Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2104-2110.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.06
Yongxin MAI1,2,4( ), Shuting ZHOU2,4, Ruijia WEN2,4, Jinfang ZHANG1(
), Shuting ZHOU2,4, Ruijia WEN2,4, Jinfang ZHANG1( ), Dongxiang ZHAN2,3,4,5(
), Dongxiang ZHAN2,3,4,5( )
)
Received:2025-03-14
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Jinfang ZHANG, Dongxiang ZHAN
E-mail:20201110039@stu.gzucm.edu.cn;zhangjf06@gzucm.edu.cn;zdxbwjs@gzucm.edu.cn
Supported by:Yongxin MAI, Shuting ZHOU, Ruijia WEN, Jinfang ZHANG, Dongxiang ZHAN. Aucubin alleviates knee osteoarthritis in mice by suppressing the NF‑κB signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2104-2110.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.06
| Gene | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
| COL2A1-Forward | GGCAATAGCAGGTTCACGTACA |
| COL2A1-Reverse | CGATAACAGTCTTGCCCCACTT |
| SOX9-Forward | TCCTCAGGCTTTGCGATTT |
| SOX9-Reverse | TGCTCGGGCACTTATTGG |
| TNF-α-Forward | CTGACGAATTACAGGGCCAAT |
| TNF-α-Reverse | TGCGTGAACCTCTTGAACAGT |
| 18S-Forward | TGGTTGCAAAGCTGAAACTTAAAG |
| 18S-Reverse | AGTCAAATTAAGCCGCAGGC |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR for amplifying mRNAs associated with cartilage matrix synthesis and inflammatory response
| Gene | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
| COL2A1-Forward | GGCAATAGCAGGTTCACGTACA |
| COL2A1-Reverse | CGATAACAGTCTTGCCCCACTT |
| SOX9-Forward | TCCTCAGGCTTTGCGATTT |
| SOX9-Reverse | TGCTCGGGCACTTATTGG |
| TNF-α-Forward | CTGACGAATTACAGGGCCAAT |
| TNF-α-Reverse | TGCGTGAACCTCTTGAACAGT |
| 18S-Forward | TGGTTGCAAAGCTGAAACTTAAAG |
| 18S-Reverse | AGTCAAATTAAGCCGCAGGC |
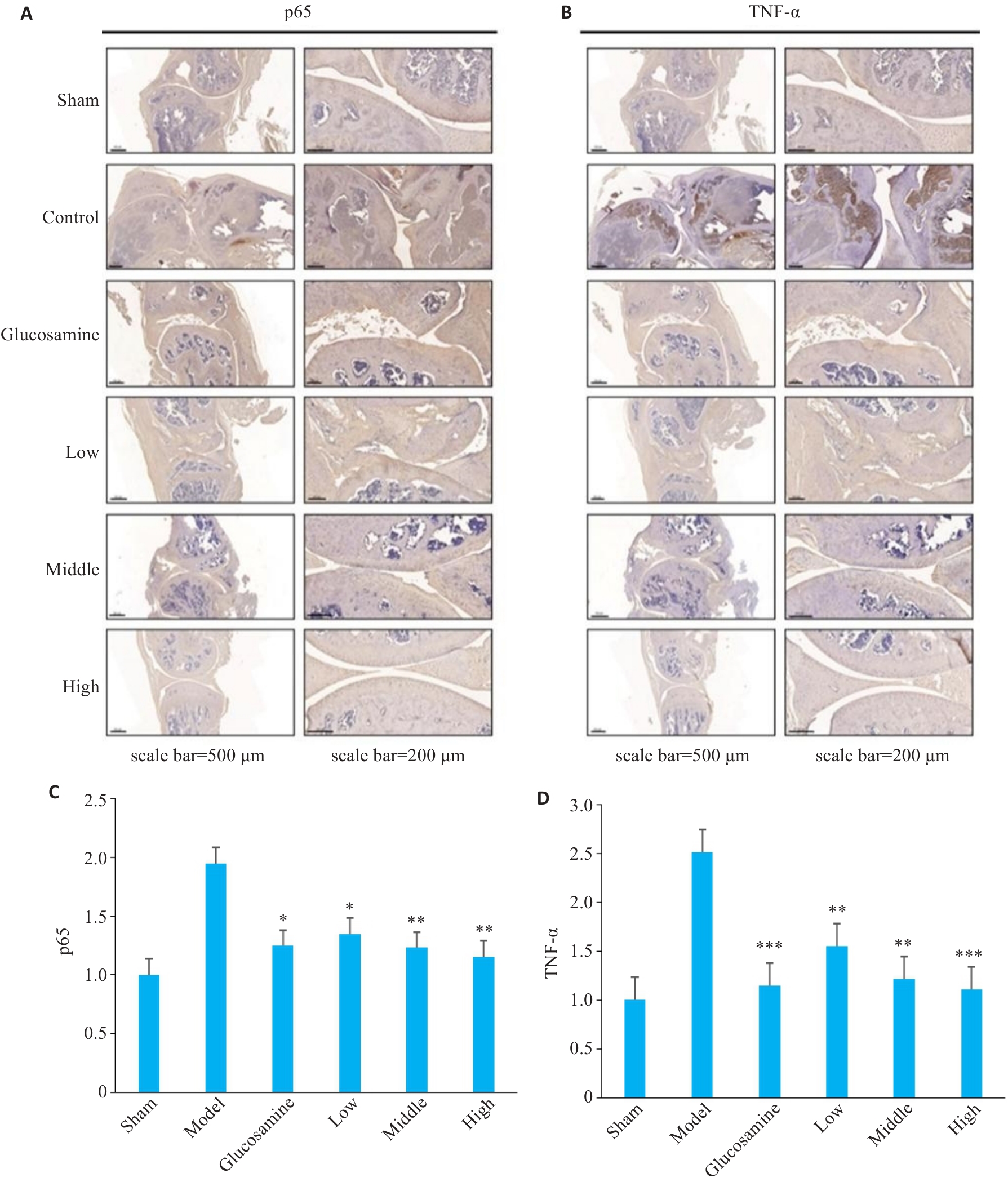
Fig.3 Immunohistochemical staining for inflammatory proteins in the cartilage tissues of the mouse models. A: p65 staining. B: TNF-α staining. C, D: Quantitative analysis of p65 and TNF-α expression levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Model group.
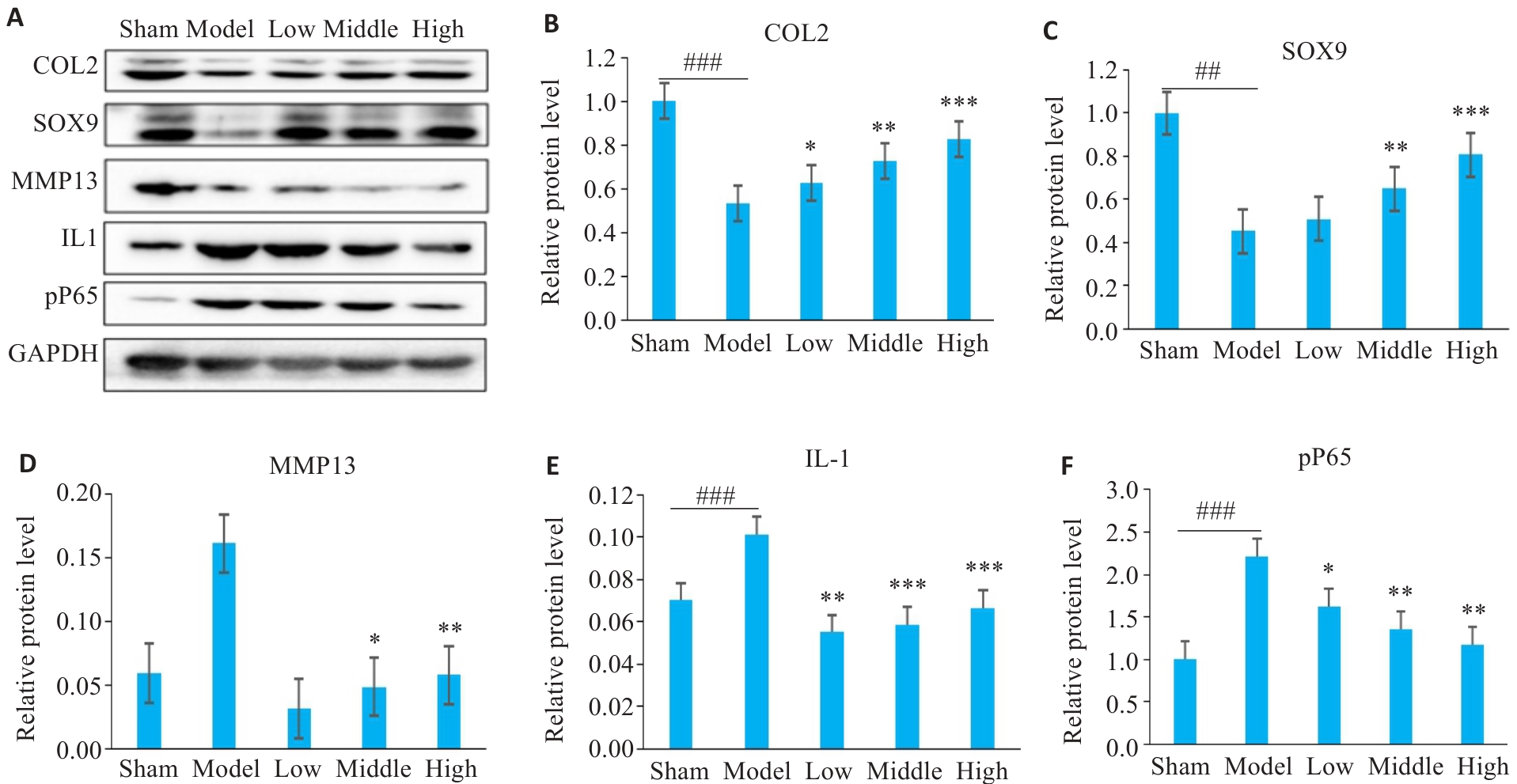
Fig.4 Western blotting of protein expressions in the chondrocyte model. A: Representative protein blots. B-F: Quantitative analysis of p-p65/p65, MMP-13, Collagen II, SOX9, and IL-1 expression levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs Model group.
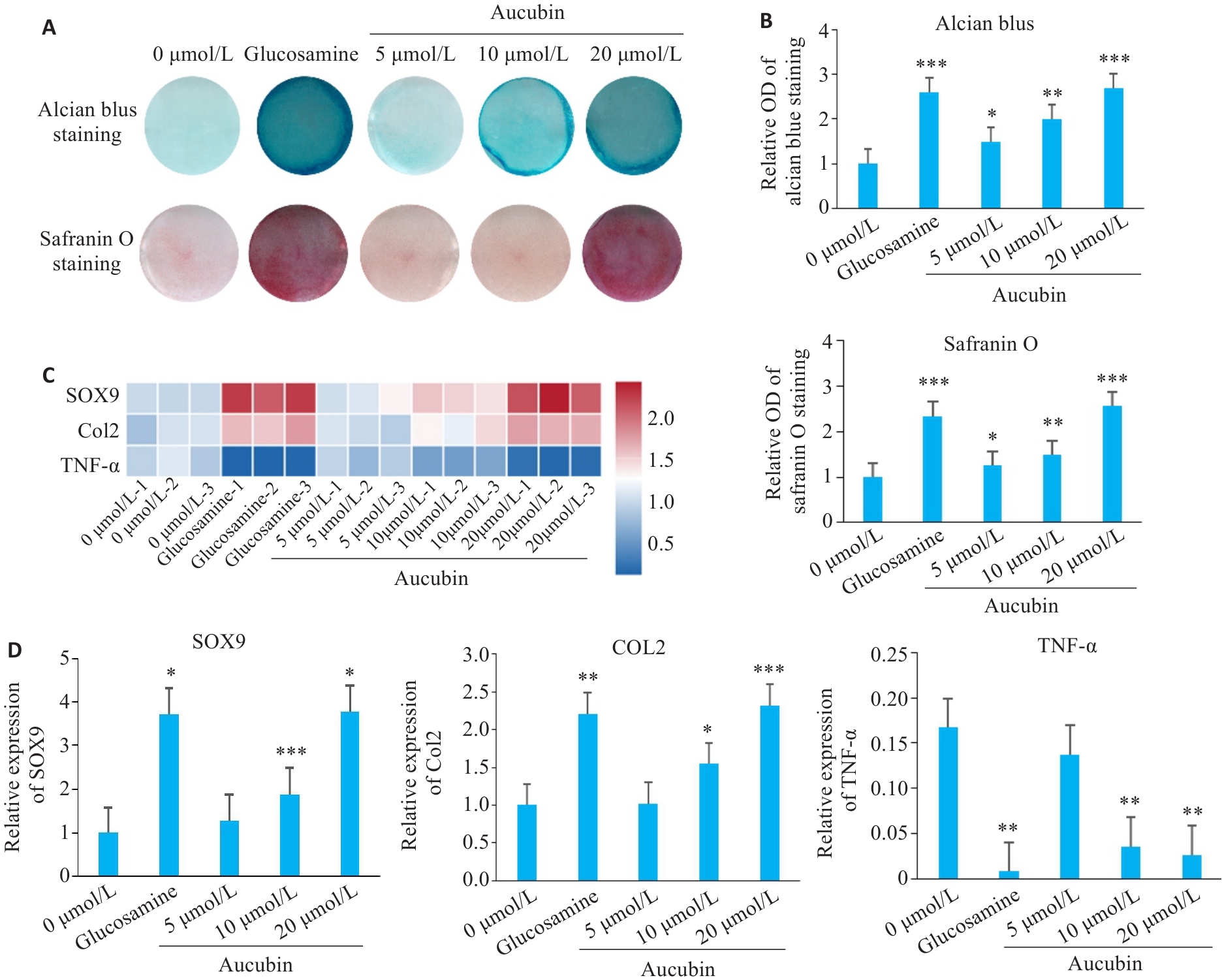
Fig.5 Alcian blue-Safranin O staining (A, B; Original magnification: ×100) and expressions levels of SOX9, COL2, and TNF-α mRNAs (C, D) in the chondrocyte model. *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.001 vs 0 μmol/L.
| [1] | 叶海东, 刘 宇, 甄朋超. 苍术素调节PINK1/Parkin信号通路对膝骨关节炎大鼠线粒体自噬的影响[J]. 微循环学杂志, 2023, 33(4): 13-20. |
| [2] | 陈后煌. 从Ras-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2信号通路探讨电针干预膝骨关节炎软骨退变的机制[D]. 福州: 福建中医药大学, 2017. |
| [3] | 曾国际, 郭夕语, 李 雨, 等. 基于虚拟现实技术的康复训练对膝骨关节炎患者康复的研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2023, 12(10): 61-5. |
| [4] | Lv Z, Yang YX, Li J, et al. Molecular classification of knee osteoarthritis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 725568. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.725568 |
| [5] | Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, et al. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappa B[J]. J Immunol, 2004, 172(4): 2522-9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.172.4.2522 |
| [6] | Baldwin AS. Series introduction: the transcription factor NF-kappaB and human disease[J]. J Clin Invest, 2001, 107(1): 3-6. doi:10.1172/jci11891 |
| [7] | Ghosh S, Hayden MS. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2008, 8(11): 837-48. doi:10.1038/nri2423 |
| [8] | Nagumo Y, Kandori S, Tanuma K, et al. PLD1 promotes tumor invasion by regulation of MMP-13 expression via NF-κB signaling in bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 511: 15-25. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.014 |
| [9] | 朱 媛, 王亚琴. 桃叶珊瑚苷的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2006, 37(6): 947-9. |
| [10] | 卢仁睿, 张 莉, 王慧慧, 等. 桃叶珊瑚苷通过调节小胶质细胞M1/M2极化抑制神经炎症[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2023, 32(9): 934-40. |
| [11] | 刁玮琳, 尹 敏, 李 翠. 桃叶珊瑚苷在烟曲霉菌角膜炎中抗炎作用及其机制[J]. 青岛大学学报: 医学版, 2023, 59(4): 501-6. |
| [12] | 钟子安, 刘 娟, 杨 柳, 等. 基于Nox4/NLRP3通路探讨桃叶珊瑚苷干预动脉粥样硬化的作用机制[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2023, 21(13): 2405-11. |
| [13] | 杨 雷, 李兆勇, 马 露, 等. 基于TLR4/NF-κB通路研究桃叶珊瑚苷联合ADSCs-exos对TBHP诱导的髓核细胞保护作用[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(19): 5294-303. |
| [14] | Wang SN, Xie GP, Qin CH, et al. Aucubin prevents interleukin-1 beta induced inflammation and cartilage matrix degradation via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in rat articular chondrocytes[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2015, 24(2): 408-15. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2014.12.029 |
| [15] | Endisha H, Datta P, Sharma A, et al. microRNA-34a-5p promotes joint destruction during osteoarthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2021, 73(3): 426-39. doi:10.1002/art.41552 |
| [16] | Wu Y, Li J, Zeng Y, et al. Exosomes rewire the cartilage microenvironment in osteoarthritis: from intercellular communi-cation to therapeutic strategies[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2022, 14(1): 40. doi:10.1038/s41368-022-00187-z |
| [17] | Wang CJ, Sun YC, Siu KK, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows site-specific effects in osteoarthritis of the knee in rats[J]. J Surg Res, 2013, 183(2): 612-9. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2013.02.006 |
| [18] | Ding H, Wei J, Zhao Y, et al. Progranulin derived engineered protein Atsttrin suppresses TNF-α-mediated inflammation in intervertebral disc degenerative disease[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(65): 109692-702. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.22766 |
| [19] | Phillips R. Targeting articular Mmp13 in OA[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2021, 17(11): 645. doi:10.1038/s41584-021-00696-x |
| [20] | Kim HH, Kim K. Enhancement of TNF-α-mediated cell death in vascular smooth muscle cells through cytochrome c-independent pathway by the proteasome inhibitor[J]. FEBS Lett, 2003, 535(1/2/3): 190-4. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03894-2 |
| [21] | Li JJ, Johnson AR. Selective MMP13 inhibitors[J]. Med Res Rev, 2011, 31(6): 863-94. doi:10.1002/med.20204 |
| [22] | Etoh T, Inoue H, Yoshikawa Y, et al. Increased expression of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) and MT1-MMP in oesophageal cancer is related to cancer aggressiveness[J]. Gut, 2000, 47(1): 50-6. doi:10.1136/gut.47.1.50 |
| [23] | Geng R, Li J, Yu C, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: Current status and research progress in treatment (Review)[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2023, 26(4): 481. doi:10.3892/etm.2023.12180 |
| [24] | Song X, Liu Y, Chen S, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of animal models and intervention of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Animal Model Exp Med, 2024, 7(2): 114-26. doi:10.1002/ame2.12389 |
| [25] | Mahida JP, Antczak C, Decarlo D, et al. A synergetic screening approach with companion effector for combination therapy: application to retinoblastoma[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): e59156. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059156 |
| [26] | Ben-Neriah Y, Karin M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-κB as the matchmaker[J]. Nat Immunol, 2011, 12(8): 715-23. doi:10.1038/ni.2060 |
| [27] | Natoli G, Chiocca S. Nuclear ubiquitin ligases, NF-κB degradation, and the control of inflammation[J]. Sci Signal, 2008, 1(1): 1103-12. doi:10.1126/stke.11pe1 |
| [28] | Zhong ZY, Umemura A, Sanchez-Lopez E, et al. NF-κB restricts inflammasome activation via elimination of damaged mitochondria[J]. Cell, 2016, 164(5): 896-910. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.057 |
| [29] | Xie ZB, Chen KM, Huang CW, et al. Correlation between macrophage chemotaxis and disease severity in patients with knee osteoarthritis[J]. Zhongguo Gu Shang, 2023, 36(6): 514-8. |
| [1] | Bing XIA, Jin PENG, Jiuyang DING, Jie WANG, Guowei TANG, Guojie LIU, Yun WANG, Changwu WAN, Cuiyun LE. ATF3 regulates inflammatory response in atherosclerotic plaques in mice through the NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [2] | Liping FU, Lixia YUAN, Jie WANG, Xuelan CHEN, Guizhi KE, Yu HUANG, Xinyi YANG, Gang LIU. Advances of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for treatment of musculoskeletal disorders in the past decade [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 661-668. |
| [3] | Na ZHONG, Huijie WANG, Wenying ZHAO, Zhengui SUN, Biao GENG. High RNF7 expression enhances PD-1 resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by promoting CXCL1 expression and myeloid-derived suppressor cell recruitment via activating NF-κB signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1704-1711. |
| [4] | Na ZHAO, Mengdi SHEN, Rui ZHAO, Di AO, Zetan LUO, Yinliang ZHANG, Zhidong XU, Fangtian FAN, Hailun ZHENG. column:Sanguinarine alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [5] | LI Yunfei, YANG Jingyi, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Caixia, WEI Yuxiang, WANG Yiying, WU Ning, SUN Jianfei, WU Zunqiu. The Miao medicine Sidaxue alleviates rheumatoid arthritis in rats possibly by downregulating matrix metalloproteinases [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 739-747. |
| [6] | Changlong FU, Yanming LIN, Shujie LAN, Yue CHEN, Chao LI, Shiyu LU, Qing LIN. Tougu Xiaotong Capsule alleviates cartilage degeneration in mice with knee osteoarthritis by modulating Nav1.7 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2074-2081. |
| [7] | ZHOU Qiao, LIU Jian, WAN lei, ZHU Yan, QI Yajun, HU Yuedi. Xinfeng Capsule alleviates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation by regulating the miR-502-5p/TRAF2/NF-κB axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 108-118. |
| [8] | ZHENG Xiang, GAO Songai, YOU Hao, WANG Haoqi, GAO Yanping, WANG Jinli, LI Jia, LI Ling. Electroacupuncture improves motor function of rats with osteoarthritis by alleviating joint inflammation through the Wnt-7B/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(4): 590-596. |
| [9] | CAO Jing, LIU Haibo, AN Qi, HAN Feng. Metformin alleviates pathologic pain in mice with radiation dermatitis by inhibiting p38MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1815-1820. |
| [10] | ZHOU Sicong, YANG Wei, ZENG Li, CAO Chunhao, YUAN Su, RONG Xiaofeng. Emodin alleviates joint inflammation and bone erosion in rats with collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting ferroptosis and degrading matrix metalloproteinases [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1776-1781. |
| [11] | CHEN Xin, QI Xiuchun, CAO Yujing, LI Yang, LI Haoliang, WANG Qianjin, AI Jinwei. Indirubin relieves inflammatory injury of chondrocytes in a mouse model of osteoarthritis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(9): 1381-1388. |
| [12] | LI Wei, SHI Yongkang, GUO Yuhua, TIAN Shengwang. Nur77 promotes invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells through the NF-κB/IL-6 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(9): 1410-1417. |
| [13] | WANG Shaoxin, CUI Lihong, LIU Xinyao, LUO Zhe, LI Hui, PU Jiang. WDSUB1 knockdown alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(8): 1119-1125. |
| [14] | CAO Chunhao, ZENG Li, RONG Xiaofeng. Therapeutic mechanism of emodin for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a network pharmacology-based analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(6): 913-921. |
| [15] | LIU Siyu, LIU Qing, PENG Qunlong, ZHANG Yuanfang, WANG Junjie. Dihydromyricetin improves cardiac insufficiency by inhibiting HMGB1 in diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(5): 641-648. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||