南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1527-1534.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.20
收稿日期:2025-03-11
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
赵丽
E-mail:1206635637@qq.com;lilily_333@sina.com
作者简介:阳亭亭,助理实验师,硕士,E-mail: 1206635637@qq.com
基金资助:Received:2025-03-11
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Li ZHAO
E-mail:1206635637@qq.com;lilily_333@sina.com
摘要:
目的 采用维生素A(VA)缺乏饲料饲喂联合低浓度CCl4诱导,制备一种稳定的慢性肝纤维化动物模型。 方法 126只Balb/c小鼠随机分3组,分别给予VA正常饲料(VAN组)、500 IU/kg VA(VAD组1)及200 IU/kg VA(VAD组2)饲料饲养,4周后每组选取6只小鼠检测血清视黄醇水平;将剩余108只小鼠平均分为未造模组与造模组,每组再分为VAN组、VAD组1、VAD组2,18只/组。造模组腹腔注射5% CCl4 10 mL/kg,2次/周,共8周。检测血清视黄醇、ALT/AST、肝脏指数;进行肝组织HE、Masson染色、纤维化程度评分和氧化应激水平检测。 结果 饲养4周后,VAD组的血清视黄醇水平均低于VAN组,VAD组2更低(P<0.05)。CCl4造模8周,肝脏指数及ALT/AST增高,肝脏表面有颗粒状突起,肝索结构紊乱、假小叶形成,可见大量蓝染纤维组织和纤维间隔;VAD组较VAN组更显著,但VAD组2肝脏坏死严重,假小叶纤维间隔处大量炎性细胞浸润,2只小鼠死亡。CCl4停止给药,VAN造模组肝脏指数及ALT/AST基本恢复,肝索结构恢复正常,纤维化自发逆转;VAD造模组血清ALT/AST、肝脏大体及病理无明显变化,VAD组1仍可见肝索结构紊乱和假小叶,VAD组2腹腔黏连严重,仍可见假小叶及大量炎性细胞浸润,纤维化分期评分为3;CCl4造模组(VAD组1)氧化损伤指标8-OHdG高于CCl4造模组(VAN组)。 结论 以含有500 U/kg VA的饲料饲喂小鼠4周,10 mL/kg CCl4干预8周,可获得中重度的肝纤维化模型,成功率100%,停药8周无自发逆转,可建立一种稳定的肝纤维化动物模型。
阳亭亭, 赵丽. 维生素A缺乏联合CCl4诱导制备稳定的小鼠慢性肝纤维化模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1527-1534.
Tingting YANG, Li ZHAO. A stable mouse model of chronic liver fibrosis induced by vitamin A deficiency and intraperitoneal CCl4 injection[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1527-1534.
| Index | Unmodeling group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.313±0.09 | 0.76±0.111b | 0.592±0.042bc | 1.278±0.073 | 0.695±0.095b | 0.514±0.034abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.25±0.658 | 4.07±0.175 | 4.41±0.969 | 6.05±0.802a | 6.37±0.195a | 6.19±0.337a |
| ALT (U/L) | 42.03±8.576 | 45.22±9.212 | 53.17±6.61bc | 70.73±8.663a | 75.73±9.886ab | 86.38±10.34abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.13±7.81 | 113.33±11.72b | 111.01±23.73bc | 136.20±13.12a | 158.72±24.34ab | 182.74±19.49abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
表1 CCl4造模8周后对小鼠血清视黄醇、ALT/AST水平及肝纤维化程度的影响
Tab.1 Effects of CCl4 treatment for 8 weeks on serum levels of retinol, ALT/AST and liver fibrosis in mice (Mean±SD)
| Index | Unmodeling group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.313±0.09 | 0.76±0.111b | 0.592±0.042bc | 1.278±0.073 | 0.695±0.095b | 0.514±0.034abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.25±0.658 | 4.07±0.175 | 4.41±0.969 | 6.05±0.802a | 6.37±0.195a | 6.19±0.337a |
| ALT (U/L) | 42.03±8.576 | 45.22±9.212 | 53.17±6.61bc | 70.73±8.663a | 75.73±9.886ab | 86.38±10.34abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.13±7.81 | 113.33±11.72b | 111.01±23.73bc | 136.20±13.12a | 158.72±24.34ab | 182.74±19.49abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
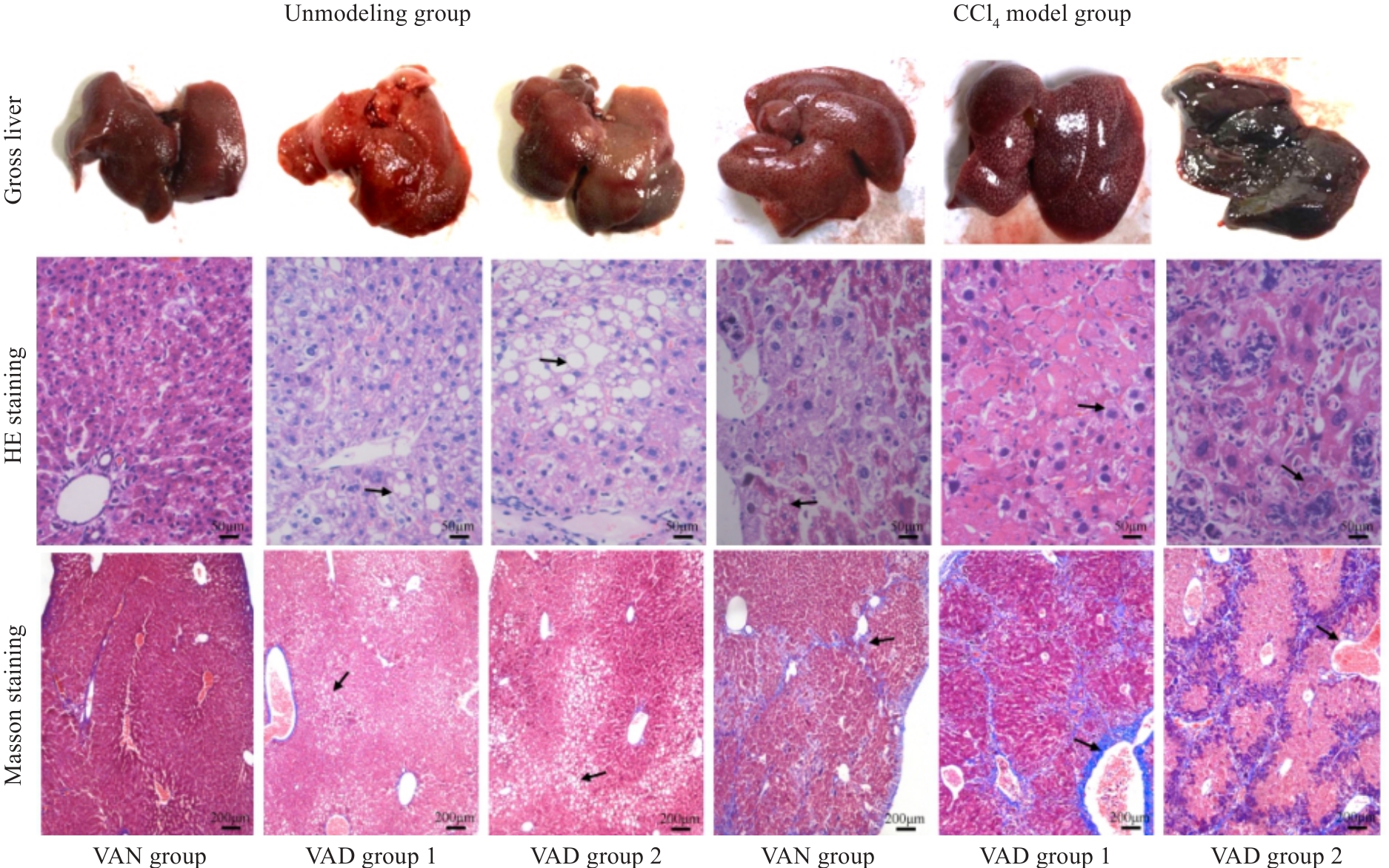
图1 CCl4造模8周后各组肝脏组织大体标本、HE染色及Masson染色
Fig.1 Gross observation of mouse livers and HE staining (Original magnification: ×400) and Masson staining (×100) of the liver tissues in each group after 8 weeks of CCl4 modeling. The arrows from "Unmodeled group" to "CCl4 model group" respectively point to: The cytoplasm is lightly stained and presents a vacuolar phenomenon,The phenomenon of inflammatory cell infiltration and the formation of blue stained fibrous tissue.
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.325±0.073 | 0.733±0.122b | 0.587±0.053bc | 1.29±0.073 | 0.707±0.083b | 0.534±0.068abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.10±0.748 | 3.98±0.226 | 4.28±0.859 | 6.32±1.228a | 6.08±0.585a | 5.85±0.947a |
| ALT (U/L) | 44.32±4.36 | 47.88±11.10 | 49.33±7.32 | 57.7±12.95a | 70.92±12.73ab | 90.33±20.40abc |
| AST (U/L) | 78.27±411.24 | 110.43±12.34b | 129.95±17.85bc | 101.43±17.53a | 147.92±22.29ab | 173.15±31.25abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
表2 CCl4停药4周各组血清视黄醇、ALT/AST水平及肝纤维化程度
Tab.2 Effects of CCl4 on serum levels of retinol, ALT/AST and liver fibrosis in mice 4 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation (Mean±SD)
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.325±0.073 | 0.733±0.122b | 0.587±0.053bc | 1.29±0.073 | 0.707±0.083b | 0.534±0.068abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.10±0.748 | 3.98±0.226 | 4.28±0.859 | 6.32±1.228a | 6.08±0.585a | 5.85±0.947a |
| ALT (U/L) | 44.32±4.36 | 47.88±11.10 | 49.33±7.32 | 57.7±12.95a | 70.92±12.73ab | 90.33±20.40abc |
| AST (U/L) | 78.27±411.24 | 110.43±12.34b | 129.95±17.85bc | 101.43±17.53a | 147.92±22.29ab | 173.15±31.25abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
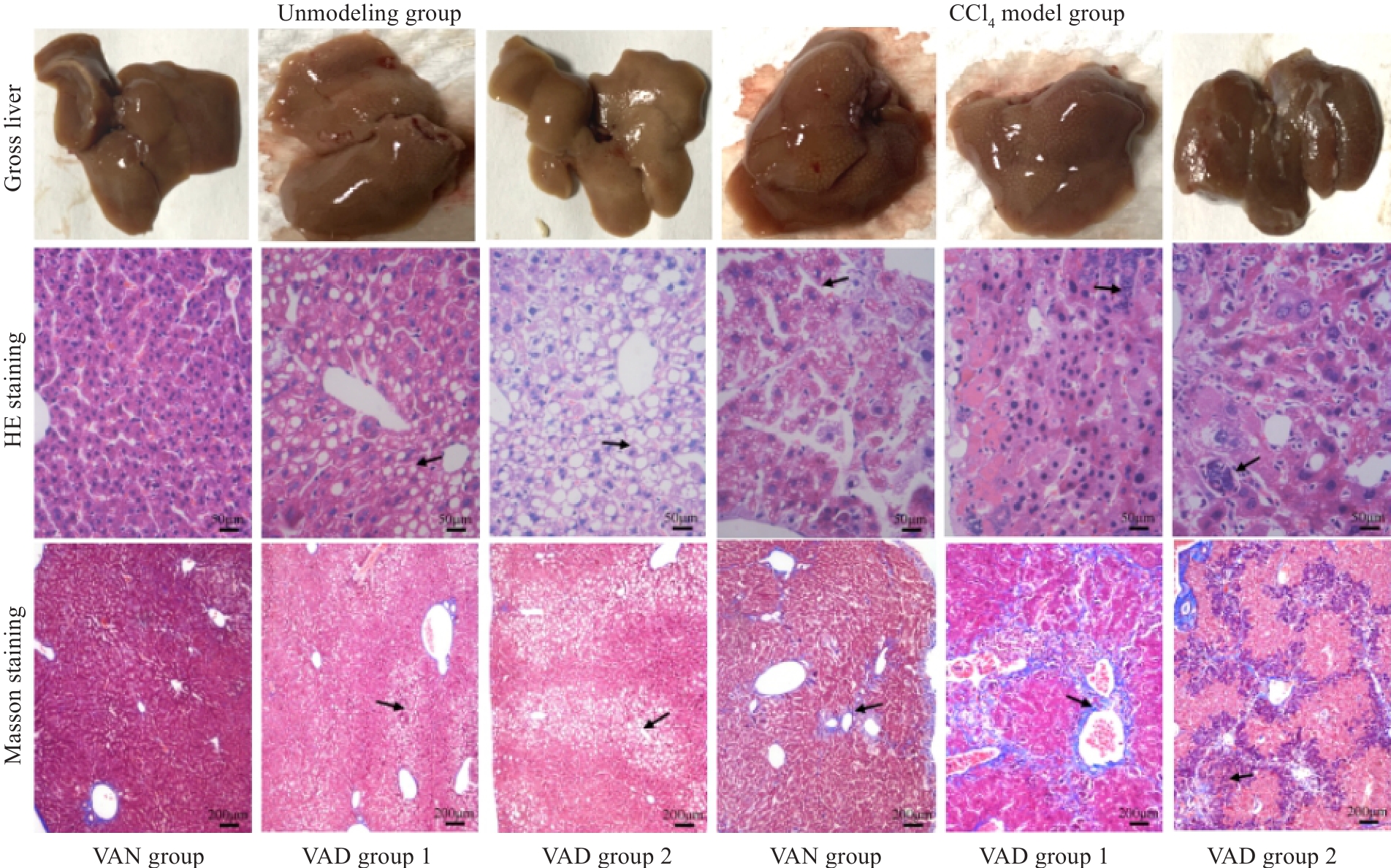
图2 CCl4停药4周后各组肝脏组织大体标本、HE染色及Masson染色
Fig.2 Gross observation of mouse livers and HE staining (×400) and Masson staining (×100) of the liver tissues in each group 4 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation. The arrows from "Unmodeled group" to "CCl4 model group" respectively point to: The cytoplasm is lightly stained and presents a vacuolar phenomenon,The phenomenon of inflammatory cell infiltration and formation of pseudolobules.
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group2 (n=3) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.37±0.08 | 0.78±0.13b | 0.60±0.10bc | 1.31±0.09 | 0.73±0.09bc | 0.55±0.10abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.06±0.472 | 4.20±0.0.85 | 4.34±0.78 | 5.68±1.01a | 6.02±0.445a | 5.87±1.63a |
| ALT (U/L) | 45.1±8.95 | 48.67±7.86 | 49.52±10.58 | 49.33±0.09 | 72.78±0.09ab | 86.57±13.91abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.40±12.19 | 114.85±9.84b | 123.0±25.21bc | 84.47±12.32 | 141.45±16.06ab | 197.4±67.92abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
表3 CCl4停药8周各组血清视黄醇、ALT/AST水平及肝纤维化程度
Tab.3 Serum levels of retinol, ALT/AST and liver fibrosis in mice 8 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation (Mean±SD)
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group2 (n=3) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.37±0.08 | 0.78±0.13b | 0.60±0.10bc | 1.31±0.09 | 0.73±0.09bc | 0.55±0.10abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.06±0.472 | 4.20±0.0.85 | 4.34±0.78 | 5.68±1.01a | 6.02±0.445a | 5.87±1.63a |
| ALT (U/L) | 45.1±8.95 | 48.67±7.86 | 49.52±10.58 | 49.33±0.09 | 72.78±0.09ab | 86.57±13.91abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.40±12.19 | 114.85±9.84b | 123.0±25.21bc | 84.47±12.32 | 141.45±16.06ab | 197.4±67.92abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
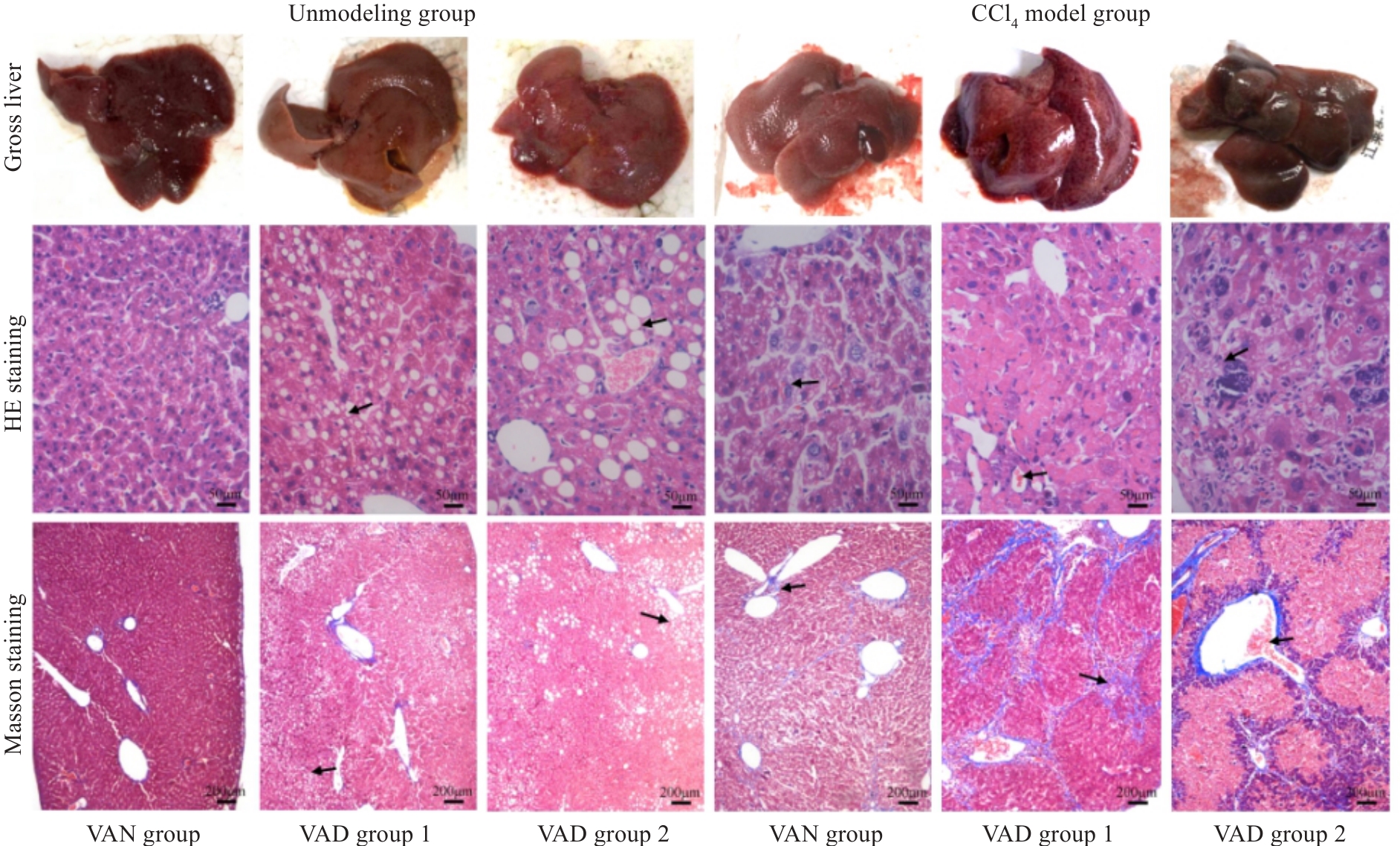
图3 CCl4停药8周后各组肝脏组织大体标本、HE染色及Masson染色
Fig.3 Gross observation of mouse livers and HE staining (×400) and Masson staining (×100) of the liver tissues in each group 8 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation. The arrows from "Unmodeled group" to "CCl4 model group" respectively point to: The cytoplasm is lightly stained and presents a vacuolar phenomenon,Disorder of hepatic cord structure and formation of pseudolobules.
| [1] | Li T, Liu HB, Hu WY, et al. Role of inflammation hepatic fibrosis[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2022, 38(10): 2368-72. |
| [2] | Roehlen N, Crouchet E, Baumert TF. Liver fibrosis: mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(4): E875. doi:10.3390/cells9040875 |
| [3] | Parola M, Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019, 65: 37-55. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2018.09.002 |
| [4] | Fan W, Liu T, Chen W, et al. ECM1 prevents activation of transforming growth factor β, hepatic stellate cells, and fibrogenesis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 157(5): 1352-67.e13. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.036 |
| [5] | 王 娟, 杨晶晶, 周仁鹏, 等. 肝纤维化小鼠模型研究现状[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2022, 32(2): 105-10. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2022.02.016 |
| [6] | 王丽春, 赵连三. 肝纤维化的实验动物模型[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2004, 12(4): 56-60. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2004.04.015 |
| [7] | Kim YO, Popov Y, Schuppan D. Optimized mouse models for liver fibrosis[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2017, 1559: 279-96. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-6786-5_19 |
| [8] | Yoneda A, Sakai-Sawada K, Niitsu Y, et al. Vitamin A and insulin are required for the maintenance of hepatic stellate cell quiescence[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2016, 341(1): 8-17. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.01.012 |
| [9] | Lee YS, Jeong WI. Retinoic acids and hepatic stellate cells in liver disease[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 27(): 75-9. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07007.x |
| [10] | Haaker MW, Vaandrager AB, Helms JB. Retinoids in health and disease: a role for hepatic stellate cells in affecting retinoid levels[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Cell Biol Lipds, 2020, 1865(6): 158674. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158674 |
| [11] | 重庆医科大学附属儿童医院.一种肝纤维化动物模型的构建方法:CN202210011928.4[P]. 2022-04-22. |
| [12] | Li JP, Gao Y, Chu SF, et al. Nrf2 pathway activation contributes to anti-fibrosis effects of ginsenoside Rg1 in a rat model of alcohol- and CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2014, 35(8): 1031-44. doi:10.1038/aps.2014.41 |
| [13] | Li J, Deng X, Wang S, et al. Resolvin D1 attenuates CCl4 Induced Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting Autophagy-Mediated HSC activation via AKT/mTOR Pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 792414. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.792414 |
| [14] | 吕艳杭, 吴姗姗, 王振常, 等. 肝纤维化动物模型造模方法的研究进展[J]. 广西医学, 2020, 42(7): 875-8. |
| [15] | Crespo Yanguas S, Cogliati B, Willebrords J, et al. Experimental models of liver fibrosis[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2016, 90(5): 1025-48. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1543-4 |
| [16] | Chow AM, Tan M, Gao DS, et al. Molecular MRI of liver fibrosis by a peptide-targeted contrast agent in an experimental mouse model[J]. Invest Radiol, 2013, 48(1): 46-54. doi:10.1097/rli.0b013e3182749c0b |
| [17] | 郑 虹, 肖 海, 吴雄健. 肝纤维化的发病机制及治疗的最新进展[J]. 赣南医学院学报, 2019, 39(3): 298-302, 308. |
| [18] | 刘甦苏, 霍桂桃, 王辰飞, 等. 四氯化碳诱导近交系C57BL/6小鼠建立肝纤维化模型[J]. 实验动物科学, 2019, 36(4): 28-30, 34. |
| [19] | 史丛晶, 邓雅方, 张志宏, 等.胆南星对四氯化碳致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 中国药房, 2022, 33(23): 2835-9. doi:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2022.23.04 |
| [20] | 平大冰, 齐婧姝, 孙 鑫, 等. 全反式维甲酸对肝纤维化氧化应激损伤自然杀伤细胞的保护作用[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2024, 40(7): 1359-63. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2024.07.003 |
| [21] | 汪 辛. VA修饰PEG-PCL纳米胶束载喜树碱选择性抑制活化态肝星状细胞糖酵解行为及小鼠肝纤维化的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. |
| [22] | 翁飞鸿, 周一平, 伊思敏, 等. 肝纤维化的病理学发生机制及诊疗研究进展[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2023, 29(5): 559-63. |
| [23] | 合肥博太医药生物技术发展有限公司. 视黄酸及其衍生物在制备治疗肝纤维化药物中的应用:CN201210029865.1[P]. 2012-07-04. |
| [24] | 周 哲. 维生素A缺乏对免疫性肝炎肝损伤影响的实验研究[D]. 天津医科大学, 2018, 11-78. |
| [25] | 杨怡静, 王雨青, 刘 杰. 辛酸癸酸聚乙二醇甘油酯在口服制剂中的应用及促吸机理[J]. 药学与临床研究, 2021, 29(6): 449-53. |
| [26] | Aasheim ET, Hofsø D, Hjelmesæth J, et al. Vitamin status in morbidly obese patients: a cross-sectional study 2[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2008, 87(2): 362-9. doi:10.1093/ajcn/87.2.362 |
| [27] | Jeyakumar SM, Vajreswari A, Sesikeran B, et al. Vitamin A supplementation induces adipose tissue loss through apoptosis in lean but not in obese rats of the WNIN/Ob strain[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2005, 35(2): 391-8. doi:10.1677/jme.1.01838 |
| [28] | Prashanth A, Jeyakumar SM, Giridharan NV, et al. Vitamin A-enriched diet modulates reverse cholesterol transport in hypercholesterolemic obese rats of the WNIN/ob strain[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2014, 21(11): 1197-207. doi:10.5551/jat.22186 |
| [29] | Ravichandra A, Schwabe RF. Mouse models of liver fibrosis[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2299: 339-56. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-1382-5_23 |
| [30] | Hisamori S, Tabata C, Kadokawa Y, et al. All-trans-retinoic acid ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice through modulating cytokine production[J]. Liver Int, 2008, 28(9): 1217-25. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01745.x |
| [31] | 庄子锐, 王明亮, 张 婷, 等. 肝肾纤维化动物模型的研究进展及评价[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2020, 28(6): 845-52. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2020.06.016 |
| [32] | Luangmonkong T, Suriguga S, Mutsaers HAM, et al. Targeting oxidative stress for the treatment of liver fibrosis[J]. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol, 2018, 175: 71-102. doi:10.1007/112_2018_10 |
| [1] | 熊一凡, 梁小珊, 梁晓涛, 李伟鹏, 钱益啸, 谢 炜. 柴胡皂甙a减轻戊四氮诱发的皮质酮抑郁模型小鼠的急性癫痫发作:基于小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 515-522. |
| [2] | 赵金宝, 贾亿卿, 毛汉丁, 王世娇, 徐凡, 李鑫, 陶冶, 薛蕾, 刘树元, 宋青, 周必业. 不同延迟降温时间对劳力型热射病大鼠病理损伤的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1858-1865. |
| [3] | 孙 伟, 陈 平, 唐小杭, 谷颖敏, 田雪松. 改良的四血管间断阻塞法制作大鼠全脑缺血再灌注损伤模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1194-1203. |
| [4] | 李 博, 王 磊, 赵 伟, 范玉涵. 雪貂食管的形态学及其分子标记物的表达谱[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 428-435. |
| [5] | 曾婧欣, 苏舒文, 冼高鹏, 曾庆春, 许顶立. 利用导管损伤制备钙化性主动脉瓣疾病小鼠模型的最优时间选择[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1532-1538. |
| [6] | 张 旭, 薛崇祥, 李 嘉, 张静怡, 谭可欣, 姜雪娇, 郑舒月, 董慧静, 俞仪萱, 胡紫馨, 崔慧娟. 表皮生长因子受体抑制剂相关皮疹动物模型的构建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 352-357. |
| [7] | 施林勇, 李 宏, 辜俊伟, 宋 憧, 李俊杰, 陈 磊, 周 强, 漆松涛, 陆云涛. 替莫唑胺诱导的小鼠胶质瘤耐药动物模型的建立[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 69-74. |
| [8] | 徐艳军,易甜甜,徐肖肖,裴夫瑜,何岳林,吴学东. 环磷酰胺对铁过载小鼠骨髓造血干细胞的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(01): 110-117. |
| [9] | 梁国栋,郑汝钢,菅洪健,张旻海,袁慧琼,洪睫敏,武 钢. 体表针刺电刺激诱发心室纤颤猪模型的构建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(11): 1370-1375. |
| [10] | 郑文霞,胡宇玲,陈笛,李英博,王莎莉. 丙戊酸钠诱导小鼠自闭症模型的改良[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(06): 718-. |
| [11] | 范艺巾,唐华均,刘瑶,李成志. 二甲基苯并蒽诱导外阴鳞状上皮内病变大鼠模型的建立[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1318-. |
| [12] | 张慧,陈名武,方涛,张甜,倪文泉. Gata4基因H435Y突变型小鼠模型的建立及验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(10): 1245-. |
| [13] | 杨天睿,苗云波,张荣平,余锦雯. 实验树鼩心肌缺血再灌注离体模型的构建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(02): 205-. |
| [14] | 罗东,罗月苹,刘宝茹,梁丹丹,蒋璟玮,汪威,陈俊林,王嫣,陈文直. 新西兰兔再生障碍性贫血模型的建立[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(12): 1660-. |
| [15] | 殷昭阳,齐思勇,成祥,郭靓,陈泓宇,施明. 经股动脉注射途径建立前列腺癌和乳腺癌骨转移模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(07): 914-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
