Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2137-2145.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.10
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhen ZHANG1,2( ), Hui LU1,2, Xiaohua CHEN1,2, Lian WANG1,2, Ziliang WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG3,4, Sitang GE1,4, Lugen ZUO1,4(
), Hui LU1,2, Xiaohua CHEN1,2, Lian WANG1,2, Ziliang WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG3,4, Sitang GE1,4, Lugen ZUO1,4( )
)
Received:2024-07-11
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Lugen ZUO
E-mail:zhangzhencg0525@163.com;zuolugen@126.com
Zhen ZHANG, Hui LU, Xiaohua CHEN, Lian WANG, Ziliang WANG, Yueyue WANG, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO. CEP192 overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation by regulating PLK1/CDK1/Cyclin B1 signaling[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2137-2145.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.10
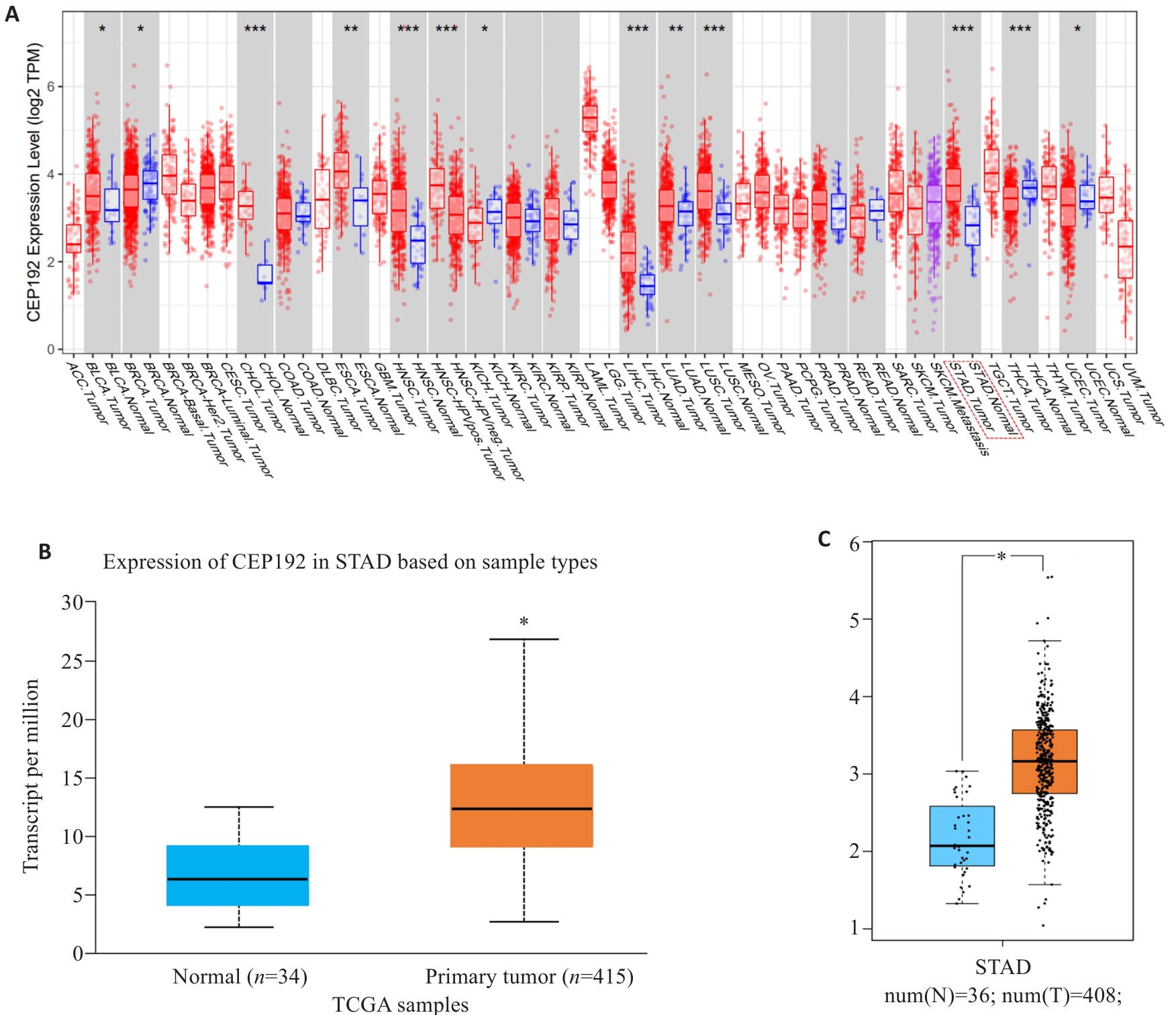
Fig. 1 CEP192 is highly expressed in multiple cancers. A: Expression of CEP192 in common human cancers. B, C: Expression of CEP192 in gastric cancer. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs normal group.

Fig.2 Immunohistochemical detection of CEP192 expression and cellular localization in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues (A) and quantitative analysis of its expression levels (B). *P<0.05 vs adjacent tissues.
| Factors | n | CEP192 expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=54) | High (n=55) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 58 | 30 (51.7%) | 28 (48.3%) | 0.236 | 0.627 |
| Female | 51 | 24 (47.1%) | 27 (52.9%) | ||
| Age (year) | |||||
| <60 | 47 | 26 (55.3%) | 21 (44.7%) | 1.103 | 0.294 |
| ≥60 | 62 | 28 (45.2%) | 34 (54.8%) | ||
| CEA (ng/mL) | |||||
| <5 | 55 | 35 (63.6%) | 20 (36.4%) | 8.823 | 0.003 |
| ≥5 | 54 | 19 (35.2%) | 35 (64.8%) | ||
| CA199 (IU/mL) | |||||
| <37 | 63 | 41 (65.1%) | 22 (34.9%) | 14.418 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 46 | 13 (28.3%) | 33 (71.7%) | ||
| Cancer cell type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 83 | 43 (51.8%) | 40 (48.2%) | 0.715 | 0.398 |
| Others | 26 | 11 (42.3%) | 15 (57.7%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| <5 | 49 | 26 (53.1%) | 23 (46.9%) | 0.441 | 0.507 |
| ≥5 | 60 | 28 (46.7%) | 32 (53.3%) | ||
| T stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 52 | 33 (63.5%) | 19 (36.5%) | 7.708 | 0.005 |
| T3-T4 | 57 | 21 (36.8%) | 36 (63.2%) | ||
| N stage | |||||
| N0-N1 | 54 | 35 (64.8%) | 19 (35.2%) | 9.987 | 0.002 |
| N2-N3 | 55 | 19 (34.5%) | 36 (65.5%) | ||
Tab.1 Relationship between CEP192 expression and clinicopathological parameters of gastric cancer patients
| Factors | n | CEP192 expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=54) | High (n=55) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 58 | 30 (51.7%) | 28 (48.3%) | 0.236 | 0.627 |
| Female | 51 | 24 (47.1%) | 27 (52.9%) | ||
| Age (year) | |||||
| <60 | 47 | 26 (55.3%) | 21 (44.7%) | 1.103 | 0.294 |
| ≥60 | 62 | 28 (45.2%) | 34 (54.8%) | ||
| CEA (ng/mL) | |||||
| <5 | 55 | 35 (63.6%) | 20 (36.4%) | 8.823 | 0.003 |
| ≥5 | 54 | 19 (35.2%) | 35 (64.8%) | ||
| CA199 (IU/mL) | |||||
| <37 | 63 | 41 (65.1%) | 22 (34.9%) | 14.418 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 46 | 13 (28.3%) | 33 (71.7%) | ||
| Cancer cell type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 83 | 43 (51.8%) | 40 (48.2%) | 0.715 | 0.398 |
| Others | 26 | 11 (42.3%) | 15 (57.7%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | |||||
| <5 | 49 | 26 (53.1%) | 23 (46.9%) | 0.441 | 0.507 |
| ≥5 | 60 | 28 (46.7%) | 32 (53.3%) | ||
| T stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 52 | 33 (63.5%) | 19 (36.5%) | 7.708 | 0.005 |
| T3-T4 | 57 | 21 (36.8%) | 36 (63.2%) | ||
| N stage | |||||
| N0-N1 | 54 | 35 (64.8%) | 19 (35.2%) | 9.987 | 0.002 |
| N2-N3 | 55 | 19 (34.5%) | 36 (65.5%) | ||

Fig. 4 Analysis of risk factors affecting the 5-year postoperative survival rate of gastric cancer patients. A: Impact of preoperative serum CEA level on the 5-year survival rate of the patients. B: Impact of preoperative serum CA199 level on the patients' survival. C: Impact of tumor T stage on the patients' survival. D: Impact of tumor N stage on the patients' survival. E: Cox regression analysis of independent risk factors affecting the 5-year postoperative survival rate of gastric cancer patients.

Fig.6 Gene functional enrichment analysis of CEP192. A: GO enrichment analysis of CEP192 and its co-expressed genes. B: REACTOME enrichment analysis of CEP192 and co-expressed genes. C-H: CEP192 and GSEA enrichment of co-expressed genes.

Fig.7 CEP192 overexpression promotes proliferation of MGC-803 cells. A: Proliferation of MGC-803 cells with CEP192 knockdown. B: Proliferation of MGC-803 cells with CEP192 overexpression. *P<0.05 vs sh-NC group.

Fig.8 CEP192 overexpression promote expressions of cell cycle proteins. A: Western blotting for detecting expressions of PLK1, CDK1 and Cyclin B1 proteins. B, C: Expression levels PLK1, CDK1 and Cyclin B1 proteins. *P<0.05 vs sh-NC or LV-NC group.

Fig.9 CEP192 overexpression promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells in nude mice. A: Tumor xenografts in different groups. B, C: Tumor weight of the nude mice. D, E: The tumor volume of the nude mice. F-H: Western blotting for detecting the expression levels of PLK1, CDK1 and Cyclin B1 proteins in the xenografts. *P<0.05 vs sh-NC or LV-NC group.
| 1 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. |
| 2 | Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-48. |
| 3 | Orditura M, Galizia G, Sforza V, et al. Treatment of gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(7): 1635-49. |
| 4 | Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, et al. Gastric cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(11): 4012. |
| 5 | Huang SH, Ma LP, Lan BY, et al. Comprehensive analysis of prognostic genes in gastric cancer[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(20): 23637-51. |
| 6 | Gong WJ, Zeng JY, Ji JF, et al. EPLIN expression in gastric cancer and impact on prognosis and chemoresistance[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(4): 547. |
| 7 | Chen LJ, Zhai WS, Zheng X, et al. Decreased IFIT2 expression promotes gastric cancer progression and predicts poor prognosis of the patients[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(1): 15-25. |
| 8 | 左芦根, 葛思堂, 张宗兵, 等. Enah在胃癌组织中的表达及临床价值研究[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2020, 45(5): 578-81. |
| 9 | Zhu F, Lawo S, Bird A, et al. The mammalian SPD-2 ortholog Cep192 regulates centrosome biogenesis[J]. Curr Biol, 2008, 18(2): 136-41. |
| 10 | Gomez-Ferreria MA, Rath U, Buster DW, et al. Human Cep192 is required for mitotic centrosome and spindle assembly[J]. Curr Biol, 2007, 17(22): 1960-6. |
| 11 | Gomez-Ferreria MA, Sharp DJ. Cep192 and the generation of the mitotic spindle[J]. Cell Cycle, 2008, 7(11): 1507-10. |
| 12 | Liu YL, Liang WM, Chang YB, et al. CEP192 is a novel prognostic marker and correlates with the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 950884. |
| 13 | Cai CZ, Song X, Yu CH. Identification of genes in hepatocellular carcinoma induced by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2020, 29(1): 69-78. |
| 14 | Moser SC, Bensaddek D, Ortmann B, et al. PHD1 links cell-cycle progression to oxygen sensing through hydroxylation of the centrosomal protein Cep192[J]. Dev Cell, 2013, 26(4): 381-92. |
| 15 | 王 炼, 夏勇生, 张 震, 等. 高表达MRPL13促进胃癌细胞增殖并影响患者预后: 基于抑制p53信号[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1558-66. |
| 16 | 王月月, 张 敏, 张 震, 等. 胃癌中PCMT1表达的预后价值及其对纺锤体组装检查点的调控作用[J]. 四川大学学报: 医学版, 2023, 54(6): 1167-75. |
| 17 | 杨 子, 张 浩, 徐梦宇, 等.胃癌中MLF1IP表达的预后价值及其对肿瘤进展的调控作用[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2023,54(1):114-121. |
| 18 | Schatten H, Ripple MO. The impact of centrosome pathologies on prostate cancer development and progression[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1095: 67-81. |
| 19 | Saatci O, Akbulut O, Cetin M, et al. Targeting TACC3 represents a novel vulnerability in highly aggressive breast cancers with centrosome amplification[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(5): 1305-19. |
| 20 | 黄晓丽. 中心体蛋白78在肌层浸润性膀胱癌中的表达及临床病理相关性研究[D].安徽医科大学,2023. |
| 21 | Ni J, Wang JC, Fu Y, et al. Functional genetic variants in centrosome-related genes CEP72 and YWHAG confer susceptibility to gastric cancer[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2020, 94(8): 2861-72. |
| 22 | Fung E, Richter C, Yang HB, et al. FBXL13 directs the proteolysis of CEP192 to regulate centrosome homeostasis and cell migration[J]. EMBO Rep, 2018, 19(3): e44799. |
| 23 | Park JG, Jeon H, Shin S, et al. Structural basis for CEP192-mediated regulation of centrosomal AURKA[J]. Sci Adv, 2023, 9(16): eadf8582. |
| 24 | Pitzen V, Sander S, Baumann O, et al. Cep192, a novel missing link between the centrosomal core and Corona in Dictyostelium amoebae[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2384. |
| 25 | 沈敏洪. 中心体蛋白FOR20在细胞周期中的功能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. |
| 26 | Gonzalez C. Centrosomes in asymmetric cell division[J]. Curr Opin Struct Biol, 2021, 66: 178-82. |
| 27 | Blanco-Ameijeiras J, Lozano-Fernández P, Martí E. Centrosome maturation-in tune with the cell cycle[J]. J Cell Sci, 2022, 135(2): jcs259395. |
| 28 | Favasuli VK, Ronchetti D, Silvestris I, et al. DIS3 depletion in multiple myeloma causes extensive perturbation in cell cycle progression and centrosome amplification[J]. Haematologica, 2024, 109(1): 231-44. |
| 29 | Yoo BH, Kang DS, Park CH, et al. CKAP2 phosphorylation by CDK1/cyclinB1 is crucial for maintaining centrosome integrity[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2017, 49(7): e354. |
| 30 | Li MM, Yang JY, Li J, et al. Epiberberine induced p53/p21-dependent G2/M cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by activating γ‑aminobutyric acid receptor‑β3[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 123: 155198. |
| 31 | Li W, Liu JY, Fu WQ, et al. 3-O-acetyl-11-keto‑β‑boswellic acid exerts anti-tumor effects in glioblastoma by arresting cell cycle at G2/M phase[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 132. |
| 32 | 陈 霞. KPNA2调控WDR62可变剪接激活PLK1促进胃癌进展的机制研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2023. |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Ting XIE, Yunyun WANG, Ting GUO, Chunhua YUAN. The peptide toxin components and nucleotide metabolites in Macrothele raveni venom synergistically inhibit cancer cell proliferation by activating the pro-apoptotic pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1460-1470. |
| [3] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [4] | Xinrui HOU, Zhendong ZHANG, Mingyuan CAO, Yuxin DU, Xiaoping WANG. Salidroside inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells by regulating the miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB glucose metabolic axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [5] | Yumei ZENG, Jike LI, Zhongxi HUANG, Yibo ZHOU. Villin-like protein VILL suppresses proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by interacting with LMO7 protein [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 954-961. |
| [6] | Yaqing YUE, Zhaoxia MU, Xibo WANG, Yan LIU. Aurora-A overexpression promotes cervical cancer cell invasion and metastasis by activating the NF-κBp65/ARPC4 signaling axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 837-843. |
| [7] | Yi ZHANG, Yu SHEN, Zhiqiang WAN, Song TAO, Yakui LIU, Shuanhu WANG. High expression of CDKN3 promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the p53/NF-κB signaling pathway and inhibiting cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [8] | Shunjie QING, Zhiyong SHEN. High expression of hexokinase 2 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by activating the JAK/STAT pathway and regulating tumor immune microenvironment [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [9] | Qingqing HUANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Lian WANG, Xue SONG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. High MYO1B expression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor patient prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [10] | Xue SONG, Yue CHEN, Min ZHANG, Nuo ZHANG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Yueyue WANG, Lian WANG, Jianguo HU. GPSM2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer to affect patient prognosis by promoting tumor cell proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [11] | Jinhua ZOU, Hui WANG, Dongyan ZHANG. SLC1A5 overexpression accelerates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting M2 polarization of macrophages [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [12] | Yu BIN, Ziwen LI, Suwei ZUO, Sinuo SUN, Min LI, Jiayin SONG, Xu LIN, Gang XUE, Jingfang WU. High expression of apolipoprotein C1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [13] | Zhoufang CAO, Yuan WANG, Mengna WANG, Yue SUN, Feifei LIU. LINC00837/miR-671-5p/SERPINE2 functional axis promotes pathological processes of fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 371-378. |
| [14] | Xiaohua CHEN, Hui LU, Ziliang WANG, Lian WANG, Yongsheng XIA, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Xue SONG, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU, Lugen ZUO. Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [15] | Liangjun XUE, Qiuyu TAN, Jingwen XU, Lu FENG, Wenjin LI, Liang YAN, Yulei LI. MiR-6838-5p overexpression inhibits proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by downregulating DDR1 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1677-1684. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||