Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 175-182.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.19
Xinli ZHAO1,2( ), Haojie WANG1,2, Yinchun SONG1,2, Shuai YUAN1,2, Zhen ZHANG1,2, Xingqi ZHOU1,2, Shanshan LI1,2, Xian LI1,2(
), Haojie WANG1,2, Yinchun SONG1,2, Shuai YUAN1,2, Zhen ZHANG1,2, Xingqi ZHOU1,2, Shanshan LI1,2, Xian LI1,2( ), Feng LI1,2(
), Feng LI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-06-22
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Xian LI, Feng LI
E-mail:1850466372@qq.com;Lixian0813@126.com;1583635955@qq.com
Xinli ZHAO, Haojie WANG, Yinchun SONG, Shuai YUAN, Zhen ZHANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Shanshan LI, Xian LI, Feng LI. ERI3 expression is elevated in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlates with poor patient prognosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 175-182.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.19
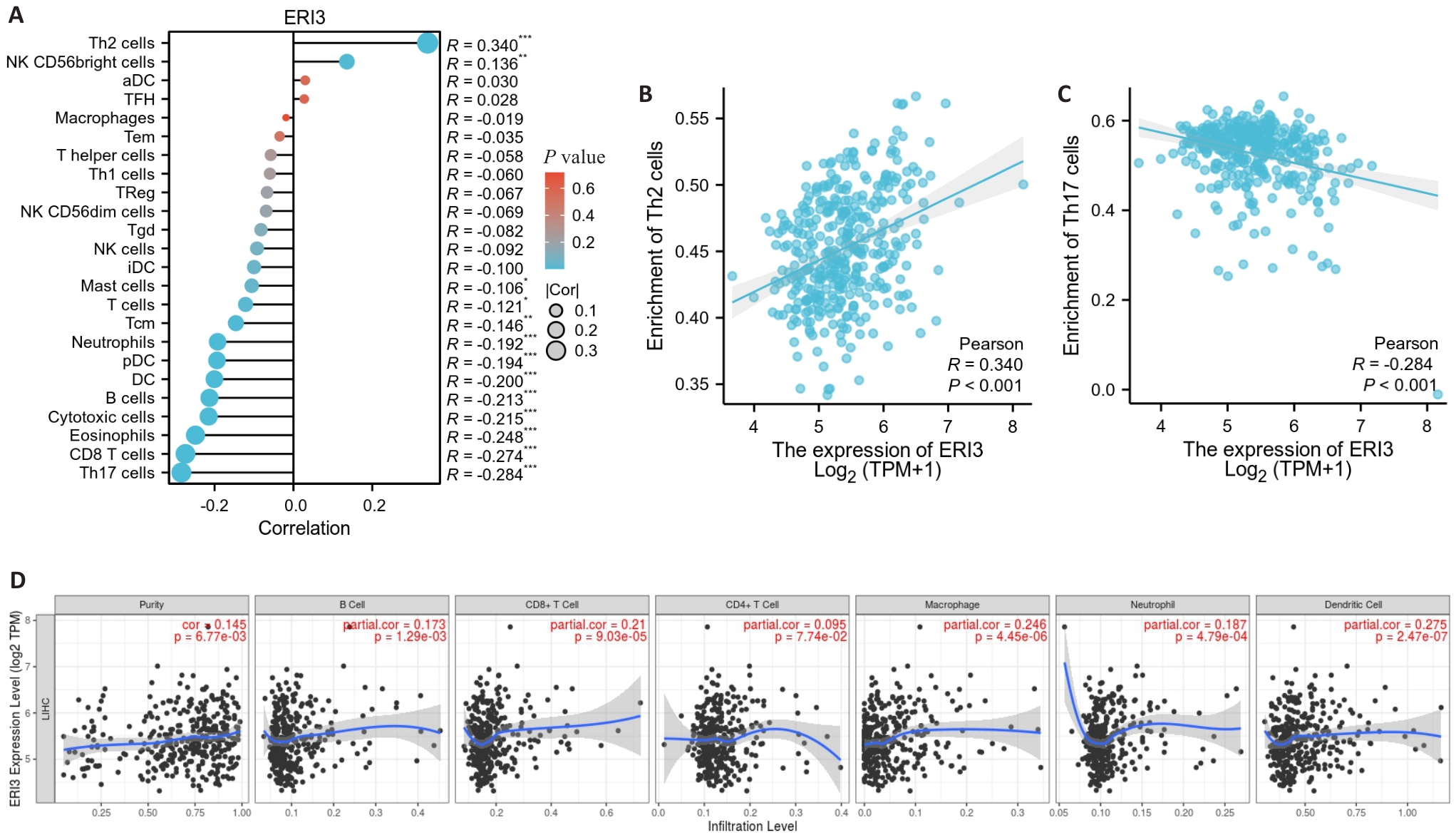
Fig.5 Tumor immune infiltration analysis. A: Lollipop chart showing the correlation between ERI3 expression and infiltration levels of 24 immune cell types. B, C: Scatter plots showing the correlation between ERI3 expression and abundance of Th2 and Th17 cells. D: Scatter plot of the correlation between ERI3 expression and B cells in HCC. n=377, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
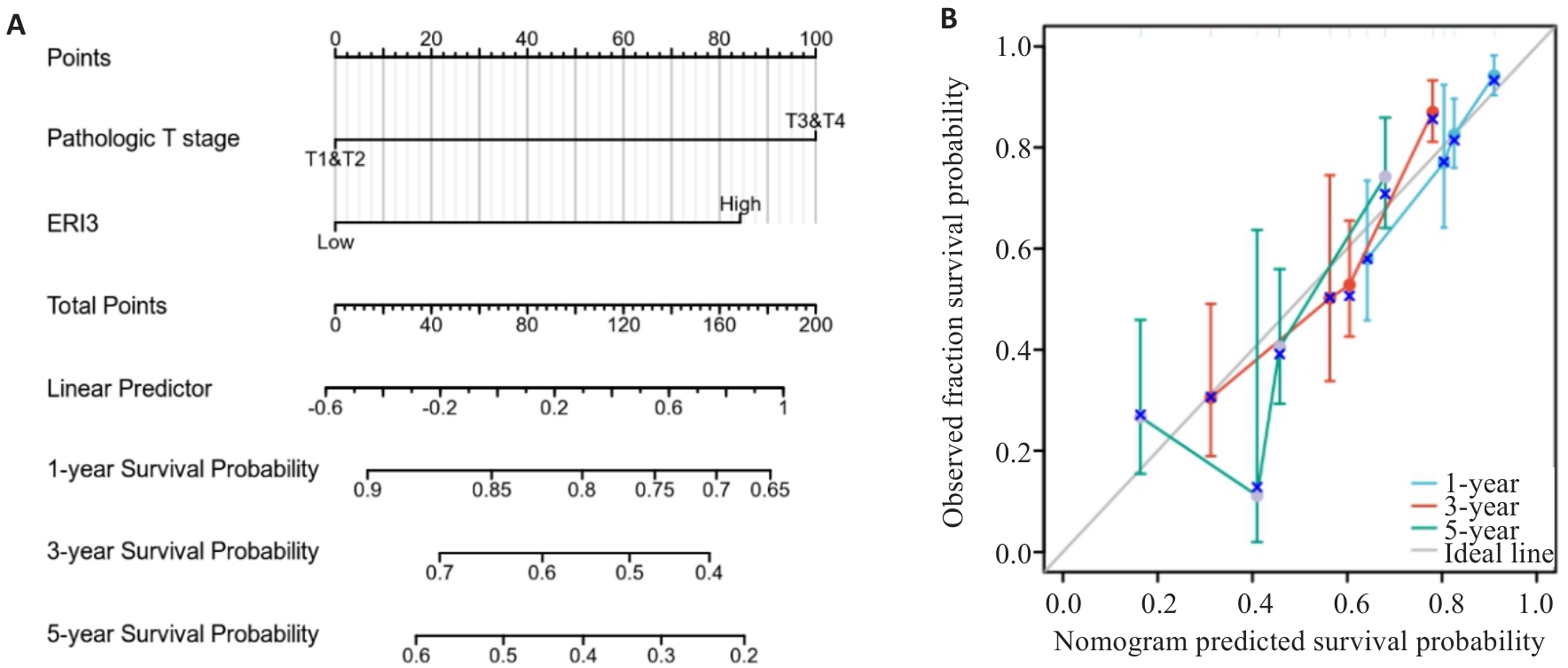
Fig.6 Nomogram and calibration curve. A: Prognostic nomogram integrating ERI3 expression and clinicopathological parameters. B: Calibration curves for 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival probability of HCC patients (n=373).
| Variable | n | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P | ||
| Pathologic T stage | 370 | ||||
| T1&T2/T3&T4 | 277/93 | 2.598 (1.826-3.697) | <0.001 | 2.467 (1.587-3.836) | <0.001 |
| Pathologic N stage | 258 | ||||
| N0/N1 | 254/4 | 2.029 (0.497-8.281) | 0.324 | ||
| Pathologic M stage | 272 | ||||
| M0/M1 | 268/4 | 4.077 (1.281-12.973) | 0.017 | 1.739 (0.531-5.697) | 0.361 |
| Gender | 373 | ||||
| Female/Male | 121/252 | 0.793 (0.557-1.130) | 0.200 | ||
| Age | 373 | ||||
| ≤60/>60 | 177/196 | 1.205 (0.850-1.708) | 0.295 | ||
| Weight | 345 | ||||
| ≤70/>70 | 184/161 | 0.941 (0.657-1.346) | 0.738 | ||
| AFP (ng/mL) | 279 | ||||
| ≤400/>400 | 215/64 | 1.075 (0.658-1.759) | 0.772 | ||
| Fibrosis ishak score | 214 | ||||
| 0 | 75 | ||||
| 1, 2&3, 4 | 59 | 0.823 (0.436-1.554) | 0.548 | ||
| 5&6 | 80 | 0.737 (0.410-1.324) | 0.307 | ||
| Vascular invasion | 317 | ||||
| No/Yes | 208/109 | 1.344 (0.887-2.035) | 0.163 | ||
| ERI3 | 373 | ||||
| Low/High | 186/187 | 2.307 (1.608-3.310) | <0.001 | 1.987 (1.256-3.142) | 0.003 |
Tab.1 Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis of overall survival in HCC patients
| Variable | n | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P | ||
| Pathologic T stage | 370 | ||||
| T1&T2/T3&T4 | 277/93 | 2.598 (1.826-3.697) | <0.001 | 2.467 (1.587-3.836) | <0.001 |
| Pathologic N stage | 258 | ||||
| N0/N1 | 254/4 | 2.029 (0.497-8.281) | 0.324 | ||
| Pathologic M stage | 272 | ||||
| M0/M1 | 268/4 | 4.077 (1.281-12.973) | 0.017 | 1.739 (0.531-5.697) | 0.361 |
| Gender | 373 | ||||
| Female/Male | 121/252 | 0.793 (0.557-1.130) | 0.200 | ||
| Age | 373 | ||||
| ≤60/>60 | 177/196 | 1.205 (0.850-1.708) | 0.295 | ||
| Weight | 345 | ||||
| ≤70/>70 | 184/161 | 0.941 (0.657-1.346) | 0.738 | ||
| AFP (ng/mL) | 279 | ||||
| ≤400/>400 | 215/64 | 1.075 (0.658-1.759) | 0.772 | ||
| Fibrosis ishak score | 214 | ||||
| 0 | 75 | ||||
| 1, 2&3, 4 | 59 | 0.823 (0.436-1.554) | 0.548 | ||
| 5&6 | 80 | 0.737 (0.410-1.324) | 0.307 | ||
| Vascular invasion | 317 | ||||
| No/Yes | 208/109 | 1.344 (0.887-2.035) | 0.163 | ||
| ERI3 | 373 | ||||
| Low/High | 186/187 | 2.307 (1.608-3.310) | <0.001 | 1.987 (1.256-3.142) | 0.003 |
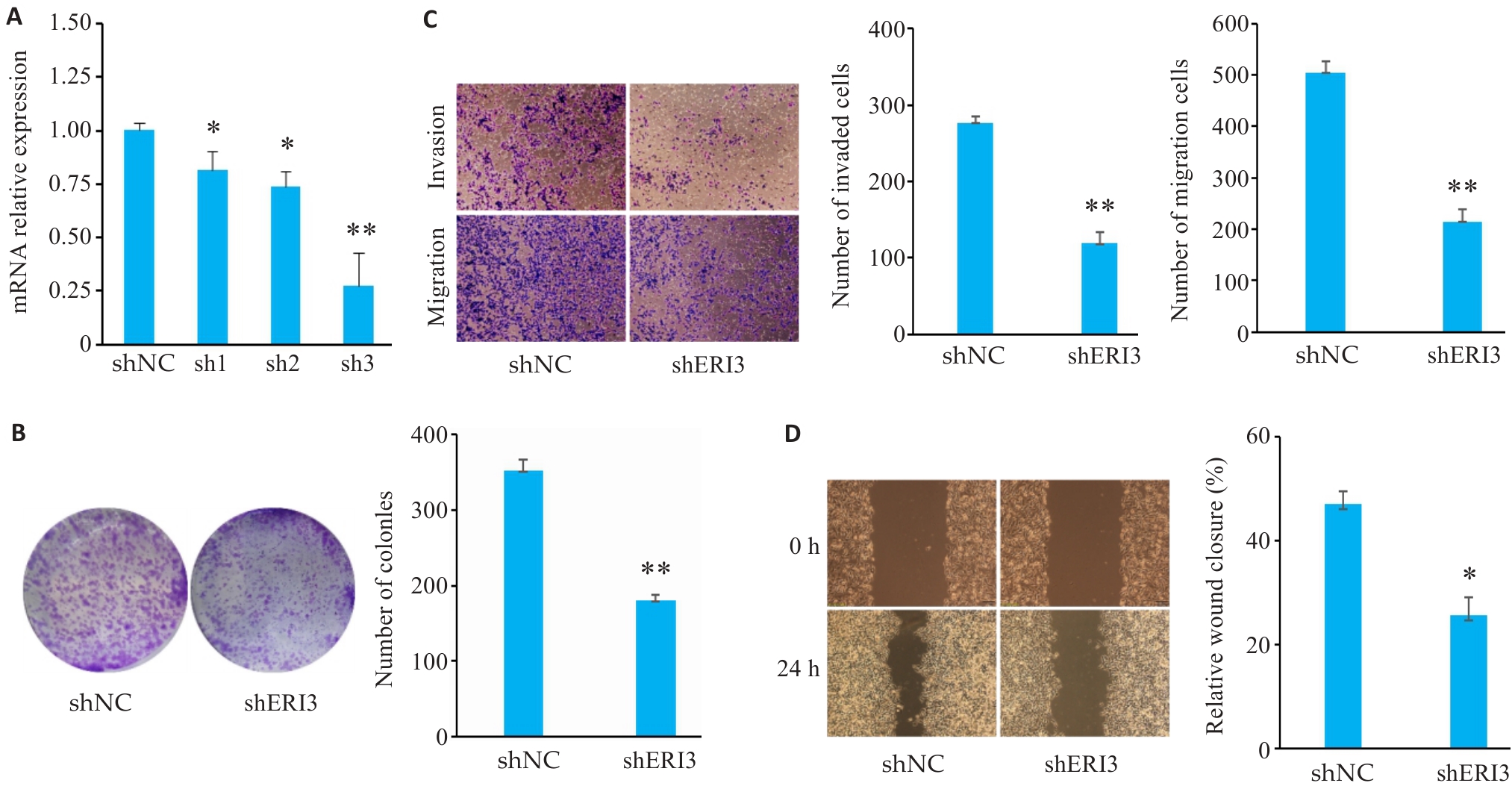
Fig7 ERI3 knockdown inhibits proliferation, invasion, and migration of HCC cells in vitro. A: PCR for assessing the efficiency of ERI3 knockdown. B: Colony formation assay for assessing cell proliferation. C: Transwell assay for assessing cell migration and invasion (Original magnification: ×10). D: ERI3 knockdown of ERI3 impairs wound healing in HCC Cells (×200). n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs shNC group.
| [1] | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA A Cancer J Clinicians, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi:10.3322/caac.21590 |
| [2] | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| [3] | Sartorius K, Sartorius B, Aldous C, et al. Global and country underestimation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in 2012 and its implications[J]. Cancer Epidemiol, 2015, 39(3): 284-90. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2015.04.006 |
| [4] | Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA A Cancer J Clinicians, 2016, 66(2): 115-32. doi:10.3322/caac.21338 |
| [5] | de Lope CR, Tremosini S, Forner A, et al. Management of HCC[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56: S75-87. doi:10.1016/s0168-8278(12)60009-9 |
| [6] | Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2016, 2: 16018. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.18 |
| [7] | Aravalli RN, Steer CJ. Immune-mediated therapies for liver cancer[J]. Genes: Basel, 2017, 8(2): E76. doi:10.3390/genes8020076 |
| [8] | Yang H, Li G, Qiu G. Bioinformatics analysis using ATAC-seq and RNA-seq for the identification of 15 gene signatures associated with the prediction of prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 726551. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.726551 |
| [9] | Liu FY, Feng XM, Ji XL, et al. Cluster classification and clinical prognostic modeling based on m6A RNA methylation regulators in liver cancer[J]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi, 2022, 30(9): 962-9. |
| [10] | Liu J, Qu J, Xu L, et al. Prediction of liver cancer prognosis based on immune cell marker genes[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1147797. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1147797 |
| [11] | Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(12): 550. doi:10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 |
| [12] | Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(1): 139-40. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616 |
| [13] | Liu JF, Lichtenberg T, Hoadley KA, et al. An integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(2): 400-16. |
| [14] | Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013, 14: 7. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-7 |
| [15] | Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer[J]. Immunity, 2013, 39(4): 782-95. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.003 |
| [16] | COHEN J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences [M]. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988. |
| [17] | Mukaka MM. Statistics corner: a guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research[J]. Malawi Med J, 2012, 24(3): 69-71. |
| [18] | Meyer T. Treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: beyond sorafenib[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 3(4): 218-20. doi:10.1016/s2468-1253(17)30255-8 |
| [19] | Currie E, Schulze A, Zechner R, et al. Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer[J]. Cell Metab, 2013, 18(2): 153-61. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.017 |
| [20] | Bechmann LP, Hannivoort RA, Gerken G, et al. The interaction of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism in liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56(4): 952-64. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.08.025 |
| [21] | Li X, Sun R, Liu RP. Natural products in licorice for the therapy of liver diseases: Progress and future opportunities[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 144: 210-26. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.04.025 |
| [22] | Thor Snaebjornsson M, Janaki-Raman S, Schulze A. Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: the role of lipid metabolism in cancer[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 31(1): 62-76. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.010 |
| [23] | Bengoechea-Alonso MT, Ericsson J. SREBP in signal transduction: cholesterol metabolism and beyond[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2007, 19(2): 215-22. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2007.02.004 |
| [24] | Li C, Sheng LN, Sun G, et al. The application of ultraviolet-induced photo-crosslinking in edible film preparation and its implication in food safety[J]. LWT, 2020, 131: 109791. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109791 |
| [25] | Wang H, Xu M, Zhang T, et al. PYCR1 promotes liver cancer cell growth and metastasis by regulating IRS1 expression through lactylation modification[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2024, 14(10): e70045. doi:10.1002/ctm2.70045 |
| [26] | Ho V, Pelland-St-Pierre L, Gravel S, et al. Endocrine disruptors: Challenges and future directions in epidemiologic research[J]. Environ Res, 2022, 204(pt a): 111969. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111969 |
| [27] | Wang X, Zhang XY, Liao NQ, et al. Identification of ribosome biogenesis genes and subgroups in ischaemic stroke[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1449158. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1449158 |
| [28] | Hiam-Galvez KJ, Allen BM, Spitzer MH. Systemic immunity in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2021, 21(6): 345-59. doi:10.1038/s41568-021-00347-z |
| [29] | Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines[J]. Immunity, 2014, 41(1): 14-20. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008 |
| [30] | Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, et al. Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2017, 14(7): 399-416. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.217 |
| [31] | Sunakawa Y, Stintzing S, Cao S, et al. Variations in genes regulating tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) to predict outcomes of bevacizumab-based treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results from TRIBE and FIRE3 trials[J]. Ann Oncol, 2015, 26(12): 2450-6. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv474 |
| [32] | Xiang X, Wang J, Lu D, et al. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to synergize tumor immunotherapy[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 75. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00484-9 |
| [33] | Guo MJ, Sheng WY, Yuan X, et al. Neutrophils as promising therapeutic targets in pancreatic cancer liver metastasis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 140: 112888. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112888 |
| [1] | Zhihui FENG, Wenyue LI, Mingxiu ZHANG, Peipei WANG, Yangyang SHUAI, Hong ZHANG. Long noncoding RNA HClnc1 promotes proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells by targeting RBBP5/KAT2B complex to enhance ODC1 transcription [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1919-1926. |
| [2] | Ying WANG, Jing LI, Yidi WANG, Mingyu HUA, Weibin HU, Xiaozhi ZHANG. Construction and verification of a prognostic model combining anoikis and immune prognostic signatures for primary liver cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [3] | Yu ZHANG, Haitao LI, Yuqing PAN, Jiexian CAO, Li ZHAI, Xi ZHANG. Pan-cancer analysis of MZB1 expression and its association with immune infiltration and clinical prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018. |
| [4] | Ziliang WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Jingjing YANG, Chen YAN, Zhizhi ZHANG, Bingyi HUANG, Meng ZHAO, Song LIU, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO, Deli CHEN. High expression of SURF4 promotes migration, invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting tight junction proteins [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [5] | Yating HUANG, Zhenyou WANG. A coupled diffusion-based model of interaction between tumor metastasis and myeloid-derived suppressive cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1768-1776. |
| [6] | Jinlong PANG, Xinli ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Haojie WANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Yumei YANG, Shanshan LI, Xiaoqiang CHANG, Feng LI, Xian LI. Overexpression of multimerin-2 promotes cutaneous melanoma cell invasion and migration and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [7] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [8] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [9] | Tianli SONG, Yimin WANG, Tong SUN, Xu LIU, Sheng HUANG, Yun RAN. Zheng Gan Decoction inhibits diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats by activating the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 799-809. |
| [10] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [11] | Qingqing HUANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Lian WANG, Xue SONG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. High MYO1B expression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor patient prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [12] | Huali LI, Ting SONG, Jiawen LIU, Yongbao LI, Zhaojing JIANG, Wen DOU, Linghong ZHOU. Prognosis-guided optimization of intensity-modulated radiation therapy plans for lung cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [13] | Xue SONG, Yue CHEN, Min ZHANG, Nuo ZHANG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Yueyue WANG, Lian WANG, Jianguo HU. GPSM2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer to affect patient prognosis by promoting tumor cell proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [14] | Jinhua ZOU, Hui WANG, Dongyan ZHANG. SLC1A5 overexpression accelerates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting M2 polarization of macrophages [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [15] | Tianwei TANG, Luan LI, Yuanhan CHEN, Li ZHANG, Lixia XU, Zhilian LI, Zhonglin FENG, Huilin ZHANG, Ruifang HUA, Zhiming YE, Xinling LIANG, Ruizhao LI. High serum cystatin C is an independent risk factor for poor renal prognosis in IgA nephropathy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||