南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1809-1817.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.01
• •
收稿日期:2025-04-09
接受日期:2025-05-17
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
张力莹
E-mail:540185181@qq.com
作者简介:/通信作者:张力莹,硕士,副主任医师,E-mail: 540185181@qq.com
Liying ZHANG( ), Tongzhen ZHANG, Xin ZHAO
), Tongzhen ZHANG, Xin ZHAO
Received:2025-04-09
Accepted:2025-05-17
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Liying ZHANG
E-mail:540185181@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨单独及联合应用动态对比增强磁共振成像(DCE)、扩散加权成像(DWI)和T2加权成像(T2WI)的形态学特征对乳腺癌的诊断价值。 方法 回顾性分析394例行3.0T磁共振成像(MRI)检查并经病理学确诊的乳腺病变患者的影像资料。由经过培训的放射科医师分析DCE、DWI和T2WI病灶的形态学特征,对良恶性病变进行组间比较。采用Logistic回归分析构建乳腺癌临床预测模型,使用受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC)和DeLong检验比较诊断效能。 结果 对于肿块样病变,所有形态学特征在DCE、DWI和T2WI上均可区分良恶性病变(P<0.05)。联合诊断方法(DCE+DWI+T2WI)的AUC(0.865)高于单独诊断方法(DCE:0.786;DWI:0.793;T2WI:0.809)(P<0.05)。对于非肿块样病变,DWI信号强度是恶性病变的显著预测因子(P=0.036),但DWI诊断模型的AUC较低(0.669)。 结论 综合分析DCE、DWI和T2WI的形态学特征可提高乳腺肿块样病变的诊断效能。
张力莹, 张同贞, 赵鑫. 基于乳腺影像报告和数据系统的DWI和T2WI形态评估对乳腺病变的诊断价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1809-1817.
Liying ZHANG, Tongzhen ZHANG, Xin ZHAO. Diagnostic value of morphological features of breast lesions on DWI and T2WI assessed using Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System lexicon descriptors[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1809-1817.
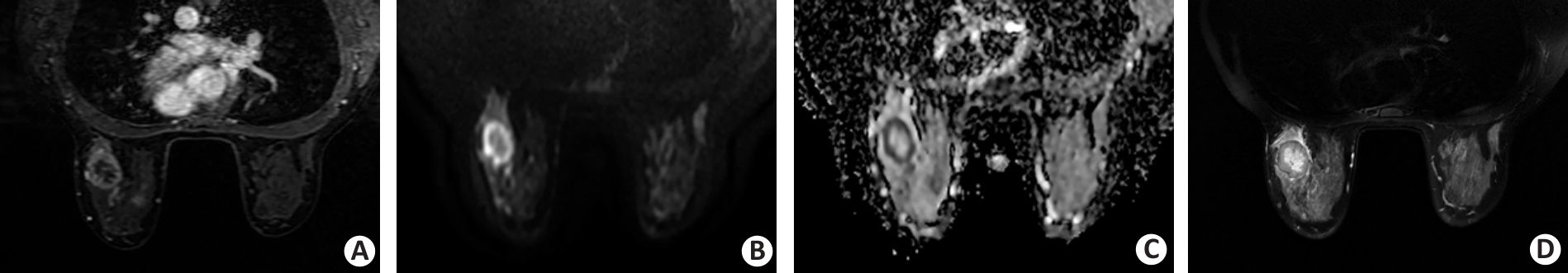
Fig.2 A 38-year-old female patient with invasive ductal breast carcinoma in the left breast. A: Dynamic contrast-enhanced image shows a round uncircumscribed mass with rim enhancement in the left breast. B, C: Diffusion-weighted image (DWI) acquired by using a b value of 800 s/mm2 shows a round, circumscribed, and high-intensity mass. The internal pattern of combined assessment of DWI and apparent diffusion coefficient is considered a rim-like pattern. D: T2-weighted image reveals the corresponding lesion as a high-intensity area surrounded by a low-intensity rim.
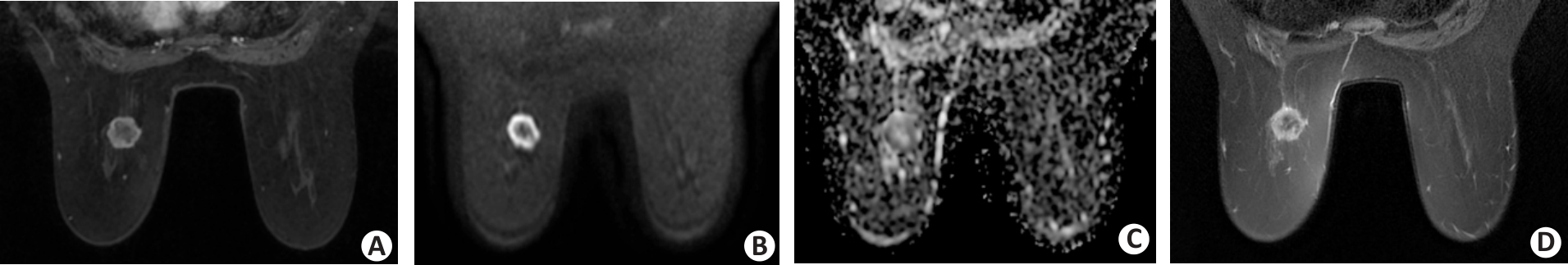
Fig.3 A 58-year-old female patient with invasive ductal breast carcinoma in the left breast. A: The dynamic contrast-enhanced image shows a round circumscribed mass with rim enhancement in the left breast. B, C: DWI acquired by using a b value of 800 s/mm2 shows a round, circumscribed, and high-intensity mass. The internal pattern of combined assessment of DWI and apparent diffusion coefficient is considered a rim-like pattern. D: T2-weighted imaging reveals the corresponding lesion as a low-intensity area surrounded by a high-intensity rim.
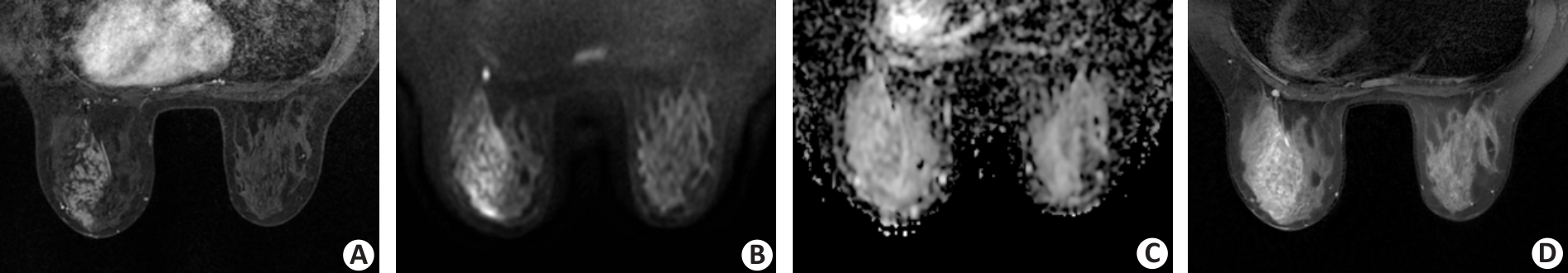
Fig.4 A 34-year-old female patient with ductal carcinoma in situ in the left breast. A: The dynamic contrast-enhanced image shows a segmental non-mass lesion with clustered ring pattern enhancement in the left breast. B, C: DWI acquired by using a b value of 800 s/mm2 shows a segmental high-intensity non-mass lesion extending from the nipple to the chest wall region anteriorly. The internal pattern of combined assessment of DWI and apparent diffusion coefficient is considered a clustered ring pattern. D: T2-weighted imaging reveals the corresponding lesion as a segmental, heterogeneous, and slight high-intensity non-mass lesion.
| Variable | Malignant (n=299) | Benign (n=95) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass (n=239) | Non-mass (n=60) | Mass (n=82) | Non-mass (n=13) | ||
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 48.8±9.8 | 50.5±10.6 | 37.9±11.5 | 35.2±9.0 | |
| Lesion size (mm, Mean±SD) | 25.8±13.1 | 53.6±20.8 | 23.7±11.8 | 49.6±24.4 | |
| Histological type | |||||
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 210 | 36 | |||
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 5 | 3 | |||
| Mucinous carcinoma | 7 | 0 | |||
| Papillary carcinoma | 7 | 2 | |||
| Apocrine carcinoma | 0 | 1 | |||
| Metaplastic carcinomas | 2 | 0 | |||
| Ductal carcinoma in situ | 8 | 18 | |||
| Fibroadenoma | 54 | 0 | |||
| Fibrocystic changes | 7 | 0 | |||
| Papilloma | 6 | 2 | |||
| Sclerosing adenosis | 4 | 1 | |||
| Phyllodes tumors | 6 | 0 | |||
| Inflammatory changes | 5 | 10 | |||
Tab.1 Clinicopathological characteristics of the patients
| Variable | Malignant (n=299) | Benign (n=95) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass (n=239) | Non-mass (n=60) | Mass (n=82) | Non-mass (n=13) | ||
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 48.8±9.8 | 50.5±10.6 | 37.9±11.5 | 35.2±9.0 | |
| Lesion size (mm, Mean±SD) | 25.8±13.1 | 53.6±20.8 | 23.7±11.8 | 49.6±24.4 | |
| Histological type | |||||
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 210 | 36 | |||
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 5 | 3 | |||
| Mucinous carcinoma | 7 | 0 | |||
| Papillary carcinoma | 7 | 2 | |||
| Apocrine carcinoma | 0 | 1 | |||
| Metaplastic carcinomas | 2 | 0 | |||
| Ductal carcinoma in situ | 8 | 18 | |||
| Fibroadenoma | 54 | 0 | |||
| Fibrocystic changes | 7 | 0 | |||
| Papilloma | 6 | 2 | |||
| Sclerosing adenosis | 4 | 1 | |||
| Phyllodes tumors | 6 | 0 | |||
| Inflammatory changes | 5 | 10 | |||
| Parameter | DCE | DWI | T2WI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC (95% CI) | Level of concordance | ICC (95% CI) | Level of concordance | ICC (95% CI) | Level of concordance | |||
| Mass-like lesions | ||||||||
| Shape | 0.908 (0.887-0.926) | Excellent | 0.910 (0.888-0.928) | Excellent | 0.941 (0.926-0.953) | Excellent | ||
| Margin | 0.890 (0.865-0.911) | Good | 0.837 (0.786-0.875) | Good | 0.759 (0.708-0.801) | Good | ||
| Internal patterns | 0.871 (0.841-0.895) | Good | 0.907 (0.886-0.925) | Excellent | 0.833 (0.796-0.864) | Good | ||
| Signal intensity | - | - | 0.897 (0.872-0.917) | Good | 0.934 (0.918-0.948) | Excellent | ||
| Non-mass-like lesions | ||||||||
| Distribution | 0.991 (0.985-0.994) | Excellent | 0.824 (0.734-0.886) | Good | 0.791 (0.687-0.863) | Good | ||
| Internal patterns | 0.789 (0.684-0.862) | Good | 0.844 (0.763-0.899) | Good | 0.802 (0.703-0.871) | Good | ||
| Signal intensity | - | - | 0.834 (0.748-0.892) | Good | 0.846 (0.765-0.900) | Good | ||
Tab.2 Interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for the qualitative parameters analyzed
| Parameter | DCE | DWI | T2WI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC (95% CI) | Level of concordance | ICC (95% CI) | Level of concordance | ICC (95% CI) | Level of concordance | |||
| Mass-like lesions | ||||||||
| Shape | 0.908 (0.887-0.926) | Excellent | 0.910 (0.888-0.928) | Excellent | 0.941 (0.926-0.953) | Excellent | ||
| Margin | 0.890 (0.865-0.911) | Good | 0.837 (0.786-0.875) | Good | 0.759 (0.708-0.801) | Good | ||
| Internal patterns | 0.871 (0.841-0.895) | Good | 0.907 (0.886-0.925) | Excellent | 0.833 (0.796-0.864) | Good | ||
| Signal intensity | - | - | 0.897 (0.872-0.917) | Good | 0.934 (0.918-0.948) | Excellent | ||
| Non-mass-like lesions | ||||||||
| Distribution | 0.991 (0.985-0.994) | Excellent | 0.824 (0.734-0.886) | Good | 0.791 (0.687-0.863) | Good | ||
| Internal patterns | 0.789 (0.684-0.862) | Good | 0.844 (0.763-0.899) | Good | 0.802 (0.703-0.871) | Good | ||
| Signal intensity | - | - | 0.834 (0.748-0.892) | Good | 0.846 (0.765-0.900) | Good | ||
| Lesion type | DCE | P | DWI | P | T2WI | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Malignant | Benign | Malignant | Benign | Malignant | ||||
| Mass-like lesions (n=321) | |||||||||
| Shape | |||||||||
| Oval | 33 (40.2) | 17 (7.1) | <0.001 | 34 (41.5) | 27 (11.3) | <0.001 | 33 (40.2) | 19 (7.9) | <0.001 |
| Round | 28 (34.1) | 115 (48.1) | 29 (35.4) | 111 (46.4) | 30 (36.6) | 120 (50.2) | |||
| Irregular | 21 (25.6) | 107 (44.8) | 19 (23.2) | 101 (42.3) | 19 (23.2) | 100 (41.8) | |||
| Margin | |||||||||
| Circumscribed | 48 (58.5) | 59 (24.7) | <0.001 | 50 (61.0) | 100 (41.8) | 0.003 | 49 (59.8) | 63 (26.4) | <0.001 |
| Not circumscribed | 34 (41.5) | 180 (75.3) | 32 (39.0) | 139 (58.2) | 33 (40.2) | 176 (73.6) | |||
| Internal patterns | |||||||||
| Homogeneous | 11 (13.4) | 25 (10.5) | <0.001 | 17 (20.7) | 43 (18.0) | <0.001 | 23 (28.0) | 69 (28.9) | <0.001 |
| Heterogeneous | 62 (75.6) | 131 (54.8) | 60 (73.2) | 127 (53.1) | 57 (69.5) | 119 (49.8) | |||
| Rim | 9 (11.0) | 83 (34.7) | 5 (6.1) | 69 (28.9) | 2 (2.4) | 51 (21.3) | |||
| Signal intensity | |||||||||
| Low-Iso | - | - | - | 6 (7.3) | 0 (0) | <0.001 | 19 (23.2) | 95 (39.7) | 0.002 |
| Slightly high | - | - | 10 (12.2) | 9 (3.8) | 9 (11.0) | 41 (17.2) | |||
| High | - | - | 66 (80.5) | 230 (96.2) | 54 (65.9) | 103 (43.1) | |||
| Non-mass-like lesions (n=73) | |||||||||
| Distribution | |||||||||
| Focal | 3 (23.1) | 6 (10.0) | 0.153 | 3 (23.1) | 6 (10.0) | 0.085 | 3 (23.1) | 8 (13.3) | 0.134 |
| Segmental | 5 (38.5) | 32 (53.3) | 4 (30.8) | 31 (51.7) | 4 (30.8) | 29 (48.3) | |||
| Regional | 5 (38.5) | 13 (21.7) | 6 (46.2) | 14 (23.3) | 6 (46.2) | 14 (23.3) | |||
| Diffuse | 0 (0) | 9 (15.0) | 0 (0) | 9 (15.0) | 0 (0) | 9 (15.0) | |||
| Internal patterns | |||||||||
| Homogeneous | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0.171 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.289 | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 1.0 |
| Heterogeneous | 8 (61.5) | 50 (83.3) | 11 (84.6) | 56 (93.3) | 13 (100.0) | 58 (96.7) | |||
| Clumped/clustered ring | 5 (38.5) | 9 (15.0) | 2 (15.4) | 4 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | |||
| Signal intensity | |||||||||
| Low-Iso | - | - | - | 2 (15.4) | 2 (3.3) | 0.036 | 6 (46.2) | 27 (45.0) | 0.608 |
| Slightly high | - | - | 5 (38.5) | 11 (18.3) | 6 (46.2) | 21 (35.0) | |||
| High | - | - | 6 (46.2) | 47 (78.3) | 1 (7.7) | 12 (20.0) | |||
Tab.3 Comparison between benign and malignant lesions for qualitative imaging findings with DCE, DWI and T2WI sequences ([n (%)])
| Lesion type | DCE | P | DWI | P | T2WI | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Malignant | Benign | Malignant | Benign | Malignant | ||||
| Mass-like lesions (n=321) | |||||||||
| Shape | |||||||||
| Oval | 33 (40.2) | 17 (7.1) | <0.001 | 34 (41.5) | 27 (11.3) | <0.001 | 33 (40.2) | 19 (7.9) | <0.001 |
| Round | 28 (34.1) | 115 (48.1) | 29 (35.4) | 111 (46.4) | 30 (36.6) | 120 (50.2) | |||
| Irregular | 21 (25.6) | 107 (44.8) | 19 (23.2) | 101 (42.3) | 19 (23.2) | 100 (41.8) | |||
| Margin | |||||||||
| Circumscribed | 48 (58.5) | 59 (24.7) | <0.001 | 50 (61.0) | 100 (41.8) | 0.003 | 49 (59.8) | 63 (26.4) | <0.001 |
| Not circumscribed | 34 (41.5) | 180 (75.3) | 32 (39.0) | 139 (58.2) | 33 (40.2) | 176 (73.6) | |||
| Internal patterns | |||||||||
| Homogeneous | 11 (13.4) | 25 (10.5) | <0.001 | 17 (20.7) | 43 (18.0) | <0.001 | 23 (28.0) | 69 (28.9) | <0.001 |
| Heterogeneous | 62 (75.6) | 131 (54.8) | 60 (73.2) | 127 (53.1) | 57 (69.5) | 119 (49.8) | |||
| Rim | 9 (11.0) | 83 (34.7) | 5 (6.1) | 69 (28.9) | 2 (2.4) | 51 (21.3) | |||
| Signal intensity | |||||||||
| Low-Iso | - | - | - | 6 (7.3) | 0 (0) | <0.001 | 19 (23.2) | 95 (39.7) | 0.002 |
| Slightly high | - | - | 10 (12.2) | 9 (3.8) | 9 (11.0) | 41 (17.2) | |||
| High | - | - | 66 (80.5) | 230 (96.2) | 54 (65.9) | 103 (43.1) | |||
| Non-mass-like lesions (n=73) | |||||||||
| Distribution | |||||||||
| Focal | 3 (23.1) | 6 (10.0) | 0.153 | 3 (23.1) | 6 (10.0) | 0.085 | 3 (23.1) | 8 (13.3) | 0.134 |
| Segmental | 5 (38.5) | 32 (53.3) | 4 (30.8) | 31 (51.7) | 4 (30.8) | 29 (48.3) | |||
| Regional | 5 (38.5) | 13 (21.7) | 6 (46.2) | 14 (23.3) | 6 (46.2) | 14 (23.3) | |||
| Diffuse | 0 (0) | 9 (15.0) | 0 (0) | 9 (15.0) | 0 (0) | 9 (15.0) | |||
| Internal patterns | |||||||||
| Homogeneous | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 0.171 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.289 | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | 1.0 |
| Heterogeneous | 8 (61.5) | 50 (83.3) | 11 (84.6) | 56 (93.3) | 13 (100.0) | 58 (96.7) | |||
| Clumped/clustered ring | 5 (38.5) | 9 (15.0) | 2 (15.4) | 4 (6.7) | 0 (0) | 1 (1.7) | |||
| Signal intensity | |||||||||
| Low-Iso | - | - | - | 2 (15.4) | 2 (3.3) | 0.036 | 6 (46.2) | 27 (45.0) | 0.608 |
| Slightly high | - | - | 5 (38.5) | 11 (18.3) | 6 (46.2) | 21 (35.0) | |||
| High | - | - | 6 (46.2) | 47 (78.3) | 1 (7.7) | 12 (20.0) | |||
| Evaluation metrics | Mass-like lesions | Non-mass-like lesions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCE | DWI | T2WI | DCE+DWI+T2WI | DWI | |
| Sensitivity (%) | 81.2 | 74.1 | 73.6 | 74.9 | 78.3 |
| Specificity (%) | 67.1 | 73.2 | 72.0 | 85.4 | 53.8 |
| PPV (%) | 87.8 | 88.9 | 88.4 | 93.7 | 88.7 |
| NPV (%) | 55.0 | 49.2 | 48.4 | 53.8 | 35.0 |
| Accuracy (%) | 77.6 | 73.8 | 73.2 | 77.6 | 74.0 |
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.786 (0.728-0.844) | 0.793 (0.735-0.850) | 0.809 (0.755-0.864) | 0.865 (0.816-0.914) | 0.669 (0.514-0.823) |
Tab.4 Diagnostic performance of the different prediction models for evaluating benign and malignant mass-like and non-mass-like lesions
| Evaluation metrics | Mass-like lesions | Non-mass-like lesions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCE | DWI | T2WI | DCE+DWI+T2WI | DWI | |
| Sensitivity (%) | 81.2 | 74.1 | 73.6 | 74.9 | 78.3 |
| Specificity (%) | 67.1 | 73.2 | 72.0 | 85.4 | 53.8 |
| PPV (%) | 87.8 | 88.9 | 88.4 | 93.7 | 88.7 |
| NPV (%) | 55.0 | 49.2 | 48.4 | 53.8 | 35.0 |
| Accuracy (%) | 77.6 | 73.8 | 73.2 | 77.6 | 74.0 |
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.786 (0.728-0.844) | 0.793 (0.735-0.850) | 0.809 (0.755-0.864) | 0.865 (0.816-0.914) | 0.669 (0.514-0.823) |
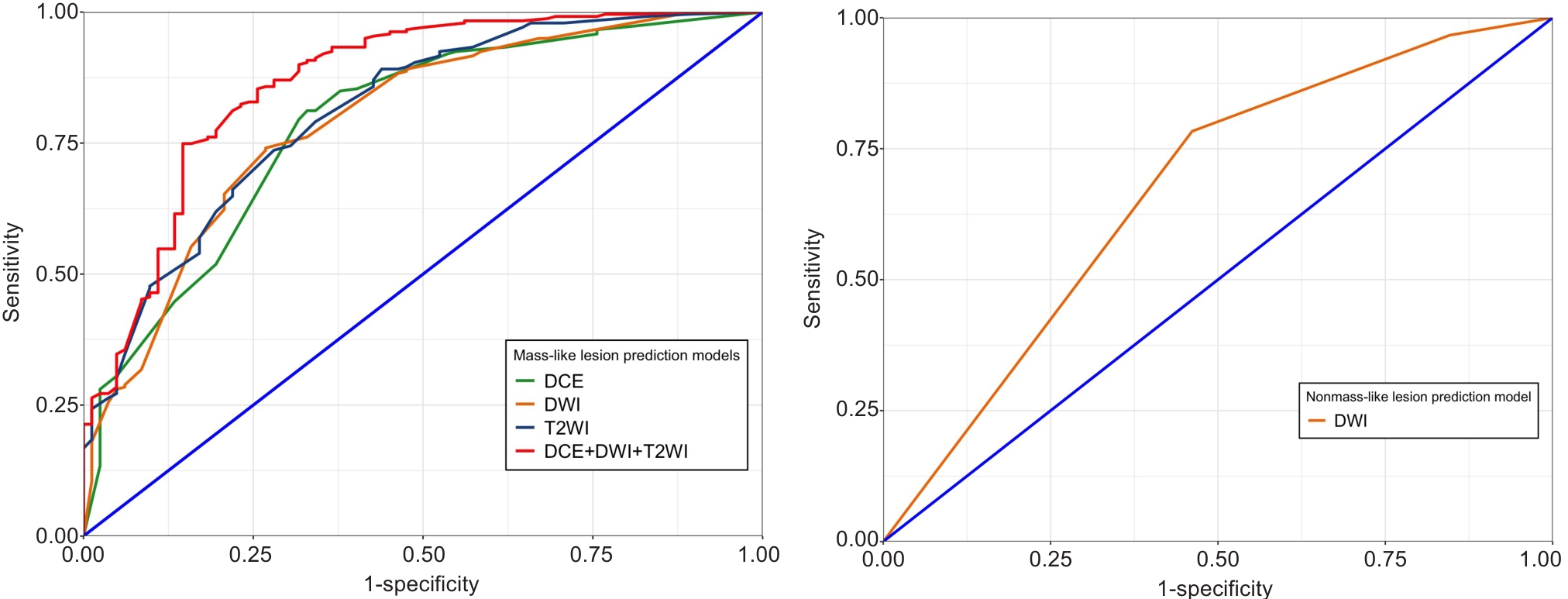
Fig.5 Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the different prediction models for evaluating benign and malignant mass-like and non-mass-like lesions.
| Model | DCE | DWI | T2WI | DCE+DWI+T2WI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCE | N/A | 0.837 | 0.293 | 0.001 |
| DWI | - | N/A | 0.522 | <0.001 |
| T2WI | - | - | N/A | 0.001 |
Tab.5 P-values for comparisons of areas under the curve between different mass-like lesion prediction models
| Model | DCE | DWI | T2WI | DCE+DWI+T2WI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCE | N/A | 0.837 | 0.293 | 0.001 |
| DWI | - | N/A | 0.522 | <0.001 |
| T2WI | - | - | N/A | 0.001 |
| [1] | Barkhausen J, Bischof A, Haverstock D, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of contrast-enhanced breast MRI versus X-ray mammography in women with different degrees of breast density [J]. Acta Radiol, 2021, 62(5): 586-93. doi:10.1177/0284185120936271 |
| [2] | Kim YE, Cha JH, Kim HH, et al. Analysis of false-negative findings of breast cancer on previous magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Acta Radiol, 2021, 62(6): 722-34. doi:10.1177/0284185120941830 |
| [3] | Tsarouchi MI, Vlachopoulos GF, Karahaliou AN, et al. Multi-parametric MRI lesion heterogeneity biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis [J]. Phys Med, 2020, 80: 101-10. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.10.007 |
| [4] | Yamaguchi K, Nakazono T, Egashira R, et al. Maximum slope of ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: comparisons with prognostic factors of breast cancer [J]. Jpn J Radiol, 2021, 39(3): 246-53. doi:10.1007/s11604-020-01049-6 |
| [5] | Sippo DA, Rutledge GM, Mercaldo SF, et al. Impact of background parenchymal enhancement on diagnostic performance in screening breast MRI [J]. Acad Radiol, 2020, 27(5): 663-71. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2019.06.020 |
| [6] | Rella R, Bufi E, Belli P, et al. Background parenchymal enhancement in breast magnetic resonance imaging: A review of current evidences and future trends [J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2018, 99(12): 815-26. doi:10.1016/j.diii.2018.08.011 |
| [7] | Kanao S, Kataoka M, Iima M, et al. Differentiating benign and malignant inflammatory breast lesions: value of T2 weighted and diffusion weighted MR images [J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 50: 38-44. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2018.03.012 |
| [8] | Nita Amornsiripanitch M. Diffusion-weighted MRI for unenhanced breast cancer screening [J]. Radiology, 2019, 293(3): 504-20. doi:10.1148/radiol.2019182789 |
| [9] | Ha SM, Chang JM, Lee SH, et al. Detection of contralateral breast cancer using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in women with newly diagnosed breast cancer: comparison with combined mammography and whole-breast ultrasound [J]. Korean J Radiol, 2021, 22(6): 867-79. doi:10.3348/kjr.2020.1183 |
| [10] | Kul S, Metin Y, Bekircavusoglu S, et al. Qualitative characterization of breast tumors with diffusion-weighted imaging has comparable accuracy to quantitative analysis [J]. Clin Imaging, 2021, 77: 17-24. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.02.025 |
| [11] | Kim JY, Kim JJ, Hwangbo L, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of invasive breast cancer: relationship to distant metastasis-free survival [J]. Radiology, 2019, 291(2): 300-07. doi:10.1148/radiol.2019181706 |
| [12] | Arponen O, Sudah M, Masarwah A, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in 3.0 Tesla breast MRI: diagnostic performance and tumor characterization using small subregions vs. whole tumor regions of interest [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): e0138702. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138702 |
| [13] | Baltzer P, Mann RM, Iima M, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast-a consensus and mission statement from the EUSOBI International Breast Diffusion-Weighted Imaging working group [J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(3): 1436-50. doi:10.1007/s00330-019-06510-3 |
| [14] | Ota R, Kataoka M, Iima M, et al. Evaluation of breast lesions based on modified BI-RADS using high-resolution readout-segmented diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging and T2/T1-weighted image [J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2023, 98: 132-9. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2022.12.024 |
| [15] | Naranjo ID, Sogani J, Saccarelli C, et al. MRI Screening of BRCA mutation carriers: comparison of standard protocol and abbreviated protocols with and without T2-weighted images [J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2022, 218(5): 810-20. doi:10.2214/ajr.21.27022 |
| [16] | Mann RM, Cho N, Moy L. Breast MRI: State of the Art [J]. Radiology, 2019, 292(3): 520-36. doi:10.1148/radiol.2019182947 |
| [17] | Mann RM, Kuhl CK, Kinkel K, et al. Breast MRI: guidelines from the European Society of Breast Imaging [J]. Eur Radiol, 2008, 18(7): 1307-18. doi:10.1007/s00330-008-0863-7 |
| [18] | Wu LM, Chen J, Hu J, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging combined with T2-weighted images in the detection of small breast cancer: a single-center multi-observer study [J]. Acta Radiol, 2014, 55(1): 24-31. doi:10.1177/0284185113492458 |
| [19] | Kawashima H, Kobayashi-Yoshida M, Matsui O, et al. Peripheral hyperintense pattern on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in breast carcinoma: correlation with early peripheral enhancement on dynamic MRI and histopathologic findings [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2010, 32(5): 1117-23. doi:10.1002/jmri.22279 |
| [20] | Yamaguchi R, Furusawa H, Nakahara H, et al. Clinicopathological study of invasive ductal carcinoma with large central acellular zone: special reference to magnetic resonance imaging findings [J]. Pathol Int, 2008, 58(1): 26-30. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2007.02184.x |
| [21] | Niko Radovic M. Evaluation of breast cancer morphology using diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: intermethod and interobserver agreement [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 49(5): 1381-90. doi:10.1002/jmri.26332 |
| [22] | Kishimoto AO, Kataoka M, Iima M, et al. The comparison of high-resolution diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) with high-resolution contrast-enhanced MRI in the evaluation of breast cancers [J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2020, 71: 161-9. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2020.03.007 |
| [23] | Christner SA, Grunz JP, Schlaiss T, et al. Breast lesion morphology assessment with high and standard b values in diffusion-weighted imaging at 3 Tesla [J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2024, 107: 100-10. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2024.01.005 |
| [24] | Yabuuchi H, Matsuo Y, Sunami S, et al. Detection of non-palpable breast cancer in asymptomatic women by using unenhanced diffusion-weighted and T2-weighted MR imaging: comparison with mammography and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging [J]. Eur Radiol, 2011, 21(1): 11-7. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-1890-8 |
| [25] | An YY. Differentiation of malignant and benign breast lesions: added value of the qualitative analysis of breast lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging at 3.0 T [J]. PLOS ONE, 2017, 12(3): e0174681. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174681 |
| [26] | Kul S, Eyuboglu I, Cansu A, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of the diffusion weighted imaging in the characterization of different types of breast lesions [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2014, 40(5): 1158-64. doi:10.1002/jmri.24491 |
| [27] | Kuroki-suzuli S. Detecting breast cancer with non-contrast MR imaging: combining diffusion-weighted and STIR imaging [J]. Magn Reson Med Sci, 2007, 6(1): 21-7. doi:10.2463/mrms.6.21 |
| [28] | Heacock L, Melsaether AN, Heller SL, et al. Evaluation of a known breast cancer using an abbreviated breast MRI protocol: correlation of imaging characteristics and pathology with lesion detection and conspicuity [J]. Eur J Radiol, 2016, 85(4): 815-23. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.01.005 |
| [29] | Ao F, Yan Y, Zhang ZL, et al. The value of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging combined with apparent diffusion coefficient in the differentiation of benign and malignant diseases of the breast [J]. Acta Radiol, 2022, 63(7): 891-900. doi:10.1177/02841851211024002 |
| [30] | Westra C, Dialani V, Mehta TS, et al. Using T2-weighted sequences to more accurately characterize breast masses seen on MRI [J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2014, 202(3): W183-190. doi:10.2214/ajr.13.11266 |
| [31] | Yuen S, Monzawa S, Yanai S, et al. The association between MRI findings and breast cancer subtypes: focused on the combination patterns on diffusion-weighted and T2-weighted images [J]. Breast Cancer, 2020, 27(5): 1029-37. doi:10.1007/s12282-020-01105-z |
| [32] | Santamaría G. Radiologic and pathologic findings in breast tumors with high signal intensity on T2-weighted MR images [J]. Radio Graphics, 2010, 30(2): 533-48. doi:10.1148/rg.302095044 |
| [33] | Baltzer PA, Benndorf M, Dietzel M, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of unenhanced MR mammography (DWI combined with T2-weighted TSE imaging, ueMRM) for the differentiation of mass lesions [J]. Eur Radiol, 2010, 20(5): 1101-10. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1654-5 |
| [1] | 马思源, 张博超, 浦春. Circ_0000437通过靶向let-7b-5p/CTPS1轴促进乳腺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移及上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [2] | 张兆君, 吴琼, 谢苗苗, 叶洳吟, 耿晨晨, 石纪雯, 杨清玲, 王文锐, 石玉荣. 层状双氢氧化物负载si-NEAT1通过miR-133b/PD-L1轴调控乳腺癌紫杉醇耐药及巨噬细胞极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1718-1731. |
| [3] | 李嘉豪, 冼瑞婷, 李荣. 下调ACADM介导的脂毒性抑制雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌细胞的侵袭与转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1163-1173. |
| [4] | 董振翔, 郭义昊, 刘蔷, 张益哲, 丘倩怡, 张晓东, 冯衍秋. 基于双极读出梯度的单重复时间腰椎定量磁化率成像[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1336-1342. |
| [5] | 陈镝, 吕莹, 郭怡欣, 张怡荣, 王蕊璇, 周小若, 陈雨欣, 武晓慧. 双氢青蒿素可显著增强阿霉素诱导的三阴性乳腺癌细胞凋亡:基于负向调控STAT3/HIF-1α通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [6] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [7] | 薛良军, 谈秋瑜, 许静文, 冯璐, 李文锦, 颜亮, 李玉磊. MiR-6838-5p过表达下调DDR1基因表达抑制乳腺癌MCF-7细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1677-1684. |
| [8] | 欧阳明子, 崔佳琦, 王慧, 梁正, 皮大锦, 陈利国, 陈前军, 吴迎朝. 开心散通过减轻前额叶皮质铁死亡缓解小鼠的阿霉素化疗性抑郁[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [9] | 刘科, 马振岩, 付磊, 张丽萍, 阿鑫, 肖少波, 张震, 张洪博, 赵蕾, 钱赓. 心脏磁共振成像整体纵向应变对急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死后左心室重构的预测价值:403例前瞻性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1033-1039. |
| [10] | 房锦存, 刘立威, 林俊豪, 陈逢生. CDHR2过表达通过抑制PI3K/Akt通路抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1117-1125. |
| [11] | 崔芝, 马萃娇, 王倩茹, 陈金豪, 严子阳, 杨建林, 吕亚丰, 曹春雨. 表达 TGF-βⅡ受体的腺相关病毒载体抑制小鼠三阴性乳腺癌4T1细胞的增殖和肺转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 818-826. |
| [12] | 曾佑琴, 陈思雨, 刘燕, 刘奕彤, 张玲, 夏姣, 吴心语, 魏常友, 冷平. AKBA联合阿霉素抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231的增殖、迁移和裸鼠移植瘤生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2449-2460. |
| [13] | 黄晓茵, 陈凤莲, 张煜, 梁淑君. 多参数多区域MRI影像组学特征与临床信息联合模型可有效预测脑胶质瘤患者生存期[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 2004-2014. |
| [14] | 何慧珊, 郭二嘉, 蒙文仪, 王 彧, 王 雯, 何文乐, 吴元魁, 阳 维. 基于磁共振图像机器学习放射组学模型预测脑胶质瘤的强化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 194-200. |
| [15] | 徐梦歧, 石宇彤, 刘俊平, 吴敏敏, 张凤梅, 何志强, 唐 敏. JAG1影响单核-巨噬细胞重塑三阴性乳腺癌转移前微环境:基于外泌体中的LncRNA MALAT1[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1525-1535. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||