Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1143-1152.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.04
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lijun HE1( ), Xiaofei CHEN1, Chenxin YAN1, Lin SHI1,2(
), Xiaofei CHEN1, Chenxin YAN1, Lin SHI1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-20
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Lin SHI
E-mail:eillyjun@163.com;shilin293@qq.com
Supported by:Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.04
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DZ8 | MOL006709 | 8-Hydroxypinoresinol | 149 | Eucommia |
| FBX3 | MOL002714 | baicalein | 83 | Pinellia |
| HQ2 | MOL000239 | Jaranol | 81 | Astragalus |
| DS10 | MOL000006 | luteolin | 80 | Codonopsis |
| DZ25 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Eucommia |
| DZ4 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Eucommia |
| HQ15 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ20 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ5 | MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ8 | MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | 80 | Astragalus |
Tab.1 Key active components of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
| Code | ID | Name | Relevance | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DZ8 | MOL006709 | 8-Hydroxypinoresinol | 149 | Eucommia |
| FBX3 | MOL002714 | baicalein | 83 | Pinellia |
| HQ2 | MOL000239 | Jaranol | 81 | Astragalus |
| DS10 | MOL000006 | luteolin | 80 | Codonopsis |
| DZ25 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Eucommia |
| DZ4 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Eucommia |
| HQ15 | MOL000422 | kaempferol | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ20 | MOL000098 | quercetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ5 | MOL000354 | isorhamnetin | 80 | Astragalus |
| HQ8 | MOL000378 | 7-O-methylisomucronulatol | 80 | Astragalus |
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| TP53 | DZ8 | -9.40 |
| TP53 | FBX3 | -9.90 |
| TP53 | HQ2 | -9.50 |
| TP53 | DS10 | -10.40 |
| TP53 | DZ25 | -10.20 |
| TP53 | DZ4 | -9.80 |
| TP53 | HQ5 | -9.60 |
| TP53 | HQ8 | -8.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ8 | -10.80 |
| AKT1 | FBX3 | -10.20 |
| AKT1 | HQ2 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DS10 | -11.10 |
| AKT1 | DZ25 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ4 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | HQ5 | -9.50 |
| AKT1 | HQ8 | -9.40 |
| HIF1A | HQ8 | -4.80 |
| HIF1A | DZ8 | -5.50 |
| HIF1A | HQ2 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | HQ5 | -5.00 |
| HIF1A | FBX3 | -5.40 |
| HIF1A | DZ4 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | DZ25 | -5.10 |
| HIF1A | DS10 | -6.00 |
Tab.2 Binding energies of the core active components of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction for NSCLC treatment for docking with the core target molecules TP53, AKT1, and HIF1A
| Target | Sample | Estimated ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| TP53 | DZ8 | -9.40 |
| TP53 | FBX3 | -9.90 |
| TP53 | HQ2 | -9.50 |
| TP53 | DS10 | -10.40 |
| TP53 | DZ25 | -10.20 |
| TP53 | DZ4 | -9.80 |
| TP53 | HQ5 | -9.60 |
| TP53 | HQ8 | -8.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ8 | -10.80 |
| AKT1 | FBX3 | -10.20 |
| AKT1 | HQ2 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DS10 | -11.10 |
| AKT1 | DZ25 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | DZ4 | -9.70 |
| AKT1 | HQ5 | -9.50 |
| AKT1 | HQ8 | -9.40 |
| HIF1A | HQ8 | -4.80 |
| HIF1A | DZ8 | -5.50 |
| HIF1A | HQ2 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | HQ5 | -5.00 |
| HIF1A | FBX3 | -5.40 |
| HIF1A | DZ4 | -4.90 |
| HIF1A | DZ25 | -5.10 |
| HIF1A | DS10 | -6.00 |
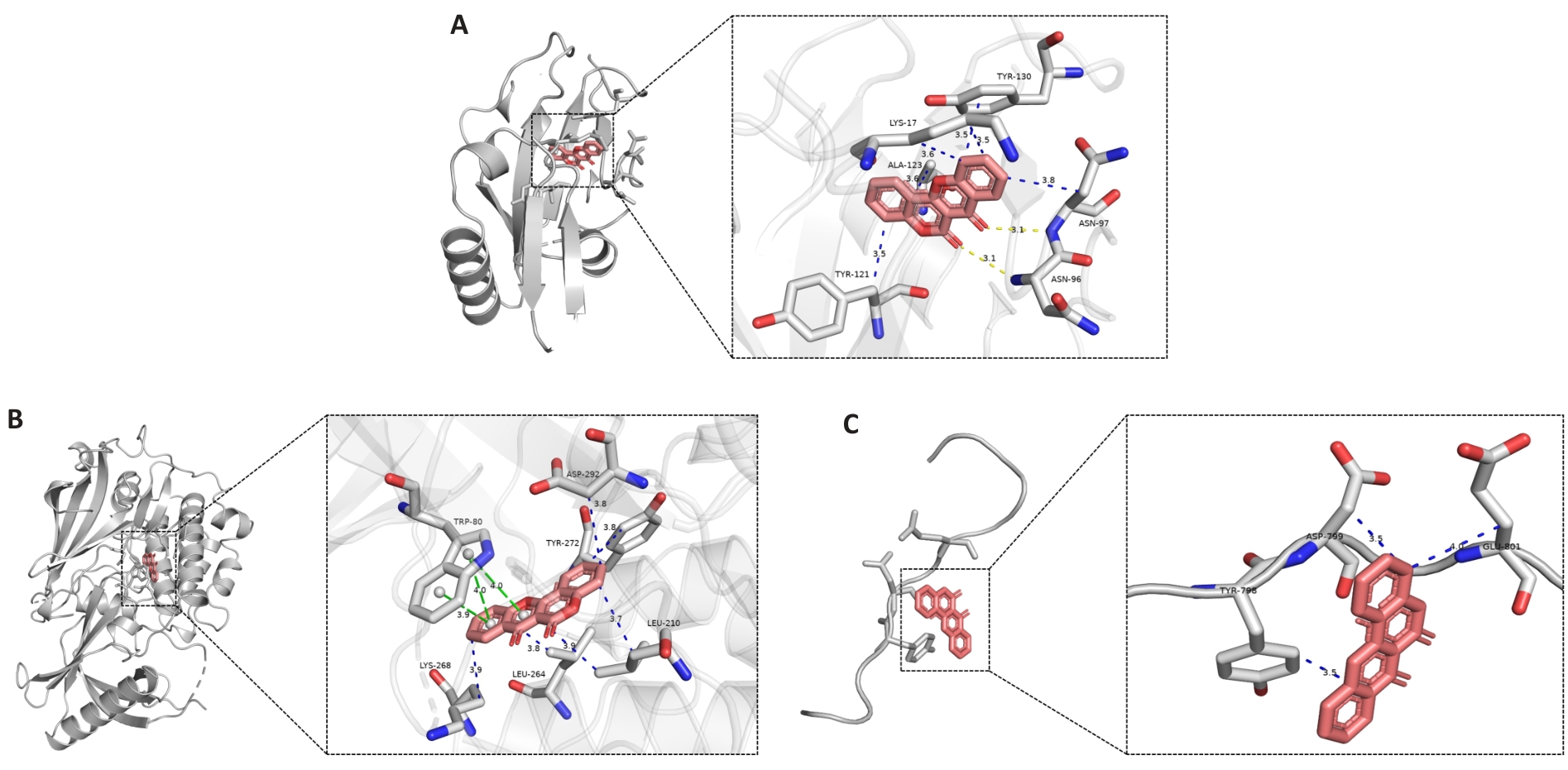
Fig.6 Visualization of the results of molecular docking analysis. A: Docked molecular conformation of TP53 with DS10; B: Molecular conformation of AKT1 docked with DS10; C: Molecular conformation of HIF1A docked with DS10.
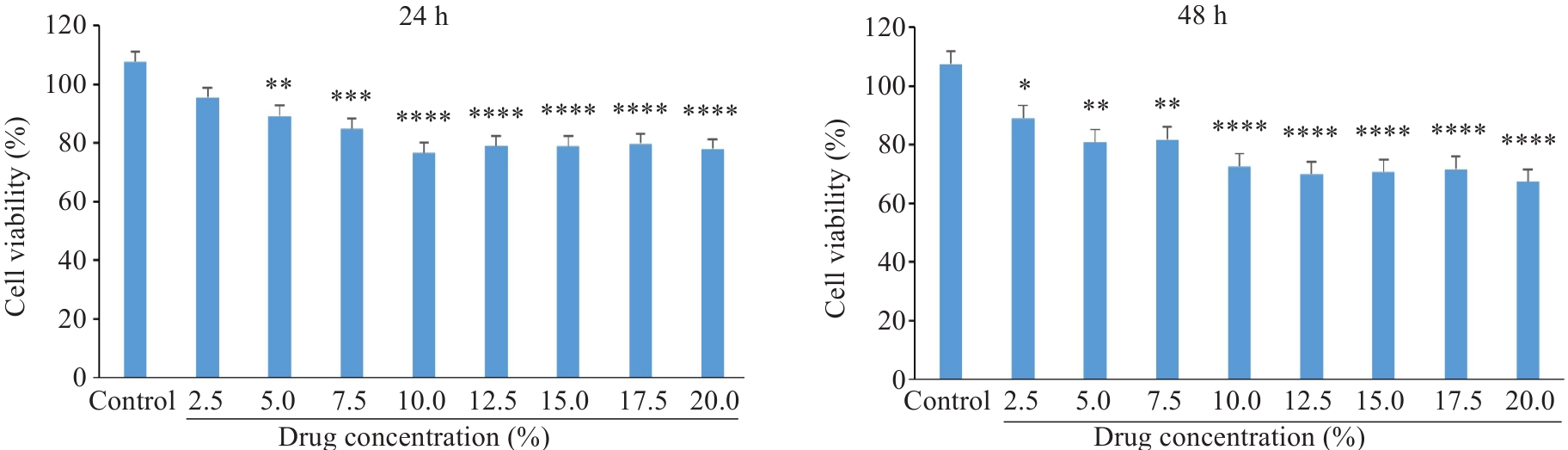
Fig.7 Changes in proliferation of A549 cells treated with Fuzheng Huaji Decoction-medicated serum detected by CCK-8 assay. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs control group.
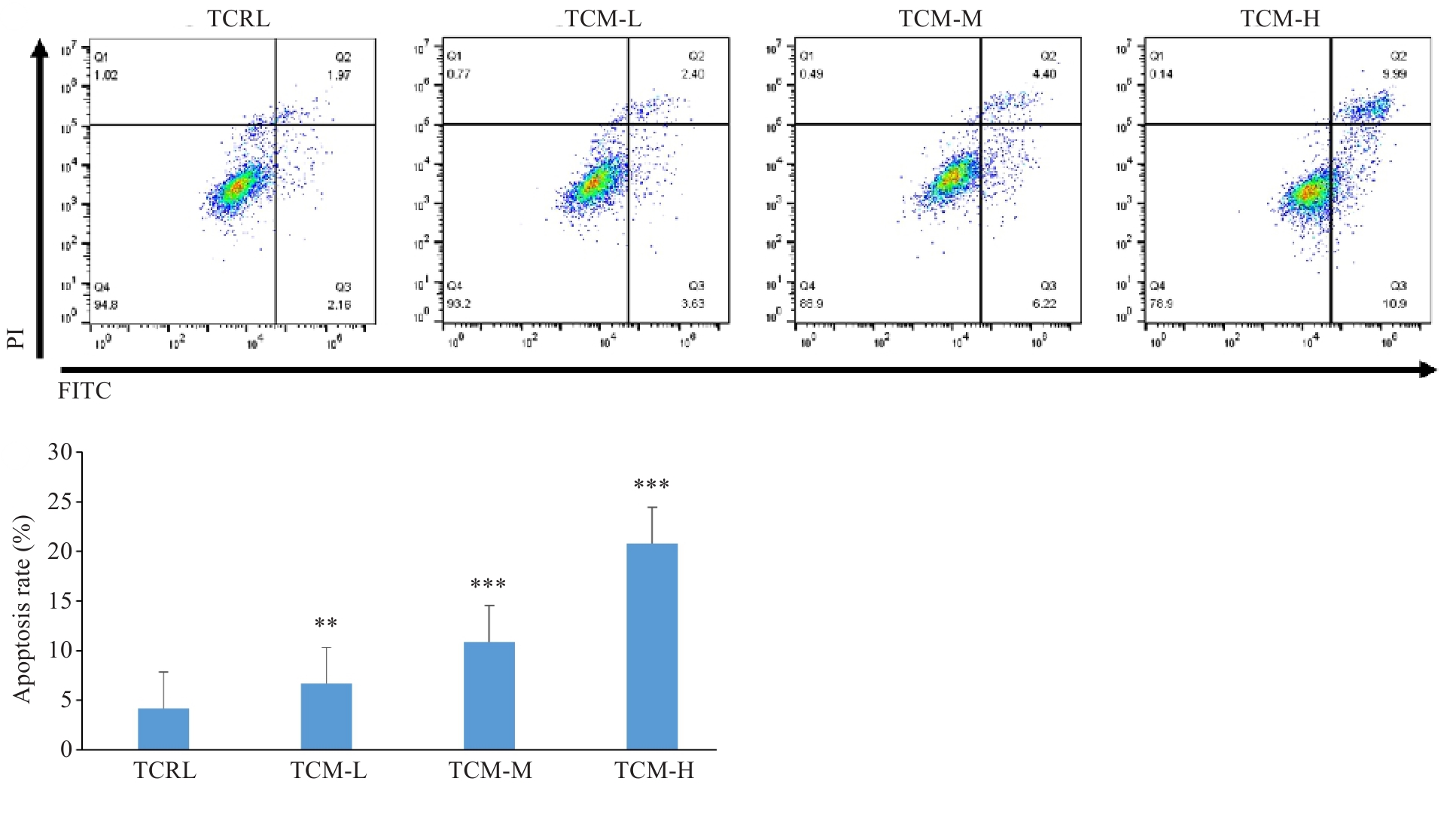
Fig.8 Apoptosis of A549 cells treated with Fuzheng Huaji Decoction-medicated serum detected by annexin V-FITC/PI staining. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs TCRL.
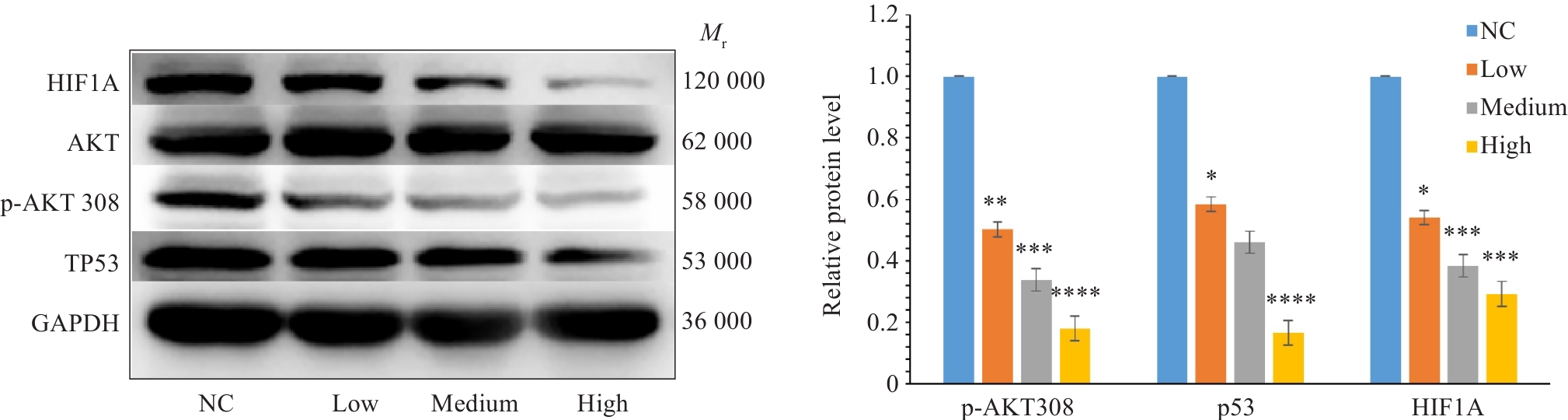
Fig.9 Effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction-medicated serum on expressions of HIF1A, p-AKT 308 and TP53 proteins in A549 cells detected by Western blotting proteins in A549 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs NCgroup.
| 1 | 郭 祯, 王 伟, 王 红, 等. 2022年全球肺癌终生罹患风险和死亡风险分析[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2025, 34(2): 81-8. doi:10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2025.02.A001 |
| 2 | Chen P, Liu Y, Wen Y, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer in China[J]. Cancer Commun: Lond, 2022, 42(10): 937-70. doi:10.1002/cac2.12359 |
| 3 | Gao S, Li N, Wang S, et al. Lung cancer in people's republic of China[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2020, 15(10): 1567-76. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.04.028 |
| 4 | Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and mana-gement of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Nature, 2018, 553(7689): 446-54. doi:10.1038/nature25183 |
| 5 | Hendriks LEL, Remon J, Faivre-Finn C, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2024, 10(1): 71. doi:10.1038/s41572-024-00551-9 |
| 6 | Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(5): 409-36. doi:10.3322/caac.21731 |
| 7 | 贺佐梅, 徐 云, 邓天好, 等. 7435份非小细胞肺癌病案中医用药规律分析[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 1157-63. |
| 8 | 骆文斌, 吴承玉. 肺癌病因病机研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2009, 11(3): 16-7. |
| 9 | 张鹏飞, 张惠娟, 梁建庆, 等. 基于“扶正祛邪”理论探讨中医药治疗非小细胞肺癌的规律及机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 42(8): 1-17. |
| 10 | 王思云, 柯 斌, 陈晓菲, 等. 加味龟鹿二仙胶汤通过抑制MAPKAP1/mTORC2/AKT通路抗NSCLC血管拟态形成[J/OL]. 中药材, 2024, (11): 2835-42. |
| 11 | 吴 静, 彭 丞, 胡学谦, 等. 非小细胞肺癌的中西医治疗研究进展[J]. 中国现代医生, 2022, 60(26): 123-7. |
| 12 | 赵亚东, 王福庆, 高亚军. 加味玉屏风散对中晚期肺癌化疗后肺脾气虚型患者生活质量及免疫功能的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2024, 33(1): 83-6. |
| 13 | 贺佳文, 韩 冰, 卢佳萱, 等. 从肿瘤微环境的重塑探索扶正解毒法治疗肿瘤的机制[J]. 环球中医药, 2024, 17(2): 273-6. |
| 14 | 赵延华, 周仲瑛, 吴勉华, 等. 基于癌毒理论探讨“抗癌解毒药”[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2022, 37(12): 7146-9. |
| 15 | 杨 柱, 唐东昕, 郭 斌, 等. 刘尚义治疗肿瘤用药经验数据挖掘分析[J]. 中医杂志, 2016, 57(19): 1641-5. doi:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2016.19.006 |
| 16 | 黄雯琪, 杨 柱, 唐东昕, 等. 基于数据挖掘分析刘尚义教授治疗肺癌的临床用药特点[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2017, 33(3): 418-21. doi:10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2017.03.024 |
| 17 | 叶懿祥, 陈冬梅, 贾立群, 等. 黄芪抗肿瘤药理作用机制与临床应用研究进展[J]. 世界中医药, 2023, 18(11): 1615-20. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2023.11.022 |
| 18 | 杨振耀, 张晓青, 王成志, 等. 黄芪甲苷抗肿瘤机制及其在肺癌中的研究进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2024, 42(8): 1-18. |
| 19 | 张 颖, 王 淳, 于 丹, 等. 黄芪多糖抑制肺腺癌A549/DDP细胞移植瘤裸鼠EMT改善顺铂耐药的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(6): 79-85. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20220527 |
| 20 | 屈子怡. 黄芪多糖联合化疗对晚期NSCLC的临床疗效及相关机制研究[D]. 天津: 天津中医药大学, 2022. |
| 21 | 武洪杨, 范向荣. 冬凌草甲素抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展[J]. 国际中医中药杂志, 2022, 44(5): 599-601. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn115398-20210511-00102 |
| 22 | 夏子昊, 赵光利, 肖翔文, 等.中药蜈蚣的研究进展[J].中药与临床,2023,14(01):103-8. |
| 23 | 张珂洋, 张永清, 杨春淼, 等. 全蝎的炮制历史沿革、化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2024, 49(4): 868-83. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230814.202 |
| 24 | Prejac J, Dedić Plavetić N, Gotovac Jerčić K, et al. A first report of a rare TP53 variant associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome manifesting as invasive breast cancer and malignant solitary fibrous tumor[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19(1): 254. doi:10.1186/s12957-021-02370-8 |
| 25 | 邓世超. 不同信号通路在非小细胞肺癌中的预测价值研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2022. |
| 26 | La Fleur L, Falk-Sörqvist E, Smeds P, et al. Mutation patterns in a population-based non-small cell lung cancer cohort and prognostic impact of concomitant mutations in KRAS and TP53 or STK11[J]. Lung Cancer, 2019, 130: 50-8. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.01.003 |
| 27 | Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Mermel CH, et al. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types[J]. Nature, 2014, 505(7484): 495-501. doi:10.1038/nature12912 |
| 28 | Rao G, Pierobon M, Kim IK, et al. Inhibition of AKT1 signaling promotes invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells with K-RAS or EGFR mutations[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 7066. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06128-9 |
| 29 | Lin H, Ai D, Liu Q, et al. Modified podophyllotoxin phenoxyacetamide phenylacetate derivatives: tubulin/AKT1 dual-targeting and potential anticancer agents for human NSCLC[J]. J Nat Prod, 2023, 86(7): 1844-54. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00384 |
| 30 | Zhang L, Gong Y, Zhang L, et al. Gou Qi Zi inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT1 signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1034750. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1034750 |
| 31 | Zhang J, Wu Y, Lin YH, et al. Prognostic value of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and prolyl 4-hydroxylase beta polypeptide overex-pression in gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(22): 2381-91. doi:10.3748/wjg.v24.i22.2381 |
| 32 | Lee SH, Golinska M, Griffiths JR. HIF-1-independent mechanisms regulating metabolic adaptation in hypoxic cancer cells[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2371. doi:10.3390/cells10092371 |
| 33 | 刘燕翔, 张 锦, 郑玉双, 等. PGC-1α、HIF1A在胃癌中的表达与临床病理特征及预后的关系[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2024, 33(6): 709-13. |
| 34 | 李海燕, 王锦伟, 金英英, 等. 缺氧对肺癌细胞中lncRNA H19的表达及耐药机制的研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2023, 33(4): 388-92. |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [5] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [6] | Dandan LI, Jiaxin CHU, Yan YAN, Wenjun XU, Xingchun ZHU, Yun SUN, Haofeng DING, Li REN, Bo ZHU. Curcumin inhibits lipid metabolism in non-small cell lung cancer by downregulating the HIF-1α pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1039-1046. |
| [7] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [10] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [13] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [15] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||