南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2209-2219.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.18
• • 上一篇
杜若丽1,2( ), 云琦2,3, 王奕人1,2, 窦欣雨4, 叶红伟1,2, 王佳慧2, 高琴1,2(
), 云琦2,3, 王奕人1,2, 窦欣雨4, 叶红伟1,2, 王佳慧2, 高琴1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-10
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-11-29
通讯作者:
高琴
E-mail:hello1112drl@126.com;bbmcgq@126.com
作者简介:杜若丽,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: hello1112drl@126.com
基金资助:
Ruoli DU1,2( ), Qi YUN2,3, Yiren WANG1,2, Xinyu DOU4, Hongwei YE1,2, Jiahui WANG2, Qin GAO1,2(
), Qi YUN2,3, Yiren WANG1,2, Xinyu DOU4, Hongwei YE1,2, Jiahui WANG2, Qin GAO1,2( )
)
Received:2024-08-10
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Qin GAO
E-mail:hello1112drl@126.com;bbmcgq@126.com
摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学探讨白花丹素是否通过减轻焦亡来抑制脓毒症心肌损伤的机制。 方法 通过网络药理学方法获得白花丹素与疾病的关键靶点,进行GO、KEGG分析,通过分子对接验证结合能。将小鼠随机分为4组,8只/组:Sham组、盲肠结扎组(CLP)、白花丹素(PLB,2 mg/kg)+CLP组和PLB(4 mg/kg)+CLP组。采用CLP诱导脓毒症小鼠心脏损伤。超声心动图和HE染色检测心肌功能和形态的变化;检测小鼠血清CK-MB、LDH、MDA和心肌ROS水平,ELISA检测小鼠血清IL-1β和IL-18水平。Western blotting测定心肌STAT3、GSDMD、Caspase-11、JAK2、P-STAT3、P-JAK2、GSDMD-N和HMGB1的蛋白水平。 结果 从交集的10个基因中筛选出5个核心靶点,分子对接显示,白花丹素与STAT3、p-STAT3和JAK2结合较好。与Sham组相比,CLP组的CO、LVEF、LVFS和SV水平下降(P<0.01)。血清 CK-MB、LDH、MDA、心肌炎症因子和ROS水平升高(P<0.01),HE染色结果显示心脏损伤;相关蛋白水平升高(P<0.05)。与CLP组相比,白花丹素处理组的心超功能指标水平升高(P<0.05);血清 CK-MB、LDH、MDA、炎症因子和心肌ROS水平降低(P<0.01);相关蛋白水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 白花丹素减轻小鼠脓毒症心肌损伤作用,其机制可能与抑制STAT3减轻焦亡有关。
杜若丽, 云琦, 王奕人, 窦欣雨, 叶红伟, 王佳慧, 高琴. 白花丹素通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路减弱焦亡对抗脓毒症心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2209-2219.
Ruoli DU, Qi YUN, Yiren WANG, Xinyu DOU, Hongwei YE, Jiahui WANG, Qin GAO. Plumbagin protect against sepsis-induced myocardial injury in mice by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway to reduce cardiomyocyte pyroptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2209-2219.
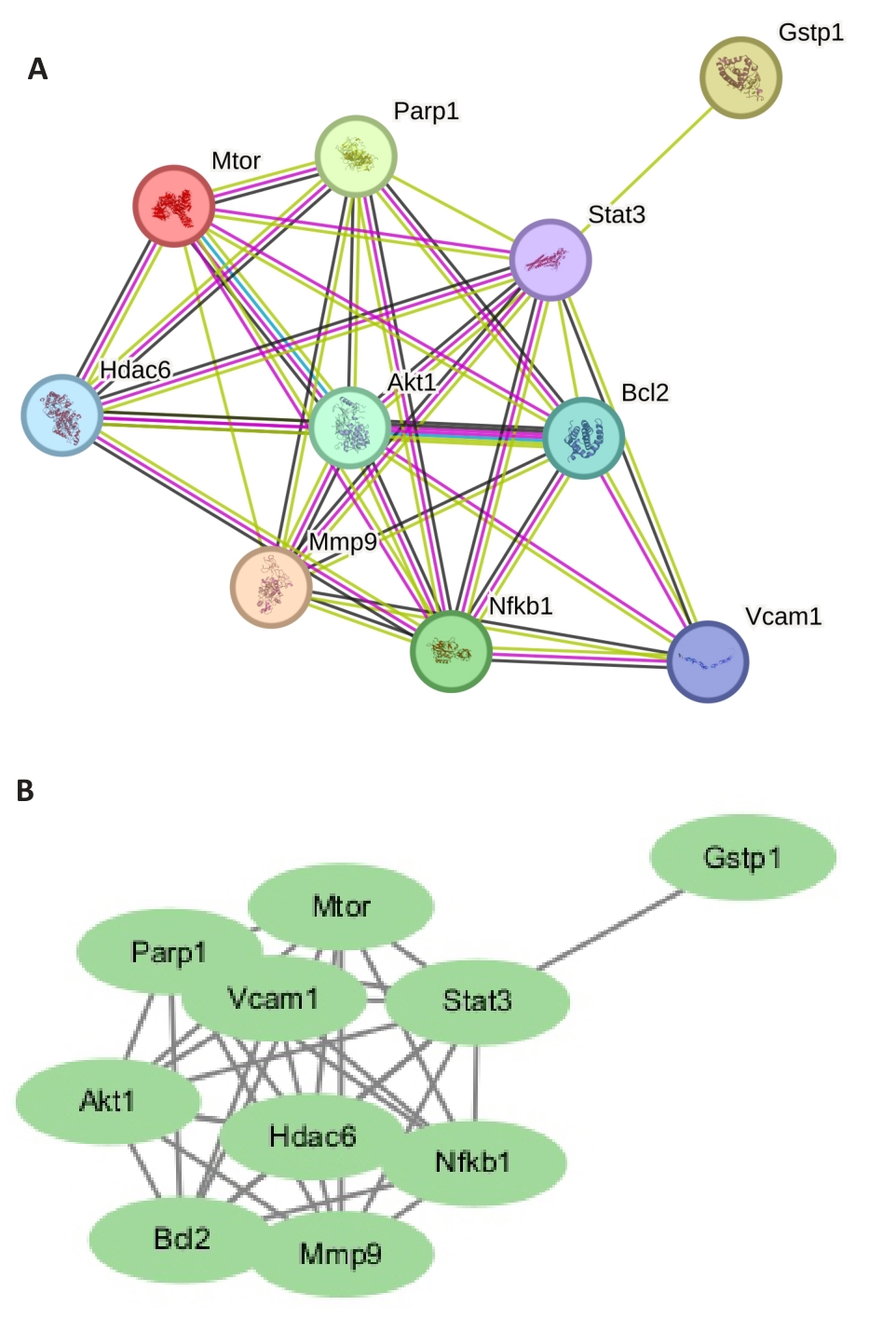
图2 核心PPI网络
Fig.2 Core protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. A: Visual regulatory network of plumbagin-sepsis myocardial injury-pyroptosis. B: PPI network of plumbagin-sepsis myocardial injury-pyroptosis related targets.
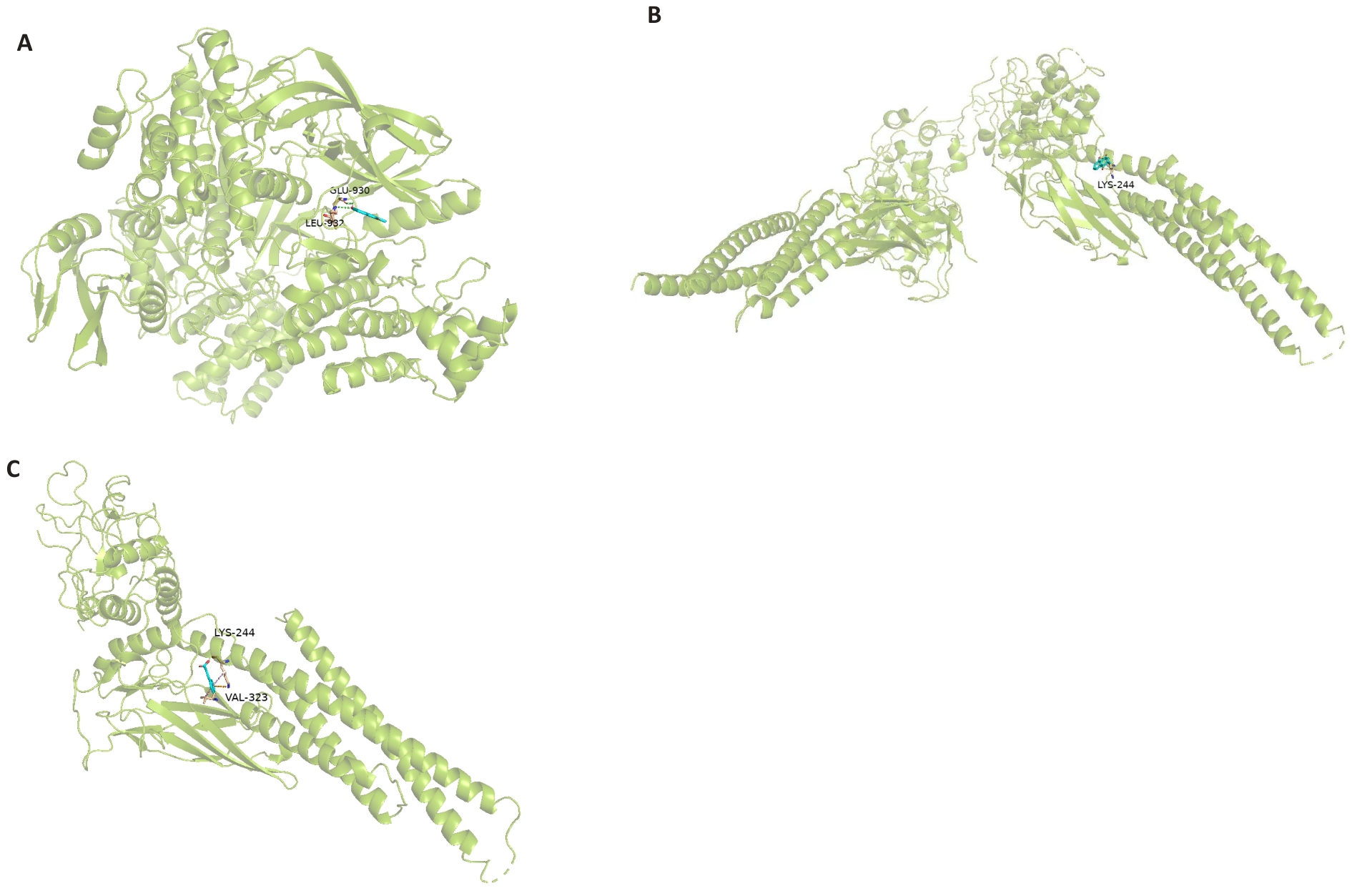
图5 分子对接结果
Fig.5 Molecular docking results. A: Molecular docking diagram of plumbagin and STAT3. B: Molecular docking diagram of plumbagin and JAK2. C: Molecular docking diagram of plumbagin and p-STAT3.
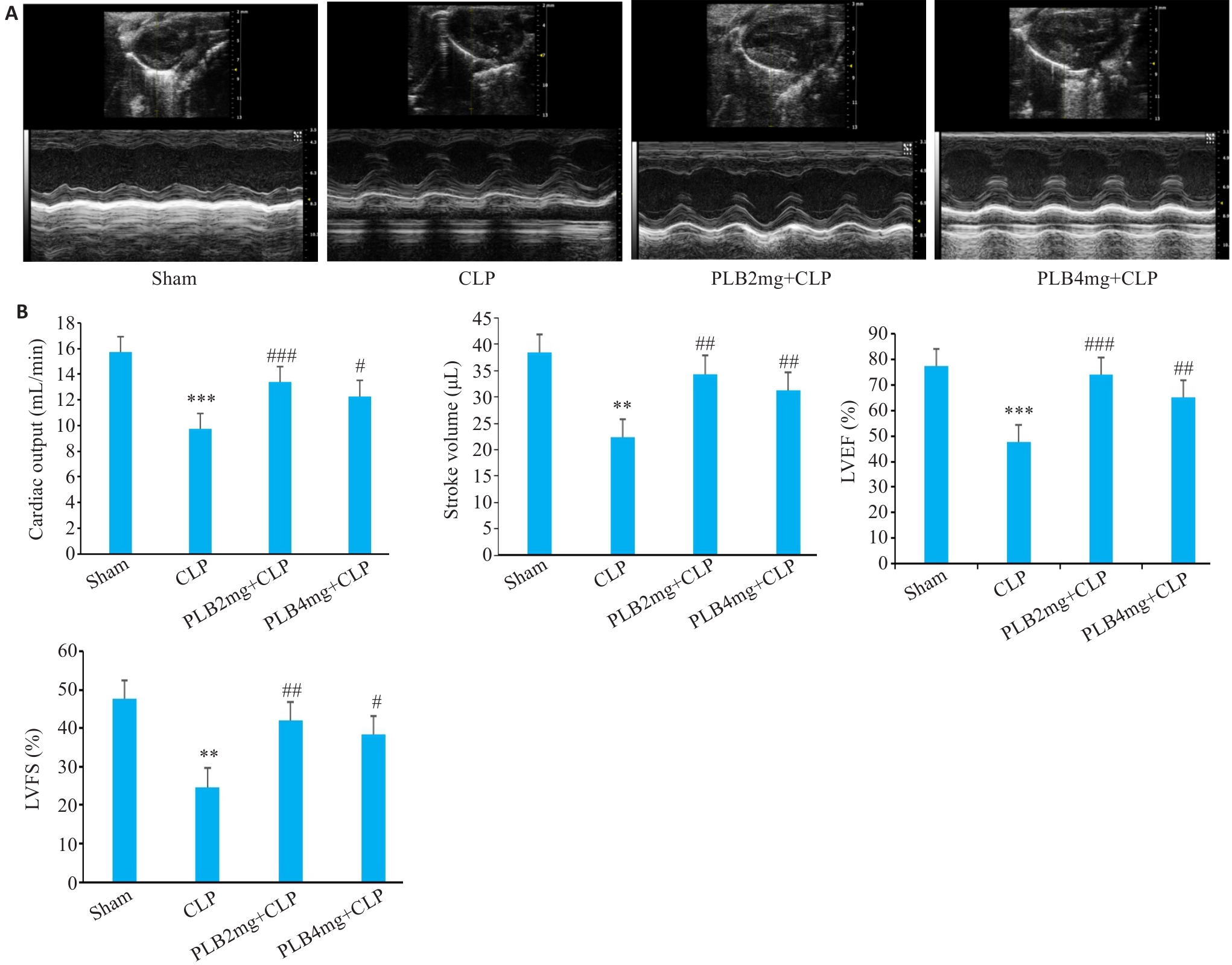
图6 各组小鼠心脏超声图像和心功能各指标变化
Fig.6 Cardiac ultrasound images and cardiac function indexes of the mice in different groups (Mean±SD, n=6). A: Evaluation of cardiac function by M-mode echocardiography. B: Comparison of the echocardiographic parameters (LVEF: Left ventricle ejection fraction; LVFS: Left ventricular fractional shortening). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Sham group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs CLP group.
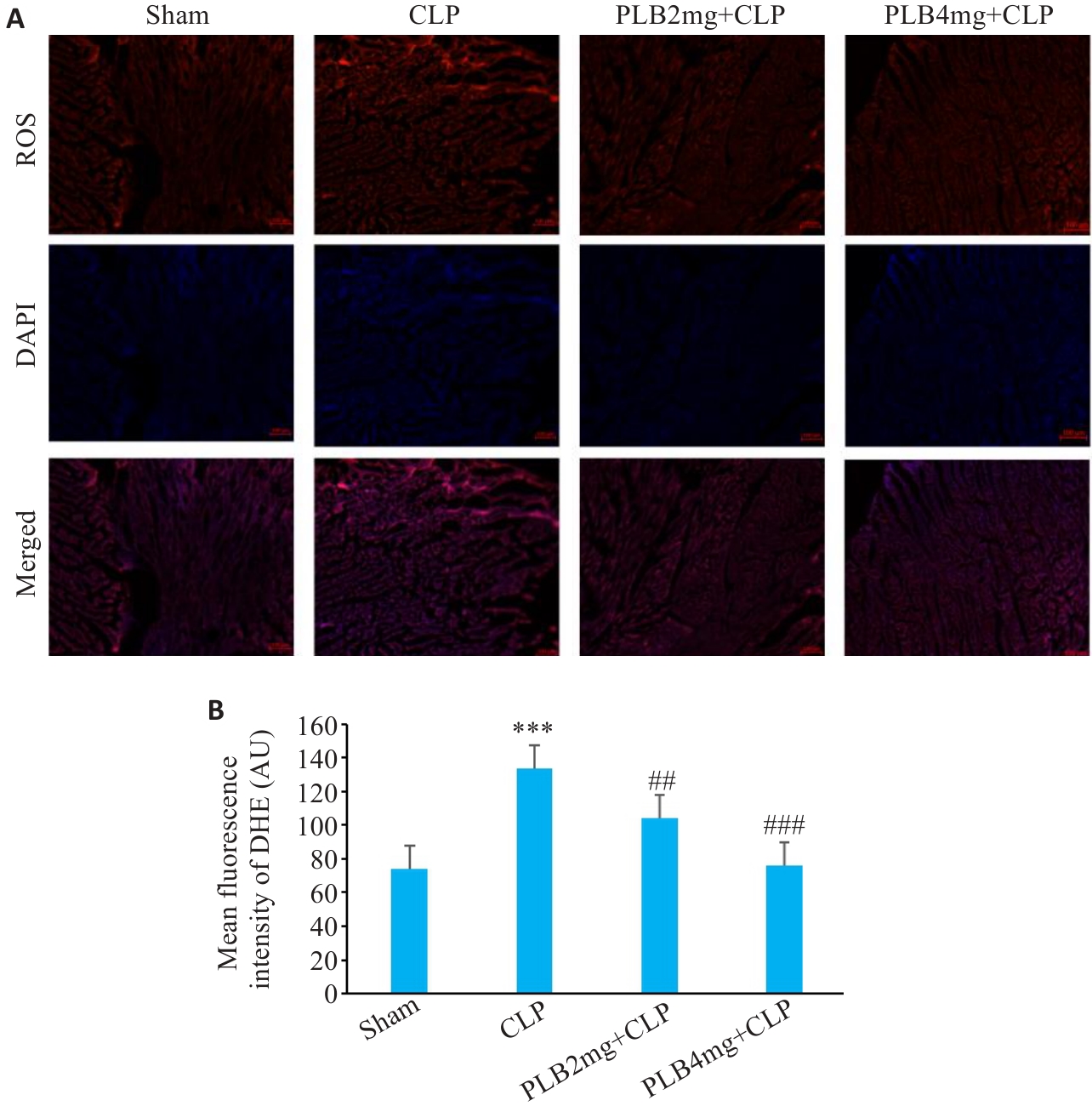
图8 各组小鼠心肌纤维DHE荧光染色代表性图片及分析
Fig.8 DHE fluorescence staining of myocardial fibers in different groups. A: Fluorescence probe for ROS in the cardiac tissues (Original magnification: ×200). B: ROS fluorescence intensity in each group (Mean±SD, n=6). ***P<0.001 vs sham group; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs the CLP group.

图9 各组小鼠血清IL-18和IL-1β的变化
Fig.9 Serum IL-18 (A) and IL-1β (B) levels in the myocardial tissue in different groups (Mean±SD, n=6). ***P<0.001 vs sham group; #P<0.05 vs CLP group.

图10 各组小鼠血清MDA、CK-MB和LDH的变化
Fig.10 Serum MDA (A), CK-MB (B) and LDH (C) levels in the myocardial tissue in different groups (Mean±SD, n=6). ***P<0.001 vs sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 ###P<0.001 vs CLP group.
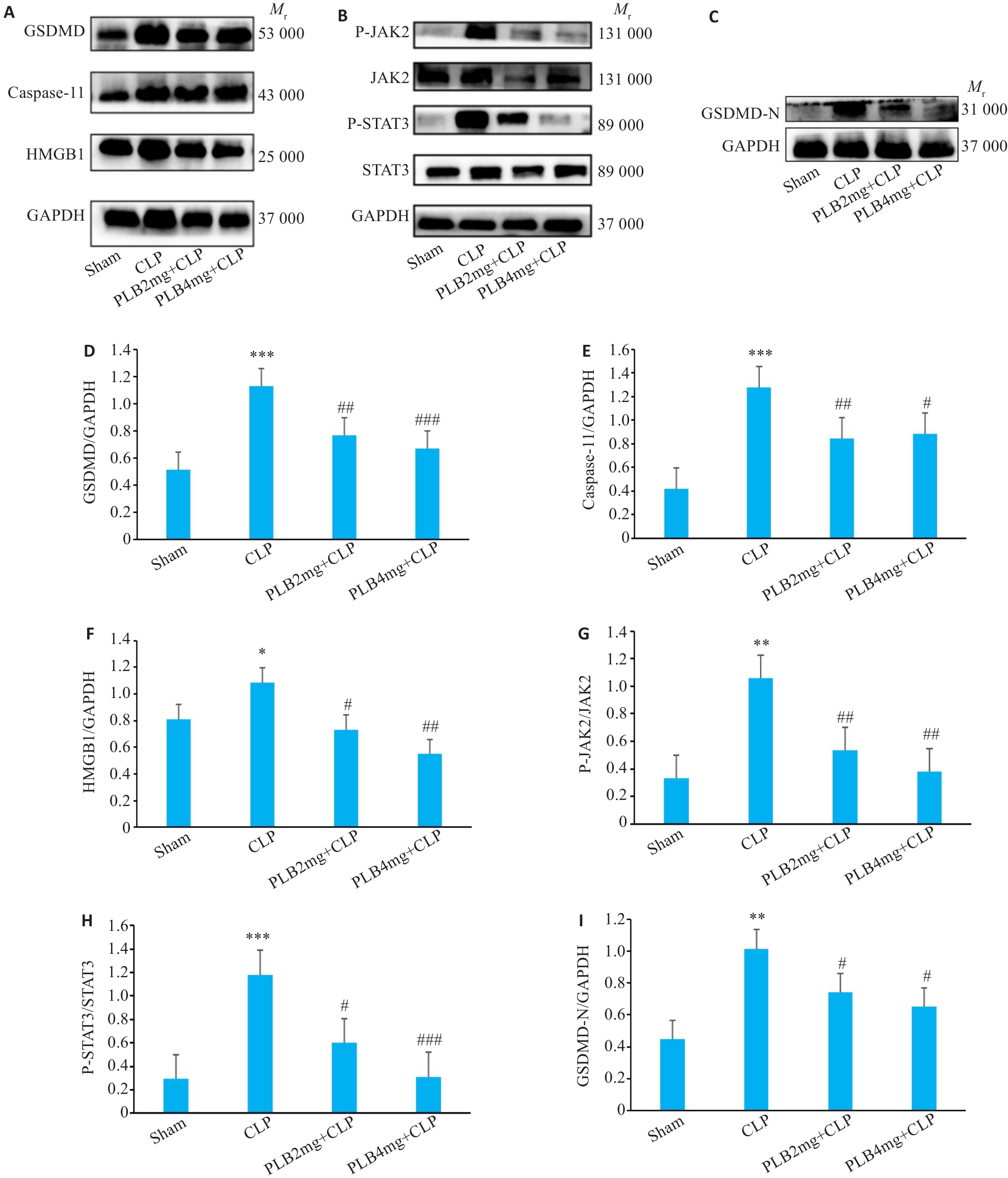
图11 各组小鼠心肌组织GSDMD、Caspase-11、HMGB1、P-JAK2、JAK2、P-STAT3、STAT3和GSDMD-N蛋白水平比较
Fig.11 Comparison of GSDMD、Caspase-11、HMGB1、P-JAK2、JAK2、P-STAT3、STAT3 and GSDMD-N protein levels in the myocardial tissues among the 4 groups. A-C: Protein bands in Western blotting. D-I: Relative protein levels of GSDMD、Caspase-11、HMGB1、P-JAK2、JAK2、P-STAT3、STAT3 and GSDMD-N proteins (Mean±SD, n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs CLP group.
| 1 | Shankar-Hari M, Phillips GS, Levy ML, et al. Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: for the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 775-87. |
| 2 | Li Z, Wu BQ, Chen J, et al. WWP2 protects against sepsis-induced cardiac injury through inhibiting cardiomyocyte ferroptosis[J]. J Transl Int Med, 2024, 12(1): 35-50. |
| 3 | Zhao XJ, Xie JG, Duan CJ, et al. ADAR1 protects pulmonary macrophages from sepsis-induced pyroptosis and lung injury through miR-21/A20 signaling[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2024, 20(2): 464-85. |
| 4 | Liu ZJ, Wei JH, Sun HB, et al. Plumbagin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathways[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2024, 28(13): e18386. |
| 5 | Zhang QR, Fu HT, Gong WJ, et al. Plumbagin protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes against TBHP-induced cytotoxicity by alleviating ROS-induced apoptosis and modulating autophagy[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2022, 24(2): 501. |
| 6 | Li Z, Chinnathambi A, Ali Alharbi S, et al. Plumbagin protects the myocardial damage by modulating the cardiac biomarkers, antioxidants, and apoptosis signaling in the doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats[J]. Environ Toxicol, 2020, 35(12): 1374-85. |
| 7 | Petrocelli G, Marrazzo P, Bonsi L, et al. Plumbagin, a natural compound with several biological effects and anti-inflammatory properties[J]. Life, 2023, 13(6): 1303. |
| 8 | Wang SX, Wang J, Shao JB, et al. Plumbagin mediates cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through nrf-2 signaling[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 22: 1250-7. |
| 9 | Zhao L, Zhang H, Li N, et al. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 309: 116306. |
| 10 | Zhang ZX, Deng WJ, Kang R, et al. Plumbagin protects mice from lethal sepsis by modulating immunometabolism upstream of PKM2[J]. Mol Med, 2016, 22: 162-72. |
| 11 | Huang YH, Li L, Li YP, et al. Knockdown of LncRNA Lcn2-204 alleviates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by regulation of iron overload and ferroptosis[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2024, 192: 79-93. |
| 12 | Wang J, Wang XT, Liu DW, et al. Induction and deduction in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: five typical categories[J]. Chin Med J, 2020, 133(18): 2205-11. |
| 13 | Kumar Arora M, Ratra A, Asdaq SMB, et al. Plumbagin alleviates intracerebroventricular-quinolinic acid induced depression-like behavior and memory deficits in wistar rats[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(6): 1834. |
| 14 | Guo YX, Liu L, Yan DZ, et al. Plumbagin prevents osteoarthritis in human chondrocytes through Nrf-2 activation[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 15(4): 2333-8. |
| 15 | Monnet X, Lai C, Teboul JL. How I personalize fluid therapy in septic shock[J]? Crit Care,2023,27(1):123. |
| 16 | Vigneron C, Py BF, Monneret G, et al. The double sides of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in sepsis[J]. Clin Sci, 2023, 137(5): 333-51. |
| 17 | Yang R, Zhang XJ. A potential new pathway for heparin treatment of sepsis-induced lung injury: inhibition of pulmonary endothelial cell pyroptosis by blocking hMGB1-LPS-induced caspase-11 activation[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 984835. |
| 18 | Sheng SY, Li JM, Hu XY, et al. Regulated cell death pathways in cardiomyopathy[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44(8): 1521-35. |
| 19 | Wu ZF, Deng JH, Zhou HW, et al. Programmed cell death in sepsis associated acute kidney injury[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9: 883028. |
| 20 | Cao ZZ, Qin HQ, Huang YH, et al. Crosstalk of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2-related mechanisms in sepsis-induced lung injury in a mouse model[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(3): 4810-20. |
| 21 | Zangiabadi S, Abdul-Sater AA. Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by posttranslational modifications[J]. J Immunol, 2022, 208(2): 286-92. |
| 22 | Jia YJ, Xiong S, Yao M, et al. HMGB1 inhibition blocks ferroptosis and oxidative stress to ameliorate sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating the Nrf2 pathway[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2024, 40(8): 710-21. |
| 23 | 梁 欢, 黄毓慧, 高 琴.非经典途径细胞焦亡在脓毒症等炎症性疾病中的作用[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2021, 46(11): 1276-84. |
| 24 | Li X, Wei SZ, Niu SQ, et al. Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against sepsis[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2022, 144: 105389. |
| 25 | Yuan ZZ, Pan YY, Leng T, et al. Progress and prospects of research ideas and methods in the network pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. J Pharm Pharm Sci, 2022, 25: 218-26. |
| 26 | Li YR, Jia YJ, Cui TF, et al. IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway regulates the proliferation and damage of intestinal epithelial cells in patients with ulcerative colitis via H3K27ac[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(2): 890. |
| 27 | Foers AD, Garnham AL, Chatfield S, et al. Extracellular vesicles in synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis patients contain miRNAs with capacity to modulate inflammation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(9): 4910. |
| 28 | Wang C, Liu N, Yang HT. Desflurane pretreatment can reduce sepsis-evoked lung injury in rats via inhibiting STAT3 pathway[J]. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, 2020, 34(3): 935-42. |
| 29 | Jiang T, Peng DW, Shi W, et al. IL-6/STAT3 signaling promotes cardiac dysfunction by upregulating FUNDC1-dependent mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes formation in sepsis mice[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 8: 790612. |
| 30 | Li RQ, Li XQ, Zhao J, et al. Mitochondrial STAT3 exacerbates LPS-induced sepsis by driving CPT1a-mediated fatty acid oxidation[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(2): 976-98. |
| 31 | Shen YN, Zhang Y, Du JY, et al. CXCR5 down-regulation alleviates cognitive dysfunction in a mouse model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy: potential role of microglial autophagy and the p38MAPK/NF‑κB/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. J Neuroinfl-ammation, 2021, 18(1): 246. |
| 32 | Xie LP, Wu YT, Zhou CY, et al. Piceatannol protects against sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction via direct inhibition of JAK2[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 96: 107639. |
| 33 | Zhen GS, Liang W, Jia HM, et al. Melatonin relieves sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Minerva Med, 2022, 113(6): 983-9. |
| 34 | 孙 永, 史兆博, 刘美香, 等. 山药多糖对脓毒症大鼠心肌损伤及JAK2/STAT3信号通路的影响[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2022, 30(8): 669-75. |
| 35 | Jiang JX, Zhang D, Liu W, et al. Overexpression of NLRP12 enhances macrophage immune response and alleviates herpes simplex keratitis[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2024, 14: 1416105. |
| [1] | 陈星梅, 刘琴文, 李镱, 钟晓宇, 樊奇灵, 马柯, 罗柳婷, 官道刚, 朱志博. 茵陈蒿汤治疗肝纤维化的核心功能成分群以及潜在通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517. |
| [2] | 张珊苑, 蔡巧燕, 祁江晗, 殷恺馨, 何晨晨, 高铸烨, 张铃, 褚剑锋. 清心解瘀颗粒抗动脉粥样硬化的药效学及调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [3] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [4] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [5] | 王琳月, 戚文月, 高记华, 田茂生, 许建成. 痛痒消洗剂可促进大鼠肛瘘术后的创面愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1256-1265. |
| [6] | 张文祥, 顾惠贤, 陈鹏德, 吴思宇, 马洪艳, 姚蓝. 复方玉液汤通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路抑制糖尿病大鼠心肌细胞凋亡和炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1306-1314. |
| [7] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [8] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [9] | 李睿镈, 高歌, 谢曦, 罗海彬. 槟榔活性成分诱导口腔黏膜下纤维化的机制:基于网络药理学结合临床样本验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 930-940. |
| [10] | 孙一鸣, 张荣, 孟莹, 朱磊, 李明强, 刘哲. 辅酶Q10通过下调焦亡信号通路缓解抑郁小鼠的抑郁样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 810-817. |
| [11] | 李云飞, 杨婧怡, 张 颖, 张财霞, 韦宇翔, 王怡颖, 吴 宁, 孙见飞, 吴遵秋. 苗药四大血减轻大鼠的类风湿性关节炎:基于下调基质金属蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [12] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [13] | 崔艺馨, 王德财, 谢东晴, 王海明, 徐睿鑫, 唐潇然, 张 印. 健脾温阳凝胶剂脐疗治疗脾胃虚弱型慢性腹泻的疗效及机制:一项临床随机对照试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 217-225. |
| [14] | 房尚萍, 孙任珂, 苏 慧, 翟科程, 项 毓, 高杨梦娜, 郭文俊. 绿原酸减轻脓毒症诱导的小鼠急性肾损伤:基于抑制caspase-1经典细胞焦亡信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 317-323. |
| [15] | 宋端怡, 李赟, 唐雪芳, 李化, 陶康. 地西泮通过let-7a-5p/MYD88轴抑制LPS诱导的细胞焦亡和炎症从而缓解小鼠肺纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2092-2101. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||