南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2658-2666.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.13
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-05-06
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
赵文红
E-mail:1693671024@qq.com;chenmeiqing567@163.com;975643018@qq. com
作者简介:马思雨,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1693671024@qq.com基金资助:
Siyu MA( ), Meiqing CHEN(
), Meiqing CHEN( ), Tianyu WU, Wenhong ZHAO(
), Tianyu WU, Wenhong ZHAO( )
)
Received:2025-05-06
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Wenhong ZHAO
E-mail:1693671024@qq.com;chenmeiqing567@163.com;975643018@qq. com
摘要:
目的 探究亚麻木酚素(SDG)对妊娠期及哺乳期母鼠反式脂肪酸(TFA)暴露致子鼠肾脏损伤的保护作用及潜在作用机制。 方法 30只C57BL/6雌鼠随机分为5组,分别为对照组、TFA暴露组、SDG低(10 mg/kg)、中(20 mg/kg)、高(30 mg/kg)干预组,6只/组。采用脲酶法和肌氨酸氧化酶法分别检测子鼠血肌酐(BUN)和血尿素氮(CRE)的水平;通过网络药理学初步探究SDG对TFA暴露致肾损伤的潜在保护机制,分子对接初步探究了SDG与Bcl2/Bax/caspase-3的结合能力。在此基础上选择凋亡相关的Bcl2/Bax/caspase-3信号轴对实验小鼠进行后续分析;蛋白免疫印迹法检测cleaved-caspase-3、Bax、Bcl2蛋白水平。 结果 动物实验发现,TFA组子鼠血清中尿素氮及肌酐水平高于对照组(P<0.05),而干预后SDG中、高剂量组子鼠血清中的尿素氮及肌酐较TFA暴露组降低(P<0.05)。网络药理学和分子对接结果提示,SDG可能通过作用凋亡相关的Bcl2/Bax/caspase-3轴改善肾损伤。进一步实验结果显示:TFA暴露组较对照组子鼠肾组织阳性凋亡细胞增多、凋亡指数上升;cleaved-caspase-3蛋白水平升高及Bcl2/Bax蛋白水平比值下降(P<0.05)。与TFA暴露组相比,低、中、高剂量SDG干预组凋亡指数下降、cleaved-caspase-3蛋白水平下降、Bcl2/Bax蛋白水平比值上升(P<0.05)。 结论 母鼠妊娠期和哺乳期TFA暴露会导致子代肾脏损伤。膳食SDG干预可以延缓因母鼠妊娠期和哺乳期TFA暴露所导致的子代肾损伤,其作用机制可能通过作用于Bcl2/Bax/caspase-3信号轴通道,抑制细胞凋亡有关。
马思雨, 陈美庆, 吴天宇, 赵文红. 膳食亚麻木酚素通过调控Bcl2/Bax/caspase3信号轴通道改善大鼠母体反式脂肪酸暴露所导致的子代肾损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2658-2666.
Siyu MA, Meiqing CHEN, Tianyu WU, Wenhong ZHAO. Dietary secoisolariciresinol diglucoside alleviates chronic kidney disease in offspring rats caused by maternal trans-fatty acid exposure by regulating the Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3 signaling axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2658-2666.
| Group | BUN (mmol/L) | CRE (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 17.08±1.53 | 44.85±6.087 |
| TFA | 22.39±6.18# | 68.54±11.89# |
| TFA+LSDG | 18.84±3.91 | 67.22±10.96 |
| TFA+MSDG | 15.56±1.86* | 60.76±7.62 |
| TFA+HSDG | 17.01±3.57* | 52.49±6.22 |
| F | 3.98 | 10.81 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.001 |
表1 各组子鼠血清肾功能指标比较
Tab.1 Comparison of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (CRE) levels among the 5 groups (Mean±SD, n=9)
| Group | BUN (mmol/L) | CRE (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 17.08±1.53 | 44.85±6.087 |
| TFA | 22.39±6.18# | 68.54±11.89# |
| TFA+LSDG | 18.84±3.91 | 67.22±10.96 |
| TFA+MSDG | 15.56±1.86* | 60.76±7.62 |
| TFA+HSDG | 17.01±3.57* | 52.49±6.22 |
| F | 3.98 | 10.81 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.001 |

图1 SDG保护TFA诱导CKD的网络药理学分析
Fig.1 Network pharmacology analysis of the protective mechanism of SDG against TFA-induced chronic kidney disease (CKD). A: Collection of SDG targets. B: DO enrichment analysis of SDG targets. C: KEGG enrichment analysis of SDG targets. D: Screening of potential targets involved in the protective effects of SDG against TFA-induced CKD. E: KEGG enrichment analysis of the pathways mediating the protective effects of SDG against CKD.
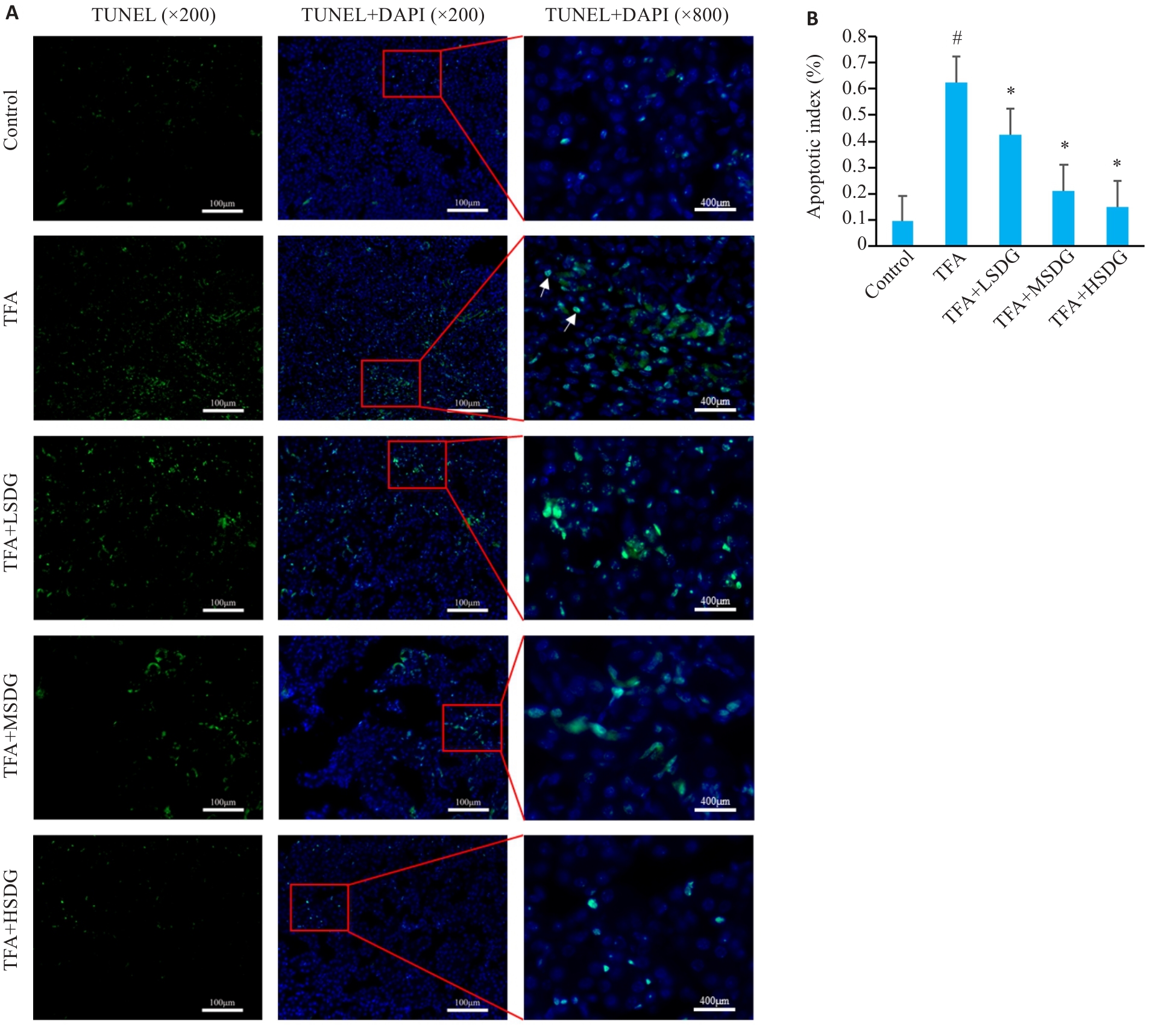
图2 各组子鼠肾组织细胞凋亡情况
Fig.2 Cell apoptosis in the kidney tissue of the offspring mice in each group. A: TUNEL staining of the kidney tissue (the white arrows indicate apoptotic cells). B: Statistical chart of cell apoptosis in kidney tissue of the offspring mice in each group. #P<0.05 vs control group; *P<0.05 vs TFA group.

图3 各组子鼠肾组织Cleaved-caspase3的IHC染色情况
Fig.3 Immunohistochemical staining for cleaved caspase-3 in the renal tissues of the offspring mice in each group (scale bar=50 μm). A: Control group. B: TFA group. C: TFA+LSDG group. D: TFA+MSDG group. E: TFA+HSDG group. F: Quantitative statistical chart. #P<0.05 vs Control group; *P<0.05 vs TFA group.
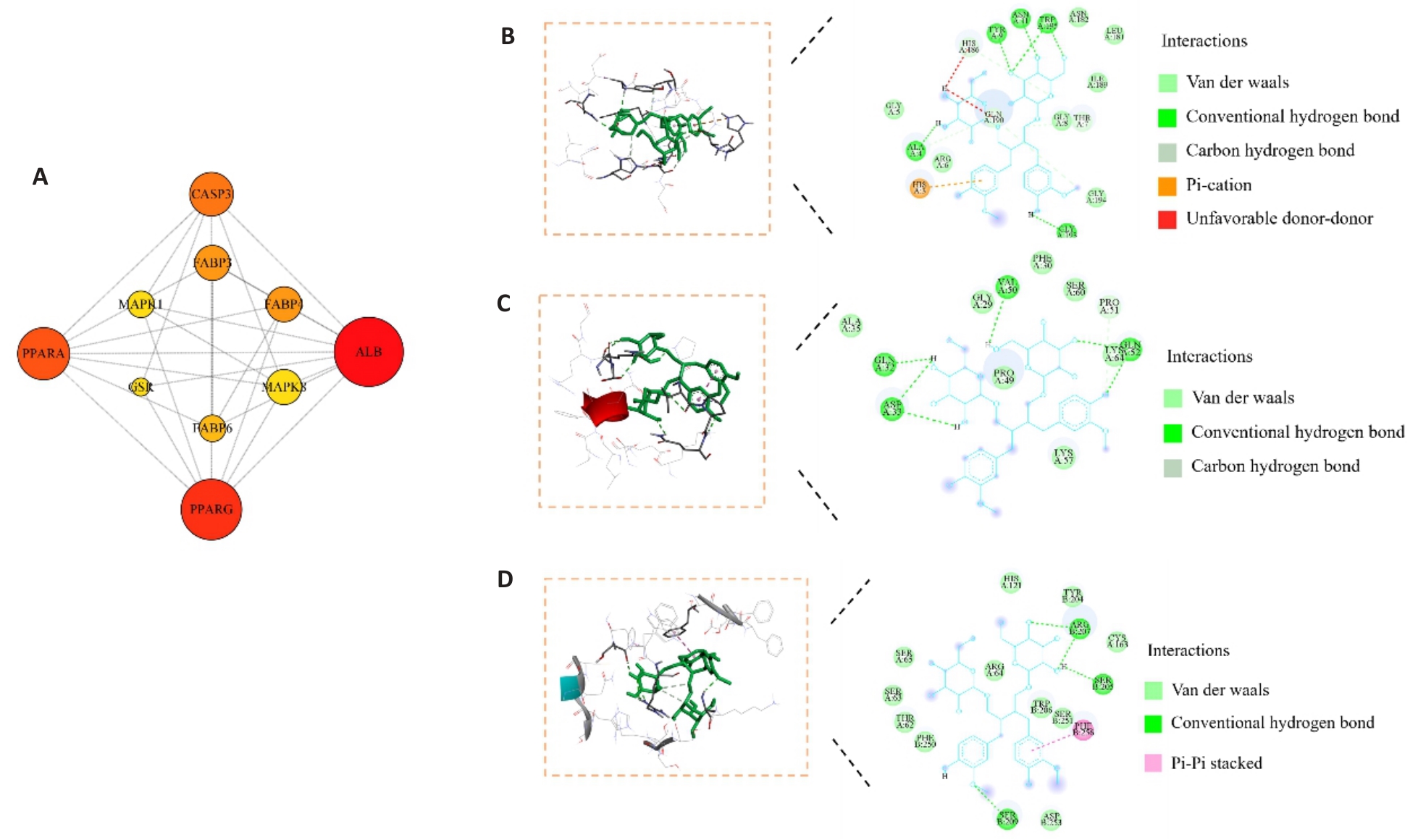
图4 SDG治疗TFA诱导CKD的核心靶点筛选及分子对接结果
Fig.4 Screening of the key targets of SDG in the treatment of TFA-induced CKD (A) and molecular docking results of Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 with SDG (B-D).
| Target | PDB ID |
|---|---|
| Bcl-2 | 1g5m |
| Bax | 4bd6 |
| Caspase-3 | 1gfw |
表2 各蛋白质的PDB数据库代码名称
Tab. 2 The PDB database code names for each protein
| Target | PDB ID |
|---|---|
| Bcl-2 | 1g5m |
| Bax | 4bd6 |
| Caspase-3 | 1gfw |
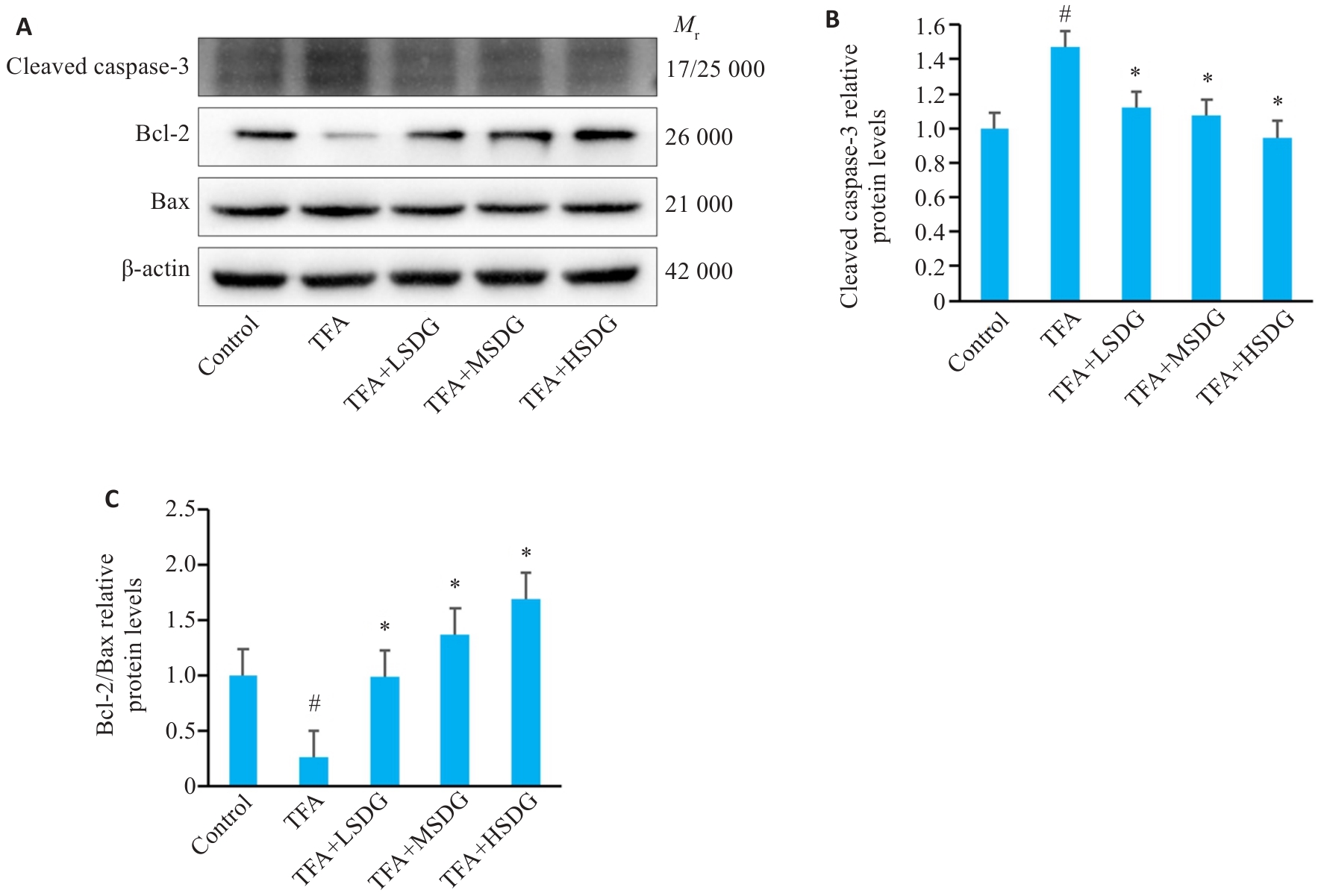
图5 各组子鼠肾组织中细胞凋亡相关因子蛋白表达检测
Fig.5 Detection of protein expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in kidney tissue of the offspring mice in each group. A: Protein bands of caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax in the kidney tissues of the offspring mice in each group detected with Western blotting. B: Gray value of caspase-3 in each group. C: Gray value ratio of Bcl2/Bax in each group. #P<0.05 vs control group; *P<0.05 vs TFA group.
| [1] | Li CY, Cobb LK, Vesper HW, et al. Global surveillance of trans-fatty acids[J]. Prev Chronic Dis, 2019, 16: E147. doi:10.5888/pcd16.190121 |
| [2] | Hatem O, Kaçar ÖF, Kaçar HK, et al. Trans isomeric fatty acids in human milk and their role in infant health and development[J]. Front Nutr, 2024, 11: 1379772. doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1379772 |
| [3] | Chandra A, Svensson M, Åsberg A, et al. Trans-fatty acids and survival in renal transplantation[J]. J Ren Nutr, 2019, 29(3): 169-80. doi:10.1053/j.jrn.2018.08.003 |
| [4] | Neuenschwander M, Barbaresko J, Pischke CR, et al. Intake of dietary fats and fatty acids and the incidence of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective observational studies[J]. PLoS Med, 2020, 17(12): e1003347. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003347 |
| [5] | Okamura T, Hashimoto Y, Majima S, et al. Trans fatty acid intake induces intestinal inflammation and impaired glucose tolerance[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 669672. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.669672 |
| [6] | Ren X, Vilhjálmsdóttir BL, Rohde JF, et al. Systematic literature review and meta-analysis of the relationship between polyunsaturated and trans fatty acids during pregnancy and offspring weight development[J]. Front Nutr, 2021, 8: 625596. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.625596 |
| [7] | Salemi F, Beigrezaei S, Arabi V, et al. Dietary trans fatty acids and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Eur J Nutr, 2023, 62(2): 563-72. |
| [8] | Michels N, Specht IO, Heitmann BL, et al. Dietary trans-fatty acid intake in relation to cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nutr Rev, 2021, 79(7): 758-76. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuaa061 |
| [9] | Fan YH, Li ZF, Shi J, et al. The association between prepregnancy dietary fatty acids and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study[J]. Clin Nutr, 2024, 43(2): 484-93. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.12.022 |
| [10] | Friesen R, Innis SM. Trans fatty acids in human milk in Canada declined with the introduction of trans fat food labeling[J]. J Nutr, 2006, 136(10): 2558-61. doi:10.1093/jn/136.10.2558 |
| [11] | Wada Y, Yoshida-Yamamoto S, Wada Y, et al. Trans fatty acid accumulation in the human placenta[J]. J Mass Spectrom, 2017, 52(3): 139-43. doi:10.1002/jms.3910 |
| [12] | Hachul ACL, Mennitti LV, de Oliveira JL, et al. Oligofructose supplementation (10%) during pregnancy and lactation does not change the inflammatory effect of concurrent trans fatty acid ingestion on 21-day-old offspring[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2013, 12: 59. doi:10.1186/1476-511x-12-59 |
| [13] | Mucci DD, Fernandes FS, Souza AD, et al. Flaxseed mitigates brain mass loss, improving motor hyperactivity and spatial memory, in a rodent model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 2015, 97: 13-9. doi:10.1016/j.plefa.2015.03.001 |
| [14] | Parikh M, Maddaford TG, Austria JA, et al. Dietary flaxseed as a strategy for improving human health[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(5): 1171. doi:10.3390/nu11051171 |
| [15] | 陈美庆, 朱润泽, 吴天宇, 等. 亚麻木酚素对母鼠反式脂肪酸暴露致子代肾氧化损伤的保护作用[J]. 中南大学学报: 医学版, 2023, 48(7): 967-78. |
| [16] | Chen YE, Li CT, Duan SN, et al. Curcumin attenuates potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation in mice[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 118: 109195. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109195 |
| [17] | 杨少华, 张 昕, 马 雯, 等.肾素拮抗剂SPH3127通过TGF-β/Smads信号通路对高血压肾损伤保护机制的研究[J].川北医学院学报,2025, 40(7): 829-35. |
| [18] | Dhibi M, Brahmi F, Mnari A, et al. The intake of high fat diet with different trans fatty acid levels differentially induces oxidative stress and non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in rats[J]. Nutr Metab (Lond), 2011, 8(1): 65. doi:10.1186/1743-7075-8-65 |
| [19] | 张畔畔, 陈美庆, 朱润泽, 等. 亚麻木酚素抑制反式脂肪酸致小鼠子代脑部氧化应激和炎症反应的作用[J]. 卫生研究, 2024, 53(5): 771-7. |
| [20] | Ge JL, Hao RL, Rong X, et al. Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside mitigates benzo [a] Pyrene-induced liver and kidney toxicity in mice via miR-101a/MKP-1-mediated p38 and ERK pathway[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2022, 159: 112733. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112733 |
| [21] | Zhu XF, Hu YQ, Dai ZC, et al. Associations between trans fatty acids and systemic immune-inflammation index: a cross-sectional study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2024, 23(1): 122. doi:10.1186/s12944-024-02109-w |
| [22] | Luan M, Tian YP, Yan DD, et al. Association of plasma trans fatty acid concentrations with blood pressure and hypertension in U.S. adults[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2024, 15: 1373095. doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1373095 |
| [23] | Di Zazzo G, Stringini G, Matteucci MC, et al. Serum creatinine levels are significantly influenced by renal size in the normal pediatric population[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011, 6(1): 107-13. doi:10.2215/cjn.00580110 |
| [24] | Downer S, Berkowitz SA, Harlan TS, et al. Food is medicine: actions to integrate food and nutrition into healthcare[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369: m2482. doi:10.1136/bmj.m2482 |
| [25] | Hu YX, Tse TJ, Shim YY, et al. A review of flaxseed lignan and the extraction and refinement of secoisolariciresinol diglucoside[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2024, 64(15): 5057-72. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2148627 |
| [26] | Moree SS, Rajesha J. Investigation of in vitro and in vivo antioxidant potential of secoisolariciresinol diglucoside[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2013, 373(1/2): 179-87. doi:10.1007/s11010-012-1487-4 |
| [27] | Kagawa T, Zárybnický T, Omi T, et al. A scrutiny of circulating microRNA biomarkers for drug-induced tubular and glomerular injury in rats[J]. Toxicology, 2019, 415: 26-36. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2019.01.011 |
| [28] | Khandouzi N, Zahedmehr A, Mohammadzadeh A, et al. Effect of flaxseed consumption on flow-mediated dilation and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with coronary artery disease: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2019, 73(2): 258-65. doi:10.1038/s41430-018-0268-x |
| [29] | Spitz AZ, Gavathiotis E. Physiological and pharmacological modulation of BAX[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 43(3): 206-20. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2021.11.001 |
| [30] | Almeer RS, Albasher G, Alotibi F, et al. Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract suppressed mercury chloride-induced nephrotoxicity via Nrf2-antioxidant pathway activation and inhibition of inflammatory and apoptotic signaling[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 5634685. doi:10.1155/2019/5634685 |
| [1] | 呼琴, 金华. 清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [2] | 常笑语, 张瀚文, 曹红亭, 侯玲, 孟鑫, 陶虹, 罗彦, 李光华. 热应激对大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞生物钟基因 Bmal1和细胞周期蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [3] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [4] | 刘柳青, 王坤, 王雪晴, 杜冰心. 枸杞多糖通过下调miR-23a减轻顺铂诱导的颗粒细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2340-2349. |
| [5] | 陶露, 陈悦, 黄林林, 郑旺, 宋雪, 项平, 胡建国. 珠子草素通过调控p38/JNK信号通路抑制肠上皮细胞凋亡保护肠屏障改善克罗恩病样肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2483-2495. |
| [6] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [7] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [8] | 王元国, 张鹏. 铁死亡抑制基因在食管癌中的高表达分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [9] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [10] | 陈桂玲, 廖晓凤, 孙鹏涛, 岑欢, 舒盛春, 李碧晶, 黎金华. 澳洲茄碱通过调控Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3信号通路促进非小细胞肺癌发生凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [11] | 孙秀颀, 蔡静, 张安邦, 庞博, 陈春艳, 查琪琪, 全菲, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过抑制NF-kB/NLRP3信号通路介导炎症和凋亡改善大鼠脑卒中后痉挛[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| [12] | 邱建国, 邱一桐, 李国荣, 张林生, 郑雪, 姚泳江, 王熙丹, 黄海阳, 张凤敏, 苏冀彦, 郑学宝, 黄晓其. 黄芩汤通过调控内质网应激减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| [13] | 兰 玉, 王凯风, 蓝智贤, 周何琪, 孙 剑. 脱醇红酒抑制肝细胞癌的发生和发展:基于诱导细胞周期的阻滞和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1297-1305. |
| [14] | 郑庆委, 邵一丹, 郑婉婷, 邹映雪. 蛹虫草代谢产物虫草素抑制舌鳞癌裸鼠移植瘤的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 873-878. |
| [15] | 石文惠, 刘小莲, 张贵明, 叶林萱, 周润华, 李亦蕾, 余 乐. RITA体外选择性抑制BAP1缺失的皮肤黑色素瘤细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 710-717. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||