Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 1-9.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.01
Wei LUO1( ), Yuhang WANG1, Yansong LIU1, Yuanyuan WANG1, Lei AI2(
), Yuhang WANG1, Yansong LIU1, Yuanyuan WANG1, Lei AI2( )
)
Received:2024-03-13
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Lei AI
E-mail:wei.luo@nsi.edu.cn;ailei_982@163.com
Supported by:Wei LUO, Yuhang WANG, Yansong LIU, Yuanyuan WANG, Lei AI. High glucose induces pro-inflammatory polarization of macrophages by inhibiting immune-responsive gene 1 expression[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 1-9.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.01
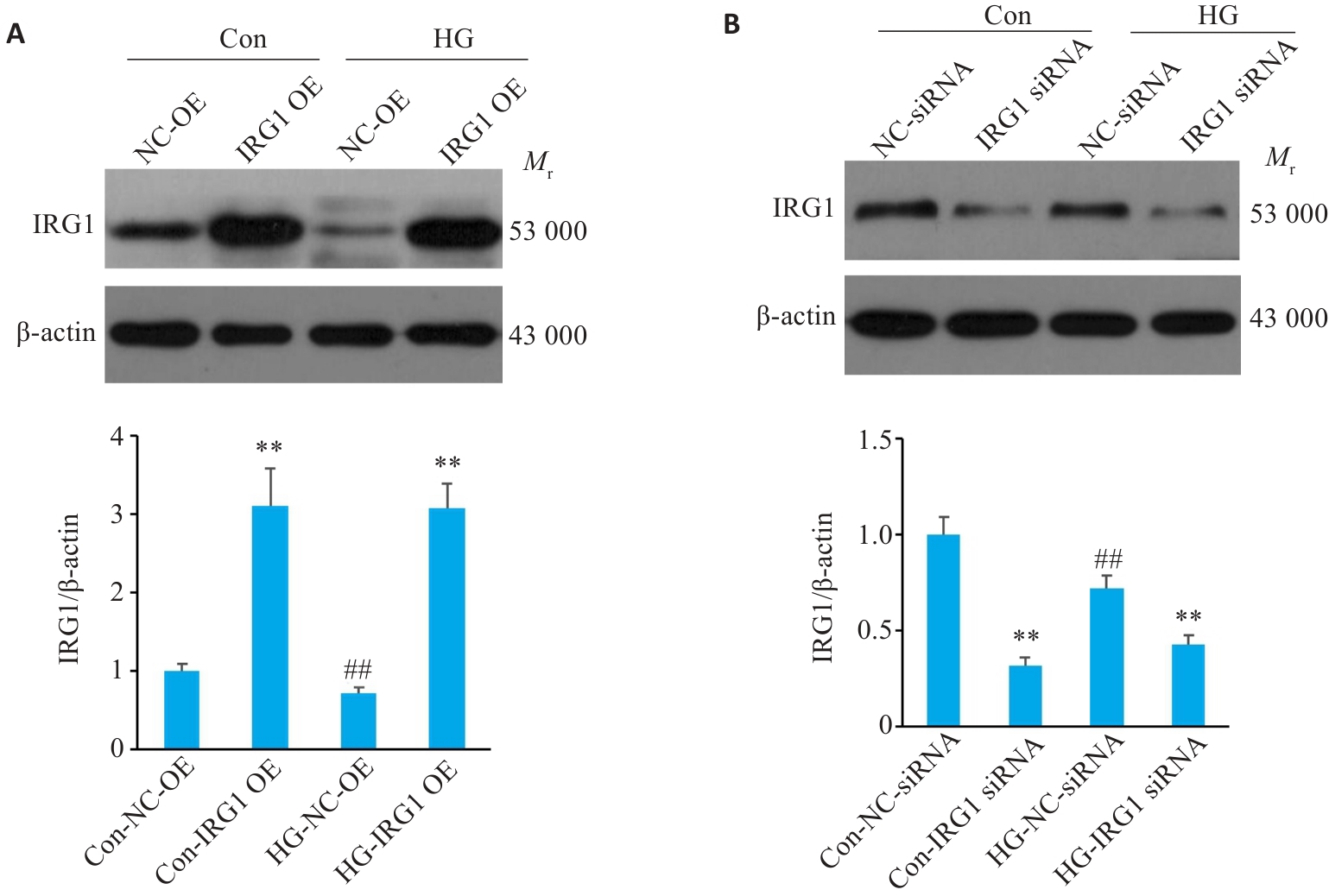
Fig.1 Validation of the efficiency of overexpression or silencing of IRG1 in macrophages under high glucose condition. A: Expression of IRG1 protein detected by Western blotting after transfection with the IRG1-overexpressing plasmid (**P<0.01 vs correspondingNC-OE groups; ##P<0.01 vs corresponding Con groups). B: Expression of IRG1 protein detected by Western blotting after IRG1 silencing (**P<0.01 vs correspondingNC-siRNA groups; ##P<0.01 vs corresponding Con groups). Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=6) if not specified otherwise. HG: High glucose.
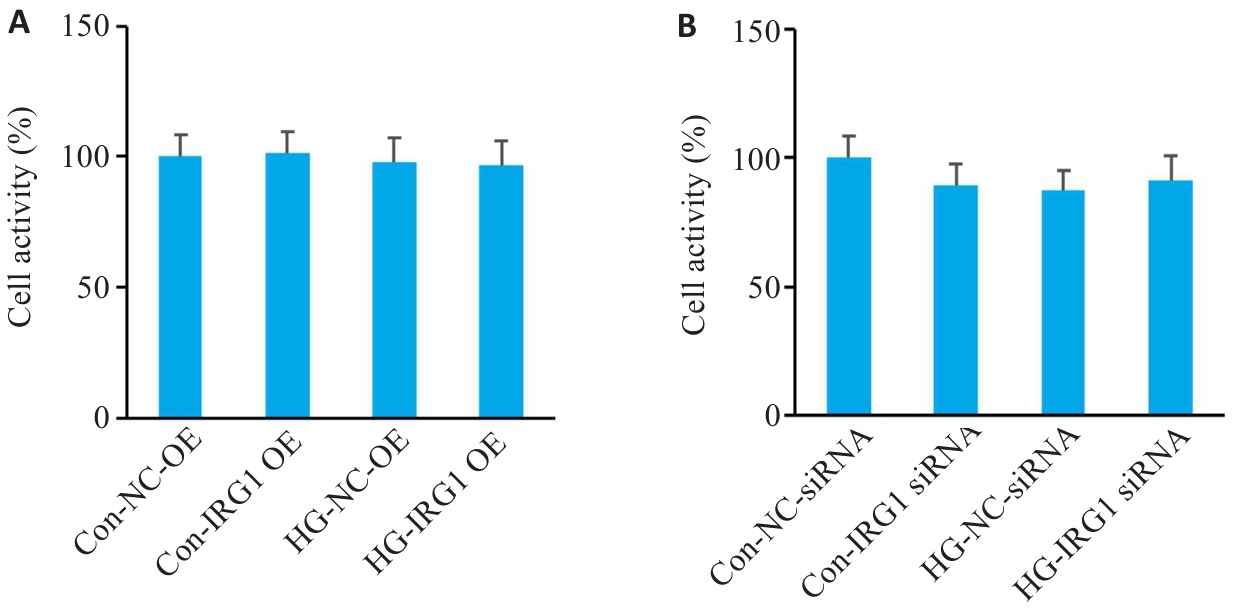
Fig.2 Effects of IRG1 overexpression (A) or silencing (B) on viability of the macrophages cultured in high glucose detected by CCK-8 assay (Mean±SD, n=6).
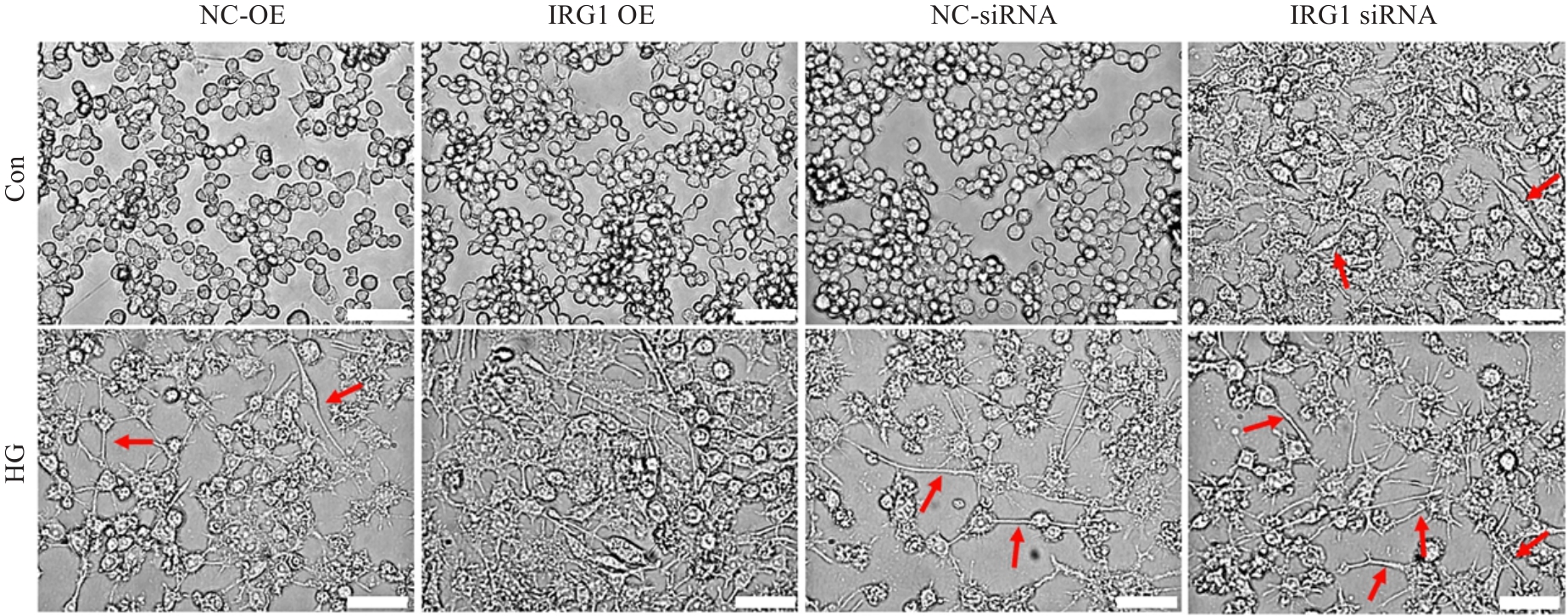
Fig.3 Effects of IRG1 overexpression or silencing on morphology of the macrophages cultured in high glucose (phase contrast microscopy, scale bar=50 μm). Arrows indicate M1-like spindle cells and pseudopodia.
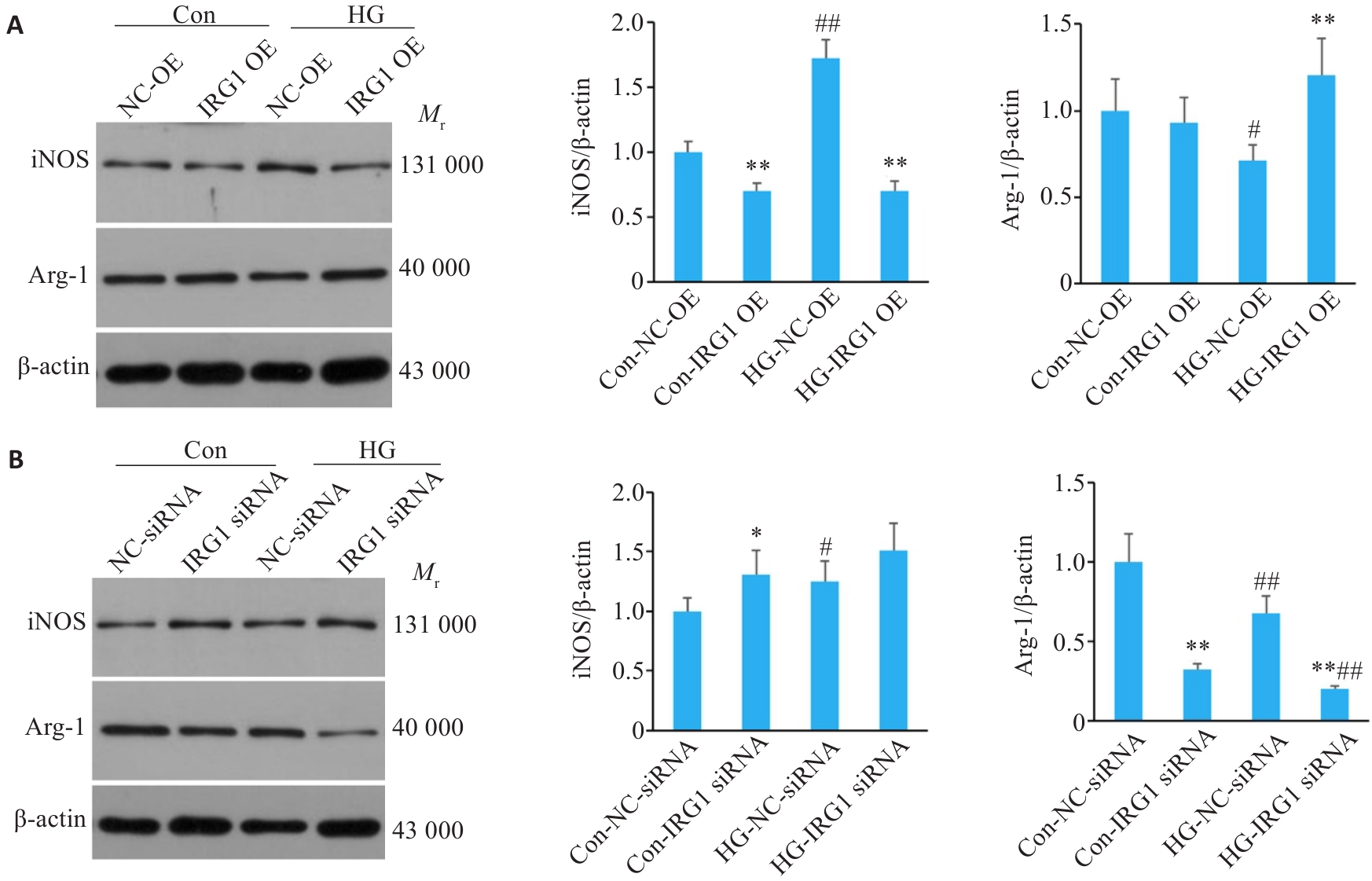
Fig.4 Effects of IRG1 overexpression (A) or silencing (B) on expressions of iNOS and Arg-1 in the macrophages cultured in high glucose detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs corresponding NC-OE group (A) or NC-siRNA group (B); #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs corresponding Con group.
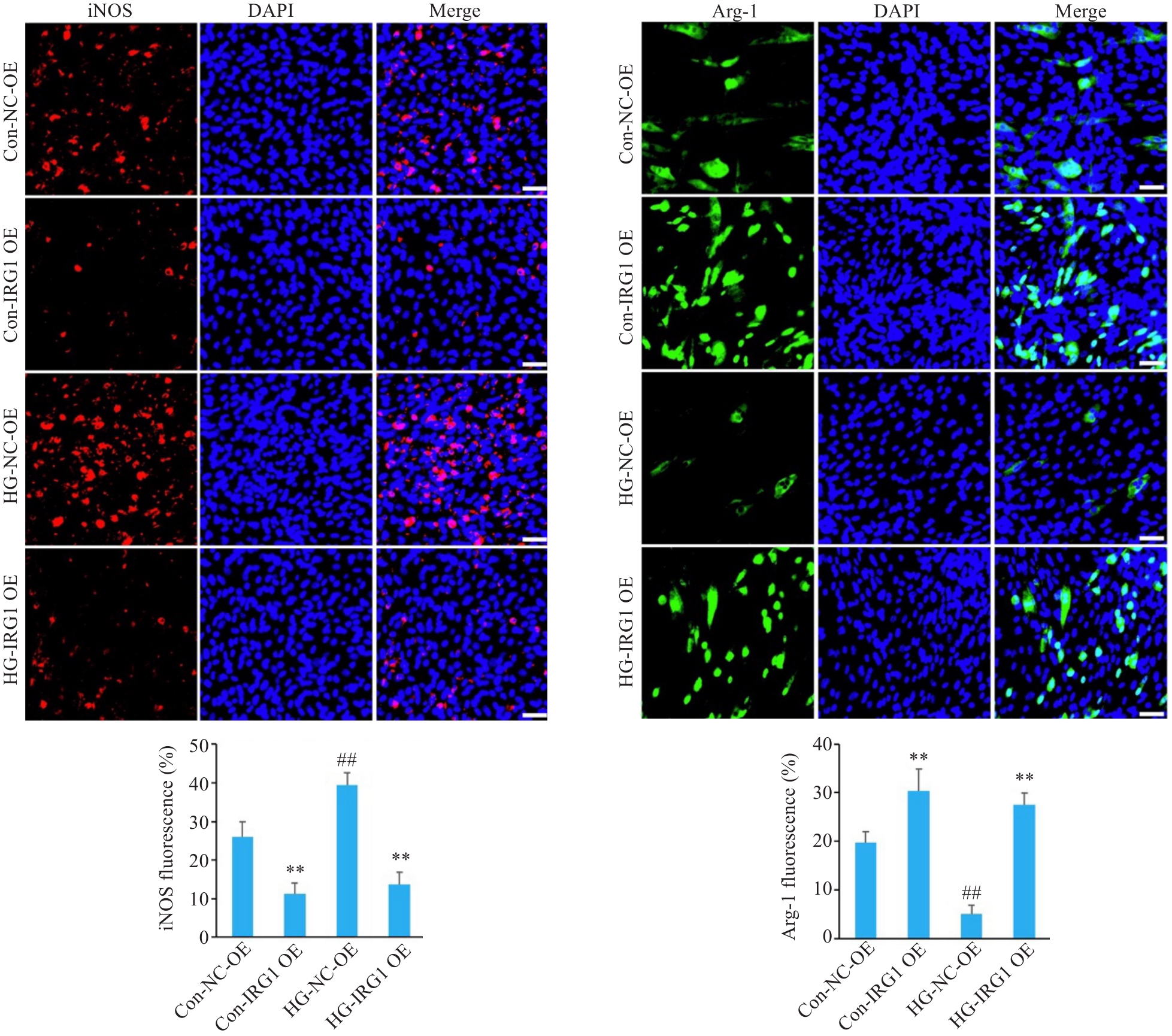
Fig.5 Immunofluorescence assay for assessing the effects of IRG1 overexpression on expressions of iNOS and Arg-1 in the macrophages cultured in high glucose (scale bar=50 μm). **P<0.01 vs corresponding NC-OE group; ##P<0.01 vs corresponding Con group.
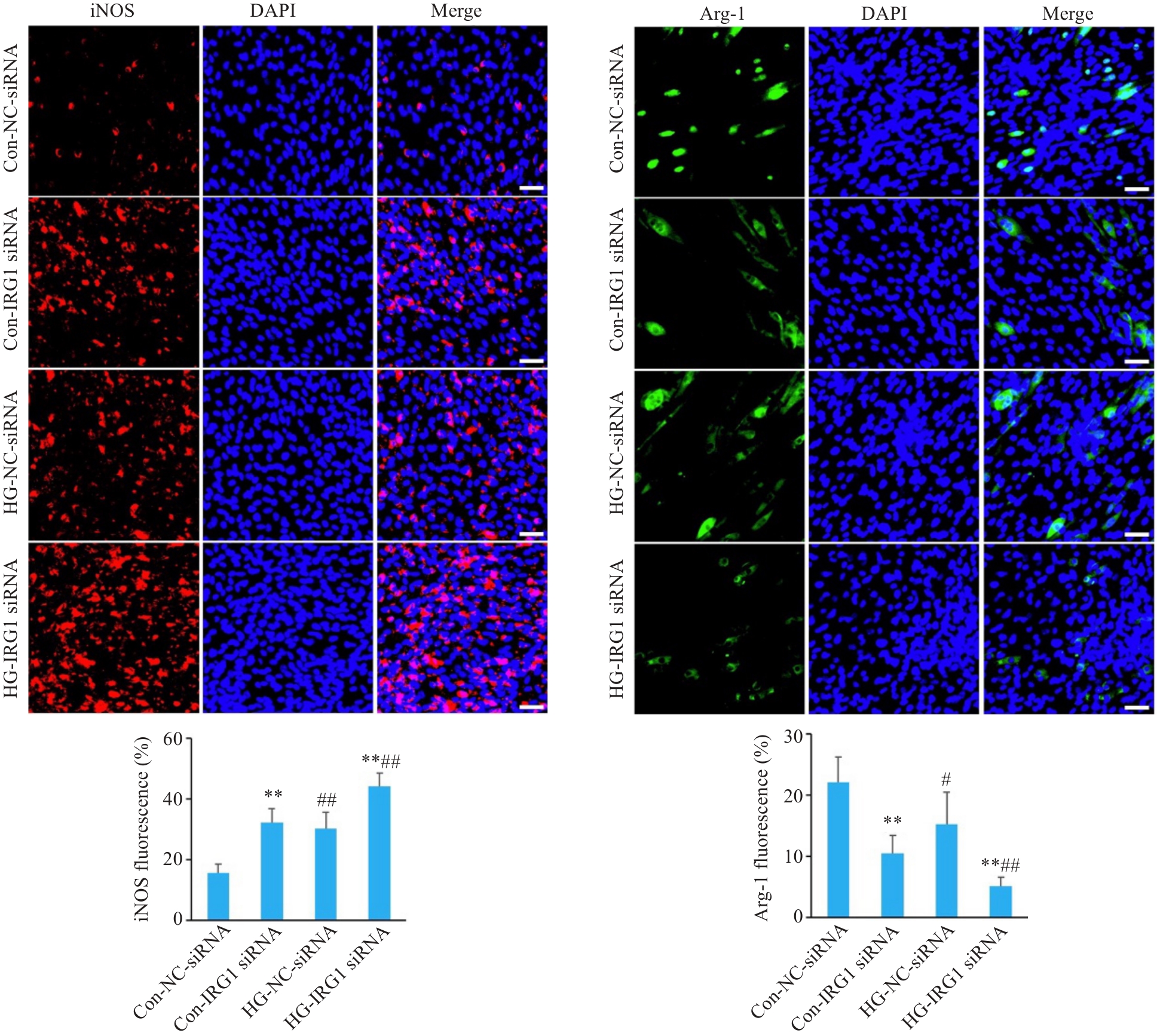
Fig.6 Immunofluorescence assay for assessing the effects of IRG1 silencing on expressions of iNOS and Arg-1 in the macrophages cultured in high glucose (scale bar=50 μm). **P<0.01 vs corresponding NC-siRNA group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs corresponding Con group.
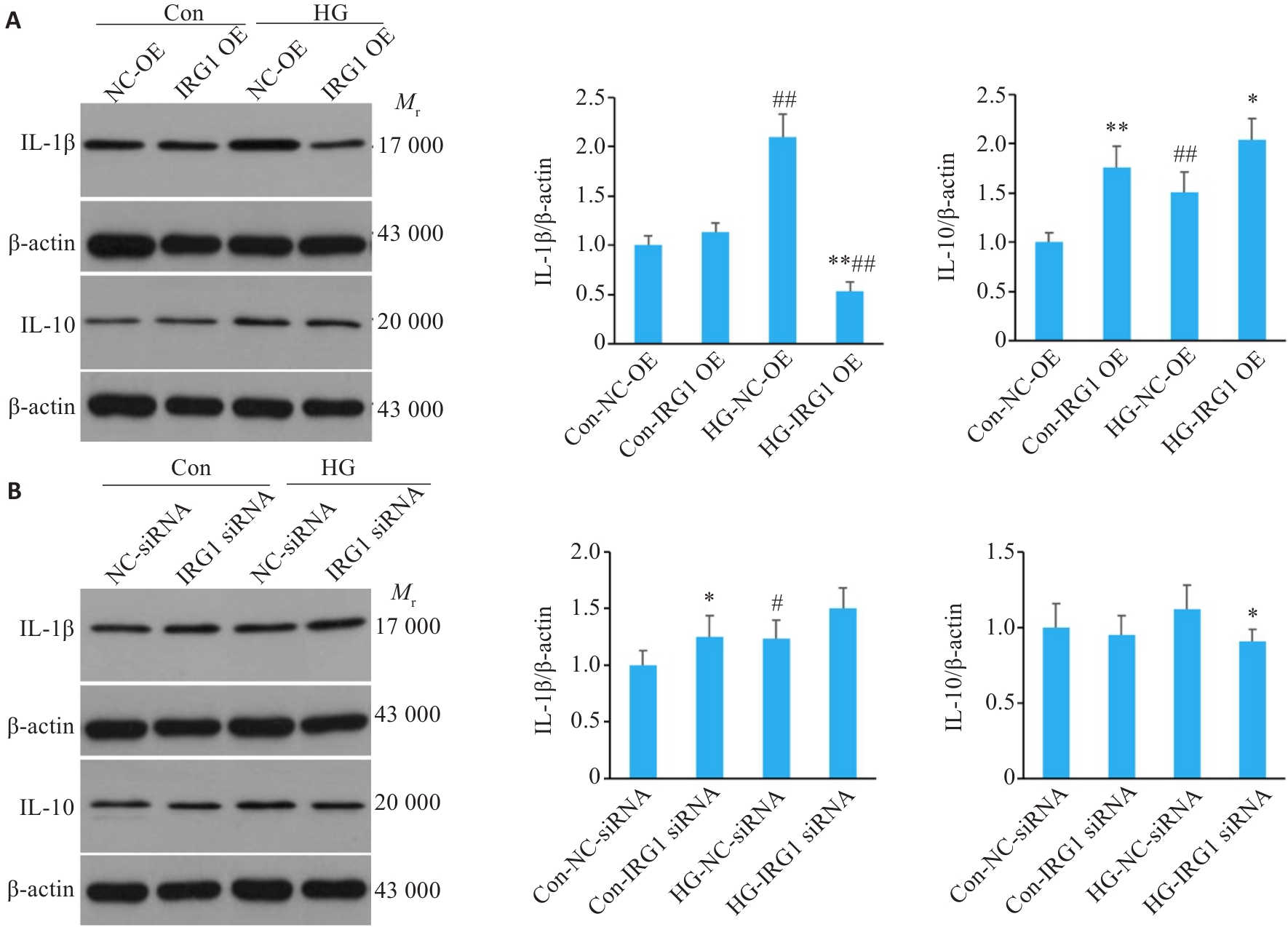
Fig.7 Western blotting for assessing the effects of IRG1 overexpression (A) or silencing (B) on expressions of IL-1β and IL-10 in the macrophages cultured in high glucose. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs corresponding NC-OE group (A) or NC-siRNA group (B); #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs corresponding Con group.
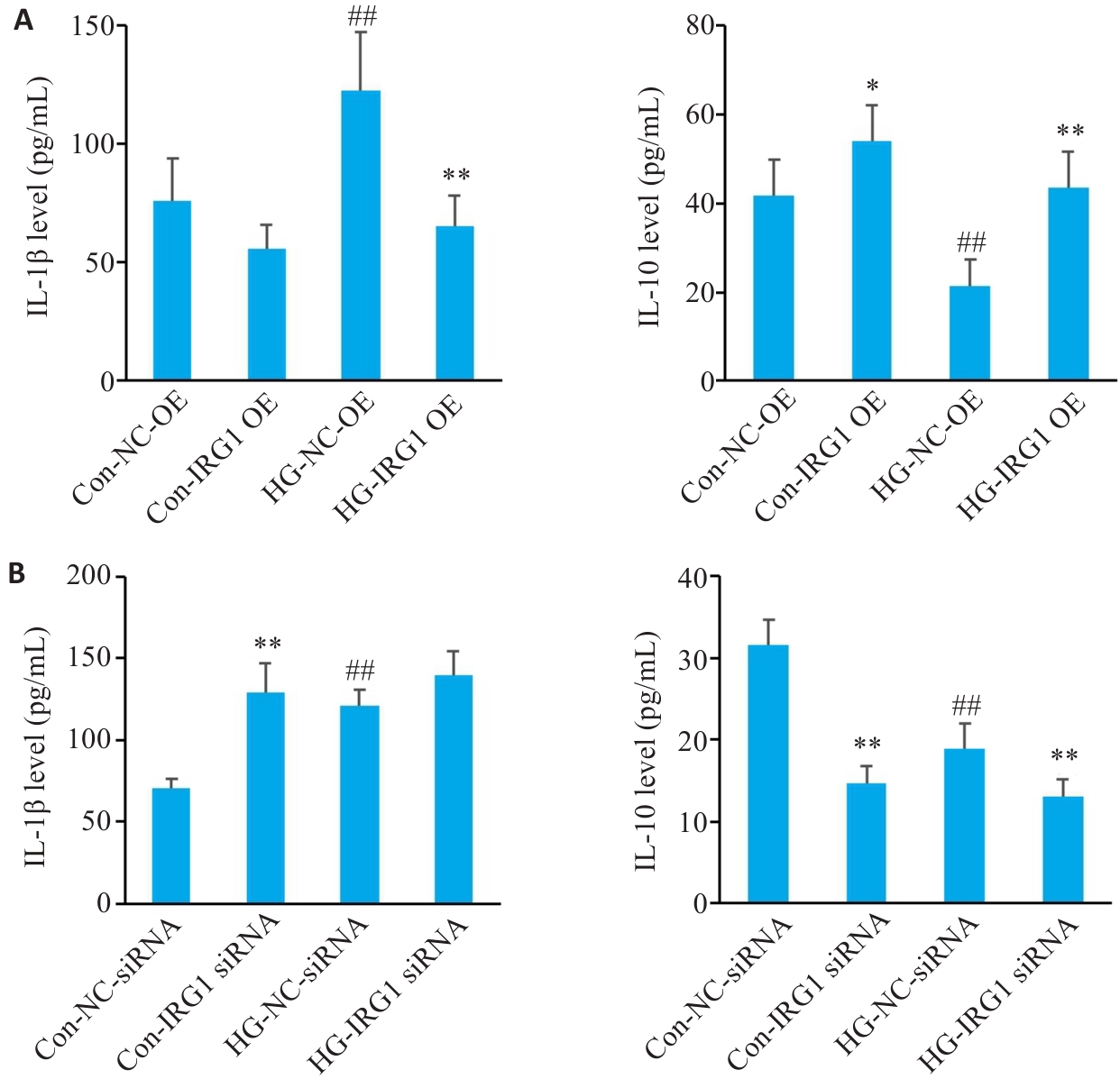
Fig.8 ELISA for detecting secretions of IL-1β and IL-10 in the supernatant of macrophages with IRG1 overexpression (A) or silencing (B) cultured in high glucose. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs corresponding NC-OE group (A) or NC-siRNA group (B); ##P<0.01 vs corresponding Con group.
| 1 | Wu XM, Xu MY, Geng MY, et al. Targeting protein modifications in metabolic diseases: molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 220. |
| 2 | Tobias DK, Merino J, Ahmad A, et al. Second international consensus report on gaps and opportunities for the clinical translation of precision diabetes medicine[J]. Nat Med, 2023, 29(10): 2438-57. |
| 3 | Lee YS, Olefsky J. Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease[J]. Genes Dev, 2021, 35(5/6): 307-28. |
| 4 | Franceschi C, Garagnani P, Parini P, et al. Inflammaging: a new immune-metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(10): 576-90. |
| 5 | Azzu V, Vacca M, Virtue S, et al. Adipose tissue-liver cross talk in the control of whole-body metabolism: implications in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(7): 1899-912. |
| 6 | Hasegawa Y, Okamura T, Nakajima H, et al. Metabolic outcomes and changes in innate immunity induced by diesel exhaust particles airway exposure and high-fat high-sucrose diet[J]. Life Sci, 2023, 326: 121794. |
| 7 | Truong TMT, Seo SH, Chung S, et al. Attenuation of hepatic fibrosis by p-Coumaric acid via modulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in C57BL/6 mice[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2023, 112: 109204. |
| 8 | Darwish NM, Elnahas YM, AlQahtany FS. Diabetes induced renal complications by leukocyte activation of nuclear factor κ-B and its regulated genes expression[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2021, 28(1): 541-9. |
| 9 | Li C, Xu MM, Wang KP, et al. Macrophage polarization and meta-inflammation[J]. Transl Res, 2018, 191: 29-44. |
| 10 | Li H, Meng Y, He SW, et al. Macrophages, chronic inflammation, and insulin resistance[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(19): 3001. |
| 11 | Wang C, Ma C, Gong LH, et al. Macrophage polarization and its role in liver disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 803037. |
| 12 | Zhang J, Muri J, Fitzgerald G, et al. Endothelial lactate controls muscle regeneration from ischemia by inducing M2-like macrophage polarization[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 31(6): 1136-53. e7. |
| 13 | Cutolo M, Campitiello R, Gotelli E, et al. The role of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis synovitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 867260. |
| 14 | Li YG, Gong WB, Li WZ, et al. The IRG1-Itaconate axis: a regulatory hub for immunity and metabolism in macrophages[J]. Int Rev Immunol, 2023, 42(5): 364-78. |
| 15 | Chen LL, Morcelle C, Cheng ZL, et al. Itaconate inhibits TET DNA dioxygenases to dampen inflammatory responses[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2022, 24(3): 353-63. |
| 16 | Lei I, Huang W, Noly PE, et al. Metabolic reprogramming by immune-responsive gene 1 up-regulation improves donor heart pres-ervation and function[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2023, 15(682): eade3782. |
| 17 | Sendra M, Saco A, Rey-Campos M, et al. Immune-responsive gene 1 (IRG1) and dimethyl itaconate are involved in the mussel immune response[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2020, 106: 645-55. |
| 18 | 罗 维, 艾 磊, 周 越.小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7细胞电穿孔转染条件的建立和验证[J].中国实验动物学报, 2020, 28(2): 193-200. |
| 19 | Johansson C, Kirsebom FCM. Neutrophils in respiratory viral infections[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2021, 14(4): 815-27. |
| 20 | 夏崇建, 黄俊杰, 张 煜, 等.膜联蛋白A1的N末端肽Ac2-26对高糖刺激的小鼠巨噬细胞极化的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2022, 38(11): 1998-2004. |
| 21 | Luo W, Zhou Y, Tang Q, et al. Downhill running and caloric restriction attenuate insulin resistance associated skeletal muscle atrophy via the promotion of M2-like macrophages through TRIB3-AKT pathway[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2024, 210: 271-85. |
| 22 | Kieler M, Hofmann M, Schabbauer G. More than just protein building blocks: how amino acids and related metabolic pathways fuel macrophage polarization[J]. FEBS J, 2021, 288(12): 3694-714. |
| 23 | Luo W, Zhou Y, Tang Q, et al. Modulation of TRIB3 and macrophage phenotype to attenuate insulin resistance after downhill running in mice[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 637432. |
| 24 | 罗 维, 艾 磊, 王博发, 等. 慢性高糖作用下小鼠骨骼肌成肌细胞对巨噬细胞极化的影响[J]. 免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(11): 935-42. |
| 25 | Xia YY, He F, Wu XY, et al. GABA transporter sustains IL-1β production in macrophages[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(15): eabe9274. |
| 26 | Eddie Ip WKE, Hoshi N, Shouval DS, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of IL-10 mediated by metabolic reprogramming of macrophages[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6337): 513-9. |
| 27 | 徐龙飞, 韩 晶, 杨 喆, 等. LRG1抑制小鼠肝巨噬细胞活化从而改善代谢相关脂肪性肝病: 基于增强TGF-β1信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1164-71. |
| 28 | Li YK, Zhang P, Wang CC, et al. Immune responsive gene 1 (IRG1) promotes endotoxin tolerance by increasing A20 expression in macrophages through reactive oxygen species[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(23): 16225-34. |
| 29 | Domínguez-Andrés J, Novakovic B, Li Y, et al. The itaconate pathway is a central regulatory node linking innate immune toler-ance and trained immunity[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 29(1): 211-20. e5. |
| 30 | Mills EL, Kelly B, Logan A, et al. Succinate dehydrogenase supports metabolic repurposing of mitochondria to drive inflammatory macrophages[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(2): 457-70. e13. |
| [1] | Zhihua TIAN, Qingqing YANG, Xin CHEN, Fangfang ZHANG, Baimao ZHONG, Hong CAO. Spermine suppresses GBP5-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages to relieve vital organ injuries in neonatal mice with enterovirus 71 infection [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 901-910. |
| [2] | Jinhua ZOU, Hui WANG, Dongyan ZHANG. SLC1A5 overexpression accelerates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting M2 polarization of macrophages [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [3] | Pengcheng LIU, Lijuan LOU, Xia LIU, Jian WANG, Ying JIANG. A risk scoring model based on M2 macrophage-related genes for predicting prognosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 827-840. |
| [4] | XU Xiaohui, FENG Jinmei, LUO Ying, HE Xinyu, ZANG Jinbao, HUANG Daochao. Adeno-associated virus-mediated hepatocyte-specific NDUFA13 overexpression protects against CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting hepatic NLRP3 activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 201-209. |
| [5] | Qi ZHANG, Zezhao JI, Abai JIASHAER∙, Youda WANG, ABUDUXUKUER∙Abulimiti. FER-1 inhibits methylglyoxal-induced ferroptosis in mouse alveolar macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2443-2448. |
| [6] | Qihui CAI, Haiqiang LAN, Bojun XIAN, Lian LIU, Nan WANG, Xiaolei HUANG, Xiaolu NIU, Xinyu HU, Chen LI, Junyi XIE, Zhaohong LIAO. E2 signaling in myofibers promots macrophage efferocytosis in mouse skeletal muscles with cardiotoxin-induced acute injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2192-2200. |
| [7] | Mengmeng CHENG, Xinguang LIU, Yanxin WEI, Xiaoxiang XING, Lan LIU, Nan XIN, Peng ZHAO. Tongsai Granules inhibit autophagy and macrophage-mediated inflammatory response to improve acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1995-2003. |
| [8] | XU Mengqi, SHI Yutong, LIU Junping, WU Minmin, ZHANG Fengmei, HE Zhiqiang, TANG Min. JAG1 affects monocytes-macrophages to reshape the pre-metastatic niche of triple-negative breast cancer through LncRNA MALAT1 in exosomes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1525-1535. |
| [9] | XU Longfei, HAN Jing, YANG Zhe, YANG Yanping, CHEN Jinhui, WU Xijun, WANG Qi, HONG Yan. LRG1 inhibits hepatic macrophage activation by enhancing TGF-β1 signaling to alleviate MAFLD in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1164-1171. |
| [10] | HUANG Yongqi, YU Wei, YOU Yuehua. Arecoline induces activation of human oral fibroblasts by promoting macrophage secretion of exosomes containing miR-155-5p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(1): 60-67. |
| [11] | XIANG Maocui, WANG Yu, MEI Renbiao, FU Jifeng, CHEN Jing, DU Changle. Interleukin-17A is closely correlated with the progression of renal epithelial-mesenchymal transition in spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(5): 772-779. |
| [12] | YANG Xuezhi, SHEN Hong, LI Qun, DAI Zichao, YANG Rongqiang, HUANG Guobin, CHEN Rui, WANG Fang, SONG Jingling, HUA Hairong. Interference of P2X4 receptor expression in tumor-associated macrophages suppresses migration and invasion of glioma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(5): 658-664. |
| [13] | ZHUO Lingjian, WANG Shuochen, LIU Xing, CHEN Baoan, LI Xiang. Estradiol inhibits differentiation of mouse macrophage into a pro-inflammatory phenotype by upregulating the IRE1α-XBP1 signaling axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(3): 432-437. |
| [14] | JIANG Weiyi, DENG Zilong, ZHAO Wanghong. NLRC4 plays a regulatory role in F. nucleatum-induced pyroptosis in macrophages [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(10): 1560-1565. |
| [15] | . Mechanism of hepatocyte mitochondrial NDUFA13 deficiency-induced liver fibrogenesis: the role of abnormal hepatic stellate cell activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(4): 529-535. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||