胞PRELID1的表达对增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响
Fig.3 Effects of PRELID1 overexpression and knockdown on proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. A: Western blotting for verifying expression of PRELID1 in gastric cancer cells after transfection. B: CCK-8 assay for analyzing the effect of PRELID1 overexpression and knockdown on proliferation of gastric cancer cells. C-E: Transwell migration and invasion assay for evaluating the effect of PRELID1 overexpression and knockdown on migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. F: Western blotting for detecting expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9. *P<0.05 vs NC; #P<0.05 vs NC.
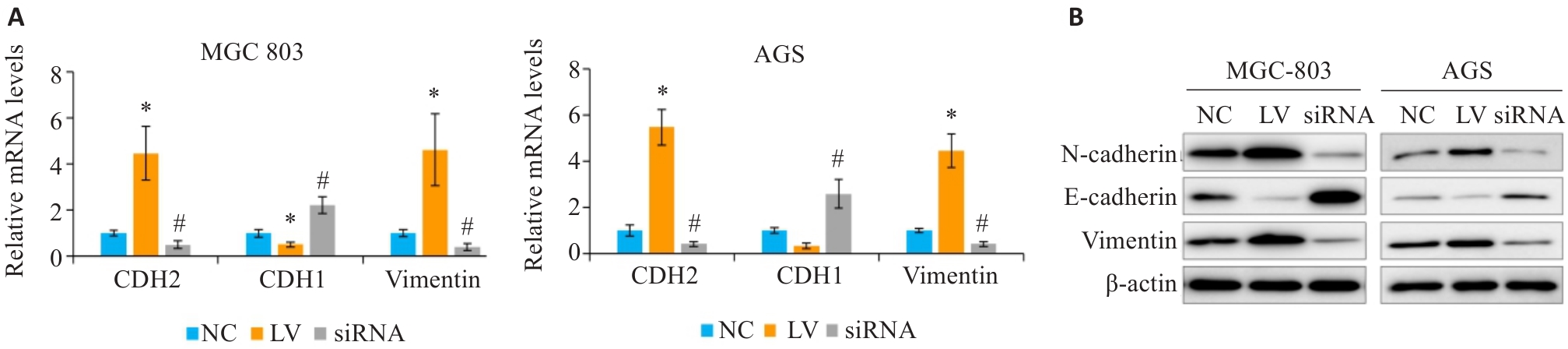
图4 调控PRELID1的表达对胃癌细胞上皮间质转化的影响
Fig.4 Effect of PRELID1 overexpression and knockdown on epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells. A: qRT-PCR analysis of the effect of PRELID1 overexpression and knockdown on mRNA expression of CDH1, CDH2 and vimentin in gastric cancer cells. B: Western blotting for detecting E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin expressions in the transfected cells. *P<0.05 vs NC, #P<0.05 vs NC.
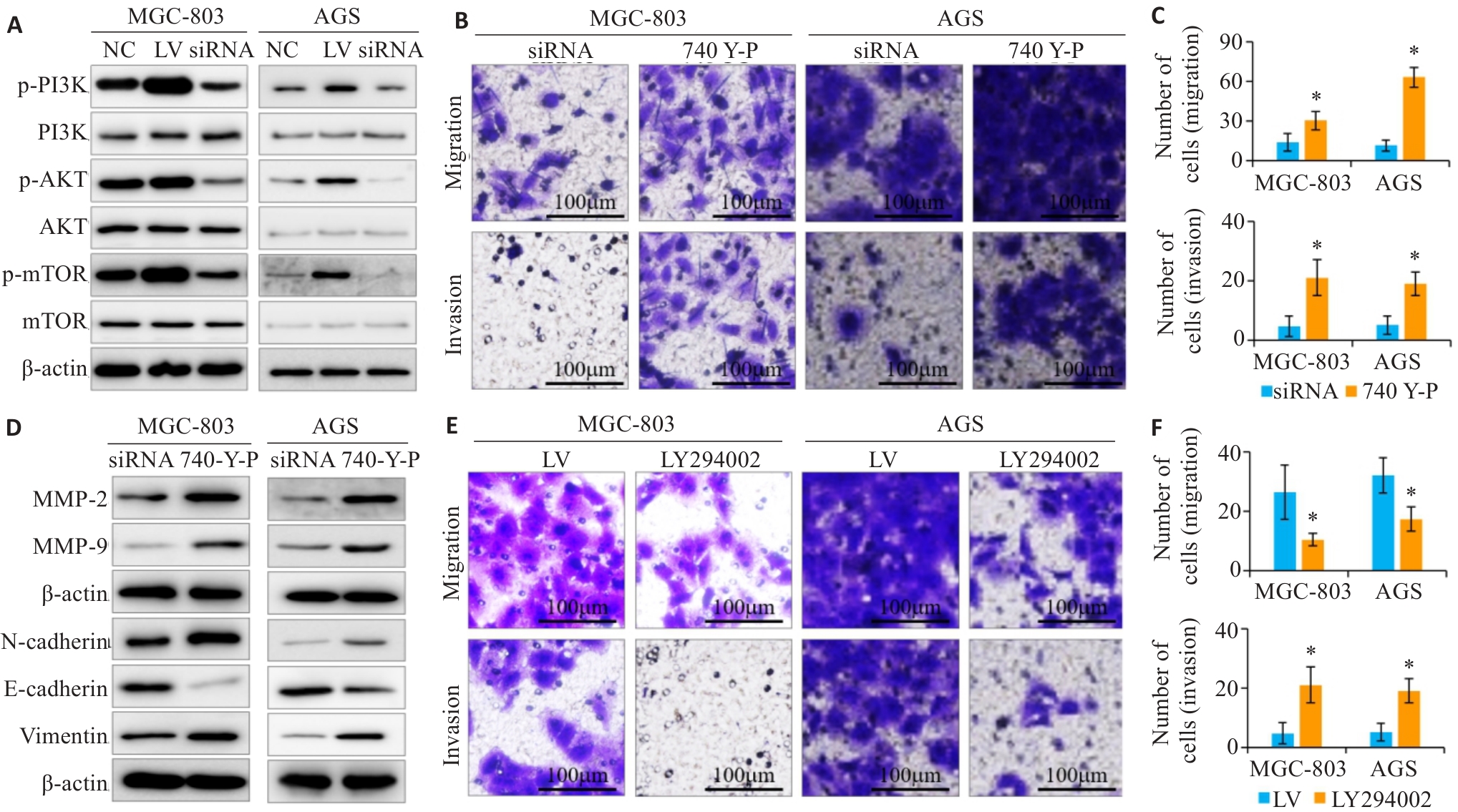
图5 评估PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路是否参与PRELID1对胃癌细胞上皮间质转化的调控作用
Fig.5 Assessment of the role of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells with PRELID1 overexpression and knockdown. A: Western blotting for detecting the expressions of p-PI3K, p-AKT and p-mTOR in the treated gastric cancer cells. B, C: Transwell migration and invasion assay to assess the effect of PI3K/AKT pathway activator (740 Y-P) on the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. D: Western blotting for detecting MMP-2, MMP-9, E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin expression levels in the treated cells. E, F: Transwell migration and invasion assay for evaluating the effects of PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitor (LY294002) on gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. *P<0.05 vs siRNA of LV.
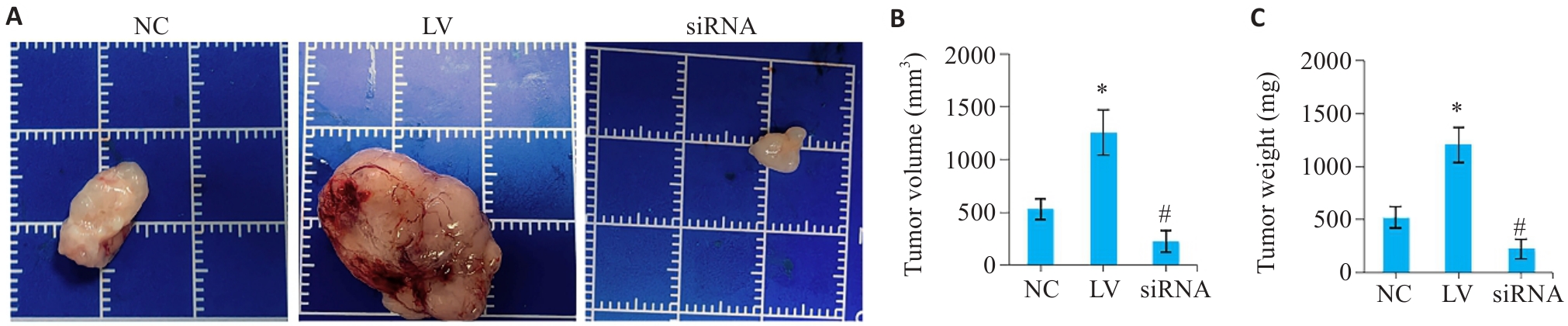
图6 在体验证调控胃癌细胞PRELID1对移植瘤生长的影响
Fig.6 Effect of PRELID1 overexpression and knockdown on growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts in nude mice. A: Gross observation of the dissected tumors in the 3 groups. B: Comparison of the tumor volume among the 3 groups. C: Comparison of tumor weight among the 3 groups. *P<0.05 vs NC, #P<0.05 vs NC.
| [1] | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| [2] | Arnold M, Park JY, Camargo MC, et al. Is gastric cancer becoming a rare disease? A global assessment of predicted incidence trends to 2035[J]. Gut, 2020, 69(5): 823-9. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320234 |
| [3] | Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-48. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31288-5 |
| [4] | Yasuda T, Wang Y. Gastric cancer immunosuppressive micro-environment heterogeneity: implications for therapy development[J]. Trends Cancer, 2024, 10(7): 627-42. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2024.03.008 |
| [5] | Guan WL, He Y, Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 57. doi:10.1186/s13045-023-01451-3 |
| [6] | Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(3): 534-42. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.045 |
| [7] | Lordick F, Carneiro F, Cascinu S, et al. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2022, 33(10): 1005-20. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.07.004 |
| [8] | Rugge M. Big data on gastric dysplasia support gastric cancer prevention[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20(6): 1226-8. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.038 |
| [9] | Rugge M, Genta RM, Malfertheiner P, et al. Steps forward in understanding gastric cancer risk[J]. Gut, 2023, 72(9): 1802-3. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328514 |
| [10] | Rawicz-Pruszyński K, Erodotou M, Pelc Z, et al. Techniques of staging laparoscopy and peritoneal fluid assessment in gastric cancer: a systematic review[J]. Int J Surg, 2023, 109(11): 3578-89. doi:10.1097/JS9.0000000000000632 |
| [11] | Li GZ, Doherty GM, Wang J. Surgical management of gastric cancer: a review[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157(5): 446-54. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2022.0182 |
| [12] | Wang J, Meng F, Mao F. Single cell sequencing analysis and transcriptome analysis constructed the liquid-liquid phase separation(LLPS)-related prognostic model for endometrial cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1005472. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1005472 |
| [13] | Gillen AE, Brechbuhl HM, Yamamoto TM, et al. Alternative po-lyadenylation of PRELID1 regulates mitochondrial ROS signaling and cancer outcomes[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2017, 15(12): 1741-51. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-17-0010 |
| [14] | Xi S, Cai H, Lu J, et al. The pseudogene PRELID1P6 promotes glioma progression via the hnHNPH1-Akt/mTOR axis[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(26): 4453-67. doi:10.1038/s41388-021-01854-x |
| [15] | Wu SY, Lin KC, Lawal B, et al. MXD3 as an onco-immunological biomarker encompassing the tumor microenvironment, disease staging, prognoses, and therapeutic responses in multiple cancer types[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2021, 19: 4970-83. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2021.08.047 |
| [16] | Pilonis ND, Tischkowitz M, Fitzgerald RC, et al. Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: approaches to screening, surveillance, and treatment[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2021, 72: 263-80. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-051019-103216 |
| [17] | Leja M. Where are we with gastric cancer screening in Europe in 2024[J]? Gut, 2024, 73(12): 2074-82. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2024-332705 |
| [18] | Wang WX, Liu M, Fu XL, et al. Hydroxysafflor yellow A ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury through PI3K/Akt and STAT3/NF‑κB signaling pathways[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 132: 155814. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155814 |
| [19] | Li D, Guo YY, Cen XF, et al. Lupeol protects against cardiac hyp-ertrophy via TLR4-PI3K-Akt-NF‑κB pathways[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2022, 43(8): 1989-2002. doi:10.1038/s41401-021-00820-3 |
| [20] | Xing CG, Zhu BS, Liu HH, et al. LY294002 induces p53-dependent apoptosis of SGC7901 gastric cancer cells[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2008, 29(4): 489-98. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00770.x |
| [21] | Li R, Wang J, Xie Z, et al. CircUSP1 as a novel marker promotes gastric cancer progression via stabilizing HuR to upregulate USP1 and Vimentin[J]. Oncogene, 2024, 43(14): 1033-49. doi:10.1038/s41388-024-02968-8 |
| [22] | Huang Z, Zhao X, Hu J, et al. Single-nanoparticle differential immunoassay for multiplexed gastric cancer biomarker monitoring[J]. Anal Chem, 2022, 94(37): 12899-906. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.2c03013 |
| [23] | Yue B, Song C, Yang L, et al. METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 142. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1065-4 |
| [24] | Dou R, Han L, Yang C, et al. Upregulation of LINC00501 by H3K27 acetylation facilitates gastric cancer metastasis through activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2023, 13(10): e1432. doi:10.1002/ctm2.1432 |
| [25] | Zeng YJ, Jin RU. Molecular pathogenesis, targeted therapies, and future perspectives for gastric cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86: 566-82. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.12.004 |
| [26] | Guo X, Peng YH, Song QY, et al. A liquid biopsy signature for the early detection of gastric cancer in patients[J]. Gastroenterology, 2023, 165(2): 402-13. e13. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.02.044 |
| [27] | So JBY, Kapoor R, Zhu F, et al. Development and validation of a serum microRNA biomarker panel for detecting gastric cancer in a high-risk population[J]. Gut, 2021, 70(5): 829-37. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322065 |
| [28] | Moriyama J, Oshima Y, Nanami T, et al. Prognostic impact of CEA/CA19-9 at the time of recurrence in patients with gastric cancer[J]. Surg Today, 2021, 51(10): 1638-48. doi:10.1007/s00595-021-02248-y |
| [29] | Li D, Wang Y, Dong C, et al. CST1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating GPX4 protein stability via OTUB1[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(2): 83-98. doi:10.1038/s41388-022-02537-x |
| [30] | Zhu Y, Huang C, Zhang C, et al. LncRNA MIR200CHG inhibits EMT in gastric cancer by stabilizing miR-200c from target-directed miRNA degradation[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 8141. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-43974-w |
| [31] | Wang C, Yang Z, Xu E, et al. Apolipoprotein C-II induces EMT to promote gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2021, 11(8): e522. doi:10.1002/ctm2.522 |
| [32] | Fattahi S, Amjadi-Moheb F, Tabaripour R, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in gastric cancer: Epigenetics and beyond[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 262: 118513. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118513 |
| [33] | Chen ML, Li HZ, Zheng SS, et al. Nobiletin targets SREBP1/ACLY to induce autophagy-dependent cell death of gastric cancer cells through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 128: 155360. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155360 |
| [1] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [3] | 王康, 李海宾, 余靖, 孟源, 张虹丽. ELFN1高表达是结肠癌的预后生物标志物并促进结肠癌细胞的增殖转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [4] | 侯鑫睿, 张振东, 曹明远, 杜予心, 王小平. 红景天苷靶向miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB糖代谢轴抑制胃癌细胞的体内外增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [5] | 马振南, 刘福全, 赵雪峰, 张晓微. DTX2促进奥沙利铂耐药的结直肠癌细胞增殖、侵袭和上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [6] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [7] | 董妍妍, 张可敬, 储俊, 储全根. 抵当汤含药血清通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路增强高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [8] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [9] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [10] | 李华莉, 宋婷, 刘嘉雯, 李永宝, 姜兆静, 窦文, 周凌宏. 预后导向的肺癌调强放疗计划优化新方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [11] | 宋雪, 陈悦, 张敏, 张诺, 左芦根, 李静, 耿志军, 张小凤, 王月月, 王炼, 胡建国. GPSM2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过促进肿瘤细胞的增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [12] | 唐天威, 李路安, 陈源汉, 张丽, 徐丽霞, 李志莲, 冯仲林, 张辉林, 华瑞芳, 叶智明, 梁馨苓, 李锐钊. 高血清胱抑素C水平是IgA肾病不良预后的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [13] | 陈晓睿, 魏青政, 张宗亮, 原江水, 宋卫青. 过表达带电多泡体蛋白2B基因抑制肾透明细胞癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [14] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [15] | 周超, 张晶晶, 唐巧, 付双楠, 张宁, 何召云, 张瑾, 张田义, 刘鹏程, 宫嫚. 血清色氨酸用于乙肝相关慢加急性肝衰竭90 d死亡风险分层管理的潜在价值:一项多中心回顾性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 59-64. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||