Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2667-2678.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.14
Du SHANG1( ), Wen LI2, Lihua CUI3, Ming CHEN1,4(
), Wen LI2, Lihua CUI3, Ming CHEN1,4( )
)
Received:2025-06-06
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Ming CHEN
E-mail:17396225313@163.com;cmtjnk@sina.com
Du SHANG, Wen LI, Lihua CUI, Ming CHEN. Hugan Decoction alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by activating the AMPK/m-TOR signaling pathway and reducing lipid synthesis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2667-2678.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.14
| Gene | Forward sequence (5'-3') | Reverse sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| r-GAPDH | AGATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTG | CTGGAAGATGGTGATGGGTT |
| r-ACC1 | GGGAACATCCCCACGCTAAA | CATGCGTTGACAAGGTGGTG |
| r-FASN | TGTACCCTCTAGCTGGACCC | CCAGGCTAAGGGCAATGGAA |
| r-AMPK | TCAAAGCCGACCCAATGACA | CTTCCTTCGCACACGCAAAT |
| r-mTOR | ACCCATCCAACCTGATGCTG | TCGAGACCGGTAACCTCCAT |
| h-GAPDH | CAAATTCCATGGCACCGTCA | GACTCCACGACGTACTCAGC |
| h-ACC1 | AGGAGCTGTCTATTCGGGGT | GGTCGCTCAGCCTGTACTTT |
| h-FASN | CCTGGCTGCCTACTACATCG | CACATTTCAAAGGCCACGCA |
| h-AMPK | TGCTTTTTGTCCAGGGCTTG | ATCCCCTAAAGAGAGGGCCA |
| h-mTOR | GCCACTGTGCGGATCATTTC | AGCGAATGTCAGGGTCAGGA |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Forward sequence (5'-3') | Reverse sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| r-GAPDH | AGATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTG | CTGGAAGATGGTGATGGGTT |
| r-ACC1 | GGGAACATCCCCACGCTAAA | CATGCGTTGACAAGGTGGTG |
| r-FASN | TGTACCCTCTAGCTGGACCC | CCAGGCTAAGGGCAATGGAA |
| r-AMPK | TCAAAGCCGACCCAATGACA | CTTCCTTCGCACACGCAAAT |
| r-mTOR | ACCCATCCAACCTGATGCTG | TCGAGACCGGTAACCTCCAT |
| h-GAPDH | CAAATTCCATGGCACCGTCA | GACTCCACGACGTACTCAGC |
| h-ACC1 | AGGAGCTGTCTATTCGGGGT | GGTCGCTCAGCCTGTACTTT |
| h-FASN | CCTGGCTGCCTACTACATCG | CACATTTCAAAGGCCACGCA |
| h-AMPK | TGCTTTTTGTCCAGGGCTTG | ATCCCCTAAAGAGAGGGCCA |
| h-mTOR | GCCACTGTGCGGATCATTTC | AGCGAATGTCAGGGTCAGGA |
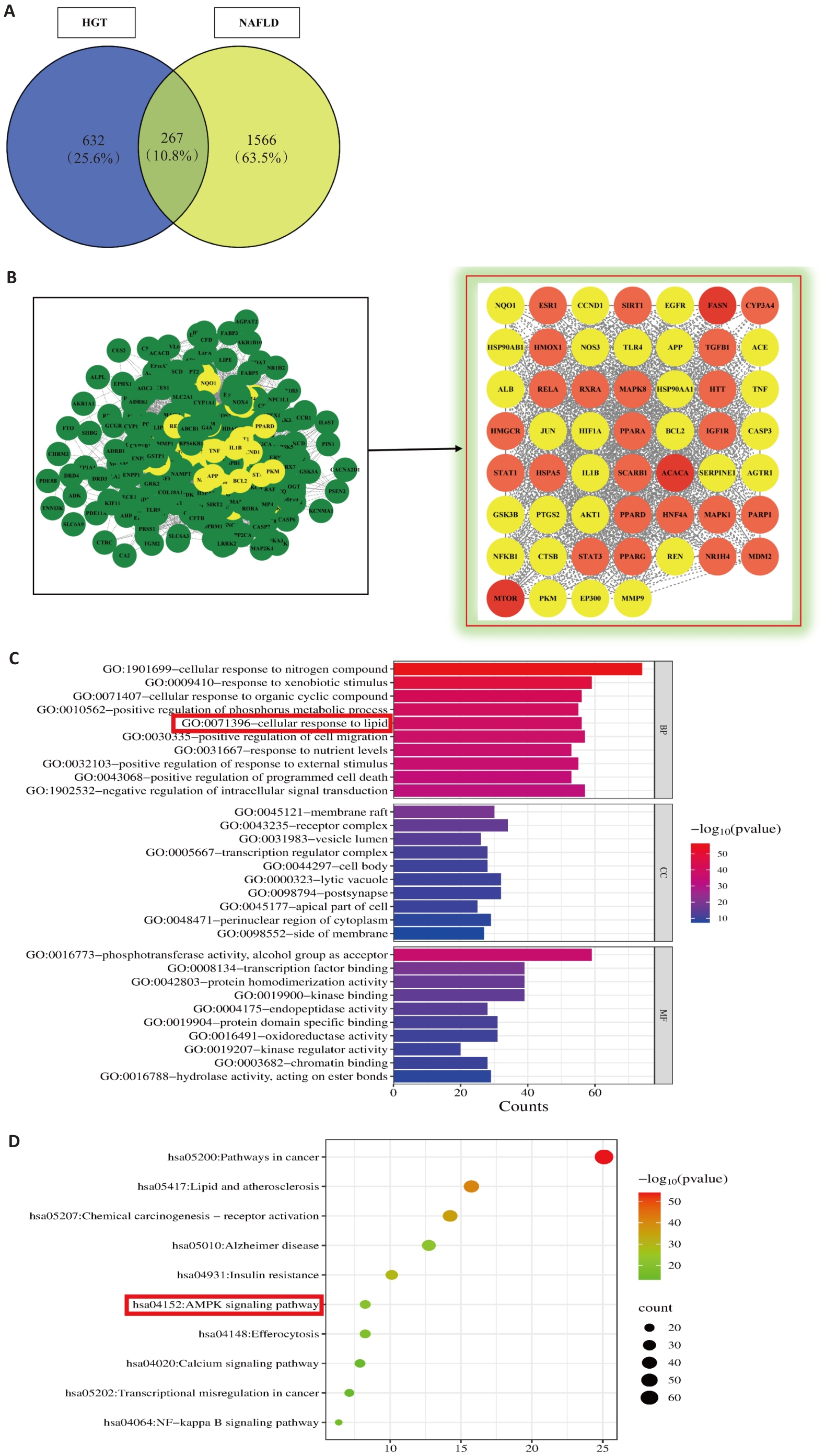
Fig.1 Network pharmacology analysis of Hugan Decoction (HGT) for treatment of NAFLD. A: Venn diagram of HGT-NAFLD common targets. B: PPI network and core target screening of HGT for NAFLD treatment. C: GO enrichment analysis of potential targets of HGT for the treatment of NAFLD. D: Bubble chart of KEGG enrichment analysis of potential targets of HGT for treatment of NAFLD.
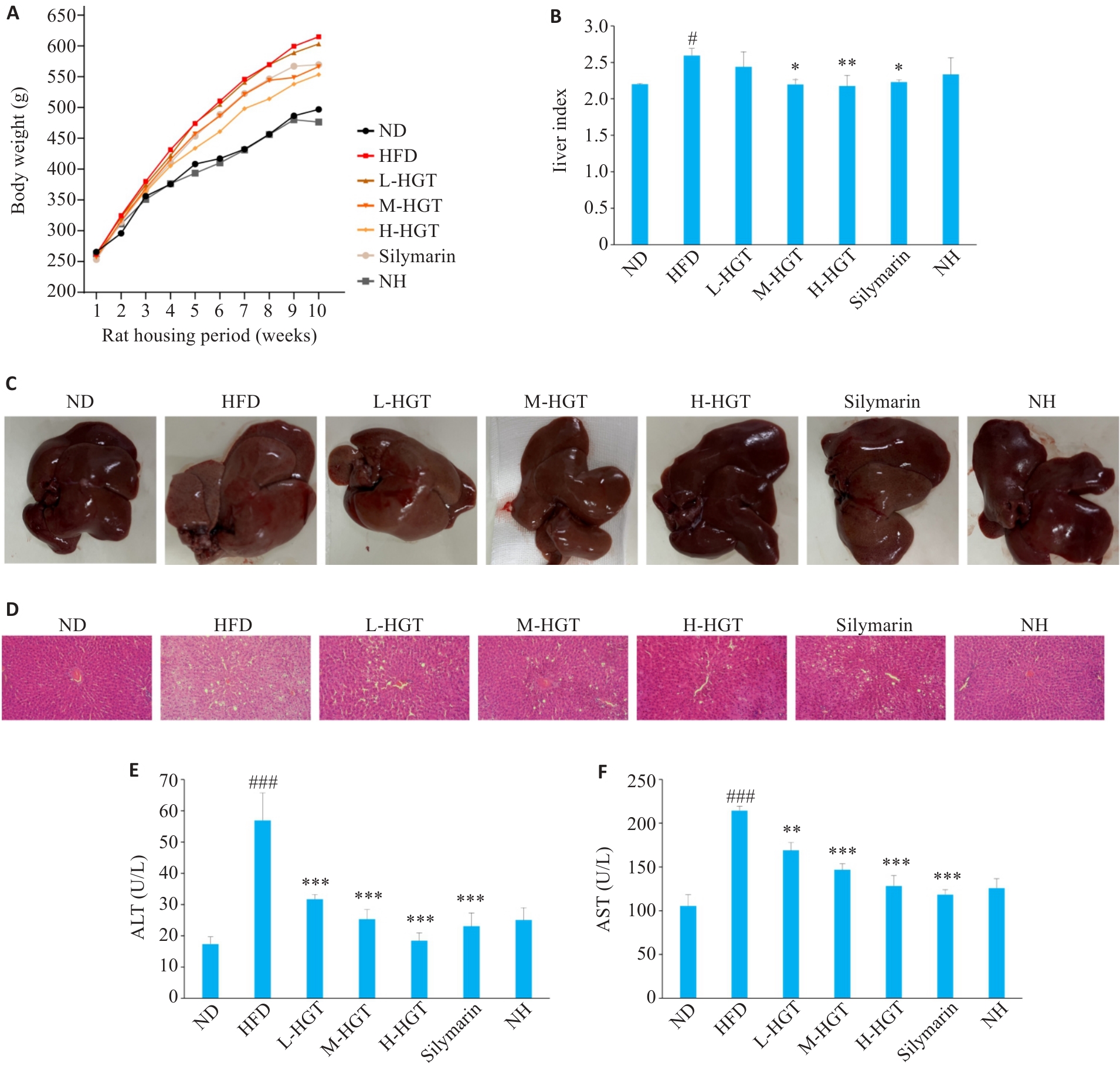
Fig.2 HGT attenuates liver injury in NAFLD rats. Effects of HGT on body weight (A), liver index (B) and liver morphology (C) in NAFLD rats (Mean±SD, n=8). D: Effects of HGT on hepatic histopathological changes in NAFLD rats (HE staining,original magnification: ×200). E, F: Effects of HGT on liver function in NAFLD rats (Mean±SD, n=8). #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs ND group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs HFD group.
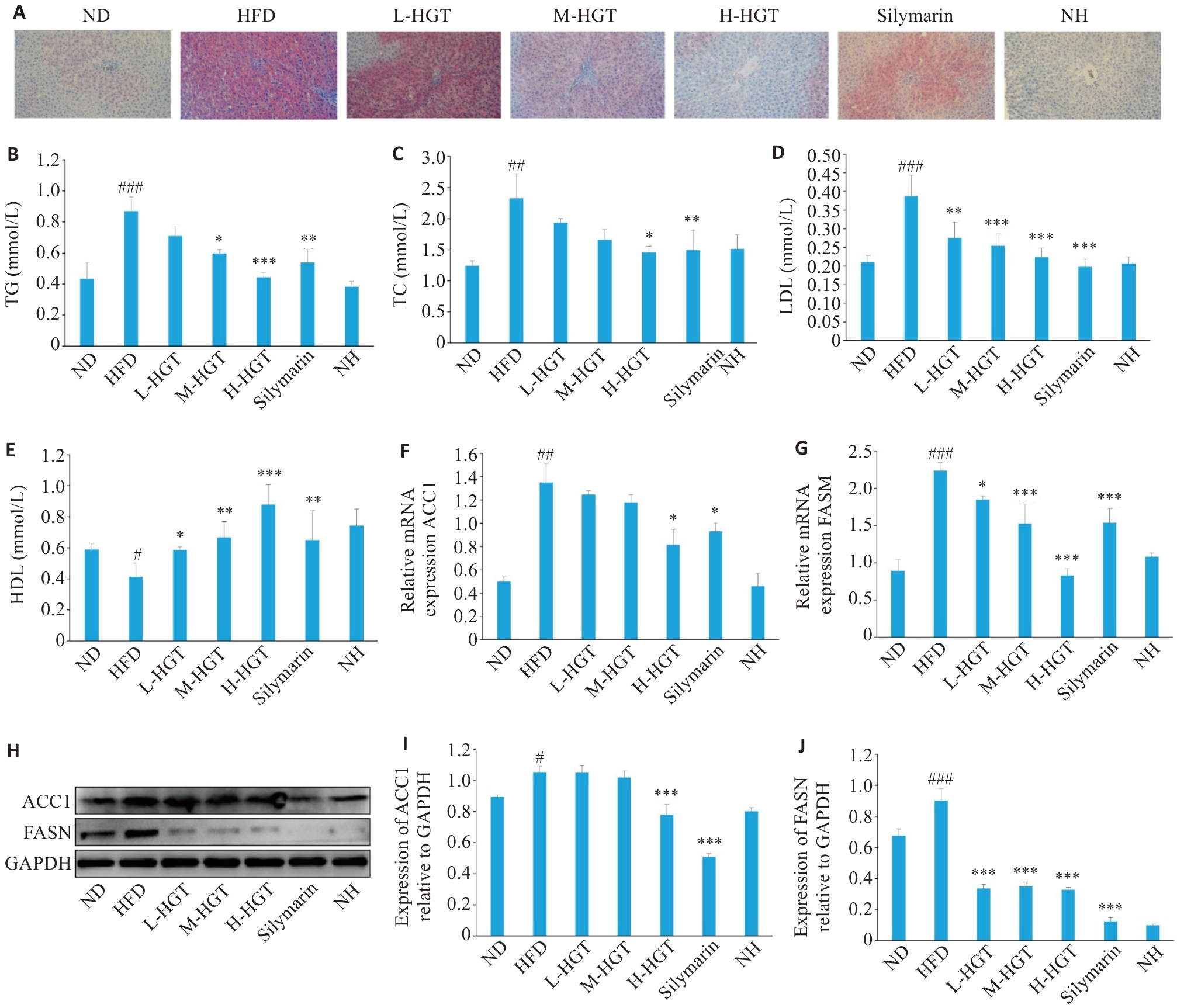
Fig3 Effects of HGT on lipid deposition in NAFLD rats. A: Oil red O staining of liver tissues in NAFLD rats in different groups (×200). B-E: Effects of HGT on blood lipids in NAFLD rats. F, G: Effects of HGT on mRNA expressions of ACC1 and FASN in NAFLD rats (Mean±SD, n=8). H-J: Effects of HGT on protein expressions of ACC1and FASN (Mean±SD, n=8). #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs ND group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs HFD group.
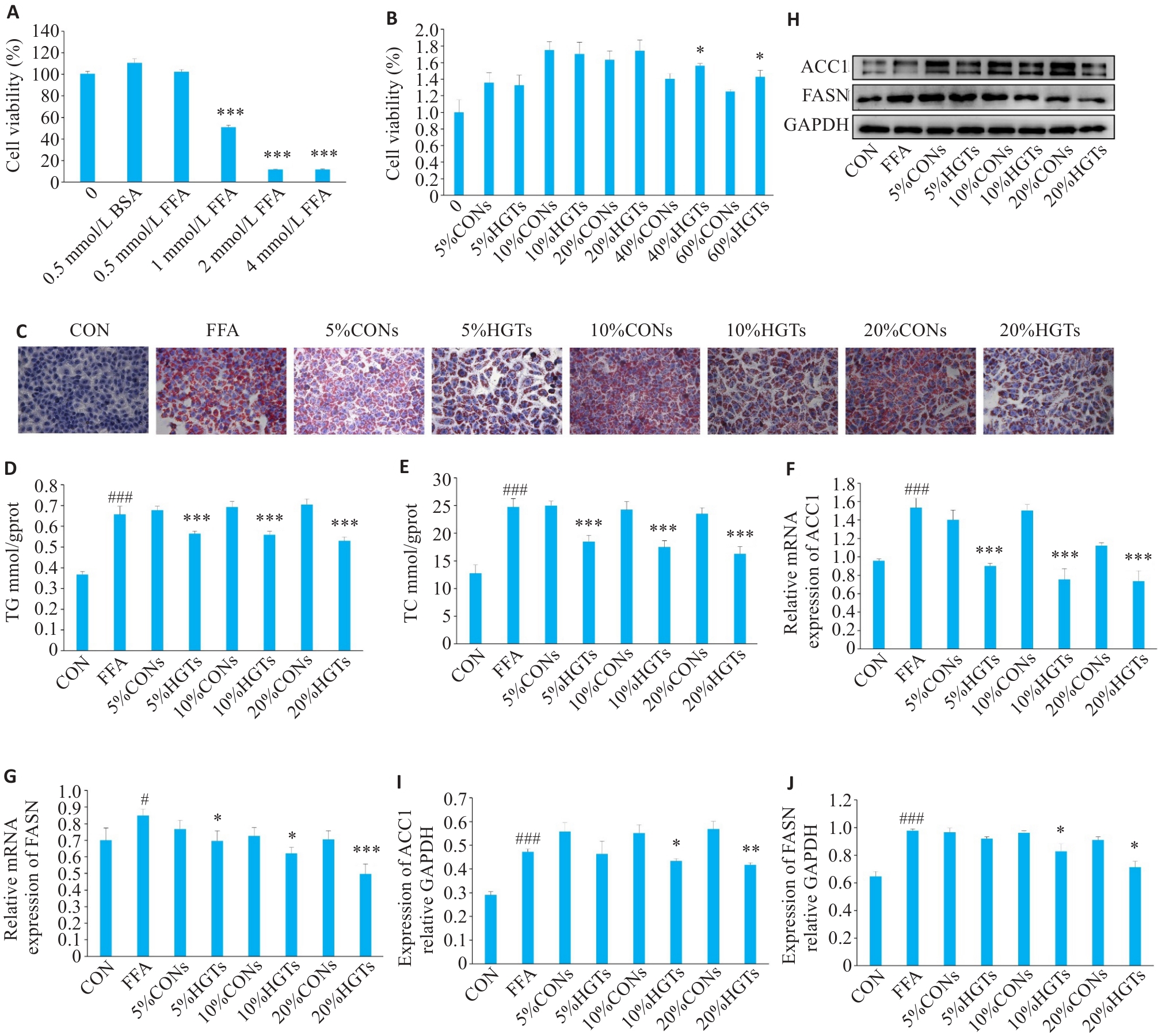
Fig.4 Effects of HGT-medicated serum on lipid deposition in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. A, B: CCK-8 assay for assessing the effect of different concentrations of FFA and HGT-medicated serum on HepG2 cell viability. C: Oil red O staining of HepG2 cells (×200). D, E: Effects of HGT-medicated serum on TG and TC in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. F, G: Effects of HGT-medicated serum on mRNA expressions of ACC1 and FASN in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. H, J: Effects of HGT-medicated serum on protein expressions of ACC1 and FASN in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs different concentrations of CONs groups.
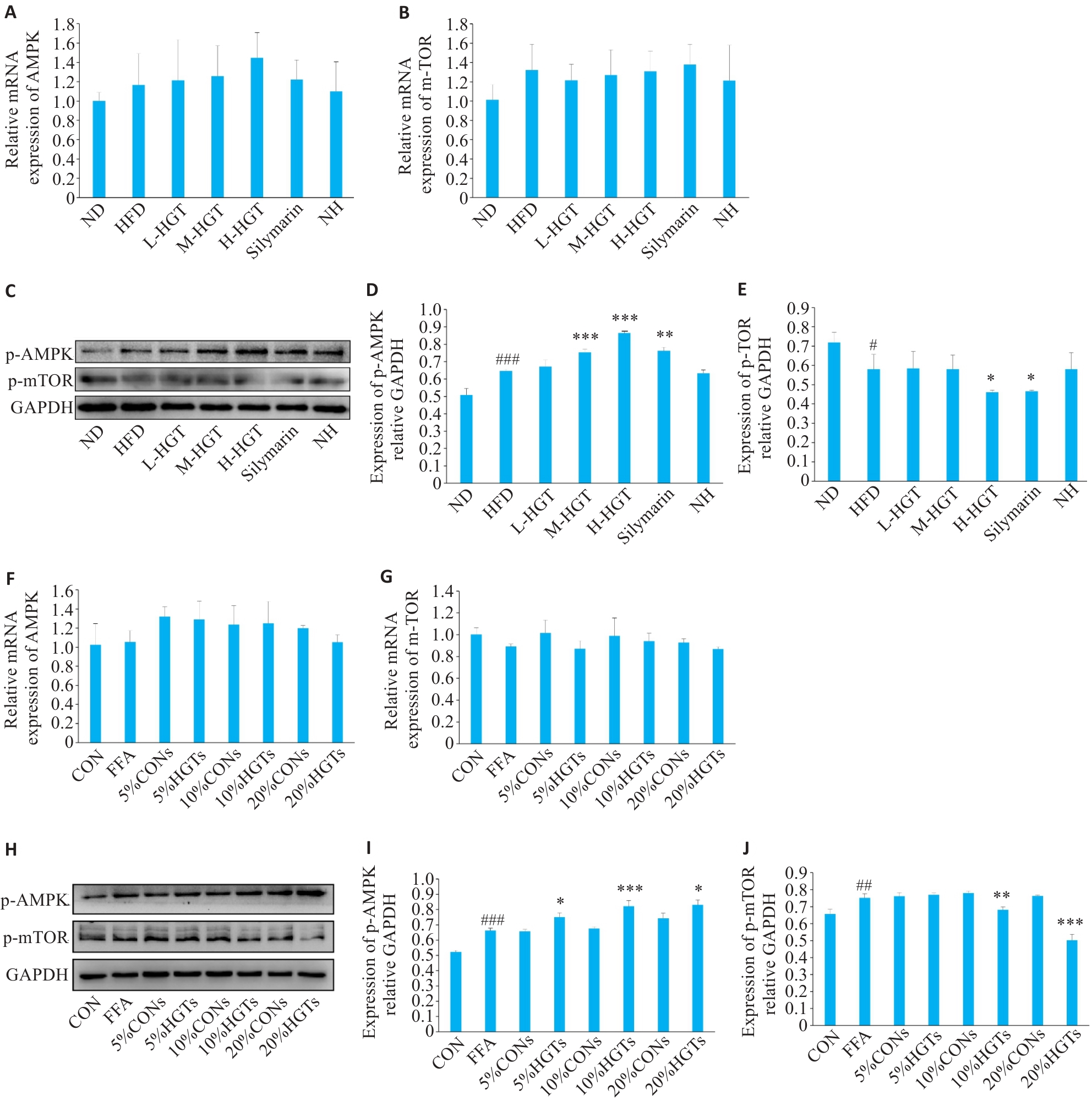
Fig.5 HGT regulates lipid synthesis in the liver of NAFLD rats and in FFA-induced HepG2 cells through the AMPK/m-TOR signaling pathway. A, B: Effects of HGT on mRNA expressions of AMPK and m-TOR in NAFLD rats (Mean±SD, n=8). C-E: Effects of HGT on AMPK/m-TOR pathway in NAFLD rats (Mean±SD, n=8). F, G: Effects of HGT-medicated serum on mRNA expressions of AMPK and m-TOR in FFA-induced HepG2 cells.H-J: Effects of HGT-medicated serum on AMPK/m-TOR signaling pathway in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs ND/CON group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs HFD/ different concentrations of CONs group.
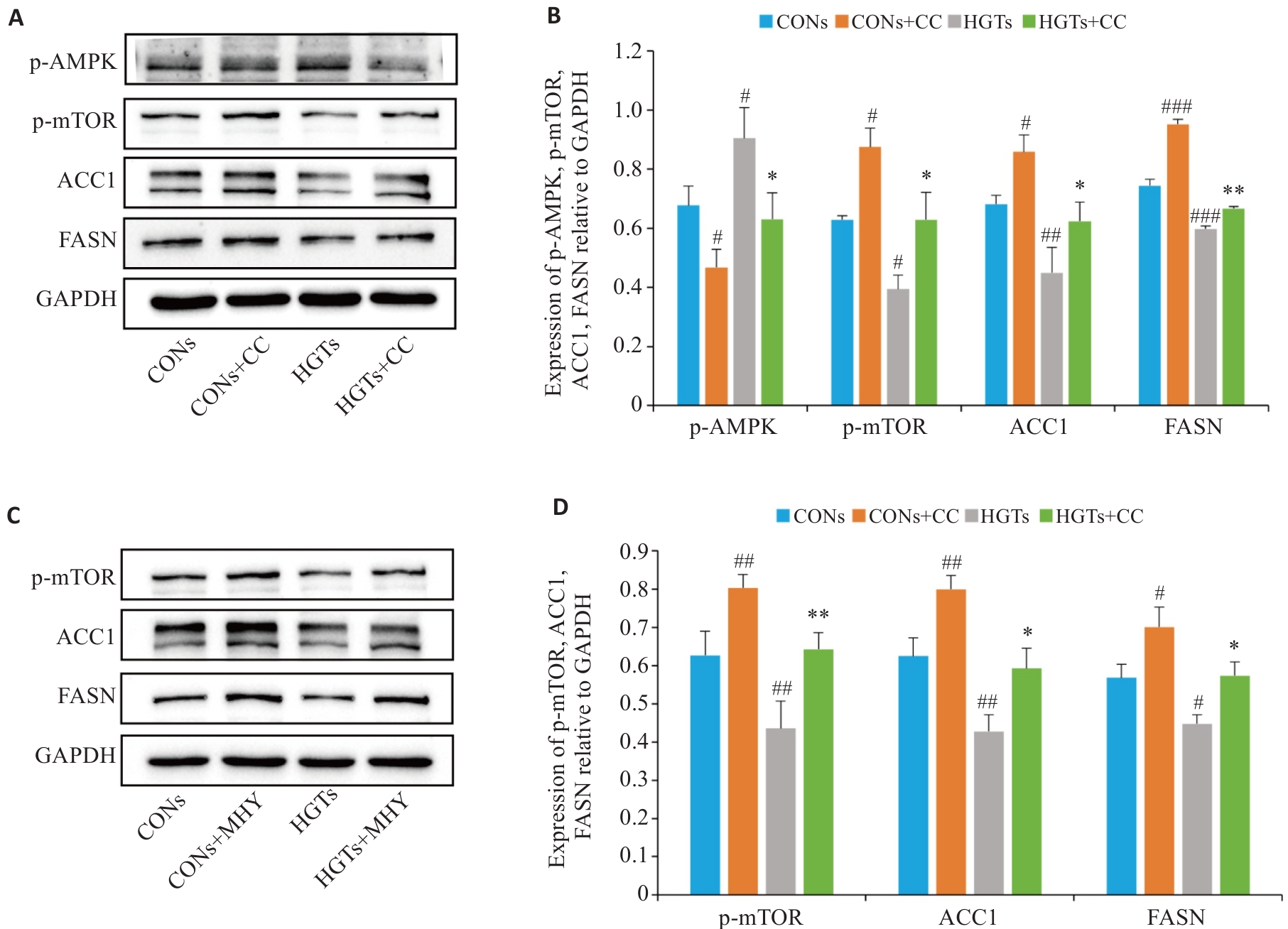
Fig.6 HGT-medicated serum regulates lipid synthesis in FFA-induced HepG2 cells via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. A, B: Effect of compound C on AMPK/m-TOR signaling pathway proteins and lipid synthesis proteins ACC1 and FASN in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. C, D: Effects of the m-TOR activator (MHY) on m-TOR proteins and ACC1 and FASN proteins in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs CONs group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs HGTs group.
| [1] | 杨蕊旭, 范建高. 欧洲代谢相关脂肪性肝病临床管理实践指南简介[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2024, 27(5): 654-8. |
| [2] | Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Siddiqui MS, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77(5): 1797-835. doi:10.1097/hep.0000000000000323 |
| [3] | Cusi K, Isaacs S, Barb D, et al. American association of clinical endocrinology clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in primary care and endocrinology clinical settings: co-sponsored by the American association for the study of liver diseases (AASLD)[J]. Endocr Pract, 2022, 28(5): 528-62. doi:10.1016/j.eprac.2022.03.010 |
| [4] | Lou TW, Yang RX, Fan JG. The global burden of fatty liver disease: the major impact of China[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2024, 13(1): 119-23. doi:10.21037/hbsn-23-556 |
| [5] | Eslam M, George J. Reply to: correspondence on "a new definition for metabolic associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement"[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(5): 1268-9. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.036 |
| [6] | 顾 棨, 芮法娟, 倪文婧, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的规范化管理[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2023, 26(4): 457-60. |
| [7] | 高改娅, 李 莎, 薛敬东, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医证型及证素研究[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(1): 89-93. |
| [8] | 陈 明, 曹泽伟. 中药护肝汤干预糖尿病大鼠肝损害的实验研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2012, 23(12): 3049-51. |
| [9] | Salvoza N, Giraudi PJ, Tiribelli C, et al. Natural compounds for counteracting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): advantages and limitations of the suggested candidates[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(5): 2764. doi:10.3390/ijms23052764 |
| [10] | 马春霞, 陈振东, 田旭东. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病动物模型制备及病证结合研究进展[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2024, 32(12): 1616-25. |
| [11] | 杨宗慧, 陈红刚, 赵文龙, 等. 大黄及有效成分治疗脂肪肝作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2025, 41(7): 113-20. |
| [12] | 赵梓硕, 朱玉光, 马燕山, 等. 不同高脂饲料配方对建立非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2024, 29(5): 543-53. |
| [13] | 曾孟颜, 姚嘉欣, 张 茜, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨四君子汤治疗非酒精性脂肪性肝病的作用机制[J]. 中医临床研究, 2022, 14(16): 1-8. |
| [14] | 徐 云. 四君子汤联合易善复胶囊对非酒精性脂肪肝的临床效果研究[J]. 心理月刊, 2019, 14(17): 221. |
| [15] | 王 敏, 周 璐, 孙 燕, 等. 大柴胡汤及其“方剂要素” 对NAFLD模型大鼠“肠-肝轴” 作用的相关分析[J]. 世界中医药, 2021, 16(3): 430-6. |
| [16] | 钟光成, 刘启华, 麦灏铭, 等. 基于网络药理学及实验验证探讨大柴胡汤抗非酒精性脂肪性肝病的作用机制[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2025, 41(3): 2-9. |
| [17] | Cui HT, Li YT, Wang YM, et al. Da-Chai-hu decoction ameliorates high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through remodeling the gut microbiota and modulating the serum metabolism[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 584090. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.584090 |
| [18] | 黄艳阳. 基于肠TPH1-肝HTR2A轴探讨茵陈蒿汤干预代谢相关脂肪性肝病的作用机制[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁中医药大学, 2024. |
| [19] | Dorn C, Riener MO, Kirovski G, et al. Expression of fatty acid synthase in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2010, 3(5): 505-14. |
| [20] | Lally JSV, Ghoshal S, DePeralta DK, et al. Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by phosphorylation or the inhibitor ND-654 suppresses lipogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 29(1): 174-82.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.020 |
| [21] | 李华君, 吕树泉, 张 辉, 等. 清热祛浊胶囊对2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠的治疗作用及机制[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2025, 45(3): 623-8. |
| [22] | 陈浩然. α-乳白蛋白肽对小鼠非酒精性脂肪肝的改善作用及机制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2023. |
| [23] | 梁娟娟. L-茶氨酸抑制非酒精性脂肪肝病的分子机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2021. |
| [24] | 张明发, 沈雅琴. 甘草及其有效成分抗脂肪肝和抗肥胖的研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2015, 38(4): 439-47. |
| [25] | 邱晓远, 胡德胜, 杨梦灵, 等. mTOR在非酒精性脂肪性肝病脂质代谢中的作用研究进展[J]. 中西医结合研究, 2024, 16(1): 50-3. |
| [26] | Zhang D, Zhang YH, Wang ZL, et al. Thymoquinone attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR/ULK1-dependent pathway in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Phytother Res, 2023, 37(3): 781-97. doi:10.1002/ptr.7662 |
| [27] | 缪 萍, 卞尧尧, 倪露露, 等. 白藜芦醇调控AMPK/mTOR信号通路改善游离脂肪酸诱导的AML-12细胞自噬功能和脂质代谢[J]. 中药材, 2024, 47(11): 2859-63. |
| [28] | Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S, et al. Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2012, 32(1): 2-11. doi:10.1128/mcb.06159-11 |
| [29] | 张笑颜, 王 谢, 王 杰, 等. 大黄酚调控AMPK/mTOR自噬信号通路改善Wilson病铜负荷大鼠认知功能[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2023, 43(5): 578-84. |
| [30] | 王蓉芝, 王琳雳, 焦靖雯, 等. 自噬途径降解肝脏脂滴的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(9): 1916-23. |
| [31] | 任前军, 李 素, 陈雨晴, 等. 基于AMPK/ACC/CPT1A信号通路探讨D-柠檬烯对原代肝细胞脂肪变性的作用机制[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2025, 41(9): 1665-72. |
| [32] | 洪祝平, 张建华, 史月姣, 等. 基于非酒精性脂肪肝细胞模型的荷叶水提物降脂作用机制研究[J]. 现代中药研究与实践, 2024, 38(2): 41-7. |
| [33] | 尚 志, 胡银璐, 徐圣麟, 等. 芹糖葛根素对非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脂代谢的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2024, 40(11): 1598-602. |
| [34] | 陆建国, 俞 松. mTOR信号通路与肿瘤研究进展[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2015, 31(2): 199-202. |
| [35] | Feng JY, Qiu ST, Zhou SP, et al. mTOR: a potential new target in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(16): 9196. doi:10.3390/ijms23169196 |
| [1] | Biyun LUO, Xin YI, Yijing CAI, Shiqing ZHANG, Peng WANG, Tong LI, Ken Kin Lam YUNG, Pingzheng ZHOU. Ching Shum Pills alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice by ameliorating lipid metabolism disorders [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1840-1849. |
| [2] | Qin HU, Hua JIN. Qingshen Granules improves renal function of patients with chronic kidney disease damp-heat syndrome by activating the miR-23b and Nrf2 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1867-1879. |
| [3] | Ziwei YANG, Chang LÜ, Zhu DONG, Shulei JI, Shenghui BI, Xuehua ZHANG, Xiaowu WANG. Rosa laevigata Michx. inhibits pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation in hypertension by modulating the Src-AKT1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1889-1902. |
| [4] | Qi YUN, Ruoli DU, Yuying HE, Yixin ZHANG, Jiahui WANG, Hongwei YE, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO. Cinnamic acid ameliorates doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in mice by attenuating cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via inhibiting TLR4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [5] | Lu RAO, Jiahe DING, Jiangping WEI, Yong YANG, Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG. Flos Sophorae improves psoriasis in mice by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [6] | Jingjing ZHANG, Song FENG, Dali ZHANG, Jian XUE, Chao ZHOU, Pengcheng LIU, Shuangnan FU, Man GONG, Hui FENG, Ning ZHANG. Altered oral microbiome and metabolites are associated with improved lipid metabolism in HBV-infected patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 2034-2045. |
| [7] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [8] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [9] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [10] | Ruimin HAN, Manke ZHAO, Junfang YUAN, Zhenhong SHI, Zhen WANG, Defeng WANG. Live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium improves glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice with circadian rhythm disruption via the SCFAs/GPR43/GLP-1 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1490-1497. |
| [11] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [12] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [13] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [14] | Dandan LI, Jiaxin CHU, Yan YAN, Wenjun XU, Xingchun ZHU, Yun SUN, Haofeng DING, Li REN, Bo ZHU. Curcumin inhibits lipid metabolism in non-small cell lung cancer by downregulating the HIF-1α pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1039-1046. |
| [15] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||