南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2210-2222.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.17
• • 上一篇
王锦帼1( ), 马扬2, 李赵鑫3, 何丽妃3, 黄英泽4(
), 马扬2, 李赵鑫3, 何丽妃3, 黄英泽4( ), 范晓明5(
), 范晓明5( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-23
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
通讯作者:
黄英泽,范晓明
E-mail:wangjinguo401@alu.glmc.edu.cn;youshxicun@glmc.edu.cn;fanxiaom1987@ glmc.edu.cn
作者简介:王锦帼,硕士,E-mail: wangjinguo401@alu.glmc.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jinguo WANG1( ), Yang MA2, Zhaoxin LI3, Lifei HE3, Yingze HUANG4(
), Yang MA2, Zhaoxin LI3, Lifei HE3, Yingze HUANG4( ), Xiaoming FAN5(
), Xiaoming FAN5( )
)
Received:2025-04-23
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Yingze HUANG, Xiaoming FAN
E-mail:wangjinguo401@alu.glmc.edu.cn;youshxicun@glmc.edu.cn;fanxiaom1987@ glmc.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 研究PDZ结合激酶(PBK)在胰腺癌(包含33种癌症类型)中的表达及其预后意义,并探索其作为治疗靶点的潜力。 方法 采用TCGA、GEO和CPTAC数据库对33种肿瘤组织中PBK的表达进行分析,采用RT-PCR、Western blotting对胰腺癌临床标本及细胞中PBK的表达进行分析。通过生存分析、Cox回归分析、ROC曲线分析和临床相关性研究评估其对胰腺癌的诊断和预后价值。通过基因富集和免疫相关性分析来探讨PBK在肿瘤微环境中的潜在作用。通过对GDSC及CTRP的数据集的分析,研究PBK表达与药物敏感性的关系。通过慢病毒沉默方法建立沉默PBK的胰腺癌BXPC-3的稳定细胞系。采用CCK-8、细胞克隆、transwell实验检测沉默PBK后,对胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响。采用免疫共沉淀和Western blotting研究PBK与非SMC凝聚素II复合亚基G2(NCAPG2)的相互作用。 结果 PBK在多种癌症组织及胰腺癌中过表达(P<0.05),具有较高的诊断价值,PBK的高表达与不良预后相关(P<0.05)。PBK的高表达还与免疫浸润和肿瘤微环境特征的改变有关。PBK高表达对MEK抑制剂(曲美替尼)及EGFR抑制剂(阿法替尼)的敏感性呈正相关,但对Bcl-2抑制剂(TW37)及氯硝柳胺的敏感性呈负相关(P<0.05)。进一步敲低PBK抑制了NCAPG2的表达,且抑制了胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭(P<0.05)。免疫共沉淀显示PBK能够与NCAPG2直接结合。 结论 PBK是胰腺癌的关键调节因子,并与NCAPG2相互作用,促进胰腺癌的进展。它可能作为胰腺癌的潜在生物标志物和治疗靶点,同时为泛癌症研究提供新的见解。
王锦帼, 马扬, 李赵鑫, 何丽妃, 黄英泽, 范晓明. PDZ结合激酶作为胰腺癌潜在预后标志物:从泛癌分析到胰腺癌验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2210-2222.
Jinguo WANG, Yang MA, Zhaoxin LI, Lifei HE, Yingze HUANG, Xiaoming FAN. PDZ-binding kinase as a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer: a pan-cancer analysis and validation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2210-2222.
| Name | Detail | Tumor (TCGA) | Normal (source) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Adrenocortical carcinoma | 77 | 77 (adrenal gland, GTEx) |
| BLCA | Bladder urothelial carcinoma | 406 | 19 (TCGA) |
| BRCA | Breast invasive carcinoma | 1085 | 99 (TCGA) |
| CESC | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma | 306 | 13 (cervix uteri, GTEx) |
| CHOL | Cholangio carcinoma | 36 | 9 (TCGA) |
| COAD | Colon adenocarcinoma | 448 | 41 (TCGA) |
| DLBC | Lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | 47 | 47 (whole blood, GTEx) |
| ESCA | Esophageal carcinoma | 182 | 13 (TCGA) |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme | 167 | 163 (brain cortex, GTEx) |
| HNSC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | 519 | 44 (TCGA) |
| KICH | Kidney chromophobe | 66 | 25 (TCGA) |
| KIRC | Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma | 531 | 25 (TCGA) |
| KIRP | Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma | 286 | 32 (TCGA) |
| LAML | Acute myeloid Leukemia | 173 | 173 (whole blood, GTEx) |
| LGG | Brain lower grade glioma | 524 | 255 (brain cortex, GTEx) |
| LIHC | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma | 369 | 50 (TCGA) |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma | 513 | 59 (TCGA) |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | 486 | 50 (TCGA) |
| MESO | Mesothelioma | 87 | 87 (heart atrial appendage, GTEx) |
| OV | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | 426 | 180 (ovary, GTEx) |
| PAAD | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | 178 | 4 (TCGA) |
| PCPG | Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma | 183 | 182 (adrenal gland, GTEx) |
| PRAD | Prostate adenocarcinoma | 499 | 52 (TCGA) |
| READ | Rectum adenocarcinoma | 158 | 10 (TCGA) |
| SARC | Sarcoma | 262 | 262 (adipose subcutaneous, GTEx) |
| SKCM | Skin cutaneous melanoma | 461 | 461 (skin sun exposed lower, GTEx) |
| STAD | Stomach adenocarcinoma | 408 | 36 (TCGA) |
| TGCT | Testicular germ cell tumors | 139 | 137 (testis, GTEx) |
| THCA | Thyroid carcinoma | 512 | 59 (TCGA) |
| THYM | Thymoma | 118 | 118 (whole blood, GTEx) |
| UCEC | Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma | 544 | 35 (TCGA) |
| UCS | Uterine carcinosarcoma | 57 | 57 (uterus, GTEx) |
| UVM | Uveal melanoma | 80 | 79 (EyeGEx retina, GTEx) |
| GSE15471 | 39 (GEO) | 39 (GEO) | |
| GSE16515 | 36 (GEO) | 16 (GEO) | |
| GSE62165 | 118 (GEO) | 13 (GEO) | |
表1 来自TCGA、GEO和GTEx的样本
Tab.1 Data of the samples from TCGA, GEO and GTEx
| Name | Detail | Tumor (TCGA) | Normal (source) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Adrenocortical carcinoma | 77 | 77 (adrenal gland, GTEx) |
| BLCA | Bladder urothelial carcinoma | 406 | 19 (TCGA) |
| BRCA | Breast invasive carcinoma | 1085 | 99 (TCGA) |
| CESC | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma | 306 | 13 (cervix uteri, GTEx) |
| CHOL | Cholangio carcinoma | 36 | 9 (TCGA) |
| COAD | Colon adenocarcinoma | 448 | 41 (TCGA) |
| DLBC | Lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | 47 | 47 (whole blood, GTEx) |
| ESCA | Esophageal carcinoma | 182 | 13 (TCGA) |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme | 167 | 163 (brain cortex, GTEx) |
| HNSC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | 519 | 44 (TCGA) |
| KICH | Kidney chromophobe | 66 | 25 (TCGA) |
| KIRC | Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma | 531 | 25 (TCGA) |
| KIRP | Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma | 286 | 32 (TCGA) |
| LAML | Acute myeloid Leukemia | 173 | 173 (whole blood, GTEx) |
| LGG | Brain lower grade glioma | 524 | 255 (brain cortex, GTEx) |
| LIHC | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma | 369 | 50 (TCGA) |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma | 513 | 59 (TCGA) |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | 486 | 50 (TCGA) |
| MESO | Mesothelioma | 87 | 87 (heart atrial appendage, GTEx) |
| OV | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | 426 | 180 (ovary, GTEx) |
| PAAD | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | 178 | 4 (TCGA) |
| PCPG | Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma | 183 | 182 (adrenal gland, GTEx) |
| PRAD | Prostate adenocarcinoma | 499 | 52 (TCGA) |
| READ | Rectum adenocarcinoma | 158 | 10 (TCGA) |
| SARC | Sarcoma | 262 | 262 (adipose subcutaneous, GTEx) |
| SKCM | Skin cutaneous melanoma | 461 | 461 (skin sun exposed lower, GTEx) |
| STAD | Stomach adenocarcinoma | 408 | 36 (TCGA) |
| TGCT | Testicular germ cell tumors | 139 | 137 (testis, GTEx) |
| THCA | Thyroid carcinoma | 512 | 59 (TCGA) |
| THYM | Thymoma | 118 | 118 (whole blood, GTEx) |
| UCEC | Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma | 544 | 35 (TCGA) |
| UCS | Uterine carcinosarcoma | 57 | 57 (uterus, GTEx) |
| UVM | Uveal melanoma | 80 | 79 (EyeGEx retina, GTEx) |
| GSE15471 | 39 (GEO) | 39 (GEO) | |
| GSE16515 | 36 (GEO) | 16 (GEO) | |
| GSE62165 | 118 (GEO) | 13 (GEO) | |
| Gene name | Sequence | Tm | Amplicon length |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBK | F: TATGACTGCTCCTGCCTTCATAAC | 60 ℃ | 115 |
| R: CACAGCTTCTTTGGGTTTCCAT | |||
| GAPDH | F: TCTCTGCTCCTCCCTGTTC | 60 ℃ | 125 |
| R: ACACCGACCTTCACCATCT |
表2 实验所需引物序列
Tab.2 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR in this study
| Gene name | Sequence | Tm | Amplicon length |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBK | F: TATGACTGCTCCTGCCTTCATAAC | 60 ℃ | 115 |
| R: CACAGCTTCTTTGGGTTTCCAT | |||
| GAPDH | F: TCTCTGCTCCTCCCTGTTC | 60 ℃ | 125 |
| R: ACACCGACCTTCACCATCT |
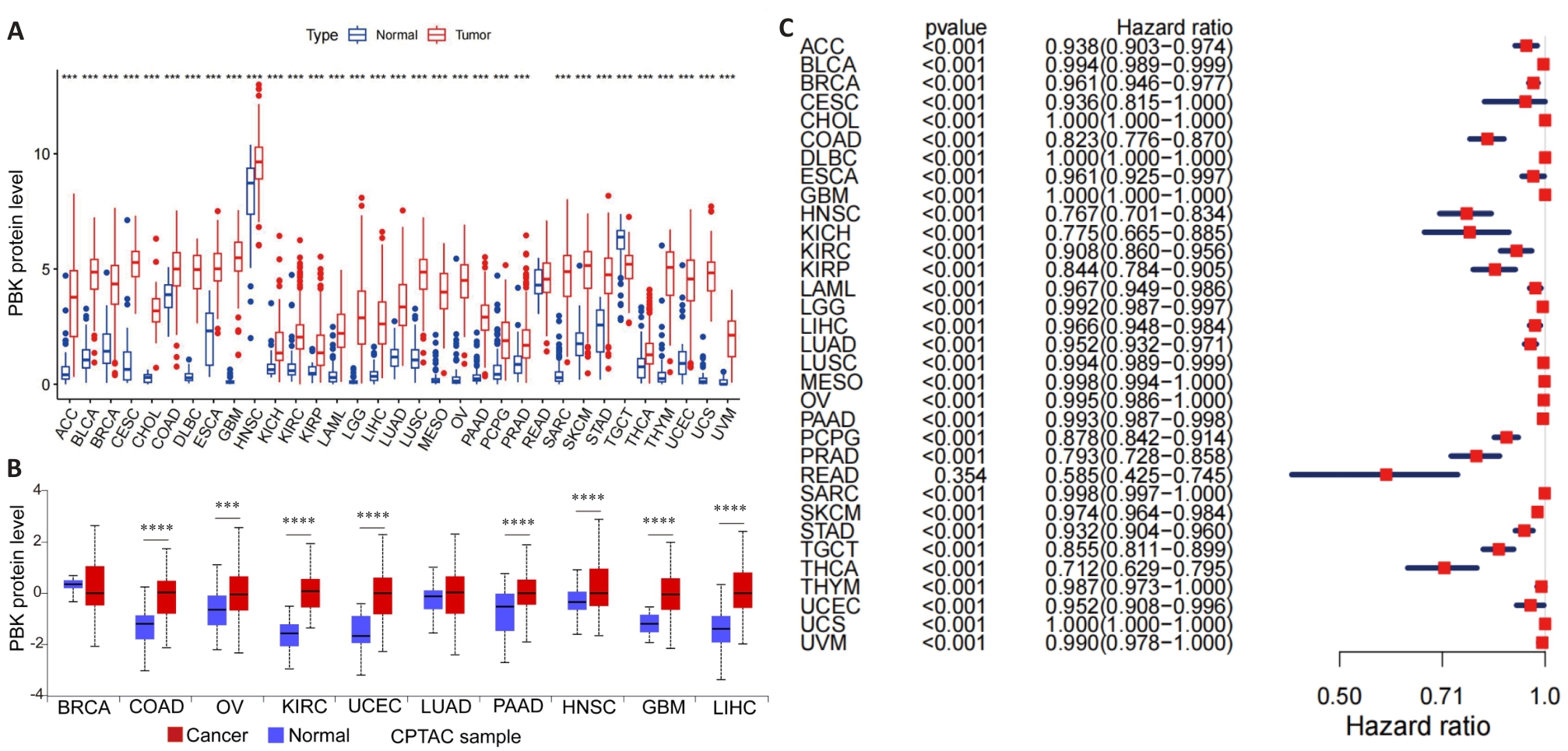
图1 PBK在33种癌症中的表达
Fig.1 PBK expression in 33 cancer types. A: Distribution of PBK mRNA expression in 33 cancer types and their normal controls based on TCGA data. B: Protein expression levels of PBK in different cancers based on data from the CPTAC database. C: ROC curve analysis of PBK in 33 cancer types, demonstrating its diagnostic ability to differentiate cancer from normal tissues. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
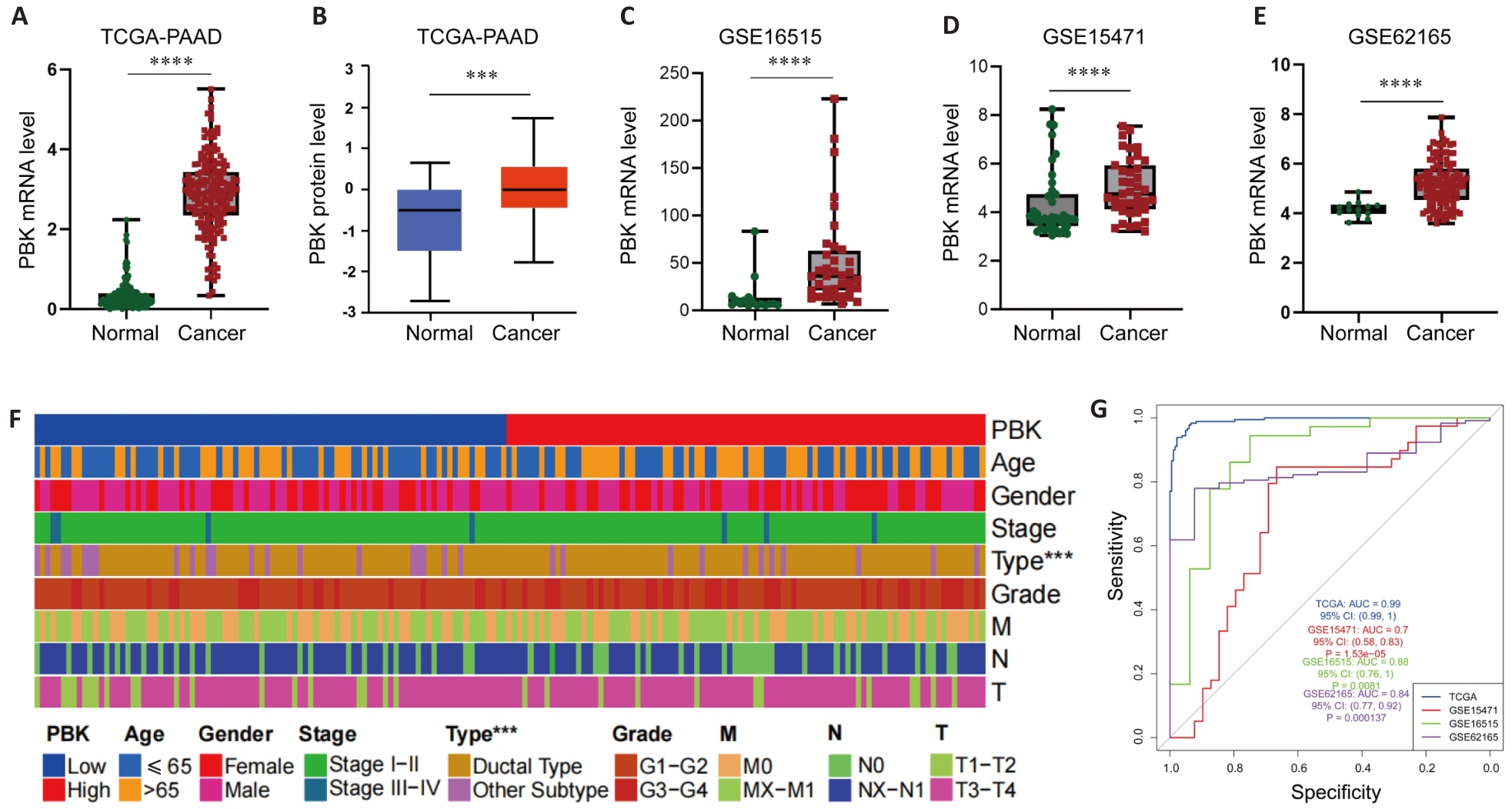
图2 PBK在胰腺癌中的表达
Fig.2 PBK expression in pancreatic cancer. A, B: TCGA and CPTAC data show significantly higher expression of PBK in pancreatic cancer tissues than in normal tissues. C-E: Differential expressions of PBK in pancreatic cancer and paired normal samples based on GSE16515, GSE15471 and GSE62165 datasets. F: Clinical feature heat map showing the association of PBK expression with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its correlation with tumor characteristics. G: ROC curves of the TCGA and GEO datasets further verify the reliability of PBK as a biomarker for diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
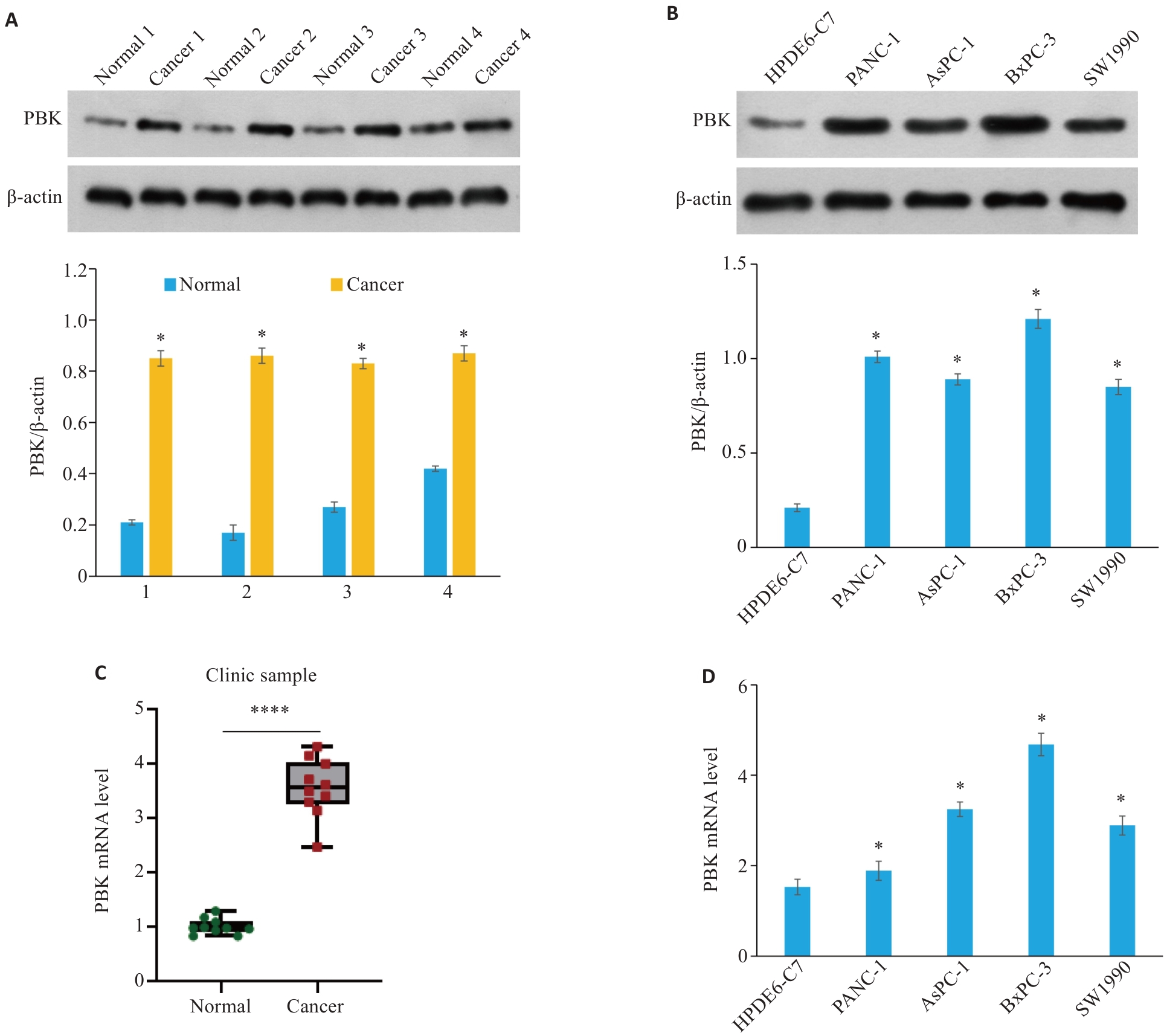
图3 PBK在胰腺癌临床样品和细胞系中高表达
Fig.3 PBK is highly expressed in clinical samples and cell lines of pancreatic cancer. A: PBK protein expression levels in 4 clinical pancreatic cancer samples and their paired normal tissues. *P<0.05 vs Normal. B: PBK protein expression levels in normal pancreatic cell line HPDE6-C7 and 4 pancreatic cancer cell lines (PANC-1, AsPC-1, BxPC-3, and SW1990). *P<0.05 vs HPDE6-C7. C: PBK mRNA expression levels in 4 clinical pancreatic cancer samples and their paired normal tissues. ****P<0.0001. D: PBK mRNA expression levels in the normal pancreatic cell line HPDE6-C7 and 4 pancreatic cancer cell lines. *P<0.05 vs HPDE6-C7.
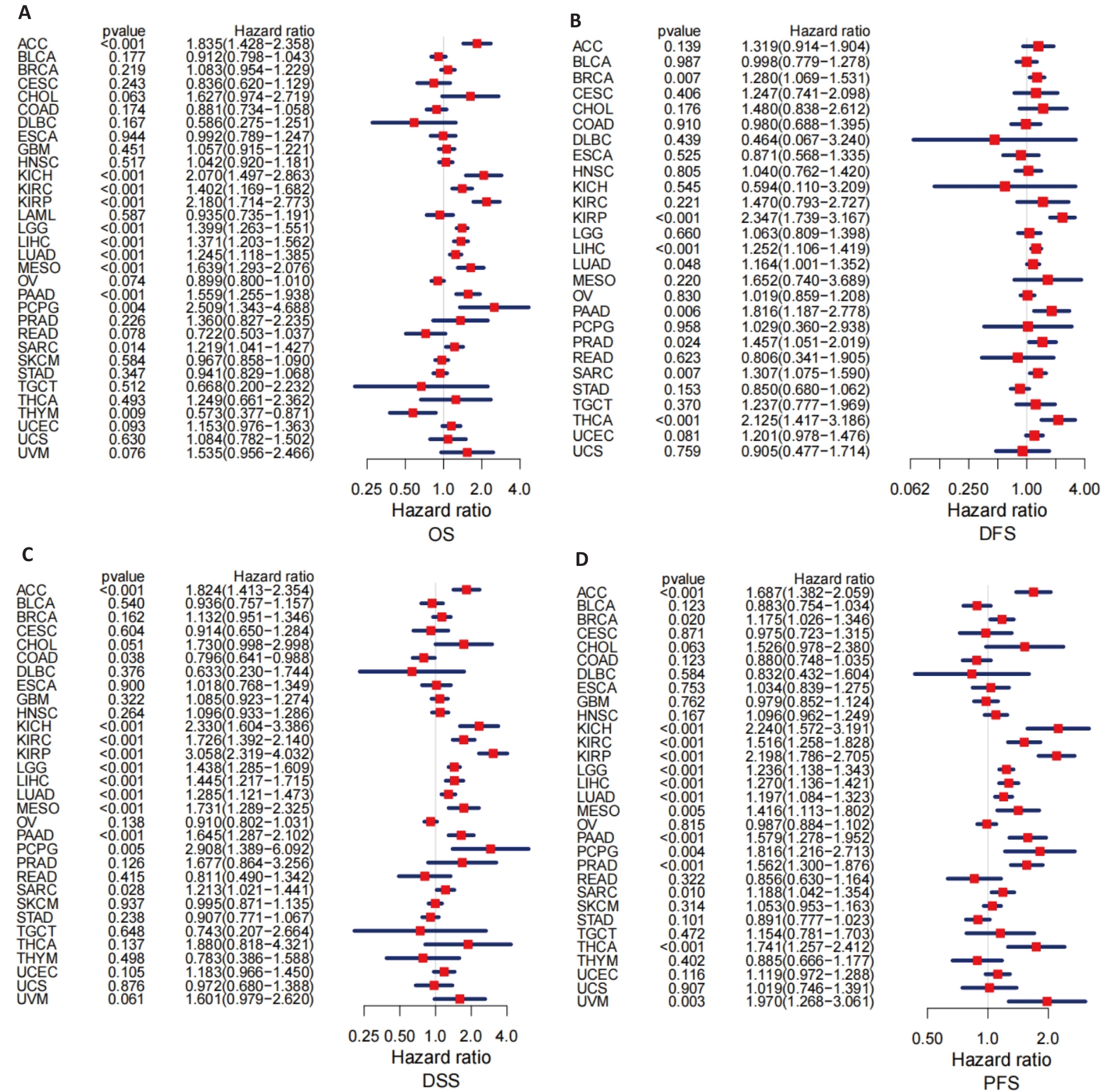
图4 PBK表达在33种癌症中的预后价值
Fig.4 Prognostic value of PBK expression across 33 cancer types. A: Forest plot analysis of overall survival (OS) showing the prognostic value of PBK across various cancers. B: Forest plot analysis of disease-free survival (DFS) highlighting the potential impact of PBK in pancreatic cancer. C: Analysis of disease-specific survival (DSS) showing the ability of PBK for predicting disease-specific mortality. D: Progression-free survival (PFS) analysis further supports the role of PBK as a prognostic indicator.
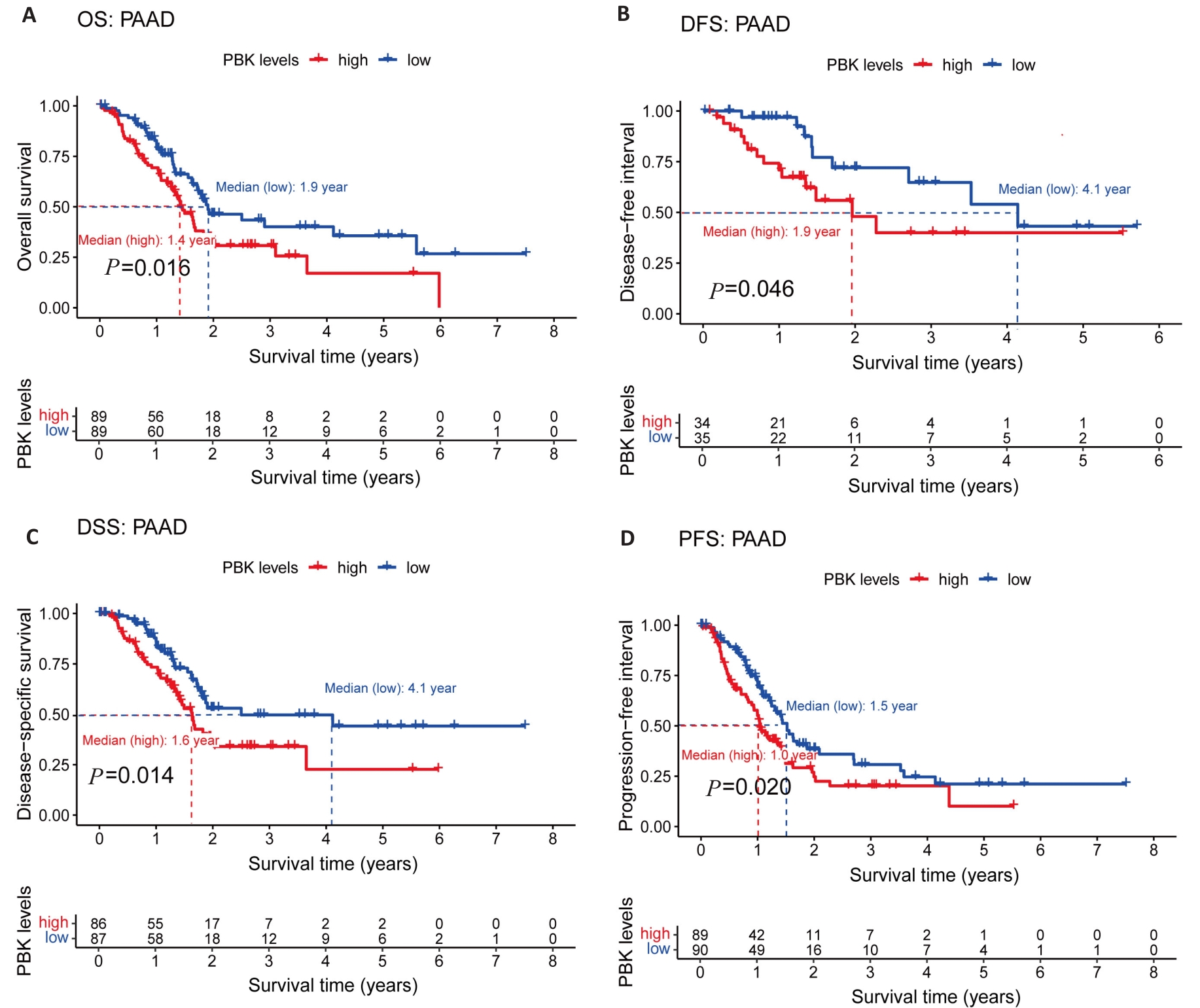
图5 PBK在胰腺癌中的表达与预后
Fig.5 PBK expression and its association with prognosis in pancreatic cancer. A: Kaplan-Meier survival curves show a significant association between high PBK expression and decreased OS. B: DFS survival curve validates the influence of PBK on disease-free survival. C: DSS survival curve highlights the relationship between high PBK expression and lower disease-specific survival. D: PFS survival curve reveals the connection between PBK expression and progression-free survival.
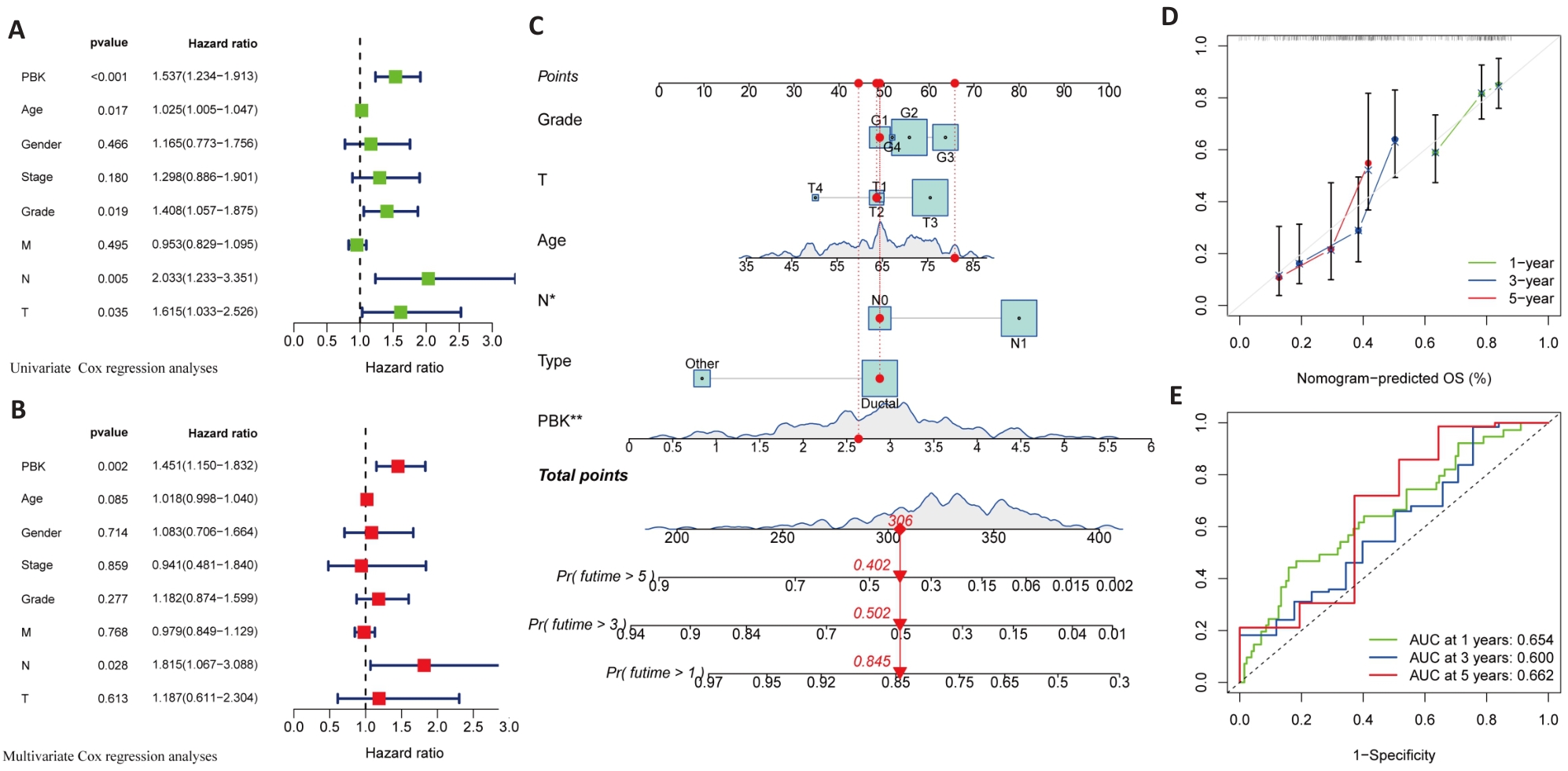
图6 胰腺癌中PBK高表达与预后的单因素及多因素分析
Fig.6 Univariate and multivariate analysis of the association of high PBK expression with prognosis of pancreatic cancer. A: Univariate analysis reveals significant association of PBK with clinicopathological factors of pancreatic cancer. B: Multivariate analysis validates PBK as an independent prognostic factor after adjusting for other clinical variables. C: A nomogram model for predicting survival probabilities of pancreatic cancer patients based on PBK expression. D: Calibration plot confirms the prediction accuracy of the nomogram model. E: ROC curves for 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival showing the predictive performance of PBK. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
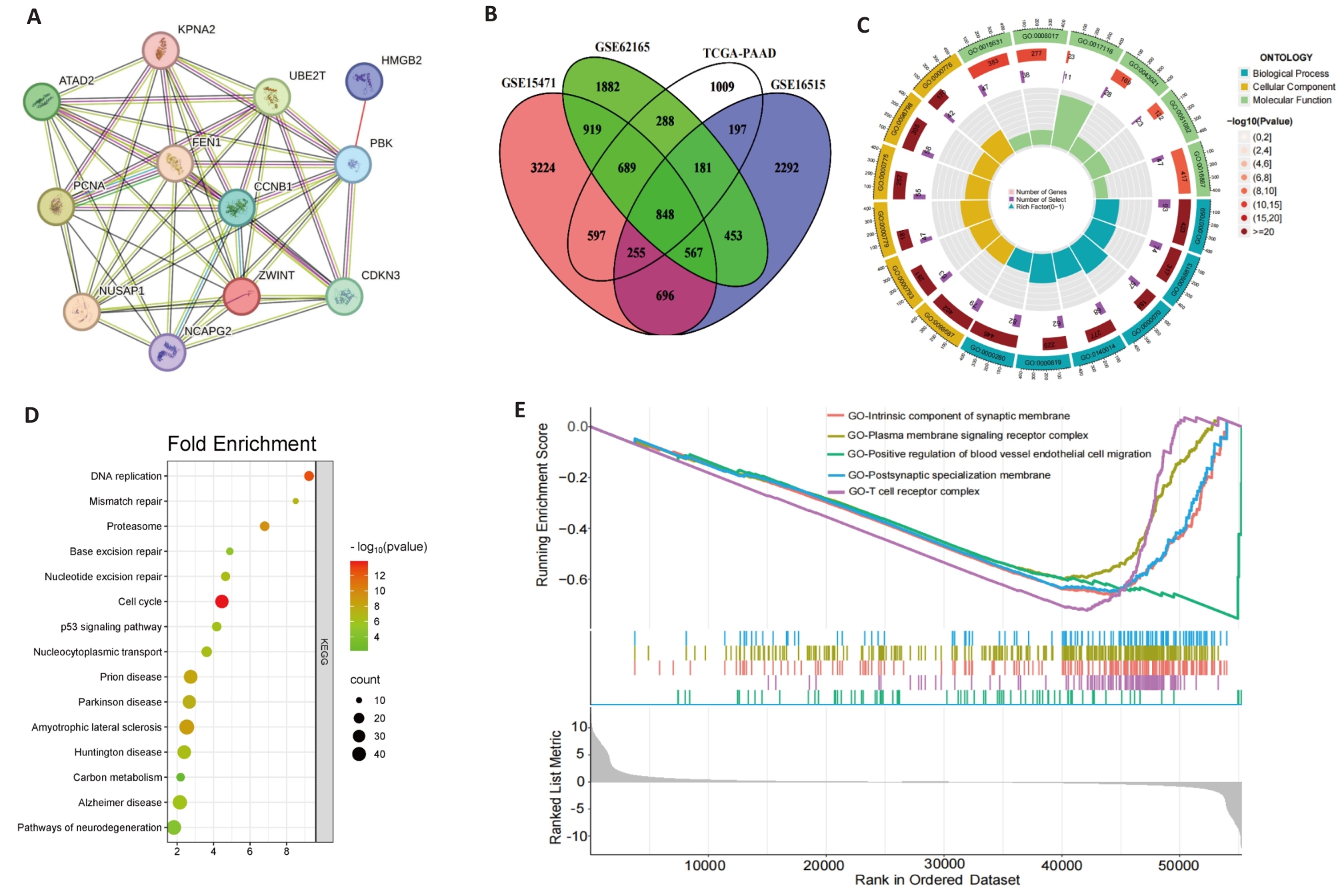
图7 基因相关及富集分析
Fig.7 Gene correlation and enrichment analysis. A: Correlation analysis of PBK with 11 co-expressed genes across 33 cancer types. B: Intersection of PBK-related genes in pancreatic cancer, revealing key associated genes. C: GO analysis showing that PBK co-expressed genes are enriched in immune and cell cycle-related biological processes. D: KEGG pathway analysis shows that PBK is involved in cancer-related signaling pathways. E: GSEA analysis validates PBK-associated gene enrichment in immune regulation and tumor-related pathways.
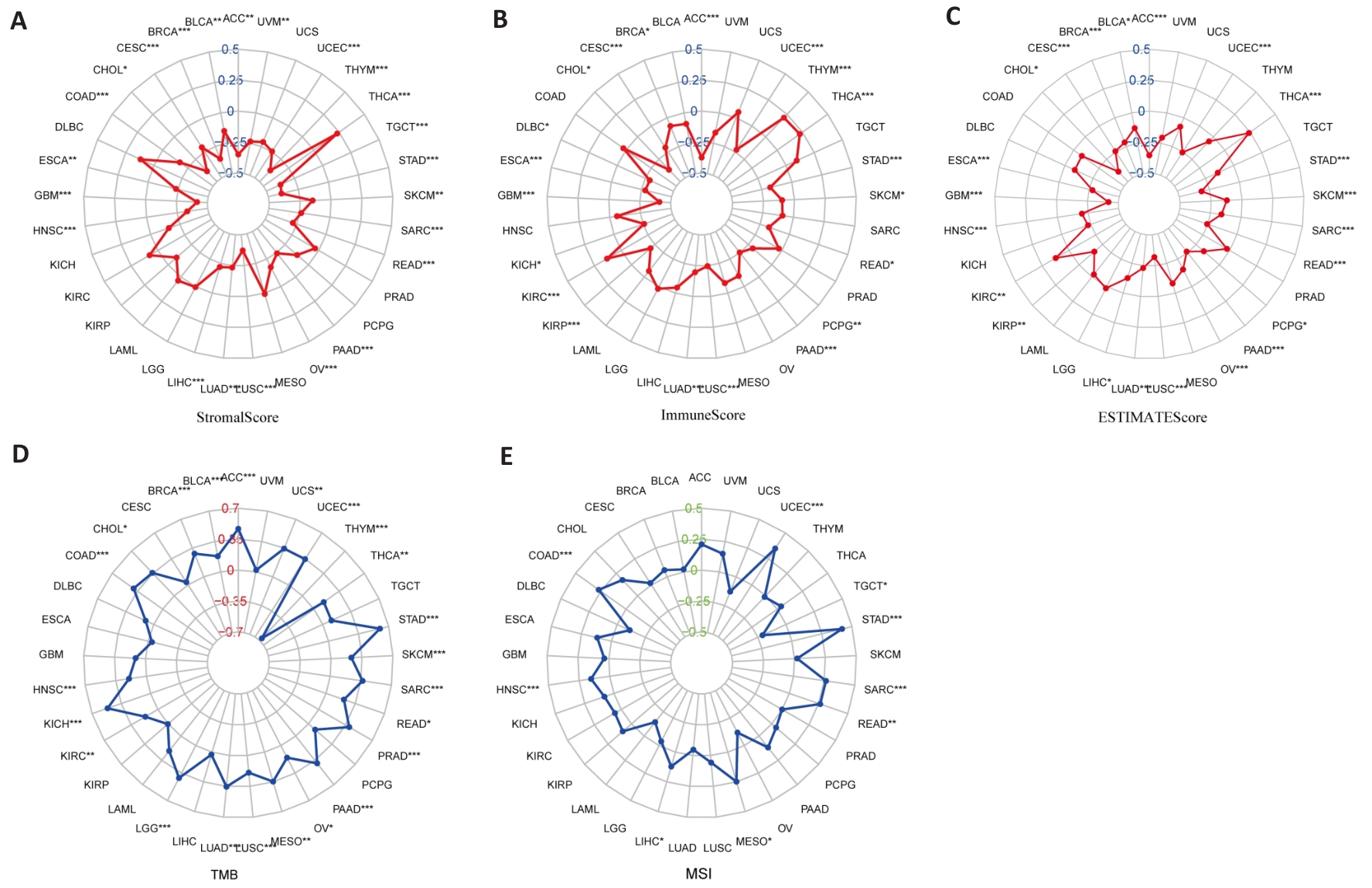
图8 PBK表达与肿瘤微环境分析
Fig.8 PBK expression and tumor microenvironment analysis. A: Stromal Score analysis shows a correlation between PBK expression and tumor stromal content. B: Immune Score analysis indicates that PBK expression is associated with tumor immune infiltration. C: ESTIMATE Score analysis validates the role of PBK in the tumor microenvironment. D: Correlation between PBK expression and tumor mutation burden (TMB). E: Correlation between PBK expression and microsatellite instability (MSI), suggesting its potential immune regulatory mechanisms. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
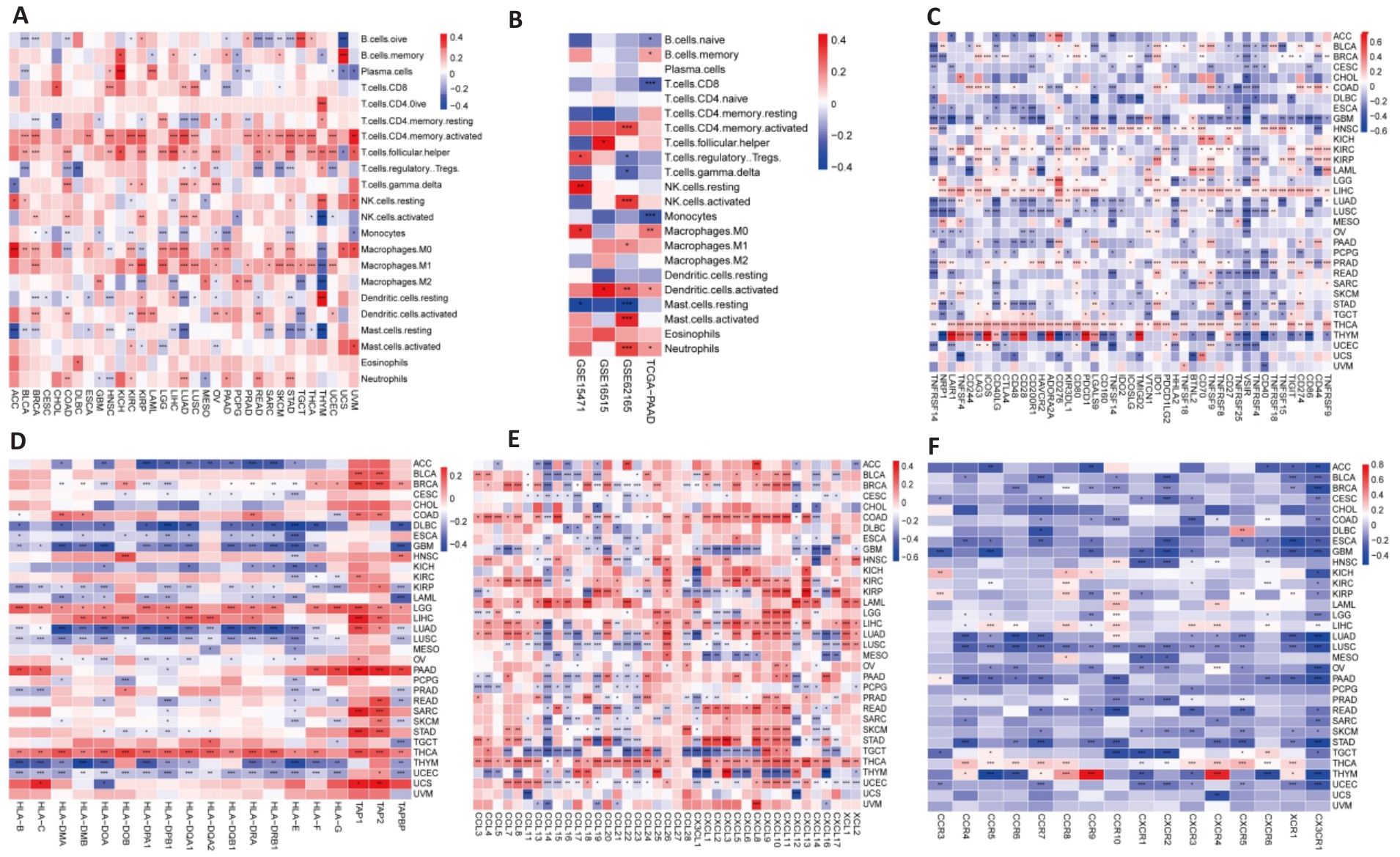
图9 PBK表达与免疫系统的关系
Fig.9 Relationship between PBK expression and immune system. A: Analysis of PBK expression and immune infiltration across 33 cancer types. B: Immune infiltration analysis of PBK in the pancreatic cancer immune microenvironment based on combined TCGA and GEO data. C: Correlation analysis of PBK expression with immune checkpoint molecules in 33 cancer types. D-F: Complex associations of PBK expression with MHC molecules (D), chemokines (E), and their receptors (F), suggesting its involvement in immune regulatory networks. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
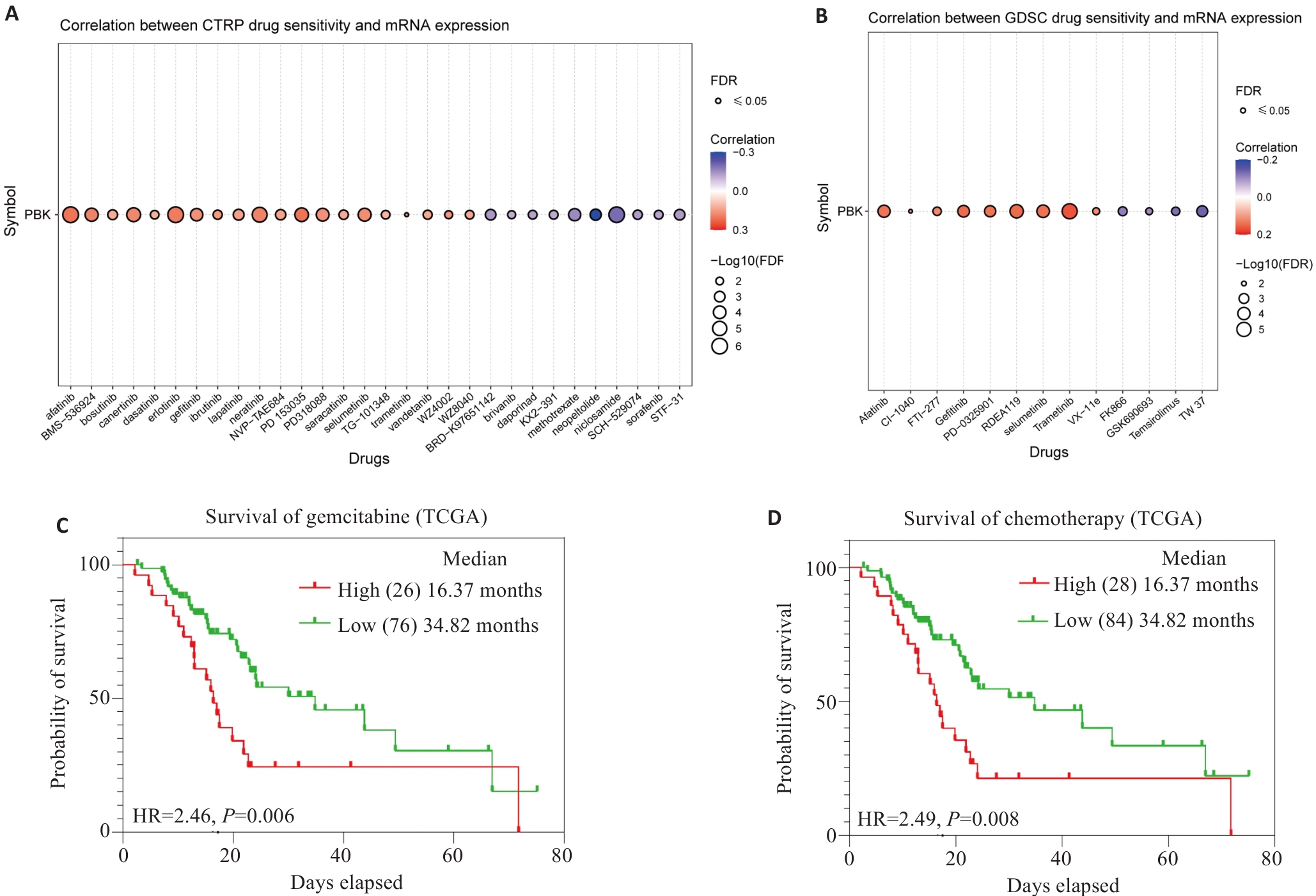
图10 PBK表达及药敏分析
Fig.10 PBK expression and drug sensitivity analysis. A: Analysis from the CTRPC database shows that PBK mRNA expression affects drug sensitivity. B: Analysis from the GDSC database shows that PBK mRNA expression affects drug sensitivity. C: High PBK expression predicts poor response to gemcitabine treatment. D: High PBK expression is associated with chemotherapeutic drug resistance, indicating its potential as a drug target.
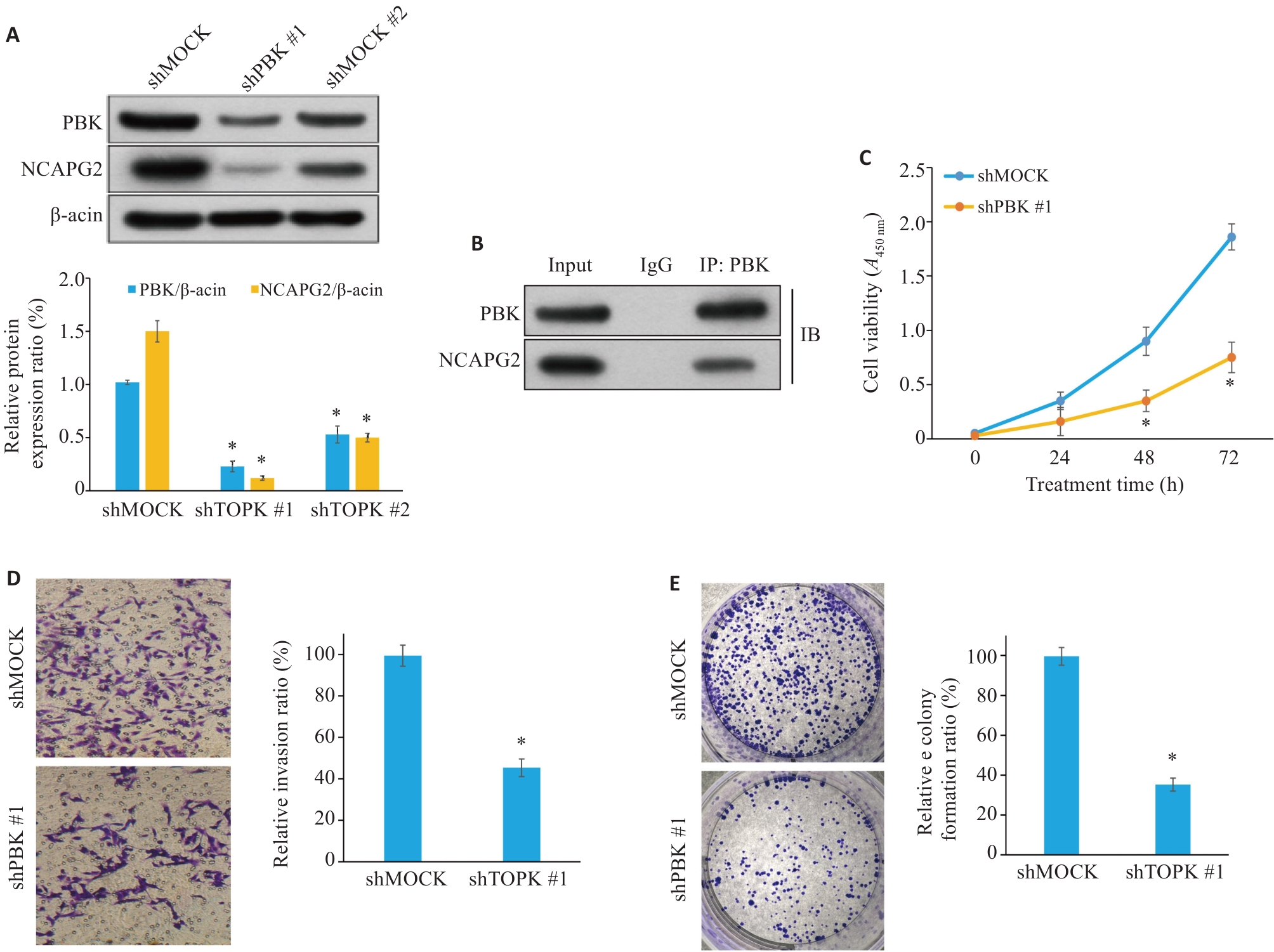
图11 PBK敲低抑制胰腺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Fig.11 PBK knockdown inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. A: Western blotting showing efficient knockdown of PBK expression. B: Co-immunoprecipitation experiment shows that PBK directly interacts with NCAPG2, suggesting that the PBK-NCAPG2 axis plays a role in tumor progression. C: CCK-8 assay shows that PBK knockdown significantly inhibits cell proliferation. D: Transwell assay validating suppressed invasion ability of pancreatic cancer cells after PBK knockdown (Original magnification: ×200). E: Effect of shPBK on clone formation ability of pancreatic cancer cells. *P<0.05 vs shMock.
| [1] | Mei QJ, Li KX, Tang TY, et al. miR-203-3p promotes senescence of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via downregulation of Pbk[J]. Aging Cell, 2024, 23(11): e14293. doi:10.1111/acel.14293 |
| [2] | Han ZP, Li LZ, Huang YY, et al. PBK/TOPK: a therapeutic target worthy of attention[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(2): 371. doi:10.3390/cells10020371 |
| [3] | Lee DH, Jeong YJ, Won JY, et al. PBK/TOPK is a favorable prognostic biomarker correlated with antitumor immunity in colon cancers[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(2): 299. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020299 |
| [4] | Herbert KJ, Ashton TM, Prevo R, et al. T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK): an emerging target for cancer-specific therapeutics[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9: 1089. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1131-7 |
| [5] | Deng MQ, Yang RY, Sun Q, et al. Small-molecule inhibitor HI-TOPK-032 improves NK-92MI cell infiltration into ovarian tumours[J]. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 2024, 134(5): 629-42. doi:10.1111/bcpt.14002 |
| [6] | Huang H, Lee MH, Liu KD, et al. PBK/TOPK: an effective drug target with diverse therapeutic potential[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(9): 2232. doi:10.3390/cancers13092232 |
| [7] | Niu NN, Shen XQ, Wang Z, et al. Tumor cell-intrinsic epigenetic dysregulation shapes cancer-associated fibroblasts heterogeneity to metabolically support pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2024, 42(5): 869-84. e9. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2024.03.005 |
| [8] | Li PY, Zhang HY, Gao XY, et al. Difference in fecal and oral microbiota between pancreatic cancer and benign/low-grade malignant tumor patients[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2024, 24(1): 527. doi:10.1186/s12866-024-03687-6 |
| [9] | De Santis MC, Bockorny B, Hirsch E, et al. Exploiting pancreatic cancer metabolism: challenges and opportunities[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2024, 30(6): 592-604. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2024.03.008 |
| [10] | Feng TT, Zhang Y, Ling SB, et al. PDZ binding kinase/T-LAK cell-derived protein kinase plays an oncogenic role and promotes immune escape in human tumors[J]. J Oncol, 2021, 2021: 8892479. doi:10.1155/2021/8892479 |
| [11] | Fan XM, Tao JY, Cai Z, et al. Eupafolin suppresses esophagus cancer growth by targeting T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 1248. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01248 |
| [12] | Lu H, Huang YZ, Ni XF, et al. TOPK promotes the development of psoriasis and worenine alleviates psoriasiform dermatitis by inhibiting TOPK activity[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2024, 38(5): 851-63. doi:10.1111/jdv.19724 |
| [13] | Brozos-Vázquez E, Toledano-Fonseca M, Costa-Fraga N, et al. Pancreatic cancer biomarkers: a pathway to advance in personalized treatment selection[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2024, 125: 102719. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102719 |
| [14] | Pratticò F, Garajová I. Focus on pancreatic cancer microenvironment[J]. Curr Oncol, 2024, 31(8): 4241-60. doi:10.3390/curroncol31080316 |
| [15] | McGuigan A, Kelly P, Turkington RC, et al. Pancreatic cancer: a review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(43): 4846-61. doi:10.3748/wjg.v24.i43.4846 |
| [16] | Cai J, Chen HD, Lu M, et al. Advances in the epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Trends, risk factors, screening, and prognosis[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 520: 1-11. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.06.027 |
| [17] | Nguyen N, Hoang TM, Huang T, et al. Macrophage-hitchhiked, effervescence-induced nanoemulsions for enhanced oral chemotherapy and immunotherapy: Impact on absorption route[J]. Biomaterials, 2025, 316: 123019. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.123019 |
| [18] | Morrison AH, Byrne KT, Vonderheide RH. Immunotherapy and prevention of pancreatic cancer[J]. Trends Cancer, 2018, 4(6): 418-28. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2018.04.001 |
| [19] | Feng TT, Jiang RB, Yin L, et al. PDZ-binding kinase aggravates pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm progression by activating the AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2023, 62(5): 716-26. doi:10.1002/mc.23519 |
| [20] | Lv BB, Zhang FN, Zhang XY, et al. PBK as a novel biomarker performed excellent diagnostic and prognostic value in HCC associated with immune infiltration and methylation[J]. J Mol Histol, 2025, 56(2): 129. doi:10.1007/s10735-024-10324-z |
| [21] | Li BX, Yao TZ, Zhang M, et al. Correlation study of PBK/TOPK expression, prognosis, and immune infiltration in breast cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2025, 15(1): 15052. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-96542-1 |
| [22] | Zhang QF, Zheng F, Chen YC, et al. The TOPK inhibitor HI-TOPK-032 enhances CAR T-cell therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating memory T cells[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2024, 12(5): 631-43. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.cir-23-0587 |
| [23] | Song WH, Yu YB, Wang SQ, et al. Metabolic reprogramming shapes the immune microenvironment in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: prognostic implications and therapeutic targets[J]. Front Immunol, 2025, 16: 1555287. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1555287 |
| [24] | Jing R, Wu N, Zhang Q, et al. DPP4 promotes an immunoenhancing tumor microenvironment through exhausted CD8+ T cells with activating IL13-IL13RA2 axis in papillary thyroid cancer[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2025, 145: 113760. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113760 |
| [25] | Pang SG, Zhang X, Li ZX, et al. TOPK inhibition enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to radiotherapy by reducing the DNA damage response[J]. Curr Med Sci, 2024, 44(3): 545-53. doi:10.1007/s11596-024-2884-0 |
| [26] | Wang Q, Li ZZ, Zhou SJ, et al. NCAPG2 could be an immunological and prognostic biomarker: From pan-cancer analysis to pancreatic cancer validation[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1097403. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1097403 |
| [27] | Mi XH, Shan HF, Kang CB, et al. MYC and NCAPG2 as molecular targets of colorectal cancer and gastric cancer in nursing[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2024, 103(18): e38029. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000038029 |
| [28] | Zhang EC, Chen ZJ, Liu WM, et al. NCAPG2 promotes prostate cancer malignancy and stemness via STAT3/c-MYC signaling[J]. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 12. doi:10.1186/s12967-023-04834-9 |
| [29] | Feng Z, Zhang LF, Liu YX, et al. NCAPG2 contributes to the progression of malignant melanoma through regulating proliferation and metastasis[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2022, 100(6): 473-84. doi:10.1139/bcb-2022-0048 |
| [30] | Ren WJ, Yang S, Chen X, et al. NCAPG2 is a novel prognostic biomarker and promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in low-grade glioma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 918606. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.918606 |
| [31] | Jiang SY, Huang JJ, He H, et al. NCAPG2 maintains cancer stemness and promotes erlotinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(18): 4395. doi:10.3390/cancers14184395 |
| [32] | Meng FZ, Zhang SG, Song RP, et al. NCAPG2 overexpression promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through activating the STAT3 and NF-κB/miR-188-3p pathways[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 44: 237-49. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.053 |
| [1] | 何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [2] | 张瑜, 李海涛, 潘玉卿, 曹杰贤, 翟丽, 张曦. MZB1基因在泛癌中的表达及其与免疫浸润及预后的关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 2006-2018. |
| [3] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [4] | 郭晓娟, 杜瑞娟, 陈丽平, 郭克磊, 周彪, 卞华, 韩立. WW结构域E3泛素连接酶1调控卵巢癌肿瘤微环境中的免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1063-1073. |
| [5] | 高志, 吴傲, 胡仲翔, 孙培养. 类风湿性关节炎中氧化应激与免疫浸润的生物信息学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [6] | 缪祥卓, 朱鹏宇, 区活辉, 朱庆, 于林源, 郭柏棠, 廖渭, 黄毓, 相乐阳, 杨定华. 高表达甲状旁腺激素样激素促进肝细胞癌的进展并与患者预后不良相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2135-2145. |
| [7] | 孙陛航, 郭煜君, 祁玉麟, 姚丹, 陈文直, 陈念芝. 低强度脉冲超声协同冬凌草甲素通过激活PIEZO1诱导胰腺癌细胞铁死亡的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2160-2170. |
| [8] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [9] | 黄燕, 覃璐璐, 管少兴, 管宴萍, 韦玉茹, 操艾伶, 李冬梅, 韦桂宁, 苏启表. 金缕半枫荷的水提取物抑制胰腺癌的作用机制:活性成分、关键靶点和信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1336-1344. |
| [10] | 陈莉莉, 吴天宇, 张铭, 丁子夏, 张妍, 杨依清, 郑佳倩, 张小楠. 类风湿关节炎的潜在生物标志物及其免疫调控机制:基于GEO数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1098-1108. |
| [11] | 周伟, 聂军, 胡佳, 蒋艺枝, 张大发. 内质网应激相关基因在主动脉夹层疾病中的差异性表达及与免疫浸润的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [12] | 王沁智, 宋冰, 郝诗睿, 肖志远, 金连辉, 郑通, 柴芳. 基于生物信息学分析CCND2在甲状腺乳头状癌中的表达及其对免疫浸润的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 981-988. |
| [13] | 张富星, 刘国庆, 董锐, 高磊, 陆伟晨, 高连霞, 赵忠扩, 陆飞, 刘牧林. 高表达CRTAC1通过调控PI3K信号通路促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移及免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2421-2433. |
| [14] | 闵静婷, 彭上, 杜娜娜, 安然, 甄翔程, 曹佳威, 周陈航, 李正红. 分泌型PD-1抗体可提高c-Met CAR-T细胞对胰腺癌细胞的杀伤作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1976-1984. |
| [15] | 姚倚钠, 刘 佳, 周想军, 刘泽宇, 邱士珍, 何颖政, 周雪琼. TTC9A在泛癌中的表达水平与多种癌症的预后和免疫微环境相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 70-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||