Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2679-2689.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.15
Jingyu CHEN( ), Jinhu ZOU, Bingliang ZHOU, Xuefeng GAO, Pengwei HUANG, Hong CAO(
), Jinhu ZOU, Bingliang ZHOU, Xuefeng GAO, Pengwei HUANG, Hong CAO( )
)
Received:2025-06-13
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Hong CAO
E-mail:2209661286@qq.com;gzhcao@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:Jingyu CHEN, Jinhu ZOU, Bingliang ZHOU, Xuefeng GAO, Pengwei HUANG, Hong CAO. Indole-3-acetic acid alleviates Cryptococcus neoformans-induced pyroptosis in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells by regulating stress granule-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2679-2689.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.15
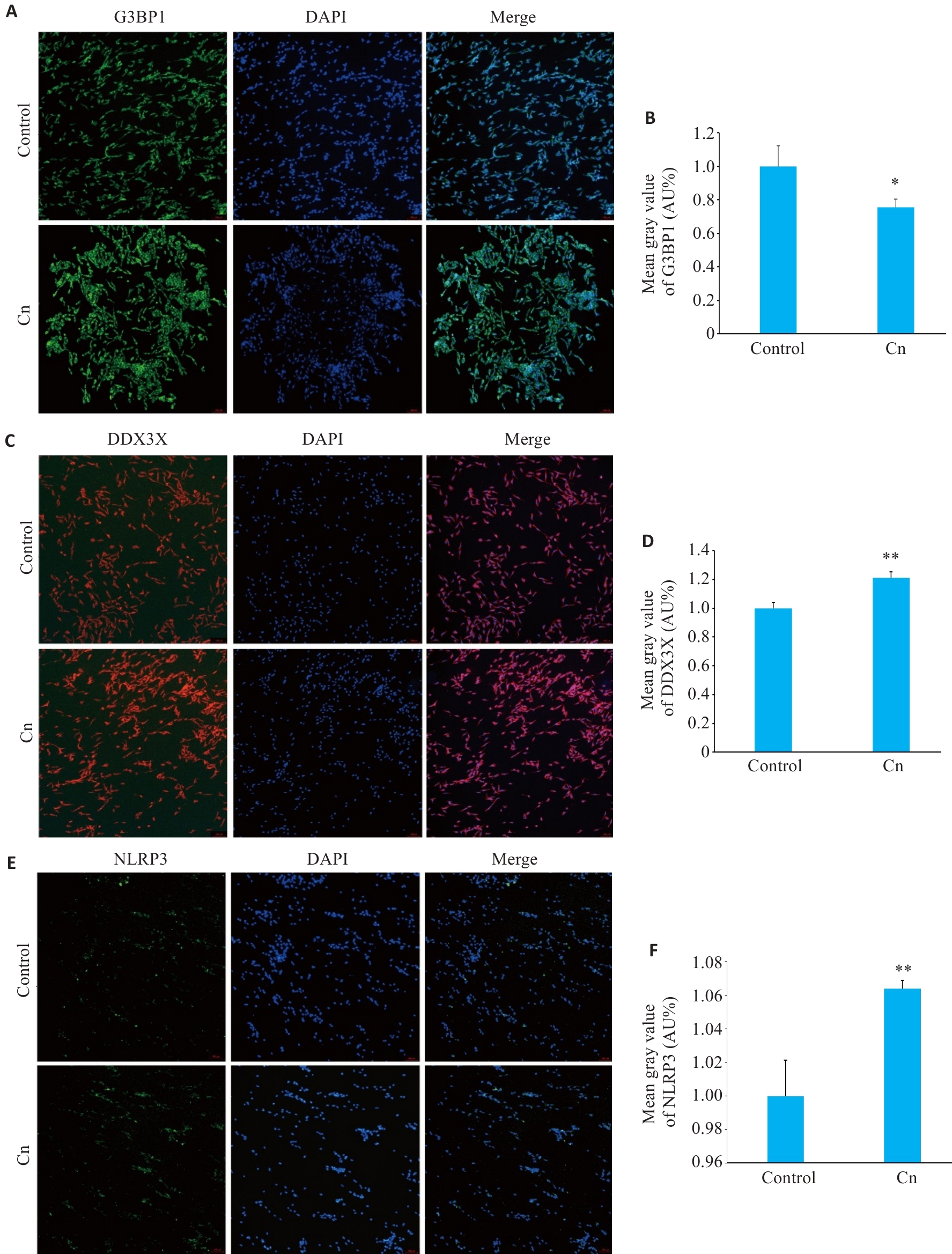
Fig.1 Immunofluorescence sataining for G3BP1 (A,B), DDX3X (C,D) and NLRP3 (E,F) in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells with Cn infection (Original magnification: ×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
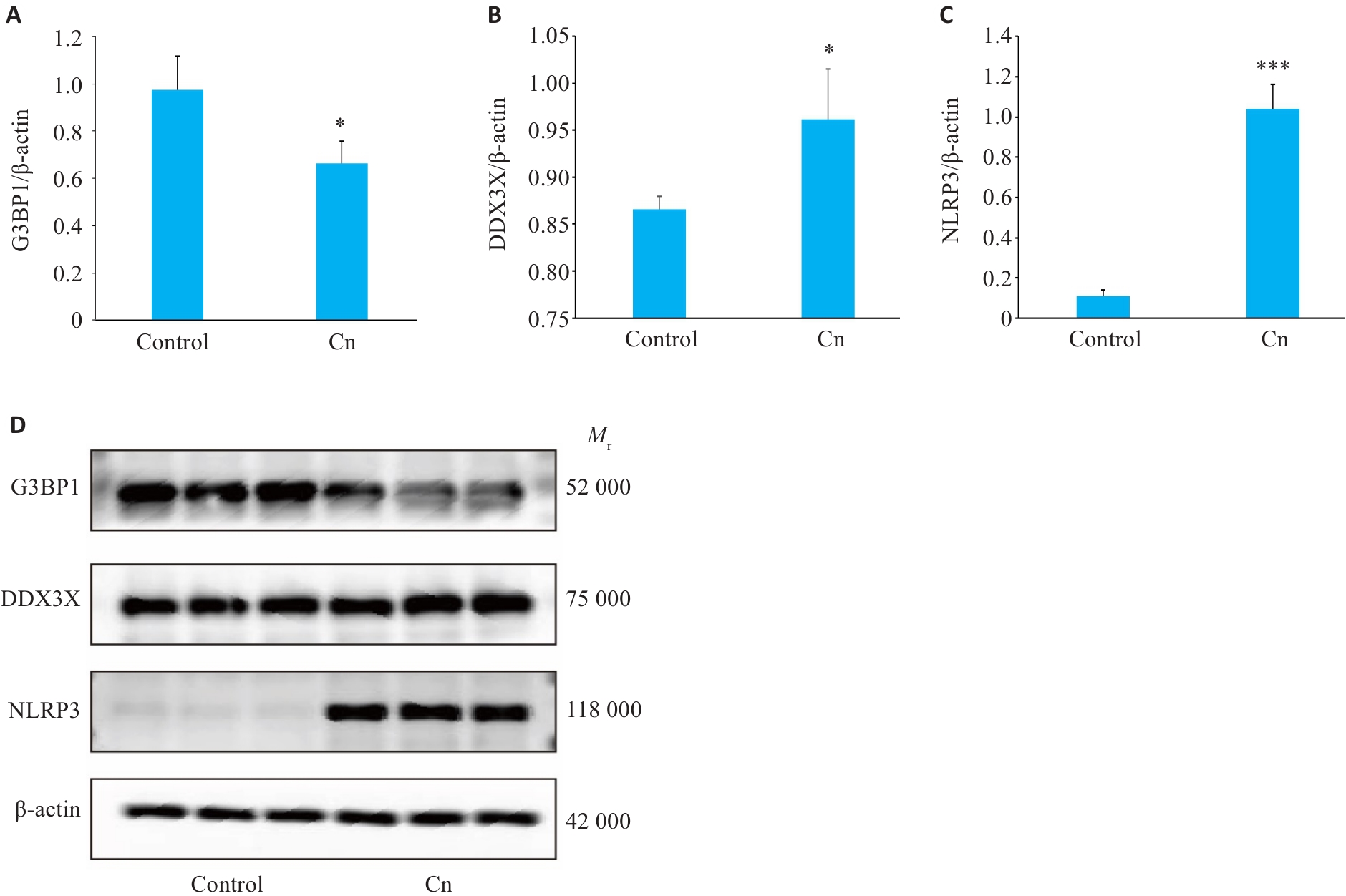
Fig.2 Western blotting for detecting G3BP1 (A), DDX3X(B) and NLRP3(C) protein expressions in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells following Cn infection. D: Protein bands in Western blotting. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.
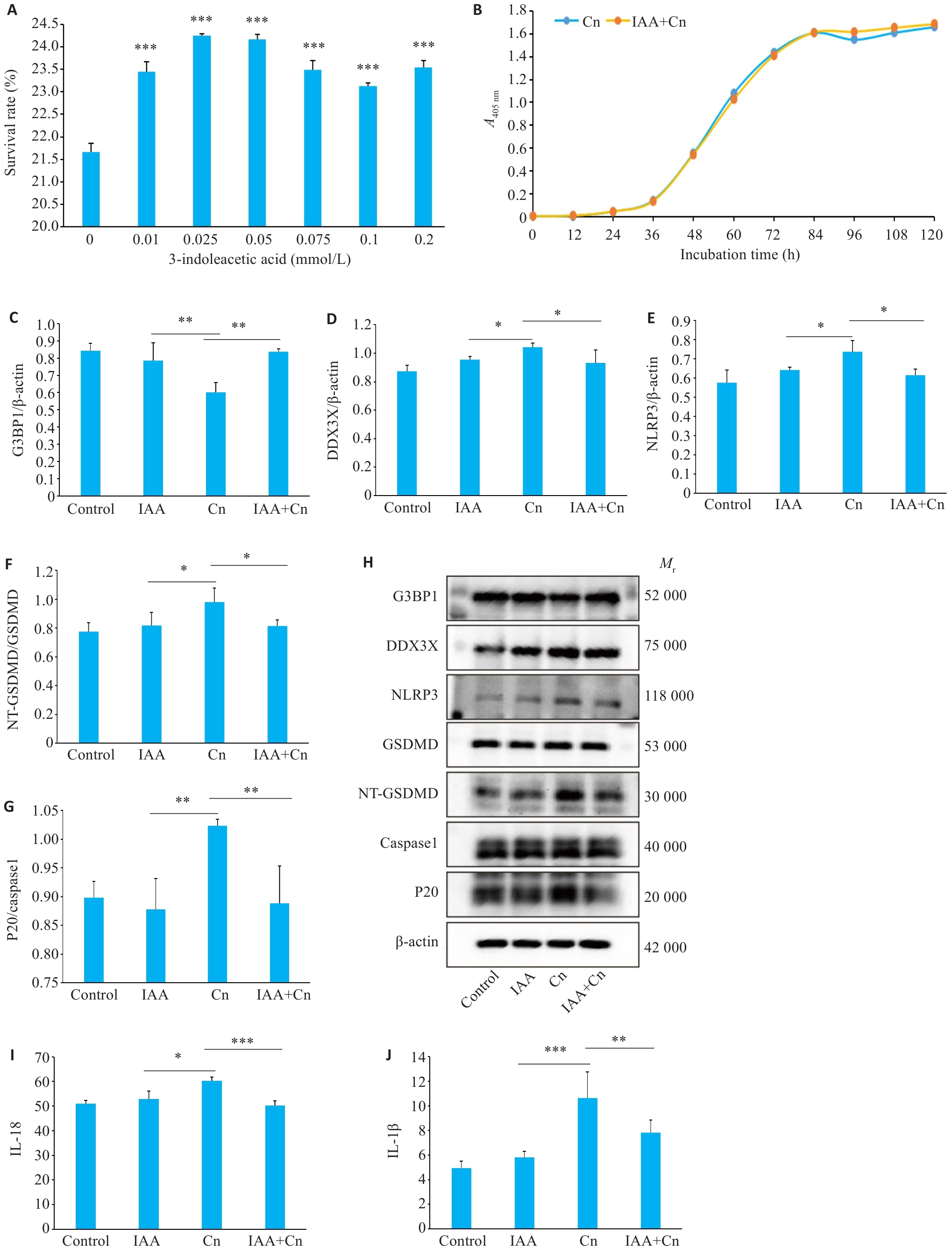
Fig.3 IAA alleviates Cn-induced pyroptosis of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. A: Survival rates of Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells treated with gradient concentrations of IAA. ***P<0.001 vs 0 mmol/L. B: The growth curve of Cn after IAA treatment. C-G: Expressions of G3BP1, DDX3X, NLRP3, NT-GSDMD /GSDMD, and P20/caspase-1 in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells with IAA treatment. H: Protein bands by Western blotting. I-J: IL-18 and IL-1β levels in the cell culture supernatant determined by ELISA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
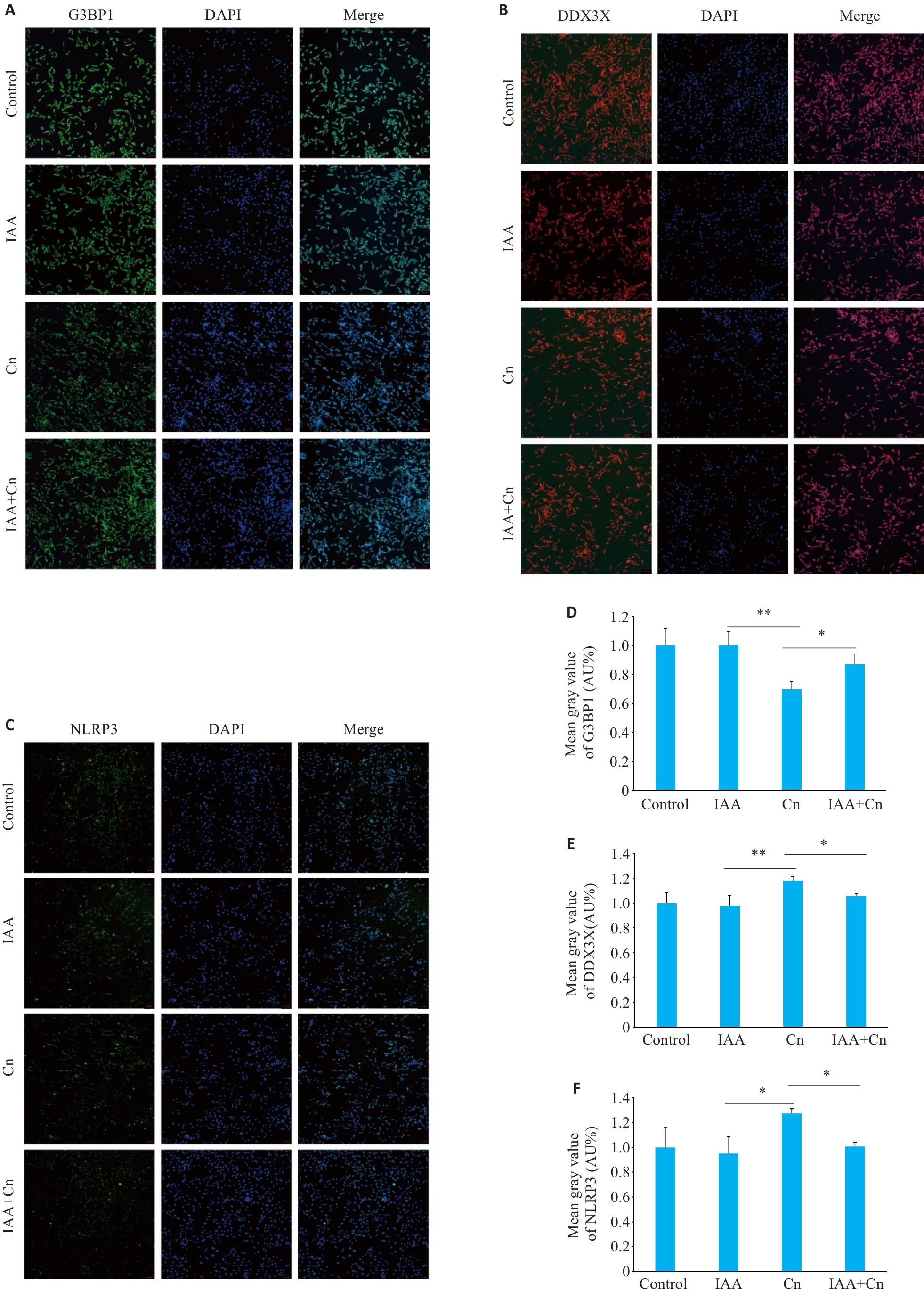
Fig.4 IAA alleviates Cn-induced changes in G3BP1, DDX3X and NLRP3 expressions in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (Immunofluorescence staining, ×100). A, D: Effect of IAA on G3BP1 expression in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. B,E: Effect of IAA on DDX3X expression in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. C,F: Effect of IAA on NLRP3 expression in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
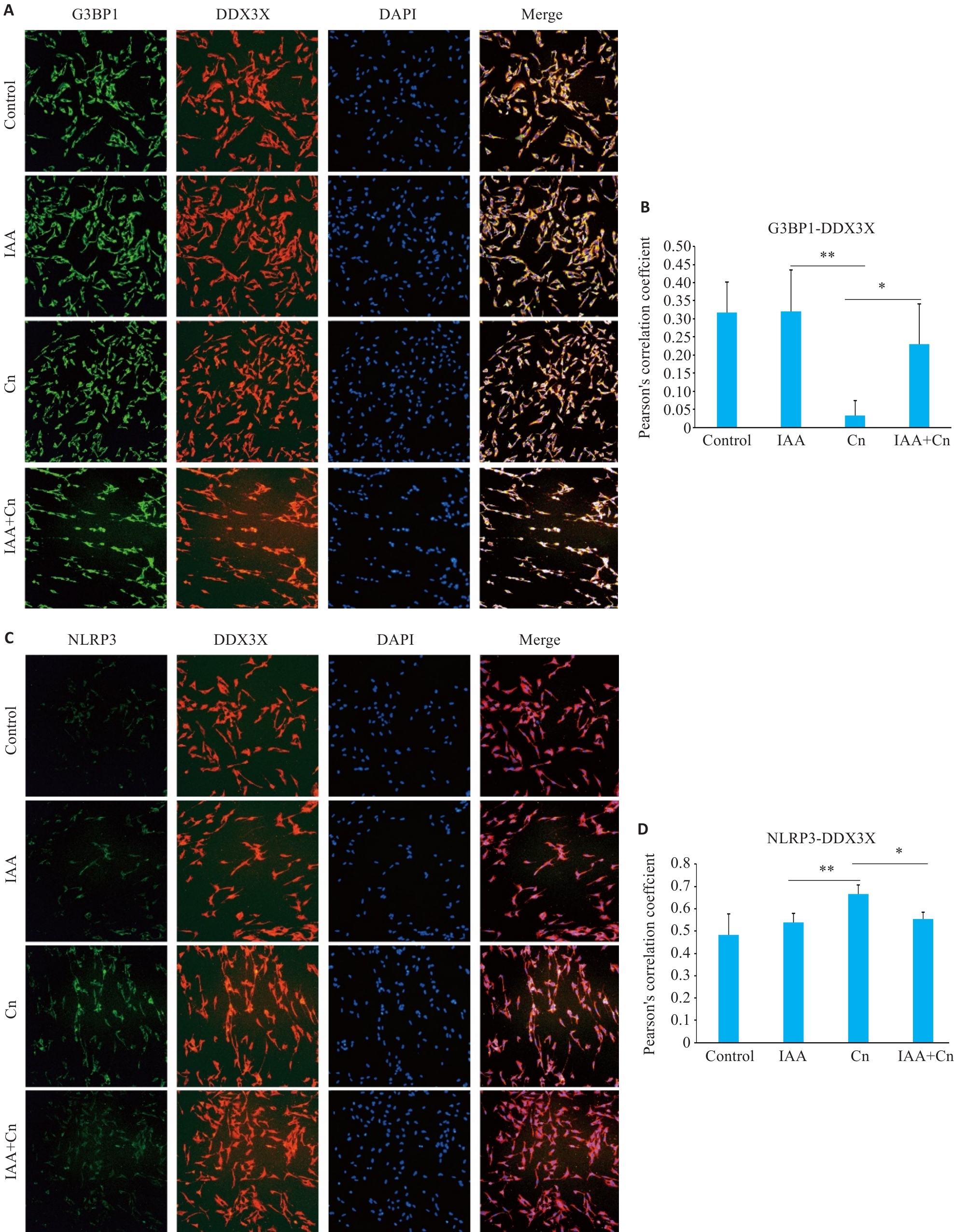
Fig.5 IAA regulates translocation of DDX3X in the formation of SGs and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in Cn-infected cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (Immunofluorescence staining, ×200). A,B: Co-localization of G3BP1 and DDX3X in cells treated with Cn and IAA. C, D: Co-localization of NLRP3 and DDX3X in cells treated with Cn and IAA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
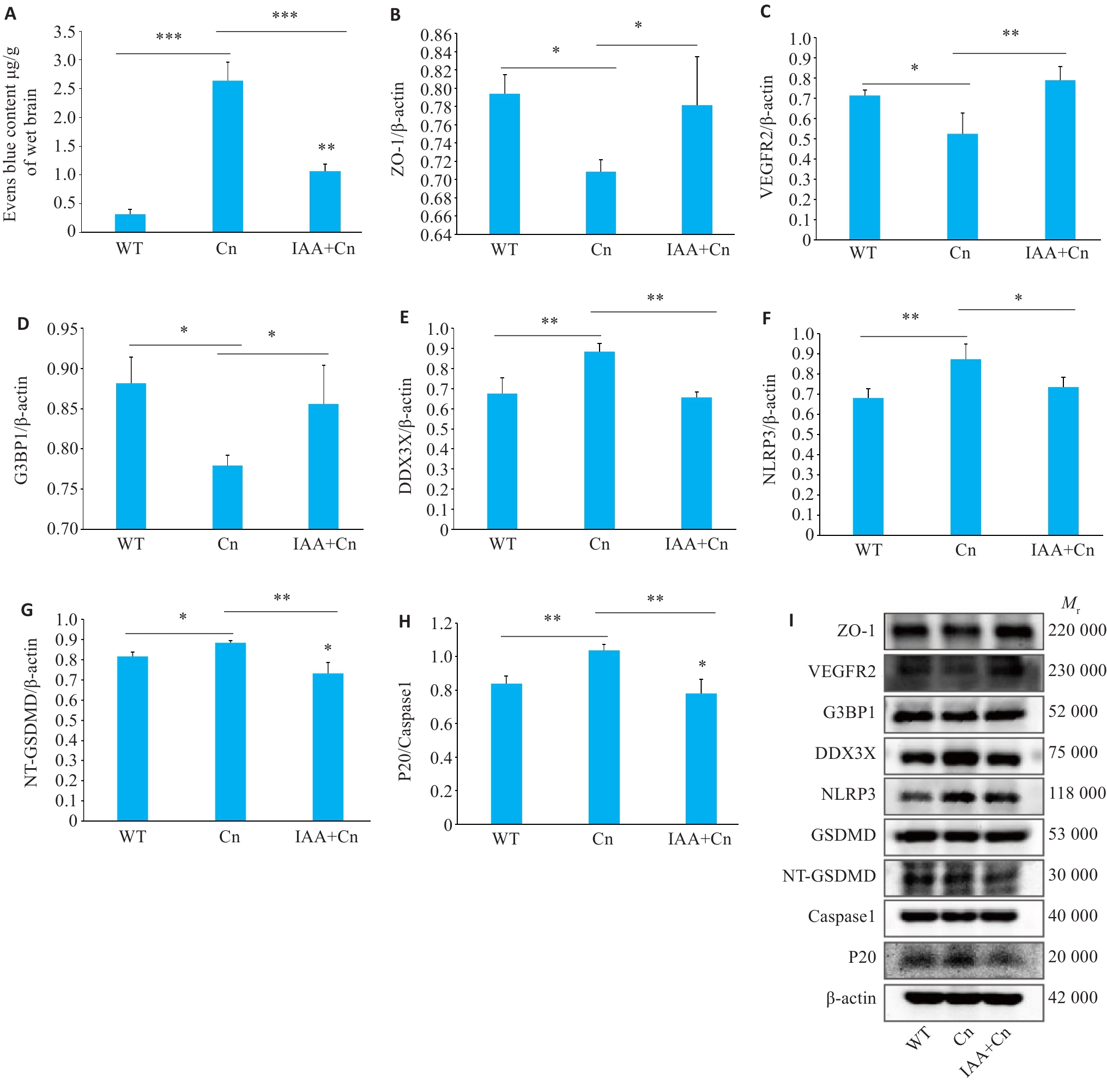
Fig.6 Regulatory effect of IAA on formation of SGs and Cn-induced pyroptosis in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in mice. A: Evans blue staining showing changes in permeability of the BBB after Cn infection and IAA treatment. B: Expression level of ZO-1 in the BBB of mice with Cn infection and IAA treatment detected by Western blotting. C-F: Expression levels of VEGFR2, G3BP1, DDX3X, and NLRP3 in the cerebral cortex of the mice detected by Western blotting. G: Expression levels of NT-GSDMD and GSDMD. H: Expression levels of P20 and caspase-1. I: Portein bands by Western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| [1] | Tugume L, Ssebambulidde K, Kasibante J, et al. Cryptococcal meningitis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2023, 9: 62. doi:10.1038/s41572-023-00472-z |
| [2] | Rajasingham R, Govender NP, Jordan A, et al. The global burden of HIV-associated cryptococcal infection in adults in 2020: a modelling analysis[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2022, 22(12): 1748-55. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(22)00499-6 |
| [3] | Liu LJ, Tang YF, Zhang L, et al. The molecular mechanisms by which the NLRP3 inflammasome regulates blood-brain barrier permeability following cryptococcal meningitis[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(23): e39653. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39653 |
| [4] | Kim J, Lee KT, Lee JS, et al. Fungal brain infection modelled in a human-neurovascular-unit-on-a-chip with a functional blood-brain barrier[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2021, 5(8): 830-46. doi:10.1038/s41551-021-00743-8 |
| [5] | Zapata-Acevedo JF, Mantilla-Galindo A, Vargas-Sánchez K, et al. Chapter one blood-brain barrier biomarkers[J]. Adv Clin Chem, 2024, 121: 1-88. doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2024.04.004 |
| [6] | Zheng ZJ, Zhu LZ, Qiu H, et al. Neferine inhibits BMECs pyroptosis and maintains blood-brain barrier integrity in ischemic stroke by triggering a cascade reaction of PGC-1α[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 14438. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-64815-w |
| [7] | Han CY, Zhai LP, Shen HP, et al. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) promote endothelial cell pyroptosis under cerebral ischemia and hypoxia via HIF-1α-RAGE-NLRP3[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 60(5): 2355-66. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03228-8 |
| [8] | Gong Z, Gao X, Li Y, et al. Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists prevent meningitic Escherichia coli-induced blood-brain barrier disruptions by targeting the CISH/JAK2/STAT5b axis[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(10): 2358. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10102358 |
| [9] | Zhang ZL, Zou JH, Luo ZF, et al. NLRP3/caspase 1/gsdmd mediated pyroptosis exerts a crucial role in blood-brain barrier pathological injury induced by Cryptococcus neoformans [J]. Blood, 2023, 142: 5417. doi:10.1182/blood-2023-184554 |
| [10] | Marcelo A, Koppenol R, de Almeida LP, et al. Stress granules, RNA-binding proteins and polyglutamine diseases: too much aggregation?[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(6): 592. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03873-8 |
| [11] | Zhang H, Mañán-Mejías PM, Miles HN, et al. DDX3X and stress granules: emerging players in cancer and drug resistance[J]. Cancers: Basel, 2024, 16(6): 1131. doi:10.3390/cancers16061131 |
| [12] | Feng D, Guo L, Liu J, et al. DDX3X deficiency alleviates LPS-induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes pyroptosis by suppressing activation of NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(6): 1389. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10825 |
| [13] | Wang Q, Kohls W, Wills M, et al. A novel stroke rehabilitation strategy and underlying stress granule regulations through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2024, 30(1): e14405. doi:10.1111/cns.14405 |
| [14] | Su X, Gao Y, Yang R. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites maintain gut and systemic homeostasis[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(15): 2296. doi:10.3390/cells11152296 |
| [15] | Krishnan S, Ding YF, Saedi N, et al. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites modulate inflammatory response in hepatocytes and macrophages[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 23(4): 1099-111. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.109 |
| [16] | Huang ZB, Zhang GP, Lu CX, et al. Gut microbiota-derived 3-indoleacetic acid confers a protection against sepsis-associated encephalopathy through microglial aryl hydrocarbon receptors[J]. Exp Neurol, 2025, 384: 115055. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.115055 |
| [17] | Zhao Q, Chen T, Ni C, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid attenuates HI-related blood-brain barrier injury in neonatal rats by modulating the PXR signaling pathway[J]. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2022, 13(19): 2897-912. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00418 |
| [18] | Huang ZB, Hu Z, Lu CX, et al. Gut microbiota-derived indole 3-propionic acid partially activates aryl hydrocarbon receptor to promote macrophage phagocytosis and attenuate septic injury[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 1015386. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.1015386 |
| [19] | 李 猛, 左春月, 靳晓飞, 等. 补阳还五汤通过抑制脑微血管内皮细胞自噬减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2025,41(3):481-91. |
| [20] | 高加巍, 崔梦迪. 当归多糖调节Caspase-1/Gasdermin D通路促进脑缺血-再灌注损伤大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞血管新生[J]. 中药材, 2024,47(4):977-83. |
| [21] | 张晋卿, 刘 伟, 谭静文, 等. 烟曲霉在不同温度和营养条件下的生长特性初探[J]. 中国真菌学杂志, 2013, 8(1): 6-9. |
| [22] | Permpalung N, Chiang TP, Manothummetha K, et al. Invasive fungal infections in inpatient solid organ transplant recipients with COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective cohort[J]. Transplantation, 2024, 108(7): 1613-22. doi:10.1097/tp.0000000000004947 |
| [23] | Zhang B, Yu JY, Liu LQ, et al. Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is required for blood-brain barrier injury-related CNS disorders caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and HIV-1 associated comorbidity factors[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2015, 15: 352. doi:10.1186/s12879-015-1075-9 |
| [24] | Lun J, Li Y, Gao X, et al. Kynurenic acid blunts A1 astrocyte activation against neurodegeneration in HIV-associated neuroco-gnitive disorders[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2023, 20(1): 87. doi:10.1186/s12974-023-02771-4 |
| [25] | Tweedie A, Nissan T. Hiding in plain sight: formation and function of stress granules during microbial infection of mammalian cells[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8: 647884. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.647884 |
| [26] | Eiermann N, Haneke K, Sun Z, et al. Dance with the devil: stress granules and signaling in antiviral responses[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(9): E984. doi:10.3390/v12090984 |
| [27] | Samir P, Kesavardhana S, Patmore DM, et al. DDX3X acts as a live-or-die checkpoint in stressed cells by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7775): 590-4. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1551-2 |
| [28] | Matsuki H, Takahashi M, Higuchi M, et al. Both G3BP1 and G3BP2 contribute to stress granule formation[J]. Genes Cells, 2013, 18(2): 135-46. doi:10.1111/gtc.12023 |
| [29] | Tornavaca O, Chia M, Dufton N, et al. ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation[J]. J Cell Biol, 2015, 208(6): 821-38. doi:10.1083/jcb.201404140 |
| [30] | Chen XY, Wan SF, Yao NN, et al. Inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 ameliorates ischemia/hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier injury through the Wnt/β‑catenin signalling pathway[J]. Mil Med Res, 2021, 8(1): 62. doi:10.1186/s40779-021-00356-x |
| [31] | Wang YJ, Guan X, Gao CL, et al. Medioresinol as a novel PGC-1α activator prevents pyroptosis of endothelial cells in ischemic stroke through PPARα-GOT1 axis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 169: 105640. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105640 |
| [32] | Lopez-Pastrana J, Ferrer LM, Li YF, et al. Inhibition of Caspase-1 Activation in Endothelial Cells Improves Angiogenesis a novel therapeutic potential for ischemia[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(28): 17485-94. doi:10.1074/jbc.m115.641191 |
| [33] | Li P, Hu Y, Liu J, et al. Naoluo Xintong Decoction activates caspase-1/Gasdermin D pathway to promote angiogenesis of rat brain microvascular endothelial cells after oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke da Xue Xue Bao, 2023, 43(7): 1093-101. |
| [1] | Shanyu LUO, Qiang ZHU, Yufei YAN, Zonghong JI, Huajie ZOU, Ruixia ZHANG, Yinggui BA. NLRP3 signaling pathway promotes hepatocyte pyroptosis in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in hypoxic environment [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 2026-2033. |
| [2] | Chenfei LIU, Wei ZHANG, Yao ZENG, Yan LIANG, Mengting WANG, Mingfang ZHANG, Xinyuan LI, Fengchao WANG, Yanqing YANG. 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1654-1662. |
| [3] | Feifei SHANG, Xiaoke SHI, Yao ZENG, Xunqian TAO, Tianzhen LI, Yan LIANG, Yanqin YANG, Chuanwang SONG. Avitinib suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ameliorates septic shock in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1697-1705. |
| [4] | Haiyi ZHOU, Siyi HE, Ruifang HAN, Yongge GUAN, Lijuan DONG, Yang SONG. Moxibustion promotes endometrial repair in rats with thin endometrium by inhibiting the NLRP3/pyroptosis axis via upregulating miR-223-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1380-1388. |
| [5] | Fenlan BIAN, Shiyao NI, Peng ZHAO, Maonanxing QI, Bi TANG, Hongju WANG, Pinfang KANG, Jinjun LIU. Asiaticoside alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 977-985. |
| [6] | Yalei SUN, Meng LUO, Changsheng GUO, Jing GAO, Kaiqi SU, Lidian CHEN, Xiaodong FENG. Amentoflavone alleviates acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting cell pyroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 692-701. |
| [7] | Zhengwang ZHU, Linlin WANG, Jinghan ZHAO, Ruixue MA, Yuchun YU, Qingchun CAI, Bing WANG, Pingsheng ZHU, Mingsan MIAO. Tuihuang Mixture improves α‑naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes via regulating farnesoid X receptor [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 718-724. |
| [8] | Ju HUANG, Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Nodakenin ameliorates TNBS-induced experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting pyroptosis of intestinal epithelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [9] | Pengwei HUANG, Jie CHEN, Jinhu ZOU, Xuefeng GAO, Hong CAO. Quercetin mitigates HIV-1 gp120-induced rat astrocyte neurotoxicity via promoting G3BP1 disassembly in stress granules [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [10] | Shicheng XIA, Huifang WEI, Weican HONG, Yuming ZHANG, Feiyang YIN, Yixin ZHANG, Linlin ZHANG, Qin GAO, Hongwei YE. Protective effect of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos extract against doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury in mice and the possible mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2527-2540. |
| [11] | Changlong FU, Ruolan CHEN, Shiqi XU, Jinxin YOU, Qing LIN, Yanfeng HUANG. Morinda officinalis polysaccharide delays osteoarthritis mouse chondrocyte degeneration by modulating the glycolysis-pyroptosis axis via targeting the lncRNA XIST [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2541-2550. |
| [12] | Siyu ZHANG, Linwu RAN, Jin ZENG, Yujiong WANG. Clostridium perfringens Beta1 toxin induces macrophage pyroptosis and ferroptosis through the purinergic receptor P2X7-Ca2+ axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2126-2134. |
| [13] | Mingyuan LI, Wei ZHANG, Mengqing HUA. Bardoxolone methyl alleviates acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1662-1669. |
| [14] | Wei ZHANG, Mengmeng DENG, Yao ZENG, Chenfei LIU, Feifei SHANG, Wenhao XU, Haoyi JIANG, Fengchao WANG, Yanqing YANG. 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone alleviates septic shock in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1024-1032. |
| [15] | Yiming SUN, Rong ZHANG, Ying MENG, Lei ZHU, Mingqiang LI, Zhe LIU. Coenzyme Q10 alleviates depression-like behaviors in mice with chronic restraint stress by down-regulating the pyroptosis signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 810-817. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||