南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1946-1958.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.14
• • 上一篇
云琦1,2( ), 杜若丽3,4, 贺玉莹1,2, 张贻欣5, 王佳慧3,4, 叶红伟3,4, 李正红1,2, 高琴3,4(
), 杜若丽3,4, 贺玉莹1,2, 张贻欣5, 王佳慧3,4, 叶红伟3,4, 李正红1,2, 高琴3,4( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-13
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
高琴
E-mail:yunqiyq1009@163.com;bbmcgq@126.com
作者简介:云 琦,硕士,E-mail: yunqiyq1009@163.com
基金资助:
Qi YUN1,2( ), Ruoli DU3,4, Yuying HE1,2, Yixin ZHANG5, Jiahui WANG3,4, Hongwei YE3,4, Zhenghong LI1,2, Qin GAO3,4(
), Ruoli DU3,4, Yuying HE1,2, Yixin ZHANG5, Jiahui WANG3,4, Hongwei YE3,4, Zhenghong LI1,2, Qin GAO3,4( )
)
Received:2025-02-13
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Qin GAO
E-mail:yunqiyq1009@163.com;bbmcgq@126.com
摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学技术结合动物实验探讨肉桂酸(CA)改善阿霉素心肌损伤(DIC)的可能机制。 方法 采用网络药理学分析得到CA改善DIC的关键靶点,并通过分子对接进行验证。6~8周龄SPF级雄性C57BL/6J小鼠被随机分为5组(6只/组):Sham组、阿霉素(DOX)组、CA(25 mg/kg)+DOX组、CA(50 mg/kg)+DOX组、CA(100 mg/kg)+DOX和铁死亡抑制剂(Ferrostatin-1 5 mg/kg)+DOX组。超声心动图和HE染色观察心肌组织病理变化;检测小鼠血清 CK-MB、LDH、MDA、IL-6、TNF-α和心肌ROS水平。蛋白免疫印迹检测心肌组织中TLR4及铁死亡通路相关蛋白表达水平。构建慢病毒介导的基因稳定敲低TLR4的小鼠心肌HL-1细胞株,细胞分为6组:阴性对照组(NC);DOX模型组(DOX);铁死亡诱导剂组(Erastin);低表达组(si-TLR4组);DOX+si-TLR4组;Erastin+si-TLR4组。CCK8测定细胞活力;荧光探针检测细胞ROS含量变化;免疫荧光检测GPX4蛋白的表达。 结果 通过网络药理学分析获得交集靶点28个,KEGG富集分析显示,CA可能通过Toll样受体信号通路作用于DIC。动物实验显示,与Sham组相比,DOX组超声心动图和HE 染色结果显示心脏损伤,血清CK-MB、LDH、MDA、炎症因子和心肌ROS水平升高(P<0.01),SLC7A11和GPX4蛋白表达降低,TLR4和PTGS2蛋白表达升高(P<0.05)。经CA处理后,心超功能指标水平升高(P<0.05);血清 CK-MB、LDH、MDA、炎症因子和心肌ROS水平降低(P<0.05);CA和铁死亡抑制剂使心肌组织SLC7A11和GPX4蛋白表达升高,TLR4和PTGS2蛋白表达降低(P<0.05)。低表达TLR4细胞株中,与NC组相比,DOX组和Erastin组细胞,ROS水平升高(P<0.001),GPX4蛋白表达降低(P<0.001);与DOX组和Erastin组相比,DOX+si-TLR4组和Erastin+si-TLR4组细胞ROS水平降低(P<0.05),GPX4蛋白表达升高(P<0.01)。 结论 CA减轻小鼠DIC,其机制可能与抑制TLR4减轻铁死亡有关。
云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958.
Qi YUN, Ruoli DU, Yuying HE, Yixin ZHANG, Jiahui WANG, Hongwei YE, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO. Cinnamic acid ameliorates doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in mice by attenuating cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via inhibiting TLR4[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958.
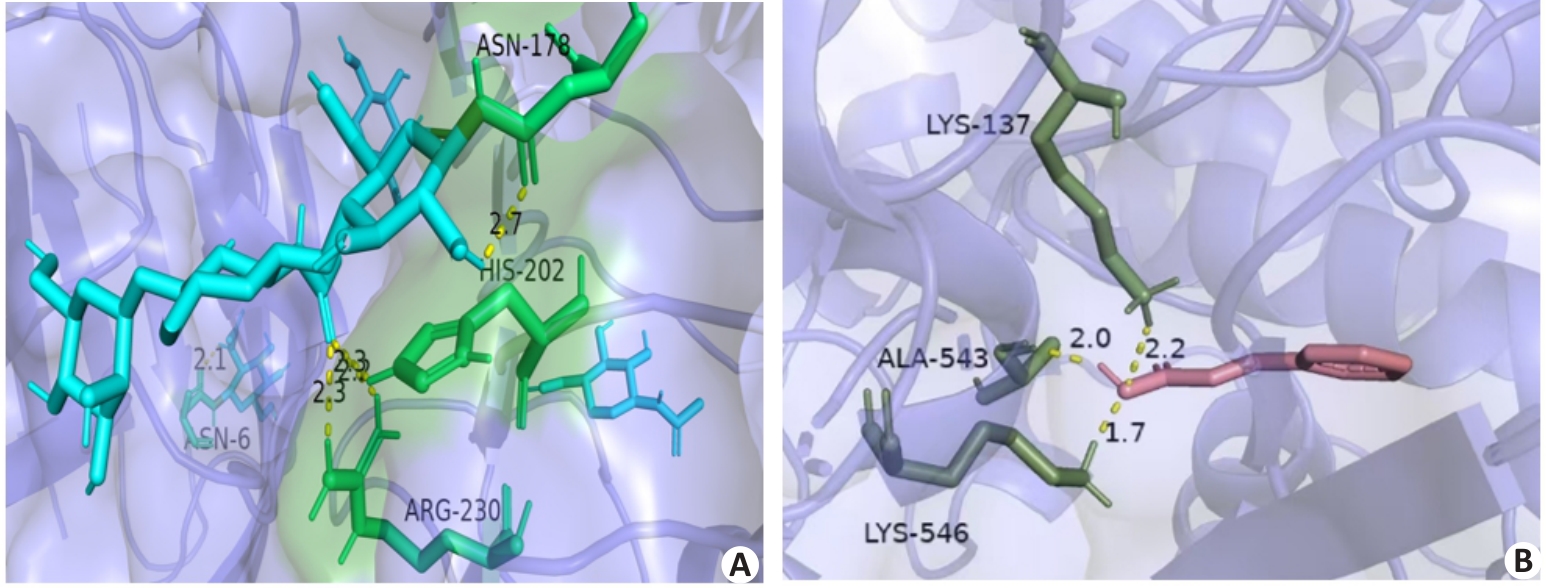
图4 分子对接可视化结果
Fig.4 Visualization of molecular docking results. A: Potential interaction between CA and TLR4. B: Potential interaction between cinnamic acid and PTGS2.
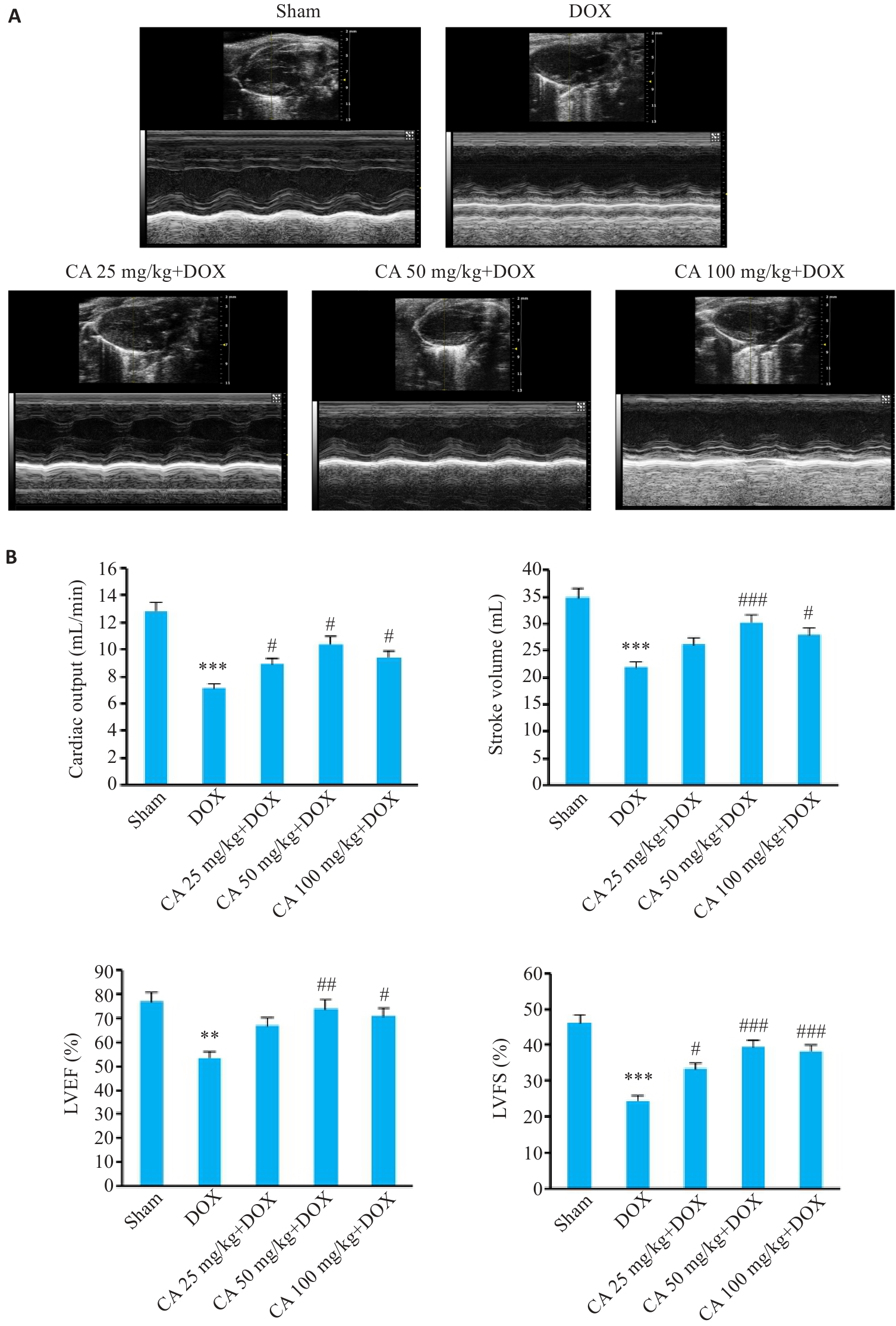
图5 各组小鼠心脏超声图像和心功能各指标变化
Fig.5 Cardiac ultrasound images and cardiac function indexes of the mice in different groups (Mean±SD, n=6). A: Evaluation of cardiac function by M-mode echocardiography. B: Comparison of echocardiographic parameters. LVEF: Left ventricle ejection fraction; LVFS: Left ventricular fractional shortening. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs the Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs the DOX group.
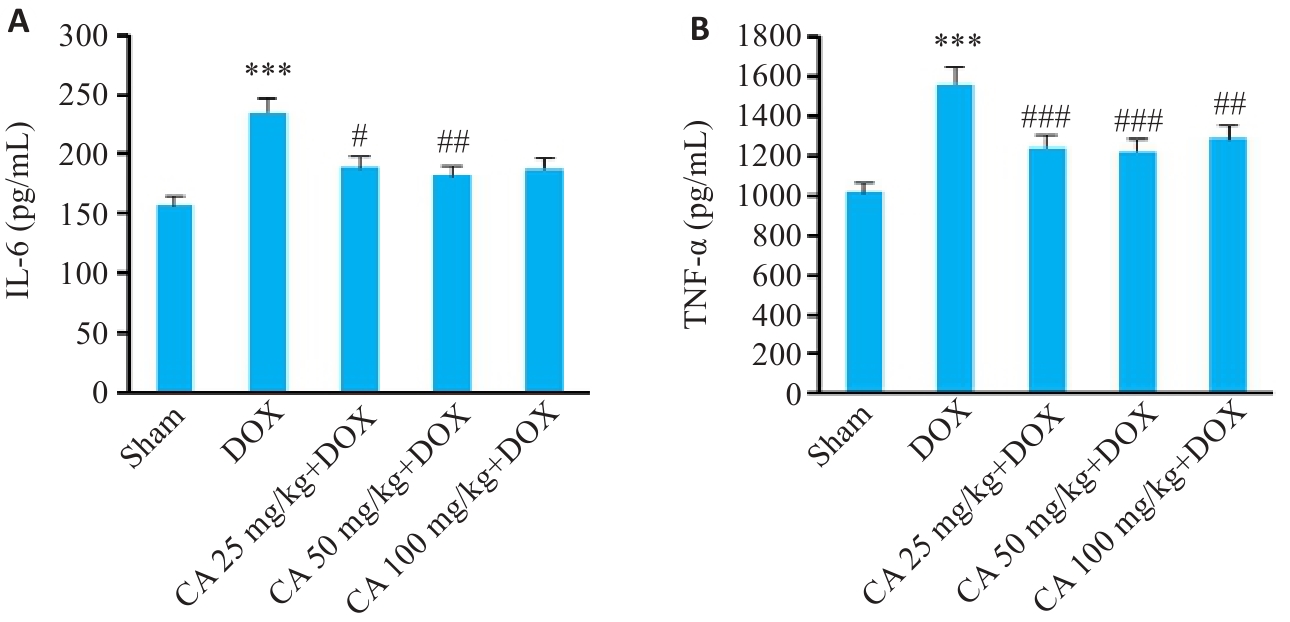
图8 各组小鼠血清IL-6和TNF-α的变化
Fig.8 Serum IL-6 (A) and TNF-α (B) levels in different groups (Mean±SD, n=6). ***P<0.001 vs the Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs the DOX group.
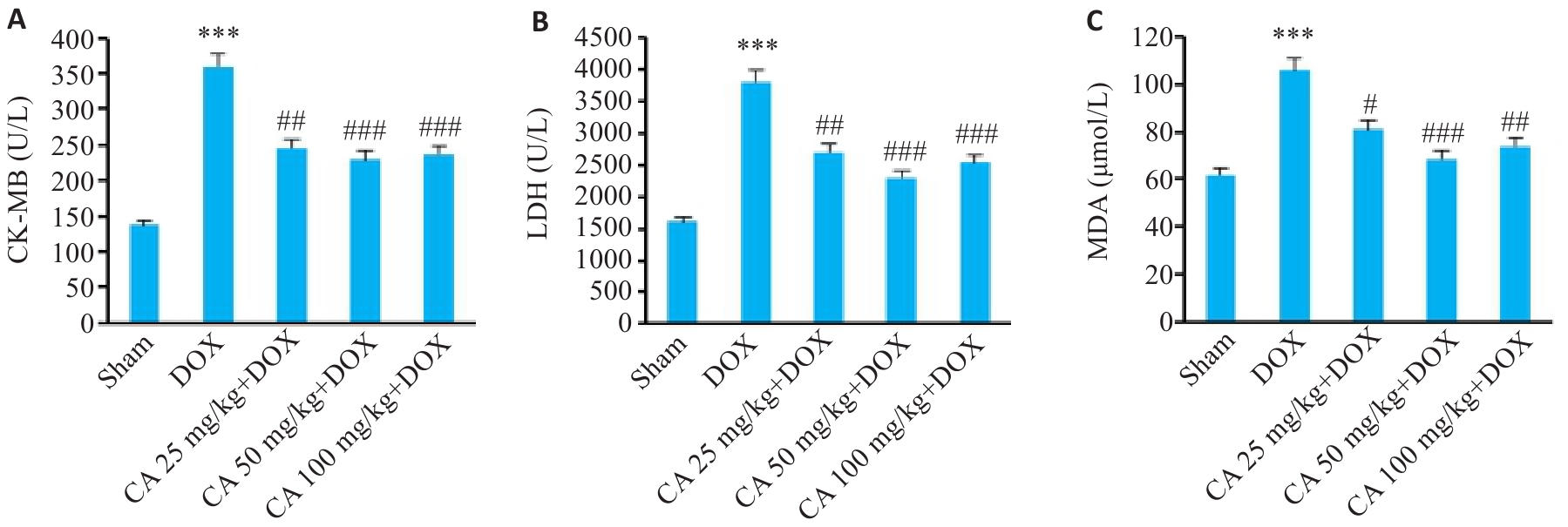
图9 各组小鼠血清CK-MB、LDH和MDA的变化
Fig.9 Serum CK-MB (A), LDH (B) and MDA (C) levels in different groups (Mean±SD, n=6). ***P<0.001 vs the Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs the DOX group.
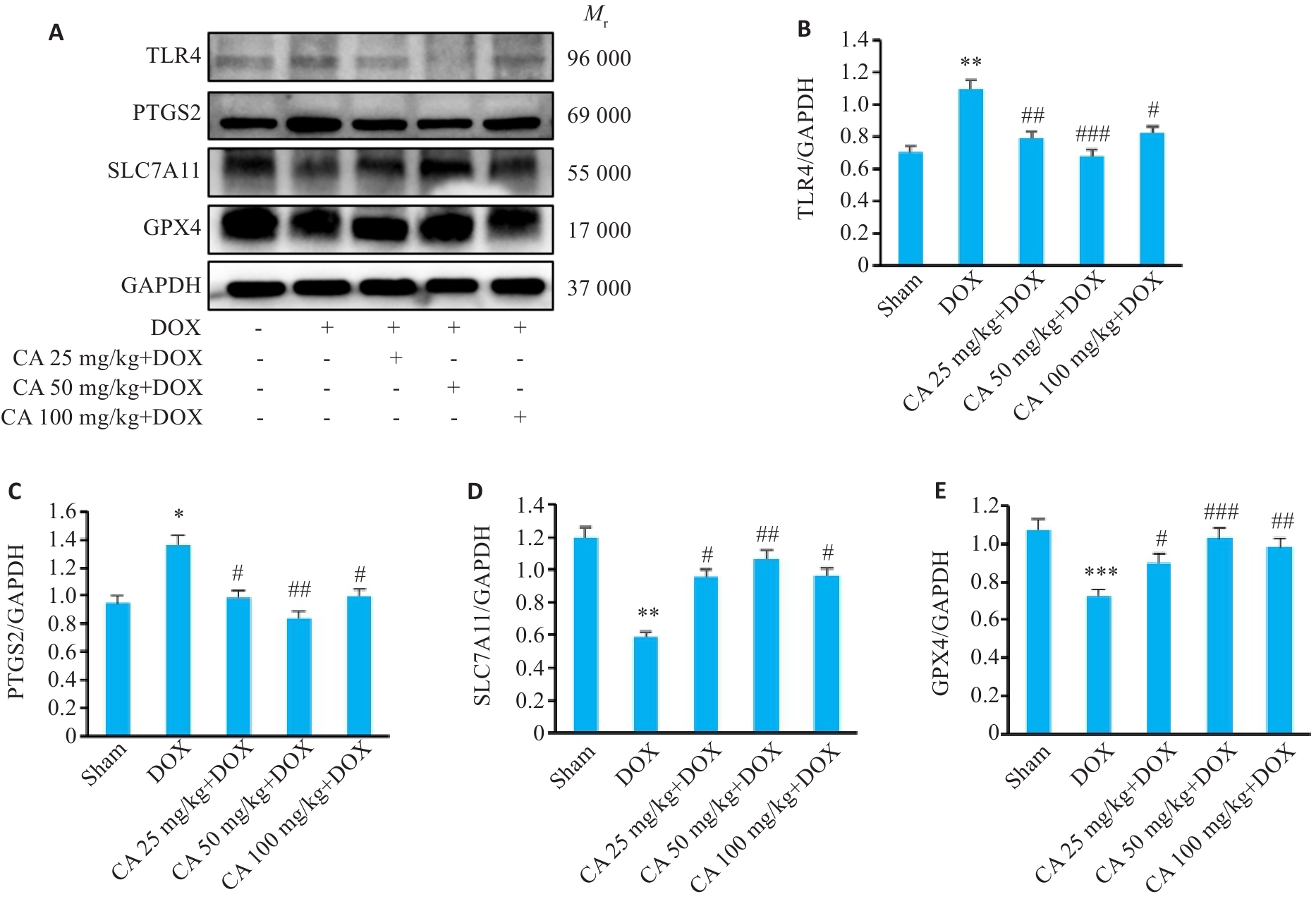
图10 各组小鼠心肌组织中TLR4、PTGS2、SLC7A11和GPX4蛋白表达的变化
Fig.10 TLR4, PTGS2, SLC7A11 and GPX4 protein expressions in the myocardial tissues in the 5 groups. A: Protein bands in Western blotting. B-E: Relative protein levels of TLR4, PTGS2, SLC7A11 and GPX4 proteins (Mean±SD, n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs the Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs the DOX group.
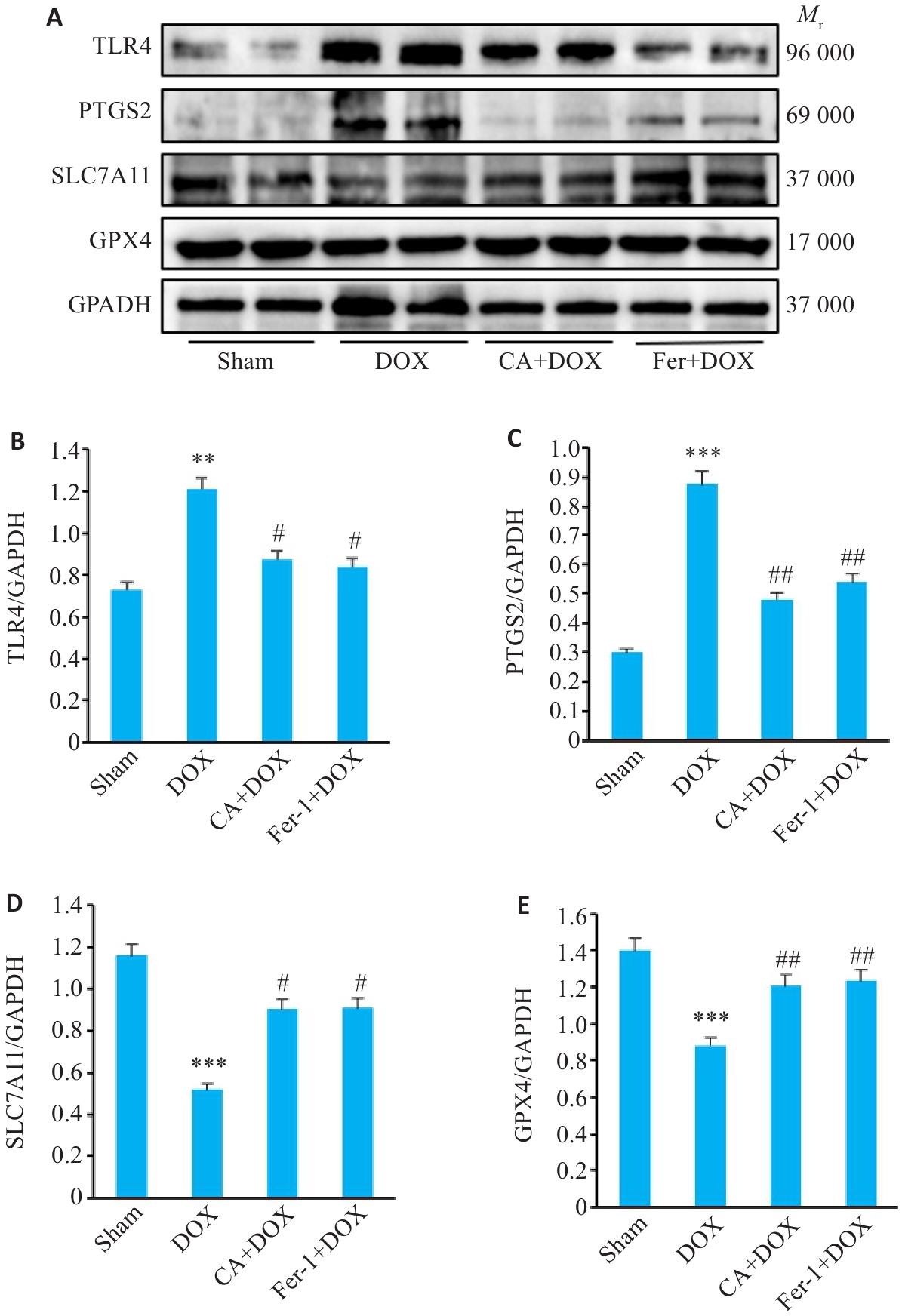
图11 各组小鼠心肌组织中TLR4、PTGS2、SLC7A11和GPX4蛋白表达的变化
Fig.11 Comparison of TLR4, PTGS2, SLC7A11 and GPX4 protein expressions in the myocardial tissues among the 4 groups. A: Protein bands in Western blotting. B-E: Relative protein levels of TLR4, PTGS2, SLC7A11 and GPX4 proteins (Mean±SD, n=3). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs the Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs the DOX group.
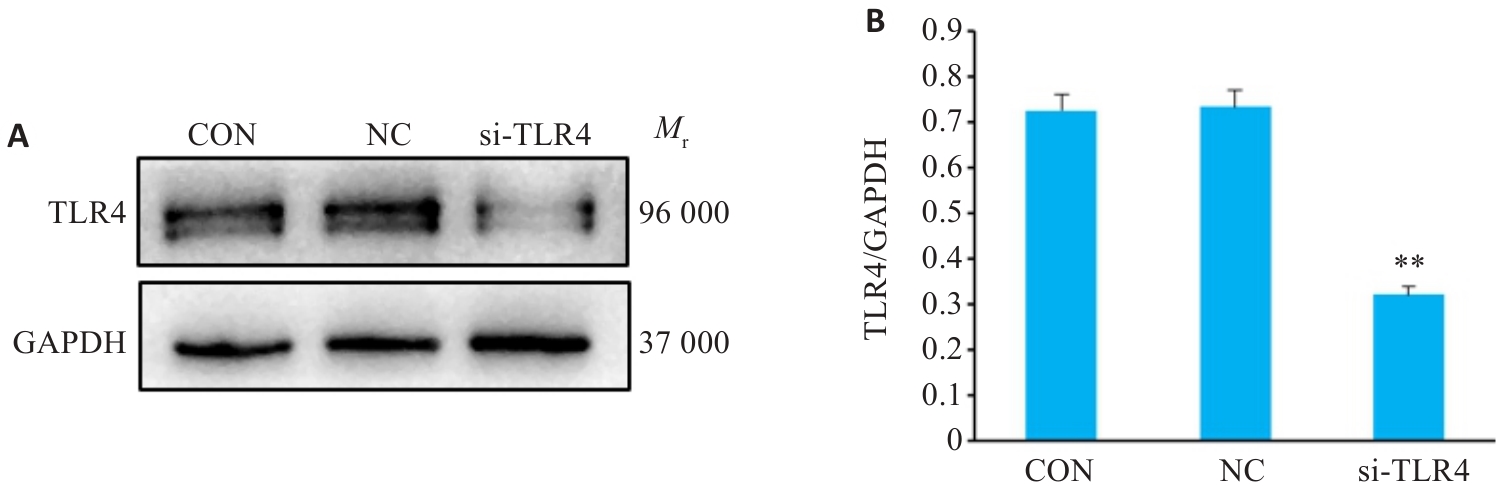
图12 Western blotting检测低表达TLR4感染效率
Fig.12 Western blotting for detection of si-TLR4 transfection efficiency. A: Protein bands in Western blotting. B: Relative protein levels of TLR4 protein (Mean±SD, n=3). **P<0.01 vs the NC group.
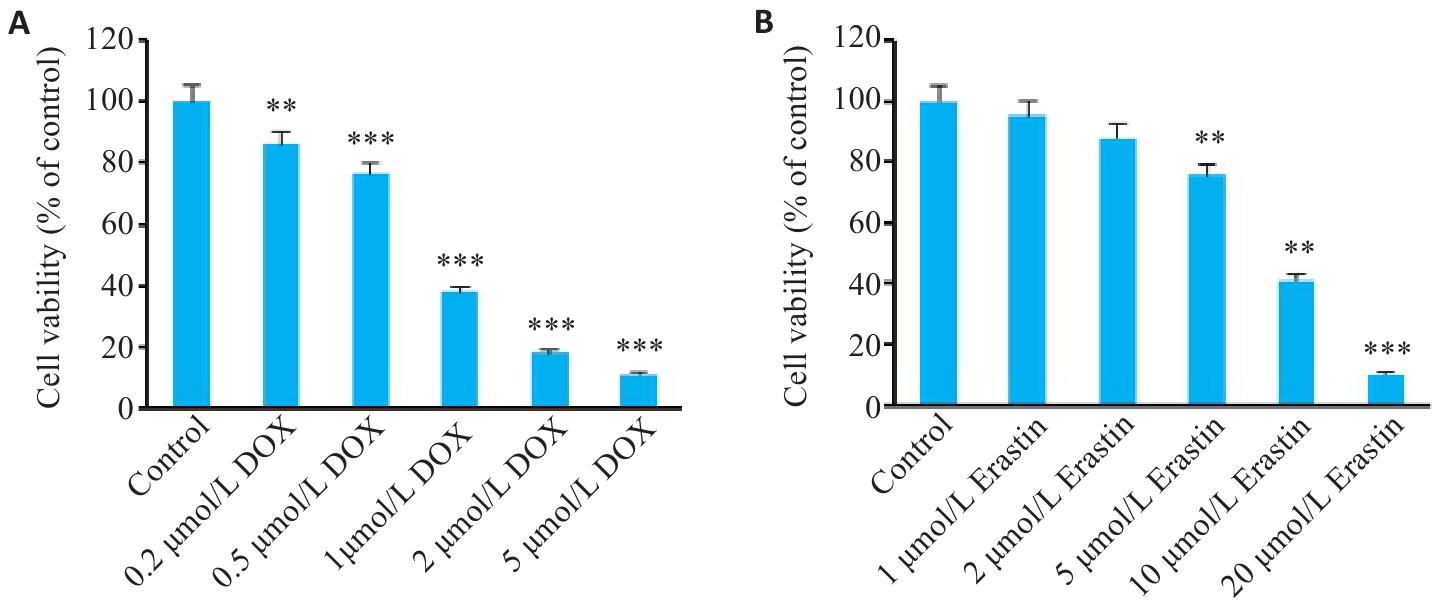
图13 HL-1心肌细胞活性
Fig.13 Viability of HL-1 cells treated with different concentrations of DOX (A) and Erastin (B). Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=6). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs the NC group.
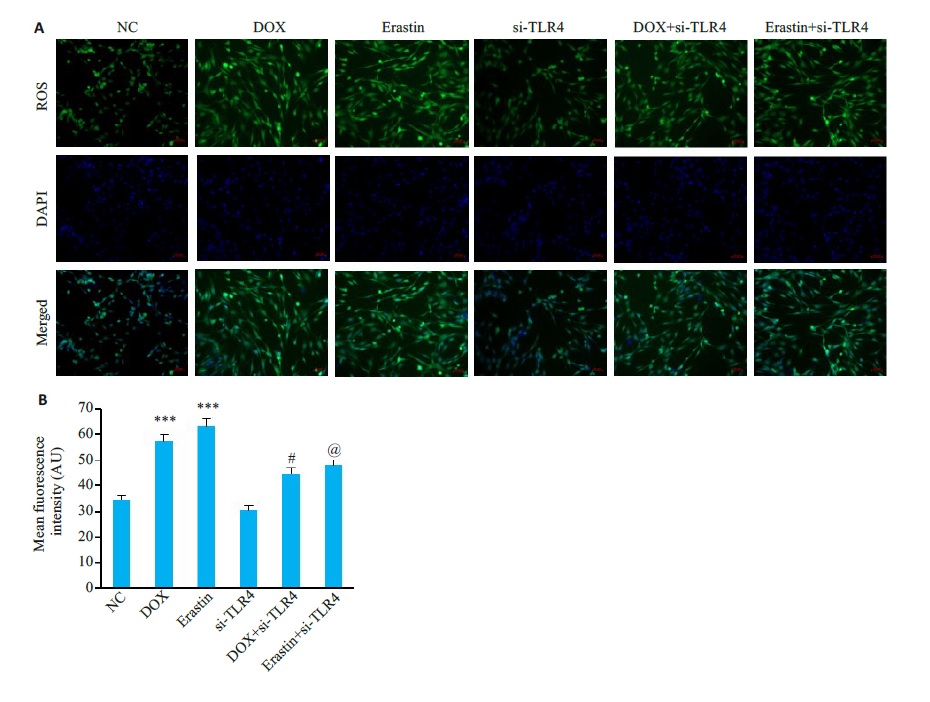
图14 HL-1细胞中ROS水平
Fig.14 ROS levels in HL-1 cardiomyocytes in each group. A:DCFH-DA staining of HL-1 of the cells (×200). B: Meanfluorescence intensity levels (Mean±SD, n=6) ***P<0.001 vs the NC group; #P<0.05 vs the DOX group; @<0.05 vs the Erastin group.
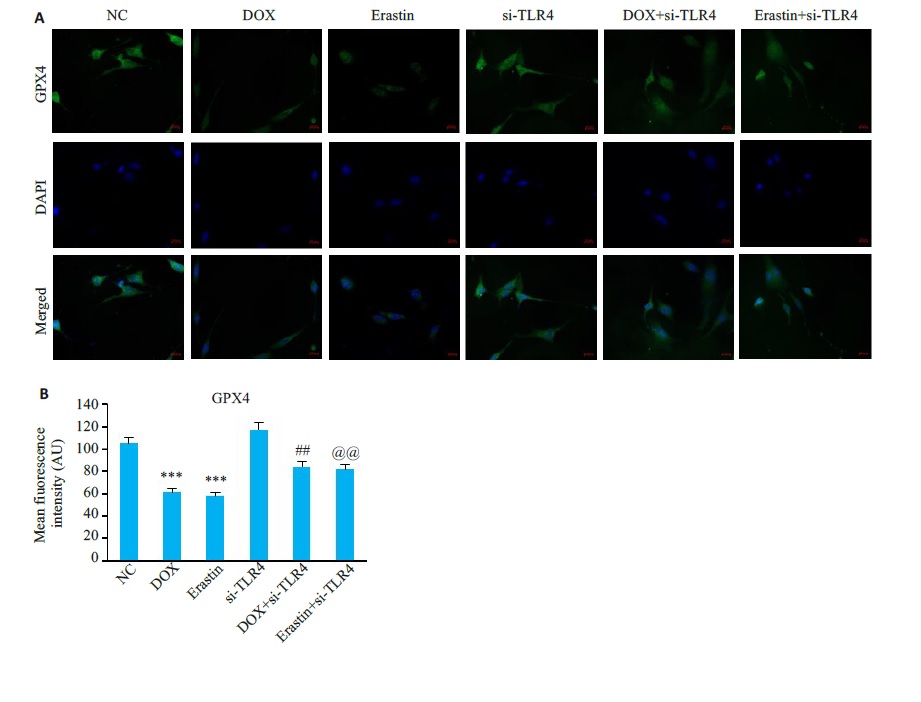
图15 HL-1细胞中GPX4免疫荧光
Fig.15 Immunofluorescence staining for GPX4 in HL-1cells in each group. A: Representative images ofimmunofluorescence staining of HL-1 cells in each group(×400). B: GPX4 fluorescence intensity in each group (Mean±SD,n=6). ***P<0.001vsP<0.01 vsthe NC group; ##P<0.01 vs the DOX group; @@P<0.01 vs the Erastin group.
| [1] | Sohail M, Sun Z, Li Y, et al. Research progress in strategies to improve the efficacy and safety of doxorubicin for cancer chemotherapy[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2021, 21(12): 1385-98. doi:10.1080/14737140.2021.1991316 |
| [2] | Prasanna PL, Renu K, Valsala Gopalakrishnan A. New molecular and biochemical insights of doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 250: 117599. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117599 |
| [3] | Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(5): 1060-72. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042 |
| [4] | Cheng YF, Zak O, Aisen P, et al. Structure of the human transferrin receptor-transferrin complex[J]. Cell, 2004, 116(4): 565-76. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00130-8 |
| [5] | Yu H, Yang C, Jian L, et al. Sulfasalazine-induced ferroptosis in breast cancer cells is reduced by the inhibitory effect of estrogen receptor on the transferrin receptor[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 42(2): 826-38. |
| [6] | Teschke R. Treatment of drug-induced liver injury[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 11(1): 15. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11010015 |
| [7] | Pontiki E, Hadjipavlou-Litina D. Multi-target cinnamic acids for oxidative stress and inflammation: design, synthesis, biological evaluation and modeling studies[J]. Molecules, 2018, 24(1): E12. doi:10.3390/molecules24010012 |
| [8] | Song F, Li H, Sun JY, et al. Protective effects of cinnamic acid and cinnamic aldehyde on isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013, 150(1): 125-30. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.08.019 |
| [9] | Sova M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of cinnamic acid derivatives[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2012, 12(8): 749-67. doi:10.2174/138955712801264792 |
| [10] | Takao K, Toda K, Saito T, et al. Synthesis of amide and ester derivatives of cinnamic acid and its analogs: evaluation of their free radical scavenging and monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase inhibitory activities[J]. Chem Pharm Bull: Tokyo, 2017, 65(11): 1020-7. doi:10.1248/cpb.c17-00416 |
| [11] | 王凤雪, 高 宇, 刘海波.中药网络药理学研究流程及代表性数据库工具[J].中国现代中药, 2021, 23(6): 1111-8. |
| [12] | Lu SM, Yang B, Tan ZB, et al. TaoHe ChengQi decoction ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through anti-ferroptosis via the Nrf2 pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 129: 155597. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155597 |
| [13] | Volkova M, Russell R. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: prevalence, pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Curr Cardiol Rev, 2011, 7(4): 214-20. doi:10.2174/157340311799960645 |
| [14] | Tacar O, Sriamornsak P, Dass CR. Doxorubicin: an update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2013, 65(2): 157-70. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01567.x |
| [15] | Wang L, Chen Q, Qi H, et al. Doxorubicin-induced systemic inflammation is driven by upregulation of toll-like receptor TLR4 and endotoxin leakage[J]. Cancer Res, 2016, 76(22): 6631-42. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-15-3034 |
| [16] | Singla DK, Johnson TA, Tavakoli Dargani Z. Exosome treatment enhances anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages and reduces inflammation-induced pyroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(10): E1224. doi:10.3390/cells8101224 |
| [17] | Lan Y, Wang Y, Huang K, et al. Heat shock protein 22 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via regulating inflammation and apoptosis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 257. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00257 |
| [18] | Hu S, Liu B, Yang M, et al. Carnosic acid protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through enhancing the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2023, 14(8): 3849-62. doi:10.1039/d2fo03904d |
| [19] | Tadokoro T, Ikeda M, Ide T, et al. Mitochondria-dependent ferroptosis plays a pivotal role in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity[J]. JCI Insight, 2020, 5(9): 132747. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.132747 |
| [20] | Fang X, Wang H, Han D, et al. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019, 116(7): 2672-80. doi:10.1073/pnas.1821022116 |
| [21] | Xu F, Wang F, Wen T, et al. Protective effect of cinnamic acid in endotoxin-poisoned mice[J]. Phytother Res, 2017, 31(12): 1946-53. doi:10.1002/ptr.5944 |
| [22] | Koczurkiewicz-Adamczyk P, Klaś K, Gunia-Krzyżak A, et al. Cinnamic acid derivatives as cardioprotective agents against oxidative and structural damage induced by doxorubicin[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(12): 6217. doi:10.3390/ijms22126217 |
| [23] | 庄延双, 蔡宝昌, 张自力. 网络药理学在中药研究中的应用进展[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2021, 37(1): 156-60. |
| [24] | 杜若丽, 云 琦, 王奕人, 等.白花丹素通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路减弱焦亡对抗脓毒症心肌损伤[J].南方医科大学学报,2024,44(11):2209-19. |
| [25] | Oo TT, Sumneang N, Ongnok B, et al. L6H21 protects against cognitive impairment and brain pathologies via toll-like receptor 4-myeloid differentiation factor 2 signalling in prediabetic rats[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2022, 179(6): 1220-36. doi:10.1111/bph.15741 |
| [26] | Alanazi AM, Fadda L, Alhusaini A, et al. Liposomal resveratrol and/or carvedilol attenuate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by modulating inflammation, oxidative stress and S100A1 in rats[J]. Antioxidants: Basel, 2020, 9(2): E159. doi:10.3390/antiox9020159 |
| [27] | Li B, Cai XY, Wang YX, et al. Circ-SKA3 enhances doxorubicin toxicity in AC16 cells through miR-1303/TLR4 axis[J]. Int Heart J, 2021, 62(5): 1112-23. doi:10.1536/ihj.20-809 |
| [28] | Xu L, Wang C, Zou Z, et al. Ozone attenuated H9c2 cell injury induced by doxorubicin[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2021, 78(1): e86-93. doi:10.1097/fjc.0000000000001043 |
| [29] | Feng PP, Yang Y, Liu N, et al. Baicalin regulates TLR4/IκBα/NFκB signaling pathway to alleviate inflammation in Doxorubicin related cardiotoxicity[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 637: 1-8. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.10.061 |
| [30] | Riad A, Bien S, Gratz M, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 deficiency attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in mice[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2008, 10(3): 233-43. doi:10.1016/j.ejheart.2008.01.004 |
| [31] | Li YC, Huang LT, Li JL, et al. Targeting TLR4 and regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway with andrographolide to suppress inflamm-ation and ferroptosis in LPS-induced acute lung injury[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2024, 22(10): 914-28. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(24)60727-2 |
| [32] | Chen D, Geng Y, Deng Z, et al. Inhibition of TLR4 alleviates heat stroke-induced cardiomyocyte injury by down-regulating inflamm-ation and ferroptosis[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(5): 2297. doi:10.3390/molecules28052297 |
| [1] | 呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | 杨子为, 吕畅, 董柱, 计书磊, 毕生辉, 张雪花, 王晓武. 金樱子通过调控Src-AKT1轴抑制肺动脉高压平滑肌增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [3] | 何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [4] | 邓楚玉, 王雪莹, 甘立祥, 王大禹, 郑晓燕, 唐纯志. 电针足三里改善高脂血症小鼠的血脂紊乱:基于肠道菌群结构的改善[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1633-1642. |
| [5] | 欧泽金, 李瀛, 陈诗, 王梓译, 何美仪, 陈志成, 唐侍豪, 孟晓静, 王致. 抑制铁死亡减轻敌草快引起的斑马鱼急性肾损伤的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1743-1750. |
| [6] | 李军仪, 陈思源, 谢力遥, 王劲, 程奥, 张绍伟, 林继瑜, 方志涵, 潘一锐, 崔翀鹤, 陈庚鑫, 张超, 李栎. 益智仁提取物谷甾醇通过抑制铁死亡中的ETS-5基因表达延长秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1751-1757. |
| [7] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [8] | 范正媛, 沈子涵, 李亚, 沈婷婷, 李高峰, 李素云. 补肺益肾方对香烟烟雾提取物诱导的人支气管上皮细胞损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1372-1379. |
| [9] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [10] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [11] | 张梦影, 赵晨玲, 田丽伟, 余郭芳, 杨文明, 董婷. 肝豆扶木汤通过GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15通路抑制铁死亡改善Wilson病小鼠的肝脏脂肪变性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478. |
| [12] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [13] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [14] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [15] | 张安邦, 孙秀颀, 庞博, 吴远华, 时靖宇, 张宁, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过调节肠道-大脑轴及Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||