南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2163-2171.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.13
• • 上一篇
凌潜龙1,2( ), 纪凯1,3, 陈金业1, 管佳佳1, 王睿朋1, 满文江1,3, 朱冰1(
), 纪凯1,3, 陈金业1, 管佳佳1, 王睿朋1, 满文江1,3, 朱冰1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-16
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-11-29
通讯作者:
朱冰
E-mail:203551716@qq.com;bbmczhubing@163.com
作者简介:凌潜龙,硕士,E-mail: 203551716@qq.com
基金资助:
Qianlong LING1,2( ), Kai JI1,3, Jinye CHEN1, Jiajia GUAN1, Ruipeng WANG1, Wenjiang MAN1,3, Bing ZHU1(
), Kai JI1,3, Jinye CHEN1, Jiajia GUAN1, Ruipeng WANG1, Wenjiang MAN1,3, Bing ZHU1( )
)
Received:2024-04-16
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Bing ZHU
E-mail:203551716@qq.com;bbmczhubing@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨鞘氨醇激酶-1(SPHK1)在胃癌(GC)组织中的表达及其靶向核因子-κB(NF-κB)调控GC细胞迁移和侵袭能力的分子机制。 方法 基于TIMER2.0、GEPIA与HPA数据库分析SPHK1在GC组织中的表达。使用Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库预测SPHK1与GC患者预后的关联。利用IHC检测GC及癌旁组织中SPHK1和MKI67的表达并分析两者相关性。运用Western blotting与qRT-PCR检测GC各细胞系中SPHK1蛋白及mRNA水平。基因富集通路数据库检索SPHK1对GC进展的生物学功能。使用慢病毒敲低HGC-27/过表达MGC-803细胞中SPHK1的表达;采用细胞划痕实验探究SPHK1对GC细胞迁移能力的影响;Transwell实验探究SPHK1对GC细胞迁移和侵袭能力的作用;通过Western blotting检测各蛋白表达情况。体内成瘤实验中,将裸鼠随机分为shNC组、shSPHK1组、oeNC组与oeSPHK1组,利用稳转株验证SPHK1的促癌作用。 结果 生物信息学表明SPHK1在GC组织中显著高表达(P<0.001);同时高表达的SPHK1预示着较差的总生存期(P<0.001)和进展后总生存期(P<0.001)以及更差的无复发生存期(P<0.001)。IHC结果表明GC组织中SPHK1与MKI67表达明显上调(P<0.001)且呈正相关(P<0.001)。基因富集通路数据库提示,SPHK1参与GC中的细胞黏附、迁移及血管生成等,且NF-κB参与GC进展(P<0.05)。细胞实验数据显示,抑制SPHK1减弱GC细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,而过表达SPHK1会产生相反的结果(P<0.01);SPHK1正向调节磷酸化P65 (p-P65)、血管内皮生长因子(VEGFA)和白细胞介素(IL-17)蛋白表达(P<0.05);利用PDTC阻断NF-κB信号通路可削弱SPHK1促进的GC细胞迁移与侵袭能力以及各蛋白表达水平(P<0.01);动物实验表明,与NC组相比,shSPHK1组肿瘤大小和质量明显减小,而oeSPHK1组显著增加(P<0.001)。 结论 SPHK1可靶向NF-κB信号通路表达进而调控GC细胞的迁移与侵袭,提示SPHK1可能是GC进展的潜在诊断分子标志物。
凌潜龙, 纪凯, 陈金业, 管佳佳, 王睿朋, 满文江, 朱冰. SPHK1靶向NF-κB信号通路调控胃癌细胞的迁移与侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2163-2171.
Qianlong LING, Kai JI, Jinye CHEN, Jiajia GUAN, Ruipeng WANG, Wenjiang MAN, Bing ZHU. Sphingosine kinase-1 regulates migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via targeting the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2163-2171.
| Characteristic | Clinicopathological characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| n | Percentage (%) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 28 | 70 |
| Female | 12 | 30 |
| Age (year) | ||
| ≥60 | 24 | 60 |
| <60 | 16 | 40 |
| Tumor size (cm) | ||
| ≥5.0 | 22 | 55 |
| <5.0 | 18 | 45 |
| Clinical stage | ||
| I+II | 14 | 35 |
| III+IV | 26 | 65 |
| N stage | ||
| N0 | 10 | 25 |
| N1+N2+N3 | 30 | 75 |
表1 SPHK1在GC中的表达与临床病理特征的关系
Tab.1 Clinicopathological characteristics of GC patients (n=40)
| Characteristic | Clinicopathological characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| n | Percentage (%) | |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 28 | 70 |
| Female | 12 | 30 |
| Age (year) | ||
| ≥60 | 24 | 60 |
| <60 | 16 | 40 |
| Tumor size (cm) | ||
| ≥5.0 | 22 | 55 |
| <5.0 | 18 | 45 |
| Clinical stage | ||
| I+II | 14 | 35 |
| III+IV | 26 | 65 |
| N stage | ||
| N0 | 10 | 25 |
| N1+N2+N3 | 30 | 75 |
| Item | Sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| shNC | GAGTCTATGACATTGCCTCA |
| shSPHK1#1 | CTTCGTGTCAGATGTTGGATAT |
| shSPHK1#2 | GCTTTGCCCTCACCCTTACAT |
| shSPHK1#3 | GCTTTGCCCTCACCCTTACAT |
| oeNC | CGCATCTAGCCTGTCAGTCC |
| oeSPHK1#1 | CTCGTGTCAGATATTGGTTAT |
| oeSPHK1#2 | ATTGTGTGAGACATCCGTAAG |
| oeSPHK1#3 | TTGAGTCCTGCTTCTTCATTG |
表2 RNA干扰和过表达序列
Tab.2 Sequences for RNA interference or gene overexpression
| Item | Sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| shNC | GAGTCTATGACATTGCCTCA |
| shSPHK1#1 | CTTCGTGTCAGATGTTGGATAT |
| shSPHK1#2 | GCTTTGCCCTCACCCTTACAT |
| shSPHK1#3 | GCTTTGCCCTCACCCTTACAT |
| oeNC | CGCATCTAGCCTGTCAGTCC |
| oeSPHK1#1 | CTCGTGTCAGATATTGGTTAT |
| oeSPHK1#2 | ATTGTGTGAGACATCCGTAAG |
| oeSPHK1#3 | TTGAGTCCTGCTTCTTCATTG |
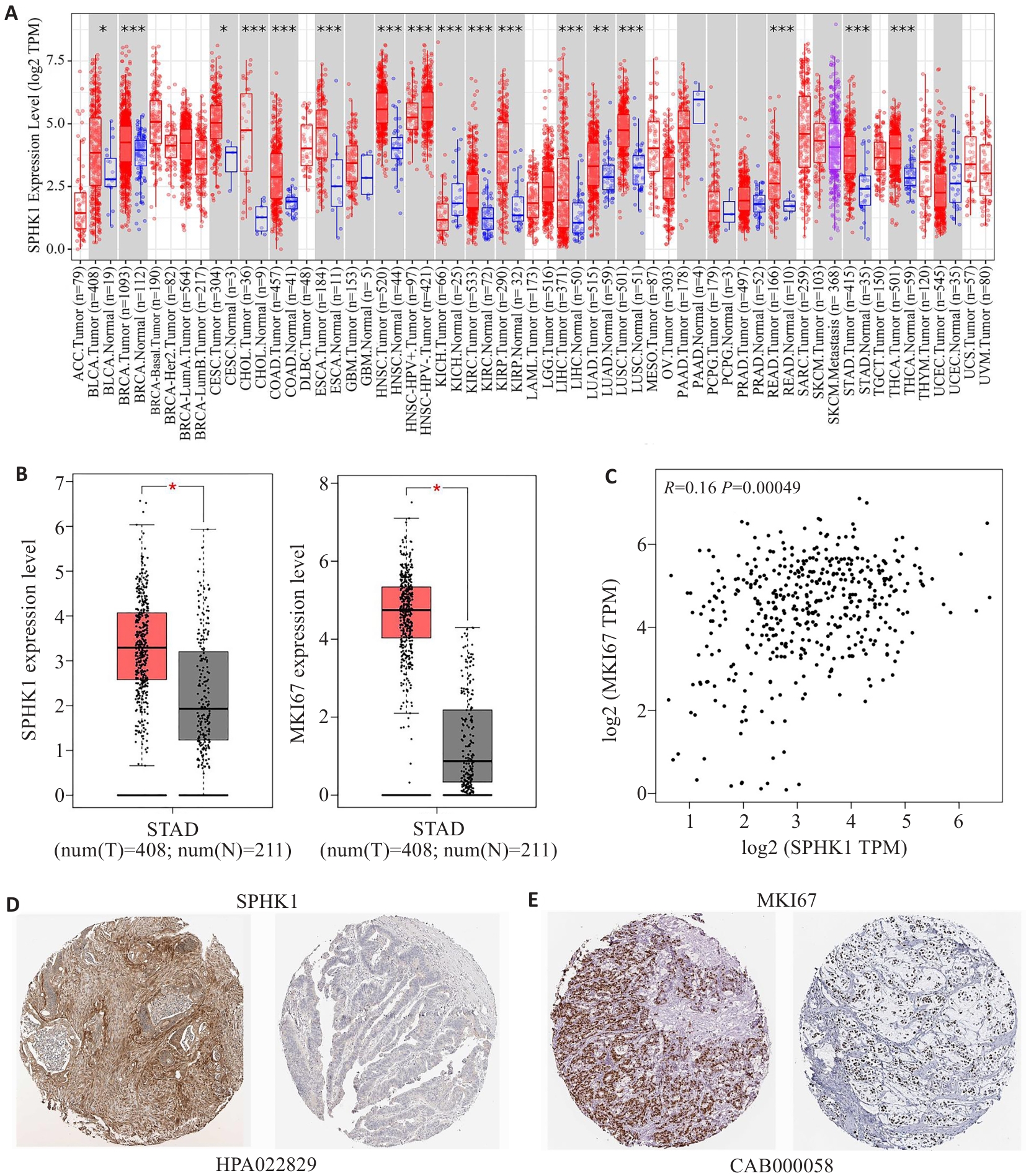
图1 SPHK1在GC组织中的表达
Fig.1 Expression of SPHK1 in GC tissues. A: Expression of SPHK1 in pan-cancer based on data retrieved from TIMER2.0 database. B: Expression of SPHK1 and MKI67 in GC tissues based on data retrieved from GEPIA database. C: GEPIA database analysis of the correlation between SPHK1 and MKI67. D, E: Immunohistochemical staining for SPHK1 and MKI67 in GC tissues from HPA database. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Tumor group.
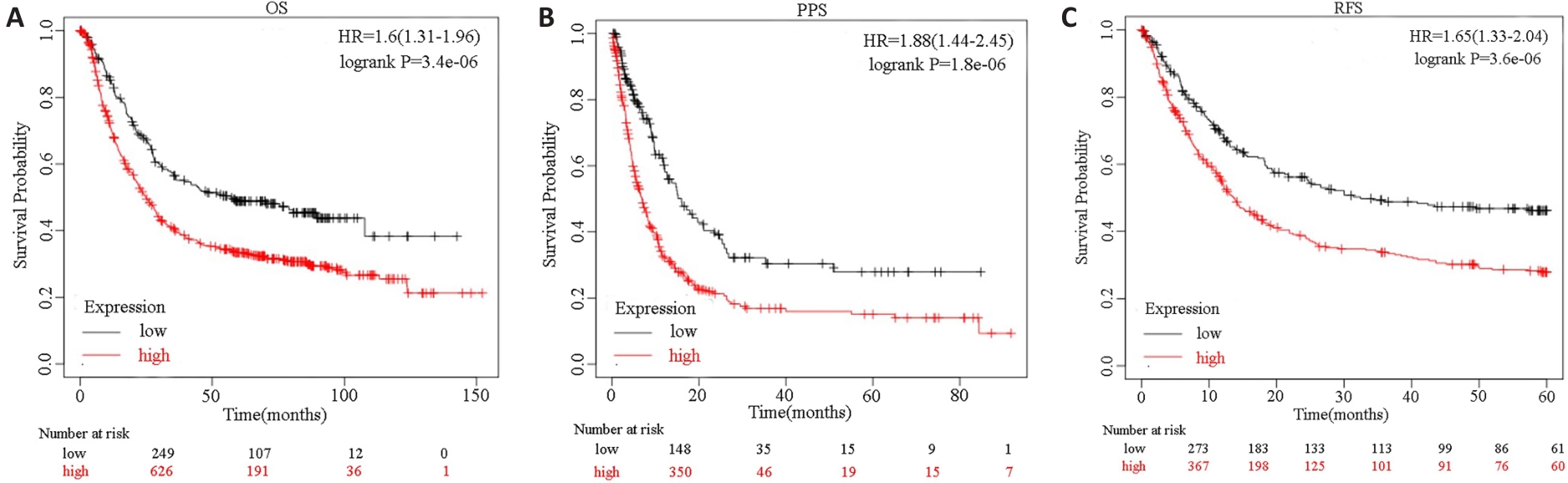
图2 SPHK1表达与GC患者预后的关联
Fig.2 Association of SPHK1 expression with overall survival (OS; A), post-progression survival (PPS; B) and recurrence-free survival (RFS; C) of GC patients predicted using Kaplan-Meier Plotter database.
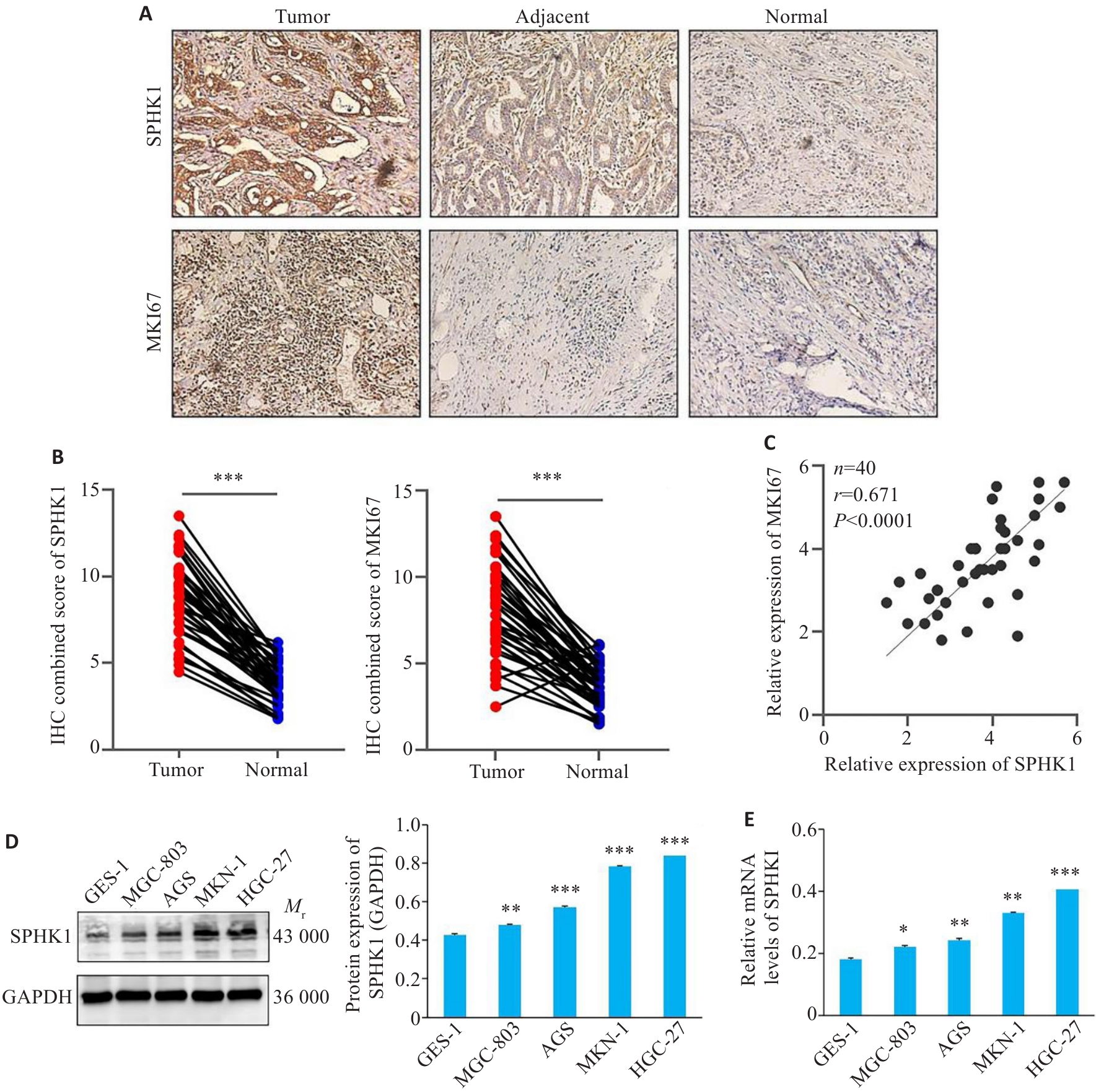
图3 GC组织中SPHK1表达的上调
Fig.3 SPHK1 expression is upregulated in GC tissue. A: Immunohistochemical staining for detecting SPHK1 and MKI67 in clinical tissue samples (Original magnification:×200). B: Immunohistochemical score of SPHK1 and MKI67. ***P<0.001. C: Correlation between SPHK1 and MKI67 expressions. D: Western blotting for detecting the expression of SPHK1 protein. E: qRT-PCR for detecting the level of SPHK1 mRNA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs GES-1 group.
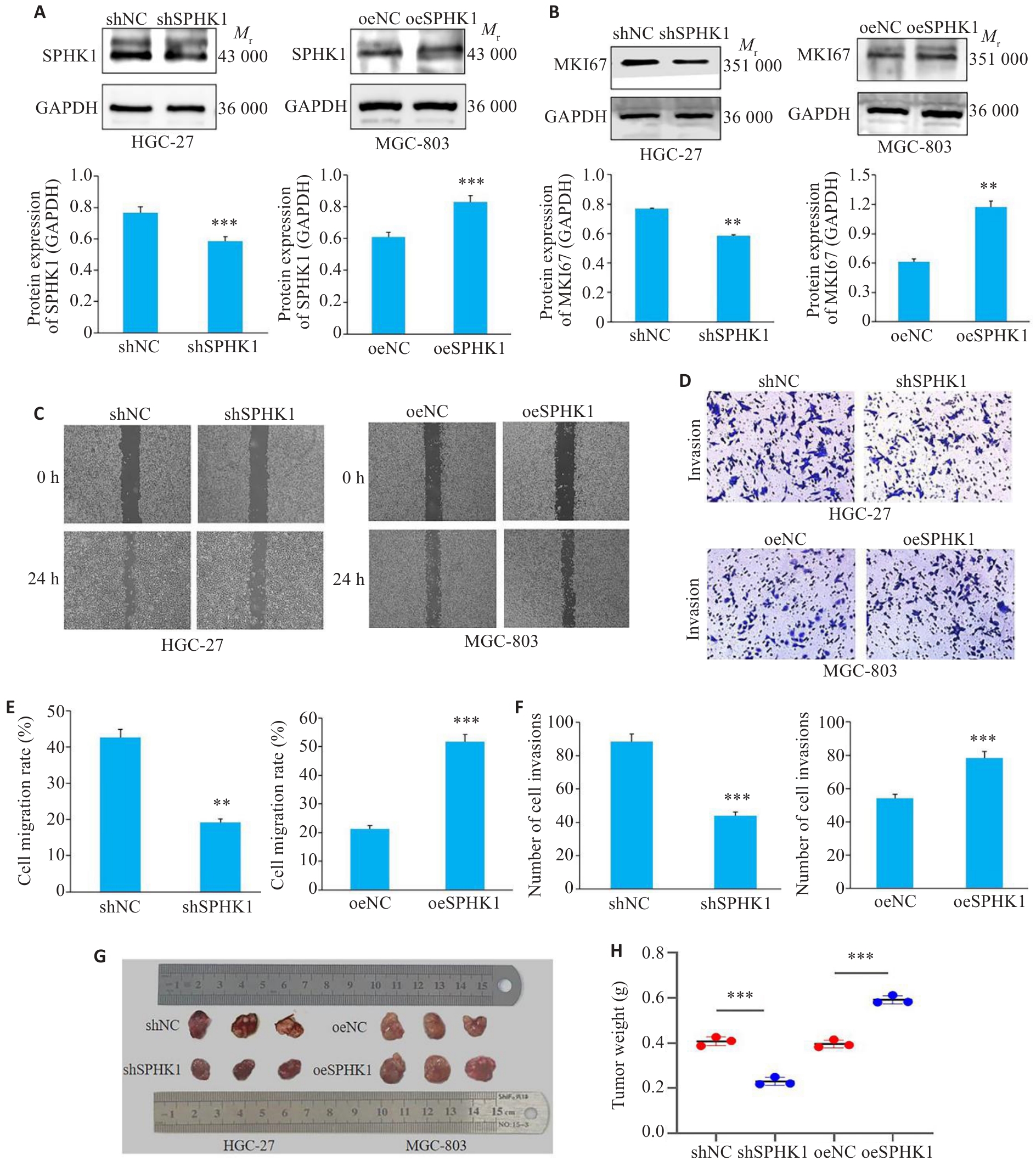
图4 SPHK1对GC细胞迁移与侵袭的影响
Fig.4 Effect of SPHK1 knockdown or overexpression on GC cell migration and invasion. A: Western blotting for assessing efficiency of lentivirus-mediated SPHK1 knockdown and overexpression. B: Western blotting for detecting MKI67 protein levels. C, E: Cell scratch assay for assessing migration ability of the cells (×40). D, F: Transwell assays for assessing invasion ability of the cells (×200). G: Size of the subcutaneous tumors in nude mice. F: Weight of the subcutaneous tumors. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs NC group.
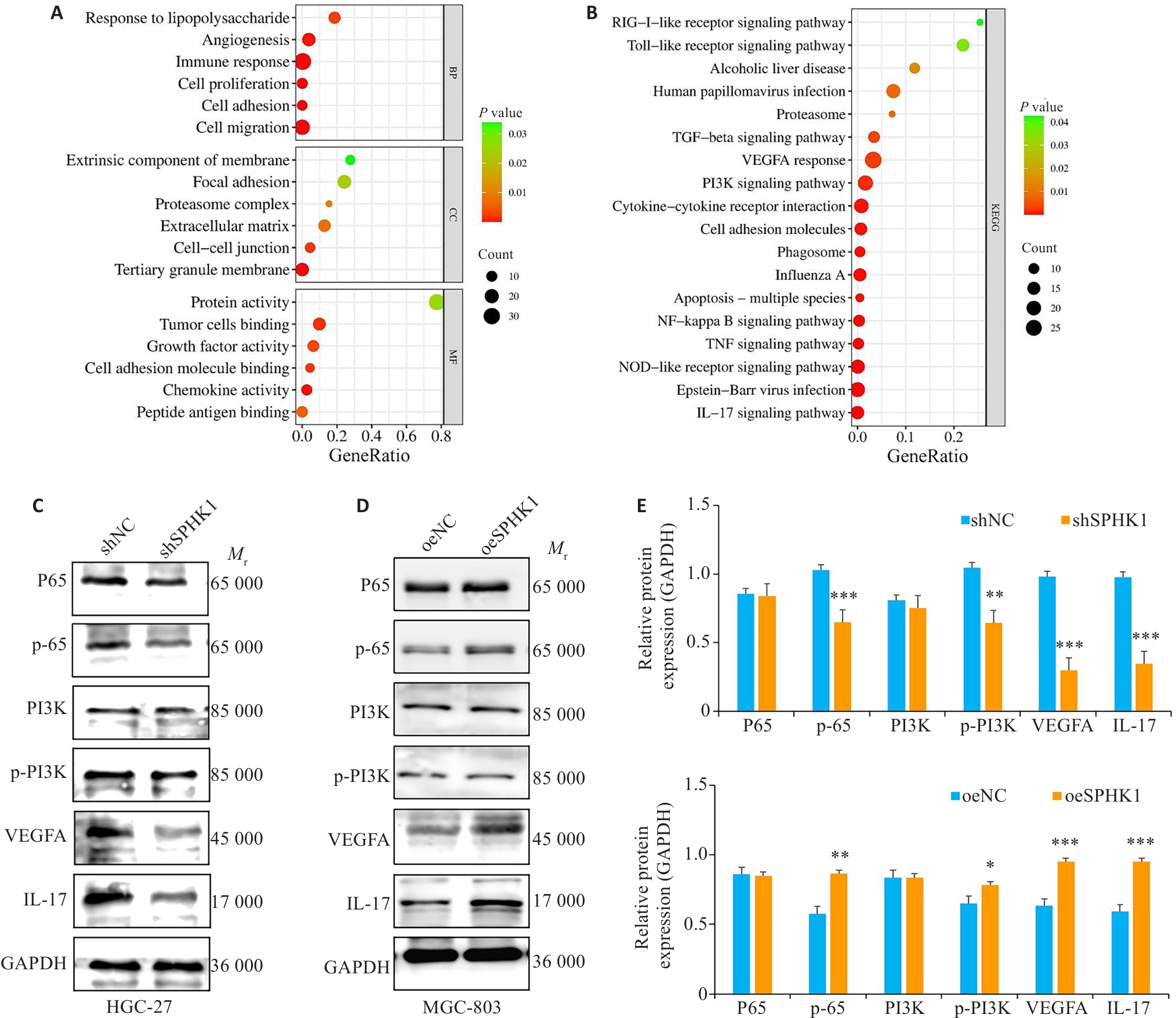
图5 SPHK1靶向NF-κB信号通路
Fig.5 SPHK1 targets the NF-κB signaling pathway. A: Results of GO enrichment analysis. B: Results of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. C, E: Expression levels of NF-κB signaling pathway proteins after SPHK1 knockdown. D, F: Expression levels of the proteins after SPHK1 overexpression. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs NC group.
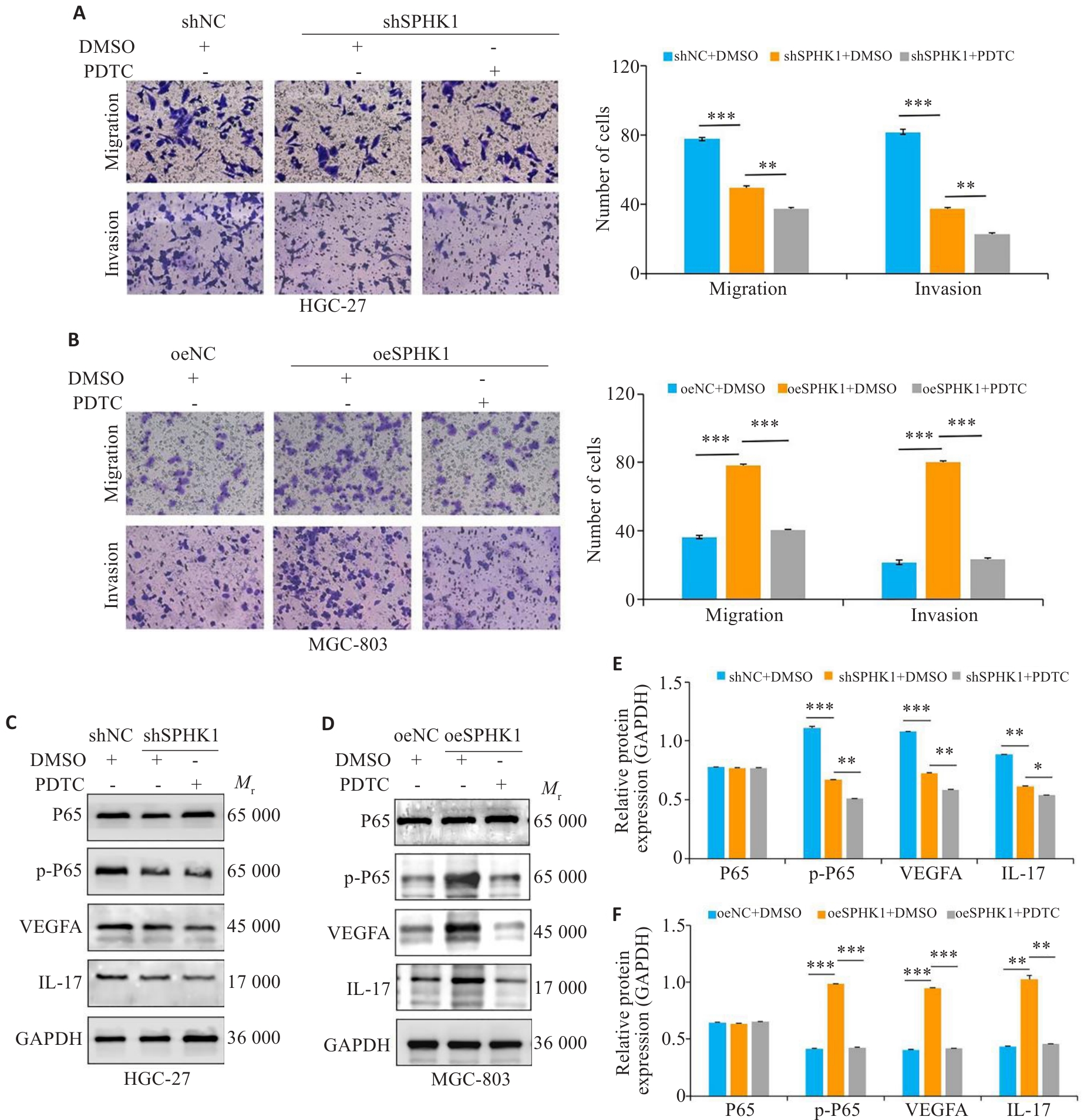
图6 阻断NF-κB信号通路, SPHK1对GC细胞的迁移与侵袭能力的影响
Fig.6 Effect of blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway on migration and invasion ability of GC cells with SPHK1 knockdown or overexpression. A, B: Transwell assay for assessing migration and invasion of GC cells treated with 100 nmol/L PDTC (a NF-κB pathway inhibitor) or DMSO for 24 h (×200). C-F: Western blotting for detecting the levels of P65, p-P65, VEGFA and IL-17 proteins.*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| 1 | 冯金华, 刘亚江, 颜慧玲, 等. 四君子汤对胃癌肿瘤干细胞标志物活性及TFAP4蛋白的作用机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2024,44(7):1739-44. |
| 2 | Wang X, Wu WKK, Gao J, et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 140. |
| 3 | Yang WJ, Zhao HP, Yu Y, et al. Updates on global epidemiology, risk and prognostic factors of gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2023, 29(16): 2452-68. |
| 4 | Yeong J, Teo CB, Tay RYK, et al. Reply to: letter to editor on the article "Choice of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assay influences clinical eligibility for gastric cancer immunotherapy"[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2022, 25(6): 1133-5. |
| 5 | Tang L, Guo CM, Li X, et al. TAF15 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer via activation of the RAF1/MEK/ERK signalling pathway[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 5846. |
| 6 | Qin ZJ, Tong H, Li TH, et al. SPHK1 contributes to cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer cells via the NONO/STAT3 axis[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 48(5): 204. |
| 7 | Bernacchioni C, Squecco R, Gamberi T, et al. S1P signalling axis is necessary for adiponectin-directed regulation of electrophysio-logical properties and oxidative metabolism in C2C12 myotubes[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(4): 713. |
| 8 | 张文路, 徐春燕. SphK1/S1P在肿瘤恶性生物学行为中的研究进展[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2023, 39(19): 2551-5, 2560. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2023.19.024 |
| 9 | Long JT, Yao ZJ, Sui Y, et al. SphK1 promotes cancer progression through activating JAK/STAT pathway and up-regulating S1PR1 expression in colon cancer cells[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2022, 22(2): 254-60. |
| 10 | Wu JN, Lin L, Luo SB, et al. SphK1-driven autophagy potentiates focal adhesion paxillin-mediated metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2021, 10(17): 6010-21. |
| 11 | Liu SQ, Xu CY, Wu WH, et al. Sphingosine kinase1 promotes the metastasis of colorectal cancer by inducing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition mediated by the FAK/AKT/MMPs axis[J]. Int J Oncol, 2019, 54(1): 41-52. |
| 12 | Yu MS, Zhang KN, Wang S, et al. Increased SPHK1 and HAS2 expressions correlate to poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 8861766. |
| 13 | Ma Y, Xing X, Kong R, et al. SphK1 promotes development of non-small cell lung cancer through activation of STAT3[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 47(1): 374-86. |
| 14 | 卢 芳, 蒋 鑫, 徐晓敏, 等.分子对接与体内验证联合探讨穿山龙复方对痛风模型大鼠TLR4/MyD88/NF-kB信号通路的影响[J].中药药理与临床, 2023, 39(08): 25-31. |
| 15 | Wang MD, Li HT, Peng LX, et al. TSPAN1 inhibits metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via suppressing NF-kB signaling[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2024, 31(3): 454-63. |
| 16 | Yang WH, Liu L, Li CX, et al. TRIM52 plays an oncogenic role in ovarian cancer associated with NF-kB pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(9): 908. |
| 17 | 张 浩, 张 震, 王秋生, 等. FJX1在胃癌组织中高表达并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 975-84. |
| 18 | Sukocheva OA, Furuya H, Ng ML, et al. Sphingosine kinase and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway in inflammatory gastrointestinal disease and cancers: a novel therapeutic target[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 207: 107464. |
| 19 | 刘加蒙, 李 明. S1PR1在胃癌组织中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2024, 32(1): 93-5. |
| 20 | Xiong HP, Wang JC, Guan HY, et al. SphK1 confers resistance to apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by downregulating Bim via stim-ulating Akt/FoxO3a signaling[J]. Oncol Rep, 2014, 32(4): 1369-73. |
| 21 | Jia ZW, Tang XF, Zhang XC, et al. MiR-153-3p attenuates the development of gastric cancer by suppressing SphK2[J]. Biochem Genet, 2022, 60(5): 1748-61. |
| 22 | Huo FC, Zhu ZM, Zhu WT, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A methylation of SPHK2 promotes gastric cancer progression by targeting KLF2[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(16): 2968-81. |
| 23 | Uxa S, Castillo-Binder P, Kohler R, et al. Ki-67 gene expression[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(12): 3357-70. |
| 24 | Leibold J, Tsanov KM, Amor C, et al. Somatic mouse models of gastric cancer reveal genotype-specific features of metastatic disease[J]. Nat Cancer, 2024, 5(2): 315-29. |
| 25 | Ruan Q, Wang CJ, Wu YT, et al. Exosome microRNA-22 inhibiting proliferation, migration and invasion through regulating Twist1/CADM1 axis in osteosarcoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 761. |
| 26 | Bhadwal P, Randhawa V, Vaiphei K, et al. Clinical relevance of CERK and SPHK1 in breast cancer and their association with metastasis and drug resistance[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 18239. |
| 27 | Jin L, Zhu J, Yao LY, et al. Targeting SphK1/2 by SKI-178 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(8): 537. |
| 28 | Chen D, Wu JN, Qiu XZ, et al. SPHK1 potentiates colorectal cancer progression and metastasis via regulating autophagy mediated by TRAF6-induced ULK1 ubiquitination[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2024, 31(3): 410-9. |
| 29 | Long XL, Hu YK, Duan SY, et al. MRGBP promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via DKK1/Wnt/β-catenin and NF-kB/p65 pathways mediated EMT[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2022, 421(1): 113375. |
| 30 | Mirzaei S, Saghari S, Bassiri F, et al. NF-κB as a regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: a focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(7): 2770-95. |
| 31 | 冯晓创. POTEE通过调控SPHK1转录激活p65磷酸化促进结直肠癌进展的机制研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2020. |
| 32 | Hou CX, Mao GY, Sun QW, et al. Metabolomic analysis reveals that SPHK1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression through NF-κB activation[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(12): 7386-99. |
| 33 | Zhang JX, Chen ZH, Chen DL, et al. Retraction Note: LINC01410-miR-532-NCF2-NF-kB feedback loop promotes gastric cancer angiogenesis and metastasis[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(14): 1158. |
| 34 | Li YF, Qiao YQ, Wang HH, et al. Intraperitoneal injection of PDTC on the NF-kB signaling pathway and osteogenesis indexes of young adult rats with anterior palatal suture expansion model[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(7): e0243108. |
| 35 | Mei L, Zheng YM, Song TY, et al. Rieske iron-sulfur protein induces FKBP12.6/RyR2 complex remodeling and subsequent pulmonary hypertension through NF‑κB/cyclin D1 pathway[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 3527. |
| 36 | Yang KX, Li JT, Zhu JH, et al. HOOK3 suppresses proliferation and metastasis in gastric cancer via the SP1/VEGFA axis[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10(1): 33. |
| 37 | Zeng K, Xie WW, Wang CY, et al. USP22 upregulates ZEB1-mediated VEGFA transcription in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(3): 194. |
| 38 | 李 燕, 王 琦, 郑 路, 等.白细胞介素-17基因多态性与山西东南地区汉族人群2型糖尿病的相关性[J].实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(05): 695-701. |
| 39 | Korbecki J, Simińska D, Gąssowska-Dobrowolska M, et al. Chronic and cycling hypoxia: drivers of cancer chronic inflammation through HIF-1 and NF‑κB activation: a review of the molecular mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10701. |
| [1] | 陈孝华, 鲁辉, 王子良, 王炼, 夏勇生, 耿志军, 张小凤, 宋雪, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国, 左芦根. ABI2在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [2] | 钟娜, 王会杰, 赵文英, 孙珍贵, 耿彪. 高表达RNF7增强非小细胞肺癌细胞的PD-1耐药:基于活化NF-kB通路促进CXCL1表达和髓源性抑制细胞的募集[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1704-1711. |
| [3] | 叶梦楠, 武鸿美, 梅琰, 张庆玲. CREM在胃癌中高表达并与患者的不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1776-1782. |
| [4] | 姜一凡, 李小荣, 耿嘉逸, 陈永锋, 唐碧, 康品方. 槲皮素通过抑制HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路减轻糖尿病引起的大鼠肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1769-1775. |
| [5] | 赵娜, 沈梦迪, 赵睿, 奥迪, 骆泽谭, 张银亮, 徐志东, 范方田, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控Nrf2/NF-κB通路缓解小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [6] | 耿志军, 杨晶晶, 牛民主, 刘馨悦, 施金冉, 刘亦珂, 姚新宇, 张雨路, 张小凤, 胡建国. 桑黄酮G通过调控PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路抑制胃癌细胞的生长、迁移和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1476-1484. |
| [7] | 庞一丹, 刘雅, 陈思嫒, 张荆雷, 曾今, 潘元明, 安娟. SPAG5在胃癌细胞恶性增殖中的生物学作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1497-1507. |
| [8] | 张珊苑, 蔡巧燕, 祁江晗, 殷恺馨, 何晨晨, 高铸烨, 张铃, 褚剑锋. 清心解瘀颗粒抗动脉粥样硬化的药效学及调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1518-1528. |
| [9] | 肖林雨, 段婷, 夏勇生, 陈悦, 孙洋, 许轶博, 徐磊, 闫兴洲, 胡建国. 蒙花苷通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路抑制小鼠脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞活化介导的神经炎症和神经元凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1589-1598. |
| [10] | 柯志勇, 黄子城, 何若琳, 张倩, 陈思旭, 崔忠凯, 丁晶. 抑制Hmga2促进小鼠脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化并加速骨缺损修复[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1227-1235. |
| [11] | 陶怀祥, 骆金光, 闻志远, 虞亘明, 苏萧, 王鑫玮, 关翰, 陈志军. STING高表达通过调控TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路和影响炎症与凋亡水平促进小鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354. |
| [12] | 崔芝, 马萃娇, 王倩茹, 陈金豪, 严子阳, 杨建林, 吕亚丰, 曹春雨. 表达 TGF-βⅡ受体的腺相关病毒载体抑制小鼠三阴性乳腺癌4T1细胞的增殖和肺转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 818-826. |
| [13] | 夏勇生, 王炼, 陈孝华, 张雨路, 孙奥飞, 陈德利. 过表达TSR2通过下调PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 913-919. |
| [14] | 杨晶晶, 殷丽霞, 段婷, 牛民主, 何震东, 陈心蕊, 张小凤, 李静, 耿志军, 左芦根. 胃癌组织中高表达ATP5A1与患者术后的不良预后和肿瘤细胞的糖代谢有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 974-980. |
| [15] | 黄秋虎, 周 建, 王子珍, 杨 堃, 陈政纲. miR-26b-3p 靶向 CREB1 调控神经胶质瘤细胞的增殖、迁移及侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 578-584. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||