南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2708-2717.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.18
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-05-22
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
傅蓉
E-mail:1228772136@qq.com;834460113@qq.com
作者简介:渠 梦,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1228772136@qq.com
基金资助:Received:2025-05-22
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Rong FU
E-mail:1228772136@qq.com;834460113@qq.com
摘要:
目的 针对12导联心电信号(ECG)自动分类任务,提出一种高效的深度学习模型,以提高分类准确率。 方法 设计了一种新型的ResLSTM-TemporalSE网络模型。该模型采用多层残差长短期记忆网络(ResLSTM),在LSTM层间引入跨层跳跃连接,构建时序特征的残差学习路径,并在传统压缩-激励模块(SE)中引入时序注意力机制,增强通道表达能力的同时捕捉ECG信号的时间依赖性,构建一个高效的多层次特征表达框架。该模型在CPSC2018数据集和南方医科大学第七附属医院私有数据集进行验证。 结果 模型在CPSC2018测试集上分类准确率达到99.70%,精确度、召回率和F1值分别为0.9966、0.9370和0.9653,在临床私有数据集上分类准确率达到82.77%,精确度、召回率和F1值分别为0.6811、0.8961和0.7723。通过消融实验验证残差连接与时序注意力模块对模型性能的贡献。 结论 ResLSTM-TemporalSE模型能够有效融合ECG信号的时空特征,在CPSC2018数据集上表现出卓越的分类性能,同时在真实临床环境中保持较强的泛化能力,为心电信号的自动分析提供了可靠的技术方案,具有潜在的临床应用价值。
渠梦, 傅蓉. ResLSTM-TemporalSE:多导联心电信号的自动分类[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2708-2717.
Meng QU, Rong FU. ResLSTM-TemporalSE: an automated classification model for multi-lead ECG signals[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2708-2717.
| Class | SR | SA | SB | ST | AF | PVC | LVLL | IRBBB | LVH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 3023 | 2080 | 1799 | 1619 | 1130 | 1157 | 1289 | 410 | 1145 |
表1 私有数据集各类别分布详情
Tab.1 Category distribution in private dataset
| Class | SR | SA | SB | ST | AF | PVC | LVLL | IRBBB | LVH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 3023 | 2080 | 1799 | 1619 | 1130 | 1157 | 1289 | 410 | 1145 |
| Class | Raw data | Data filtering |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 918 | 1128 |
| AF | 1098 | 1540 |
| I-AVB | 704 | 869 |
| LBBB | 207 | 248 |
| RBBB | 1695 | 2099 |
| PAC | 556 | 902 |
| PVC | 672 | 1149 |
| STD | 825 | 949 |
| STE | 202 | 271 |
| Total | 6877 | 9155 |
表2 CPSC2018数据分割处理后各类样本分布
Tab.2 Distribution of sample categories in cpsc2018 dataset after truncation processing
| Class | Raw data | Data filtering |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 918 | 1128 |
| AF | 1098 | 1540 |
| I-AVB | 704 | 869 |
| LBBB | 207 | 248 |
| RBBB | 1695 | 2099 |
| PAC | 556 | 902 |
| PVC | 672 | 1149 |
| STD | 825 | 949 |
| STE | 202 | 271 |
| Total | 6877 | 9155 |
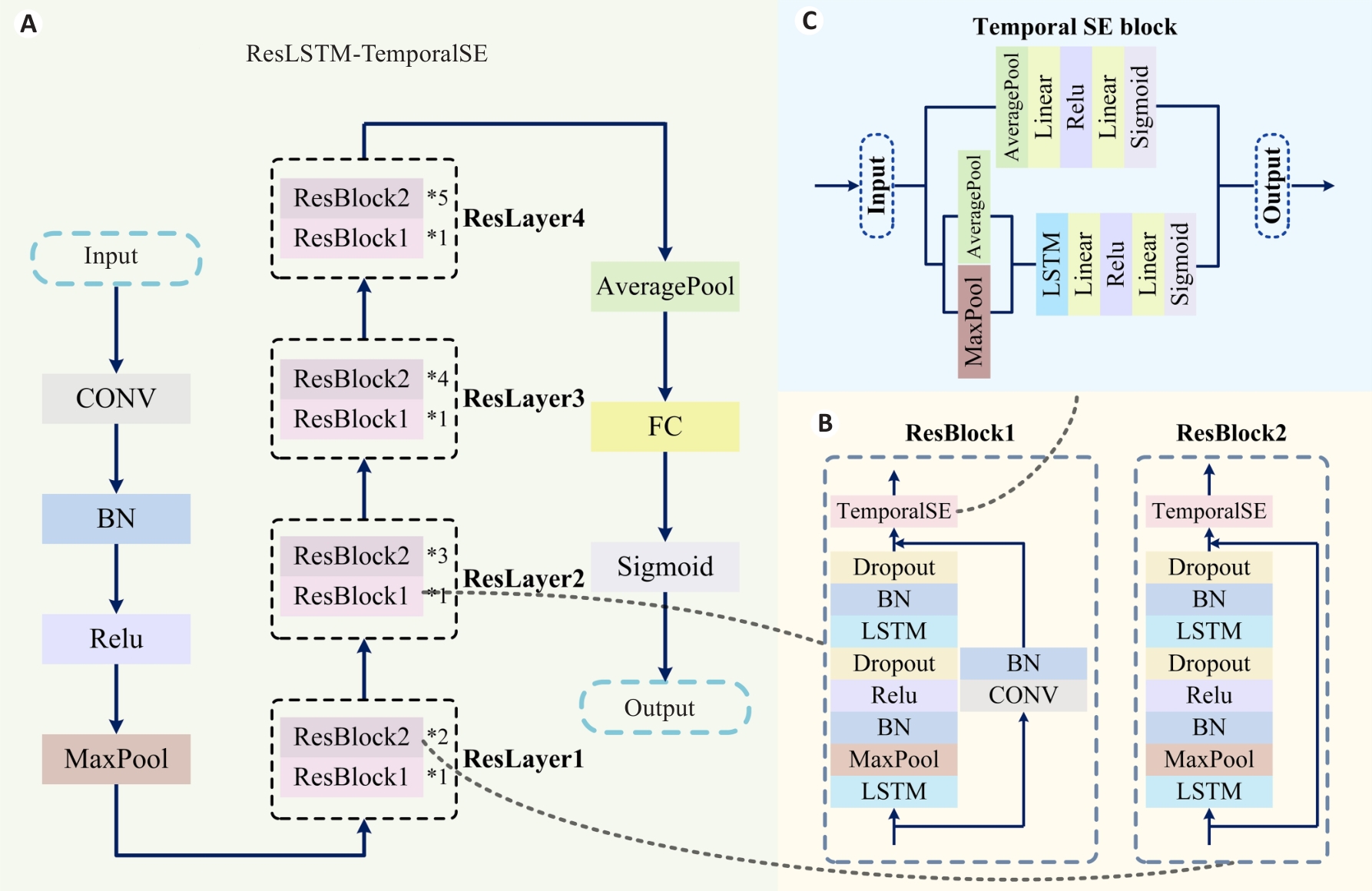
图2 ResLSTM-TemporalSE模型结构图
Fig.2 Architecture of the ResLSTM-TemporalSE model. A: ResLSTM-TemporalSE model architecture. B: ResBlock structures. C: Temporal SE block.
| Dataset | Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPSC2018 | ResLSTM-perTemporalSE | 73.46% | 0.7515 | 0.6676 | 0.6797 | 0.049033 |
| ResLSTM-LastTemporalSE | 89.41% | 0.9083 | 0.8424 | 0.8653 | 0.044679 | |
| Ours | 99.70% | 0.9966 | 0.9370 | 0.9653 | 0.024851 | |
| Private dataset | ResLSTM-perTemporalSE | 43.97% | 0.3145 | 0.6109 | 0.4123 | 0.222588 |
| ResLSTM-LastTemporalSE | 73.78% | 0.7442 | 0.7049 | 0.7171 | 0.024013 | |
| Ours | 82.77% | 0.6811 | 0.8961 | 0.7723 | 0.023127 |
表3 不同变体模型在ECG信号分类任务中的性能对比
Tab.3 Performance comparison of the variant models in ECG signal classification tasks
| Dataset | Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPSC2018 | ResLSTM-perTemporalSE | 73.46% | 0.7515 | 0.6676 | 0.6797 | 0.049033 |
| ResLSTM-LastTemporalSE | 89.41% | 0.9083 | 0.8424 | 0.8653 | 0.044679 | |
| Ours | 99.70% | 0.9966 | 0.9370 | 0.9653 | 0.024851 | |
| Private dataset | ResLSTM-perTemporalSE | 43.97% | 0.3145 | 0.6109 | 0.4123 | 0.222588 |
| ResLSTM-LastTemporalSE | 73.78% | 0.7442 | 0.7049 | 0.7171 | 0.024013 | |
| Ours | 82.77% | 0.6811 | 0.8961 | 0.7723 | 0.023127 |
| Dataset | Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPSC2018 | Ribeiro et al. [ | 96.62% | 0.9309 | 0.9041 | 0.9151 | 0.048194 |
| Zhang et al.[ | 97.91% | 0.9791 | 0.9314 | 0.9547 | 0.036724 | |
| Hwang et al. [ | 99.51% | 0.9961 | 0.9357 | 0.9644 | 0.024788 | |
| Ours | 99.70% | 0.9966 | 0.9370 | 0.9653 | 0.024851 | |
| Private dataset | Ribeiro et al. [ | 61.36% | 0.3841 | 0.3435 | 0.3301 | 0.049832 |
| Zhang et al.[ | 80.36% | 0.7174 | 0.8396 | 0.7674 | 0.040777 | |
| Hwang et al. [ | 67.78% | 0.7126 | 0.5028 | 0.5801 | 0.095033 | |
| Ours | 82.77% | 0.6811 | 0.8961 | 0.7723 | 0.023127 |
表4 不同模型在数据集的分类性能指标
Tab.4 Classification performance metrics of different models on the dataset
| Dataset | Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPSC2018 | Ribeiro et al. [ | 96.62% | 0.9309 | 0.9041 | 0.9151 | 0.048194 |
| Zhang et al.[ | 97.91% | 0.9791 | 0.9314 | 0.9547 | 0.036724 | |
| Hwang et al. [ | 99.51% | 0.9961 | 0.9357 | 0.9644 | 0.024788 | |
| Ours | 99.70% | 0.9966 | 0.9370 | 0.9653 | 0.024851 | |
| Private dataset | Ribeiro et al. [ | 61.36% | 0.3841 | 0.3435 | 0.3301 | 0.049832 |
| Zhang et al.[ | 80.36% | 0.7174 | 0.8396 | 0.7674 | 0.040777 | |
| Hwang et al. [ | 67.78% | 0.7126 | 0.5028 | 0.5801 | 0.095033 | |
| Ours | 82.77% | 0.6811 | 0.8961 | 0.7723 | 0.023127 |
| Dataset | Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPSC2018 | ResNet | 96.65% | 0.9665 | 0.9194 | 0.9424 | 0.029559 |
| ResLSTM | 98.31% | 0.9869 | 0.9237 | 0.9535 | 0.022480 | |
| ResNet-SE | 99.58% | 0.9956 | 0.9331 | 0.9624 | 0.021720 | |
| ResLSTM-SE | 99.62% | 0.9910 | 0.9367 | 0.9624 | 0.022866 | |
| Ours | 99.70% | 0.9966 | 0.9370 | 0.9653 | 0.024851 | |
| Private dataset | ResNet | 69.71% | 0.6028 | 0.7415 | 0.6614 | 0.067322 |
| ResLSTM | 81.41% | 0.8084 | 0.7906 | 0.7981 | 0.028402 | |
| ResNet-SE | 79.37% | 0.7795 | 0.7357 | 0.7507 | 0.030583 | |
| ResLSTM-SE | 81.98% | 0.6887 | 0.8757 | 0.7704 | 0.019994 | |
| Ours | 82.77% | 0.6811 | 0.8961 | 0.7723 | 0.023127 |
表5 消融实验模型性能对比
Tab.5 Ablation study model performance comparison
| Dataset | Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPSC2018 | ResNet | 96.65% | 0.9665 | 0.9194 | 0.9424 | 0.029559 |
| ResLSTM | 98.31% | 0.9869 | 0.9237 | 0.9535 | 0.022480 | |
| ResNet-SE | 99.58% | 0.9956 | 0.9331 | 0.9624 | 0.021720 | |
| ResLSTM-SE | 99.62% | 0.9910 | 0.9367 | 0.9624 | 0.022866 | |
| Ours | 99.70% | 0.9966 | 0.9370 | 0.9653 | 0.024851 | |
| Private dataset | ResNet | 69.71% | 0.6028 | 0.7415 | 0.6614 | 0.067322 |
| ResLSTM | 81.41% | 0.8084 | 0.7906 | 0.7981 | 0.028402 | |
| ResNet-SE | 79.37% | 0.7795 | 0.7357 | 0.7507 | 0.030583 | |
| ResLSTM-SE | 81.98% | 0.6887 | 0.8757 | 0.7704 | 0.019994 | |
| Ours | 82.77% | 0.6811 | 0.8961 | 0.7723 | 0.023127 |
| [1] | Gaziano TA, Bitton A, Anand S, et al. Growing epidemic of coronary heart disease in low- and middle-income countries[J]. Curr Probl Cardiol, 2010, 35(2): 72-115. doi:10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2009.10.002 |
| [2] | Roth GA, Johnson C, Abajobir A, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2017, 70(1): 1-25. |
| [3] | 刘明波, 何新叶, 杨晓红, 等. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2023》要点解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(1): 20-38. |
| [4] | Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(10): e56-e528. |
| [5] | Zhai XL, Tin C. Automated ECG classification using dual heartbeat coupling based on convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 27465-72. doi:10.1109/access.2018.2833841 |
| [6] | Yan ZL, Zhou J, Wong WF. Energy efficient ECG classification with spiking neural network[J]. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2021, 63: 102170. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102170 |
| [7] | Jyotishi D, Dandapat S. An ECG biometric system using hierarchical LSTM with attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Sens J, 2022, 22(6): 6052-61. doi:10.1109/jsen.2021.3139135 |
| [8] | Allam JP, Samantray S, Ari S. SpEC: a system for patient specific ECG beat classification using deep residual network[J]. Biocybern Biomed Eng, 2020, 40(4): 1446-57. doi:10.1016/j.bbe.2020.08.001 |
| [9] | Hoekema R, Uijen GJH, van Oosterom A. Geometrical aspects of the interindividual variability of multilead ECG recordings[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2001, 48(5): 551-9. doi:10.1109/10.918594 |
| [10] | Akan T, Alp S, Nobel Bhuiyan MA. ECGformer: leveraging transformer for ECG heartbeat arrhythmia classification[C]//2023 International Conference on Computational Science and Com-putational Intelligence (CSCI). December 13-15, 2023, Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2023: 1412-7. doi:10.1109/csci62032.2023.00231 |
| [11] | Malik J, Devecioglu OC, Kiranyaz S, et al. Real-time patient-specific ECG classification by 1D self-operational neural networks[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2022, 69(5): 1788-801. doi:10.1109/tbme.2021.3135622 |
| [12] | Wang JK, Qiao X, Liu CC, et al. Automated ECG classification using a non-local convolutional block attention module[J]. Comput Meth Programs Biomed, 2021, 203: 106006. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106006 |
| [13] | He RN, Liu Y, Wang KQ, et al. Automatic cardiac arrhythmia classification using combination of deep residual network and bidirectional LSTM[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 102119-35. doi:10.1109/access.2019.2931500 |
| [14] | Yıldırım Ö, Pławiak P, Tan RS, et al. Arrhythmia detection using deep convolutional neural network with long duration ECG signals[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2018, 102: 411-20. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.09.009 |
| [15] | 邓 力, 傅 蓉. 基于心拍的端到端心律失常分类[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(9): 1071-7. |
| [16] | Brito C, Machado A, Sousa A. Electrocardiogram beat-classification based on a ResNet network[J]. Stud Health Technol Inform, 2019, 264: 55-9. doi:10.3233/shti190182 |
| [17] | Luo CS, Jiang HX, Li QC, et al. Multi-label classification of abnormalities in 12-lead ECG using 1D CNN and LSTM[M]//Machine Learning and Medical Engineering for Cardiovascular Health and Intravascular Imaging and Computer Assisted Stenting. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 55-63. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-33327-0_7 |
| [18] | Zhang HP, Gu HZ, Gao JL, et al. An effective atrial fibrillation detection from short single-lead electrocardiogram recordings using MCNN-BLSTM network[J]. Algorithms, 2022, 15(12): 454. doi:10.3390/a15120454 |
| [19] | Li D, Sun TT, Nan JF, et al. A novel R-peak detection model and SE-ResNet-based PVC recognition for 12-lead ECGs[J]. Circuits Syst Signal Process, 2024, 43(7): 4460-86. doi:10.1007/s00034-024-02662-w |
| [20] | Zhu ZW, Lan X, Zhao TT, et al. Identification of 27 abnormalities from multi-lead ECG signals: an ensembled SE_ResNet framework with Sign Loss function[J]. Physiol Meas, 2021, 42(6): 1088. doi:10.1088/1361-6579/ac08e6 |
| [21] | Le KH, Pham HH, Nguyen TB, et al. Enhancing deep learning-based 3-lead ECG classification with heartbeat counting and demographic data integration[C]//2022 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES). December 7-9, 2022, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. IEEE, 2022: 154-9. doi:10.1109/iecbes54088.2022.10079267 |
| [22] | Liu FF, Liu CY, Zhao LN, et al. An open access database for evaluating the algorithms of electrocardiogram rhythm and morphology abnormality detection[J]. J Med Imaging Hlth Inform, 2018, 8(7): 1368-73. doi:10.1166/jmihi.2018.2442 |
| [23] | Li JH, Pang SP, Xu FZ, et al. Two-dimensional ECG-based cardiac arrhythmia classification using DSE-ResNet[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12: 14485. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-18664-0 |
| [24] | Han H, Wang WY, Mao BH. Borderline-SMOTE: a new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning[C]//Advances in Intelligent Computing. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2005: 878-87. doi:10.1007/11538059_91 |
| [25] | He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 27-30, 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 770-8. doi:10.1109/cvpr.2016.90 |
| [26] | Ji LP, Wei ZH, Hao J, et al. An intelligent diagnostic method of ECG signal based on Markov transition field and a ResNet[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2023, 242: 107784. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107784 |
| [27] | Luo XY, Yang LY, Cai HY, et al. Multi-classification of arrhythmias using a HCRNet on imbalanced ECG datasets[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2021, 208: 106258. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106258 |
| [28] | Saadatnejad S, Oveisi M, Hashemi M. LSTM-based ECG classification for continuous monitoring on personal wearable devices[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2020, 24(2): 515-23. doi:10.1109/jbhi.2019.2911367 |
| [29] | Hiriyannaiah S, G M S, M H M K, et al. A comparative study and analysis of LSTM deep neural networks for heartbeats classification[J]. Health Technol, 2021, 11(3): 663-71. doi:10.1007/s12553-021-00552-8 |
| [30] | Hua J, Zou JW, Rao J, et al. ECG signals deep compressive sensing framework based on multiscale feature fusion and SE block[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 104359-72. doi:10.1109/access.2023.3316487 |
| [31] | Houssein EH, Hassaballah M, Ibrahim IE, et al. An automatic arrhythmia classification model based on improved Marine Predators Algorithm and Convolutions Neural Networks[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2022, 187: 115936. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115936 |
| [32] | Yao QH, Wang RX, Fan XM, et al. Multi-class Arrhythmia detection from 12-lead varied-length ECG using Attention-based Time-Incremental Convolutional Neural Network[J]. Inf Fusion, 2020, 53: 174-82. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2019.06.024 |
| [33] | Ribeiro AH, Ribeiro MH, Paixão GMM, et al. Automatic diagnosis of the 12-lead ECG using a deep neural network[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 1760. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15432-4 |
| [34] | Zhang DD, Yang S, Yuan XH, et al. Interpretable deep learning for automatic diagnosis of 12-lead electrocardiogram[J]. iScience, 2021, 24(4): 102373. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.102373 |
| [35] | Hwang S, Cha J, Heo J, et al. Multi-label abnormality classification from 12-lead ECG using a 2D residual U-net[C]//ICASSP 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). April 14-19, 2024, Seoul, Korea, Republic of. IEEE, 2024: 2265-9. doi:10.1109/icassp48485.2024.10448259 |
| [1] | 吴秋岑, 卢学麒, 温耀棋, 洪永, 吴煜良, 陈超敏. II导联心电图中心肌梗死检测与定位:基于多尺度残差模块融合改进通道注意力模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1777-1790. |
| [2] | 郑子瑜, 杨夏颖, 吴圣杰, 张诗婕, 吕国荣, 柳培忠, 王珺, 何韶铮. 多特征融合的产时超声胎方位识别模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1563-1570. |
| [3] | 谢辉荣, 胡潮滨, 梁国华, 韩红喆, 黄牧, 冯前进. 大学生心理压力智能评估:基于融合文本与影像的多模态模型的设计及验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2504-2510. |
| [4] | 贺亚迪, 周炫汝, 金锦辉, 宋婷. 基于PE-CycleGAN网络的鼻咽癌自适应放疗CBCT-sCT生成研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 179-186. |
| [5] | 方威扬, 肖慧, 王爽, 林晓明, 陈超敏. 基于MRI影像和临床参数特征融合的深度学习模型预测术前肝细胞癌的细胞角蛋白19状态[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1738-1751. |
| [6] | 欧嘉志, 詹长安, 杨丰. 一维卷积神经网络的自编码癫痫发作异常检测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1796-1804. |
| [7] | 汪辰, 蒙铭强, 李明强, 王永波, 曾栋, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于双域Transformer耦合特征学习的CT截断数据重建模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 950-959. |
| [8] | 龙楷兴, 翁丹仪, 耿 舰, 路艳蒙, 周志涛, 曹 蕾. 基于多模态多示例学习的免疫介导性肾小球疾病自动分类方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 585-593. |
| [9] | 肖 慧, 方威扬, 林铭俊, 周振忠, 费洪文, 陈超敏. 基于两阶段分析的多尺度颈动脉斑块检测方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 387-396. |
| [10] | 刘操林, 邹青清, 王梦虹, 杨芹枚, 宋丽文, 陆紫箫, 冯前进, 赵英华. 鉴别原发性骨肿瘤骨样和软骨样基质矿化:基于CT和临床特征的深度学习融合模型的多中心回顾性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2412-2420. |
| [11] | 弥 佳, 周宇佳, 冯前进. 基于正交视角X线图像重建的3D/2D配准方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1636-1643. |
| [12] | 楚智钦, 屈耀铭, 钟 涛, 梁淑君, 温志波, 张 煜. 磁共振酰胺质子转移模态的胶质瘤IDH基因分型识别:基于深度学习的Dual-Aware框架[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1379-1387. |
| [13] | 于佳弘, 张昆鹏, 靳 爽, 苏 哲, 徐晓桐, 张 华. 弦图插值结合UNIT网络图像转换的CT金属伪影校正[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1214-1223. |
| [14] | 滕 琳, 王 斌, 冯前进. 头颈癌放疗计划剂量分布的预测方法:基于深度学习的算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 1010-1016. |
| [15] | 周 昊, 曾 栋, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于半监督网络的组织感知CT图像对比度的增强方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 985-993. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
