南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 2006-2018.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.20
• • 上一篇
张瑜1( ), 李海涛1, 潘玉卿2, 曹杰贤2, 翟丽1, 张曦1(
), 李海涛1, 潘玉卿2, 曹杰贤2, 翟丽1, 张曦1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-15
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
张曦
E-mail:15520858743@163.com;zhangxi@kmmu.edu.cn
作者简介:张 瑜,硕士,检验师,E-mail: 15520858743@163.com
基金资助:
Yu ZHANG1( ), Haitao LI1, Yuqing PAN2, Jiexian CAO2, Li ZHAI1, Xi ZHANG1(
), Haitao LI1, Yuqing PAN2, Jiexian CAO2, Li ZHAI1, Xi ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-05-15
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Xi ZHANG
E-mail:15520858743@163.com;zhangxi@kmmu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨边缘区B细胞及B1细胞特异性蛋白(MZB1)在泛癌中的表达水平及其与患者预后、肿瘤微环境的关系。 方法 利用UCSC数据库提取MZB1在33种癌症中的表达数据、临床病理参数和生存数据。利用R软件分析MZB1与临床分期、患者预后、免疫调节基因、免疫检查点基因、肿瘤干性、免疫细胞浸润、肿瘤突变负荷(TMB)以及微卫星不稳定性(MSI)的相关性,使用cBioPortal在线数据库分析MZB1在泛癌中基因突变情况,利用ROC曲线分析MZB1的癌症诊断价值,利用RT-qPCR和Western blotting检测MZB1在髓系白血病和肾癌中的表达,利用EdU法检测干扰MZB1后细胞的增殖情况。 结果 与正常组织相比,MZB1在肾透明细胞癌(KIRC)、乳腺浸润性癌(BRCA)、急性髓系白血病(LAML)等20种肿瘤中高表达(P<0.05),并且与多种肿瘤的TNM分期和临床分期以及部分肿瘤的总生存期(OS)和无进展生存期(PFS)相关(P<0.05)。在大多数肿瘤中,MZB1的表达与免疫调节基因(CCL4、CXCL10、CCL5、CCR4、CCR7、XCR1、MHC、IL-10、TGF-β)、免疫检查点基因(LAG3、TIGIT、BTLA、PDCD1、CTLA4)、肿瘤的干性指数、免疫细胞浸润(B细胞、CD4+T细胞、CD8+T细胞、中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞、树突状细胞等)、TMB、MSI相关(P<0.05)。此外,MZB1在泛癌中的基因突变类型以扩增为主,并且对皮肤黑色素瘤(SKCM)、肾透明细胞癌(KIRC)和头颈部鳞状细胞癌(HNSC)均有较高的诊断价值。RT-qPCR和Western blotting结果均显示在髓系白血病细胞(HL60、KG-1、U937、MV-4-11)和肾癌细胞(786-O、769-P、OSRC-2)中MZB1呈高表达(P<0.05),下调MZB1表达后可降低HL60和769-P的增殖水平。 结论 MZB1在多种肿瘤中高表达,其异常表达影响多种肿瘤的发生及预后,有望成为新的肿瘤标志物和免疫调节靶点。
张瑜, 李海涛, 潘玉卿, 曹杰贤, 翟丽, 张曦. MZB1基因在泛癌中的表达及其与免疫浸润及预后的关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018.
Yu ZHANG, Haitao LI, Yuqing PAN, Jiexian CAO, Li ZHAI, Xi ZHANG. Pan-cancer analysis of MZB1 expression and its association with immune infiltration and clinical prognosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018.
| Cancer type abbreviation | Full name of cancer type |
|---|---|
| ACC | Adrenocortical carcinoma |
| BLCA | Bladder urothelial carcinoma |
| BRCA | Breast invasive carcinoma |
| CESC | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma |
| CHOL | Cholangiocarcinoma |
| COAD | Colon adenocarcinoma |
| COADREAD | Colon adenocarcinoma/rectum adenocarcinoma esophageal carcinoma |
| ESCA | Esophageal carcinoma |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| GBMLGG | Glioma |
| HNSC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| KICH | Kidney chromophobe |
| KIPAN | Pan-kidney cohort (kich+kirc+kirp) |
| KIRC | Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma |
| KIRP | Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma |
| LAML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| LGG | Brain lower grade glioma |
| LIHC | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| MESO | Mesothelioma |
| OV | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma |
| PAAD | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma |
| PCPG | Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma |
| PRAD | Prostate adenocarcinoma |
| READ | Rectum adenocarcinoma |
| SARC | Sarcoma |
| STAD | Stomach adenocarcinoma |
| SKCM | Skin cutaneous melanoma |
| STES | Stomach and esophageal carcinoma |
| TGCT | Testicular germ cell tumors |
| THCA | Thyroid carcinoma |
| THYM | Thymoma |
| UCEC | Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma |
| UCS | Uterine carcinosarcoma |
| WT | High-risk wilms tumor |
表1 泛癌数据中相关肿瘤的英文缩写
Tab.1 English abbreviations of relevant cancers in pan-cancer data
| Cancer type abbreviation | Full name of cancer type |
|---|---|
| ACC | Adrenocortical carcinoma |
| BLCA | Bladder urothelial carcinoma |
| BRCA | Breast invasive carcinoma |
| CESC | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma |
| CHOL | Cholangiocarcinoma |
| COAD | Colon adenocarcinoma |
| COADREAD | Colon adenocarcinoma/rectum adenocarcinoma esophageal carcinoma |
| ESCA | Esophageal carcinoma |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| GBMLGG | Glioma |
| HNSC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| KICH | Kidney chromophobe |
| KIPAN | Pan-kidney cohort (kich+kirc+kirp) |
| KIRC | Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma |
| KIRP | Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma |
| LAML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| LGG | Brain lower grade glioma |
| LIHC | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| MESO | Mesothelioma |
| OV | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma |
| PAAD | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma |
| PCPG | Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma |
| PRAD | Prostate adenocarcinoma |
| READ | Rectum adenocarcinoma |
| SARC | Sarcoma |
| STAD | Stomach adenocarcinoma |
| SKCM | Skin cutaneous melanoma |
| STES | Stomach and esophageal carcinoma |
| TGCT | Testicular germ cell tumors |
| THCA | Thyroid carcinoma |
| THYM | Thymoma |
| UCEC | Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma |
| UCS | Uterine carcinosarcoma |
| WT | High-risk wilms tumor |
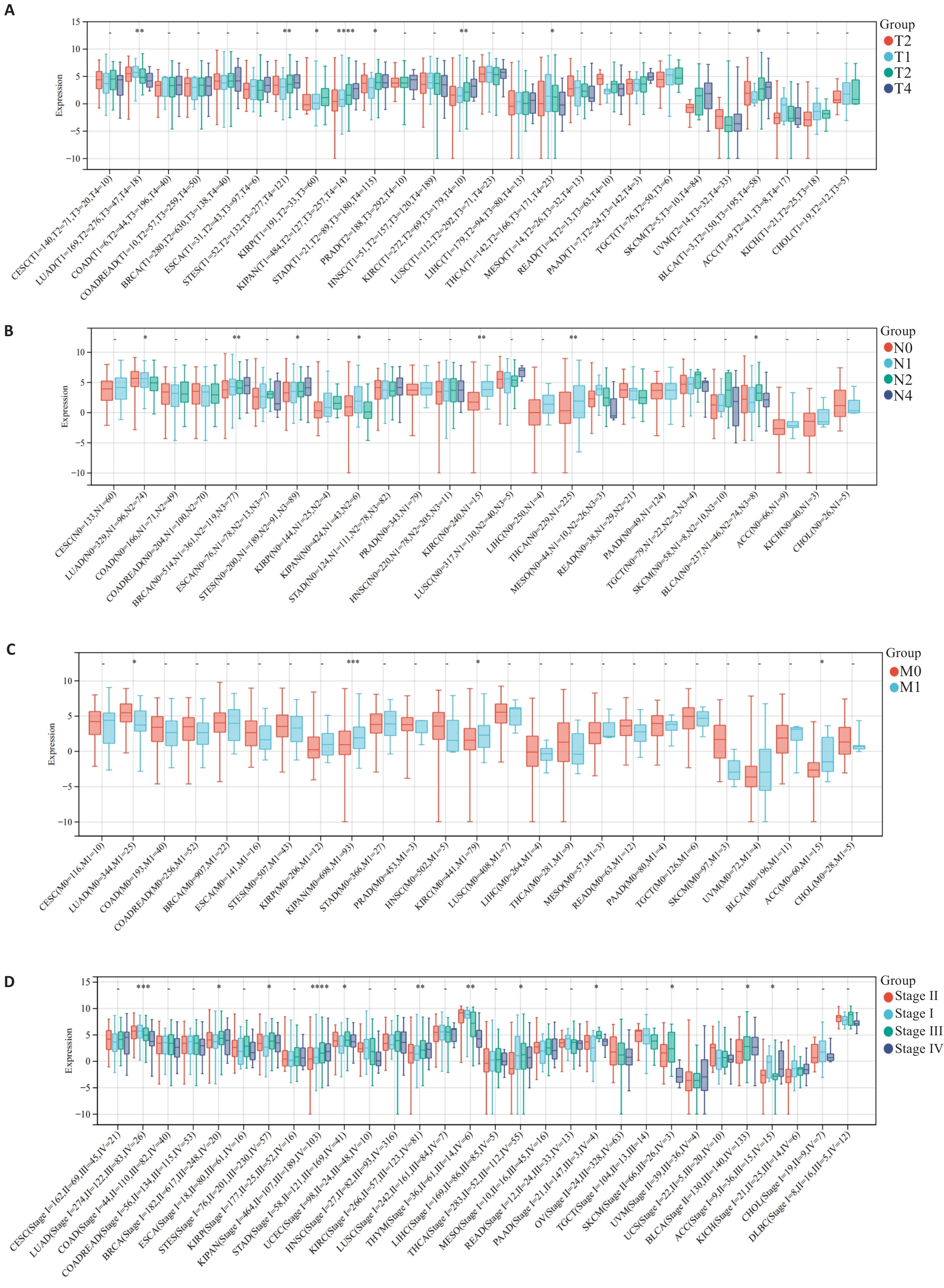
图2 MZB1与肿瘤病理分期的关系
Fig.2 Relationship between MZB1 and tumor pathological stage. A-C: Relationship between MZB1 and tumor TNM stage. D: Relationship between MZB1 and tumor stage. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
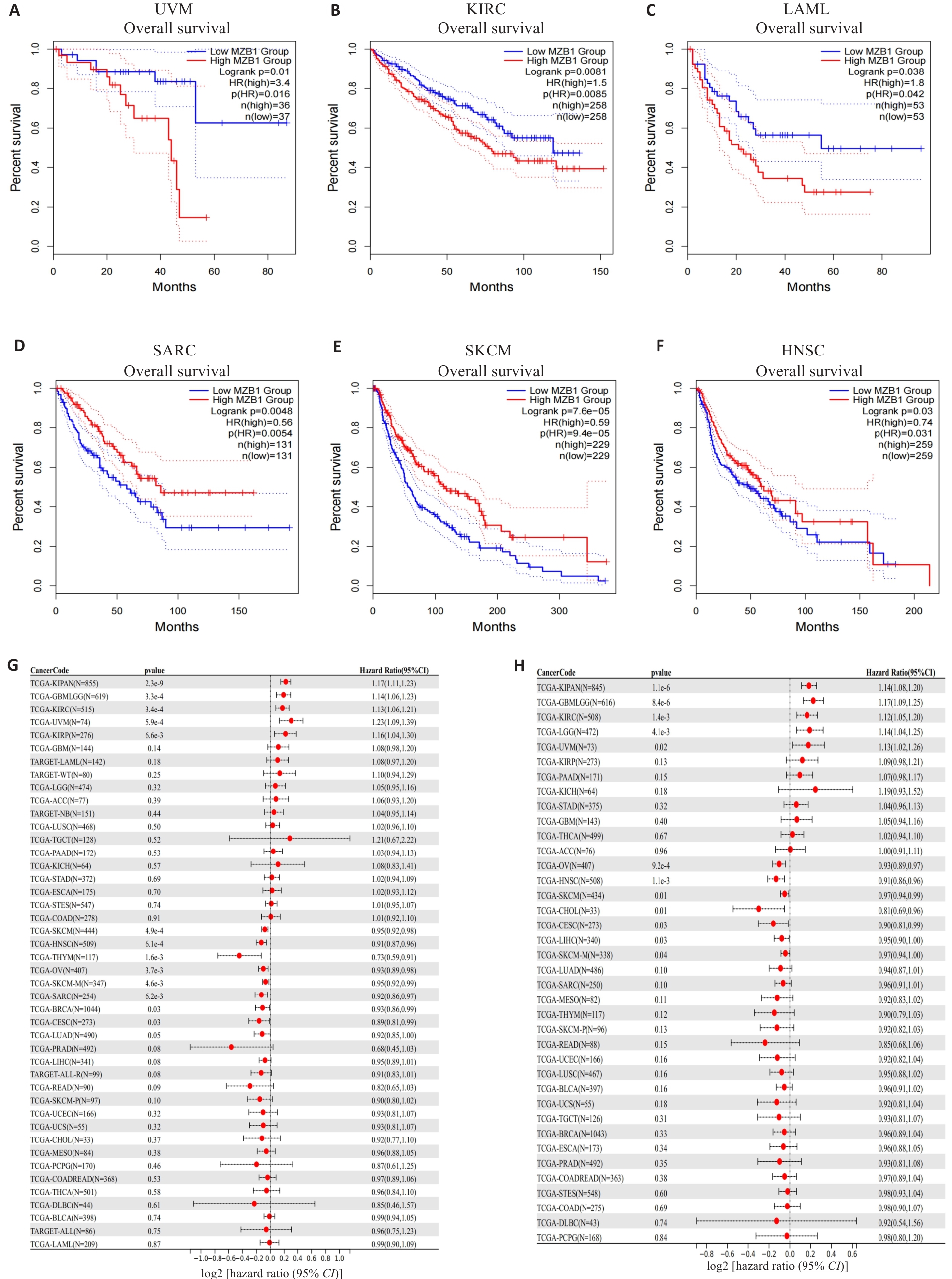
图3 MZB1对癌症预后的影响
Fig.3 Effect of MZB1 on cancer prognosis. A-F: Kaplan-Meier survival curves of MZB1 expression in UVM, KIRC,LAML, SARC, SKCM, and HNSC. G, H: Prognostic analysis of the effect of MZB1 expression on overall survival (G) and progression-free survival (H).
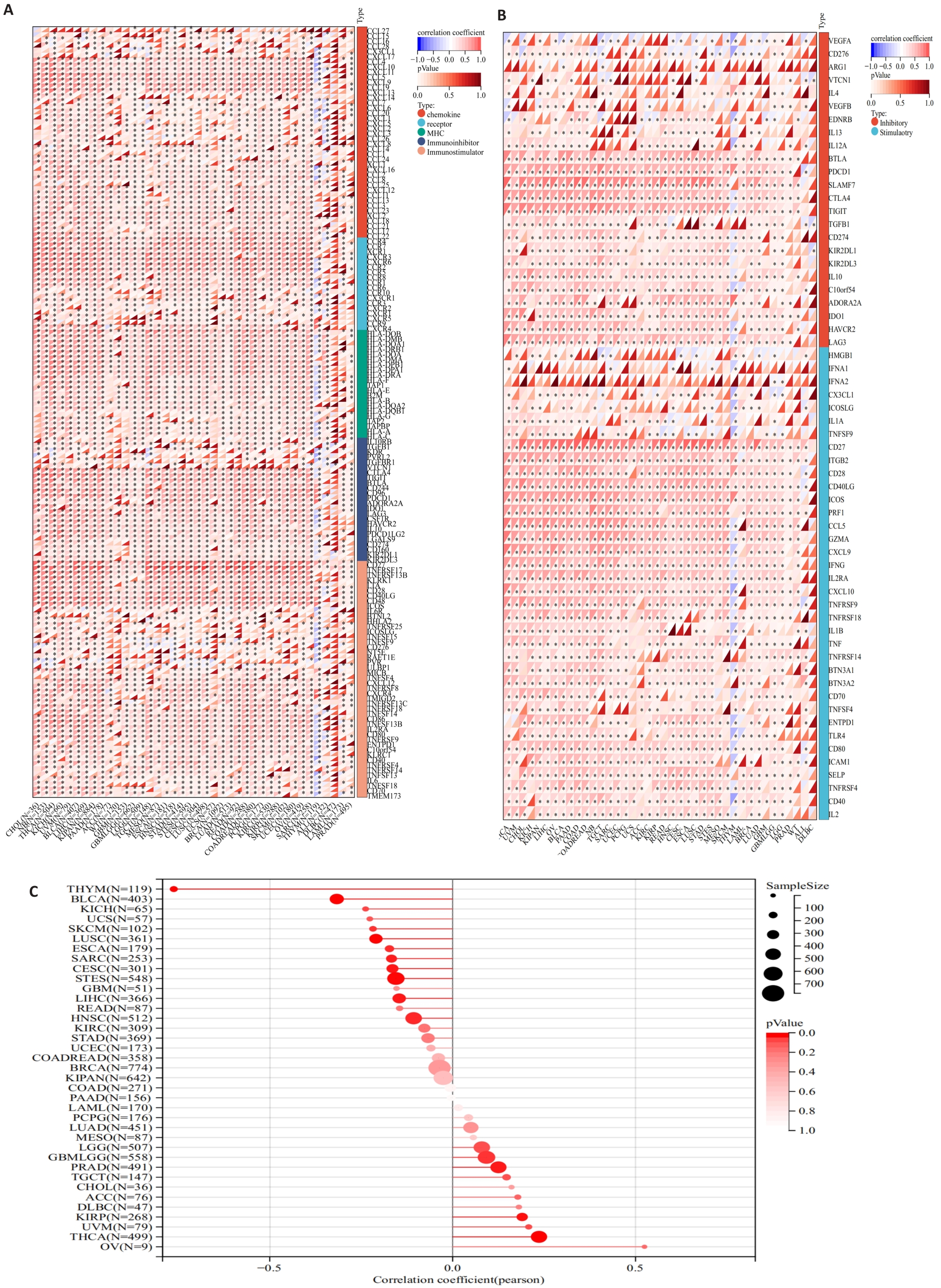
图4 MZB1的免疫学特征分析以及与肿瘤干性的相关性
Fig.4 Immunological characterization of MZB1 and correlation between MZB1 and tumor stemness. A: Relationship between MZB1 and immunomodulatory genes. B: Relationship between MZB1 and immune checkpoint genes. C: Relationship between MZB1 and tumor stemness indices.
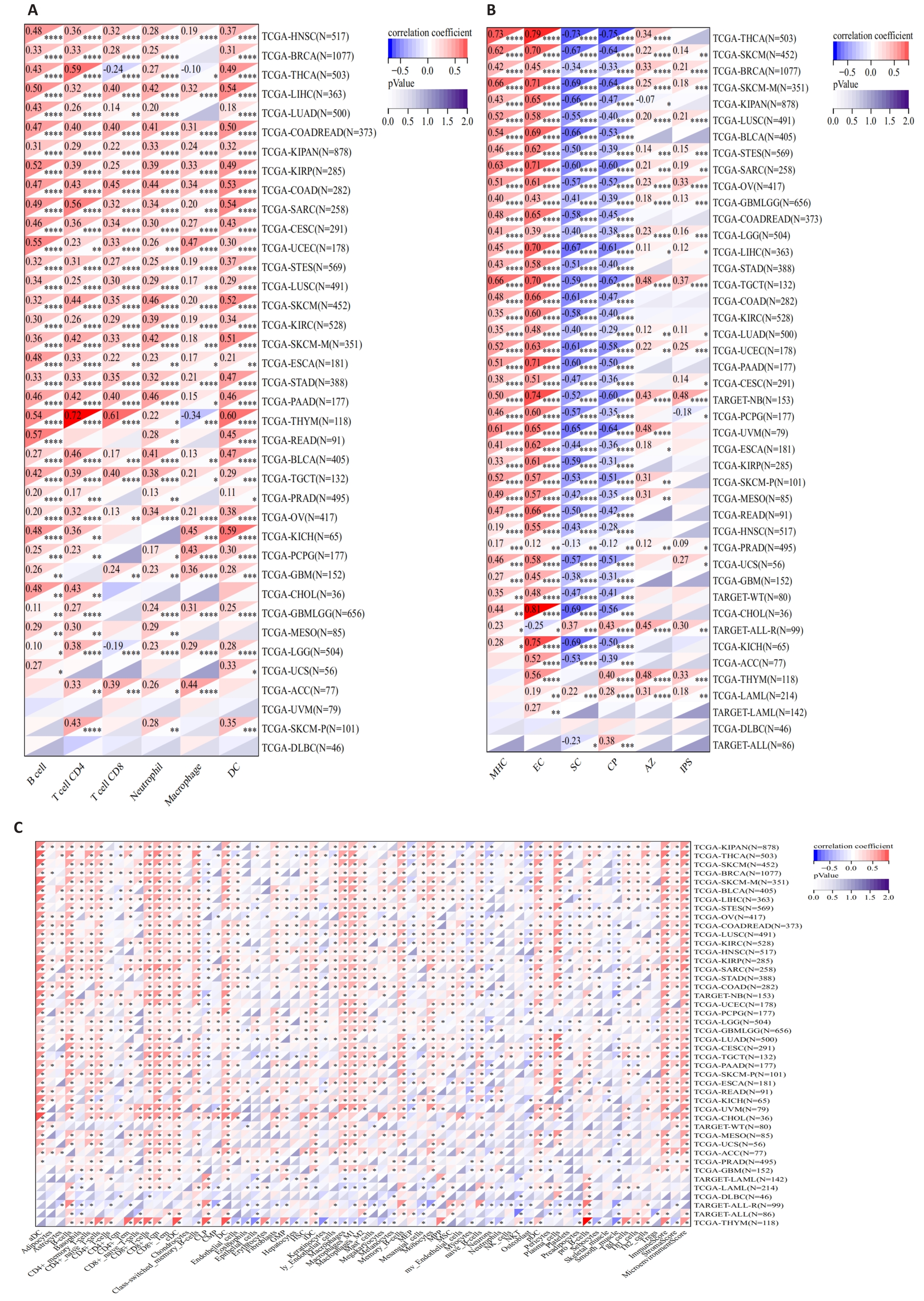
图5 MZB1与泛癌中免疫细胞浸润水平的相关性
Fig.5 Correlation between MZB1 and immune cell infiltration levels in pan-cancer. A: TIMER. B: IPS. C: xCELL. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
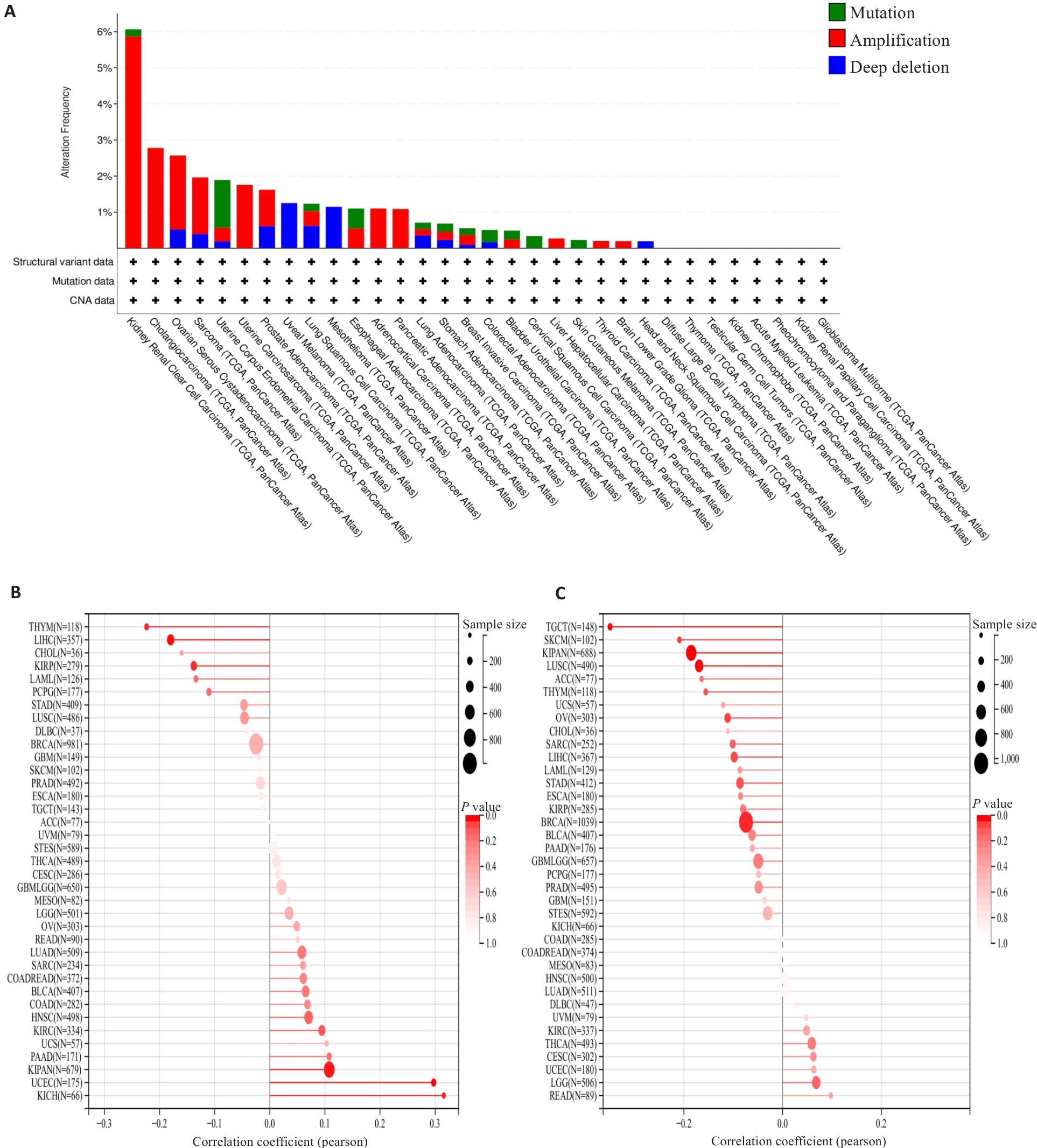
图6 MZB1的突变分析以及与TMB、MSI的相关性
Fig.6 Mutation analysis of MZB1 and its correlation with TMB and MSI. A. Mutation analysis of MZB1 in tumors. B: Correlation of MZB1 with tumor TMB. C: Correlation of MZB1 with tumor MSI.
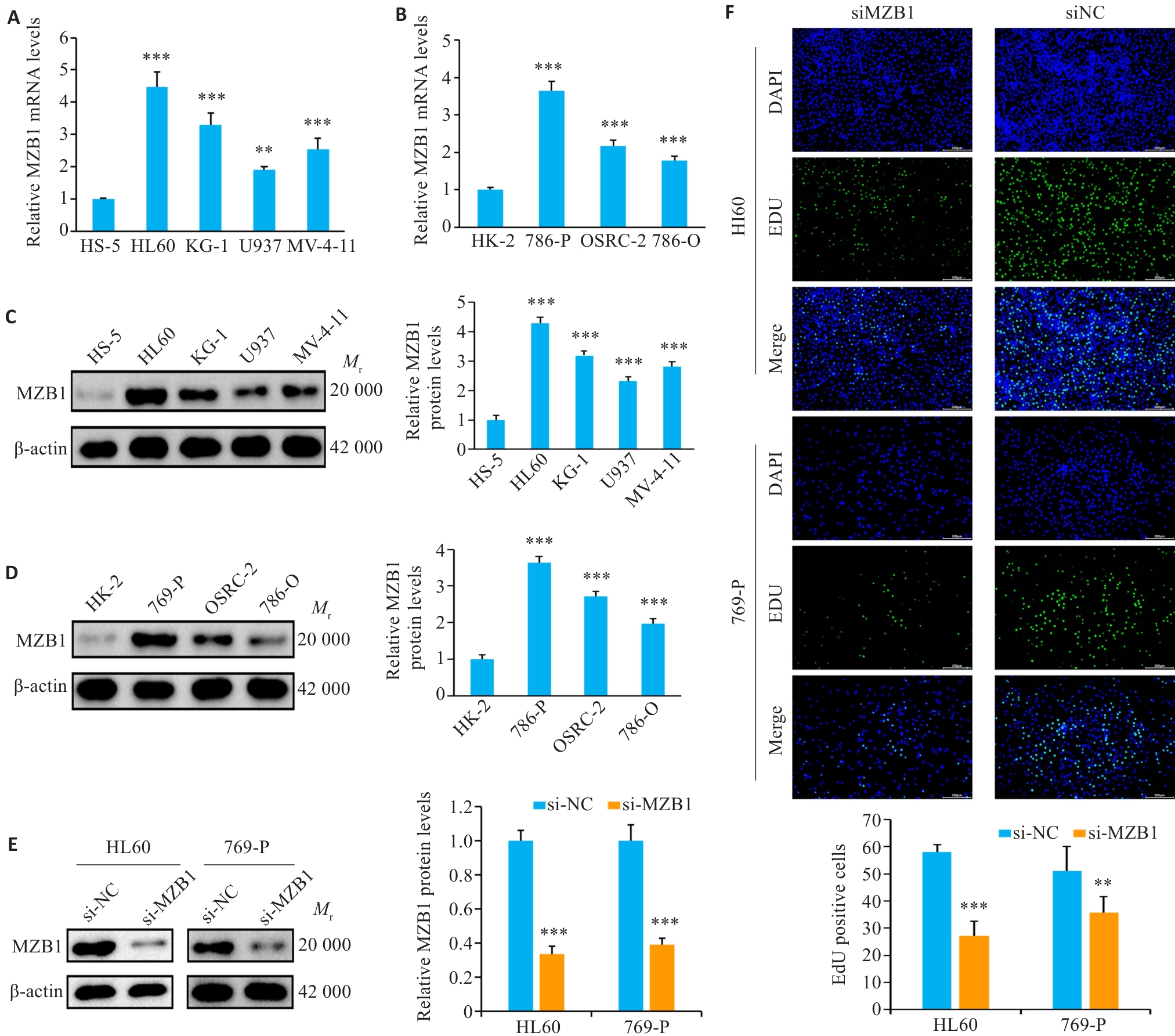
图8 体外验证MZB1在白血病和肾癌细胞系中的表达及体外实验验证
Fig. 8 In vitro validation of MZB1 expression and functional assays in leukemia and renal carcinoma cell lines. A-D: Expression of MZB1 in leukemia and renal carcinoma cell lines determined using RT-qPCR and Western blotting. E: Expression levels of MZB1 in HL60 and 769-P cells following MZB1 knockdown. F: Changes in cell proliferation capacity after MZB1 knockdown assessed using EdU assay (scale bar= 200 μm). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs HS-5/HK-2/si-NC.
| [1] | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-63. doi:10.3322/caac.21834 |
| [2] | Li QR, Xia CF, Li H, et al. Disparities in 36 cancers across 185 countries: secondary analysis of global cancer statistics[J]. Front Med, 2024, 18(5): 911-20. doi:10.1007/s11684-024-1058-6 |
| [3] | Rui R, Zhou LQ, He SM. Cancer immunotherapies: advances and bottlenecks[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1212476. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1212476 |
| [4] | Gauci ML, Lanoy E, Champiat S, et al. Long-term survival in patients responding to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy and disease outcome upon treatment discontinuation[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 25(3): 946-56. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-18-0793 |
| [5] | Wei H, Wang JY. Role of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in IgA and IgM transcytosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(5): 2284. doi:10.3390/ijms22052284 |
| [6] | Kapoor T, Corrado M, Pearce EL, et al. MZB1 enables efficient interferon α secretion in stimulated plasmacytoid dendritic cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 21626. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78293-3 |
| [7] | Rosenbaum M, Andreani V, Kapoor T, et al. MZB1 is a GRP94 cochaperone that enables proper immunoglobulin heavy chain biosynthesis upon ER stress[J]. Genes Dev, 2014, 28(11): 1165-78. doi:10.1101/gad.240762.114 |
| [8] | Flach H, Rosenbaum M, Duchniewicz M, et al. Mzb1 protein regulates calcium homeostasis, antibody secretion, and integrin activation in innate-like B cells[J]. Immunity, 2010, 33(5): 723-35. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2010.11.013 |
| [9] | Xiong EM, Li YQ, Min Q, et al. MZB1 promotes the secretion of J-chain-containing dimeric IgA and is critical for the suppression of gut inflammation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2019, 116(27): 13480-9. doi:10.1073/pnas.1904204116 |
| [10] | Xu MT, Feng Y, Xiang XL, et al. MZB1 regulates cellular proliferation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation and targets the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in acute pancreatitis[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 118: 111143. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111143 |
| [11] | Herold T, Mulaw MA, Jurinovic V, et al. High expression of MZB1 predicts adverse prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and is associated with a unique gene expression signature[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2013, 54(8): 1652-7. doi:10.3109/10428194.2012.753445 |
| [12] | Zhai YY, Chen YL, Li QZ, et al. Exploration of the hub genes and miRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(2): 1713-22. |
| [13] | Chanukuppa V, Paul D, Taunk K, et al. Proteomics and functional study reveal marginal zone B and B1 cell specific protein as a candidate marker of multiple myeloma[J]. Int J Oncol, 2020, 57(1): 325-37. doi:10.3892/ijo.2020.5056 |
| [14] | Watanabe M, Shibata M, Inaishi T, et al. MZB1 expression indicates poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(5): 198. doi:10.3892/ol.2020.12059 |
| [15] | Ji C, Li YM, Yang K, et al. Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma[J]. Open Med (Wars), 2020, 15(1): 531-9. doi:10.1515/med-2020-0190 |
| [16] | Liu JF, Lichtenberg T, Hoadley KA, et al. An integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(2): 400-16.e11. |
| [17] | Malta TM, Sokolov A, Gentles AJ, et al. Machine learning identifies stemness features associated with oncogenic dedifferentiation[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(2): 338-54.e15. |
| [18] | Zeng DQ, Ye ZL, Shen RF, et al. IOBR: multi-omics immuno-oncology biological research to decode tumor microenvironment and signatures[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 687975. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.687975 |
| [19] | Beroukhim R, Mermel CH, Porter D, et al. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7283): 899-905. |
| [20] | Bonneville R, Krook MA, Kautto EA, et al. Landscape of microsatellite instability across 39 cancer types[J]. JCO Precis Oncol, 2017, 2017: PO.17.00073. doi:10.1200/po.17.00073 |
| [21] | Miyake K, Mori R, Homma Y, et al. MZB1 in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer resected after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy[J]. J Surg Res, 2017, 220: 391-401. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2017.07.003 |
| [22] | Kanda M, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, et al. Epigenetic suppression of the immunoregulator MZB1 is associated with the malignant phenotype of gastric cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2016, 139(10): 2290-8. doi:10.1002/ijc.30286 |
| [23] | Chen W. TGF-β regulation of T cells[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2023, 41: 483-512. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-101921-045939 |
| [24] | Ouyang WJ, Rutz S, Crellin NK, et al. Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2011, 29: 71-109. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101312 |
| [25] | Zhu XH, Liu D, Wang YB, et al. Salidroside suppresses nonsmall cell lung cancer cells proliferation and migration via microRNA-103-3p/Mzb1[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2020, 31(7): 663-71. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000000926 |
| [26] | Barcellos-Hoff MH, Lyden D, Wang TC. The evolution of the cancer niche during multistage carcinogenesis[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2013, 13(7): 511-8. doi:10.1038/nrc3536 |
| [27] | Song L, Ouyang ZY, Cohen D, et al. Comprehensive characterizations of immune receptor repertoire in tumors and cancer immunotherapy studies[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2022, 10(7): 788-99. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.cir-21-0965 |
| [28] | Kontomanolis EN, Koutras A, Syllaios A, et al. Role of oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes in carcinogenesis: a review[J]. Anticancer Res, 2020, 40(11): 6009-15. doi:10.21873/anticanres.14622 |
| [29] | Picard E, Verschoor CP, Ma GW, et al. Relationships between immune landscapes, genetic subtypes and responses to immunotherapy in colorectal cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 369. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00369 |
| [1] | 何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [2] | 王莹, 李静, 王伊迪, 华明钰, 胡玮彬, 张晓智. 原发性肝癌患者的临床结局与治疗反应预测模型:基于失巢凋亡和免疫基因[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [3] | 王子良, 陈孝华, 杨晶晶, 严晨, 张志郅, 黄炳轶, 赵萌, 刘嵩, 葛思堂, 左芦根, 陈德利. 高表达SURF4通过抑制紧密连接蛋白表达促进胃癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742. |
| [4] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [5] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [6] | 王康, 李海宾, 余靖, 孟源, 张虹丽. ELFN1高表达是结肠癌的预后生物标志物并促进结肠癌细胞的增殖转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [7] | 郭晓娟, 杜瑞娟, 陈丽平, 郭克磊, 周彪, 卞华, 韩立. WW结构域E3泛素连接酶1调控卵巢癌肿瘤微环境中的免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1063-1073. |
| [8] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [9] | 高志, 吴傲, 胡仲翔, 孙培养. 类风湿性关节炎中氧化应激与免疫浸润的生物信息学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [10] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [11] | 李华莉, 宋婷, 刘嘉雯, 李永宝, 姜兆静, 窦文, 周凌宏. 预后导向的肺癌调强放疗计划优化新方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [12] | 宋雪, 陈悦, 张敏, 张诺, 左芦根, 李静, 耿志军, 张小凤, 王月月, 王炼, 胡建国. GPSM2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过促进肿瘤细胞的增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | 唐天威, 李路安, 陈源汉, 张丽, 徐丽霞, 李志莲, 冯仲林, 张辉林, 华瑞芳, 叶智明, 梁馨苓, 李锐钊. 高血清胱抑素C水平是IgA肾病不良预后的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [14] | 陈晓睿, 魏青政, 张宗亮, 原江水, 宋卫青. 过表达带电多泡体蛋白2B基因抑制肾透明细胞癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [15] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||