Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 974-980.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.20
• Clinical Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jingjing YANG1,2( ), Lixia YIN3,4, Ting DUAN2,5, Minzhu NIU3, Zhendong HE2, Xinrui CHEN2, Xiaofeng ZHANG6,7, Jing LI4,7, Zhijun GENG6,7, Lugen ZUO1,7(
), Lixia YIN3,4, Ting DUAN2,5, Minzhu NIU3, Zhendong HE2, Xinrui CHEN2, Xiaofeng ZHANG6,7, Jing LI4,7, Zhijun GENG6,7, Lugen ZUO1,7( )
)
Received:2024-03-22
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-06
Contact:
Lugen ZUO
E-mail:20231002102@stu.bbmc.edu.cn;zuolugen@126.com
Jingjing YANG, Lixia YIN, Ting DUAN, Minzhu NIU, Zhendong HE, Xinrui CHEN, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO. High expression of ATP5A1 in gastric carcinoma is correlated with a poor prognosis and enhanced glucose metabolism in tumor cells[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 974-980.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.20
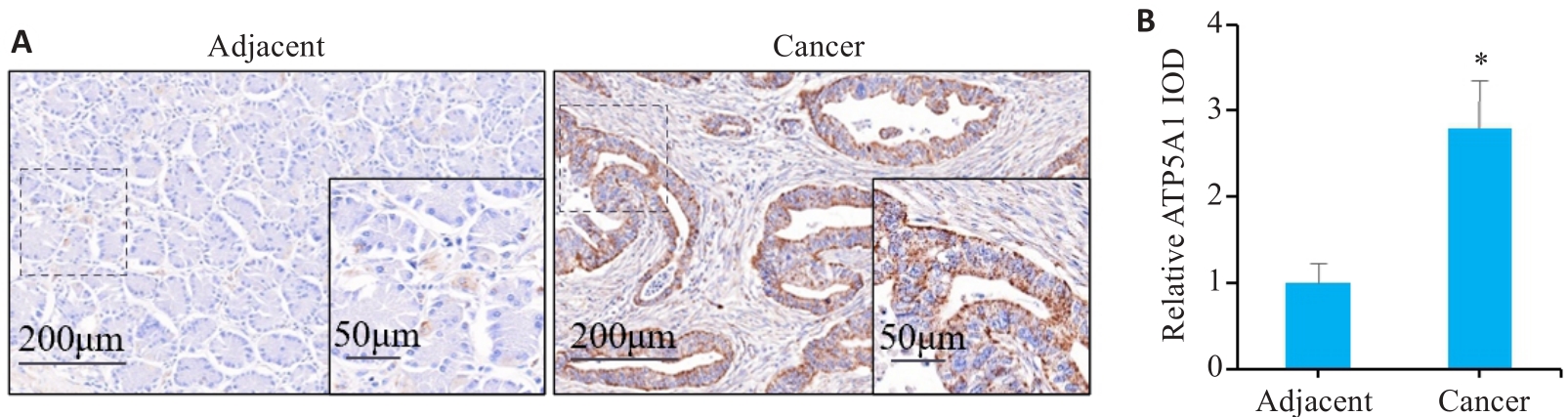
Fig.1 ATP5A1 is overexpressed in gastric carcinoma tissues. A: Immunohistochemistry of ATP5A1 in gastric carcinoma and adjacent tissues. B: IOD values of ATP5A1 expression in gastric carcinoma and adjacent tissues. *P<0.05 vs adjacent tissue.
| Factors | n | ATP5A1 expression (n, %) | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=57) | High (n=58) | |||||
| Gender | Male | 85 | 42 (49.41%) | 43 (50.59%) | 0.003 | 0.956 |
| Female | 30 | 15 (50.00%) | 15 (50.00%) | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 40 | 20 (50.00%) | 20 (50.00%) | 0.005 | 0.946 |
| ≥60 | 75 | 37 (49.33%) | 38 (50.67%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | <5 | 54 | 35 (64.81%) | 19 (35.19%) | 9.470 | 0.002 |
| ≥5 | 61 | 22 (36.07%) | 39 (63.93%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | <37 | 55 | 38 (69.09%) | 17 (30.91%) | 16.077 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 60 | 19 (31.67%) | 41 (68.33%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | <5 | 53 | 30 (56.60%) | 23 (43.40%) | 1.948 | 0.163 |
| ≥5 | 62 | 27 (43.55%) | 35 (56.45%) | |||
| Pathological grading | G1-2 | 60 | 36 (60.00%) | 24 (40.00%) | 5.464 | 0.019 |
| G3-4 | 55 | 21 (38.18%) | 34 (61.82%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 90 | 47 (52.22%) | 43 (47.78%) | 1.169 | 0.280 |
| Other | 25 | 10 (40.00%) | 15 (60.00%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 60 | 38 (63.33%) | 22 (36.67%) | 9.513 | 0.002 |
| T3-T4 | 55 | 19 (34.55%) | 36 (65.45%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 66 | 43 (65.15%) | 23 (34.85%) | 15.053 | <0.001 |
| N2-N3 | 49 | 14 (28.57%) | 35 (71.43%) | |||
Tab.1 Clinical data of 115 patients with gastric carcinoma
| Factors | n | ATP5A1 expression (n, %) | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=57) | High (n=58) | |||||
| Gender | Male | 85 | 42 (49.41%) | 43 (50.59%) | 0.003 | 0.956 |
| Female | 30 | 15 (50.00%) | 15 (50.00%) | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 40 | 20 (50.00%) | 20 (50.00%) | 0.005 | 0.946 |
| ≥60 | 75 | 37 (49.33%) | 38 (50.67%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | <5 | 54 | 35 (64.81%) | 19 (35.19%) | 9.470 | 0.002 |
| ≥5 | 61 | 22 (36.07%) | 39 (63.93%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | <37 | 55 | 38 (69.09%) | 17 (30.91%) | 16.077 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 60 | 19 (31.67%) | 41 (68.33%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | <5 | 53 | 30 (56.60%) | 23 (43.40%) | 1.948 | 0.163 |
| ≥5 | 62 | 27 (43.55%) | 35 (56.45%) | |||
| Pathological grading | G1-2 | 60 | 36 (60.00%) | 24 (40.00%) | 5.464 | 0.019 |
| G3-4 | 55 | 21 (38.18%) | 34 (61.82%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 90 | 47 (52.22%) | 43 (47.78%) | 1.169 | 0.280 |
| Other | 25 | 10 (40.00%) | 15 (60.00%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 60 | 38 (63.33%) | 22 (36.67%) | 9.513 | 0.002 |
| T3-T4 | 55 | 19 (34.55%) | 36 (65.45%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 66 | 43 (65.15%) | 23 (34.85%) | 15.053 | <0.001 |
| N2-N3 | 49 | 14 (28.57%) | 35 (71.43%) | |||
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ 2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (female vs male) | 1.436 | 0.231 | ||||
| Age (≥60 year vs <60 year) | 0.745 | 0.388 | ||||
| ATP5A1 expression (high vs low) | 30.968 | <0.001 | 2.771 | 1.458-5.267 | 0.002 | |
| CEA (≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 16.152 | <0.001 | 2.003 | 1.097-3.658 | 0.024 | |
| CA19-9 (≥37 kU/L vs <37kU/L) | 35.142 | <0.001 | 3.348 | 1.666-6.728 | 0.001 | |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 0.077 | 0.782 | ||||
| Pathological grading (G3-G4 vs G1-G2) | 32.142 | <0.001 | 2.759 | 1.484-5.128 | 0.001 | |
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 1.251 | 0.263 | ||||
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 27.798 | <0.001 | 2.056 | 1.122-3.768 | 0.020 | |
| N stage (N2-N3 vs N0-N1) | 28.006 | <0.001 | 2.251 | 1.211-4.187 | 0.010 | |
Tab.2 Factors affecting postoperative survival of patients with gastric carcinoma
| Factors | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ 2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | ||
| Gender (female vs male) | 1.436 | 0.231 | ||||
| Age (≥60 year vs <60 year) | 0.745 | 0.388 | ||||
| ATP5A1 expression (high vs low) | 30.968 | <0.001 | 2.771 | 1.458-5.267 | 0.002 | |
| CEA (≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 16.152 | <0.001 | 2.003 | 1.097-3.658 | 0.024 | |
| CA19-9 (≥37 kU/L vs <37kU/L) | 35.142 | <0.001 | 3.348 | 1.666-6.728 | 0.001 | |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 0.077 | 0.782 | ||||
| Pathological grading (G3-G4 vs G1-G2) | 32.142 | <0.001 | 2.759 | 1.484-5.128 | 0.001 | |
| Cancer cell type (adenocarcinoma vs other) | 1.251 | 0.263 | ||||
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 27.798 | <0.001 | 2.056 | 1.122-3.768 | 0.020 | |
| N stage (N2-N3 vs N0-N1) | 28.006 | <0.001 | 2.251 | 1.211-4.187 | 0.010 | |
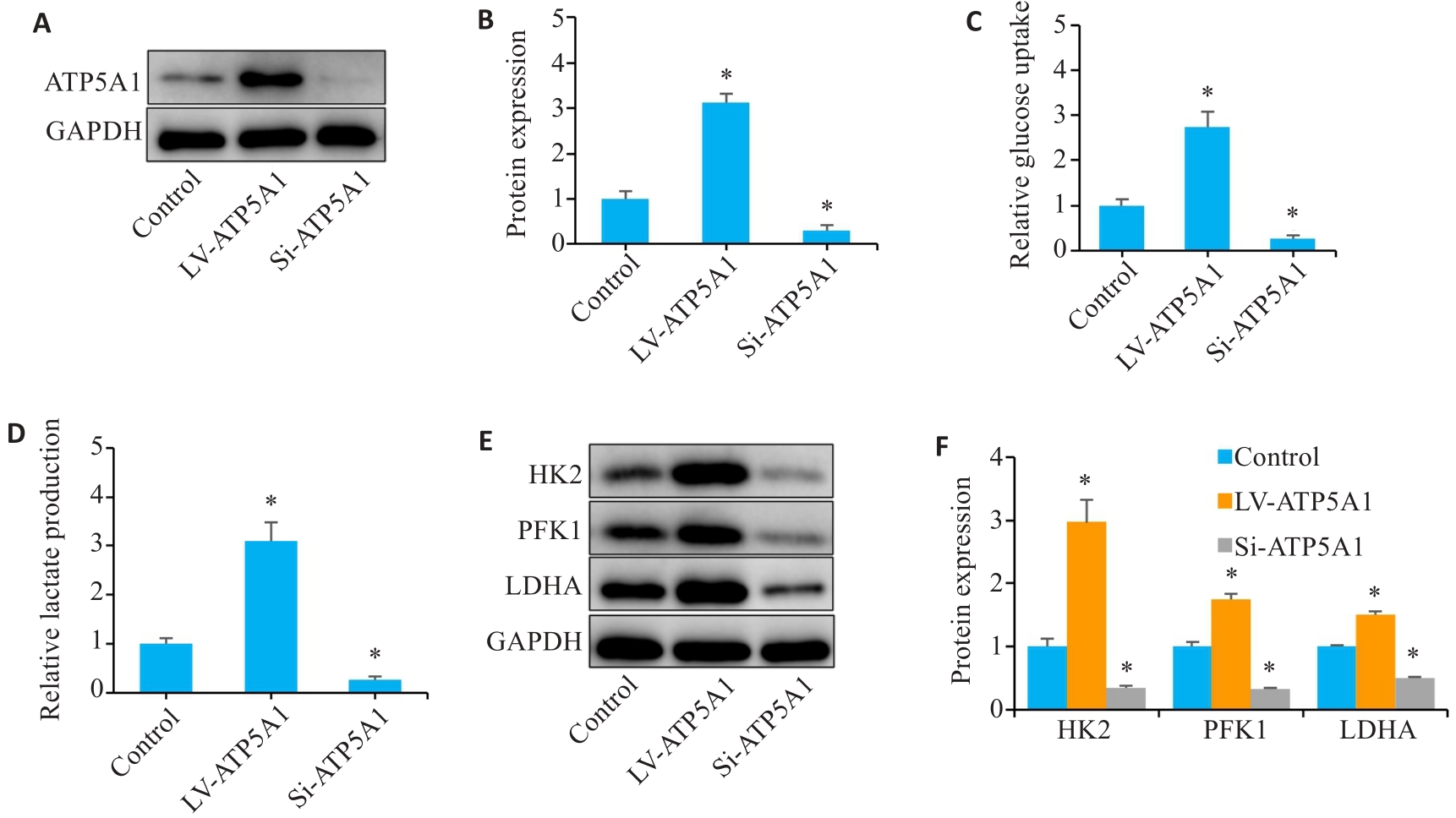
Fig.4 Overexpression of ATP5A1 accelerates glucose metabolism in gastric carcinoma cells. A, B: Western blotting for detecting ATP5A1 protein after lentivirus transfection. C, D: Glucose uptake and lactate production of the gastric cancer cells. E, F: Western blotting for the proteins related to glucose metabolism. *P<0.05 vs Control.
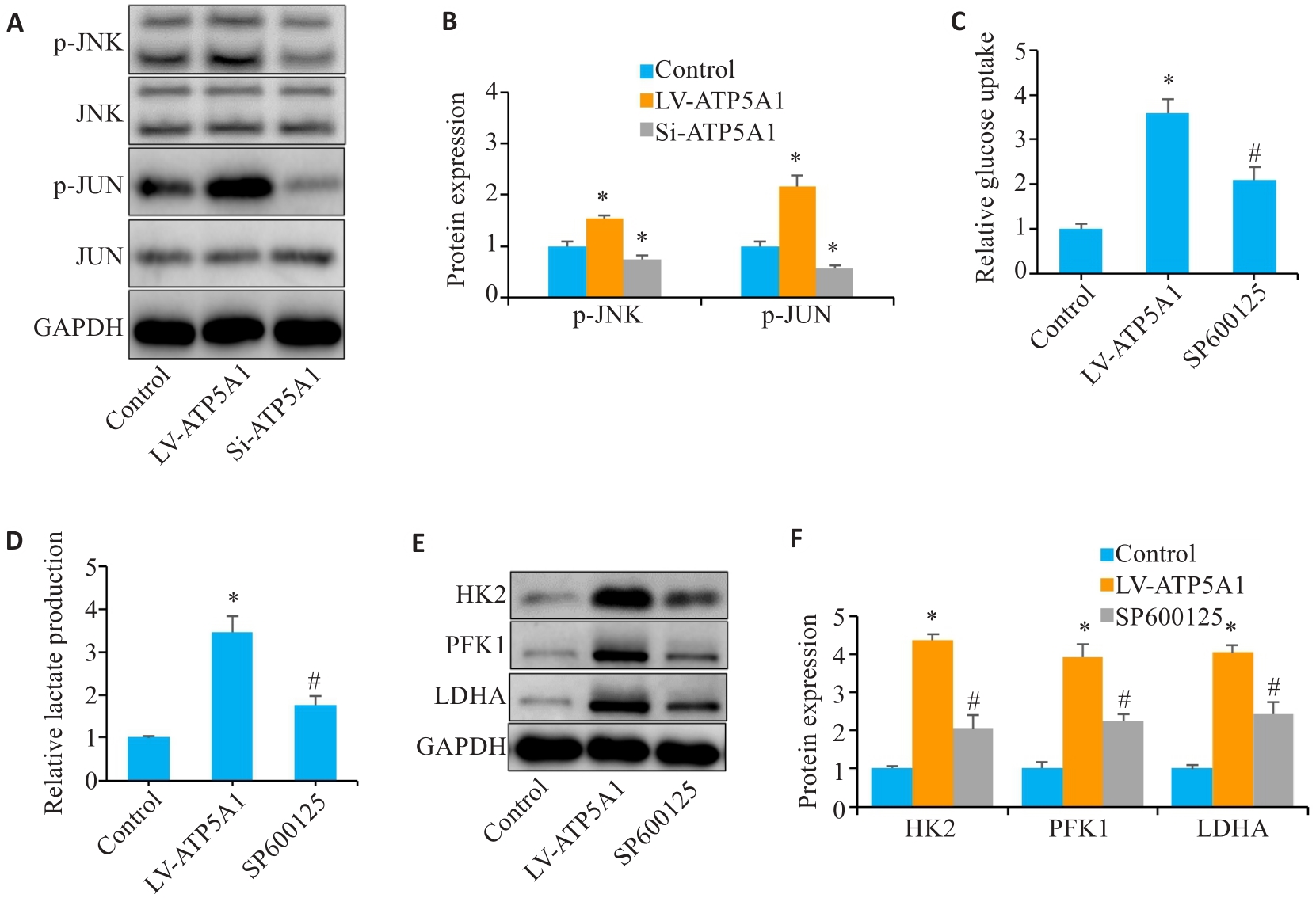
Fig.5 ATP5A1 promotes glucose metabolism by activating the JNK/JUN signaling pathway. A, B: Phosphorylation levels of JNK and JUN detected by Western blotting. C, D: Glucose uptake and lactate production in gastric cancer cells. E, F: Western blotting for detecting glucose metabolism-related protein expressions. *P<0.05 vs Control. #P<0.05 vs LV-ATP5A1.
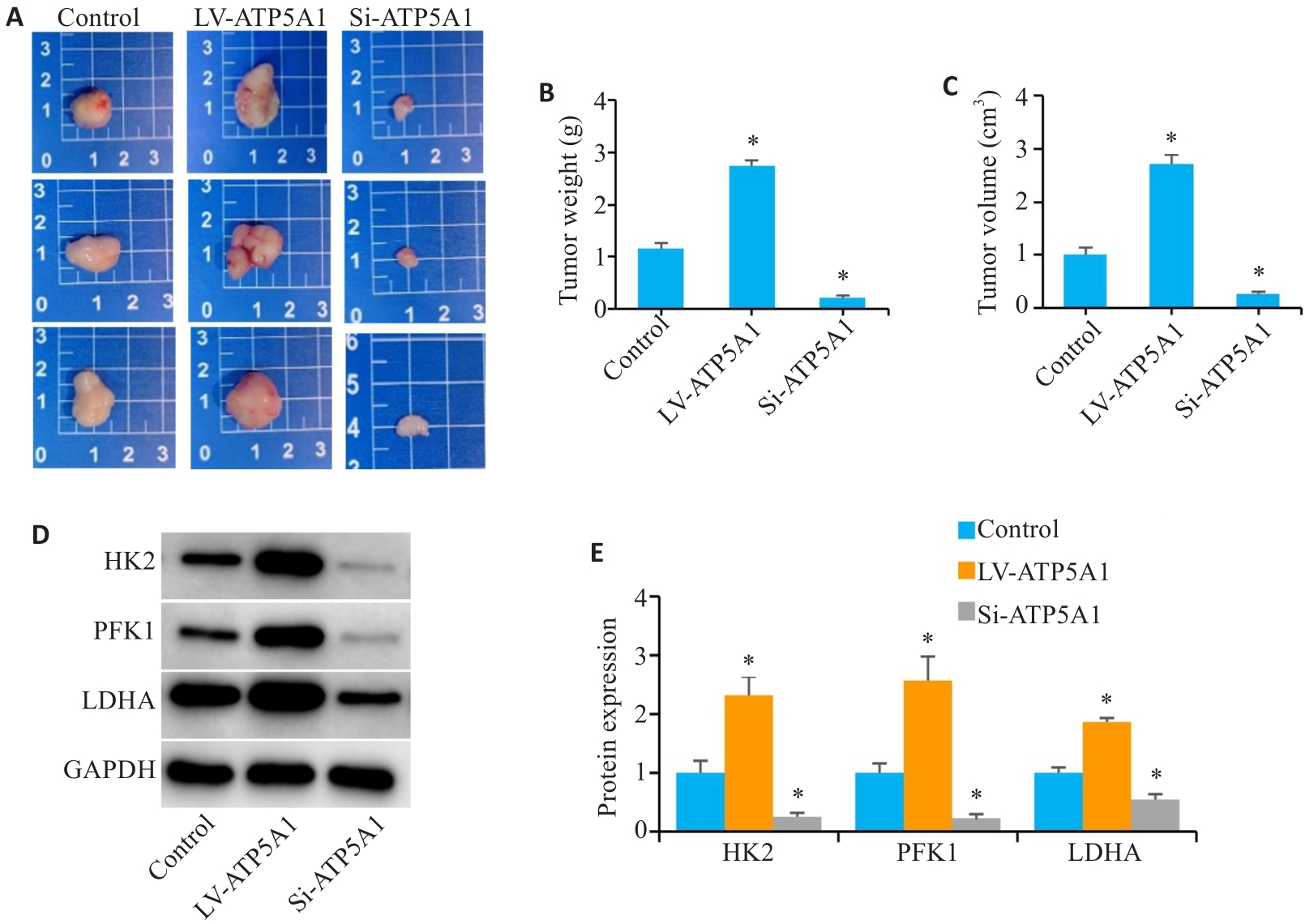
Fig.6 Overexpression of ATP5A1 accelerates tumor growth and glucose metabolism in nude mice. A: Tumor xenografts in the 3 groups. B: Weight of the transplanted tumors. C: Volume of the transplanted tumors. D, E: Protein expressions of HK2, PFK1 and LDHA in xenografts detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs Control.
| 1 | Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-48. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31288-5 |
| 2 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660 |
| 3 | Xia CF, Dong XS, Li H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(5): 584-90. DOI: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000002108 |
| 4 | Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144(8): 1941-53. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31937 |
| 5 | Zhang KC, Chen L. Chinese consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer with liver metastases[J]. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2020, 12: 1758835920904803. DOI: 10.1177/1758835920904803 |
| 6 | Tan ZY. Recent advances in the surgical treatment of advanced gastric cancer: a review[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 3537-41. DOI: 10.12659/msm.916475 |
| 7 | Yang YQ, Ma YF, Xiang XY, et al. The prognostic value of the lymph node ratio for local advanced gastric cancer patients with intensity-modulated radiation therapy and concurrent chemotherapy after radical gastrectomy in China[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2020, 15(1): 237. DOI: 10.1186/s13014-020-01687-0 |
| 8 | Nakayama I, Takahari D. The role of angiogenesis targeted therapies in metastatic advanced gastric cancer: a narrative review[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(9): 3226. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12093226 |
| 9 | Lin JX, Lian NZ, Gao YX, et al. m6A methylation mediates LHPP acetylation as a tumour aerobic glycolysis suppressor to improve the prognosis of gastric cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(5): 463. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-04859-w |
| 10 | Zhao HY, Jiang RK, Feng ZJ, et al. Transcription factor LHX9 (LIM Homeobox 9) enhances pyruvate kinase PKM2 activity to induce glycolytic metabolic reprogramming in cancer stem cells, promoting gastric cancer progression[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 833. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04658-7 |
| 11 | Pouysségur J, Marchiq I, Parks SK, et al. ‘Warburg effect' controls tumor growth, bacterial, viral infections and immunity-Genetic deconstruction and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86(Pt 2): 334-46. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.07.004 |
| 12 | Jonckheere AI, Smeitink JAM, Rodenburg RJT. Mitochondrial ATP synthase: architecture, function and pathology[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2012, 35(2): 211-25. DOI: 10.1007/s10545-011-9382-9 |
| 13 | Jana S, Heaven MR, Stauft CB, et al. HIF-1α-dependent metabolic reprogramming, oxidative stress, and bioenergetic dysfunction in SARS-CoV-2-infected hamsters[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 24(1): 558. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010558 |
| 14 | Li JB, Wang JZ, Pan TH, et al. USP25 deficiency promotes T cell dysfunction and transplant acceptance via mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 117: 109917. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109917 |
| 15 | 梁亚敏. TET2/ATP5A1在低剪切应力诱导内皮间质转化中的作用及机制研究[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2022. |
| 16 | Ba YS, Ma FW, Ma YW, et al. ATP5A1 participates in transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of cancer-associated genes by modulating their expression and alternative splicing profiles in HeLa cells[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 20: 15330338211039126. DOI: 10.1177/15330338211039126 |
| 17 | Pan J, Sun LC, Tao YF, et al. ATP synthase ecto-α-subunit: a novel therapeutic target for breast cancer[J]. J Transl Med, 2011, 9: 211. DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-211 |
| 18 | 杨素丽. ATP5A1在大肠癌中的表达及其临床意义[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. |
| 19 | Li M, Wang M, Xi Y, et al. Isolation and identification of a Tibetan pig porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus strain and its biological effects on IPEC-J2 cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(4): 2200. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042200 |
| 20 | Choi Y, Park J, Choi Y, et al. C-Jun N-terminal kinase activation has a prognostic implication and is negatively associated with FOXO1 activation in gastric cancer[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2016, 16(1): 59. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-016-0473-9 |
| 21 | Zhang L, Gao YG. ICOSLG acts as an oncogene to promote glycolysis, proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer cells[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2024, 752: 109841. DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109841 |
| 22 | Peng CZ, Yang X, Li X, et al. ALDOB plays a tumor-suppressive role by inhibiting AKT activation in gastric cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2023, 14(12): 2255-62. DOI: 10.7150/jca.83456 |
| 23 | Xu GY, Li JY. ATP5A1 and ATP5B are highly expressed in glioblastoma tumor cells and endothelial cells of microvascular proliferation[J]. J Neurooncol, 2016, 126(3): 405-13. DOI: 10.1007/s11060-015-1984-x |
| 24 | Yuan LS, Chen L, Qian KY, et al. A novel correlation between ATP5A1 gene expression and progression of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma identified by co-expression analysis[J]. Oncol Rep, 2018, 39(2): 525-36. |
| 25 | Martínez-Esquivias F, Gutiérrez-Angulo M, Becerra-Ruiz JS, et al. Bioinformatic analysis of the effect of silver nanoparticles on colorectal cancer cell line[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022: 6828837. DOI: 10.1155/2022/6828837 |
| 26 | Zhang GF, Zhong JM, Lin L, et al. Loss of ATP5A1 enhances proliferation and predicts poor prognosis of colon adenocarcinoma[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2022, 230: 153679. DOI: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153679 |
| 27 | Bose S, Zhang C, Le A. Glucose metabolism in cancer: the Warburg effect and beyond[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2021, 1311: 3-15. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-65768-0_1 |
| 28 | Liberti MV, Locasale JW. The Warburg effect: how does it benefit cancer cells?[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2016, 41(3): 211-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.12.001 |
| 29 | Yang HL, Lin PY, Vadivalagan C, et al. Coenzyme Q0 defeats NLRP3-mediated inflammation, EMT/metastasis, and Warburg effects by inhibiting HIF-1α expression in human triple-negative breast cancer cells[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2023, 97(4): 1047-68. DOI: 10.1007/s00204-023-03456-w |
| 30 | Mi YS, Li QH, Liu BT, et al. Ubiquitous mitochondrial creatine kinase promotes the progression of gastric cancer through a JNK-MAPK/JUN/HK2 axis regulated glycolysis[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2023, 26(1): 69-81. DOI: 10.1007/s10120-022-01340-7 |
| [1] | Jinlong PANG, Xinli ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Haojie WANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Yumei YANG, Shanshan LI, Xiaoqiang CHANG, Feng LI, Xian LI. Overexpression of multimerin-2 promotes cutaneous melanoma cell invasion and migration and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [2] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [3] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [4] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [5] | Qingqing HUANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Lian WANG, Xue SONG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. High MYO1B expression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor patient prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [6] | Huali LI, Ting SONG, Jiawen LIU, Yongbao LI, Zhaojing JIANG, Wen DOU, Linghong ZHOU. Prognosis-guided optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy plans for lung cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [7] | Xue SONG, Yue CHEN, Min ZHANG, Nuo ZHANG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Yueyue WANG, Lian WANG, Jianguo HU. GPSM2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer to affect patient prognosis by promoting tumor cell proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [8] | Tianwei TANG, Luan LI, Yuanhan CHEN, Li ZHANG, Lixia XU, Zhilian LI, Zhonglin FENG, Huilin ZHANG, Ruifang HUA, Zhiming YE, Xinling LIANG, Ruizhao LI. High serum cystatin C is an independent risk factor for poor renal prognosis in IgA nephropathy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [9] | Xiaorui CHEN, Qingzheng WEI, Zongliang ZHANG, Jiangshui YUAN, Weiqing SONG. Overexpression of CHMP2B suppresses proliferation of renal clear cell carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [10] | Yaobin WANG, Liuyan CHEN, Yiling LUO, Jiqing SHEN, Sufang ZHOU. Predictive value of NUF2 for prognosis and immunotherapy responses in pan-cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [11] | Chao ZHOU, Jingjing ZHANG, Qiao TANG, Shuangnan FU, Ning ZHANG, Zhaoyun HE, Jin ZHANG, Tianyi ZHANG, Pengcheng LIU, Man GONG. Value of serum tryptophan in stratified management of 90-day mortality risk in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: a multicenter retrospective study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 59-64. |
| [12] | Xiaohua CHEN, Hui LU, Ziliang WANG, Lian WANG, Yongsheng XIA, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Xue SONG, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU, Lugen ZUO. Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [13] | Mengnan YE, Hongmei WU, Yan MEI, Qingling ZHANG. High expression of CREM is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1776-1782. |
| [14] | Kai JI, Guanyu YU, Leqi ZHOU, Tianshuai ZHANG, Qianlong LING, Wenjiang MAN, Bing ZHU, Wei ZHANG. HNRNPA1 gene is highly expressed in colorectal cancer: its prognostic implications and potential as a therapeutic target [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [15] | Yan WANG, Yuqing RUAN, Can CUI, Xiu WANG. Jiaotaiwan improves brain glucose metabolism in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 894-903. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||