南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2646-2657.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.12
• • 上一篇
孙心悦( ), 王宽宇(
), 王宽宇( ), 王钢, 代清泉, 陈静, 孔祥定, 栾佳
), 王钢, 代清泉, 陈静, 孔祥定, 栾佳
收稿日期:2025-06-01
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
王宽宇
E-mail:429050968@qq.com;wangkuanyu_1964@163.com
作者简介:孙心悦,主治医师,博士,E-mail: 429050968@qq.com
基金资助:
Xinyue SUN( ), Kuanyu WANG(
), Kuanyu WANG( ), Gang WANG, Qingquan DAI, Jing CHEN, Xiangding KONG, Jia LUAN
), Gang WANG, Qingquan DAI, Jing CHEN, Xiangding KONG, Jia LUAN
Received:2025-06-01
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Kuanyu WANG
E-mail:429050968@qq.com;wangkuanyu_1964@163.com
摘要:
目的 基于扶正祛邪理论探究扶正消岩颗粒对乳腺癌化疗期癌因性疲乏(CRF)的治疗效果及作用机制。 方法 将90例正虚毒瘀型乳腺癌 CRF 患者随机分为对照组(化疗及对症治疗)、研究组(加服扶正消岩颗粒),45例/组。比较两组Piper 疲乏量表(PFS)、Karnofsky 功能状态(KPS)量表及中医证候评分。利用多数据库分析药物活性成分、靶点及疾病相关靶点,构建 PPI 网络并富集分析,通过分子对接和动力学模拟研究主要成分槲皮素与AKT1等核心靶点作用情况。构建乳腺癌 CRF 小鼠模型,设正常对照组、模型组和扶正消岩颗粒灌胃治疗组,检测不同组小鼠运动功能改变、腓肠肌组织凋亡相关蛋白AKT1、p-AKT1、BCL-2、BAD表达及血清 IL-6、IL-1β水平。 结果 研究组治疗后PFS、KPS及中医证候评分结果均优于治疗前和对照组(P<0.05);筛选出57个药物与疾病交集靶标,确定5个关键靶点,发现主要成分槲皮素与AKT1等核心靶点强结合,并可能通过凋亡通路发挥作用;扶正消岩颗粒可改善小鼠运动能力,逆转腓肠肌凋亡蛋白表达异常,降低血清IL-6、IL-1β水平(P<0.05)。 结论 扶正消岩颗粒可缓解乳腺癌患者化疗期癌因性疲乏,改善中医证候和生活质量,改善疲乏模型小鼠体能,可能通过调控 AKT1/BAD/BCL-2通路抑制骨骼肌凋亡,下调 IL-6、IL-1β水平发挥作用。
孙心悦, 王宽宇, 王钢, 代清泉, 陈静, 孔祥定, 栾佳. 扶正消岩颗粒通过调控AKT1/BAD/BCL-2通路改善乳腺癌化疗期癌因性疲乏[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2646-2657.
Xinyue SUN, Kuanyu WANG, Gang WANG, Qingquan DAI, Jing CHEN, Xiangding KONG, Jia LUAN. Fuzheng Xiaoyan Granules ameliorate cancer-related fatigue during breast cancer chemotherapy by regulating the AKT1/BAD/BCL-2 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2646-2657.
| Group | Behavioral dimension | Emotion dimension | Physical dimension | Cognition dimension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 5.84±0.69 | 4.88±0.65 | 5.93±0.84 | 4.32±1.06 | 5.17±1.12 | 4.64±0.54 | 6.39±1.09 | 4.29±1.32 |
| Treatment | 5.55±0.88 | 3.14±1.23a | 5.60±0.92 | 2.77±1.56a | 5.38±0.51 | 2.96±1.00a | 6.35±0.97 | 2.87±1.41a |
| t | 1.754 | 8.381 | 1.799 | 6.617 | -1.138 | 9.894 | 0.187 | 4.93 |
| P | 0.083 | <0.001 | 0.075 | <0.001 | 0.258 | <0.001 | 0.852 | <0.001 |
表1 两组患者治疗前后PFS评分比较
Tab.1 Comparison of PFS scores between the two groups before and after treatment (Mean±SD, n=45)
| Group | Behavioral dimension | Emotion dimension | Physical dimension | Cognition dimension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 5.84±0.69 | 4.88±0.65 | 5.93±0.84 | 4.32±1.06 | 5.17±1.12 | 4.64±0.54 | 6.39±1.09 | 4.29±1.32 |
| Treatment | 5.55±0.88 | 3.14±1.23a | 5.60±0.92 | 2.77±1.56a | 5.38±0.51 | 2.96±1.00a | 6.35±0.97 | 2.87±1.41a |
| t | 1.754 | 8.381 | 1.799 | 6.617 | -1.138 | 9.894 | 0.187 | 4.93 |
| P | 0.083 | <0.001 | 0.075 | <0.001 | 0.258 | <0.001 | 0.852 | <0.001 |
| Group | Before treatment | After treatment | Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 70 (60, 80) | 80 (70, 80) | -4.849 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 70 (70, 80) | 80 (80, 90) | -6.474 | <0.001 |
| Z | -0.720 | -3.499 | ||
| P | 0.471 | <0.001 |
表2 两组患者治疗前后KPS评分比较
Tab.2 Comparison of KPS scores between the two groups before and after treatment [M (P25, P75), n=45]
| Group | Before treatment | After treatment | Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 70 (60, 80) | 80 (70, 80) | -4.849 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 70 (70, 80) | 80 (80, 90) | -6.474 | <0.001 |
| Z | -0.720 | -3.499 | ||
| P | 0.471 | <0.001 |
| Group | Tiredness and weakness | Nausea and vomiting | Dizziness and dim vision | Palpitations and insomnia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 2.87±0.50 | 1.96±0.21 | 2.80±0.55 | 1.91±0.36 | 2.49±0.63 | 1.84±0.47 | 1.78±1.08 | 1.27±0.84 |
| Treatment | 2.87±0.46 | 0.91±0.29a | 2.87±0.46 | 1.36±0.74a | 2.33±0.64 | 0.69±0.56a | 1.76±1.00 | 0.91±0.73a |
| Z | -0.339 | -8.866 | -0.666 | -3.846 | -1.226 | -7.36 | -2.40 | -2.18 |
| P | 0.735 | <0.001 | 0.505 | <0.001 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.810 | 0.029 |
表3 两组患者治疗前后中医证候评分比较
Tab.3 Comparison of TCM Syndrome Scores between the two groups of patients before and after treatment (Mean±SD, n=45)
| Group | Tiredness and weakness | Nausea and vomiting | Dizziness and dim vision | Palpitations and insomnia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | Before treatment | After treatment | |
| Control | 2.87±0.50 | 1.96±0.21 | 2.80±0.55 | 1.91±0.36 | 2.49±0.63 | 1.84±0.47 | 1.78±1.08 | 1.27±0.84 |
| Treatment | 2.87±0.46 | 0.91±0.29a | 2.87±0.46 | 1.36±0.74a | 2.33±0.64 | 0.69±0.56a | 1.76±1.00 | 0.91±0.73a |
| Z | -0.339 | -8.866 | -0.666 | -3.846 | -1.226 | -7.36 | -2.40 | -2.18 |
| P | 0.735 | <0.001 | 0.505 | <0.001 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.810 | 0.029 |
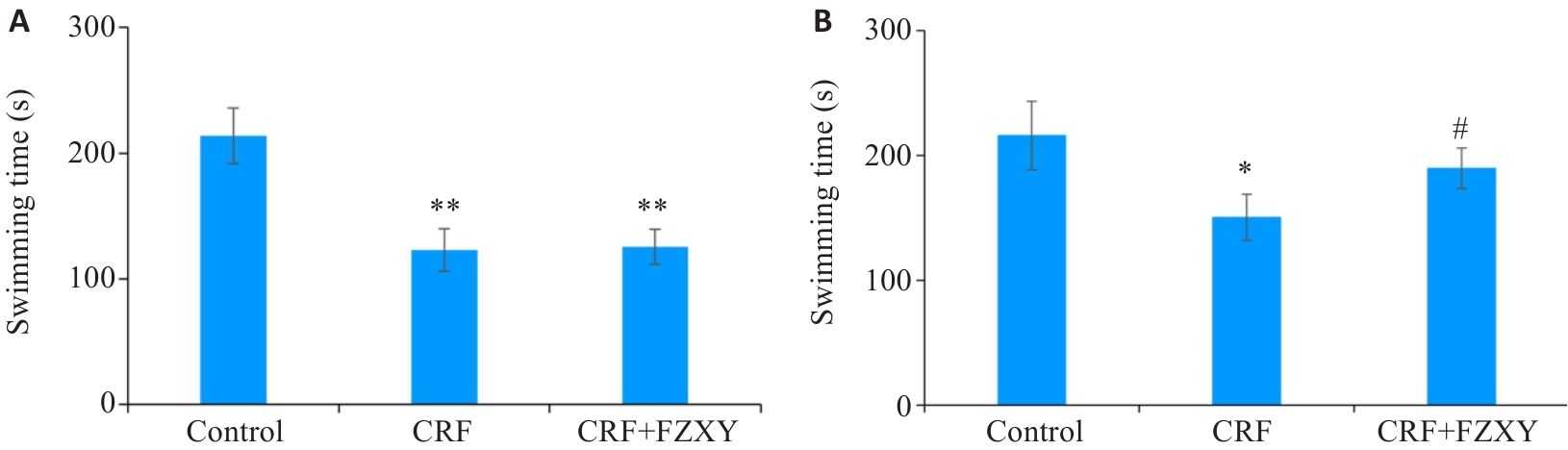
图9 各组小鼠强迫游泳实验比较
Fig.9 Performance of the mice in forced swimming test in different groups. A: After successful model establishment; B: After FZXY intervention. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs CRF group.
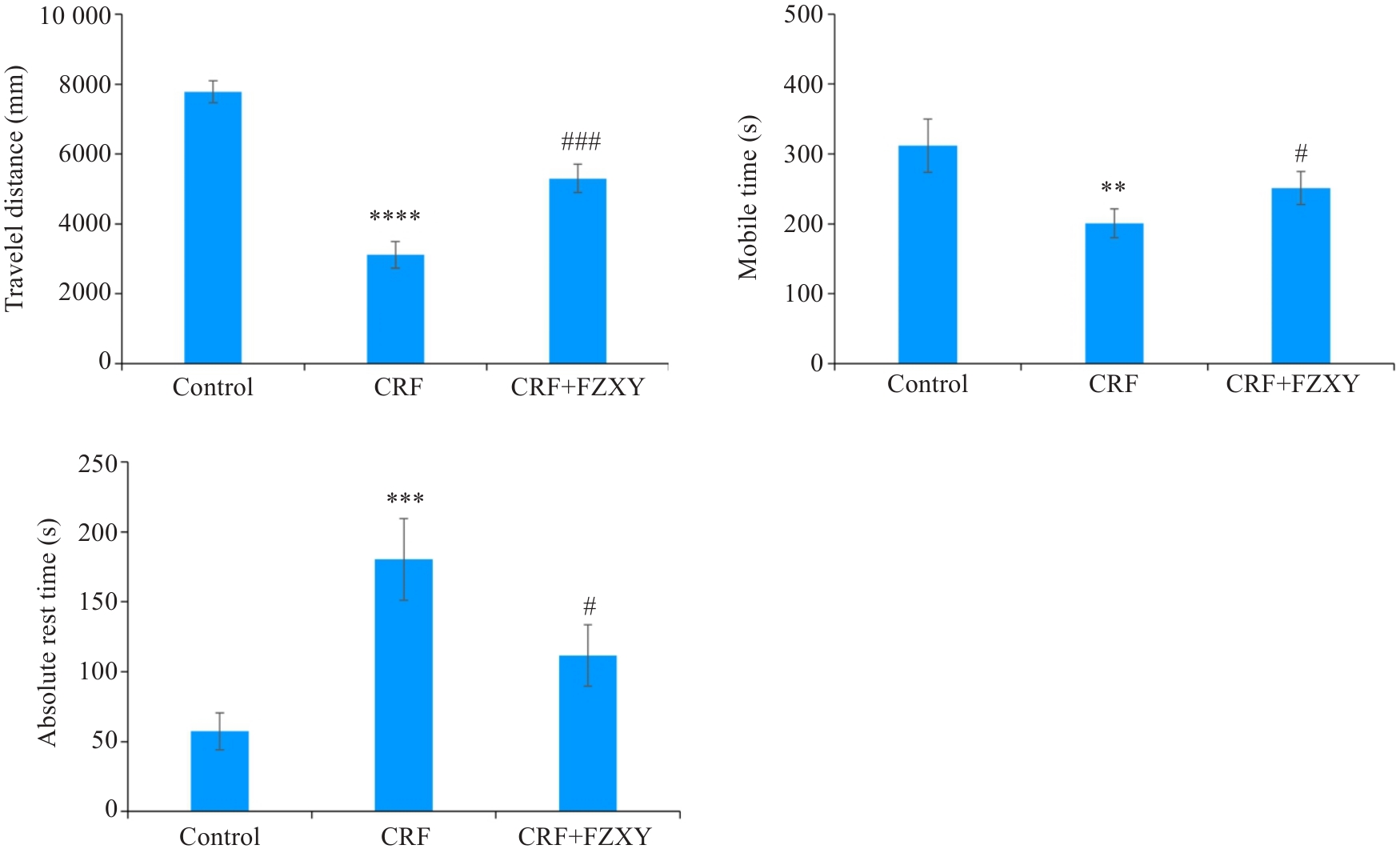
图10 各组小鼠旷场实验、悬尾实验比较
Fig.10 Comparison of open field test and tail suspension test of mice in different groups. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs Control group; #P<0.05,###P<0.001 vs CRF group.

图11 各组小鼠体质量、腓肠肌质量比较
Fig.11 Comparison of body weight and gastrocnemius muscle weight of the mice among the 3 groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CRF group. Day 1 is defined as the day of doxorubicin injection.
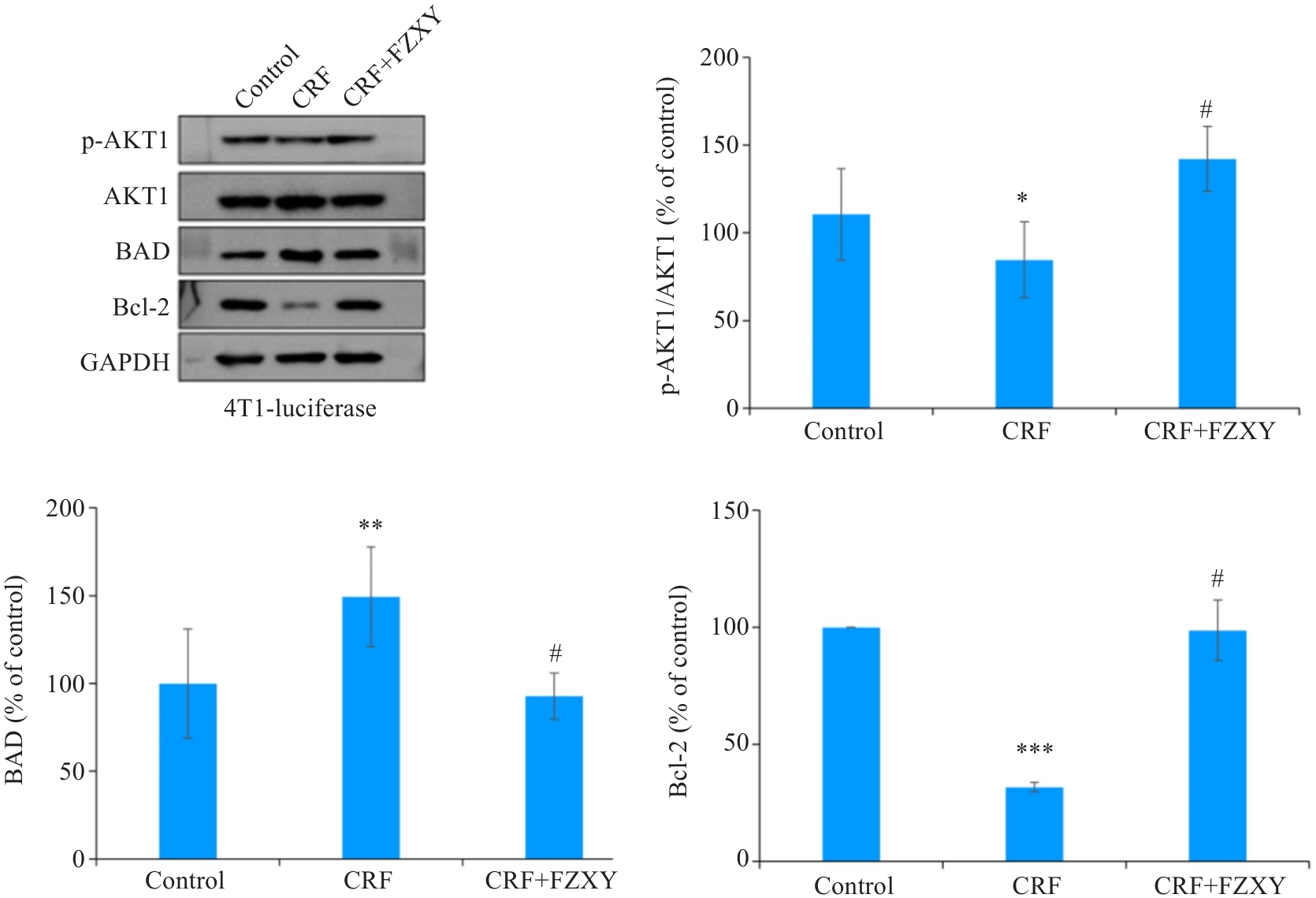
图13 各组腓肠肌蛋白表达水平比较
Fig.13 Comparison of protein expression levels in the gastrocnemius muscles of the mice among the 3 groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs CRF group.
| [1] | Mock V, Atkinson A, Barsevick A, et al. NCCN practice guidelines for cancer-related fatigue[J]. Oncology: Williston Park, 2000, 14(11a): 151-61. |
| [2] | 曹玉瑶, 宋 祎, 陈凤敏, 等. 有氧运动对乳腺癌化疗患者癌因性疲乏的影响及相关机制[J]. 天津医药, 2016, 44(4): 401-4. |
| [3] | 谢晓冬, 张潇宇. 癌因性疲乏最新进展 —NCCN(2018 版) 癌因性疲乏指南解读[J]. 中国肿瘤临床,2018, 45(16): 817-20. |
| [4] | Groenvold M, Petersen MA, Idler E, et al. Psychological distress and fatigue predicted recurrence and survival in primary breast cancer patients[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2007, 105(2): 209-19. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9447-x |
| [5] | Fabi A, Bhargava R, Fatigoni S, et al. Cancer-related fatigue: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31(6): 713-23. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.02.016 |
| [6] | 李泽龙,鲁 凯. 八珍汤联合靶向治疗HER-2阳性乳腺癌气血亏虚证的效果观察 [J]. 实用中西医结合临床, 2025, 25 (12): 28-30, 34. |
| [7] | 杨书贤,洪 禹,曹丽娟. 癌因性疲乏发病机制及中医药干预研究进展 [J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2025, 41 (06): 838-46. |
| [8] | 莫文菊,黄孝闻,叶魏武,等. 去壁灵芝孢子粉改善乳腺癌患者辅助化疗期间癌因性疲乏研究 [J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2024, 41 (14): 1921-8. |
| [9] | 王子承,王海波,王 颖,等.《中成药治疗优势病种临床应用指南》标准化项目组. 中成药治疗癌因性疲乏临床应用指南(2020年) [J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2021, 41(5): 534-41. |
| [10] | “虚劳干血”理论指导下复元活血汤合大黄蛰虫丸对乳腺癌癌因性疲乏的干预效果研究 [J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2025, 43 (02): 84-7. |
| [11] | 陈 静,樊锐锋,李 威,等.扶正消岩汤抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞增殖的机制研究[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(02):302-5. |
| [12] | 王 钢,陈 静,孔祥定,等.扶正消岩汤对气阴两虚型乳腺癌术后化疗患者生存质量的改善作用观察[J].中国中医药科技,2022,29(06):1011-3. |
| [13] | 冯月男,孙思邈,孔祥定,等.扶正消岩汤对乳腺癌肿瘤微环境调控机制的研究[J].中医药学报,2021,49(12):52-6. |
| [14] | 中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会 .中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)乳腺癌诊疗指南-2022[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2022. |
| [15] | Portenoy RK, Itri LM. Cancer-related fatigue: guidelines for evaluation and management[J]. Oncologist, 1999, 4(1): 1-10. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.4-1-1 |
| [16] | 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典-一部: 2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020. |
| [17] | 中国抗癌协会癌症康复与姑息治疗专业委员会,中国临床肿瘤学会肿瘤支持与康复治疗专家委员会 .癌症相关性疲乏诊断与治疗中国专家共识[J].中华医学杂志,2022,102(3):10. |
| [18] | Sprangers MA, Cull A, Groenvold M, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer approach to developing questionnaire modules: an update and overview. EORTC Quality of Life Study Group[J]. Qual Life Res, 1998, 7(4): 291-300. doi:10.1023/a:1024977728719 |
| [19] | 金 铭,谢露露,毛 妮,等. 癌因性疲劳动物模型的研究进展 [J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48 (07): 738-42. |
| [20] | Zombeck JA, Fey EG, Lyng GD, et al. A clinically translatable mouse model for chemotherapy-related fatigue[J]. Comp Med, 2013, 63(6): 491-7. |
| [21] | 徐叔云. 药理实验方法学[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2002: 1560-8. |
| [22] | Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of the polysaccharides extracted from Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) on cancer-related fatigue in mice[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(21): 10602-14. doi:10.1039/d1fo00375e |
| [23] | 吴人杰, 谢长生. 癌因性疲乏发病机制及治疗的研究进展[J].肿瘤学杂志,2020,26(3):240-4. |
| [24] | 沈志祥,陆为民,石 川,等. 徐氏参芪苡术汤联合化疗治疗胃癌术后癌因性疲乏脾虚瘀毒型的临床观察及机制 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31 (08): 143-51. |
| [25] | Mohandas H, Jaganathan SK, Mani MP, et al. Cancer-related fatigue treatment: an overview[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2017, 13(6): 916-29. |
| [26] | Chuang CH, Tai YA, Wu TJ, et al. Quercetin attenuates cisplatin-induced fatigue through mechanisms associated with the regulation of the HPA axis and MCP-1 signaling[J]. Front Nutr, 2025, 12: 1530132. doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1530132 |
| [27] | Wang YF, Liu MF, Huang N, et al. Quercetin-targeted AKT1 regulates the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway to protect against doxorubicin-induced nephropathy in mice[J]. Tissue Cell, 2023, 85: 102229. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2023.102229 |
| [28] | 陈 言,代 婷,郭长胜,等. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路探讨中医药治疗肌肉减少症的研究进展 [J/OL]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 1-19[2025-06-12]. |
| [29] | Regué L, Ji F, Flicker D, et al. IMP2 increases mouse skeletal muscle mass and voluntary activity by enhancing autocrine insulin-like growth factor 2 production and optimizing muscle metabolism[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 39(7): e00528-18. doi:10.1128/mcb.00528-18 |
| [30] | Hu M, Han M, Zhang H, et al. Curcumin (CUMINUP60®) mitigates exercise fatigue through regulating PI3K/Akt/AMPK/mTOR pathway in mice[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2023, 15(6): 2308-20. doi:10.18632/aging.204614 |
| [31] | Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ. BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 1998, 16: 395-419. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.395 |
| [32] | Liu S, Meng F, Zhang D, et al. Lonicera caerulea berry polyphenols extract alleviates exercise fatigue in mice by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, skeletal muscle cell apoptosis, and by increasing cell proliferation[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 853225. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.853225 |
| [33] | Hiensch AE, Bolam KA, Mijwel S, et al. Doxorubicin-induced skeletal muscle atrophy: Elucidating the underlying molecular pathways[J]. Acta Physiol: Oxf, 2020, 229(2): e13400. doi:10.1111/apha.13400 |
| [34] | Cruz FM, Munhoz BA, Alves BC, et al. Biomarkers of fatigue related to adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: evaluation of plasma and lymphocyte expression[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2015, 4: 4. doi:10.1186/s40169-015-0051-8 |
| [35] | Wang XS, Williams LA, Krishnan S, et al. Serum sTNF-R1, IL-6, and the development of fatigue in patients with gastrointestinal cancer undergoing chemoradiation therapy[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2012, 26(5): 699-705. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2011.12.007 |
| [36] | Bower JE, Ganz PA, Irwin MR, et al. Inflammation and behavioral symptoms after breast cancer treatment: do fatigue, depression, and sleep disturbance share a common underlying mechanism?[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(26): 3517-22. doi:10.1200/jco.2011.36.1154 |
| [37] | Guo W, Liu S, Xia H, et al. Shenqi Fuzheng injection facilitates skeletal muscle mitophagy mediated by the ubiquitination of HIF-1α to ameliorate cancer-associated fatigue[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2024, 28(12): e18455. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18455 |
| [38] | 何 晶,王林元,陈亚文,等. 基于JAK2/STAT3通路研究灵芝孢子多糖通过免疫调节改善脾虚证小鼠癌因性疲乏的机制 [J/OL]. 中国中药杂志, 2025: 1-9[2025-06-21]. |
| [39] | 崔艺馨,米继伟,冯 宇,等. 黄芪四君子汤治疗乳腺癌癌因性疲乏的疗效及机制:基于94例临床随机对照实验和网络药理学 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42 (05): 649-57. |
| [1] | 张力莹, 张同贞, 赵鑫. 基于乳腺影像报告和数据系统的DWI和T2WI形态评估对乳腺病变的诊断价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1809-1817. |
| [2] | 呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [3] | 杨子为, 吕畅, 董柱, 计书磊, 毕生辉, 张雪花, 王晓武. 金樱子通过调控Src-AKT1轴抑制肺动脉高压平滑肌增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [4] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [5] | 饶璐, 丁家和, 魏江平, 阳勇, 张小梅, 王计瑞. 槐花通过抑制PI3K/AKT通路减轻炎症反应治疗银屑病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [6] | 马思源, 张博超, 浦春. Circ_0000437通过靶向let-7b-5p/CTPS1轴促进乳腺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移及上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [7] | 张兆君, 吴琼, 谢苗苗, 叶洳吟, 耿晨晨, 石纪雯, 杨清玲, 王文锐, 石玉荣. 层状双氢氧化物负载si-NEAT1通过miR-133b/PD-L1轴调控乳腺癌紫杉醇耐药及巨噬细胞极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1718-1731. |
| [8] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [9] | 王立明, 陈宏睿, 杜燕, 赵鹏, 王玉洁, 田燕歌, 刘新光, 李建生. 益气滋肾方通过抑制PI3K/Akt/NF-κB通路改善小鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [10] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [11] | 何丽君, 陈晓菲, 闫陈昕, 师林. 扶正化积汤治疗非小细胞肺癌的分子机制:基于网络药理学及体外实验验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [12] | 李嘉豪, 冼瑞婷, 李荣. 下调ACADM介导的脂毒性抑制雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌细胞的侵袭与转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1163-1173. |
| [13] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [14] | 管丽萍, 颜燕, 卢心怡, 李智峰, 高晖, 曹东, 侯晨曦, 曾靖宇, 李欣怡, 赵洋, 王俊杰, 方会龙. 复方积雪草减轻小鼠日本血吸虫引起的肝纤维化:通过调控TLR4/MyD88通路抑制炎症-纤维化级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [15] | 唐培培, 谈勇, 殷燕云, 聂晓伟, 黄菁宇, 左文婷, 李玉玲. 调周滋阴方治疗早发性卵巢功能不全的疗效、安全性及作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||