南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2628-2638.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.10
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-05-29
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
姜业臻
E-mail:doctorchaoli@163.com;jyzbhh@163.com
作者简介:李 超,博士,主治医师,E-mail: doctorchaoli@163.com
基金资助:
Chao LI1( ), Guozhi YIN2, Xiao CHENG3, Yezhen JIANG2,3(
), Guozhi YIN2, Xiao CHENG3, Yezhen JIANG2,3( )
)
Received:2025-05-29
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Yezhen JIANG
E-mail:doctorchaoli@163.com;jyzbhh@163.com
摘要:
目的 研究血管相关迁移细胞蛋白(AAMP)异常高表达在肝细胞癌(HCC)中的临床意义和对肝癌细胞侵袭转移的影响。 方法 基于网络数据库中HCC队列资料分析AAMP基因在肝癌和癌旁组织中的表达差异以及与临床分期和预后的关系。免疫组化检测60对HCC及癌旁组织标本中AAMP表达,分析AAMP表达与患者临床病理特征的相关性。通过慢病毒转染下调HCC细胞(Mahlavu和Huh-7)内AAMP表达水平。EdU掺入实验、流式细胞仪、划痕愈合实验、transwell迁移/侵袭小室和裸鼠肺转移瘤模型分别检测敲低AAMP表达对HCC细胞体外增殖、凋亡、迁移、侵袭和体内肺转移能力的影响。Western blotting和免疫荧光检测上皮间质转化标志物E-cadherin、N-cadherin、Vimentin、Snail表达情况。RT-qPCR和Western blotting检测敲低AAMP对RhoA mRNA和蛋白表达的影响。分别使用MG-132和CHX处理敲低AAMP的HCC细胞,Western blotting检测细胞内RhoA蛋白表达变化。免疫组化染色分析HCC组织中AAMP和RhoA蛋白的表达相关性。 结果 生物信息学分析显示,AAMP基因表达水平在HCC组织中升高(P<0.05),AAMP高表达与患者临床分期较晚和不良预后相关(P<0.05)。免疫组化结果显示,HCC组织的AAMP染色评分高于对应癌旁组织(P<0.05),AAMP高表达与Edmondson-Steiner分级(III+IV)、血管侵犯及TNM分期(III+IV期)相关(P<0.05)。敲低AAMP对HCC细胞增殖和凋亡无显著影响(P>0.05),但能抑制HCC细胞的迁移、侵袭和体内肺转移能力(P<0.05)。敲低AAMP后HCC细胞内E-cadherin蛋白表达升高而N-cadherin、Vimentin和Snail的表达水平降低(P<0.05),相应蛋白的免疫荧光染色强度变化趋势与Western blotting检测结果一致。敲低AAMP对RhoA基因mRNA表达水平无显著影响(P>0.05),但降低了RhoA蛋白的表达量(P<0.05),并且MG-132处理阻断了敲低AAMP导致的RhoA蛋白表达下调(P<0.05)。相关性分析显示,HCC组织内AAMP和RhoA蛋白的表达水平呈正相关关系(P<0.05)。 结论 AAMP高表达与HCC恶性临床特征密切相关,AAMP可能通过维持RhoA蛋白稳定表达来促进HCC细胞发生上皮间质转化,进而增强HCC的侵袭转移能力。
李超, 殷国志, 程萧, 姜业臻. 血管相关迁移细胞蛋白在肝细胞癌中高表达并促进肝癌细胞侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2628-2638.
Chao LI, Guozhi YIN, Xiao CHENG, Yezhen JIANG. Angio-associated migratory cell protein is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2628-2638.
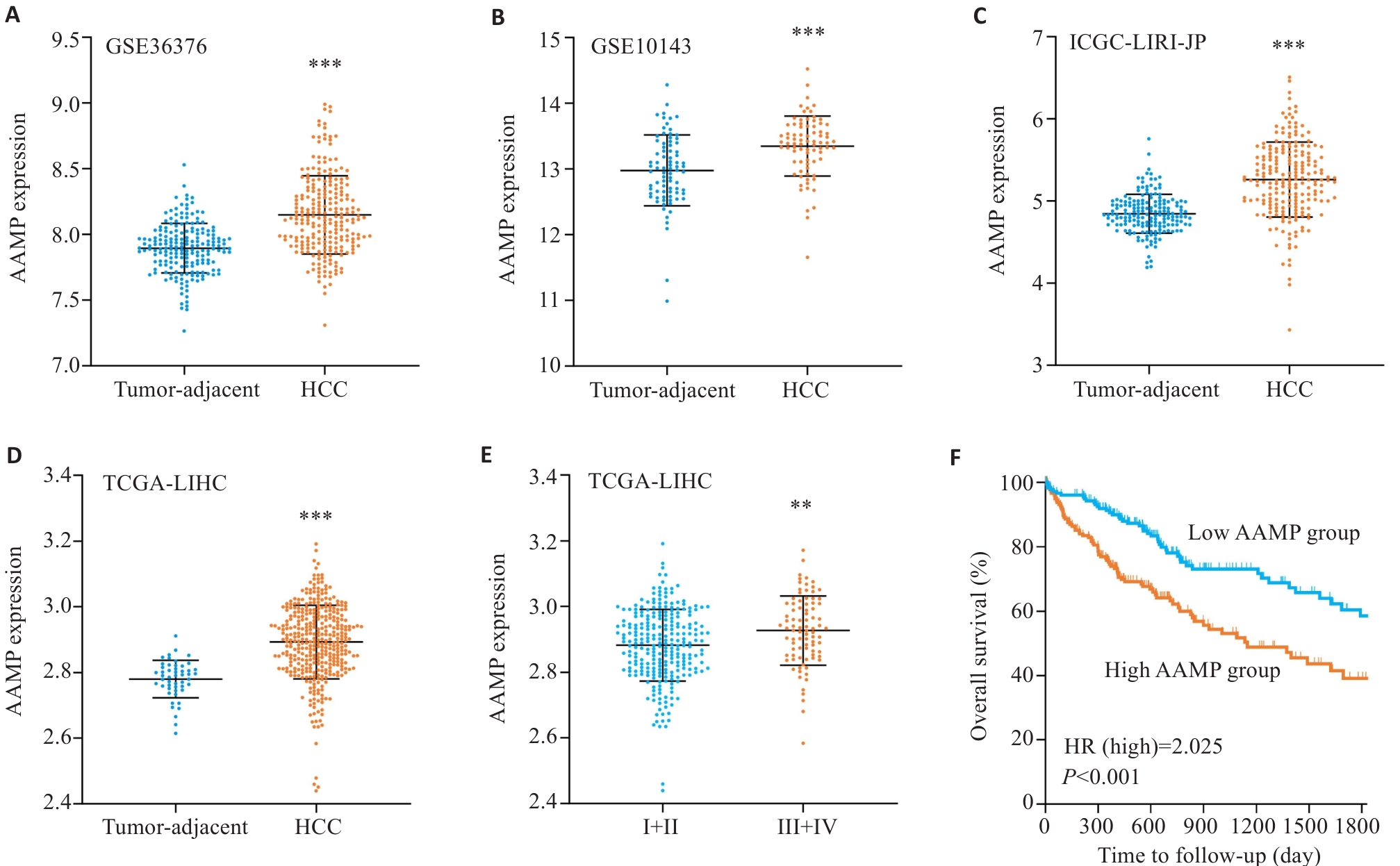
图1 分析AAMP在HCC公共数据库中的表达及临床意义
Fig.1 Bioinformatics analysis of AAMP expression in HCC. A-D: Data from different HCC datasets from GEO (A, B), ICGC (C) and TCGA (D) databases all show up-regulated AAMP expression in HCC. ***P<0.001 vs tumor-adjacent tissues. E: AAMP expression is higher in advanced TNM stages. **P<0.01 vs I+II. F: High expression of AAMP predicted unfavorable prognosis.
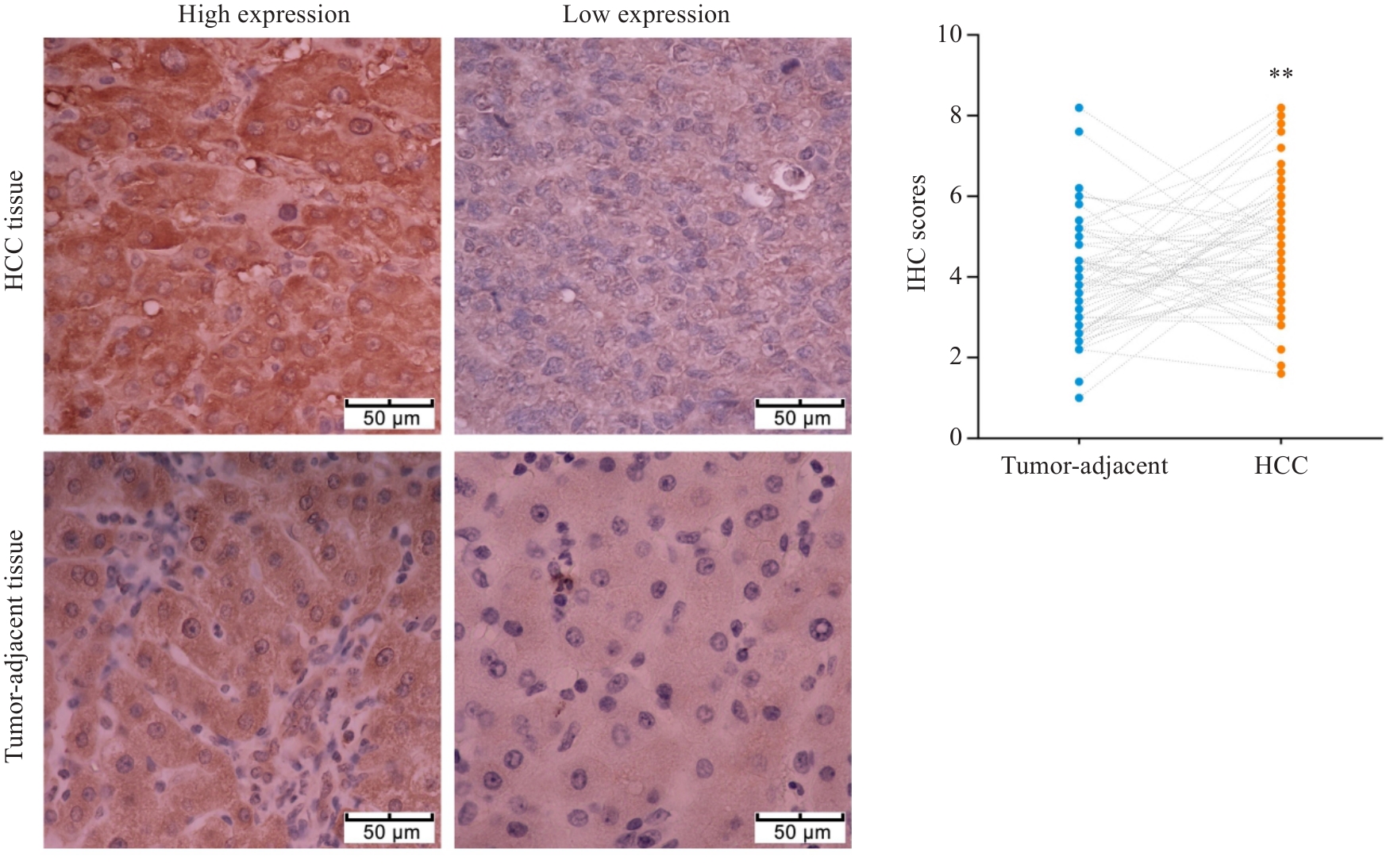
图2 AAMP在HCC及癌旁组织中的表达
Fig.2 Immunohistochemical detection of AAMP expression in HCC and adjacent tissues (Original magnification: ×400). **P<0.01 vs Tumor-adjacent.
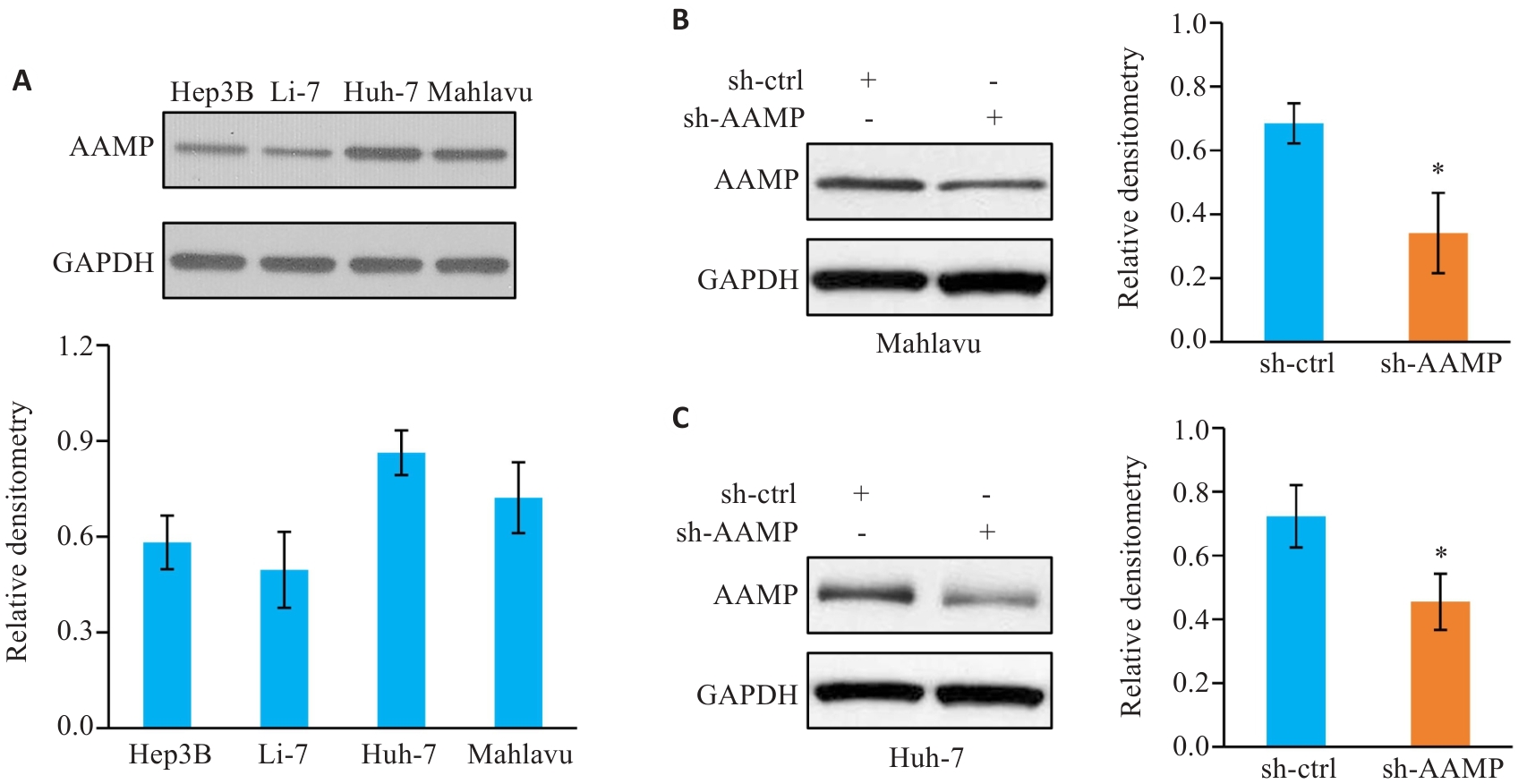
图3 慢病毒转染敲低HCC细胞中AAMP表达
Fig.3 Knockdown of AAMP in HCC cells by lentivirus transduction. A: Expression of AAMP in 4 HCC cell lines (Hep3B, Li-7, Huh-7, and Mahlavu). B, C: Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of AAMP in Mahlavu (B) and Huh-7 (C) cells, *P<0.05 vs sh-ctrl group.

图4 敲低AAMP对HCC细胞增殖凋亡无显著影响
Fig.4 Knockdown of AAMP does not affect proliferation or apoptosis of HCC cells. A, B: Knockdown of AAMP does not affect proliferation of Mahlavu (A) and Huh-7 (B) cells. C, D: Knockdown of AAMP does not affect apoptosis of Mahlavu (C) and Huh-7 (D) cells.
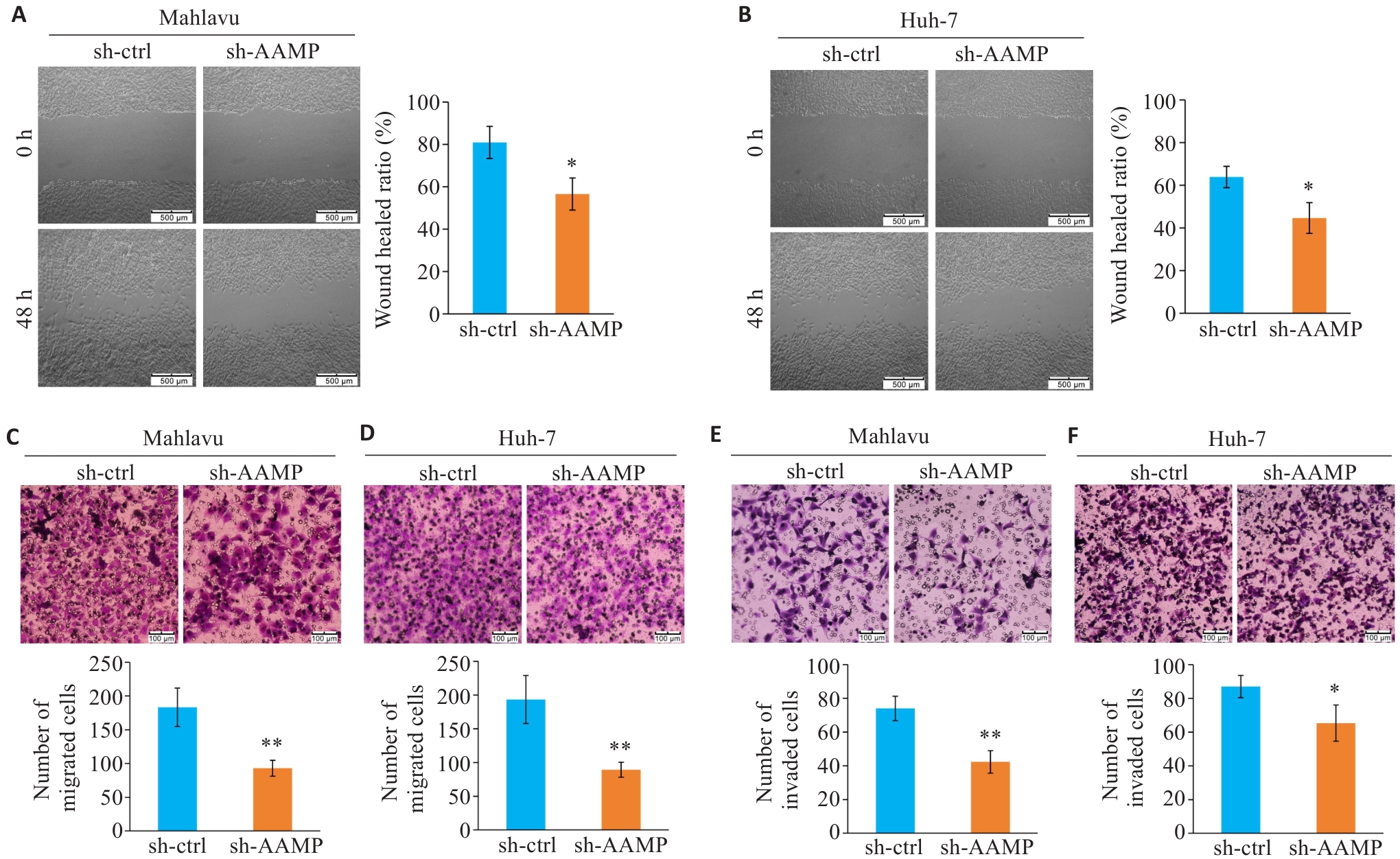
图5 敲低AAMP抑制HCC细胞迁移和侵袭
Fig. 5 Knockdown of AAMP inhibits migration and invasion of HCC cells. A, B: Knockdown of AAMP inhibits wound healing of Mahlavu (A) and Huh-7 (B) cells (*P<0.05 vs sh-ctrl group). C, D: Knockdown of AAMP attenuates Transwell migration ability of Mahlavu (C) and Huh-7 (D) cells (**P<0.01 vs sh-ctrl group). E, F: Knockdown of AAMP suppresses Transwell invasion ability of Mahlavu (E) and Huh-7 (F) cells (*P<0.05 vs sh-ctrl group, **P<0.01 vs sh-ctrl group). n=3 per group.
| Clinical features | AAMP expression | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=30) | High (n=30) | ||||
| Gender | Male | 21 | 22 | 0.082 | 0.774 |
| Female | 9 | 8 | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 5 | 3 | 0.144 | 0.704 |
| ≥60 | 25 | 27 | |||
| HBsAg | Negative | 5 | 7 | 0.417 | 0.519 |
| Positive | 25 | 23 | |||
| Liver cirrhosis | Absent | 10 | 8 | 0.317 | 0.573 |
| Present | 20 | 22 | |||
| Tumor size(cm) | ≤5 | 15 | 10 | 1.714 | 0.190 |
| >5 | 15 | 20 | |||
| Venous infiltration | No | 18 | 9 | 5.455 | 0.020 |
| Yes | 12 | 21 | |||
| Edmondson-steiner grading | I+II | 19 | 10 | 5.406 | 0.020 |
| III+IV | 11 | 20 | |||
| Serum AFP level (ng/mL) | <400 | 16 | 9 | 3.360 | 0.067 |
| ≥400 | 14 | 21 | |||
| TNM stage | I+II | 17 | 9 | 4.344 | 0.037 |
| III+IV | 13 | 21 | |||
表1 AAMP高表达在肝细胞癌中的临床意义
Tab.1 Clinical significance of high AAMP expression level in HCC
| Clinical features | AAMP expression | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=30) | High (n=30) | ||||
| Gender | Male | 21 | 22 | 0.082 | 0.774 |
| Female | 9 | 8 | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 5 | 3 | 0.144 | 0.704 |
| ≥60 | 25 | 27 | |||
| HBsAg | Negative | 5 | 7 | 0.417 | 0.519 |
| Positive | 25 | 23 | |||
| Liver cirrhosis | Absent | 10 | 8 | 0.317 | 0.573 |
| Present | 20 | 22 | |||
| Tumor size(cm) | ≤5 | 15 | 10 | 1.714 | 0.190 |
| >5 | 15 | 20 | |||
| Venous infiltration | No | 18 | 9 | 5.455 | 0.020 |
| Yes | 12 | 21 | |||
| Edmondson-steiner grading | I+II | 19 | 10 | 5.406 | 0.020 |
| III+IV | 11 | 20 | |||
| Serum AFP level (ng/mL) | <400 | 16 | 9 | 3.360 | 0.067 |
| ≥400 | 14 | 21 | |||
| TNM stage | I+II | 17 | 9 | 4.344 | 0.037 |
| III+IV | 13 | 21 | |||
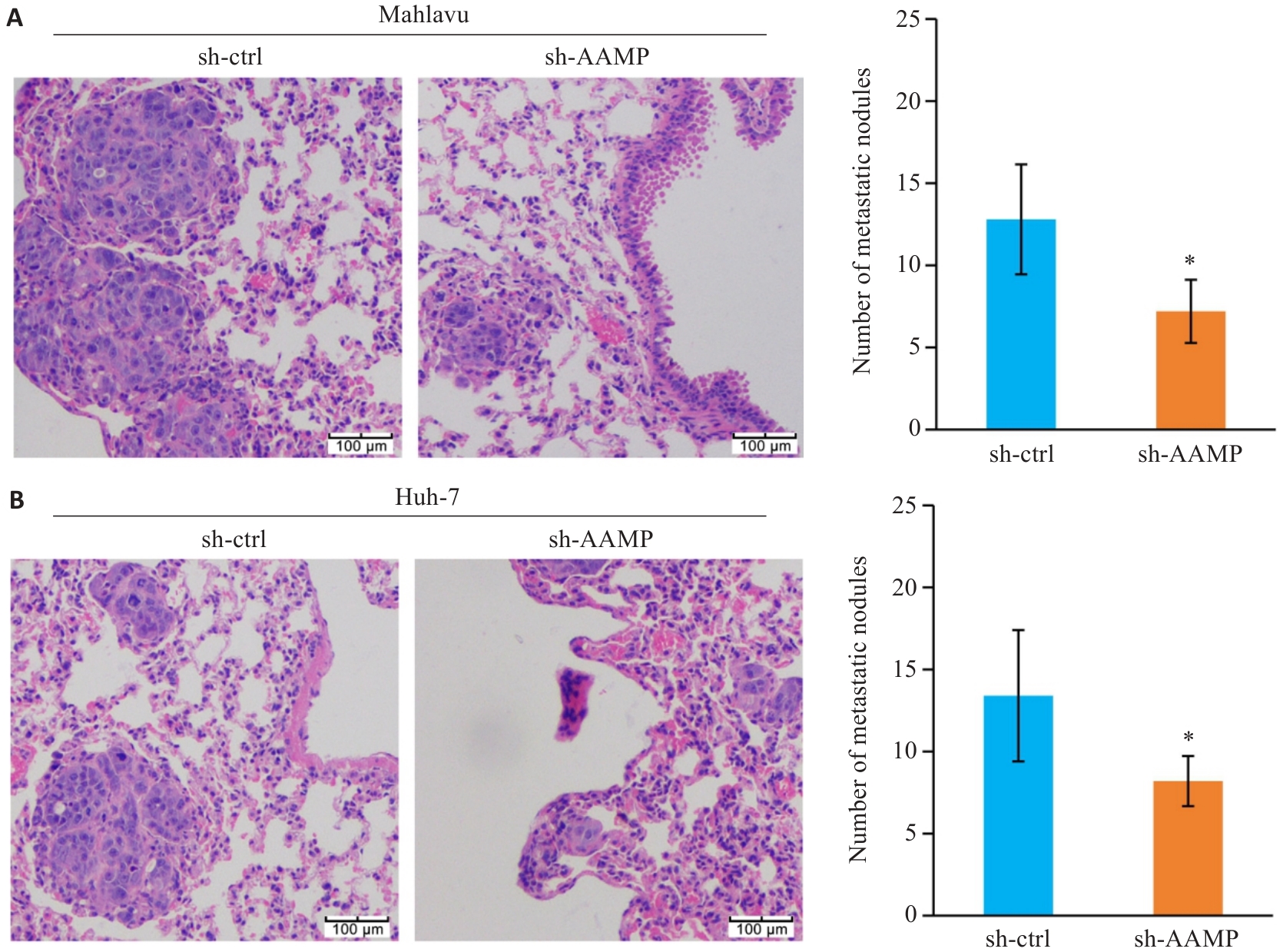
图6 敲低AAMP抑制HCC细胞裸鼠肺转移瘤形成
Fig.6 Knockdown of AAMP suppresses HCC lung metastasis in nude mice. A, B: Knockdown of AAMP decreases lung metastatic nodule numbers formed by Mahlavu (A) and Huh-7 (B) cells in nude mice (×100). *P<0.05 vs sh-ctrl group (n=5).
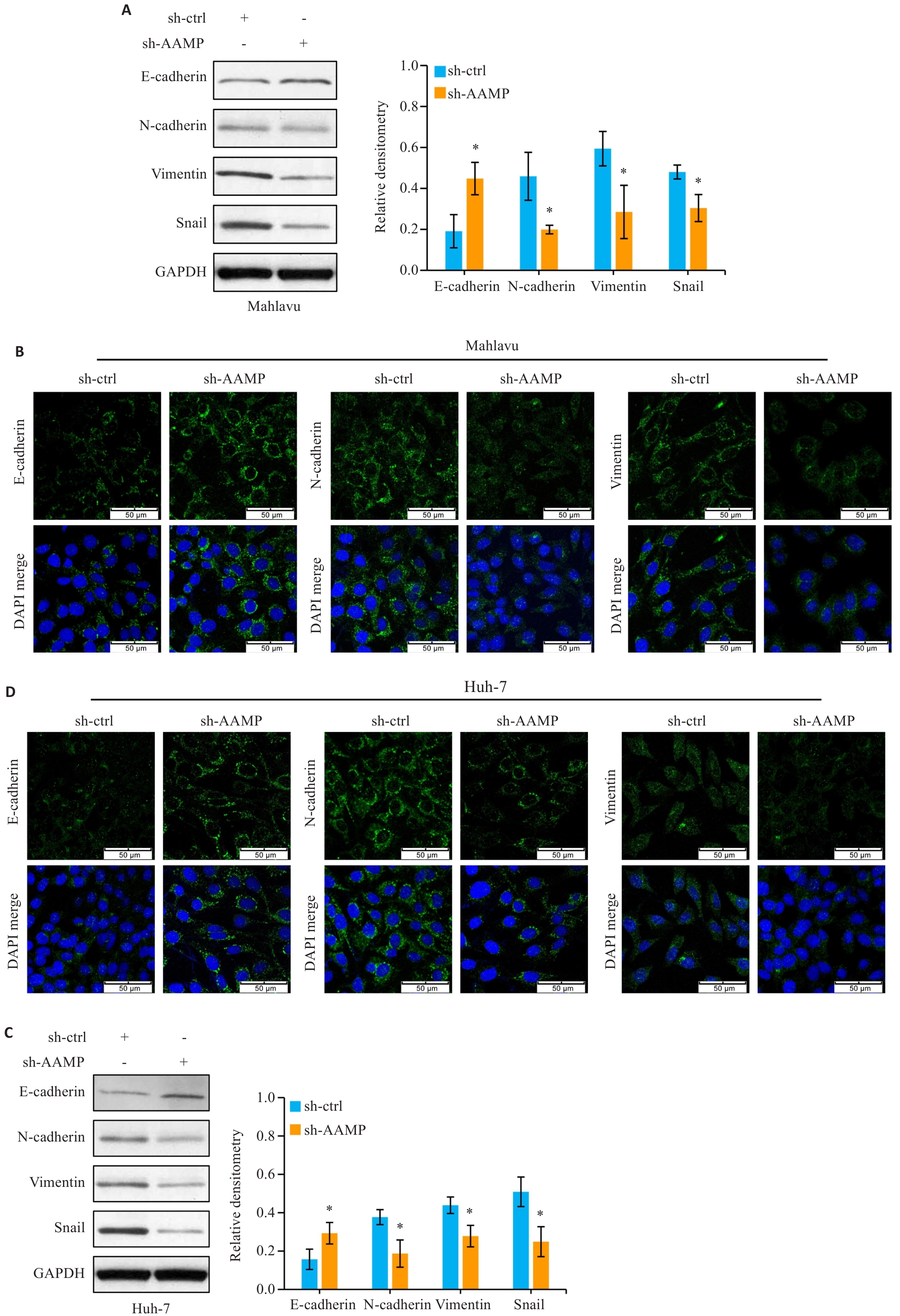
图7 敲低AAMP抑制HCC细胞EMT相关蛋白表达
Fig.7 Knockdown of AAMP inhibits expressions of EMT-related proteins in HCC cells. A, C: AAMP knockdown increases E-cadherin expression and reduces N-cadherin, vimentin and Snail protein expressions in Mahlavu (A) and Huh-7 (C) cells (*P<0.05 vs sh-ctrl group, n=3). B, D: Immunofluorescence staining for detecting the proteins in Mahlavu (B) and Huh-7 (D) cells.

图8 敲低AAMP促进HCC细胞内RhoA蛋白降解
Fig.8 Knockdown of AAMP promotes degradation of RhoA protein in HCC cells. A: Knockdown of AAMP does not affect mRNA expression levels of RhoA in Mahlavu or Huh-7 cells. B: Knockdown of AAMP down-regulates protein expression levels of RhoA in Mahlavu and Huh-7 cells (*P<0.05 vs sh-ctrl group). C: MG-132 treatment restores protein expression levels of RhoA in Mahlavu and Huh-7 cells with AAMP knockdown. D: CHX treatment does not rescue RhoA protein expression in Mahlavu or Huh-7 cells with AAMP knockdown (**P<0.01 vs sh-ctrl group, n=3). E: RhoA and AAMP expressions are positively correlated in HCC tissues.
| [1] | Siegel RL, Kratzer TB, Giaquinto AN, et al. Cancer statistics, 2025[J]. CA A Cancer J Clinicians, 2025, 75(1): 10-45. doi:10.3322/caac.21871 |
| [2] | Beckner ME, Krutzsch HC, Stracke ML, et al. Identification of a new immunoglobulin superfamily protein expressed in blood vessels with a heparin-binding consensus sequence[J]. Cancer Res, 1995, 55(10): 2140-9. |
| [3] | Wang X, Chen S, Gao Y, et al. microRNA-125b inhibits the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by platelet-derived growth factor BB[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(2): 791-8. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10223 |
| [4] | Reid HM, Wikström K, Kavanagh DJ, et al. Interaction of angio-associated migratory cell protein with the TPα and TPβ isoforms of the human thromboxane A₂ receptor[J]. Cell Signal, 2011, 23(4): 700-17. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.12.003 |
| [5] | Xu Y, Tian J, Wang M, et al. Co-regulated CeRNA network mediated by circRNA and lncRNA in patients with gouty arthritis[J]. BMC Med Genomics, 2024, 17(1): 264. doi:10.1186/s12920-024-02038-8 |
| [6] | 陈 奇, 武惠韬, 孙金秀, 等. 胃癌转移的分子特征分析及预后评估[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2019, 40(8):745-9. |
| [7] | Oreskovic E, Wheeler EC, Mengwasser KE, et al. Genetic analysis of cancer drivers reveals cohesin and CTCF as suppressors of PD-L1[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(7): e2120540119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2120540119 |
| [8] | Ning Y, Zheng M, Zhang Y, et al. RhoA-ROCK2 signaling possesses complex pathophysiological functions in cancer progression and shows promising therapeutic potential[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2024, 24(1): 339. doi:10.1186/s12935-024-03519-7 |
| [9] | Zhang X, Zhao YY, Li M, et al. A synergistic regulation works in matrix stiffness-driven invadopodia formation in HCC[J]. Cancer Lett, 2024, 582: 216597. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216597 |
| [10] | 牛小行, 蒋立柱, 罗胜勇, 等. RNF8调控肝细胞癌增殖和迁移的作用及机制[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2025, 41(7): 1305-11. |
| [11] | Podieh F, Overboom MC, Knol JC, et al. AAMP and MTSS1 are novel negative regulators of endothelial barrier function identified in a proteomics screen[J]. Cells, 2024, 13(19): 1609. doi:10.3390/cells13191609 |
| [12] | Vogt F, Zernecke A, Beckner M, et al. Blockade of angio-associated migratory cell protein inhibits smooth muscle cell migration and neointima formation in accelerated atherosclerosis[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2008, 52(4): 302-11. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.03.055 |
| [13] | 李 超, 陈双江, 姜业臻. 过表达miR-607通过下调TRPC5表达抑制肝细胞癌的生长和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11):1587-93. |
| [14] | 陈芊伊, 尚书涵, 鲁 欢, 等. 金盏花苷E通过自噬途径下调GPX4和SLC7A11抑制肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1327-35. |
| [15] | Wang Y, Liu T, Zhang K, et al. Pan-cancer analysis from multi-omics data reveals AAMP as an unfavourable prognostic marker[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2023, 28(1): 258. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01234-z |
| [16] | Ghosh S, Datta R, Thakur S. Network-based meta-analysis of gene expression reveals novel prognostic biomarkers for the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hum Gene, 2024, 42: 201357. doi:10.1016/j.humgen.2024.201357 |
| [17] | 国际肝胆胰协会中国分会, 中国抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会, 中国研究型医院学会肝胆胰外科专业委员会, 等. 乙肝病毒相关肝细胞癌抗病毒治疗中国专家共识(2023版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22(1): 29-41. |
| [18] | Yin Y, Sanders AJ, Jiang WG. The impact of angio-associated migratory cell protein (AAMP) on breast cancer cells in vitro and its clinical significance[J]. Anticancer Res, 2013, 33(4): 1499-509. |
| [19] | Yao S, Shi FF, Wang YY, et al. Angio-associated migratory cell protein interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor and enhances proliferation and drug resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Cell Signal, 2019, 61: 10-9. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.05.004 |
| [20] | Yao S, Shi FF, Mu N, et al. Angio-associated migratory cell protein (AAMP) interacts with cell division cycle 42 (CDC42) and enhances migration and invasion in human non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 502: 1-8. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.11.050 |
| [21] | 林 杰, 区活辉, 王卫东, 等. 过表达CLEC5A基因抑制肝细胞癌增殖和转移并逆转上皮-间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(1):85-91. |
| [22] | 邓乾蓉, 占方彪, 谢朝政, 等. AAMP通过调节YAP信号通路促进骨肉瘤细胞转移的机制研究[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2024, 51(6):440-7. |
| [23] | Wang T, Rao D, Yu C, et al. RHO GTPase family in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Hematol Oncol, 2022, 11(1): 91-102. doi:10.1186/s40164-022-00344-4 |
| [24] | Yan Z, Guo D, Tao R, et al. Fluid shear stress induces cell migration via RhoA-YAP1-autophagy pathway in liver cancer stem cells[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2022, 16(1): 94-106. doi:10.1080/19336918.2022.2103925 |
| [25] | Gao JH, He AD, Liu LM, et al. Direct interaction of platelet with tumor cell aggravates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by activating TLR4/ADAM10/CX3CL1 axis[J]. Cancer Lett, 2024, 585: 216674. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216674 |
| [26] | Li H, Wang ZW, Zhang W, et al. Fbxw7 regulates tumor apoptosis, growth arrest and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in part through the RhoA signaling pathway in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2016, 370(1): 39-55. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.10.006 |
| [27] | Guo DF, Rahmouni K. The Bardet-Biedl syndrome protein complex regulates cell migration and tissue repair through a Cullin-3/RhoA pathway[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2019, 317(3): C457-65. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00498.2018 |
| [28] | Niu H, Bi F, Zhao W, et al. Smurf1 regulates ameloblast polarization by ubiquitination-mediated degradation of RhoA[J]. Cell Prolif, 2023, 56(4): e13387. doi:10.1111/cpr.13387 |
| [29] | Wu Y, Liu B, Lin W, et al. AAMP promotes colorectal can-cermetastasis by suppressing SMURF2-mediatedubiquitination and degradation of RhoA[J]. Mol Ther Oncolytics, 2021, 23: 515-30. doi:10.1016/j.omto.2021.11.007 |
| [30] | Hu JJ, Qiu JH, Zheng YM, et al. AAMP regulates endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis through RhoA/rho kinase signaling[J]. Ann Biomed Eng, 2016, 44(5): 1462-74. doi:10.1007/s10439-015-1442-0 |
| [1] | 马思源, 张博超, 浦春. Circ_0000437通过靶向let-7b-5p/CTPS1轴促进乳腺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移及上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [2] | 王子良, 陈孝华, 杨晶晶, 严晨, 张志郅, 黄炳轶, 赵萌, 刘嵩, 葛思堂, 左芦根, 陈德利. 高表达SURF4通过抑制紧密连接蛋白表达促进胃癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [3] | 黄亚婷, 王振友. 基于耦合扩散的肿瘤转移与骨髓来源的抑制细胞相互作用模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1768-1776. |
| [4] | 龚秀莹, 侯顺福, 赵苗苗, 王晓娜, 张致涵, 刘清华, 尹崇高, 李洪利. LncRNA SNHG15通过miR-30b-3p调控COX6B1轴促进肺腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的分子机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1498-1505. |
| [5] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [6] | 李嘉豪, 冼瑞婷, 李荣. 下调ACADM介导的脂毒性抑制雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌细胞的侵袭与转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1163-1173. |
| [7] | 翁诺舟, 谭彬, 曾文涛, 古家宇, 翁炼基, 郑克鸿. 过表达RGL1通过激活CDC42/RAC1复合体上调运动型黏着斑组装促进结直肠癌转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1031-1038. |
| [8] | 马振南, 刘福全, 赵雪峰, 张晓微. DTX2促进奥沙利铂耐药的结直肠癌细胞增殖、侵袭和上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [9] | 岳雅清, 牟召霞, 王希波, 刘艳. Aurora-A过表达通过激活NF-κBp65/ARPC4信号轴促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 837-843. |
| [10] | 庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [11] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [12] | 缪祥卓, 朱鹏宇, 区活辉, 朱庆, 于林源, 郭柏棠, 廖渭, 黄毓, 相乐阳, 杨定华. 高表达甲状旁腺激素样激素促进肝细胞癌的进展并与患者预后不良相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2135-2145. |
| [13] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | 陈孝华, 鲁辉, 王子良, 王炼, 夏勇生, 耿志军, 张小凤, 宋雪, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国, 左芦根. ABI2在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [15] | 纪凯, 于冠宇, 周乐其, 张天帅, 凌潜龙, 满文江, 朱冰, 张卫. HNRNPA1基因在结直肠癌组织中高表达及其潜在的诊断和治疗价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||