Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 179-186.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.21
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yadi HE1,2( ), Xuanru ZHOU1, Jinhui JIN1, Ting SONG1(
), Xuanru ZHOU1, Jinhui JIN1, Ting SONG1( )
)
Received:2024-07-15
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Ting SONG
E-mail:540651179@qq.com;tingsong2015@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:Yadi HE, Xuanru ZHOU, Jinhui JIN, Ting SONG. PE-CycleGAN network based CBCT-sCT generation for nasopharyngeal carsinoma adaptive radiotherapy[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 179-186.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.21
| Method | MAE(HU) | PSNR(dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | 81.06±15.86 | 21.54±2.37 | 0.86±0.05 |
| CycleGAN | 63.92±12.08 | 24.89±2.15 | 0.89±0.04 |
| PE-CycleGAN | 56.89±13.84 | 26.69±2.41 | 0.92±0.02 |
Tab.1 Quantitative comparison of image quality between sCT,CBCT and reference CT images (Mean±SD)
| Method | MAE(HU) | PSNR(dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | 81.06±15.86 | 21.54±2.37 | 0.86±0.05 |
| CycleGAN | 63.92±12.08 | 24.89±2.15 | 0.89±0.04 |
| PE-CycleGAN | 56.89±13.84 | 26.69±2.41 | 0.92±0.02 |
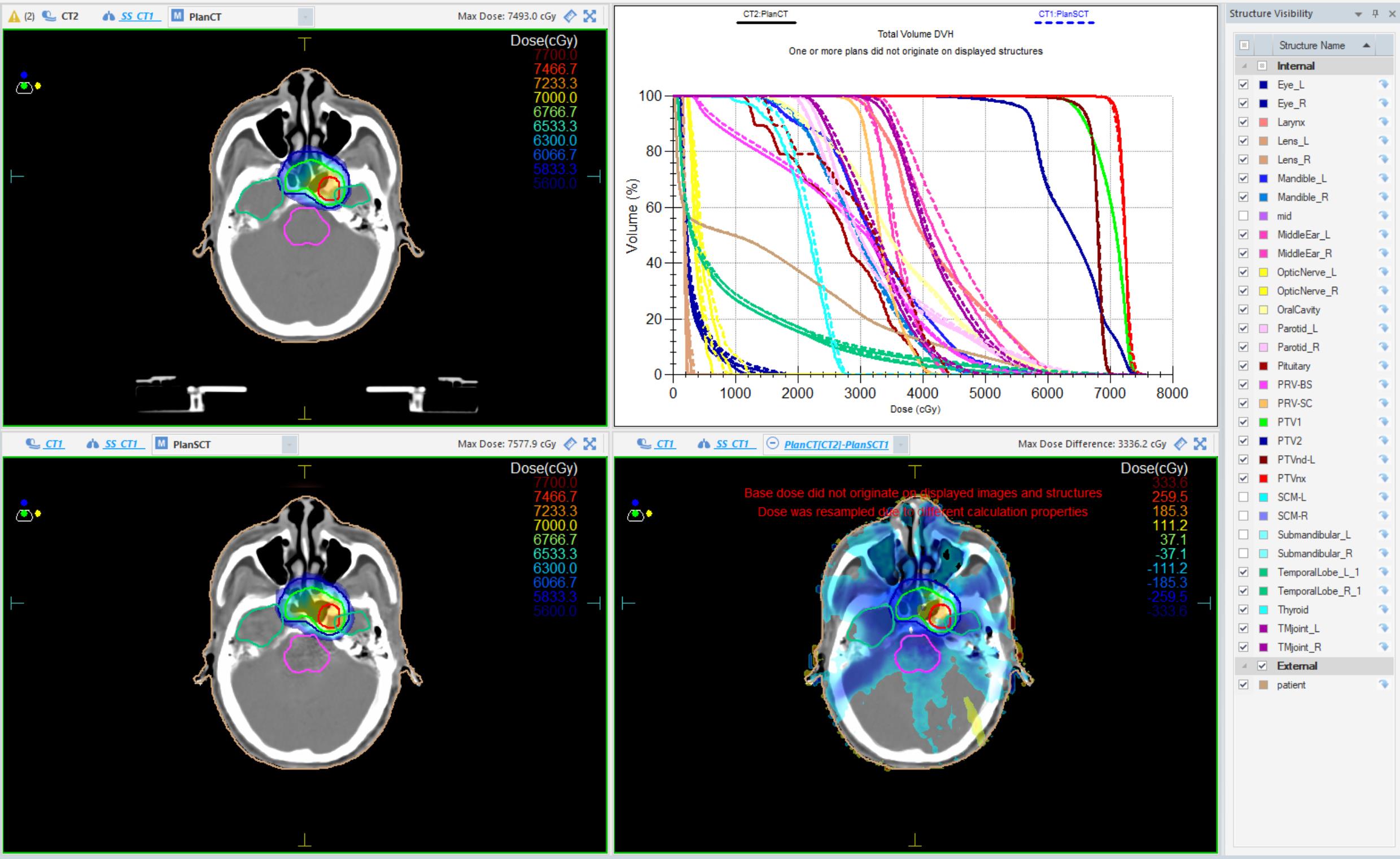
Fig.4 Dose distribution on CT and PE-CycleGAN-generated sCT images for a patient. Top left: Dose distribution on planning CT; Top right: Dose-volume histogram (DVH) for planning CT and sCT; Bottom left: Dose distribution on sCT; Bottom right: Dose distribution difference between planning CT and sCT.
| Method | 2 mm/2% | 3 mm/3% | P value (vs CBCT) | P value (vs CycleGan) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | (81.65±3.92) % | (86.92±3.51) % | - | - |
| CycleGAN | (87.69±3.50) % | (94.58±2.23) % | - | - |
| PE-CycleGAN | (90.13±3.75) % | (97.20±2.52) % | <0.001 (2 mm/2%), <0.001 (3 mm/3%) | <0.05 (2 mm/2%), <0.01 (3 mm/3%) |
Tab.2 Gamma pass rates for sCT and CBCT
| Method | 2 mm/2% | 3 mm/3% | P value (vs CBCT) | P value (vs CycleGan) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT | (81.65±3.92) % | (86.92±3.51) % | - | - |
| CycleGAN | (87.69±3.50) % | (94.58±2.23) % | - | - |
| PE-CycleGAN | (90.13±3.75) % | (97.20±2.52) % | <0.001 (2 mm/2%), <0.001 (3 mm/3%) | <0.05 (2 mm/2%), <0.01 (3 mm/3%) |
| Structure | Parameter | CT | sCT | Relative deviation (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTVnx | HI | 1.07±0.02 | 1.08±0.03 | 0.93±0.93 | 0.28 |
| CI | 0.58±0.13 | 0.59±0.12 | 1.72±1.72 | 0.36 | |
| PTVnd | HI | 1.11±0.07 | 1.11±0.06 | 0.00±0.90 | 0.95 |
| CI | 0.13±0.10 | 0.13±0.10 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 | |
| PTV1 | HI | 1.17±0.03 | 1.17±0.03 | 0.00±0.85 | 0.89 |
| CI | 0.46±0.14 | 0.47±0.14 | 2.17±2.17 | 0.42 | |
| PTV2 | HI | 1.41±0.09 | 1.39±0.06 | -1.42±1.42 | 0.18 |
| CI | 0.68±0.14 | 0.69±0.13 | 1.47±1.47 | 0.33 | |
| PRV_SC | Dmax (Gy) | 45.59±5.13 | 45.51±4.84 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 36.10±4.14 | 35.98±3.97 | -0.33±0.33 | 0.65 | |
| PRV_BS | Dmax (Gy) | 61.91±7.33 | 62.03±7.38 | 0.19±0.19 | 0.78 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 27.55±7.20 | 27.73±7.38 | 0.65±0.65 | 0.52 | |
| Parotid | V30 (%) | 49.91±8.82 | 49.41±8.64 | -1.00±1.00 | 0.31 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 33.67±3.83 | 33.55±3.89 | -0.36±0.36 | 0.64 | |
| Temp | Dmax (Gy) | 67.04±9.74 | 67.92±9.98 | 1.31±1.31 | 0.22 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 11.16±7.90 | 11.41±8.03 | 2.24±2.24 | 0.14 | |
| Larynx | Dmean (Gy) | 41.78±6.56 | 41.72±7.06 | -0.14±0.14 | 0.87 |
| Oral | Dmean (Gy) | 36.20±5.51 | 36.20±5.70 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 |
| Mandible | Dmax (Gy) | 63.50±7.06 | 63.66±6.97 | 0.25±0.25 | 0.73 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 35.59±6.73 | 35.53±6.65 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 | |
| Lens | Dmax (Gy) | 3.55±2.47 | 3.67±2.51 | 3.38±3.38 | 0.09 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 5.81±4.07 | 5.84±4.08 | 0.52±0.52 | 0.67 | |
| Eye | Dmax (Gy) | 24.95±27.58 | 25.28±27.22 | 1.32±1.32 | 0.25 |
| PRV_ON | Dmean (Gy) | 18.90±2.95 | 18.87±2.90 | -0.16±0.16 | 0.84 |
Tab.3 Comparison of target and key organ-at-risk doses between PE-CycleGAN-generated sCT and CT images (Mean±SD)
| Structure | Parameter | CT | sCT | Relative deviation (%) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTVnx | HI | 1.07±0.02 | 1.08±0.03 | 0.93±0.93 | 0.28 |
| CI | 0.58±0.13 | 0.59±0.12 | 1.72±1.72 | 0.36 | |
| PTVnd | HI | 1.11±0.07 | 1.11±0.06 | 0.00±0.90 | 0.95 |
| CI | 0.13±0.10 | 0.13±0.10 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 | |
| PTV1 | HI | 1.17±0.03 | 1.17±0.03 | 0.00±0.85 | 0.89 |
| CI | 0.46±0.14 | 0.47±0.14 | 2.17±2.17 | 0.42 | |
| PTV2 | HI | 1.41±0.09 | 1.39±0.06 | -1.42±1.42 | 0.18 |
| CI | 0.68±0.14 | 0.69±0.13 | 1.47±1.47 | 0.33 | |
| PRV_SC | Dmax (Gy) | 45.59±5.13 | 45.51±4.84 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 36.10±4.14 | 35.98±3.97 | -0.33±0.33 | 0.65 | |
| PRV_BS | Dmax (Gy) | 61.91±7.33 | 62.03±7.38 | 0.19±0.19 | 0.78 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 27.55±7.20 | 27.73±7.38 | 0.65±0.65 | 0.52 | |
| Parotid | V30 (%) | 49.91±8.82 | 49.41±8.64 | -1.00±1.00 | 0.31 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 33.67±3.83 | 33.55±3.89 | -0.36±0.36 | 0.64 | |
| Temp | Dmax (Gy) | 67.04±9.74 | 67.92±9.98 | 1.31±1.31 | 0.22 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 11.16±7.90 | 11.41±8.03 | 2.24±2.24 | 0.14 | |
| Larynx | Dmean (Gy) | 41.78±6.56 | 41.72±7.06 | -0.14±0.14 | 0.87 |
| Oral | Dmean (Gy) | 36.20±5.51 | 36.20±5.70 | 0.00±0.00 | 1.00 |
| Mandible | Dmax (Gy) | 63.50±7.06 | 63.66±6.97 | 0.25±0.25 | 0.73 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 35.59±6.73 | 35.53±6.65 | -0.17±0.17 | 0.82 | |
| Lens | Dmax (Gy) | 3.55±2.47 | 3.67±2.51 | 3.38±3.38 | 0.09 |
| Dmean (Gy) | 5.81±4.07 | 5.84±4.08 | 0.52±0.52 | 0.67 | |
| Eye | Dmax (Gy) | 24.95±27.58 | 25.28±27.22 | 1.32±1.32 | 0.25 |
| PRV_ON | Dmean (Gy) | 18.90±2.95 | 18.87±2.90 | -0.16±0.16 | 0.84 |
| 1 | 吴伟伟, 李韶今, 尹 慧, 等. 局部晚期鼻咽癌调强放疗中解剖结构改变及剂量分布变化研究[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2017, 37(11): 826-31. |
| 2 | Zhao SH, Han J, Yang ZY, et al. Anatomical and dosimetric variations during volumetric modulated arc therapy in patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma after induction therapy: implications for adaptive radiation therapy[J]. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol, 2024, 49: 100861. |
| 3 | Liu YZ, Lei Y, Wang TH, et al. CBCT-based synthetic CT generation using deep-attention cycleGAN for pancreatic adaptive radiotherapy[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(6): 2472-83. |
| 4 | Liang X, Chen LY, Nguyen D, et al. Generating synthesized computed tomography (CT) from cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) using CycleGAN for adaptive radiation therapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2019, 64(12): 125002. |
| 5 | Chen LY, Liang X, Shen CY, et al. Synthetic CT generation from CBCT images via deep learning[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(3): 1115-25. |
| 6 | 全科润, 程品晶, 陈榕钦, 等. 基于循环生成对抗网络的鼻咽癌CBCT图像修正[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2021, 38(5): 582-6. |
| 7 | 亓孟科, 李永宝, 吴艾茜, 等. 基于生成对抗网络的鼻咽癌患者伪CT合成方法研究[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2020, 29(4): 267-72. |
| 8 | Hansen DC, Landry G, Kamp F, et al. ScatterNet: a convolutional neural network for cone-beam CT intensity correction[J]. Med Phys, 2018, 45(11): 4916-26. |
| 9 | 周 琼, 李永武, 王 奇, 等. 基于形变配准和伪CT的鼻咽癌自适应放疗剂量评估[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2019, 36(8): 892-7. |
| 10 | Rusanov B, Hassan GM, Reynolds M, et al. Deep learning methods for enhancing cone-beam CT image quality toward adaptive radiation therapy: a systematic review[J]. Med Phys, 2022, 49(9): 6019-54. |
| 11 | Kida S, Kaji, Nawa K, et al. Visual enhancement of Cone-beam CT by use of CycleGAN[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(3): 998-1010. |
| 12 | Liu JW, Yan H, Cheng HL, et al. CBCT-based synthetic CT generation using generative adversarial networks with disentangled representation[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2021, 11(12): 4820-34. |
| 13 | Wang TH, Lei Y, Fu YB, et al. Machine learning in quantitative PET: a review of attenuation correction and low-count image reconstruction methods[J]. Phys Med, 2020, 76: 294-306. |
| 14 | 潘 丹, 贾龙飞, 曾 安. 生成式对抗网络在医学图像处理中的应用[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2018, 35(6): 970-6. |
| 15 | Ronneberger O. Invited talk: U-net convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[M]//Informatik aktuell. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2017: 3. |
| 16 | He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 27-30, 2016. Las Vegas, NV, USA. IEEE, 2016: 770-8. |
| 17 | Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[J]. IEEE TPAMI, 2021, 43(12): 4254-67. |
| 18 | Wang R, Wu ZX, Weng ZJ, et al. Cross-domain contrastive learning for unsupervised domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Trans Multimedia, 2023, 25: 1665-73. |
| 19 | Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2004, 13(4): 600-12. |
| 20 | Galić I, Habijan M, Leventić H, et al. Machine learning empowering personalized medicine: a comprehensive review of medical image analysis methods[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(21): 4411. |
| 21 | Huynh E, Hosny A, Guthier C, et al. Artificial intelligence in radiation oncology[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2020, 17(12): 771-81. |
| 22 | Wendling M, Morrow A, Hoggarth M, et al. An efficient protocol for radiotherapy quality control with machine learning[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(4): 1526-34. |
| 23 | Lei Y, Tang XY, Higgins K, et al. Learning-based CBCT correction using alternating random forest based on auto-context model[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(2): 601-18. |
| 24 | Jiang J, Sharfo AWM, Mak RH, et al. Development and validation of an MRI‐only synthetic CT generation method using cycle‐consistent generative adversarial networks for prostate radiotherapy[J]. Med Phys, 2021, 48(1): 416-29. |
| 25 | Thummerer A, Zaffino P, Meijers A, et al. Comparison of CBCT based synthetic CT methods suitable for proton dose calculations in adaptive proton therapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2020, 65(9): 095002. |
| 26 | Pulliam KB, Huang JY, Howell RM, et al. Comparison of 2D and 3D gamma analyses[J]. Med Phys, 2014, 41(2): 021710. |
| 27 | 孙鸿飞, 倪昕晔, 杨建华. 基于深度学习方法的伪CT图像合成技术研究及在放疗中的应用进展[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2021, 41(3): 222-8. |
| 28 | Lei Y, Harms J, Wang TH, et al. MRI-only based synthetic CT generation using dense cycle consistent generative adversarial networks[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(8): 3565-81. |
| 29 | Liu Y, Lei Y, Wang Y, et al. Evaluation of a deep learning-based synthetic CT generation method for MRI-only breast radiotherapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2020, 65(8): 085020. |
| 30 | Maspero M, Savenije MHF, Dinkla AM, et al. Dose evaluation of fast synthetic-CT generation using a generative adversarial network for general pelvis MR-only radiotherapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2018, 63(18): 185001. |
| 31 | Kim J, Park S, Yu H, et al. Deep learning-based synthetic CT generation from MR images for PET attenuation correction: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. IEEE T Radiat Plasma, 2022, 6(3): 273-287. |
| 32 | Sonke JJ, Aznar M, Rasch C. Adaptive radiotherapy for anatomical changes[J]. Semin Radiat Oncol, 2019, 29(3): 245-57. |
| 33 | Dona Lemus OM, Cao MS, Cai B, et al. Adaptive radiotherapy: next-generation radiotherapy[J]. Cancers, 2024, 16(6): 1206. |
| [1] | Ziyu ZHENG, Xiaying YANG, Shengjie WU, Shijie ZHANG, Guorong LYU, Peizhong LIU, Jun WANG, Shaozheng HE. A multi-feature fusion-based model for fetal orientation classification from intrapartum ultrasound videos [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1563-1570. |
| [2] | Wenwei LI, Zerui MAO, Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jing HUANG. A sparse-view cone-beam CT reconstruction algorithm based on bidirectional flow field- guided projection completion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 395-408. |
| [3] | Weiyang FANG, Hui XIAO, Shuang WANG, Xiaoming LIN, Chaomin CHEN. A deep learning model based on magnetic resonance imaging and clinical feature fusion for predicting preoperative cytokeratin 19 status in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1738-1751. |
| [4] | Jiazhi OU, Chang'an ZHAN, Feng YANG. An autoencoder model based on one-dimensional neural network for epileptic EEG anomaly detection [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1796-1804. |
| [5] | Chen WANG, Mingqiang MENG, Mingqiang LI, Yongbo WANG, Dong ZENG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA. Reconstruction from CT truncated data based on dual-domain transformer coupled feature learning [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 950-959. |
| [6] | LONG Kaixing, WENG Danyi, GENG Jian, LU Yanmeng, ZHOU Zhitao, CAO Lei. Automatic classification of immune-mediated glomerular diseases based on multi-modal multi-instance learning [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 585-593. |
| [7] | XIAO Hui, FANG Weiyang, LIN Mingjun, ZHOU Zhenzhong, FEI Hongwen, CHEN Chaomin. A multiscale carotid plaque detection method based on two-stage analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 387-396. |
| [8] | Caolin LIU, Qingqing ZOU, Menghong WANG, Qinmei YANG, Liwen SONG, Zixiao LU, Qianjin FENG, Yinghua ZHAO. Identification of osteoid and chondroid matrix mineralization in primary bone tumors using a deep learning fusion model based on CT and clinical features: a multi-center retrospective study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2412-2420. |
| [9] | MI Jia, ZHOU Yujia, FENG Qianjin. A 3D/2D registration method based on reconstruction of orthogonal-view Xray images [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1636-1643. |
| [10] | CHU Zhiqin, QU Yaoming, ZHONG Tao, LIANG Shujun, WEN Zhibo, ZHANG Yu. A Dual-Aware deep learning framework for identification of glioma isocitrate dehydrogenase genotype using magnetic resonance amide proton transfer modalities [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1379-1387. |
| [11] | LIU Yuxuan, CHU Zhiqin, ZHANG Yu. Physical model-based cascaded generative adversarial networks for accelerating quantitative multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1402-1409. |
| [12] | YU Jiahong, ZHANG Kunpeng, JIN Shuang, SU Zhe, XU Xiaotong, ZHANG Hua. Sinogram interpolation combined with unsupervised image-to-image translation network for CT metal artifact correction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1214-1223. |
| [13] | TENG Lin, WANG Bin, FENG Qianjin. Deep learning-based dose prediction in radiotherapy planning for head and neck cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 1010-1016. |
| [14] | ZHOU Hao, ZENG Dong, BIAN Zhaoying, MA Jianhua. A semi-supervised network-based tissue-aware contrast enhancement method for CT images [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 985-993. |
| [15] | WU Xueyang, ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Hua, ZHONG Tao. Whole-brain parcellation for macaque brain magnetic resonance images based on attention mechanism and multi-modality feature fusion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2118-2125. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||