Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 90-99.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.12
Previous Articles Next Articles
Qing LIU1( ), Jing LIU1, Yihang ZHENG1, Jin LEI2, Jianhua HUANG1, Siyu LIU1, Fang LIU1, Qunlong PENG1, Yuanfang ZHANG1, Junjie WANG1, Yujuan LI2(
), Jing LIU1, Yihang ZHENG1, Jin LEI2, Jianhua HUANG1, Siyu LIU1, Fang LIU1, Qunlong PENG1, Yuanfang ZHANG1, Junjie WANG1, Yujuan LI2( )
)
Received:2024-06-27
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Yujuan LI
E-mail:liuqing@xnu.edu.cn;Li_yujuan1001@163.com
Qing LIU, Jing LIU, Yihang ZHENG, Jin LEI, Jianhua HUANG, Siyu LIU, Fang LIU, Qunlong PENG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Junjie WANG, Yujuan LI. Quercetin mediates the therapeutic effect of Centella asiatica on psoriasis by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation to inhibit the IL-23/IL-17A axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 90-99.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.12
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3')-F | Primer sequences (5'-3')-R | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA | 123 |
| IL-23 | GTGGCATCGAGAAACTGT | GAGCCACCCAGGAAAGTA | 116 |
| IL-17A | ACTACCTCAACCGTTCCACG | TTCCTCCGCATTGACACAG | 120 |
| TNF-α | ATGAGCACAGAAAGCATGATC | GGTCTGGGCCATAGAACTGATG | 231 |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | 76 |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3')-F | Primer sequences (5'-3')-R | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA | 123 |
| IL-23 | GTGGCATCGAGAAACTGT | GAGCCACCCAGGAAAGTA | 116 |
| IL-17A | ACTACCTCAACCGTTCCACG | TTCCTCCGCATTGACACAG | 120 |
| TNF-α | ATGAGCACAGAAAGCATGATC | GGTCTGGGCCATAGAACTGATG | 231 |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | 76 |
| Number | MOL ID | Compound Name | Oral Bioavailability | Drug Likeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| A 2 | MOL007312 | Asiaticoside | 10.22 | 0.7 |
| A 3 | MOL007253 | Asiatic acid | 16.69 | 0.72 |
| A 4 | MOL000359 | Sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| A 5 | MOL007313 | Xanthanoic acid | 48.07 | 0.16 |
| A 6 | MOL007320 | 8-acetoxycentellynol | 65.94 | 0.12 |
| A 7 | MOL006370 | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 19.61 | 0.33 |
| A 8 | MOL000008 | Qpigenin | 23.06 | 0.21 |
| A 9 | MOL007201 | Brahmic acid | 17.6 | 0.7 |
| A 10 | MOL006387 | Chlorogenic acid | 25.58 | 0.33 |
| A 11 | MOL007323 | Madasiatic acid | 18.42 | 0.72 |
| A 12 | MOL007303 | Madecassoside | 16.89 | 0.7 |
| A 13 | MOL006407 | Neochlorogenic acid | 18.05 | 0.33 |
| A 14 | MOL001434 | Quercetin 3-O-rhamnopyranosyl | 22.24 | 0.28 |
| A 15 | MOL000511 | Ursolic acid | 16.77 | 0.75 |
Tab.2 Basic information of the active components in Centella asiatica
| Number | MOL ID | Compound Name | Oral Bioavailability | Drug Likeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 | MOL000098 | Quercetin | 46.43 | 0.28 |
| A 2 | MOL007312 | Asiaticoside | 10.22 | 0.7 |
| A 3 | MOL007253 | Asiatic acid | 16.69 | 0.72 |
| A 4 | MOL000359 | Sitosterol | 36.91 | 0.75 |
| A 5 | MOL007313 | Xanthanoic acid | 48.07 | 0.16 |
| A 6 | MOL007320 | 8-acetoxycentellynol | 65.94 | 0.12 |
| A 7 | MOL006370 | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 19.61 | 0.33 |
| A 8 | MOL000008 | Qpigenin | 23.06 | 0.21 |
| A 9 | MOL007201 | Brahmic acid | 17.6 | 0.7 |
| A 10 | MOL006387 | Chlorogenic acid | 25.58 | 0.33 |
| A 11 | MOL007323 | Madasiatic acid | 18.42 | 0.72 |
| A 12 | MOL007303 | Madecassoside | 16.89 | 0.7 |
| A 13 | MOL006407 | Neochlorogenic acid | 18.05 | 0.33 |
| A 14 | MOL001434 | Quercetin 3-O-rhamnopyranosyl | 22.24 | 0.28 |
| A 15 | MOL000511 | Ursolic acid | 16.77 | 0.75 |
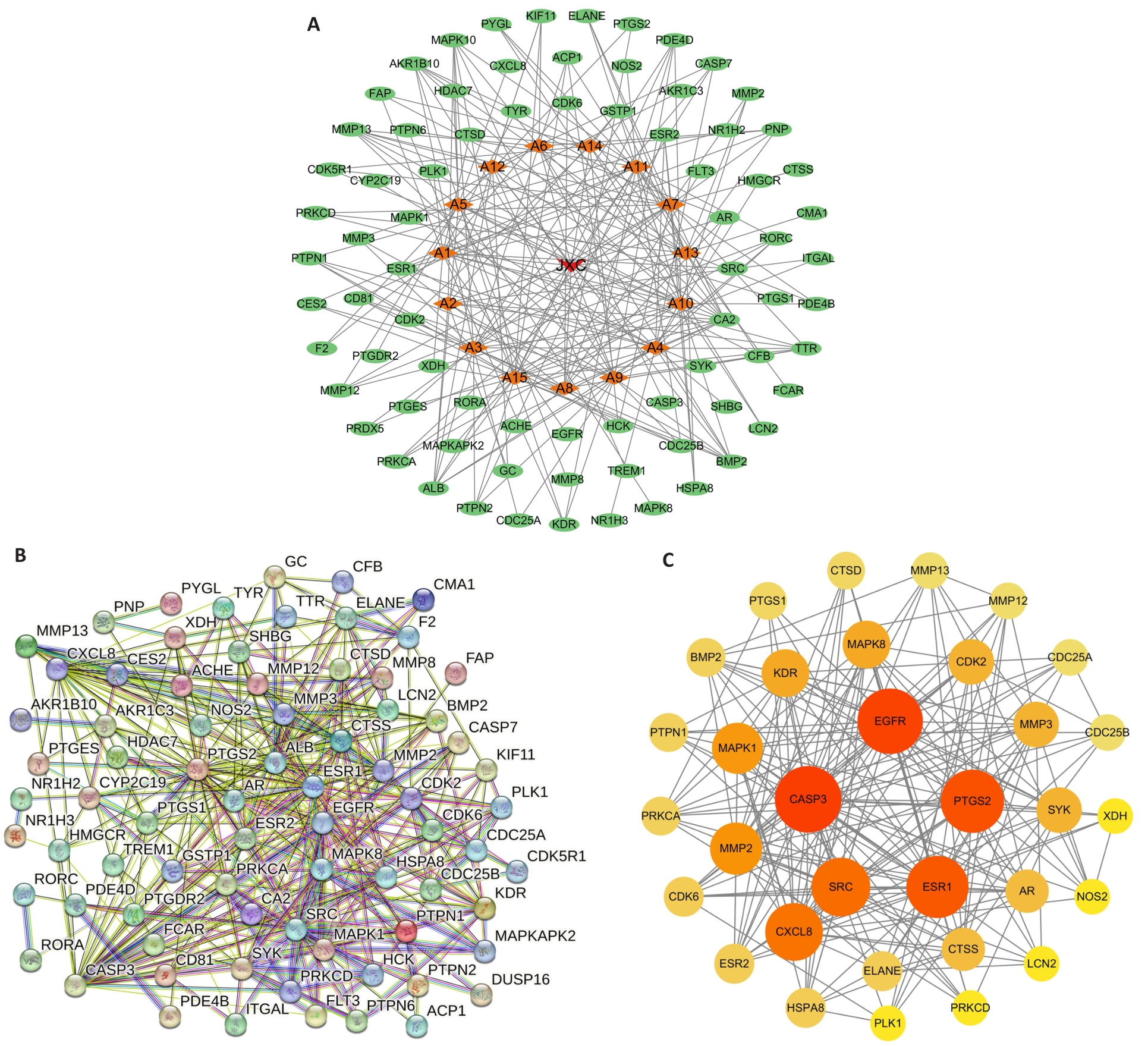
Fig.2 Drug-active ingredient-targets and PPI network diagram. A: Drug-active ingredient-targets network diagram. B: PPI network diagram. C: Core targets network diagram.
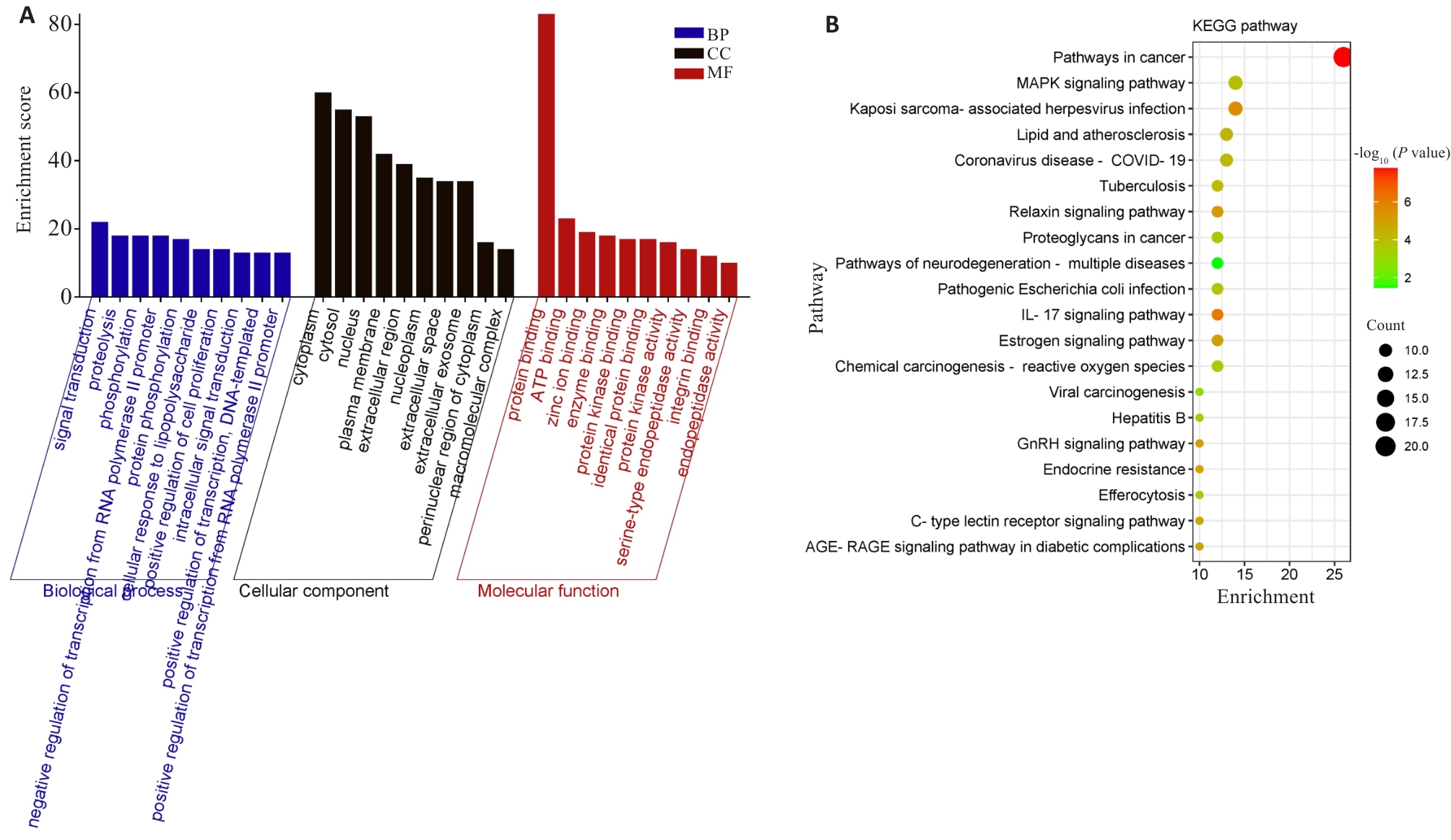
Fig. 3 GO functional annotation and KEGG signal pathway analysis of the anti-psoriasis effect of Centella asiatica. A: GO functional annotation. B: KEGG signal pathway analysis.
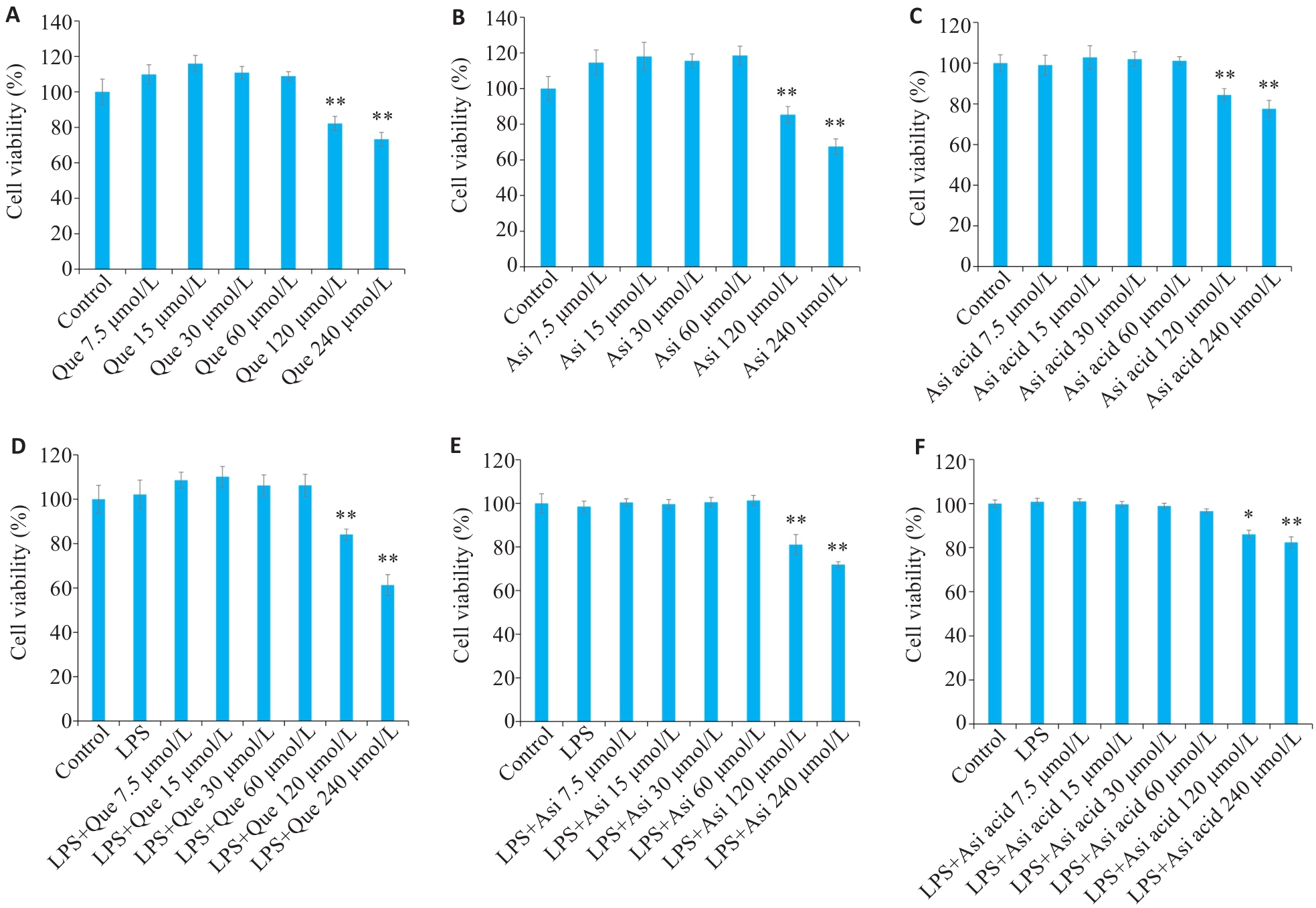
Fig.4 Effect of active components in Centella asiatica on the growth of RAW264.7 cells. A-C: Effects of Que, Asi, and Asi acid on viability of RAW264.7 cells. D-F: Effects of Que, Asi, and Asi acid on viability of RAW264.7 cells treated with LPS (100 ng/mL). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control group.
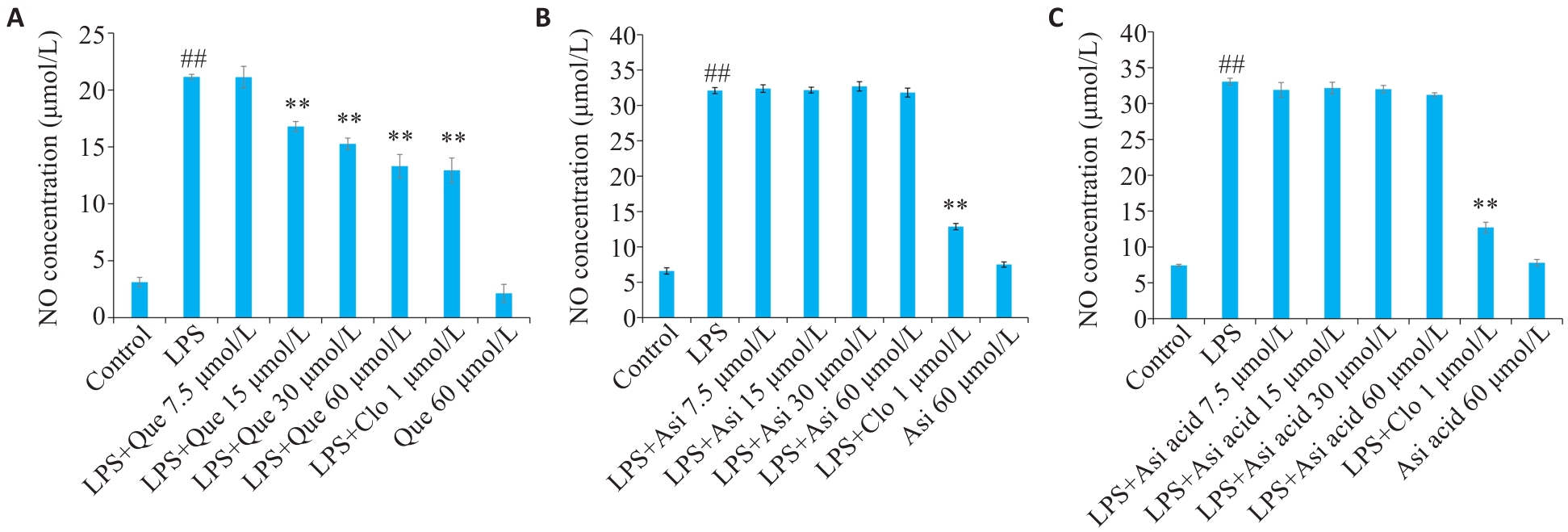
Fig. 5 Effect of Que (A), Asi (B) and Asi acid (C) on NO levels in the cell culture media of LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells determined by Griess assay. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
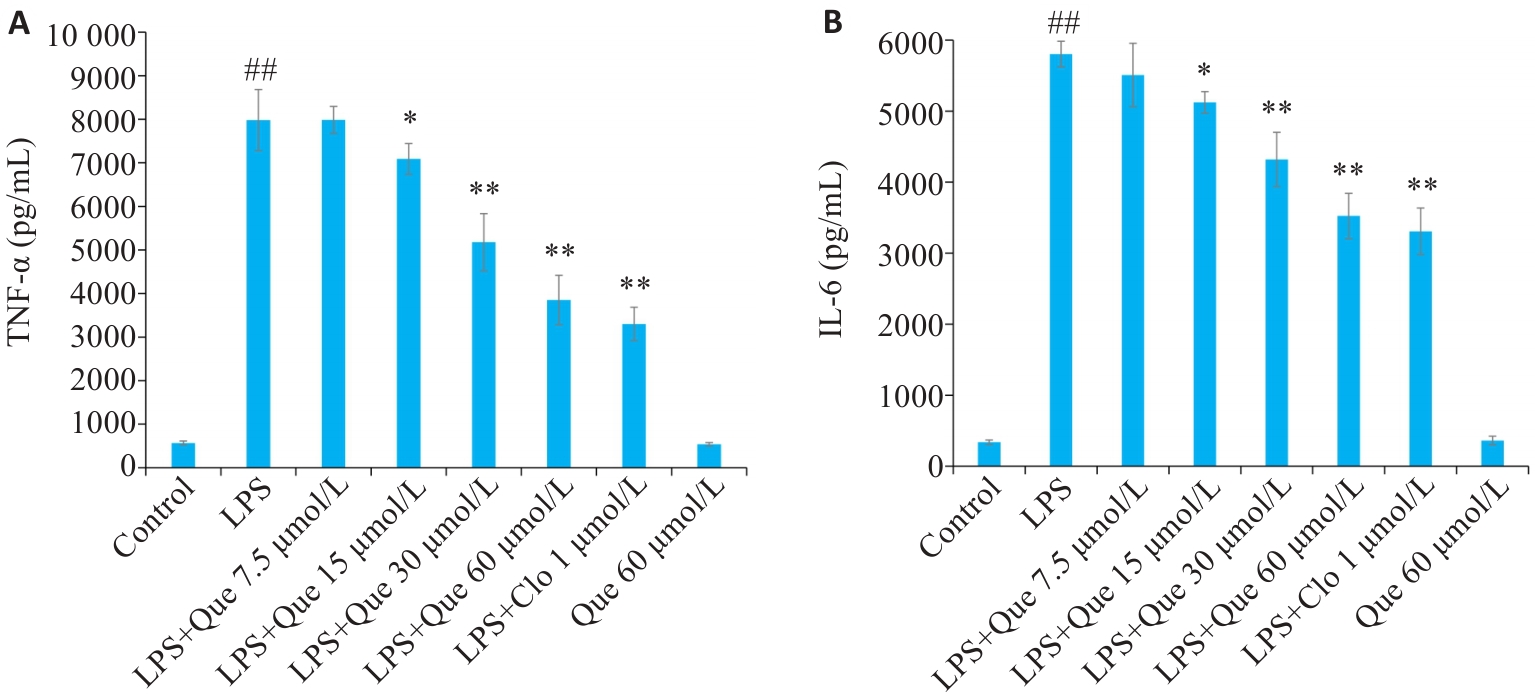
Fig. 6 Inhibitory effects of Que on secretion of TNF-α (A) and IL-6 (B) in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
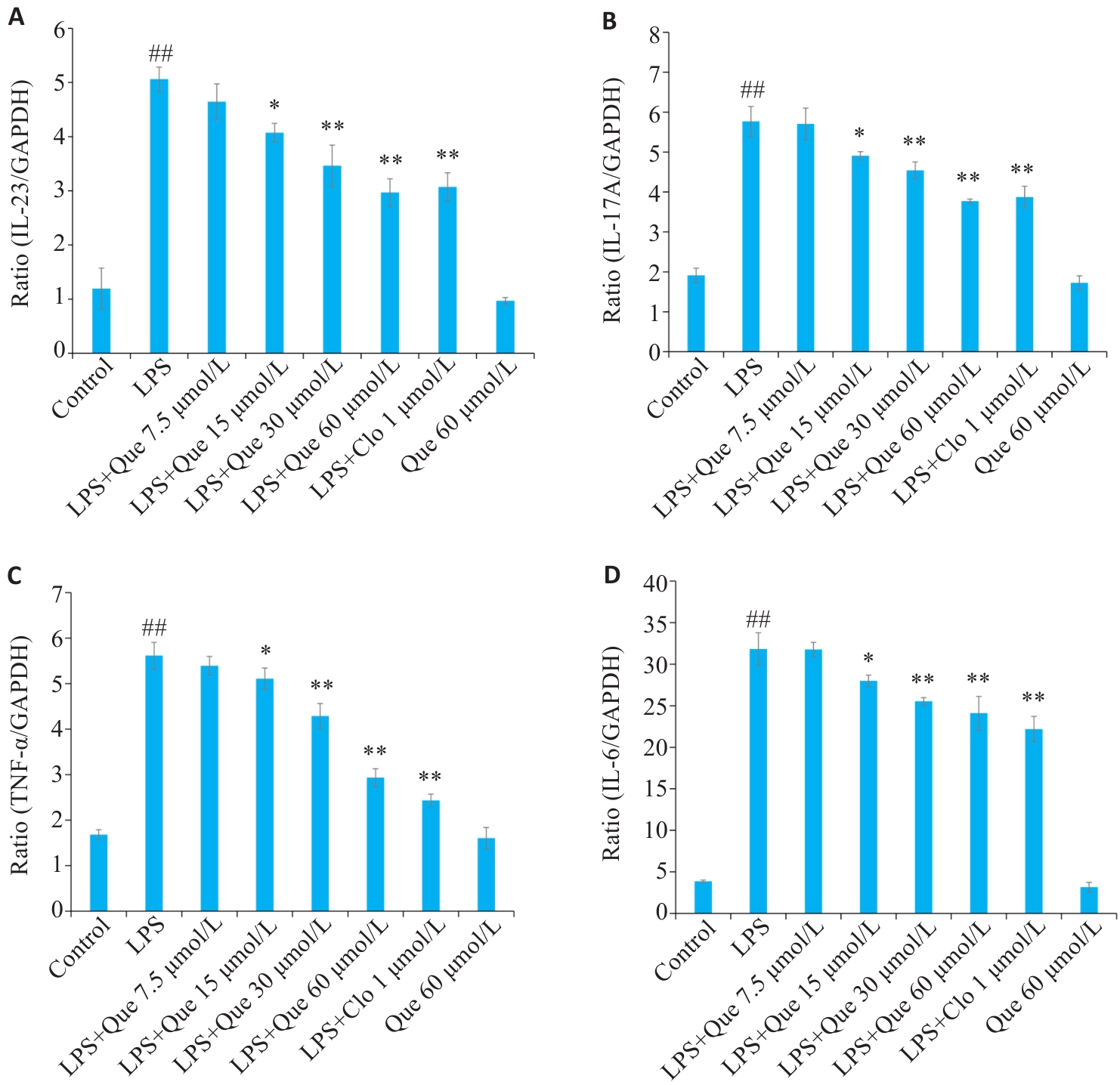
Fig. 7 Inhibitory effects of Que on mRNA expressions of IL-23 (A), IL-17A (B), TNF-α (C), and IL-6 (D) in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
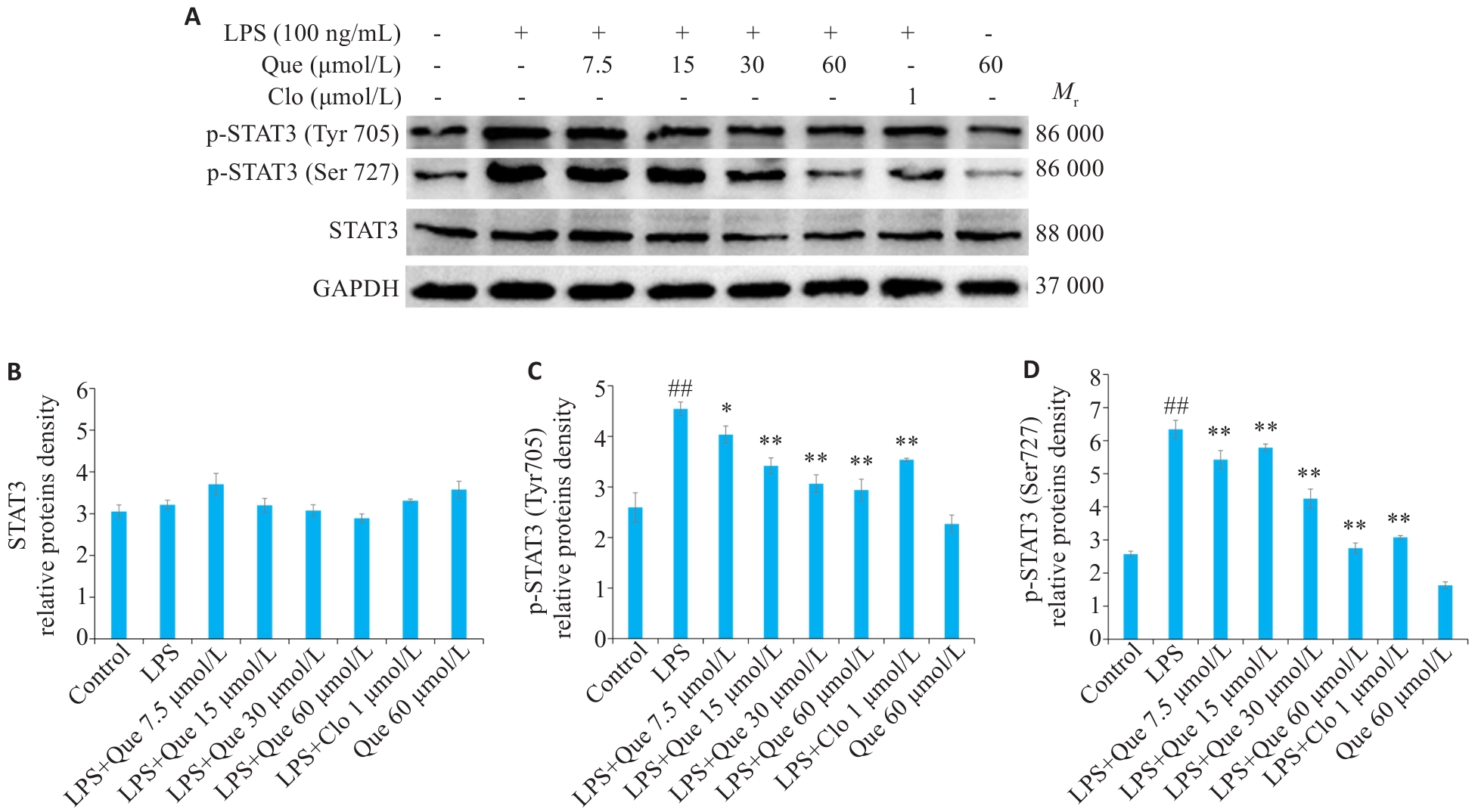
Fig. 8 Effect of Que on STAT3 protein phosphorylation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. A: Western blotting for detecting expressions of STAT3, p-STAT3 (Tyr705), and p-STAT3 (Ser727). B-D: Semi-quantitative analysis of STAT3, p-STAT3(Tyr705), and p-STAT3(Ser727) expression levels. ##P<0.01 vs Control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs LPS group.
| 1 | Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis[J]. Lancet (London, England), 2015, 386(9997): 983-94. |
| 2 | Raharja A, Mahil SK, Barker JN. Psoriasis: a brief overview[J]. Clin Med, 2021, 21(3): 170-3. |
| 3 | Takuathung MN, Potikanond S, Sookkhee S, et al. Anti-psoriatic and anti-inflammatory effects of Kaempferia parviflora in keratinocytes and macrophage cells[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2021, 143: 112229. |
| 4 | Kim SY, Han SD, Kim M, et al. Mentha arvensis essential oil exerts anti-inflammatory in LPS-stimulated inflammatory responses via inhibition of ERK/NF‑κB signaling pathway and anti-atopic dermatitis-like effects in 2, 4-dinitrochlorobezene-induced BALB/c mice[J]. Antioxidants, 2021, 10(12): 1941. |
| 5 | Li PH, Li YL, Jiang H, et al. Glabridin, an isoflavan from licorice root, ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation of BALB/c mice[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 59: 243-51. |
| 6 | Tan RZ, Zhong X, Han RY, et al. Macrophages mediate psoriasis via Mincle-dependent mechanism in mice[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1): 140. |
| 7 | Kamata M, Tada Y. Dendritic cells and macrophages in the pathogenesis of psoriasis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 941071. |
| 8 | Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(20): 7488. |
| 9 | Silvagni E, Missiroli S, Perrone M, et al. From bed to bench and back: TNF‑α, IL-23/IL-17A, and JAK-dependent inflammation in the pathogenesis of psoriatic synovitis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 672515. |
| 10 | Brembilla NC, Senra L, Boehncke WH. The IL-17 family of cytokines in psoriasis: IL-17A and beyond[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1682. |
| 11 | Sharma A, Upadhyay DK, Gupta GD, et al. IL-23/Th17 axis: a potential therapeutic target of psoriasis[J]. Curr Drug Res Rev, 2022, 14(1): 24-36. |
| 12 | Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2009, 129(6): 1339-50. |
| 13 | Reid C, Griffiths CEM. Psoriasis and treatment: past, present and future aspects[J]. Acta Derm Venereol, 2020, 100(3): adv00032. |
| 14 | Bakshi H, Nagpal M, Singh M, et al. Treatment of psoriasis: a comprehensive review of entire therapies[J]. Curr Drug Saf, 2020, 15(2): 82-104. |
| 15 | Gohil KJ, Patel JA, Gajjar AK. Pharmacological review on Centella asiatica: a potential herbal cure-all[J]. Indian J Pharm Sci, 2010, 72(5): 546-56. |
| 16 | Lin P, Shi HY, Lu YY, et al. Centella asiatica alleviates psoriasis through JAK/STAT3-mediated inflammation: an in vitro and in vivo study[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 317: 116746. |
| 17 | Dagar N, Kale A, Jadhav HR, et al. Nutraceuticals and network pharmacology approach for acute kidney injury: a review from the drug discovery aspect[J]. Fitoterapia, 2023, 168: 105563. |
| 18 | Su YY, Bai Q, Tao HX, et al. Prospects for the application of traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology in food science research[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2023, 103(11): 5183-200. |
| 19 | Dai HB, Shan Y, Yu MS, et al. Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental verification of the mechanism of huangqi-jixuecao herb pair in treatment of peritoneal fibrosis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 318(Pt A): 116874. |
| 20 | Bhoir SS, Vishwapathi V, Singh KK. Antipsoriatic potential of Annona squamosa seed oil: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 54: 265-77. |
| 21 | Ayoub R, Jilani J, Jarrar Q, et al. Synthesis and In-vivo evaluation of benzoxazole derivatives as promising anti-psoriatic drugs for clinical use[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(9): 3023. |
| 22 | Liu Q, Xiao XH, Hu LB, et al. Anhuienoside C ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis through inhibition of MAPK and NF‑κB signaling pathways[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 299. |
| 23 | Rendon A, Schäkel K. Psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(6): 1475. |
| 24 | Guo J, Zhang HY, Lin WR, et al. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 437. |
| 25 | Wu MJ, Dai C, Zeng FF. Cellular mechanisms of psoriasis pathogenesis: a systemic review[J]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol, 2023, 16: 2503-15. |
| 26 | Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(19): 1945-60. |
| 27 | Lee HJ, Kim M. Challenges and future trends in the treatment of psoriasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(17): 13313. |
| 28 | Li TT, Gao S, Han W, et al. Potential effects and mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of psoriasis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 294: 115275. |
| 29 | Wang JY, Zhang CS, Zhang AL, et al. Chinese herbal medicine bath therapy for psoriasis vulgaris using topical calcipotriol as the comparator: a systematic review with meta-analysis and association rule analysis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 330: 118166. |
| 30 | Lee Y, Choi HK, N'Deh KPU, et al. Inhibitory effect of Centella asiatica extract on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in HaCaT cells and BALB/c mice[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(2): 411. |
| 31 | Ghoreschi K, Balato A, Enerback C, et al. Therapeutics targeting the IL-23 and IL-17 pathway in psoriasis[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10275): 754-66. |
| 32 | Hawkes JE, Yan BY, Chan TC, et al. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway and the treatment of psoriasis[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 201(6): 1605-13. |
| 33 | Kukula O, Kırmızıkan S, Tiryaki ES, et al. Asiatic acid exerts an anti-psoriatic effect in the imiquimod-induced psoriasis model in mice[J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 2022, 44(3): 367-72. |
| 34 | Wang HL, Peters T, Sindrilaru A, et al. Key role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of CD18 hypomorphic murine model of psoriasis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2009, 129(5): 1100-14. |
| 35 | Stratis A, Pasparakis M, Rupec RA, et al. Pathogenic role for skin macrophages in a mouse model of keratinocyte-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2006, 116(8): 2094-104. |
| 36 | Zhou W, Hu MM, Zang XH, et al. Luteolin attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice via suppression of inflammation response[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2020, 131: 110696. |
| 37 | Calautti E, Avalle L, Poli V. Psoriasis: a STAT3-centric view[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(1): 171. |
| 38 | Kanda N. Psoriasis: pathogenesis, comorbidities, and therapy updated[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(6): 2979. |
| 39 | Kanemaru K, Matsuyuki A, Nakamura Y, et al. Obesity exacerbates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like epidermal hyperplasia and interleukin-17 and interleukin-22 production in mice[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2015, 24(6): 436-42. |
| 40 | Cai L, Jiang CJ, Zhang GQ, et al. A multicentre randomized double-blind placebo-controlled phase III study of the efficacy andsafety ofxeligekimab (GR1501) in patients withmoderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2024, 191(3): 336-43. |
| 41 | Dong WL, Nie XY, Wang JX, et al. Randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ dose escalation and expansion trial of GR1501 in patients with plaque psoriasis: study protocol[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(11): e039067. |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [7] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [10] | Hongyan SUN, Guoqing LU, Chengwen FU, Mengwen XU, Xiaoyi ZHU, Guoquan XING, Leqiang LIU, Yufei KE, Lemei CUI, Ruiyang CHEN, Lei WANG, Pinfang KANG, Bi TANG. Quercetin ameliorates myocardial injury in diabetic rats by regulating L-type calcium channels [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 531-541. |
| [11] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [12] | Pengwei HUANG, Jie CHEN, Jinhu ZOU, Xuefeng GAO, Hong CAO. Quercetin mitigates HIV-1 gp120-induced rat astrocyte neurotoxicity via promoting G3BP1 disassembly in stress granules [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [13] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [14] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [15] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||