南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2726-2737.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.20
• • 上一篇
肖丹庭1( ), 唐海军1, 杨明秀1, 滕洪材1, 梁积铭1, 谢天裕2, 冯文宇3, 刘尚玉1, 戴薇1, 李河柠4, 刘云1(
), 唐海军1, 杨明秀1, 滕洪材1, 梁积铭1, 谢天裕2, 冯文宇3, 刘尚玉1, 戴薇1, 李河柠4, 刘云1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-08-10
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
刘云
E-mail:szsyxdt@163.com;liuyun200450250@sina.com
作者简介:肖丹庭,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: szsyxdt@163.com
基金资助:
Danting XIAO1( ), Haijun TANG1, Mingxiu YANG1, Hongcai TENG1, Jiming LIANG1, Tianyu XIE2, Wenyu FENG3, Shangyu LIU1, Wei DAI1, Hening LI4, Yun LIU1(
), Haijun TANG1, Mingxiu YANG1, Hongcai TENG1, Jiming LIANG1, Tianyu XIE2, Wenyu FENG3, Shangyu LIU1, Wei DAI1, Hening LI4, Yun LIU1( )
)
Received:2025-08-10
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Yun LIU
E-mail:szsyxdt@163.com;liuyun200450250@sina.com
摘要:
目的 探讨重楼皂苷VII(PP7)的抗骨肉瘤疗效及其分子机制。 方法 采用超高效液相色谱串联质谱分析鉴定重楼的主要成分。建立骨肉瘤患者来源异种移植瘤(PDX)模型,将构建的6只PDX模型的裸鼠随机分为实验组和对照组,3只/组。实验组接受2 mg/kg PP7灌胃(2 d/次,共用药28 d),对照组给予等量生理盐水,测量两组肿瘤的体积和质量。在143B和HOS细胞中,采用CCK-8法检测不同浓度PP7(0、1.25、2.5、5、10 μmol/L)对肿瘤细胞增殖的影响并确定起效浓度。通过Transwell实验分析PP7对细胞迁移和侵袭的作用。结合单细胞转录组测序(scRNA-seq)、批量转录组测序(bulk RNA-seq)和分子对接预测PP7的作用靶点,采用Western blotting验证PP7对该靶点的调控作用。构建沉默SOHLH1的骨肉瘤细胞,设置对照组、PP7干预组(5 μmol/L)、沉默SOHLH1组及PP7+沉默SOHLH1组,分别检测各组细胞迁移、侵袭能力以及铁死亡相关指标ROS和LPO的水平。 结果 质谱分析发现PP7为重楼主要活性成分之一。体内实验中,PP7处理组肿瘤体积与质量均显著低于对照组(P<0.05)。体外实验显示,PP7以浓度依赖方式抑制骨肉瘤细胞增值,并在5 μmol/L浓度下抑制细胞增殖(P<0.05),且该浓度抑制细胞迁移与侵袭(P<0.05)。多组学分析确定SOHLH1为PP7潜在作用靶点。Western blotting证实PP7可上调SOHLH1 mRNA及蛋白表达(P<0.05)。SOHLH1沉默削弱了PP7对细胞迁移、侵袭的抑制作用,并减弱了PP7诱导的铁死亡(P<0.05)。 结论 PP7通过上调SOHLH1表达,诱导骨肉瘤细胞铁死亡,进而抑制其恶性进展。
肖丹庭, 唐海军, 杨明秀, 滕洪材, 梁积铭, 谢天裕, 冯文宇, 刘尚玉, 戴薇, 李河柠, 刘云. 重楼皂苷VII通过SOHLH1诱导骨肉瘤铁死亡抑制肿瘤进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2726-2737.
Danting XIAO, Haijun TANG, Mingxiu YANG, Hongcai TENG, Jiming LIANG, Tianyu XIE, Wenyu FENG, Shangyu LIU, Wei DAI, Hening LI, Yun LIU. Polyphyllin VII inhibits osteosarcoma xenograft growth in mice by inducing ferroptosis via upregulating SOHLH1[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2726-2737.

图1 重楼药材的质谱分析结果
Fig.1 Mass spectrometry results for P. polyphylla. A: Base peak ion plots of P. polyphylla in positive ion modes. PP7 was detected at the retention time of 38.38 min (red box). B: Base peak ion plots of P. polyphylla in negative ion modes. C: Molecular formula of PP7.
| No. | Retention time (min) | Accurate molecular weight | Ionic form | ppm | Compound name | Molecular formula | First and second level fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.798 | 402.4792 | M+K | -3.17 | Acetyl tributyl citrate | C20H34O8 | 441.5761, 199.0983, 215.0932, 229.142, 257.1379, 259.1531, 267.123, 287.1467, 299.1497, 303.18014 |
| 2 | 1.982 | 610.5175 | M+H | -1.96 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 611.5242, 123.0442, 245.0442, 593.146, |
| 3 | 4.618 | 274.3978 | M+H | -2.54 | Nandrolone | C18H26O2 | 275.4051, 83.0852, 131.0843, 153.1279, 177.1264, 275.2006 |
| 4 | 14.503 | 855.017 | M+H | 2.57 | Polyphyllin I | C44H70O16 | 856.0271, 428.5142, |
| 5 | 21.452 | 592.7606 | M+H | 1.35 | Agavoside A | C33H52O9 | 593.7685, 123.1132, 291.1961, 475.3434, 519.3343, |
| 6 | 21.687 | 903.0583 | M+H | 7.96 | Trigofoenoside A | C45H74O18 | 904.059, 577.3734, 683.4028, 753.4484, 829.4611 |
| 7 | 25.211 | 293.3663 | M+Na | 4.43 | Anastrozole | C17H19N5 | 316.3553, 55.0295, 240.1509, 173.1073, 187.1236, 225.1122 |
| 8 | 25.474 | 738.9018 | M+H | -1.89 | Polyphyllin VI | C39H62O13 | 739.9083, 433.2632, 578.383, 397.3106 |
| 9 | 27.384 | 430.62 | M+H | 3.94 | Pennogenin | C27H42O4 | 431.6296 |
| 10 | 27.499 | 414.6206 | M+H | 0.96 | Diosgenin | C27H42O3 | 415.6289, 81.0693, 105.0697 |
| 11 | 28.371 | 480.6341 | M+H | 9.34 | Crustecdysone | C27H44O7 | 481.6467, 59.0493, 127.1128, 279.1596, 305.1737, 307.1907, |
| 12 | 28.877 | 191.1867 | M+H | 5.72 | Carbendazim | C9H9N3O2 | 192.1957 |
| 13 | 29.455 | 1015.1848 | M+H | -2.85 | Polyphyllin B | C51H82O20 | 1016.1898, 293.1246, 723.4232 |
| 14 | 29.455 | 1015.1848 | M+H | -2.85 | Polyphyllin E | C51H82O20 | 1016.1898 |
| 15 | 29.455 | 1015.1848 | M+H | 5.51 | Polyphyllin F | C51H82O20 | 1016.1983 |
| 16 | 30.536 | 869.0436 | M+H | 1.72 | Dioscin | C45H72O16 | 870.0534, 89.0600, 121.1013, 127.0393, 147.0616, 249.1868, 291.1082, 457.3314 |
| 17 | 32.939 | 696.8651 | M+H | 9.03 | Momordicoside E | C37H60O12 | 697.8793, 489.3545 |
| 18 | 33.402 | 404.4105 | M+H | 0.34 | Kaempferol 7-O-Neohesperidoside | C27H30O15 | 595.5262, 223.0970, 373.1257 |
| 19 | 37.217 | 323.5133 | M+H | -0.31 | Linoleoyl Ethanolamide | C20H37NO2 | 324.5211, 83.0849 |
| 20 | 37.434 | 278.3435 | M+K | -1.89 | Dibutyl Phthalate | C16H22O4 | 317.4412 |
| 21 | 37.434 | 317.5072 | M+H | 0.63 | Phytosphingosine | C18H39NO3 | 318.5153, 65.038, 69.0704 |
| 22 | 38.378 | 1049.1990 | M+H | -4.00 | Polyphyllin VII | C51H84O22 | 1050.2032, 721.4158, 575.3579, |
| 23 | 51.839 | 196.2429 | M+H | 3.55 | Loliolide | C11H16O3 | 197.2516, 67.0547, 111.0446 |
表1 正离子模式下的鉴定结果
Tab.1 Ientification results in the positive ion mode
| No. | Retention time (min) | Accurate molecular weight | Ionic form | ppm | Compound name | Molecular formula | First and second level fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.798 | 402.4792 | M+K | -3.17 | Acetyl tributyl citrate | C20H34O8 | 441.5761, 199.0983, 215.0932, 229.142, 257.1379, 259.1531, 267.123, 287.1467, 299.1497, 303.18014 |
| 2 | 1.982 | 610.5175 | M+H | -1.96 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 611.5242, 123.0442, 245.0442, 593.146, |
| 3 | 4.618 | 274.3978 | M+H | -2.54 | Nandrolone | C18H26O2 | 275.4051, 83.0852, 131.0843, 153.1279, 177.1264, 275.2006 |
| 4 | 14.503 | 855.017 | M+H | 2.57 | Polyphyllin I | C44H70O16 | 856.0271, 428.5142, |
| 5 | 21.452 | 592.7606 | M+H | 1.35 | Agavoside A | C33H52O9 | 593.7685, 123.1132, 291.1961, 475.3434, 519.3343, |
| 6 | 21.687 | 903.0583 | M+H | 7.96 | Trigofoenoside A | C45H74O18 | 904.059, 577.3734, 683.4028, 753.4484, 829.4611 |
| 7 | 25.211 | 293.3663 | M+Na | 4.43 | Anastrozole | C17H19N5 | 316.3553, 55.0295, 240.1509, 173.1073, 187.1236, 225.1122 |
| 8 | 25.474 | 738.9018 | M+H | -1.89 | Polyphyllin VI | C39H62O13 | 739.9083, 433.2632, 578.383, 397.3106 |
| 9 | 27.384 | 430.62 | M+H | 3.94 | Pennogenin | C27H42O4 | 431.6296 |
| 10 | 27.499 | 414.6206 | M+H | 0.96 | Diosgenin | C27H42O3 | 415.6289, 81.0693, 105.0697 |
| 11 | 28.371 | 480.6341 | M+H | 9.34 | Crustecdysone | C27H44O7 | 481.6467, 59.0493, 127.1128, 279.1596, 305.1737, 307.1907, |
| 12 | 28.877 | 191.1867 | M+H | 5.72 | Carbendazim | C9H9N3O2 | 192.1957 |
| 13 | 29.455 | 1015.1848 | M+H | -2.85 | Polyphyllin B | C51H82O20 | 1016.1898, 293.1246, 723.4232 |
| 14 | 29.455 | 1015.1848 | M+H | -2.85 | Polyphyllin E | C51H82O20 | 1016.1898 |
| 15 | 29.455 | 1015.1848 | M+H | 5.51 | Polyphyllin F | C51H82O20 | 1016.1983 |
| 16 | 30.536 | 869.0436 | M+H | 1.72 | Dioscin | C45H72O16 | 870.0534, 89.0600, 121.1013, 127.0393, 147.0616, 249.1868, 291.1082, 457.3314 |
| 17 | 32.939 | 696.8651 | M+H | 9.03 | Momordicoside E | C37H60O12 | 697.8793, 489.3545 |
| 18 | 33.402 | 404.4105 | M+H | 0.34 | Kaempferol 7-O-Neohesperidoside | C27H30O15 | 595.5262, 223.0970, 373.1257 |
| 19 | 37.217 | 323.5133 | M+H | -0.31 | Linoleoyl Ethanolamide | C20H37NO2 | 324.5211, 83.0849 |
| 20 | 37.434 | 278.3435 | M+K | -1.89 | Dibutyl Phthalate | C16H22O4 | 317.4412 |
| 21 | 37.434 | 317.5072 | M+H | 0.63 | Phytosphingosine | C18H39NO3 | 318.5153, 65.038, 69.0704 |
| 22 | 38.378 | 1049.1990 | M+H | -4.00 | Polyphyllin VII | C51H84O22 | 1050.2032, 721.4158, 575.3579, |
| 23 | 51.839 | 196.2429 | M+H | 3.55 | Loliolide | C11H16O3 | 197.2516, 67.0547, 111.0446 |
| No. | Retention time (min) | Accurate molecular weight | Ionic form | ppm | Compound name | Molecular formula | First and second level fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.609 | 402.4792 | M-H | 8.97 | Acetyl Tributyl Citrate | C20H34O8 | 401.4748, 245.103, 255.1215, 289.0943 |
| 2 | 7.238 | 430.62 | M-H | -1.40 | Pennogenin | C27H42O4 | 429.6114 |
| 3 | 10.321 | 610.5175 | M+Cl | 8.36 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 645.9759, 163.0600, 193.0131 |
| 4 | 11.516 | 414.6206 | M+Cl | 3.55 | Diosgenin | C27H42O3 | 450.0752 |
| 5 | 14.868 | 738.9018 | M+Cl | 4.52 | Polyphyllin VI | C39H62O13 | 774.3583 |
| 6 | 21.72 | 592.7606 | M-H | 7.60 | Agavoside A | C33H52O9 | 591.7571, 73.0284, 315.2324, 355.2267, 359.2231, 413.3022 |
| 7 | 26.119 | 191.1867 | M-H | 1.58 | Carbendazim | C9H9N3O2 | 190.1790, 104.0244, 158.0367 |
| 8 | 29.339 | 594.5181 | M-H | 0.74 | Kaempferol 7-O-Neohesperidoside | C27H30O15 | 593.5102, 111.0446, 251.0915, 265.0710, 375.1415 |
| 9 | 29.917 | 696.8651 | M+Cl | 2.32 | Momordicoside E | C37H60O12 | 732.3134, 121.0515, 341.2867, 505.3542, 605.381 |
| 10 | 34.047 | 317.5072 | M-H | -8.21 | Phytosphingosine | C18H39NO3 | 316.4966, 352.9604 |
| 11 | 34.395 | 480.6341 | M+Cl | 0 | Crustecdysone | C27H44O7 | 516.0871, 75.0456, 99.0812, 115.0761, 141.0934, 145.0868, 291.1613, 301.1825, 445.2586 |
| 12 | 36.535 | 903.0583 | M+Cl | 0.53 | Trigofoenoside A | C45H74O18 | 938.5118, 547.3687, 593.3664, 709.4143 |
| 13 | 40.653 | 196.2429 | M-H | 6.15 | Loliolide | C11H16O3 | 195.2362, 179.0700, 195.1020 |
| 14 | 41.316 | 278.3435 | M+Cl | -6.05 | Dibutyl Phthalate | C16H22O4 | 313.7946, 55.0548, 147.0078, 167.034, 183.1388 |
| 15 | 42.043 | 869.0436 | M-H | -3.34 | Dioscin | C45H72O16 | 868.0327, 101.0238, 557.3476, 575.3569 |
| 16 | 45.297 | 274.3978 | M-H | 5.49 | Nandrolone | C18H26O2 | 273.3914, 147.0822, 173.0955, 239.1447 |
表2 负离子模式下的鉴定结果
Tab.2 Identification results in the negative ion mode
| No. | Retention time (min) | Accurate molecular weight | Ionic form | ppm | Compound name | Molecular formula | First and second level fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.609 | 402.4792 | M-H | 8.97 | Acetyl Tributyl Citrate | C20H34O8 | 401.4748, 245.103, 255.1215, 289.0943 |
| 2 | 7.238 | 430.62 | M-H | -1.40 | Pennogenin | C27H42O4 | 429.6114 |
| 3 | 10.321 | 610.5175 | M+Cl | 8.36 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 645.9759, 163.0600, 193.0131 |
| 4 | 11.516 | 414.6206 | M+Cl | 3.55 | Diosgenin | C27H42O3 | 450.0752 |
| 5 | 14.868 | 738.9018 | M+Cl | 4.52 | Polyphyllin VI | C39H62O13 | 774.3583 |
| 6 | 21.72 | 592.7606 | M-H | 7.60 | Agavoside A | C33H52O9 | 591.7571, 73.0284, 315.2324, 355.2267, 359.2231, 413.3022 |
| 7 | 26.119 | 191.1867 | M-H | 1.58 | Carbendazim | C9H9N3O2 | 190.1790, 104.0244, 158.0367 |
| 8 | 29.339 | 594.5181 | M-H | 0.74 | Kaempferol 7-O-Neohesperidoside | C27H30O15 | 593.5102, 111.0446, 251.0915, 265.0710, 375.1415 |
| 9 | 29.917 | 696.8651 | M+Cl | 2.32 | Momordicoside E | C37H60O12 | 732.3134, 121.0515, 341.2867, 505.3542, 605.381 |
| 10 | 34.047 | 317.5072 | M-H | -8.21 | Phytosphingosine | C18H39NO3 | 316.4966, 352.9604 |
| 11 | 34.395 | 480.6341 | M+Cl | 0 | Crustecdysone | C27H44O7 | 516.0871, 75.0456, 99.0812, 115.0761, 141.0934, 145.0868, 291.1613, 301.1825, 445.2586 |
| 12 | 36.535 | 903.0583 | M+Cl | 0.53 | Trigofoenoside A | C45H74O18 | 938.5118, 547.3687, 593.3664, 709.4143 |
| 13 | 40.653 | 196.2429 | M-H | 6.15 | Loliolide | C11H16O3 | 195.2362, 179.0700, 195.1020 |
| 14 | 41.316 | 278.3435 | M+Cl | -6.05 | Dibutyl Phthalate | C16H22O4 | 313.7946, 55.0548, 147.0078, 167.034, 183.1388 |
| 15 | 42.043 | 869.0436 | M-H | -3.34 | Dioscin | C45H72O16 | 868.0327, 101.0238, 557.3476, 575.3569 |
| 16 | 45.297 | 274.3978 | M-H | 5.49 | Nandrolone | C18H26O2 | 273.3914, 147.0822, 173.0955, 239.1447 |

图2 PP7体内抑制骨肉瘤生长
Fig.2 PP7 inhibits osteosarcoma xenograft growth in nude mice. A: Macroscopic observation of osteosarcoma xenograft in nude mice after PP7 intervention. B: Macroscopic observation of the dissected tumors after PP7 intervention. C: Comparison of tumor volume between the two groups. D: Comparison of tumor weight between the two groups. *P<0.05 vs Control.

图3 PP7体外可抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖、侵袭与迁移
Fig.3 PP7 inhibits proliferation, invasion, and migration of osteosarcoma cells in vitro. A, B: Results of CCK-8 assay showing dose-dependent inhibition of 143B cell proliferation by PP7 (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs 0 μmol/L). C-F: Transwell assays showing that 5 μmol/L PP7 significantly suppresses cell migration and invasion (Original magnification: ×200). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control.
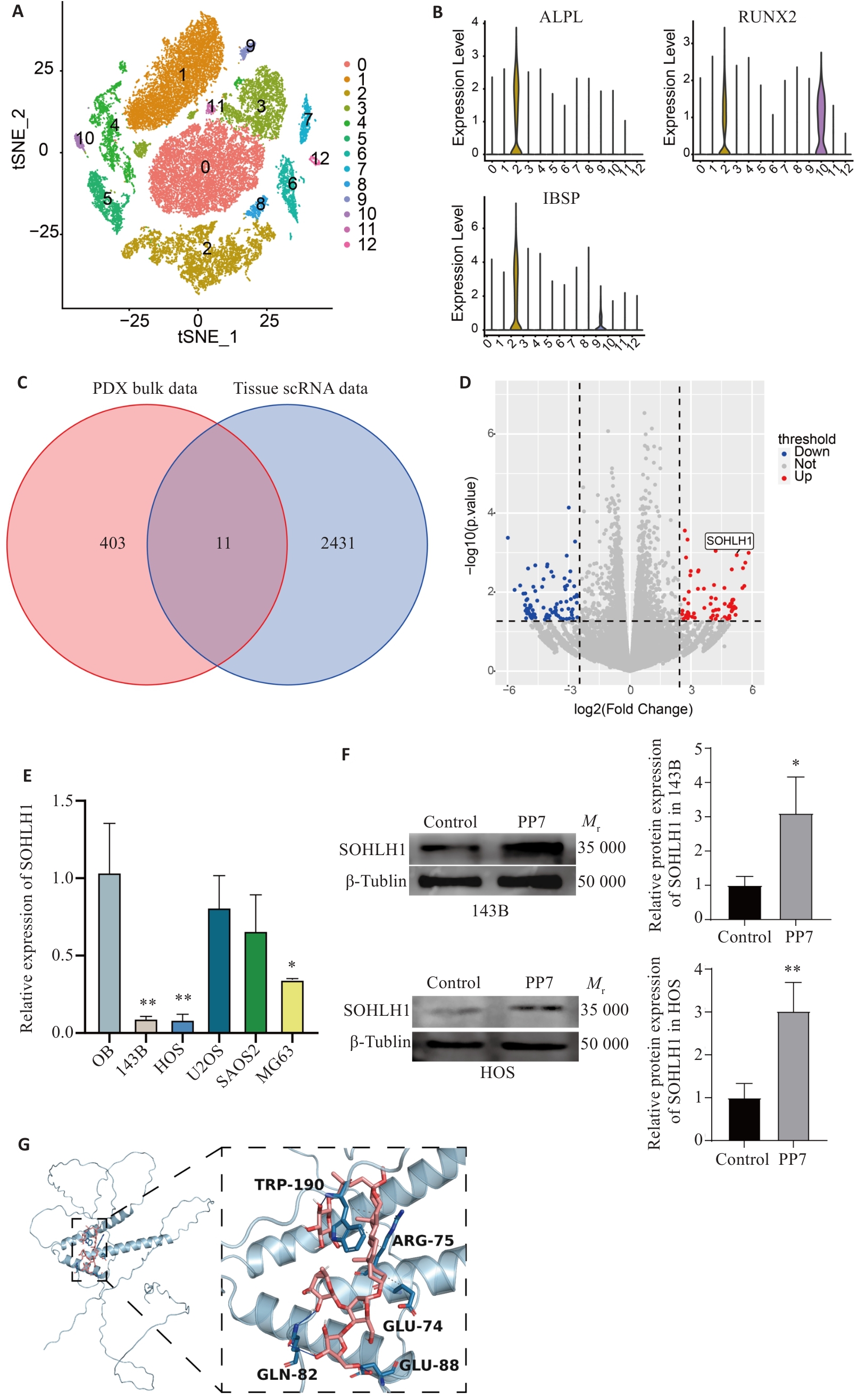
图4 PP7可能通过SOHLH1发挥抗骨肉瘤作用
Fig.4 The inhibitory effect of PP7 against osteosarcoma is mediated possibly by SOHLH1. A: UMAP plot of scRNA-seq data. B: ALPL, RUNX2, and IBSP are highly expressed in cluster 2. C: Intersection of bulk RNA-seq and scRNA-seq data. D: SOHLH1 expression is significantly upregulated in PP7-treated PDX tumors [log2(fold change)=2.487]. E: SOHLH1 is lowly expressed in osteosarcoma cell lines detected by qRT-PCR (*P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs OB). F: Western blotting showing PP7 upregulates SOHLH1 protein levels in both 143B and HOS cell lines (*P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control). G: The binding energy of PP7 to SOHLH1 was -6.9 kcal/mol by molecular docking.

图5 SOHLH1抑制骨肉瘤迁移与侵袭
Fig.5 SOHLH1 inhibits osteosarcoma migration and invasion. A, B: Validation of SOHLH1 silencing efficiency by qRT-PCR in 143B (A) and HOS (B) cells transfected with specific siRNAs (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control). C-E: Effects of SOHLH1 overexpression or knockdown on migration and invasion abilities of 143B cells (Crystal violet staining, ×200). F-H: Effects of SOHLH1 overexpression or knockdown on migration and invasion abilities of HOS cells (Crystal violet staining, ×200). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
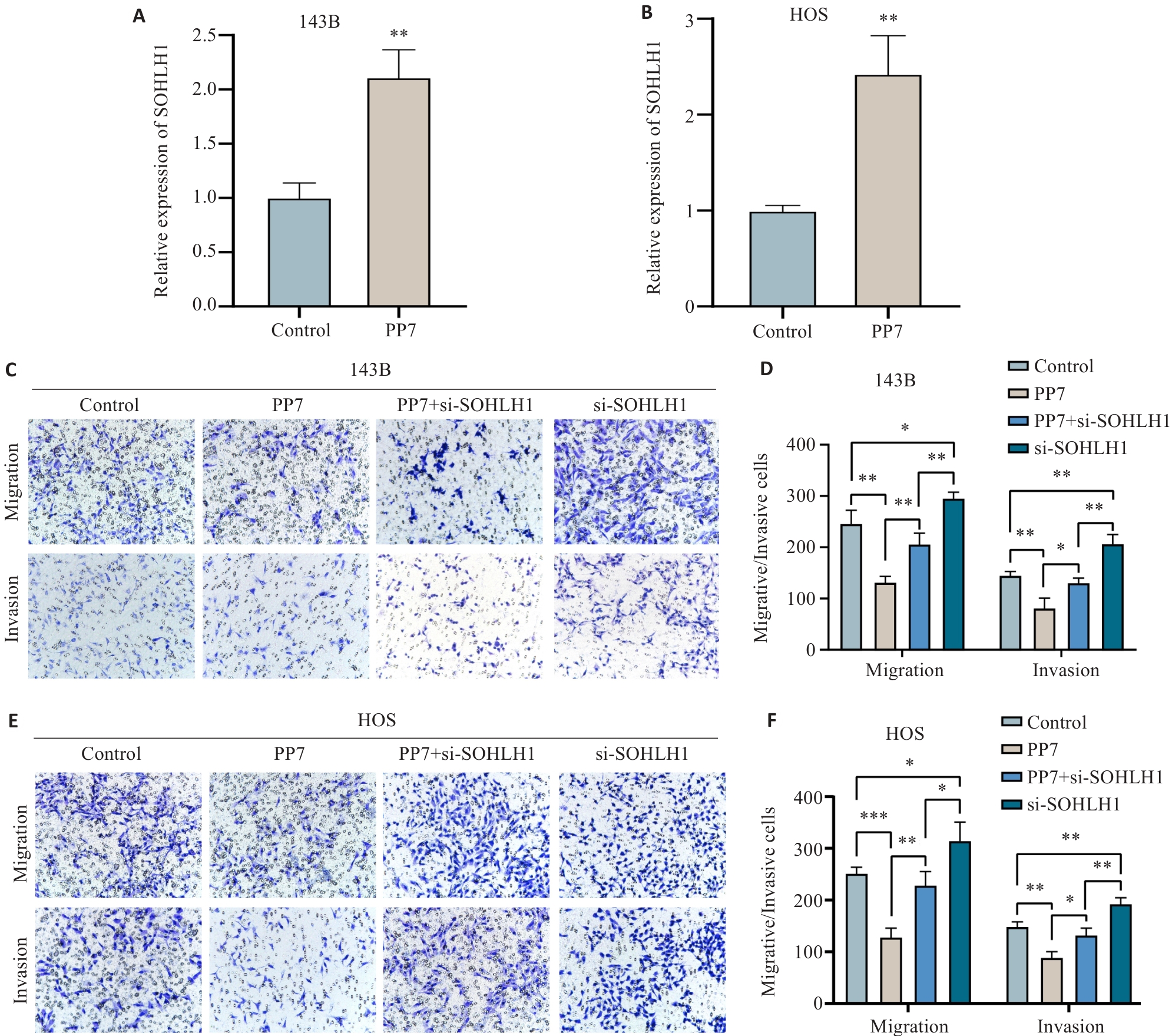
图6 PP7通过上调SOHLH1抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移与侵袭能力
Fig.6 PP7 inhibits migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by upregulating SOHLH1. A, B: SOHLH1 mRNA expression in 143B (A) and HOS (B) cells after PP7 treatment detected by qRT-PCR (**P<0.01 vs Control). C, D: Effects of PP7 treatment, SOHLH1 knockdown, and their combination on migration and invasion of 143B cells (×200). E, F: Effects of PP7 treatment, SOHLH1 knockdown, and their combination on migration and invasion of HOS cells (×200). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.

图7 PP7可能通过上调SOHLH1诱导骨肉瘤细胞铁死亡
Fig.7 PP7 induces ferroptosis in osteosarcoma cells possibly by upregulating SOHLH1. A-D: Effects of SOHLH1 knockdown, PP7 treatment and their combination on ROS (A, B) and LPO (C, D) levels in 143B cells. E-H: Effects of SOHLH1 knockdown, PP7 treatment and their combination on ROS (E, F) and LPO (G, H) levels in HOS cells (×200). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
| [1] | Rojas GA, Hubbard AK, Diessner BJ, et al. International trends in incidence of osteosarcoma (1988-2012)[J]. Int J Cancer, 2021, 149(5): 1044-53. doi:10.1002/ijc.33673 |
| [2] | Cui JC, Dean D, Hornicek FJ, et al. The role of extracelluar matrix in osteosarcoma progression and metastasis[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 39(1): 178. doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01685-w |
| [3] | Papakonstantinou E, Stamatopoulos A, Athanasiadis DI, et al. Limb-salvage surgery offers better five-year survival rate than amputation in patients with limb osteosarcoma treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Bone Oncol, 2020, 25: 100319. doi:10.1016/j.jbo.2020.100319 |
| [4] | Isakoff MS, Bielack SS, Meltzer P, et al. Osteosarcoma: current treatment and a collaborative pathway to success[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(27): 3029-35. doi:10.1200/jco.2014.59.4895 |
| [5] | Zheng CX, Tang F, Min L, et al. PTEN in osteosarcoma: Recent advances and the therapeutic potential[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2020, 1874(2): 188405. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188405 |
| [6] | Lin SY, Zhou LN, Dong Y, et al. Alpha-(1, 6)-fucosyltransferase (FUT8) affects the survival strategy of osteosarcoma by remodeling TNF/NF-κB2 signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(12): 1124. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04416-x |
| [7] | Lin ZJ, Xie XB, Lu SY, et al. Noncoding RNAs in osteosarcoma: Implications for drug resistance[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 504: 91-103. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.02.007 |
| [8] | Ghosh S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug[J]. Bioorg Chem, 2019, 88: 102925. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.102925 |
| [9] | Zhang B, Zhang Y, Li RZ, et al. The efficacy and safety comparison of first-line chemotherapeutic agents (high-dose methotrexate, doxorubicin, cisplatin, and ifosfamide) for osteosarcoma: a network meta-analysis[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2020, 15(1): 51. doi:10.1186/s13018-020-1576-0 |
| [10] | Liu YM, Yang SS, Wang KL, et al. Cellular senescence and cancer: Focusing on traditional Chinese medicine and natural products[J]. Cell Prolif, 2020, 53(10): e12894. doi:10.1111/cpr.12894 |
| [11] | Wang S, Fu JL, Hao HF, et al. Metabolic reprogramming by traditional Chinese medicine and its role in effective cancer therapy[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 170: 105728. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105728 |
| [12] | Zhou N, Xu LF, Park SM, et al. Genetic diversity, chemical components, and property of biomass Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis [J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2021, 9: 713860. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.713860 |
| [13] | Wang HQ, Xiao XJ, Li ZZ, et al. Polyphyllin VII, a novel moesin inhibitor, suppresses cell growth and overcomes bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2022, 537: 215647. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215647 |
| [14] | Zhang C, Li QR, Qin GZ, et al. Anti-angiogenesis and anti-metastasis effects of Polyphyllin VII on Hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo [J]. Chin Med, 2021, 16(1): 41. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00447-w |
| [15] | Cui JX, Man SL, Cui NN, et al. The synergistic anticancer effect of formosanin C and polyphyllin VII based on caspase-mediated cleavage of Beclin1 inhibiting autophagy and promoting apoptosis[J]. Cell Prolif, 2019, 52(1): e12520. doi:10.1111/cpr.12520 |
| [16] | Hsieh MJ, Chien SY, Lin JT, et al. Polyphyllin G induces apoptosis and autophagy cell death in human oral cancer cells[J]. Phytomedicine, 2016, 23(13): 1545-54. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2016.09.004 |
| [17] | Li XD, Liu Y, Liao SJ, et al. Polyphyllin VII induces apoptosis and autophagy via mediating H2O2 levels and the JNK pathway in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells[J]. Oncol Rep, 2021, 45(1): 180-90. doi:10.3892/or.2020.7866 |
| [18] | Liu Y, Feng WY, Dai Y, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the complexity of the tumor microenvironment of treatment-naive osteosarcoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 709210. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.709210 |
| [19] | Hassan NM, Alhossary AA, Mu YG, et al. Protein-ligand blind docking using QuickVina-W with inter-process spatio-temporal integration[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 15451. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-15571-7 |
| [20] | Feng FF, Cheng P, Wang CC, et al. Polyphyllin I and VII potentiate the chemosensitivity of A549/DDP cells to cisplatin by enhancing apoptosis, reversing EMT and suppressing the CIP2A/AKT/mTOR signaling axis[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(5): 5428-36. |
| [21] | Pang DJ, Li C, Yang CC, et al. Polyphyllin VII promotes apoptosis and autophagic cell death via ROS-inhibited AKT activity, and sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 1805635. doi:10.1155/2019/1805635 |
| [22] | Li J, Jia JH, Zhu WW, et al. Therapeutic effects on cancer of the active ingredients in rhizoma paridis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1095786. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1095786 |
| [23] | Zhang Q, Chang S, Yang Y, et al. Endophyte-inoculated rhizomes of Paris polyphylla improve polyphyllin biosynthesis and yield: a transcriptomic analysis of the underlying mechanism[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1261140. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1261140 |
| [24] | Xiang YC, Wan F, Ren YL, et al. Polyphyllin VII induces autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in human gastric cancer through targeting T-lymphokine-activated killer cell-originated protein kinase[J]. Phytother Res, 2023, 37(12): 5803-20. doi:10.1002/ptr.7986 |
| [25] | Wu YZ, Yang L, Li ZZ, et al. Polyphyllin VII enhances the antitumor activity of cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells by inducing ferroptosis and enhancing apoptosis[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2025, 39(4): e70186. doi:10.1002/jbt.70186 |
| [26] | Liu YH, Wu WT, Cai CJ, et al. Patient-derived xenograft models in cancer therapy: technologies and applications[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 160. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01419-2 |
| [27] | Abdolahi S, Ghazvinian Z, Muhammadnejad S, et al. Patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models, applications and challenges in cancer research[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 206. doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03405-8 |
| [28] | Pangas SA, Choi Y, Ballow DJ, et al. Oogenesis requires germ cell-specific transcriptional regulators Sohlh1 and Lhx8[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103(21): 8090-5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0601083103 |
| [29] | Matson CK, Murphy MW, Griswold MD, et al. The mammalian doublesex homolog DMRT1 is a transcriptional gatekeeper that controls the mitosis versus meiosis decision in male germ cells[J]. Dev Cell, 2010, 19(4): 612-24. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.09.010 |
| [30] | Liu XY, Gao Q, Zhao N, et al. Sohlh1 suppresses glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2018, 57(4): 494-502. doi:10.1002/mc.22774 |
| [31] | Dixon SJ. Ferroptosis: bug or feature?[J]. Immunol Rev, 2017, 277(1): 150-7. doi:10.1111/imr.12533 |
| [32] | Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(2): 88. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2 |
| [33] | Kwun MS, Lee DG. Ferroptosis-like death in microorganisms: a novel programmed cell death following lipid peroxidation[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2023, 33(8): 992-7. doi:10.4014/jmb.2307.07002 |
| [34] | Mou YH, Wang J, Wu JC, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12(1): 34. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0720-y |
| [35] | Wang Y, Zhou XR, Yao L, et al. Capsaicin enhanced the efficacy of photodynamic therapy against osteosarcoma via a pro-death strategy by inducing ferroptosis and alleviating hypoxia[J]. Small, 2024, 20(26): e2306916. doi:10.1002/smll.202306916 |
| [36] | Wen RJ, Dong X, Zhuang HW, et al. Baicalin induces ferroptosis in osteosarcomas through a novel Nrf2/xCT/GPX4 regulatory axis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 116: 154881. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154881 |
| [1] | 何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [2] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [3] | 欧泽金, 李瀛, 陈诗, 王梓译, 何美仪, 陈志成, 唐侍豪, 孟晓静, 王致. 抑制铁死亡减轻敌草快引起的斑马鱼急性肾损伤的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1743-1750. |
| [4] | 李军仪, 陈思源, 谢力遥, 王劲, 程奥, 张绍伟, 林继瑜, 方志涵, 潘一锐, 崔翀鹤, 陈庚鑫, 张超, 李栎. 益智仁提取物谷甾醇通过抑制铁死亡中的ETS-5基因表达延长秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1751-1757. |
| [5] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [6] | 张梦影, 赵晨玲, 田丽伟, 余郭芳, 杨文明, 董婷. 肝豆扶木汤通过GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15通路抑制铁死亡改善Wilson病小鼠的肝脏脂肪变性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478. |
| [7] | 张安邦, 孙秀颀, 庞博, 吴远华, 时靖宇, 张宁, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过调节肠道-大脑轴及Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [8] | 张林落, 李长青, 皇玲玲, 周学平, 娄媛媛. 梓醇扶正制毒配伍从SLC7A11/GPX4通路抑制铁死亡减轻雷公藤甲素肝毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 810-818. |
| [9] | 郭涛, 陈柏霖, 石金沙, 匡显锋, 余腾跃, 魏嵩, 刘雄, 肖蓉, 李娟娟. 天麻素通过激活GPX4/SLC7A11/FTH1信号抑制铁死亡减轻新生小鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2071-2081. |
| [10] | 张思雨, 冉林武, 曾瑾, 王玉炯. 产气荚膜梭菌Beta1毒素通过P2X7-Ca2+轴诱导巨噬细胞焦亡和铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2126-2134. |
| [11] | 孙陛航, 郭煜君, 祁玉麟, 姚丹, 陈文直, 陈念芝. 低强度脉冲超声协同冬凌草甲素通过激活PIEZO1诱导胰腺癌细胞铁死亡的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2160-2170. |
| [12] | 季春斐, 左宗超, 王钧, 李妙男. N-乙酰神经氨酸中通过抑制Nrf2轴促进缺氧/复氧损伤的H9C2心肌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 72-79. |
| [13] | 陈凯, 孟兆菲, 闵静婷, 王佳慧, 李正红, 高琴, 胡俊锋. 姜黄素通过抑制TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4通路介导的铁死亡减轻脓毒症小鼠肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1805-1813. |
| [14] | 欧阳明子, 崔佳琦, 王慧, 梁正, 皮大锦, 陈利国, 陈前军, 吴迎朝. 开心散通过减轻前额叶皮质铁死亡缓解小鼠的阿霉素化疗性抑郁[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [15] | 张银亮, 骆泽谭, 赵睿, 赵娜, 徐志东, 奥迪, 丛古一, 刘新宇, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控STUB1/GPX4诱导直肠癌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||