Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 977-985.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.10
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fenlan BIAN1,3( ), Shiyao NI2,3, Peng ZHAO1,3, Maonanxing QI1,3, Bi TANG1, Hongju WANG1, Pinfang KANG1,3(
), Shiyao NI2,3, Peng ZHAO1,3, Maonanxing QI1,3, Bi TANG1, Hongju WANG1, Pinfang KANG1,3( ), Jinjun LIU1,3(
), Jinjun LIU1,3( )
)
Received:2024-11-18
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Pinfang KANG, Jinjun LIU
E-mail:1174672677@qq.com;kangpinfang.1016@163.com;ljj19740828101@163.com
Supported by:Fenlan BIAN, Shiyao NI, Peng ZHAO, Maonanxing QI, Bi TANG, Hongju WANG, Pinfang KANG, Jinjun LIU. Asiaticoside alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 977-985.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.10
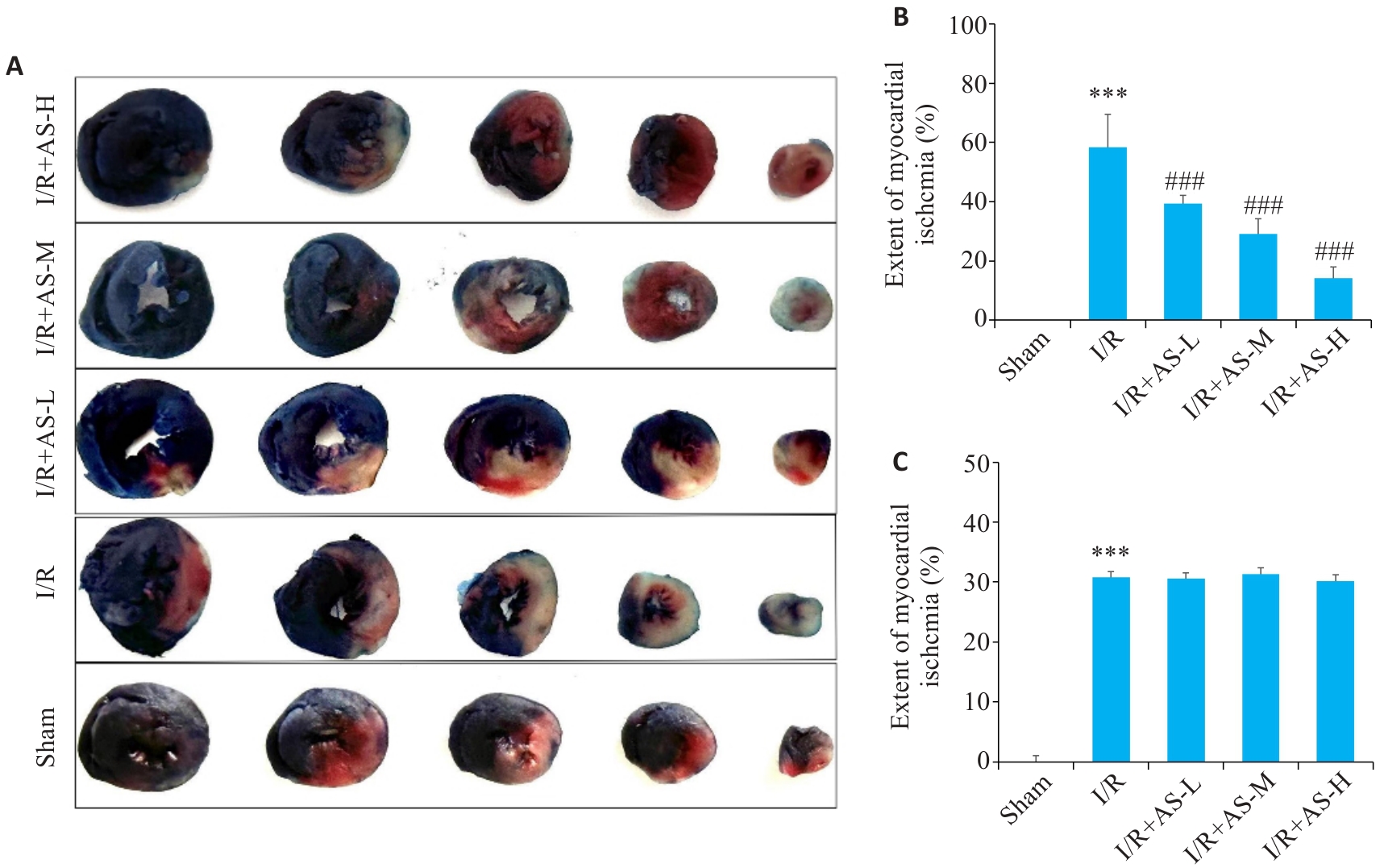
Fig.2 TTC-Evans blue staining of rat cardiac tissues (A) and comparison of the extent of myocardial infarction (B) and ischemia (C) among the 5 groups. ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; ###P<0.001 vs I/R group (Mean±SD, n=3).
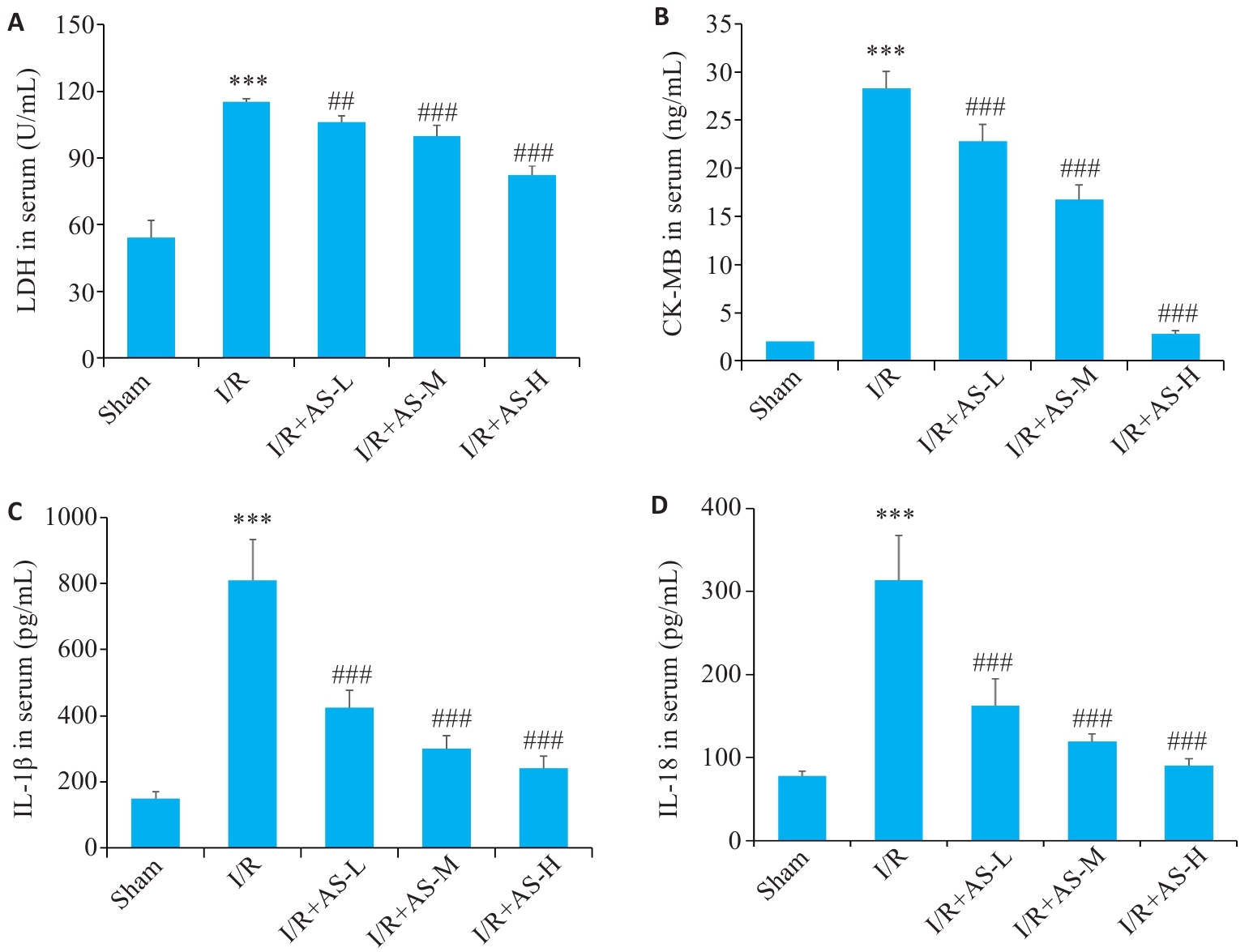
Fig.3 Effect of AS pretreatment on serum levels of LDH (A), CK-MB (B), IL-1β (C) and IL-18 (D) in MIRI rats. ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs I/R group (Mean±SD, n=6).
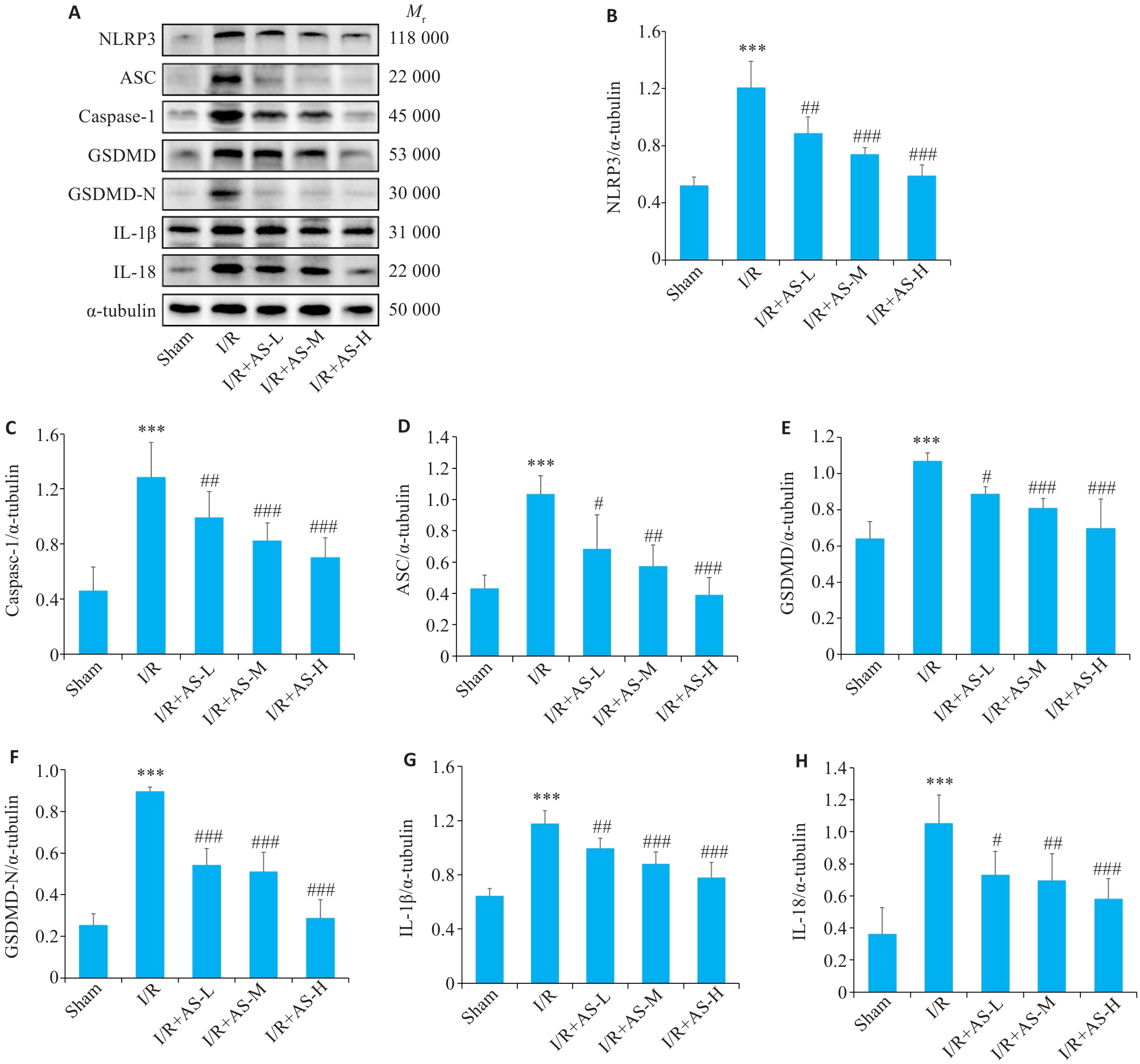
Fig.5 Western blotting for detecting protein expressions in the myocardial tissue of the rats in each group. A: Western blots of NLRP3, caspase-1, ASC, GSDMD, GSDMD-N, IL-1β and IL-18 in the myocardial tissues of the rats. B-H: Quantitative analysis of pyroptosis-related proteins in each group. ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs I/R group (Mean±SD, n=4).
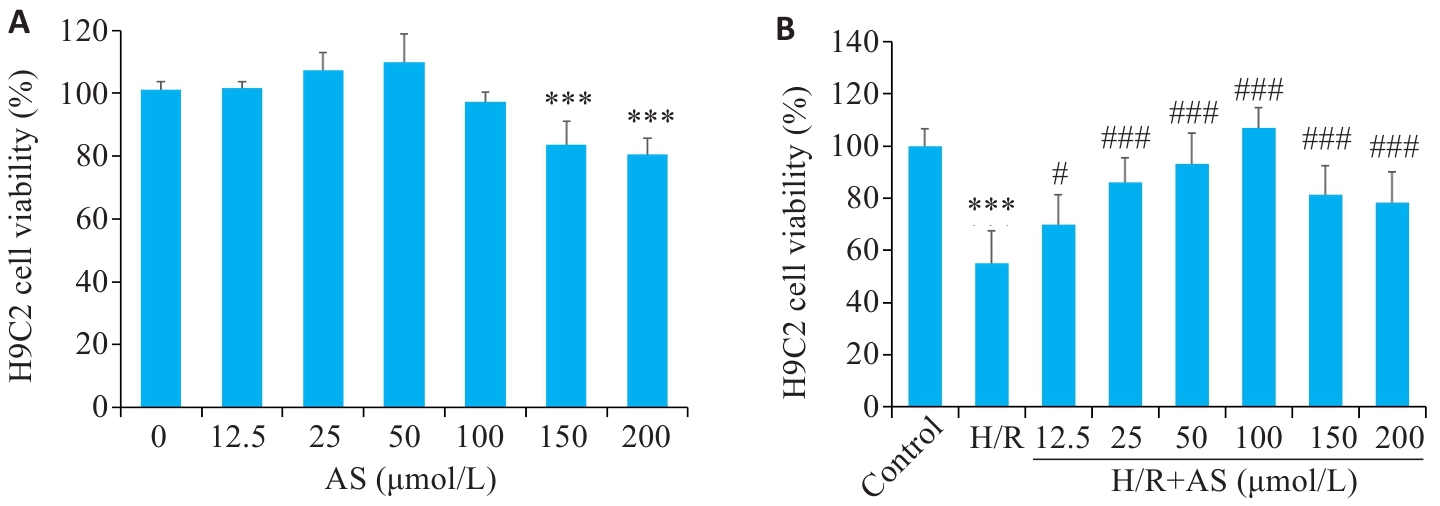
Fig.6 Effects of different concentrations of AS on viability of H9C2 cells. A: Effect of AS on viability of H9C2 cells. B: Effect of AS pretreatment on viability of H9C2 cells with hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. ***P<0.001 vs Control group; #P<0.05,###P<0.001 vs H/R group (Mean±SD, n=3).
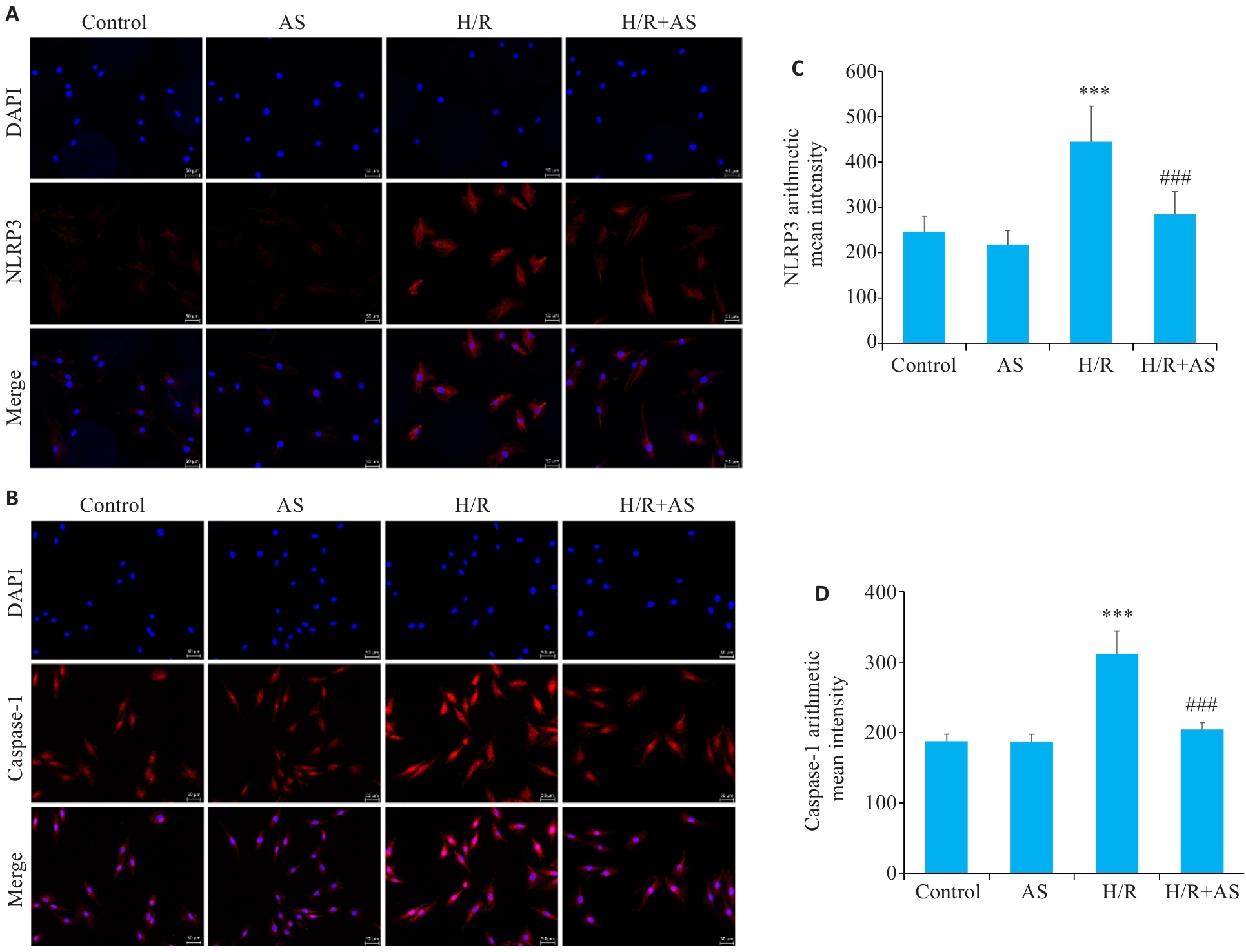
Fig.7 Immunofluorescence staining showing NLRP3 and caspase-1 protein expressions in H9C2 cells in each group. A: Immunofluorescence staining of NLRP3 in H9C2 cells in each group (Original magnification: ×20). B: Immunofluorescence staining of caspase-1 in H9C2 cells in each group (×20). C: Average fluorescence intensity of NLRP3 in each group. D: Average fluorescence intensity of caspase-1 in each group. ***P<0.001 vs Control group; ###P<0.001 vs H/R group (Mean±SD, n=3).
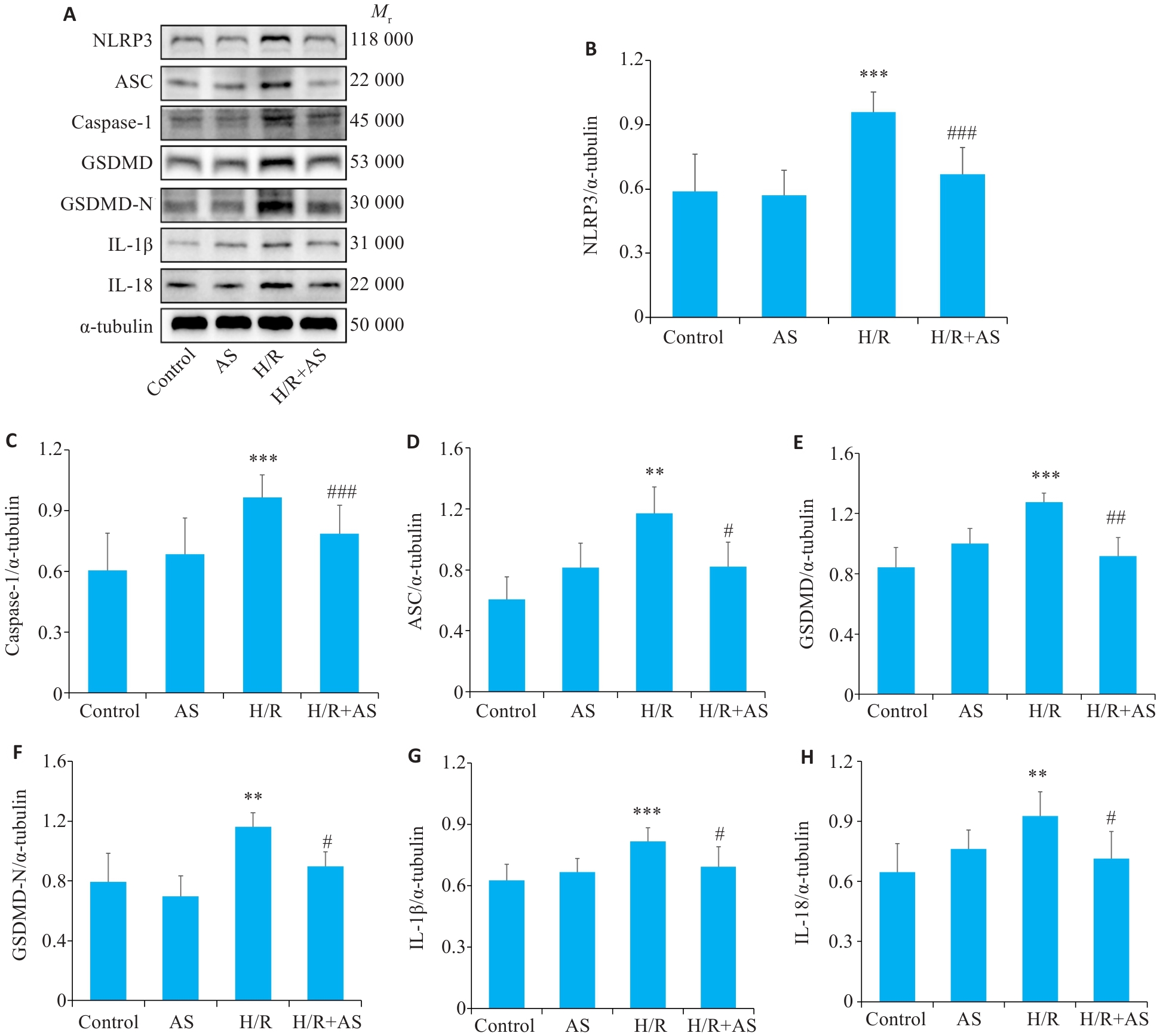
Fig.8 Western blotting for detecting protein expressions in H9C2 cells in each group. A: Western blots of NLRP3, caspase-1, ASC, GSDMD, GSDMD-N, IL-1β and IL-18 in H9C2 cells in each group. B-H: Quantitative analysis of expressions of the pyroptosis-related proteins in H9C2 cells in each group. **P<0.01,***P<0.001 vs Control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs H/R group (Mean±SD, n=4).
| 1 | Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(10): e56-528. |
| 2 | Tibaut M, Mekis D, Petrovic D. Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction and acute management strategies[J]. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem, 2017, 14(3): 150-9. |
| 3 | Dauerman HL, Ibanez B. The edge of time in acute myocardial infarction[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2021, 77(15): 1871-4. |
| 4 | Thuny F, Lairez O, Roubille F, et al. Post-conditioning reduces infarct size and edema in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2012, 59(24): 2175-81. |
| 5 | Larose E, Rodés-Cabau J, Pibarot P, et al. Predicting late myocardial recovery and outcomes in the early hours of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction traditional measures compared with microvascular obstruction, salvaged myocardium, and necrosis characteristics by cardiovascular magnetic resonance[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2010, 55(22): 2459-69. |
| 6 | Toldo S, Mauro AG, Cutter Z, et al. Inflammasome, pyroptosis, and cytokines in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2018, 315(6): H1553-68. |
| 7 | Zeng ZL, Li GH, Wu SY, et al. Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular disease[J]. Cell Prolif, 2019, 52(2): e12563. |
| 8 | Zhang J, Huang L, Shi X, et al. Metformin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cell pyroptosis via AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2020, 12(23): 24270-87. |
| 9 | Liu S, Bi Y, Han T, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting pyroptosis via negative regulation of PGAM5/MAVS/NLRP3 axis[J]. Cell Discov, 2024, 10(1): 24. |
| 10 | SWANSON K V, DENG M, TING J P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics [J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2019, 19(8): 477-89. |
| 11 | Bandopadhyay S, Mandal S, Ghorai M, et al. Therapeutic properties and pharmacological activities of asiaticoside and madecassoside: a review[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2023, 27(5): 593-608. |
| 12 | 阳 飞, 黄 辉, 王 芳, 等. 积雪草苷对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用以及MAPK通路的影响[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2021, 41(15): 1514-8. DOI: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2021.15.06 |
| 13 | 卢国庆, 孙红燕, 孙正宇, 等. 积雪草苷对离体大鼠胸主动脉的舒张作用及其机制 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(03): 523-32. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.03.14 |
| 14 | Liu Y, Zhao JF, Mu XR, et al. Asiaticoside-nitric oxide promoting diabetic wound healing through the miRNA-21-5p/TGF-β1/SMAD7/TIMP3 signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 319: 117266. |
| 15 | He ZL, Hu YY, Zhang Y, et al. Asiaticoside exerts neuroprotection through targeting NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 127: 155494. |
| 16 | Li Y, Li Z, Liu J, et al. miR-190-5p alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting PHLPP1[J]. Dis Markers, 2021, 2021: 8709298. |
| 17 | Pagliaro P, Penna C. Inhibitors of NLRP3 inflammasome in ischemic heart disease: focus on functional and redox aspects[J]. Antioxidants: Basel, 2023, 12(7): 1396. |
| 18 | Luan F, Rao ZL, Peng LX, et al. Cinnamic acid preserves against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 100: 154047. |
| 19 | Ahmad F, Marzook H, Gupta A, et al. GSK-3α aggravates inflammation, metabolic derangement, and cardiac injury post-ischemia/reperfusion[J]. J Mol Med, 2023, 101(11): 1379-96. |
| 20 | Peng LX, Lei ZQ, Rao ZL, et al. Cardioprotective activity of ethyl acetate extract of Cinnamomi Ramulus against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 93: 153798. |
| 21 | Shen SC, He F, Cheng C, et al. Uric acid aggravates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via ROS/NLRP3 pyroptosis pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 133: 110990. |
| 22 | Wang Y, Liu X, Shi H, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome, an immune-inflammatory target in pathogenesis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2020, 10(1): 91-106. |
| 23 | Blevins HM, Xu Y, Biby S, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome pathway: a review of mechanisms and inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2022, 14: 879021. |
| 24 | Chai X, Liang Z, Zhang J, et al. Chlorogenic acid protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by inhibiting Lnc Neat1/NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 17803. |
| 25 | Li H, Yang DH, Zhang Y, et al. Geniposide suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via the AMPK signaling pathway to mitigate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Chin Med, 2022, 17(1): 73. |
| 26 | Xie DN, Guo HL, Li MB, et al. Splenic monocytes mediate inflammatory response and exacerbate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in a mitochondrial cell-free DNA-TLR9-NLRP3-dependent fashion[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2023, 118(1): 44. |
| 27 | Bylka W, Znajdek-Awiżeń P, Studzińska-Sroka E, et al. Centella asiatica in cosmetology[J]. Postepy Dermatol Alergol, 2013, 30(1): 46-9. |
| 28 | He ZL, Hu YY, Niu ZQ, et al. A review of pharmacokinetic and pharmacological properties of asiaticoside, a major active constituent of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 302: 115865. |
| 29 | Ye CM, Yao ZC, Wang YY, et al. Asiaticoside promoted ferroptosis and suppressed immune escape in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating the Wnt/β‑catenin pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 134: 112175. |
| 30 | Liu X, Liu T, Yang K, et al. Antifatigue effect of asiaticoside in mice by attenuating oxidative stress[J]. Discov Med, 2023, 35(176): 275-82. |
| 31 | Liu K, Yin Y, Shi C, et al. Asiaticoside ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting inflammatory response, protecting intestinal barrier and regulating intestinal microecology[J]. Phytother Res, 2024, 38(4): 2023-40. |
| 32 | Zeng X, Yu J, Liu P, et al. Asiaticoside alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via activating the PI3K-AKT-GSK3β pathway in vivo and in vitro [J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10(2): 69. |
| 33 | Yao M, Wang J, Zhang J, et al. Asiaticoside attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-caused injury of cardiomyocytes by inhibiting autophagy[J]. J Appl Toxicol, 2023, 43(6): 789-98. |
| [1] | Haiyi ZHOU, Siyi HE, Ruifang HAN, Yongge GUAN, Lijuan DONG, Yang SONG. Moxibustion promotes endometrial repair in rats with thin endometrium by inhibiting the NLRP3/pyroptosis axis via upregulating miR-223-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1380-1388. |
| [2] | Zhihua TIAN, Qingqing YANG, Xin CHEN, Fangfang ZHANG, Baimao ZHONG, Hong CAO. Spermine suppresses GBP5-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages to relieve vital organ injuries in neonatal mice with enterovirus 71 infection [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 901-910. |
| [3] | Yalei SUN, Meng LUO, Changsheng GUO, Jing GAO, Kaiqi SU, Lidian CHEN, Xiaodong FENG. Amentoflavone alleviates acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting cell pyroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 692-701. |
| [4] | Zhengwang ZHU, Linlin WANG, Jinghan ZHAO, Ruixue MA, Yuchun YU, Qingchun CAI, Bing WANG, Pingsheng ZHU, Mingsan MIAO. Tuihuang Mixture improves α‑naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes via regulating farnesoid X receptor [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 718-724. |
| [5] | Ju HUANG, Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Nodakenin ameliorates TNBS-induced experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting pyroptosis of intestinal epithelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [6] | Mingyuan LI, Wei ZHANG, Mengqing HUA. Bardoxolone methyl alleviates acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1662-1669. |
| [7] | Huaixiang TAO, Jinguang LUO, Zhiyuan WEN, Genming YU, Xiao SU, Xinwei WANG, Han GUAN, Zhijun CHEN. High STING expression exacerbates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and promoting inflammation and apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354. |
| [8] | Wei ZHANG, Mengmeng DENG, Yao ZENG, Chenfei LIU, Feifei SHANG, Wenhao XU, Haoyi JIANG, Fengchao WANG, Yanqing YANG. 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone alleviates septic shock in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [9] | Yiming SUN, Rong ZHANG, Ying MENG, Lei ZHU, Mingqiang LI, Zhe LIU. Coenzyme Q10 alleviates depression-like behaviors in mice with chronic restraint stress by down-regulating the pyroptosis signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 810-817. |
| [10] | LU Guoqing, SUN Hongyan, SUN Zhengyu, LIU Leqiang, WANG Lei, ZHANG Ningning, WANG Yuhang, HE Yiming, JI Jiahui, LI Xinyue, KANG Pinfang, TANG Bi. Effect of asiaticoside on systolic blood pressure and relaxation of isolated thoracic aorta of rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 523-532. |
| [11] | CHEN Guodong, LUO Suxin. Colchicine alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by activating AMPK [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 226-235. |
| [12] | FANG Shangping, SUN Renke, SU Hui, ZHAI Kecheng, XIANG Yu, GAO Yangmengna, GUO Wenjun. Chlorogenic acid alleviates acute kidney injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes and the caspase-1 canonical pyroptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 317-323. |
| [13] | LING Xuguang, XU Wenwen, PANG Guanlai, HONG Xuxing, LIU Fengqin, LI Yang. Tea polyphenols ameliorates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 381-386. |
| [14] | XU Xiaohui, FENG Jinmei, LUO Ying, HE Xinyu, ZANG Jinbao, HUANG Daochao. Adeno-associated virus-mediated hepatocyte-specific NDUFA13 overexpression protects against CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting hepatic NLRP3 activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 201-209. |
| [15] | Duanyi SONG, Yun LI, Xuefang TANG, Hua LI, Kang TAO. Diazepam alleviates pulmonary fibrosis in mice by inhibiting LPS-induced pyroptosis and inflammation via the let-7a-5p/MYD88 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2092-2101. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||