南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2456-2465.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.18
黄晴晴1,4( ), 杨晶晶4, 姜雪凝4, 张文静1, 汪煜4, 左芦根2,4, 王炼2,4, 王月月1,4, 张小凤3,4, 宋雪3,4, 胡建国1,4(
), 杨晶晶4, 姜雪凝4, 张文静1, 汪煜4, 左芦根2,4, 王炼2,4, 王月月1,4, 张小凤3,4, 宋雪3,4, 胡建国1,4( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-15
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-11-28
通讯作者:
胡建国
E-mail:hqq10100@163.com;jghu9200@bbmc.edu.cn
作者简介:黄晴晴,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: hqq10100@163.com
基金资助:
Qingqing HUANG1,4( ), Jingjing YANG4, Xuening JIANG4, Wenjing ZHANG1, Yu WANG4, Lugen ZUO2,4, Lian WANG2,4, Yueyue WANG1,4, Xiaofeng ZHANG3,4, Xue SONG3,4, Jianguo HU1,4(
), Jingjing YANG4, Xuening JIANG4, Wenjing ZHANG1, Yu WANG4, Lugen ZUO2,4, Lian WANG2,4, Yueyue WANG1,4, Xiaofeng ZHANG3,4, Xue SONG3,4, Jianguo HU1,4( )
)
Received:2025-04-15
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Jianguo HU
E-mail:hqq10100@163.com;jghu9200@bbmc.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨刺桐碱(HYP)对小鼠克罗恩病(CD)样结肠炎的作用及其分子机制。 方法 本研究采用2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸(TNBS)诱导构建小鼠CD样结肠炎模型。将30只C57BL/6J雄性小鼠随机分为3组:WT组、TNBS组和HYP组,10只/组。TNBS组和HYP组采用TNBS诱导结肠炎,HYP组每日灌胃15 mg/kg HYP,其余2组给予等量生理盐水。通过疾病活动指数(DAI)评分、体质量变化、结肠长度及组织病理学评分等指标,评估HYP对小鼠CD样结肠炎的治疗效果。在体外实验中,采用LPS刺激的Caco-2细胞建立肠上皮炎症模型,分为Control组、LPS组和LPS+HYP组。采用qRT-PCR、免疫荧光等技术检测HYP对肠上皮炎症反应及屏障功能的影响。进一步通过GO和KEGG富集分析预测HYP的作用机制,并利用Western blotting验证关键信号通路的调控。 结果 体内研究结果显示,HYP干预可改善TNBS诱导的小鼠结肠炎症状,具体表现为:体质量下降趋势减缓、结肠长度缩短程度改善、DAI评分及组织炎症评分降低,同时结肠黏膜中促炎因子表达水平下调(P<0.05)。在肠屏障功能方面,HYP干预后TNBS模型小鼠结肠组织TEER值升高,细菌移位率(肠系膜淋巴结、肝脏、脾脏)降低,血清中I-FABP和FITC-Dextran的浓度下降(P<0.05)。此外,HYP干预还可增加结肠组织杯状细胞数量,并上调MUC2和紧密连接蛋白(Claudin-1、ZO-1)表达(P<0.05)。体外研究结果显示,与LPS组相比,HYP处理可抑制Caco-2细胞促炎因子表达并恢复紧密连接蛋白水平(P<0.05)。Western blotting分析显示,HYP在体内外模型中均能下调TLR4/MyD88信号通路关键蛋白的表达(P<0.05)。 结论 HYP可能通过抑制肠上皮炎症反应并改善肠屏障功能,从而缓解小鼠CD样结肠炎。
黄晴晴, 杨晶晶, 姜雪凝, 张文静, 汪煜, 左芦根, 王炼, 王月月, 张小凤, 宋雪, 胡建国. 刺桐碱通过抑制肠上皮炎症反应并改善肠屏障功能缓解小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2456-2465.
Qingqing HUANG, Jingjing YANG, Xuening JIANG, Wenjing ZHANG, Yu WANG, Lugen ZUO, Lian WANG, Yueyue WANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Xue SONG, Jianguo HU. Hypaphorine alleviates Crohn's disease-like colitis in mice by inhibiting intestinal epithelial inflammatory response and protecting intestinal barrier function[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2456-2465.
| Gene name | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
| TNF-α | Forward:5'-CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC-3' |
| Reverse:5'-CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG-3' | |
| IL-6 | Forward:5'-TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA-3' |
| Reverse:5'-GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT-3' | |
| IL-1β | Forward:5'-GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG-3' |
| Reverse:5'-TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG-3' | |
| GAPDH | Forward:5'-AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG-3' |
| Reverse:5'-GGGGTCGTTGATGGCAACA-3' |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR in this study
| Gene name | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
| TNF-α | Forward:5'-CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC-3' |
| Reverse:5'-CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG-3' | |
| IL-6 | Forward:5'-TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA-3' |
| Reverse:5'-GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT-3' | |
| IL-1β | Forward:5'-GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG-3' |
| Reverse:5'-TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG-3' | |
| GAPDH | Forward:5'-AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG-3' |
| Reverse:5'-GGGGTCGTTGATGGCAACA-3' |

图1 HYP给药可缓解TNBS模型小鼠CD样结肠炎
Fig.1 HYP treatment alleviates CD-like colitis in TNBS-treated mice. A: Body weight changes. B: DAI score. C: Gross observation of the dissected colon from each groups. D: Colon length in each group. E: HE staining of colonic sections of the mice from each group (scale bar=1 mm or 100 μm). F: Colonic inflammation scores in each group. *P<0.05 vs WT, #P<0.05 vs TNBS.

图2 HYP给药降低TNBS模型小鼠结肠黏膜中炎症介质水平
Fig.2 HYP treatment reduces the levels of inflammatory mediators in the colonic mucosa of TNBS-treated mice. A-C: Expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNAs in mouse colonic mucosal tissue. D-F: Expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β proteins in mouse colonic mucosal tissue. *P<0.05 vs WT, #P<0.05 vs TNBS.

图3 HYP给药改善TNBS模型小鼠肠屏障损伤
Fig.3 HYP ameliorates intestinal barrier damage in TNBS-treated mice. A: TEER values of mouse colon tissues in each group. B-D: Bacterial translocation rate in the mesenteric lymph nodes, liver, and spleen. E, F: Serum levels of I-FABP and FD4 in each group. G: AB-PAS and immunohistochemical staining of colonic sections (scale bar=100 μm). H, I: Number of goblet cells per crypt and MUC2 expression level in mouse colon tissue in the 3 groups. J, L: Immunofluorescence staining of colonic sections from each group (scale bar=100 μm). K, M: Expression levels of claudin-1 and ZO-1 in mouse colon tissues in each group. *P<0.05 vs WT, #P<0.05 vs TNBS.
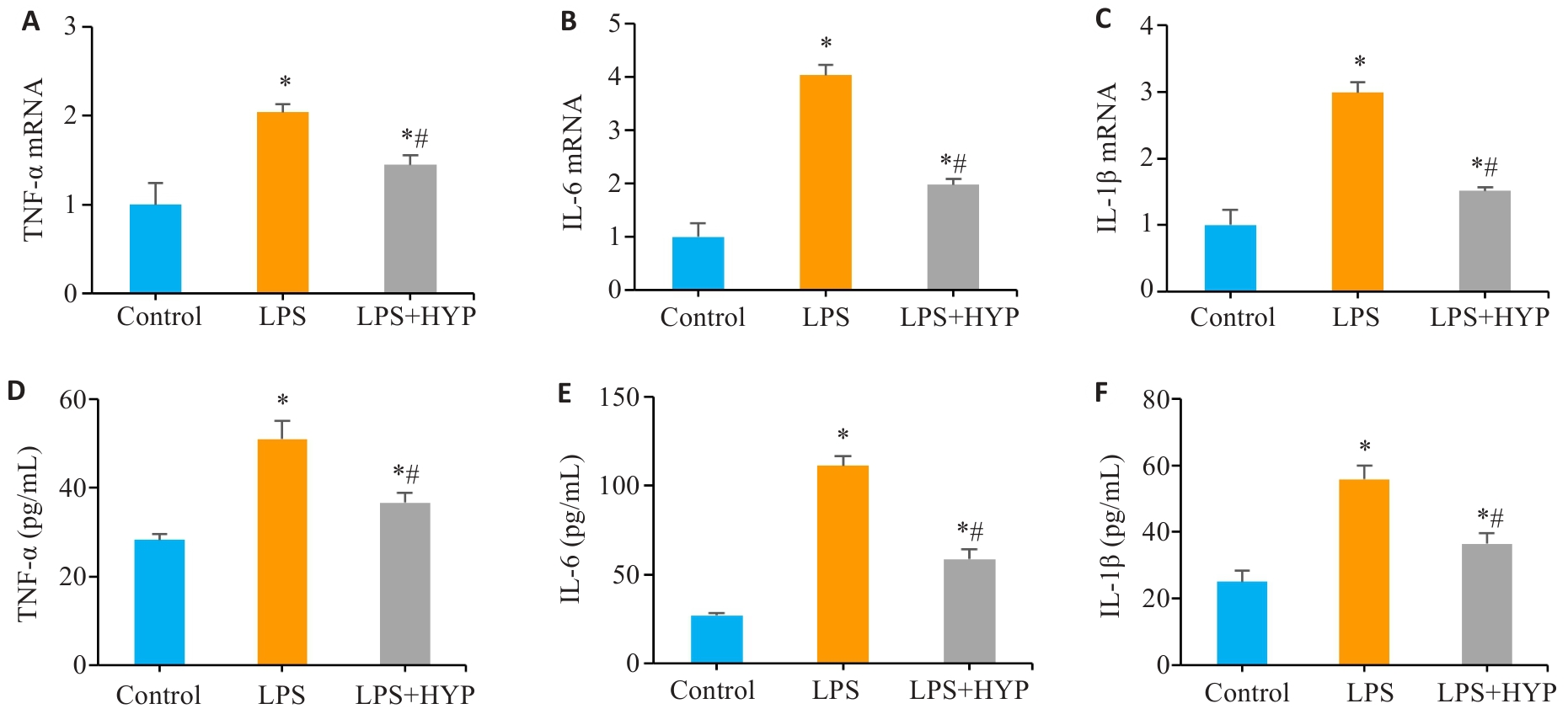
图4 HYP干预降低LPS诱导的Caco-2细胞中炎症介质水平
Fig.4 HYP treatment reduces inflammatory mediator levels in LPS-induced Caco-2 cells. A-C: Expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNAs in Caco-2 cells with different treatments. D-F: Protein levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in Caco-2 cells with different treatments. *P<0.05 vs Control, #P<0.05 vs LPS.
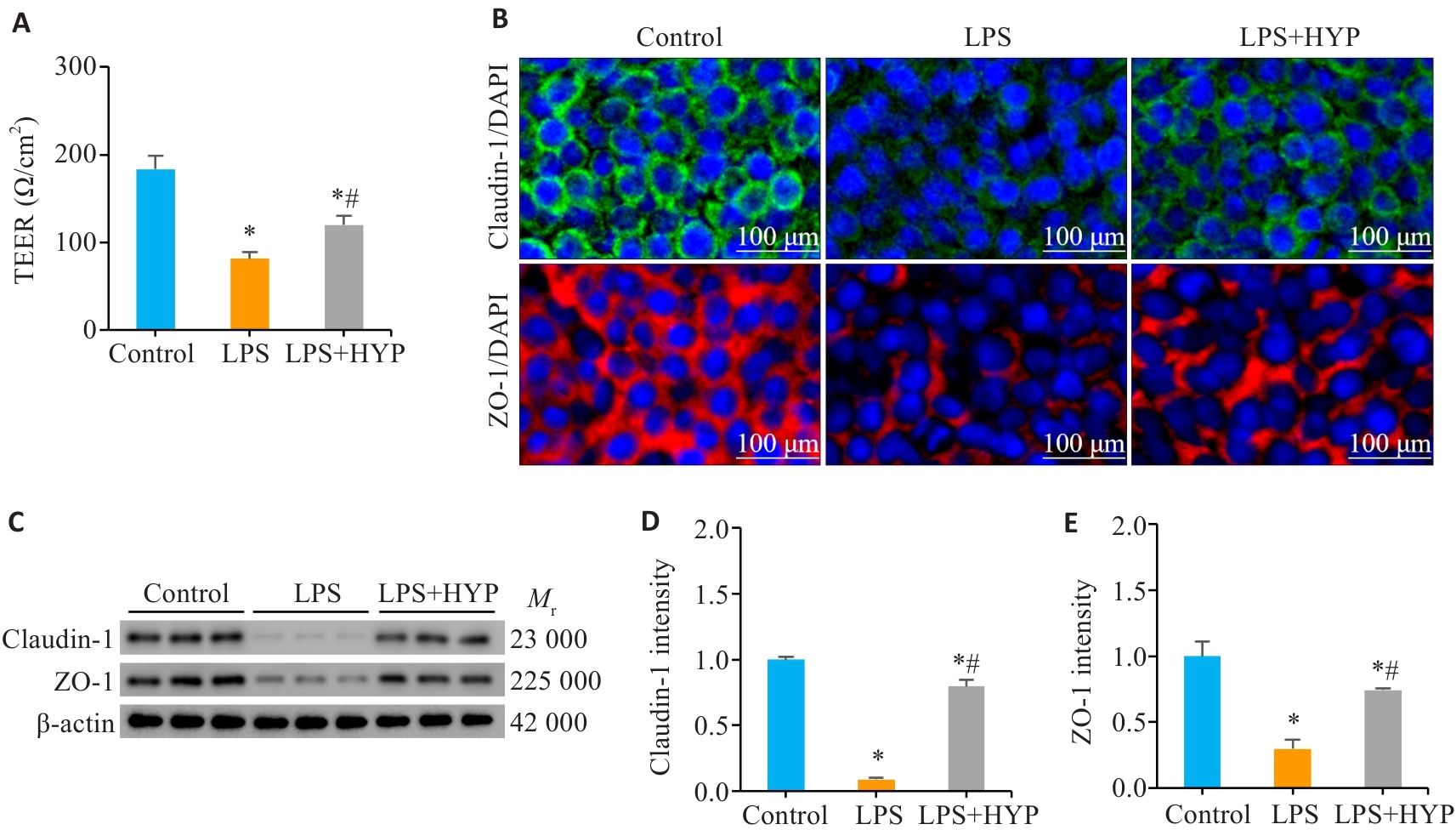
图5 HYP干预改善LPS诱导的Caco-2细胞屏障损伤
Fig.5 HYP treatment ameliorates LPS-induced barrier damage in Caco-2 cells. A: TEER value of Caco-2 cells. B: Immunofluorescence staining of Caco-2 cells with different treatments (scale bar=100 μm). C-E: Expression levels of claudin-1 and ZO-1 in Caco-2 cells with different treatments. *P<0.05 vs Control, #P<0.05 vs LPS.

图6 HYP缓解CD样肠炎可能与炎症反应和TLR信号通路有关
Fig.6 Therapeutic mechanism of HYP for CD may involve inflammatory response and TLR signaling pathway. A, B: GO and KEGG enrichment analyses.
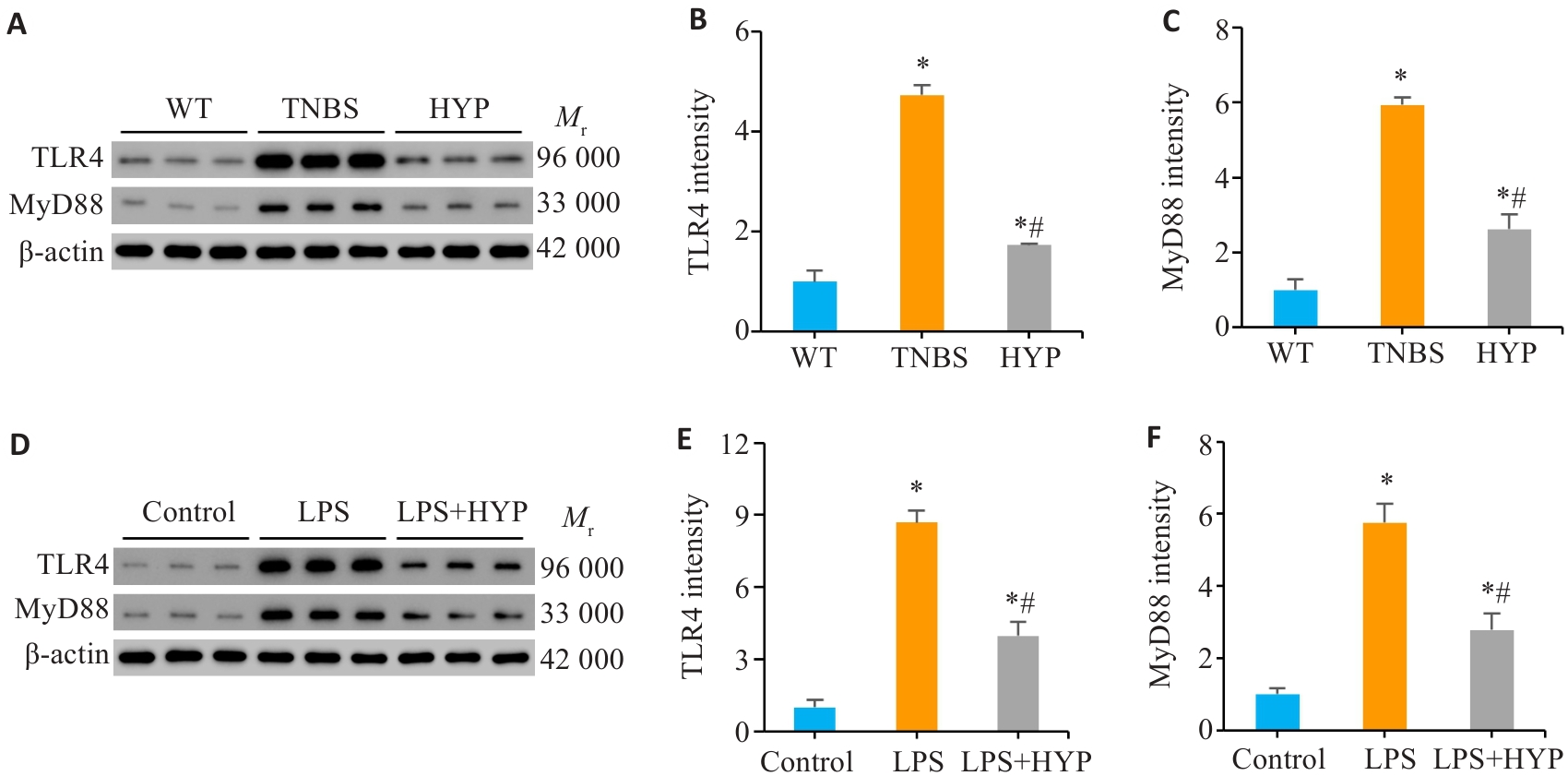
图7 HYP可下调TLR4/MyD88信号通路
Fig.7 HYP downregulates the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in both the mouse and cell models. A-C: Protein levels of TLR4 and MyD88 in mouse colonic mucosa tissues. D-F: Protein levels of TLR4 and MyD88 in Caco-2 cells with different treatments. *P<0.05 vs WT or Control, #P<0.05 vs TNBS or LPS.
| [1] | Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, et al. Crohn's disease[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10080): 1741-55. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31711-1 |
| [2] | Roda G, Chien Ng S, Kotze PG, et al. Crohn's disease[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6(1): 22. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-0156-2 |
| [3] | Leibovitzh H, Lee SH, Raygoza Garay JA, et al. Immune response and barrier dysfunction-related proteomic signatures in preclinical phase of Crohn's disease highlight earliest events of pathogenesis[J]. Gut, 2023, 72(8): 1462-71. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328421 |
| [4] | Song X, Zhang XF, Zhang M, et al. The JNK/P38 signalling pathway activated by testin protects the intestinal epithelial barrier against Crohn's disease-like colitis[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2024, 403: 111222. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111222 |
| [5] | Yang Y, Guo LQ, Wei L, et al. Da-Yuan-Yin decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting complement activation, LPS-TLR4/NF‑κB signaling pathway and NET formation[J]. J Ethno-pharmacol, 2024, 332: 118392. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118392 |
| [6] | Wang Y, Li M, Zha AS. Adjuvant treatment of Crohn's disease with traditional Chinese medicine: a meta-analysis[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2019, 2019: 6710451. doi:10.1155/2019/6710451 |
| [7] | Gomollón F, Dignass A, Annese V, et al. 3rd European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn's disease 2016: part 1: diagnosis and medical management[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2017, 11(1): 3-25. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw168 |
| [8] | Spinelli A, Sacchi M, Fiorino G, et al. Risk of postoperative recurrence and postoperative management of Crohn's disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2011, 17(27): 3213-9. |
| [9] | Cushing K, Higgins PDR. Management of crohn disease: a review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(1): 69-80. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.18936 |
| [10] | Doherty G, Katsanos KH, Burisch J, et al. European Crohn's and colitis organisation topical review on treatment withdrawal ['Exit strategies'] in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2018, 12(1): 17-31. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx101 |
| [11] | Barnes EL. Postoperative Crohn's disease management[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2020, 36(4): 277-83. doi:10.1097/mog.0000000000000638 |
| [12] | Xie J, Huang Y, Wu HG, et al. Acupuncture and moxibustion for treatment of Crohn's disease: a brief review[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(25): 3001-3. doi:10.3748/wjg.v28.i25.3001 |
| [13] | Yuan S, Li Y, Li J, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine and natural products: potential approaches for inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 892790. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.892790 |
| [14] | Sałaga M, Zatorski H, Sobczak M, et al. Chinese herbal medicines in the treatment of IBD and colorectal cancer: a review[J]. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2014, 15(3): 405-20. doi:10.1007/s11864-014-0288-2 |
| [15] | Zhang ZN, Zuo LG, Song X, et al. Arjunolic acid protects the intestinal epithelial barrier, ameliorating Crohn’s disease-like colitis by restoring gut microbiota composition and inactivating TLR4 signalling[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 123: 155223. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155223 |
| [16] | 马博凯, 钱 冲, 王茂媛, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定药材牛大力中刺桐碱、芒柄花素和高丽槐素[J]. 分析科学学报, 2022, 38(2): 203-8. |
| [17] | 曹斯琼, 吴文平, 罗宇琴, 等. 王不留行炮制前后的UPLC指纹图谱比较及刺桐碱和王不留行黄酮苷的含量测定[J]. 中国药房, 2020, 31(19): 2365-70. |
| [18] | Sun H, Zhu X, Cai W, et al. Hypaphorine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial inflammation via regulation of TLR4 and PPAR-γ dependent on PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(4): E844. doi:10.3390/ijms18040844 |
| [19] | Ding YH, Miao RX, Zhang Q. Hypaphorine exerts anti-inflammatory effects in sepsis induced acute lung injury via modulating DUSP1/p38/JNK pathway[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2021, 37(10): 883-93. doi:10.1002/kjm2.12418 |
| [20] | Li QQ, Li J, Yin LX, et al. Sophoricoside improved Crohn's disease-like colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 131: 111886. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111886 |
| [21] | Zhang Y, Huang J, Gan L, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of Niudali (Callerya speciosa) root aqueous extracts against tetrachloro-methane-induced acute liver injury and inflammation[J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2023, 11(11): 7026-38. doi:10.1002/fsn3.3626 |
| [22] | 蔡维维, 侯 豹, 陈旭红, 等. 王不留行中刺桐碱的分离鉴定及抗炎活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2018, 30(4): 616-20. |
| [23] | Wang L, Song X, Zhou YQ, et al. Sclareol protected against intestinal barrier dysfunction ameliorating Crohn's disease-like colitis via Nrf2/NF-B/MLCK signalling[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 133: 112140. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112140 |
| [24] | Yang T, Liu DD, Li YL, et al. Chemoproteomics reveals Sofalcone inhibits the inflammatory response of Caco-2 cells by covalently targeting HMGB1[J]. Chem Commun, 2023, 59(58): 8981-4. doi:10.1039/d3cc00577a |
| [25] | Geng Z, Zuo L, Li J, et al. Ginkgetin improved experimental colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(14): e23817. doi:10.1096/fj.202400211rr |
| [26] | Neurath M, Fuss I, Strober W. TNBS-colitis[J]. Int Rev Immunol, 2000, 19(1): 51-62. doi:10.3109/08830180009048389 |
| [27] | Antoniou E, Margonis GA, Angelou A, et al. The TNBS-induced colitis animal model: an overview[J]. Ann Med Surg, 2016, 11: 9-15. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2016.07.019 |
| [28] | 蔡维维, 张仕杰, 文嫄媛, 等. 刺桐碱促伤口愈合的网络药理学分析及实验验证[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2024, 36(11):1959-71,1958. |
| [29] | Matar A, Damianos JA, Jencks KJ, et al. Intestinal barrier impairment, preservation, and repair: an update[J]. Nutrients, 2024, 16(20): 3494. doi:10.3390/nu16203494 |
| [30] | Neurath MF, Artis D, Becker C. The intestinal barrier: a pivotal role in health, inflammation, and cancer[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2025, 10(6): 573-92. doi:10.1016/s2468-1253(24)00390-x |
| [31] | Qiao YR, He CE, Xia YX, et al. Intestinal mucus barrier: a potential therapeutic target for IBD[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2025, 24(2): 103717. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103717 |
| [32] | Wang Z, Shen J. The role of goblet cells in Crohn' s disease[J]. Cell Biosci, 2024, 14(1): 43. doi:10.1186/s13578-024-01220-w |
| [33] | Macura B, Kiecka A, Szczepanik M. Intestinal permeability disturbances: causes, diseases and therapy[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2024, 24(1): 232. doi:10.1007/s10238-024-01496-9 |
| [34] | Luo X, Yu Z, Deng C, et al. Baicalein ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by suppressing TLR4/MyD88 signaling cascade and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 16374. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12562-6 |
| [35] | Li CZ, Xi YB, Li S, et al. Berberine ameliorates TNBS induced colitis by inhibiting inflammatory responses and Th1/Th17 differentiation[J]. Mol Immunol, 2015, 67(2): 444-54. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2015.07.013 |
| [36] | Shen JC, Qi Q, Han D, et al. Moxibustion improves experimental colitis in rats with Crohn's disease by regulating bile acid enterohepatic circulation and intestinal farnesoid X receptor[J]. J Integr Med, 2023, 21(2): 194-204. doi:10.1016/j.joim.2023.01.001 |
| [37] | Stephens M, von der Weid PY. Lipopolysaccharides modulate intestinal epithelial permeability and inflammation in a species-specific manner[J]. Gut Microbes, 2020, 11(3): 421-32. doi:10.1080/19490976.2019.1629235 |
| [38] | Pereira M, Durso DF, Bryant CE, et al. The IRAK4 scaffold integrates TLR4-driven TRIF and MYD88 signaling pathways[J]. Cell Rep, 2022, 40(7): 111225. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111225 |
| [39] | Endale M, Park SC, Kim S, et al. Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF‑κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells[J]. Immunobiology, 2013, 218(12): 1452-67. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019 |
| [1] | 何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [2] | 刘辰菲, 张玮, 曾尧, 梁艳, 王梦婷, 张明芳, 李新元, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1654-1662. |
| [3] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [4] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [5] | 申琳, 宋翠豪, 王聪敏, 高西, 安俊红, 李承新, 梁斌, 李霞. 溃疡性结肠炎并发坏疽性脓皮病患者发生营养风险的因素及预测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 514-521. |
| [6] | 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 张可妮, 耿志军, 胡建国, 李江艳, 李静. 升麻素抑制MAPK通路调节辅助性T细胞免疫平衡改善小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [7] | 黄菊, 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 耿志军, 左芦根, 李静, 胡建国. 紫花前胡苷通过抑制肠上皮细胞焦亡改善2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [8] | 陶露, 陈悦, 黄林林, 郑旺, 宋雪, 项平, 胡建国. 珠子草素通过调控p38/JNK信号通路抑制肠上皮细胞凋亡保护肠屏障改善克罗恩病样肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2483-2495. |
| [9] | 张可妮, 乔通, 尹林, 黄菊, 耿志军, 左芦根, 胡建国, 李静. 球松素靶向肠上皮细胞PI3K/AKT/CCL2轴抑制巨噬细胞肠道浸润缓解葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2199-2209. |
| [10] | 赵娜, 沈梦迪, 赵睿, 奥迪, 骆泽谭, 张银亮, 徐志东, 范方田, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控Nrf2/NF-κB通路缓解小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [11] | 于官正, 程炜强, 涂星, 张满, 李鸿, 聂娟. 隔山消治疗溃疡性结肠炎的机制:基于UPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及代谢组学技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [12] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [13] | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 张 晨, 张雨路, 王 锐, 申 林, 李 静, 宋 雪. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症:基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [14] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 段婷, 黄菊, 李静, 耿志军, 胡建国, 宋传旺. 川续断皂苷VI通过抑制PI3K/AKT/NF-κB通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡缓解TNBS诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2335-2346. |
| [15] | 邱建国, 邱一桐, 李国荣, 张林生, 郑雪, 姚泳江, 王熙丹, 黄海阳, 张凤敏, 苏冀彦, 郑学宝, 黄晓其. 黄芩汤通过调控内质网应激减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||