南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2747-2755.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.22
• • 上一篇
周仁杰1,2( ), 杨晶晶1,2, 宋博文1,2, 陈孝华1,2, 王炼1,2, 王月月2, 左芦根1,2, 朱冰1(
), 杨晶晶1,2, 宋博文1,2, 陈孝华1,2, 王炼1,2, 王月月2, 左芦根1,2, 朱冰1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-07
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
朱冰
E-mail:18879997869@163.com;bbmczhubing@163.com
作者简介:周仁杰,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 18879997869@163.com
基金资助:
Renjie ZHOU1,2( ), Jingjing YANG1,2, Bowen SONG1,2, Xiaohua CHEN1,2, Lian WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2, Bing ZHU1(
), Jingjing YANG1,2, Bowen SONG1,2, Xiaohua CHEN1,2, Lian WANG1,2, Yueyue WANG2, Lugen ZUO1,2, Bing ZHU1( )
)
Received:2025-05-07
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Bing ZHU
E-mail:18879997869@163.com;bbmczhubing@163.com
摘要:
目的 探究26S蛋白酶体非ATP酶调节亚基11(PSMD11)在胃癌中的表达情况及其对患者远期预后价值。 方法 纳入我院2016年1月~2019年12月94例胃癌患者,通过免疫组化检测胃癌及癌旁组织中PSMD11、Ki67的表达水平,分析其与患者临床病理参数及术后5年生存情况的关系。通过GEPIA和UALCAN数据库分析PSMD11在胃癌中的表达情况,利用KM-plotter数据库预测其预后5年生存率。采用KEGG和GO富集分析预测PSMD11的生物学功能及潜在机制,构建PSMD11敲低和过表达的HGC-27细胞模型,采用划痕愈合实验、Transwell实验评估胃癌细胞迁移侵袭能力,Western blotting检测上皮-间质转化(EMT)标志物及TGF-β/Smad通路关键分子表达水平。 结果 数据库联合分析显示PSMD11在胃癌中高表达,且与Ki67表达呈正相关(r=0.73,P<0.05)。KM-plotter数据库及本院患者临床数据生存分析显示,PSMD11高表达与胃癌预后较差呈正相关,并经单因素、多因素Cox回归分析显示,PSMD11为影响胃癌患者预后的独立危险因素(HR:2.167,95% CI:1.159~4.051,P=0.015)。富集分析结果提示PSMD11与胃癌EMT进程和TGF-β信号通路相关。细胞划痕和Transwell实验结果显示,上调PSMD11后HGC-27细胞的迁移和侵袭能力增强,下调PSMD11则减弱(P<0.05)。Western blotting结果显示,上调PSMD11可增加Vimentin、N-cadherin、TGF-β和p-Smad2/3的表达水平,减少E-cadherin的表达,下调PSMD11则相反(P<0.05)。 结论 PSMD11在胃癌中高表达并影响患者预后,其可能通过激活TGF-β/Smad信号通路来驱动胃癌细胞EMT进程。
周仁杰, 杨晶晶, 宋博文, 陈孝华, 王炼, 王月月, 左芦根, 朱冰. 高表达PSMD11促进胃癌细胞上皮-间质转化进程并影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2747-2755.
Renjie ZHOU, Jingjing YANG, Bowen SONG, Xiaohua CHEN, Lian WANG, Yueyue WANG, Lugen ZUO, Bing ZHU. PSMD11 overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer and affects patient prognosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2747-2755.
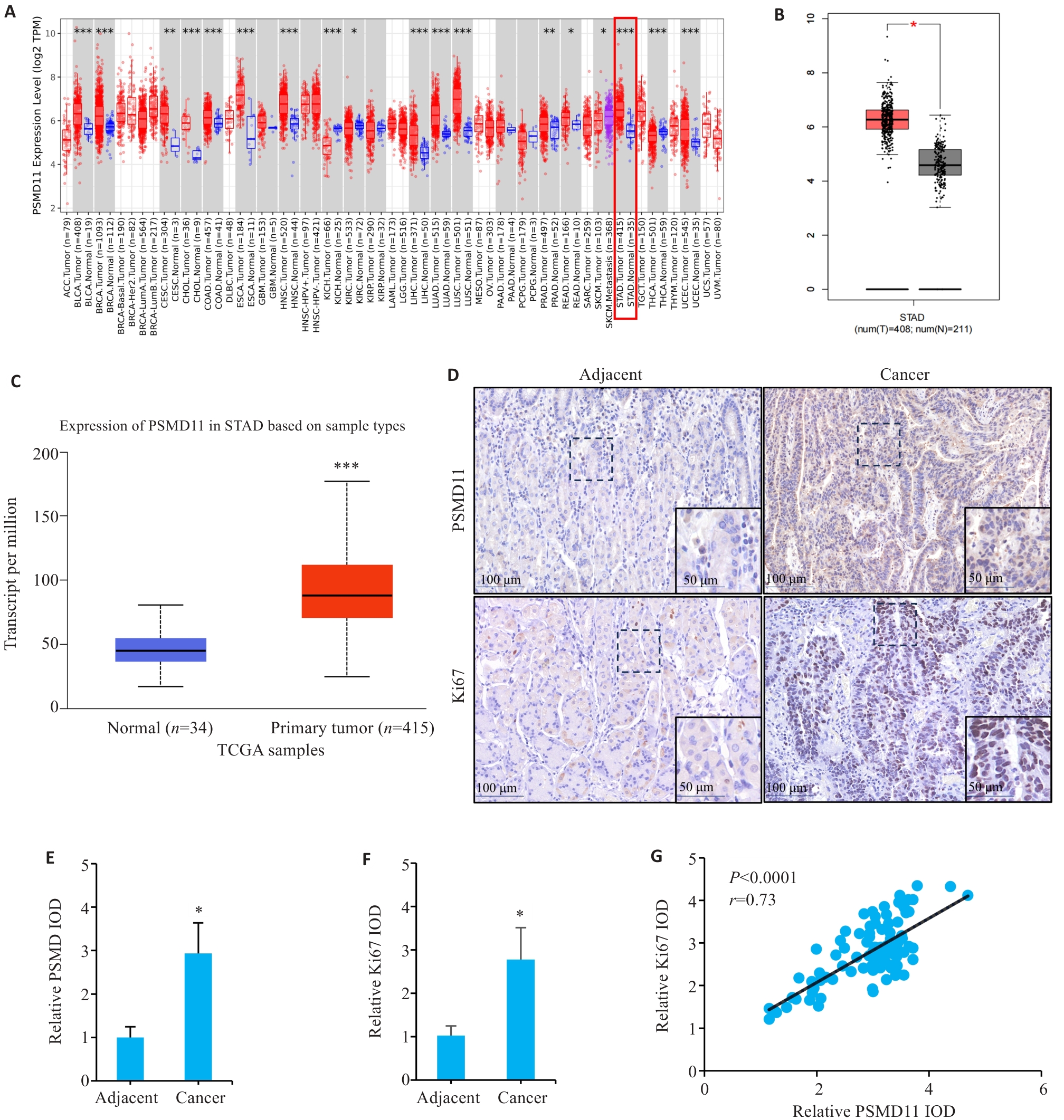
图1 胃癌组织中PSMD11和Ki67的表达及相关性分析
Fig.1 Expressions and correlation analysis of PSMD11 and Ki67 in gastric cancer tissues. A: Expression of PSMD11 in pan-cancer. B, C: Expression of PSMD11 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues. D: Immunohistochemical staining of PSMD11 and Ki67. E, F: Relative IOD values of PSMD11 and Ki67. G: Correlation between PSMD11 and Ki67. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Normal/Adjacent group.
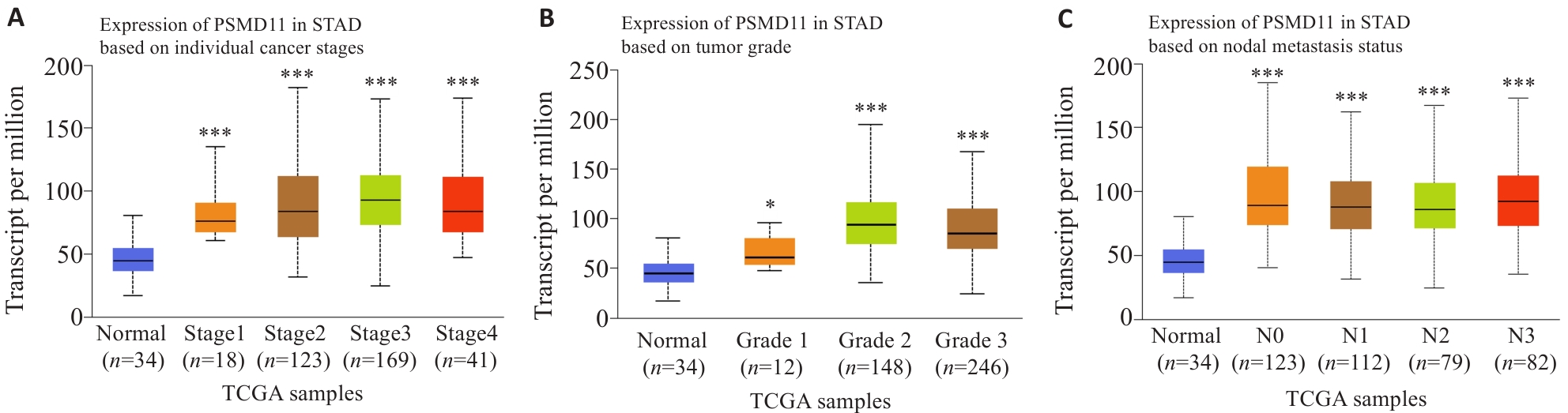
图2 胃癌组织中PSMD11的表达与临床病理学参数的关系
Fig.2 Relationship between PSMD11 expression in gastric cancer tissues and clinicopathological parameters of the patients. A, B: Correlation of PSMD11 expression levels with tumor grades and stages. C: Correlation of PSMD11 expression level with lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs adjacent tissue.
| Characteristics | n | PSMD11 expression (n=47) | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Gender | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| Female | 31 | 15 (48.39%) | 16 (51.61%) | ||
| Male | 63 | 32 (50.79%) | 31 (49.21%) | ||
| Age (year) | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| <60 | 31 | 16 (51.61%) | 15 (48.39%) | ||
| ≥60 | 63 | 31 (49.21%) | 32 (50.79%) | ||
| Pathohistological type | 0.052 | 0.82 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 67 | 34 (50.75%) | 33 (49.25%) | ||
| Other | 27 | 13 (48.15%) | 14 (51.85%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 13.155 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 35 | 26 (74.29%) | 9 (25.71%) | ||
| ≥5 | 59 | 21 (35.59%) | 38 (64.41%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 10.938 | 0.001 | |||
| <37 | 44 | 30 (68.18%) | 14 (31.82%) | ||
| ≥37 | 50 | 17 (34%) | 33 (66%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.549 | 0.213 | |||
| <5 | 42 | 24 (57.14%) | 18 (42.86%) | ||
| ≥5 | 52 | 23 (44.23%) | 29 (55.77%) | ||
| Histological Grading | 4.257 | 0.039 | |||
| G1-G2 | 46 | 28 (60.87%) | 18 (39.13%) | ||
| G3-G4 | 48 | 19 (39.58%) | 29 (60.42%) | ||
| T Stage | 11.525 | 0.001 | |||
| T1-T2 | 36 | 26 (72.22%) | 10 (27.78%) | ||
| T3-T4 | 58 | 21 (36.21%) | 37 (63.79%) | ||
| N Stage | 11.141 | 0.001 | |||
| N0-N1 | 40 | 28 (70%) | 12 (30%) | ||
| N2-N3 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | ||
表1 胃癌组织中PSMD11表达水平与胃癌恶性进展参数的关系
Tab.1 Relationship between PSMD11 expression level in gastric cancer tissues and parameters of malignant progression in gastric cancer patients (n, %)
| Characteristics | n | PSMD11 expression (n=47) | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Gender | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| Female | 31 | 15 (48.39%) | 16 (51.61%) | ||
| Male | 63 | 32 (50.79%) | 31 (49.21%) | ||
| Age (year) | 0.048 | 0.826 | |||
| <60 | 31 | 16 (51.61%) | 15 (48.39%) | ||
| ≥60 | 63 | 31 (49.21%) | 32 (50.79%) | ||
| Pathohistological type | 0.052 | 0.82 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 67 | 34 (50.75%) | 33 (49.25%) | ||
| Other | 27 | 13 (48.15%) | 14 (51.85%) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 13.155 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 35 | 26 (74.29%) | 9 (25.71%) | ||
| ≥5 | 59 | 21 (35.59%) | 38 (64.41%) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 10.938 | 0.001 | |||
| <37 | 44 | 30 (68.18%) | 14 (31.82%) | ||
| ≥37 | 50 | 17 (34%) | 33 (66%) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.549 | 0.213 | |||
| <5 | 42 | 24 (57.14%) | 18 (42.86%) | ||
| ≥5 | 52 | 23 (44.23%) | 29 (55.77%) | ||
| Histological Grading | 4.257 | 0.039 | |||
| G1-G2 | 46 | 28 (60.87%) | 18 (39.13%) | ||
| G3-G4 | 48 | 19 (39.58%) | 29 (60.42%) | ||
| T Stage | 11.525 | 0.001 | |||
| T1-T2 | 36 | 26 (72.22%) | 10 (27.78%) | ||
| T3-T4 | 58 | 21 (36.21%) | 37 (63.79%) | ||
| N Stage | 11.141 | 0.001 | |||
| N0-N1 | 40 | 28 (70%) | 12 (30%) | ||
| N2-N3 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | ||
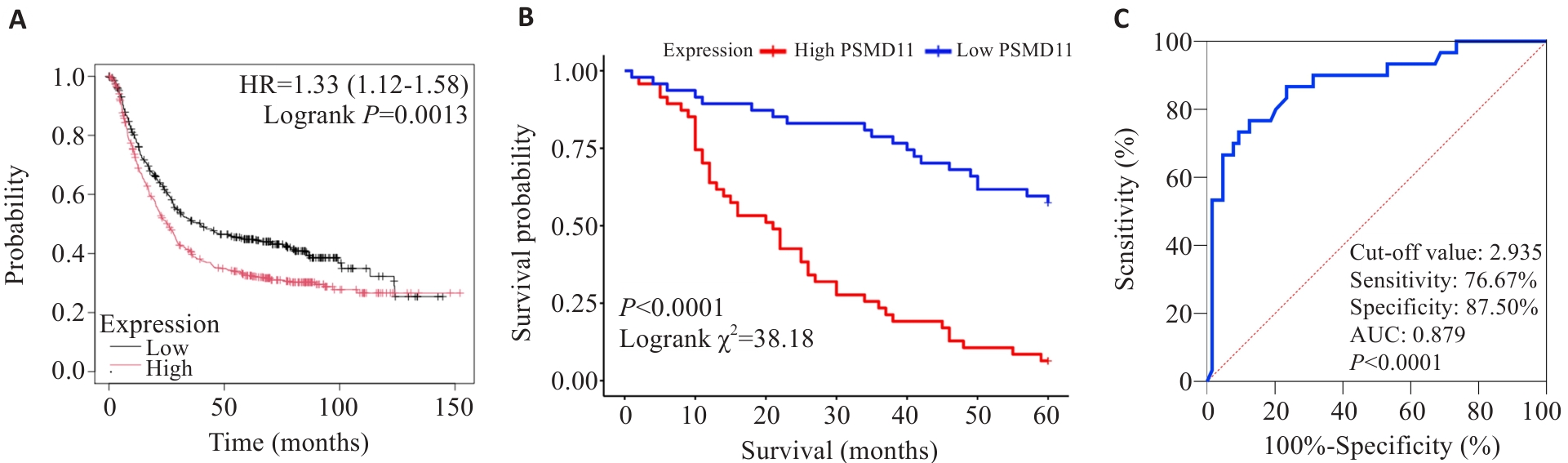
图3 PSMD11对胃癌患者预后的影响
Fig.3 Effect of PSMD11 on prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. A: Kaplan-Meier analysis. B: Survival curves. C: Predictive value of PSMD11 for 5-year postoperative survival in gastric cancer patients.
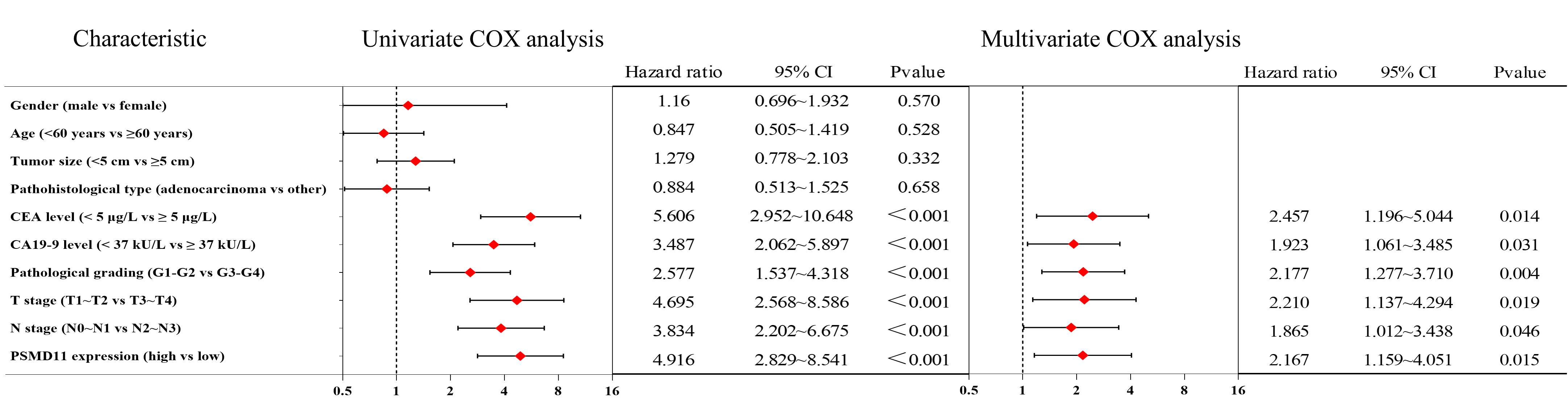
图4 胃癌患者术后5年生存情况的单因素分析及多因素Cox回归
Fig.4 Univariate analysis and multifactorial Cox regression of survival of gastric cancer patients within 5 years after surgery.
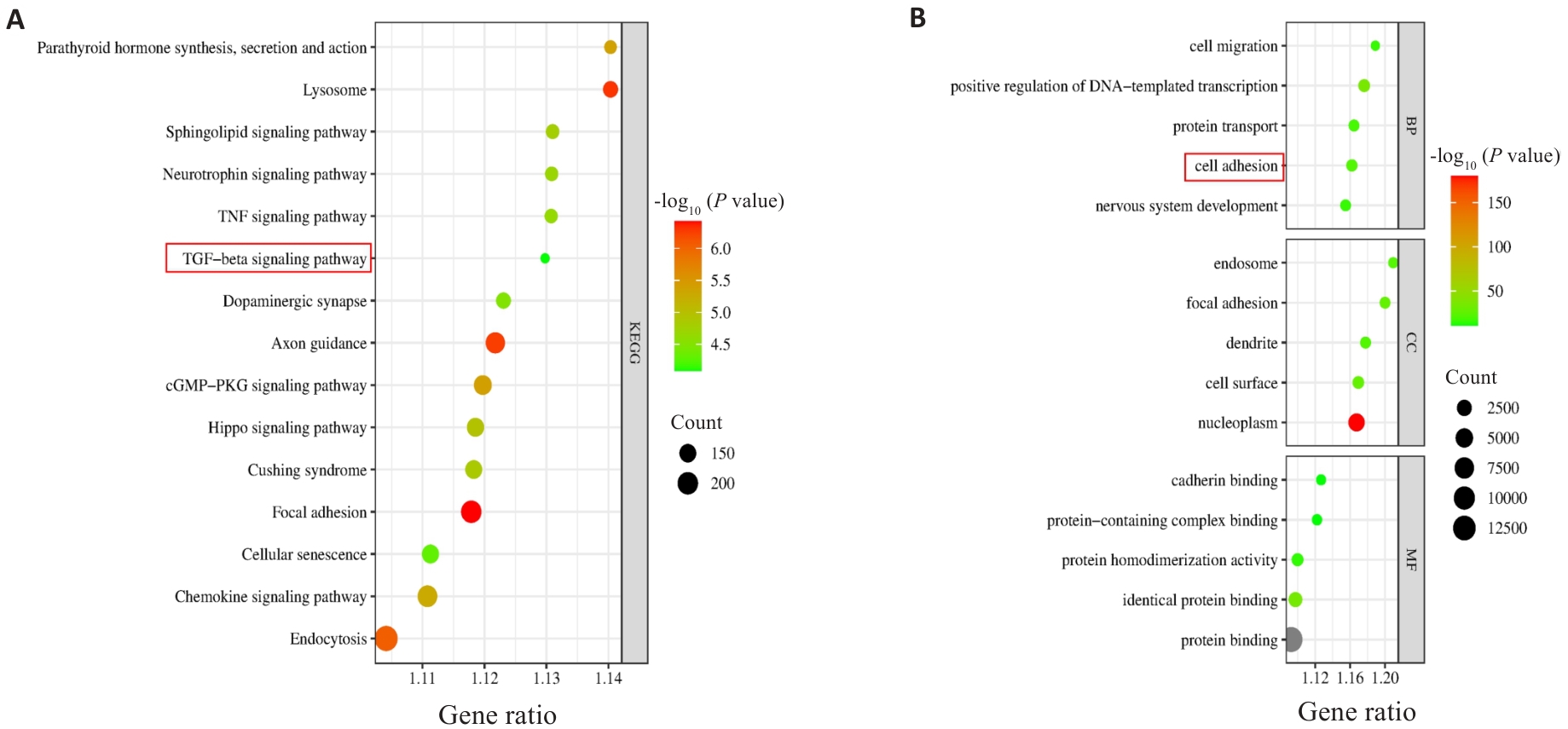
图5 PSMD11与胃癌共表达基因的KEGG和GO富集分析
Fig.5 KEGG and GO enrichment analyses of PSMD11 and gastric cancer co-expressed genes. A: KEGG enrichment analysis results. B: GO enrichment analysis results.

图6 PSMD11促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭(Transwell实验)
Fig.6 PSMD11 overexpression promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells (Transwell assay). A-C: Lentivirus-mediated knockdown and overexpression of PSMD11 in HGC-27 cells. D-I: Migration and invasion of the transfected HGC-27 cells (n=3), Si: siRNA; LV: Overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
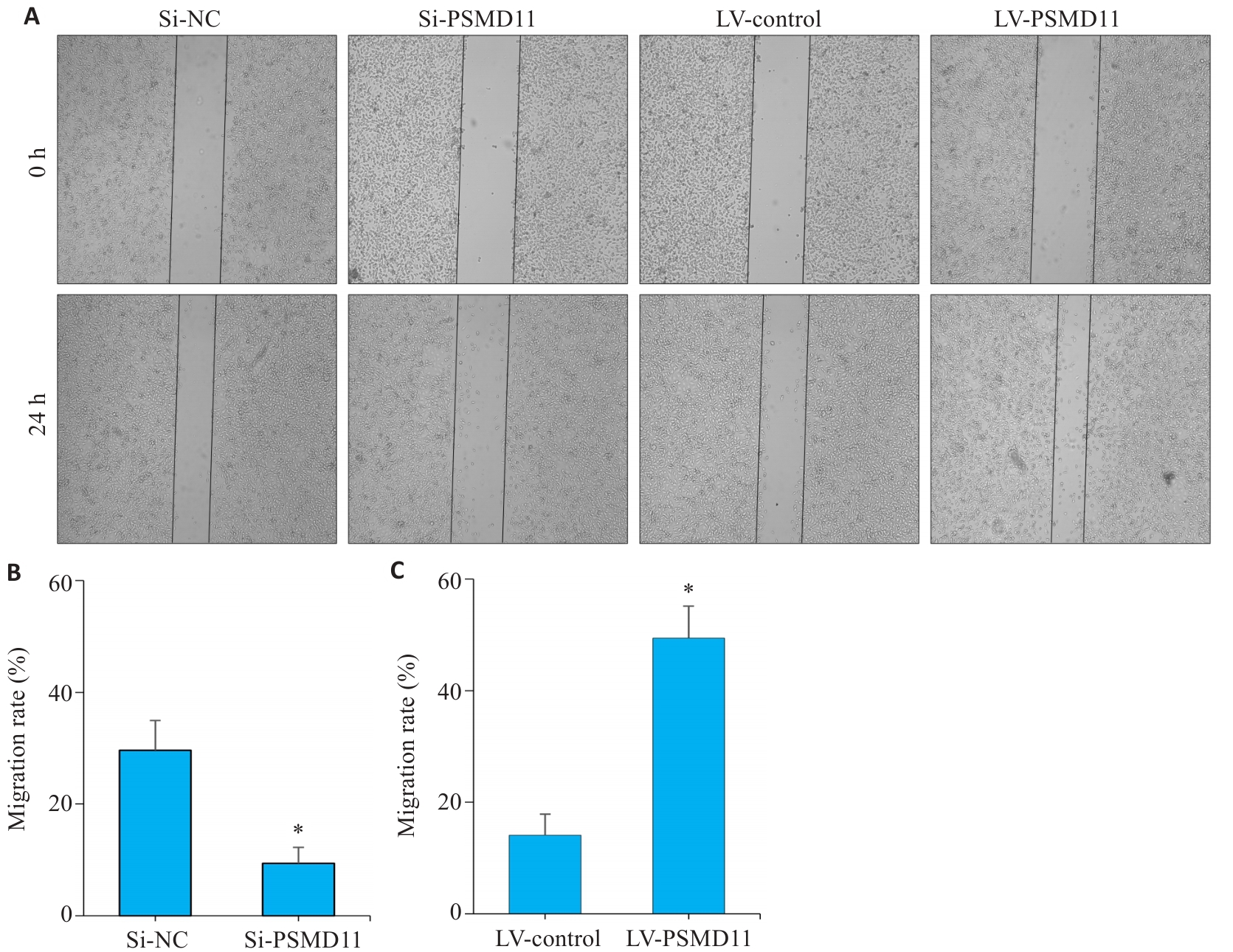
图7 PSMD11促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭(划痕实验)
Fig.7 Wound healing assay showing that PSMD11 overexpression promotes migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. A-C: PSMD11 overexpression promotes HGC-27 cell migration in Wound-Healing assay. n=3, Si: siRNA; LV: overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
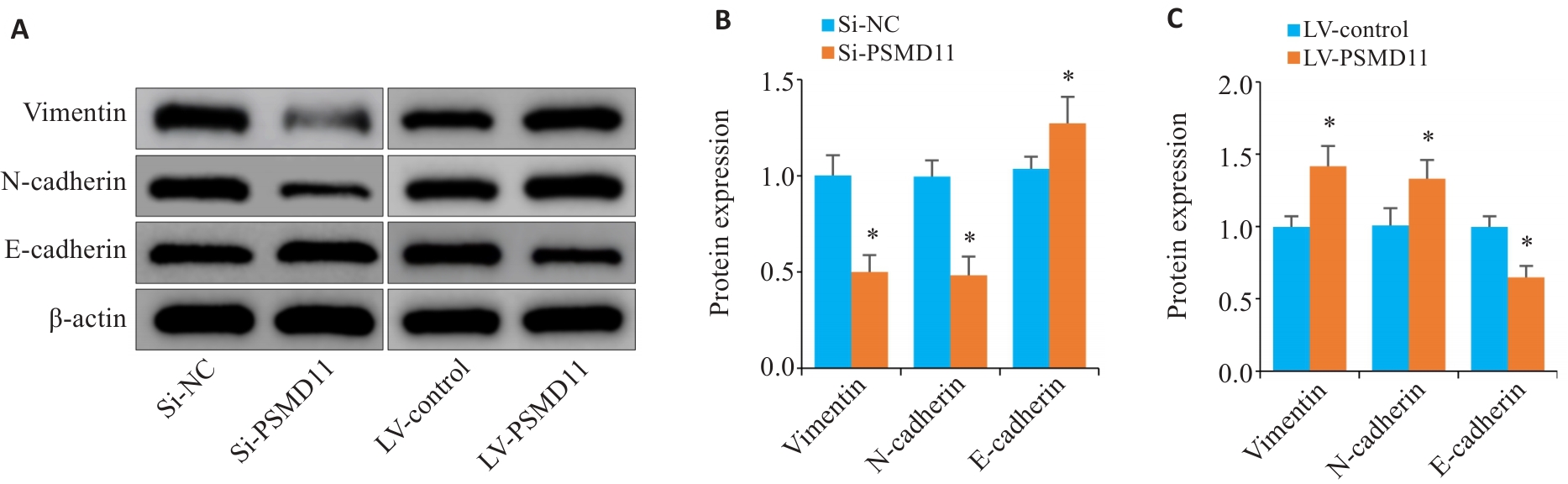
图8 PSMD11促进胃癌细胞的EMT进程
Fig.8 PSMD11 promotes EMT process in gastric cancer cells. A-C: Expressions of key proteins of EMT in gastric cancer cells (n=3). Si: siRNA. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
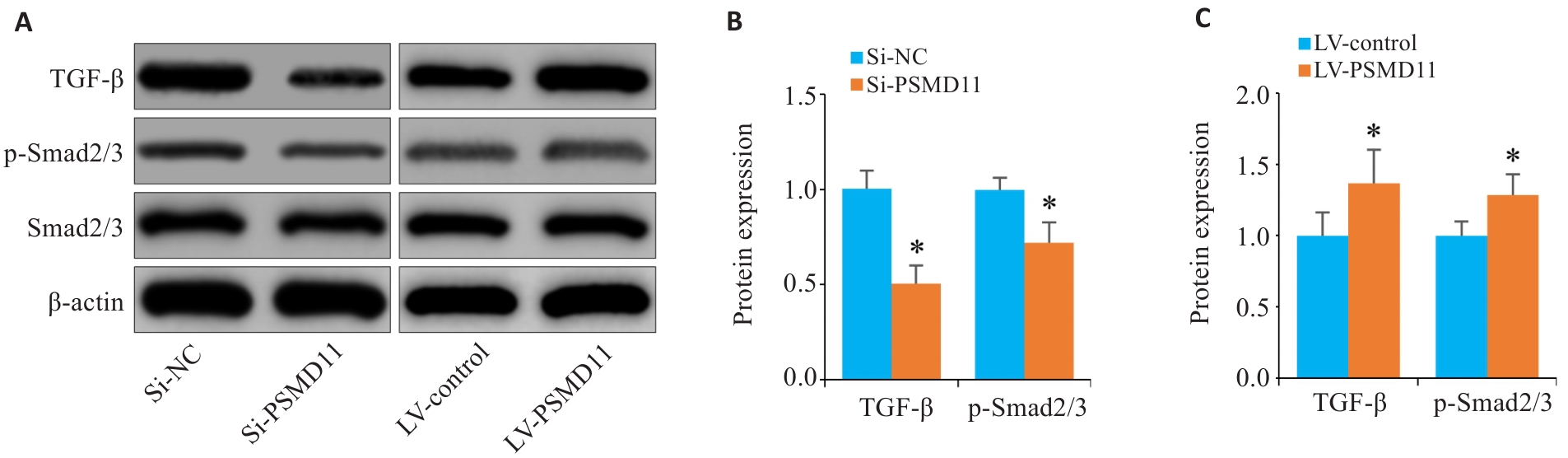
图9 PSMD11高表达激活TGF-β/Smad信号通路
Fig.9 Overexpression of PSMD11 in gastric cancer activates the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. A-C: Expressions of TGF-β1, p-Smad2/3, and Smad2/3 in HGC-27 cells. *P<0.05 vs Si-NC or LV-Control.
| [1] | Huang JJ, Lucero-Prisno DE III, Zhang L, et al. Updated epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancers in east Asia[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(5): 271-87. doi:10.1038/s41575-022-00726-3 |
| [2] | Zhao LL, Zhao DB, Chen YT. Neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced gastric cancer[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2020, 42(11): 907-11. |
| [3] | Shah MA, Kennedy EB, Alarcon-Rozas AE, et al. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy for advanced gastroesophageal cancer: ASCO guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41(7): 1470-91. |
| [4] | Fiorica F, Cartei F, Enea M, et al. The impact of radiotherapy on survival in resectable gastric carcinoma: a meta-analysis of literature data[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2007, 33(8): 729-40. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.08.005 |
| [5] | Carter SK, Comis RL. Gastric cancer: current status of treatment[J]. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst, 1977, 58(3): 567-78. doi:10.1093/jnci/58.3.567 |
| [6] | 王 阳, 张保贵. 胃癌上皮间质转化相关LncRNA研究进展[J]. 济宁医学院学 报, 2024, 47(2): 165-8. |
| [7] | Vaquero J, Guedj N, Clapéron A, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma: from clinical evidence to regulatory networks[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(2): 424-41. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.010 |
| [8] | Vilchez D, Boyer L, Morantte I, et al. Increased proteasome activity in human embryonic stem cells is regulated by PSMD11[J]. Nature, 2012, 489(7415): 304-8. doi:10.1038/nature11468 |
| [9] | 孙 亮. PSMD11通过调控CDK4的泛素化降解促进肝细胞癌的增殖[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2024. |
| [10] | Zhang C, Xu T, Ji K, et al. An integrative analysis reveals the prognostic value and potential functions of PSMD11 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2023, 62(9): 1355-68. doi:10.1002/mc.23568 |
| [11] | Sahni S, Krisp C, Molloy MP, et al. PSMD11, PTPRM and PTPRB as novel biomarkers of pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Gen Subj, 2020, 1864(11): 129682. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129682 |
| [12] | Zhou XJ, Liu XF, Wang X, et al. SITP: a single cell bioinformatics analysis flow captures proteasome markers in the development of breast cancer[J]. Methods, 2025, 233: 1-10. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.11.011 |
| [13] | Huang Q, Tian R, Yu J, et al. Identification of PSMD11 as a novel cuproptosis- and immune-related prognostic biomarker promoting lung adenocarcinoma progression[J]. Cancer Med, 2024, 13(11): e7379. doi:10.1002/cam4.7379 |
| [14] | Xu Z, Liao H, Huang L, et al. IBPGNET: lung adenocarcinoma recurrence prediction based on neural network interpretability[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2024, 25(3): bbae080. doi:10.1093/bib/bbae080 |
| [15] | 褚以忞. MiR-1254下调PSMD10抑制结直肠癌细胞迁移的机制研究[D]: 第 二军医大学, 2018. |
| [16] | 刘志勇. PSMD14促进骨肉瘤进展及安罗替尼耐药的功能和机制研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2023. |
| [17] | Wang R, Huang W, Cai K, et al. FLOT1 promotes gastric cancer progression and metastasis through BCAR1/ERK signaling[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(16): 5104-19. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82606 |
| [18] | Zhang L, Li Q, Yang J, et al. Cytosolic TGM2 promotes malignant progression in gastric cancer by suppressing the TRIM21-mediated ubiquitination/degradation of STAT1 in a GTP binding-dependent modality[J]. Cancer Commun: Lond, 2023, 43(1): 123-49. doi:10.1002/cac2.12386 |
| [19] | Moreno D, Viana R, Sanz P. Two-hybrid analysis identifies PSMD11, a non-ATPase subunit of the proteasome, as a novel interaction partner of AMP-activated protein kinase[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2009, 41(12): 2431-9. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.002 |
| [20] | Yang YH, Xing ZH, Wang H, et al. PSMD11 and PSMD14 may serve as novel biomarkers for the prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2025, 15: 1555649. doi:10.3389/fonc.2025.1555649 |
| [21] | Sun L, Liu ZT, Wu ZY, et al. PSMD11 promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the ubiquitination degradation of CDK4[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 121: 111279. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111279 |
| [22] | Wang L, Zhao L, Wei G, et al. Homoharringtonine could induce quick protein synthesis of PSMD11 through activating MEK1/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(8): 6644-56. doi:10.1002/jcb.26847 |
| [23] | Salah Fararjeh A, Al-Khader A, Al-Saleem M, et al. The prognostic significance of proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase (PSMD) genes for bladder urothelial carcinoma patients[J]. Cancer Inform, 2021, 20: 11769351211067692. doi:10.1177/11769351211067692 |
| [24] | Li S, Cong X, Gao H, et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils induce EMT by IL-17a to promote migration and invasion in gastric cancer cells[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 6. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-1003-0 |
| [25] | Wang R, Sun Y, Yu W, et al. Downregulation of miRNA-214 in cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through targeting FGF9 and inducing EMT[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 20. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0995-9 |
| [26] | Baum B, Georgiou M. Dynamics of adherens junctions in epithelial establishment, maintenance, and remodeling[J]. J Cell Biol, 2011, 192(6): 907-17. doi:10.1083/jcb.201009141 |
| [27] | Macara IG, Guyer R, Richardson G, et al. Epithelial homeostasis[J]. Curr Biol, 2014, 24(17): R815-25. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.068 |
| [28] | Park YJ, Bang IJ, Jeong MH, et al. Effects of β-sitosterol from corn silk on TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung alveolar epithelial cells[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(35): 9789-95. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02730 |
| [29] | Deng L, Bao W, Zhang B, et al. AZGP1 activation by lenvatinib suppresses intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the TGF‑β1/Smad3 pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(9): 590. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06092-5 |
| [30] | Chen J, Zhu H, Liu Q, et al. DEPTOR induces a partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via autocrine TGFβ1 signaling and is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 273. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1220-1 |
| [31] | Fan C, González-Prieto R, Kuipers TB, et al. The lncRNA LETS1 promotes TGF‑β‑induced EMT and cancer cell migration by transcriptionally activating a TβR1-stabilizing mechanism[J]. Sci Signal, 2023, 16(790): eadf1947. doi:10.1126/scisignal.adf1947 |
| [1] | 王莹, 李静, 王伊迪, 华明钰, 胡玮彬, 张晓智. 原发性肝癌患者的临床结局与治疗反应预测模型:基于失巢凋亡和免疫基因[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [2] | 张瑜, 李海涛, 潘玉卿, 曹杰贤, 翟丽, 张曦. MZB1基因在泛癌中的表达及其与免疫浸润及预后的关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018. |
| [3] | 王子良, 陈孝华, 杨晶晶, 严晨, 张志郅, 黄炳轶, 赵萌, 刘嵩, 葛思堂, 左芦根, 陈德利. 高表达SURF4通过抑制紧密连接蛋白表达促进胃癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [4] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [5] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [6] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [7] | 王康, 李海宾, 余靖, 孟源, 张虹丽. ELFN1高表达是结肠癌的预后生物标志物并促进结肠癌细胞的增殖转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [8] | 侯鑫睿, 张振东, 曹明远, 杜予心, 王小平. 红景天苷靶向miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB糖代谢轴抑制胃癌细胞的体内外增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [9] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [10] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [11] | 李华莉, 宋婷, 刘嘉雯, 李永宝, 姜兆静, 窦文, 周凌宏. 预后导向的肺癌调强放疗计划优化新方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [12] | 宋雪, 陈悦, 张敏, 张诺, 左芦根, 李静, 耿志军, 张小凤, 王月月, 王炼, 胡建国. GPSM2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过促进肿瘤细胞的增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | 唐天威, 李路安, 陈源汉, 张丽, 徐丽霞, 李志莲, 冯仲林, 张辉林, 华瑞芳, 叶智明, 梁馨苓, 李锐钊. 高血清胱抑素C水平是IgA肾病不良预后的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [14] | 宋博文, 周仁杰, 徐盈, 施金冉, 张志郅, 李静, 耿志军, 宋雪, 王炼, 王月月, 左芦根. TMCO1在胃癌中高表达与患者不良预后相关并通过抑制调亡促进肿瘤恶性进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2385-2393. |
| [15] | 姜雪凝, 黄晴晴, 徐盈, 王舜印, 张小凤, 王炼, 王月月, 左芦根. 高表达YEATS2通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进胃癌细胞上皮-间质转化进程[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2416-2426. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||