南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2092-2101.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.05
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-02-08
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-11-29
通讯作者:
宋端怡
E-mail:songduanyi1@163.com
作者简介:宋端怡,硕士,副主任医师,E-mail: songduanyi1@163.com
基金资助:
Duanyi SONG( ), Yun LI, Xuefang TANG, Hua LI, Kang TAO
), Yun LI, Xuefang TANG, Hua LI, Kang TAO
Received:2024-02-08
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Duanyi SONG
E-mail:songduanyi1@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨地西泮(Dia)如何通过介导let-7a-5p与MYD88之间的靶向调控作用,来减轻由脂多糖(LPS)诱导的细胞焦亡和炎症反应,从而缓解肺纤维化的进程。 方法 MRC-5细胞分为正常对照组(NC)、LPS组、LPS+Dia组,LPS+Dia+let-7a-5p mimic组、LPS+Dia+let-7a-5p mimic+pc-DNA-MYD88组。RT-qPCR检测let-7a-5p和MYD88的表达。ELISA检测炎症因子的表达,Western blotting检测纤维化和焦亡相关蛋白的表达。C57BL/6小鼠随机分为NC组、LPS组、LPS+Dia、LPS+Dia+let-7a-5p mimic组、LPS+Dia+ST2825(MYD88抑制剂)组、LPS+Dia+let-7a-5p mimic+pc-DNA-MYD88组。Masson染色观察小鼠肺纤维化,免疫荧光检测α-SMA的表达。 结果 与NC组比较,LPS组let-7a-5p的表达下调(P<0.01),MYD88的表达上调(P<0.01)。炎症相关因子IL-4、IL-6、TGF-β和TNF-α的浓度均升高(P<0.001),此外,纤维化相关蛋白Col-Ⅰ、Col-Ⅲ、α-SMA和细胞焦亡相关蛋白NLRP3、Caspase-1、ASC、GSDMD-N的表达量也升高(P<0.05)。与LPS组相比,LPS+Dia组有效抑制了炎症相关因子、纤维化相关蛋白、细胞焦亡相关蛋白的表达。动物实验中,与LPS组相比,LPS+Dia组小鼠肺组织纤维化程度降低,α-SMA相对荧光密度降低(P<0.05)。此外,与LPS+Dia组相比,LPS+Dia+let-7a-5p mimic组或LPS+Dia+ST2825的处理进一步促进了Dia的作用(P<0.05)。而过表达MYD88又削弱了let-7a-5p mimic对Dia的作用(P<0.05)。 结论 Dia可以通过上调let-7a-5p的表达负调控MYD88抑制LPS诱导的细胞焦亡和炎症反应从而缓解肺纤维化。
宋端怡, 李赟, 唐雪芳, 李化, 陶康. 地西泮通过let-7a-5p/MYD88轴抑制LPS诱导的细胞焦亡和炎症从而缓解小鼠肺纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2092-2101.
Duanyi SONG, Yun LI, Xuefang TANG, Hua LI, Kang TAO. Diazepam alleviates pulmonary fibrosis in mice by inhibiting LPS-induced pyroptosis and inflammation via the let-7a-5p/MYD88 axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2092-2101.
| Target | Sequence |
|---|---|
| let-7a-5p | F: 5'-TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT-3' |
| R: 5'-AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT-3' | |
| MYD88 | F: 5'-GGCTGCTCTCAACATGCGA-3' |
| R: 5'-CTGTGTCCGCACGTTCAAGA-3' | |
| U6 | F: 5'-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3' |
| R: 5'-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3' | |
| GAPDH | F: 5'-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3' |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Sequences of primers for RT-qPCR
| Target | Sequence |
|---|---|
| let-7a-5p | F: 5'-TGAGGTAGTAGGTTGTATAGTT-3' |
| R: 5'-AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT-3' | |
| MYD88 | F: 5'-GGCTGCTCTCAACATGCGA-3' |
| R: 5'-CTGTGTCCGCACGTTCAAGA-3' | |
| U6 | F: 5'-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3' |
| R: 5'-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3' | |
| GAPDH | F: 5'-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3' |
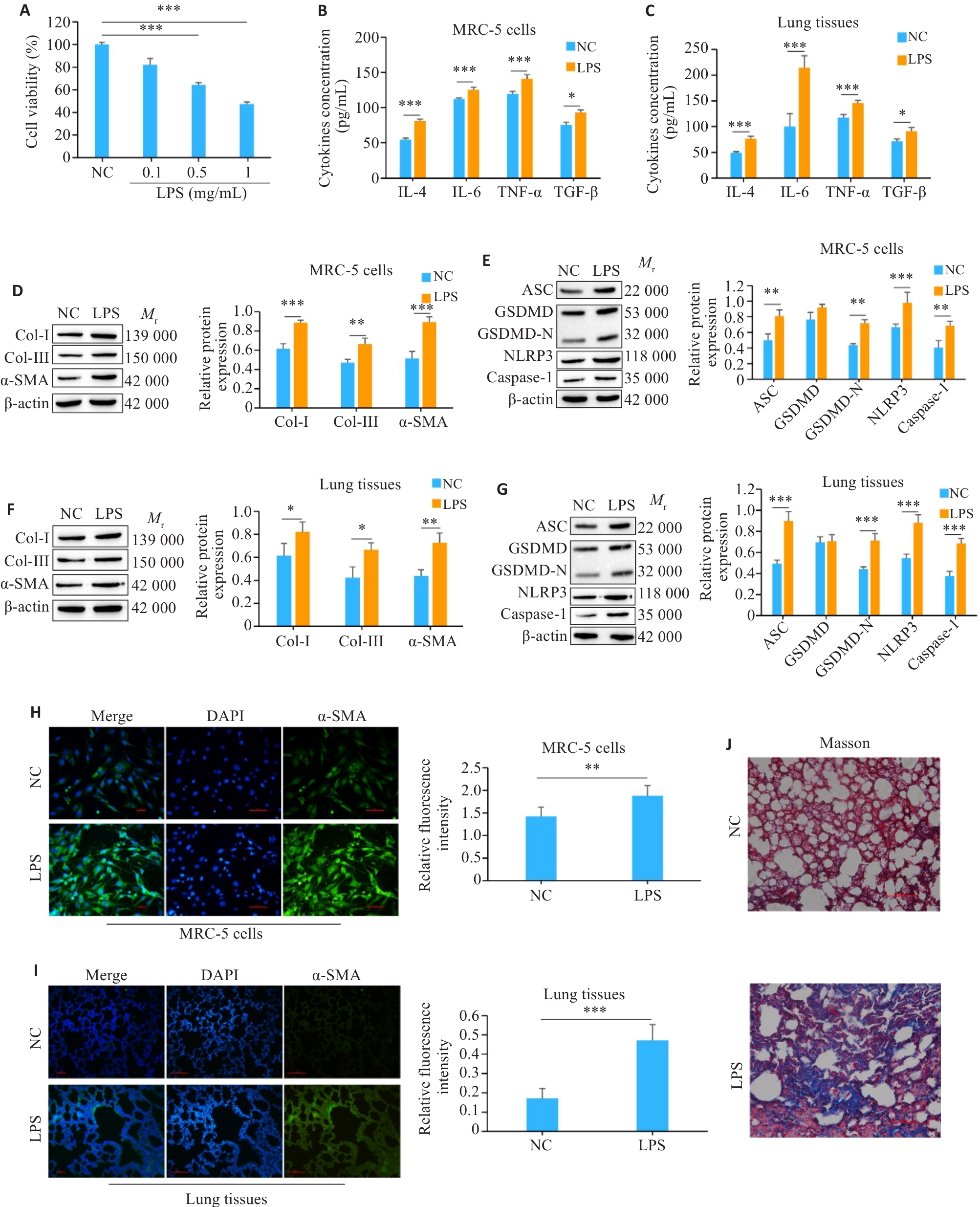
图1 LPS诱导细胞焦亡和炎症并且引起肺纤维化
Fig.1 LPS induces pyroptosis and inflammation and causes pulmonary fibrosis. A: Effects of different concentrations of LPS on proliferation of MRC-5 cells. B: Detection of the levels of inflammation-related factors in MRC-5 cells by ELISA. C: Detection of the levels of inflammatory factors in mouse lung tissues by ELISA. D, E: Detection of the expressions of fibrosis- and pyroptosis-related proteins in MRC-5 cells by Western blotting. F, G: Detection of the expressions of fibrosis- and pyroptosis-related proteins in mouse lung tissues by Western blotting. H, I: Immunofluorescence staining of α-SMA in MRC-5 cells and mouse lung tissues (Scale bar=100 μm). J: Masson staining of mouse lung tissues (Scale bar=100 μm). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
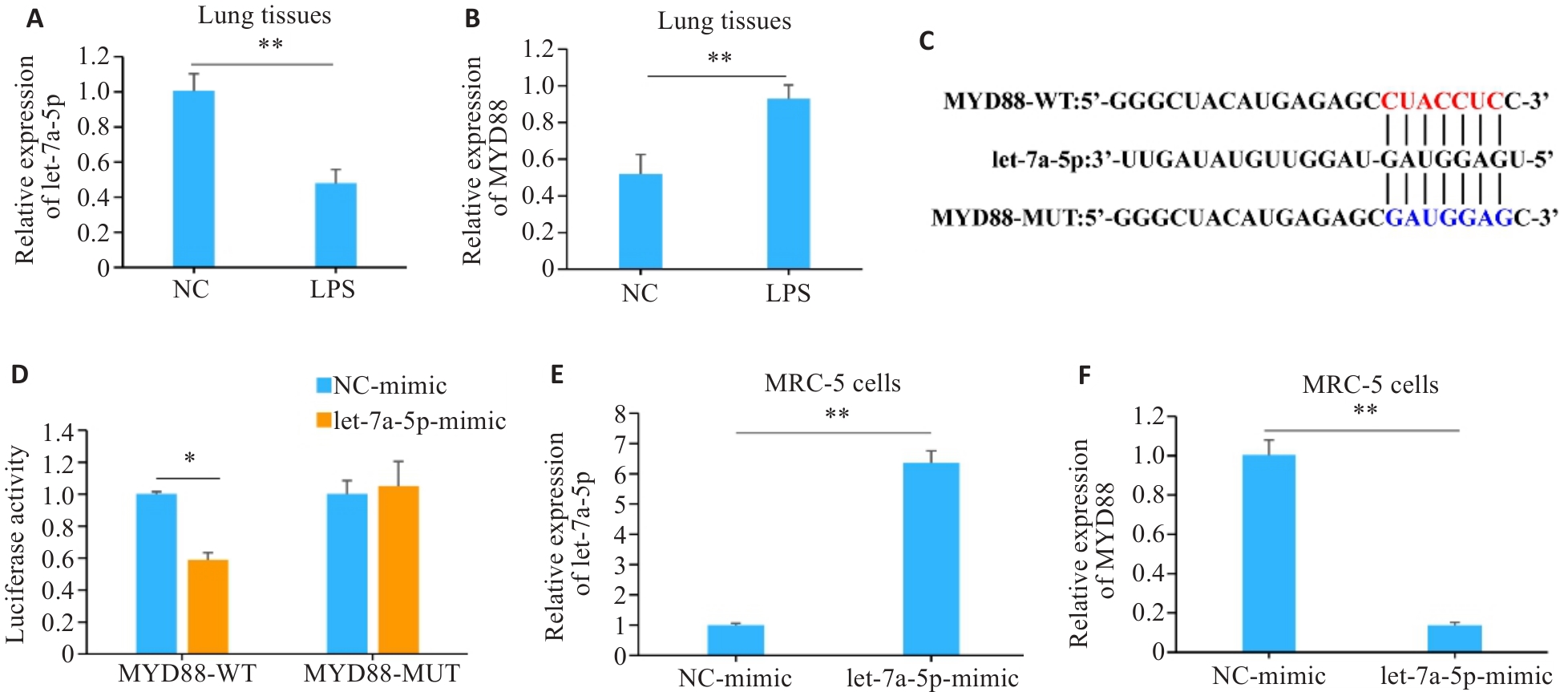
图2 let-7a-5p和MYD88在肺组织中的表达及其靶向关系验证
Fig.2 Verification of expressions of let-7a-5p and MYD88 in mouse lung tissues and their targeting relationship. A: Detection of let-7a-5p expression in lung tissues by RT-qPCR. B: Detection of MYD88 expression in mouse lung tissues by RT-qPCR. C: Target-binding sequences of let-7a- 5p and MYD88. D: Verification of the targeting relationship between let-7a-5p and MYD88 by dual-luciferase assay. E: Confirmation of the transfection efficiency of let-7a-5p mimic. F: Detection of the expression of MYD88 by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
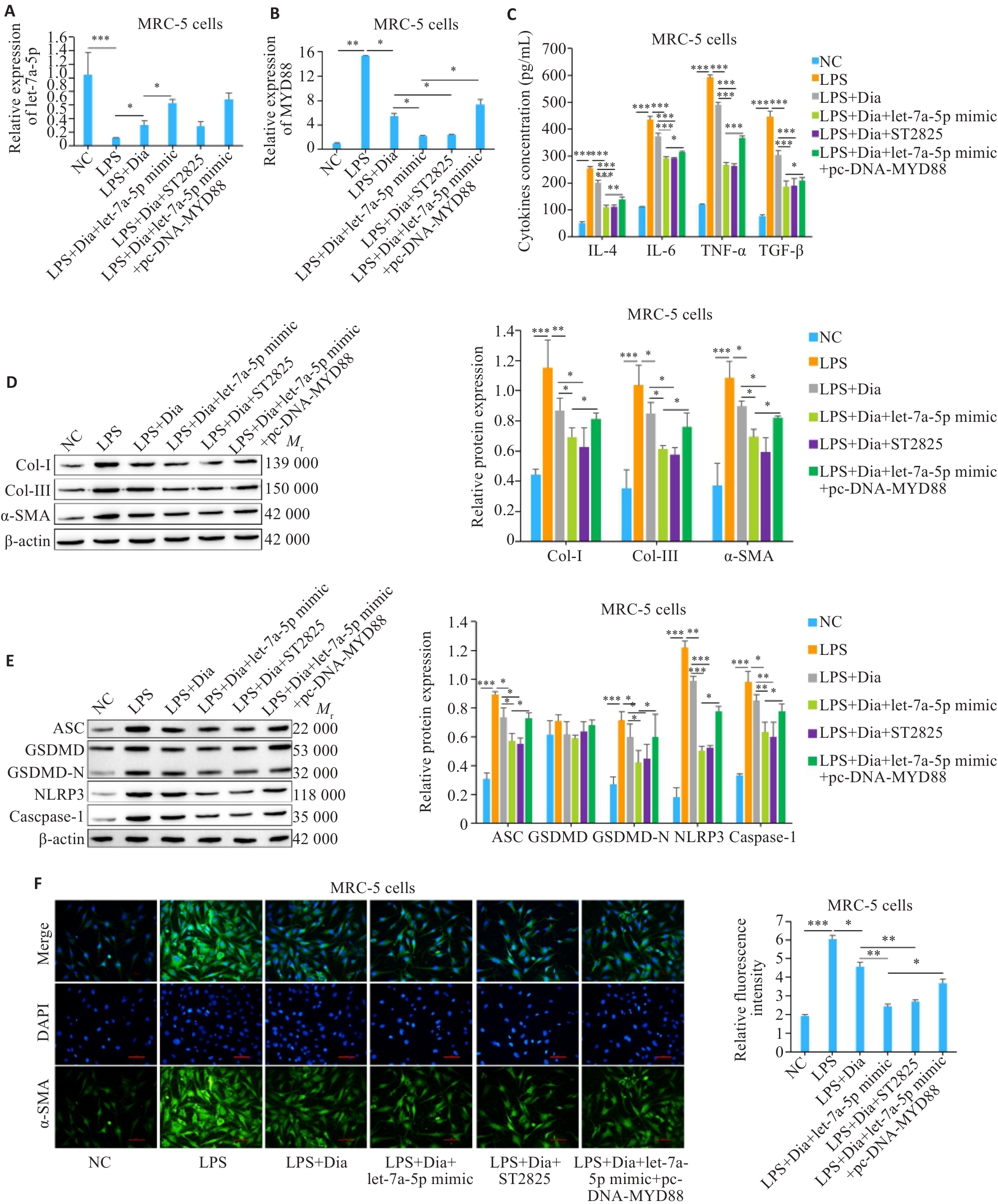
图4 Dia通过let-7a-5p/MYD88轴抑制LPS诱导的MRC-5细胞焦亡和炎症反应
Fig.4 Diazepam inhibits LPS-induced pyroptosis and inflammatory response in MRC-5 cells through the let-7a-5p/MYD88 axis. A: Expression of let-7a-5p in MRC-5 cells. B: Expression of MYD88 in MRC-5 cells. C: Levels of inflammatory factors in MRC-5 cells detected by ELISA. D: Expressions of fibrosis-related proteins in MRC-5 cells detected by Western blotting. E: Expressions of pyroptosis-related proteins in MRC-5 cells detected by Western blotting. F: Immunofluorescence staining of α-SMA in MRC-5 cells (Scale bar=100 μm).*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
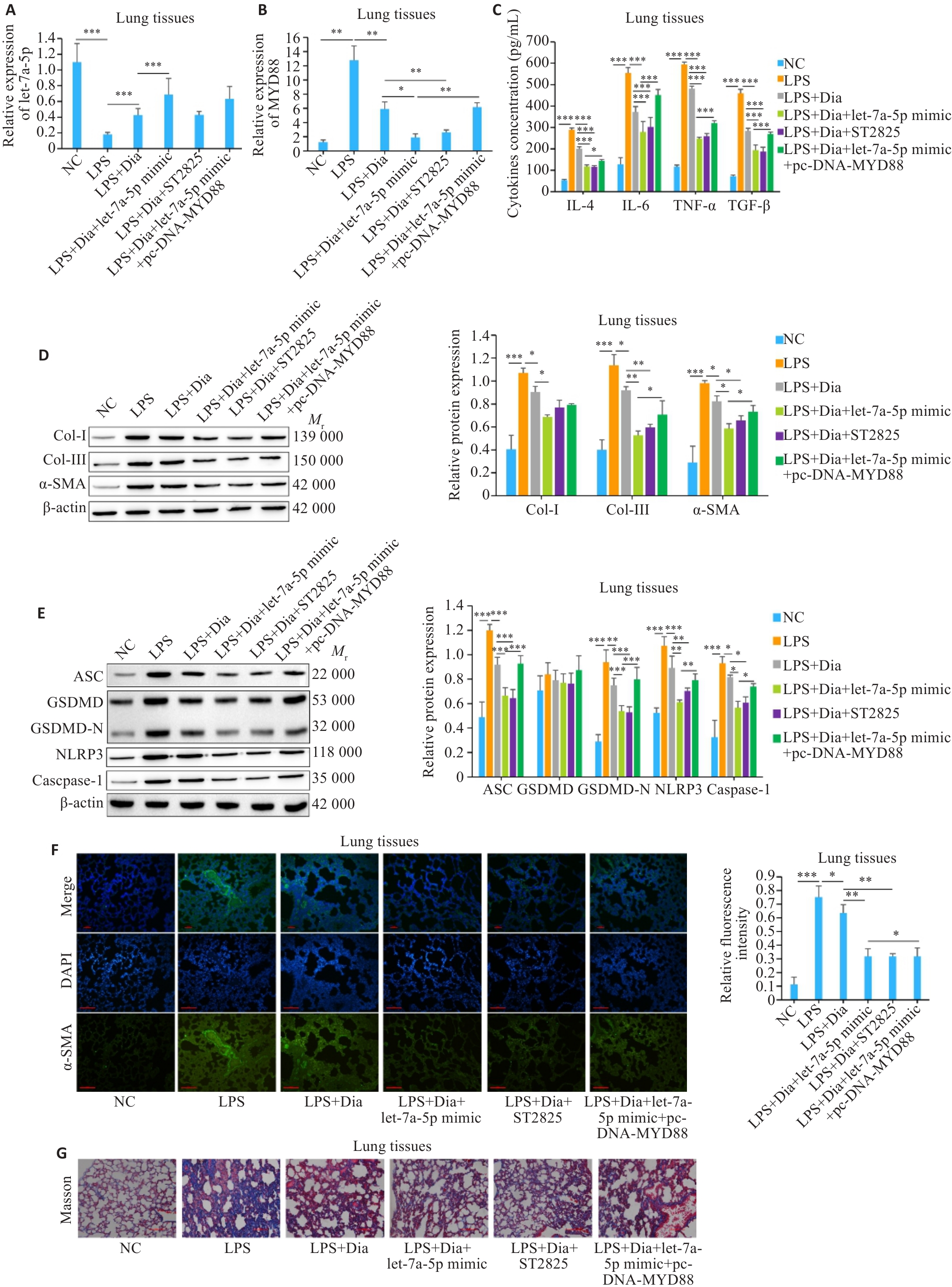
图5 Dia通过let-7a-5p/MYD88轴抑制LPS诱导的细胞焦亡和炎症反应缓解肺纤维化
Fig.5 Diazepam inhibits LPS-induced pyroptosis and inflammatory response and alleviates pulmonary fibrosis in mice through the let-7a-5p/MYD88 axis. A, B: Expression of let-7a-5p and MYD88 in mouse lung tissues. C: Levels of inflammatory factors in mouse lung tissues detected by ELISA. D, E: Expressions of fibrosis- and pyroptosis-related proteins in mouse lung tissues detected by Western blotting. F: Immunofluorescence staining of α-SMA in mouse lung tissues (Scale bar=100 μm). G: Masson staining of mouse lung tissues (Scale bar=100 μm).*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| 1 | Kishaba T. Evaluation and management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis[J]. Respir Investig, 2019, 57(4): 300-11. |
| 2 | Shi J, Zhou LR, Wang XS, et al. KLF2 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and inflammation with regulation of AP-1[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 495(1): 20-6. |
| 3 | Suzuki T, Tada, Gladson S, et al. Vildagliptin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Respir Res, 2017, 18(1): 177. |
| 4 | Zhou Y, Li P, Duan JX, et al. Aucubin alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model[J]. Inflammation, 2017, 40(6): 2062-73. |
| 5 | Cesta MF, Ryman-Rasmussen JP, Wallace DG, et al. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide enhances PDGF signaling and pulmonary fibrosis in rats exposed to carbon nanotubes[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2010, 43(2): 142-51. |
| 6 | Wang DS, Zurek AA, Lecker I, et al. Memory deficits induced by inflammation are regulated by α5-subunit-containing GABAA receptors[J]. Cell Rep, 2012, 2(3): 488-96. |
| 7 | Yocum GT, Turner DL, Danielsson J, et al. GABAA receptor α4-subunit knockout enhances lung inflammation and airway reactivity in a murine asthma model[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2017, 313(2): L406-15. |
| 8 | Cui JJ, Zhou ZQ, Yang HY, et al. MST1 suppresses pancreatic cancer progression via ROS-induced pyroptosis[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2019, 17(6): 1316-25. |
| 9 | Lee S, Suh GY, Ryter SW, et al. Regulation and function of the nucleotide binding domain leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor, pyrin domain-containing-3 inflammasome in lung disease[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2016, 54(2): 151-60. |
| 10 | Panganiban RA, Sun MY, Dahlin A, et al. A functional splice variant associated with decreased asthma risk abolishes the ability of gasdermin B to induce epithelial cell pyroptosis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 142(5): 1469-78. e2. |
| 11 | He DK, Chen JF, Shao YR, et al. Adenovirus-delivered angiopoietin-1 ameliorates phosgene-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Inhal Toxicol, 2018, 30(4/5): 187-94. |
| 12 | Hou L, Yang ZW, Wang ZK, et al. NLRP3/ASC-mediated alveolar macrophage pyroptosis enhances HMGB1 secretion in acute lung injury induced by cardiopulmonary bypass[J]. Lab Invest, 2018, 98(8): 1052-64. |
| 13 | Xu WJ, Wang XX, Jin JJ, et al. Inhibition of GGPPS1 attenuated LPS-induced acute lung injury and was associated with NLRP3 inflammasome suppression[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2019, 316(3): L567-L577. |
| 14 | Li ZY, Jia YF, Feng Y, et al. Methane alleviates sepsis-induced injury by inhibiting pyroptosis and apoptosis: in vivo and in vitro experiments[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(4): 1226-39. |
| 15 | Liu L, Sun BW. Neutrophil pyroptosis: new perspectives on sepsis[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(11): 2031-42. |
| 16 | Yokoyama S, Cai Y, Murata M, et al. A novel pathway of LPS uptake through syndecan-1 leading to pyroptotic cell death[J]. Elife, 2018, 7: e37854. |
| 17 | O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, et al. Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2018, 9: 402. |
| 18 | Ma YX, Shen N, Wicha MS, et al. The roles of the let-7 family of microRNAs in the regulation of cancer stemness[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2415. |
| 19 | Duan SY, Li JX, Tian JQ, et al. Crosstalk between let-7a-5p and BCL-xL in the Initiation of Toxic Autophagy in Lung Cancer[J]. Mol Ther Oncolytics, 2019, 15: 69-78. |
| 20 | Chen SY, Chen YL, Li PC, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles carrying let-7a-5p for alleviating inflammation in acute lung injury[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2024, 31(1): 30. |
| 21 | Deguine J, Barton GM. MyD88: a central player in innate immune signaling[J]. F1000Prime Rep, 2014, 6: 97. |
| 22 | Oda K, Kitano H. A comprehensive map of the toll-like receptor signaling network[J]. Mol Syst Biol, 2006, 2: 2006.0015. |
| 23 | Akira S. Toll-like receptor signaling[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(40): 38105-8. |
| 24 | Li Y, Song DY, Bo FY, et al. Diazepam inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‑induced pyroptotic cell death and alleviated pulmonary fibrosis in mice by specifically activating GABAA receptor α4-subunit[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 118: 109239. |
| 25 | Gu NN, Xing SP, Chen SH, et al. Lipopolysaccharide induced the proliferation of mouse lung fibroblasts by suppressing FoxO3a/p27 pathway[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2018, 42(10): 1311-20. |
| 26 | Dong ZW, Yuan YF. Juglanin suppresses fibrosis and inflammation response caused by LPS in acute lung injury[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 41(6): 3353-65. |
| 27 | de Lima CB, Sakai M, Latorre AO, et al. Effects of different doses and schedules of diazepam treatment on lymphocyte parameters in rats[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2010, 10(11): 1335-43. |
| 28 | Nicolás FH, Cristian F, Lucía R, et al. Diazepam effects on immune cells actively involved during the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2015, 6: 224. |
| 29 | Fernández Hurst N, Zanetti SR, Báez NS, et al. Diazepam treatment reduces inflammatory cells and mediators in the central nervous system of rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2017, 313: 145-51. |
| 30 | Sanders RD, Grover V, Goulding J, et al. Immune cell expression of GABAA receptors and the effects of diazepam on influenza infection[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2015, 282: 97-103. |
| 31 | Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou RB. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18(9): 2114-27. |
| 32 | Song C, He LJ, Zhang J, et al. Fluorofenidone attenuates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via inhibiting the activation of NALP3 inflammasome and IL-1β/IL-1R1/MyD88/NF‑κB pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2016, 20(11): 2064-77. |
| 33 | Wang T, Zhu H, Yang SF, et al. Let-7a-5p may participate in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy through targeting HMGA2[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19(5): 4229-37. |
| 34 | Zhang L, Hao CF, Zhai RN, et al. Downregulation of exosomal let-7a-5p in dust exposed-workers contributes to lung cancer development[J]. Respir Res, 2018, 19(1): 235. |
| 35 | Di Padova F, Quesniaux VFJ, Ryffel B. MyD88 as a therapeutic target for inflammatory lung diseases[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2018, 22(5): 401-8. |
| 36 | Liu L, Zhou L, Wang LL, et al. MUC1 attenuates neutrophilic airway inflammation in asthma by reducing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis through the inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J]. Respir Res, 2023, 24(1): 255. |
| 37 | Li CC, Yu Y, Li WJ, et al. Phycocyanin attenuates pulmonary fibrosis via the TLR2-MyD88-NF‑κB signaling pathway[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 5843. |
| [1] | 何 程, 陈 炜, 张念志, 栾 军, 王三凤, 张 尤. 参七虫草方通过ASS1/src/STAT3信号通路改善肺纤维化大鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 644-651. |
| [2] | 房尚萍, 孙任珂, 苏 慧, 翟科程, 项 毓, 高杨梦娜, 郭文俊. 绿原酸减轻脓毒症诱导的小鼠急性肾损伤:基于抑制caspase-1经典细胞焦亡信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 317-323. |
| [3] | 舒萍, 袁孟珂, 杨珂, 何伟志, 刘丽. 槲皮素通过抑制NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD信号通路抑制小鼠成纤维细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1874-1880. |
| [4] | 孔 祥, 张 腾, 张 妍, 高灵犀, 汪 文, 汪梦燕, 王国栋, 吕 坤. 过表达lncRNA HEM2M改善非酒精性脂肪肝病小鼠的肝脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 1-8. |
| [5] | 梁梓琛, 余常辉, 梁世秀, 周梓聪, 周子丽, 孟晓静, 邹 飞, 蔡绍曦. 桔梗素D通过下调成纤维细胞TRPC6表达改善小鼠肺纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 60-69. |
| [6] | 吴 迪, 王小乐, 高雅婷, 童佳兵, 杨勤军, 丁焕章, 张 璐, 李泽庚. 参芪温肺方减轻慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠的肺气虚证:基于调节NLRP3/GSDMD细胞焦亡通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1500-1508. |
| [7] | 李洪涛, 邓 宇, 王添乐, 黄克勇, 于传沛, 陈朝俊. 丹参新醌乙减轻ox-LDL诱导的内皮细胞损伤:基于抑制NF-κB/NLRP3信号通路介导的细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1425-1431. |
| [8] | 张 蒙, 张源源, 牛梦竹, 朱 悦, 童诗逸, 寇现娟. 双氢杨梅素通过诱导自噬减轻慢性帕金森病小鼠的细胞焦亡和坏死性凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1268-1278. |
| [9] | 李佩佩, 胡音琦, 刘 佳, 王丽娜, 吴元洁, 胡建鹏. 脑络欣通促进氧糖剥夺/再灌注损伤大鼠的脑微血管内皮细胞血管新生:基于激活caspase-1/Gasdermin D通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | 姜 勇, 葛文婷, 赵 莹, 吴煜格, 霍一鸣, 潘岚婷, 曹 爽. LINC00926通过募集ELAVL1促进低氧诱导的人脐静脉血管内皮细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 807-814. |
| [11] | 熊凤梅, 刘瑞萍, 李 洋, 孙 娜. 和厚朴酚可体外减轻阿霉素诱导的心肌毒性:基于激活AMPK/Nrf2信号通路抑制细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1205-1211. |
| [12] | 王露琳, 汪 元, 刘 健, 黄传兵, 张皖东, 万 磊, 孙 玥, 黄 旦. 新风胶囊含药血清抑制脂多糖诱导的类风湿关节炎大鼠的滑膜成纤维细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1846-1851. |
| [13] | 房尚萍, 袁 冉, 孙任珂, 马同军. 敲除S1PR3可缓解小鼠的急性肺损伤:基于抑制MAPK信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1815-1821. |
| [14] | 王佳慧, 梁 欢, 方 典, 黄毓慧, 苗雅琼, 于 影, 高 琴. 抑制线粒体活性氧自由基可减轻高糖诱导的心肌细胞焦亡和铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 980-987. |
| [15] | 吴 宁, 袁桃花, 姬进忠, 程 瑶, 李明义, 梁 玺, 孙见飞, 刘 华, 吴昌学. 苗药验方四大血对人类风湿性关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞凋亡和焦亡的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(10): 1473-1483. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||