南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1712-1719.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.11
左涵珺( ), 段兆达, 王朝, 郭涛, 石金沙, 石浩龙, 李娟娟(
), 段兆达, 王朝, 郭涛, 石金沙, 石浩龙, 李娟娟( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-23
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-09-30
通讯作者:
李娟娟
E-mail:zhj2020320@163.com;lijuanjuan@kmmu.edu.cn
作者简介:左涵珺,在读博士研究生,E-mail: zhj2020320@163.com
基金资助:
Hanjun ZUO( ), Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI(
), Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI( )
)
Received:2024-01-23
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-09-30
Contact:
Juanjuan LI
E-mail:zhj2020320@163.com;lijuanjuan@kmmu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨天麻素通过PI3K/AKT信号通路对新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤(HIBD)后活化小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应的作用机制。 方法 将39只3日龄新生SD大鼠随机分为假手术组(sham,n=9)、缺氧缺血模型组(HIBD,n=15)、天麻素处理组(HIBD+G,n=15)。采用Western blotting检测HIBD后TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-10和TGF-β1蛋白的表达;网络药理学筛选天麻素治疗HIBD的潜在作用靶点;Western blotting检测HIBD和氧糖剥夺(OGD)诱导活化的小胶质细胞中PI3K/AKT信号通路的表达;CCK8检测PI3K/AKT通路特异性抑制剂LY294002对BV-2小胶质细胞的细胞毒性作用;RT-qPCR检测LY294002干预后天麻素对TNF-α和TGF-β1的mRNA水平的影响。 结果 Western blotting显示,与HIBD组相比,天麻素降低缺血侧胼胝体区TNF-α和IL-1β的蛋白表达(P<0.05),促进IL-10和TGF-β1的蛋白表达(P<0.05);网络药理学显示,PI3K/AKT信号通路显著富集,且天麻素与PI3K之间具有较好的结合能力;Western blotting显示,与HIBD组、OGD组相比,天麻素促进PI3K和AKT的磷酸化水平(P<0.05);CCK8结果显示LY294002在0~120 μmol/L浓度范围内对BV-2小胶质细胞没有细胞毒性作用;RT-qPCR结果显示,与对照组相比,OGD组TNF-α的mRNA水平升高,TGF-β1的mRNA水平降低(P<0.05);天麻素干预后降低TNF-α的mRNA水平,升高TGF-β1的mRNA水平(P<0.05);LY294002处理后TNF-α的mRNA水平进一步升高,TGF-β1的mRNA水平进一步降低(P<0.05);而LY294002与天麻素联合用药后TNF-α和TGF-β1的mRNA水平无明显变化。 结论 天麻素能抑制HIBD后活化小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应,其作用机制与PI3K/AKT信号通路有关。
左涵珺, 段兆达, 王朝, 郭涛, 石金沙, 石浩龙, 李娟娟. 天麻素经PI3K/AKT通路改善新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤后小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719.
Hanjun ZUO, Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI. Gastrodin improves microglia-mediated inflammatory response after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719.
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| TGF-β1 F | GCTGAACCAAGGAGACGGAA |
| TGF-β1 R | TCTTCTCTGTGGAGCGTTGAT |
| TNF-α F | ACCCTCACACTCACAAACCA |
| TNF-α R | GGCAGAGAGGAGGTTGACTTT |
| β-actin F | GTGGGAATGGGTCAGAAGGA |
| β-actin R | TACATGGCTGGGGTGTTGAA |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| TGF-β1 F | GCTGAACCAAGGAGACGGAA |
| TGF-β1 R | TCTTCTCTGTGGAGCGTTGAT |
| TNF-α F | ACCCTCACACTCACAAACCA |
| TNF-α R | GGCAGAGAGGAGGTTGACTTT |
| β-actin F | GTGGGAATGGGTCAGAAGGA |
| β-actin R | TACATGGCTGGGGTGTTGAA |
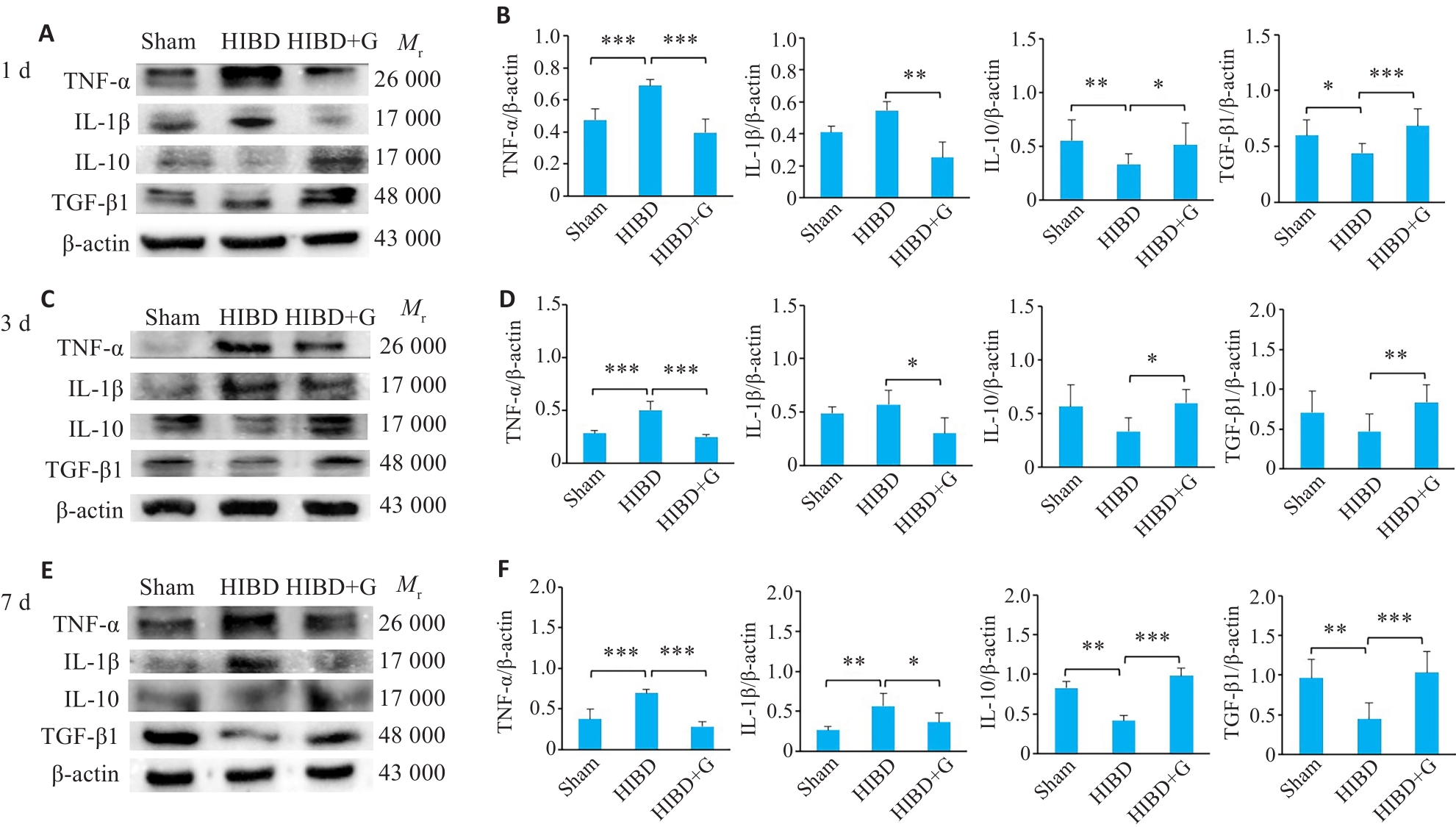
图1 蛋白印迹法检测HIBD后天麻素对炎性因子TNF-α、IL-1β、抗炎因子IL-10和转化生长因子TGF-β1蛋白表达的影响
Fig.1 Effect of gastrodin on expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10 and TGF-β1 proteins in the in brain tissue of neonatal rats at 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days after HIBD detected by Western blotting. A, C, E: Protein blots of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10, and TGF-β1. B, D, F: Quantification of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10, and TGF-β1 expression levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (n=3).
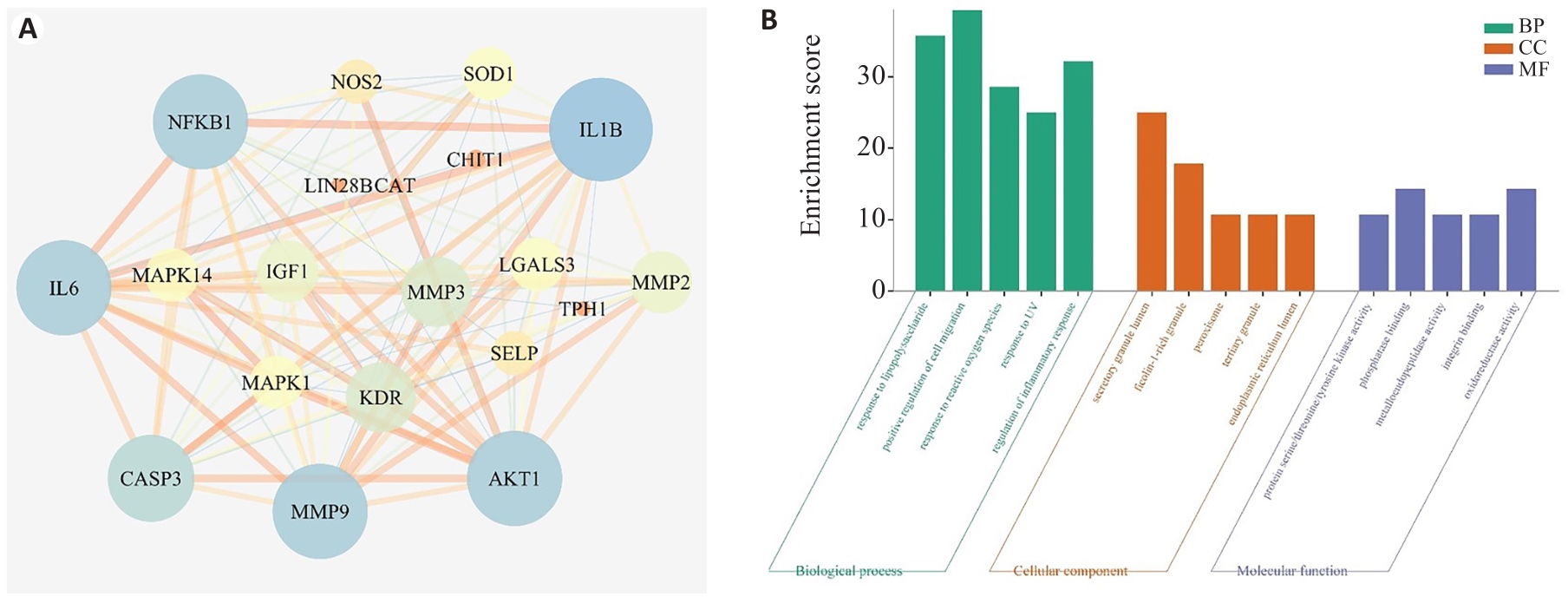
图2 天麻素治疗HIBD潜在核心靶点的PPI网络图和GO富集分析
Fig.2 PPI network diagram and GO enrichment analysis of potential core target of gastrodin treatment of HIBD. A: PPI network diagram. B: GO enrichment analysis.
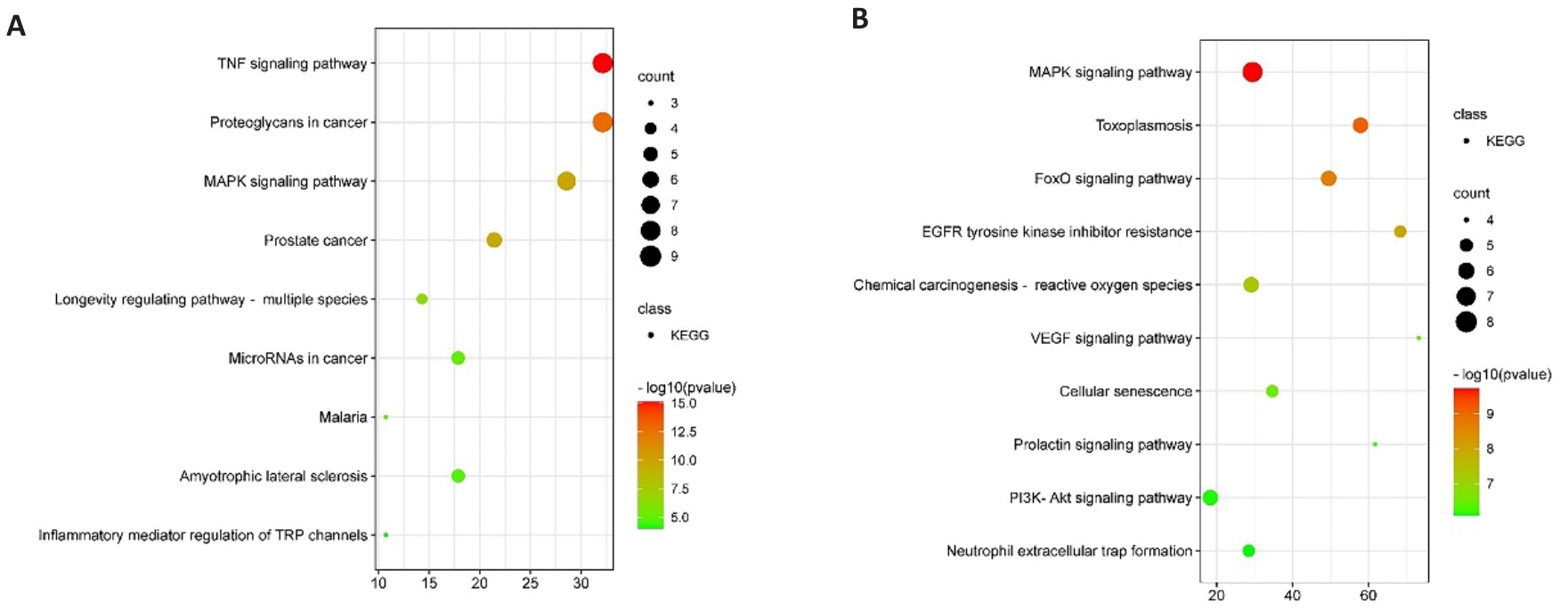
图3 天麻素治疗HIBD潜在核心靶点的KEGG富集分析
Fig.3 KEGG enrichment analysis of potential core targets for gastrodin treatment of HIBD. A, B: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
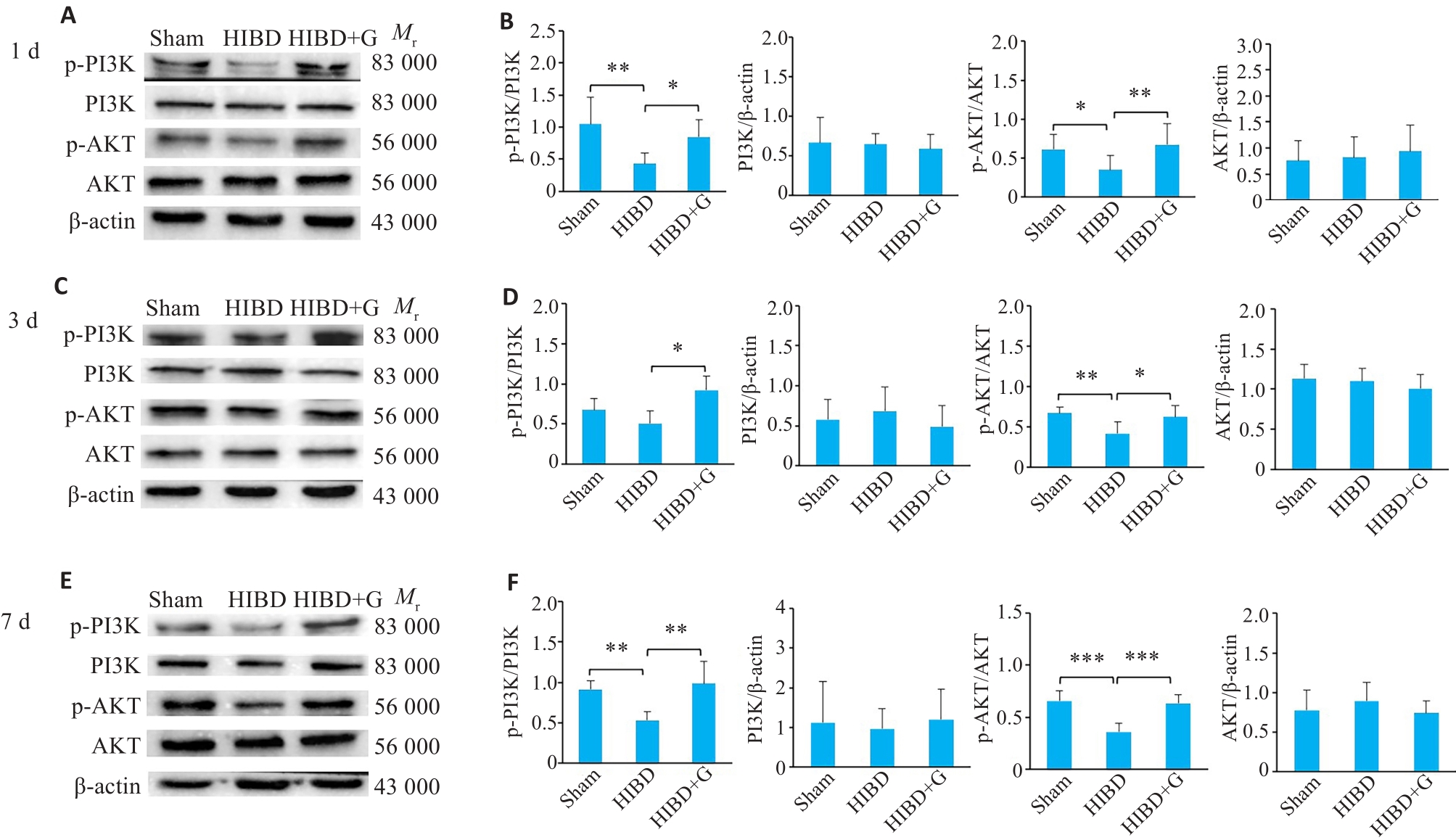
图5 蛋白印迹法检测HIBD后天麻素对活化小胶质细胞中PI3K/AKT信号通路表达的影响
Fig.5 Effect of gastrodin on expressions of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in activated microglia of neonatal rats at 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days after HIBD detected by Western blotting. A, C, E: Western blots of the related proteins in PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. B, D, F: Quantification of P-PI3K, PI3K, P-AKT, and AKT protein levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (n=3).
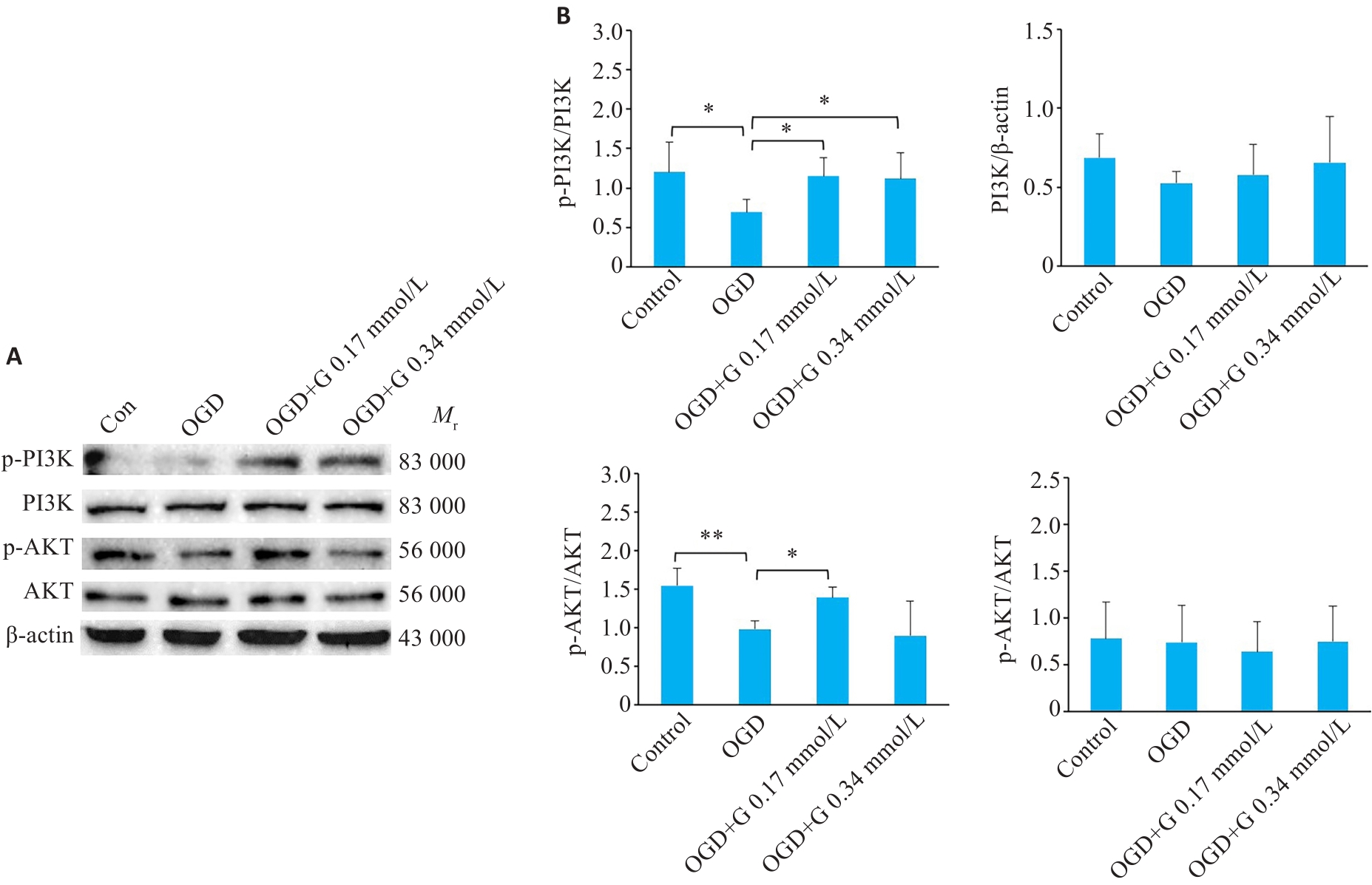
图6 蛋白印迹法检测OGD后天麻素对活化小胶质细胞中PI3K/AKT信号通路表达的影响
Fig.6 Effect of gastrodin on expression of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in activated microglia BV-2 cells after OGD detected by western blotting. A: Western blots of the related proteins in PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in BV-2 cells. B: Quantification of P-PI3K, PI3K, P-AKT, and AKT protein levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (n=3).
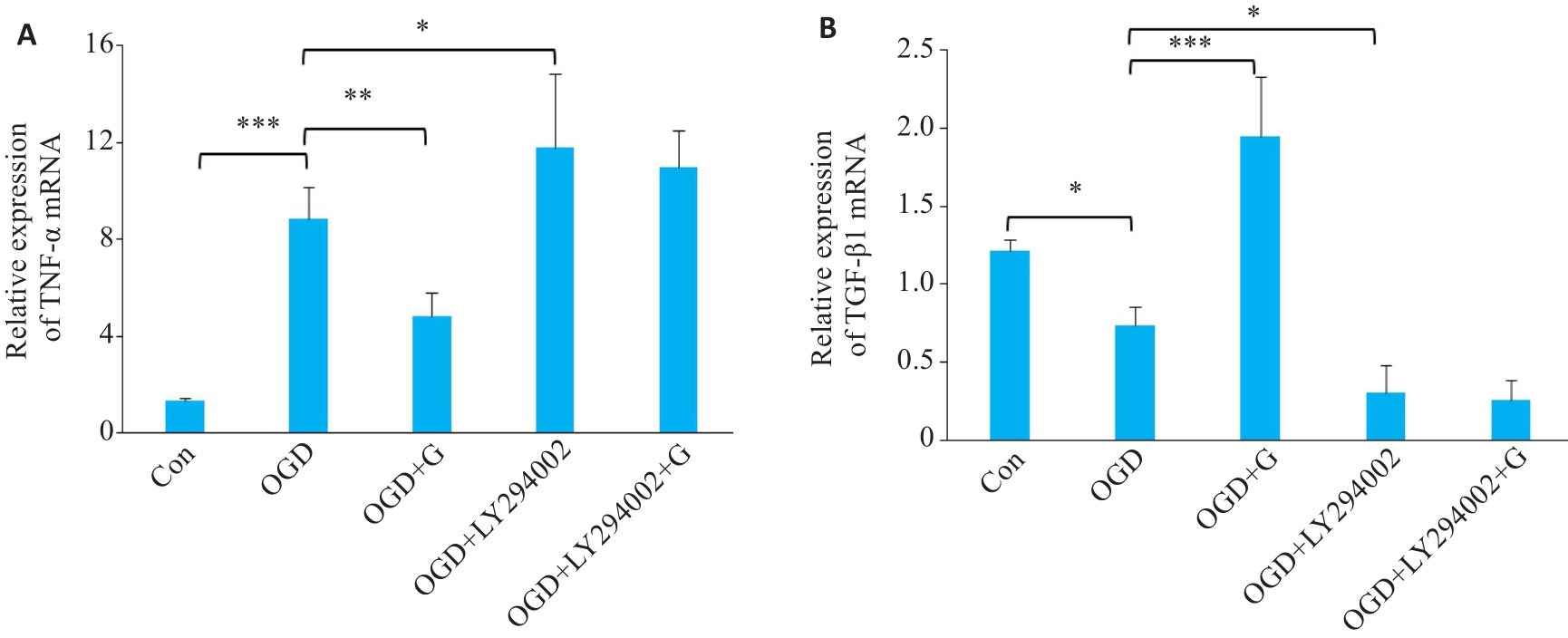
图8 RT-qPCR检测OGD后天麻素通过PI3K/AKT信号通路对活化小胶质细胞中炎症因子TNF-α和转化生长因子TGF-β1 mRNA水平表达变化的影响
Fig.8 Effect of gastrodin and LY294002 on TNF-α (A) and TGF-β1 mRNA (B) expressions in BV-2 cells with OGD detected by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (n=3).
| 1 | Le K, Song ZP, Deng J, et al. Quercetin alleviates neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury by inhibiting microglia-derived oxidative stress and TLR4-mediated inflammation[J]. Inflamm Res, 2020, 69(12): 1201-13. |
| 2 | Lawn JE, Blencowe H, Oza S, et al. Every Newborn: progress, priorities, and potential beyond survival[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384(9938): 189-205. |
| 3 | Douglas-Escobar M, Weiss MD. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review for the clinician[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2015, 169(4): 397-403. |
| 4 | Zalewska T, Jaworska J, Ziemka-Nalecz M. Current and experimental pharmacological approaches in neonatal hypoxic- ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2015, 21(11): 1433-9. |
| 5 | Gunn AJ, Thoresen M. Neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2019, 162: 217-37. |
| 6 | Wassink G, Davidson JO, Dhillon SK, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2019, 19(2): 2. |
| 7 | Wood T, Osredkar D, Puchades M, et al. Treatment temperature and insult severity influence the neuroprotective effects of therapeutic hypothermia[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 23430. |
| 8 | Wu YW, Mathur AM, Chang T, et al. High-dose erythropoietin and hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a phase II trial[J]. Pediatrics, 2016, 137(6): e20160191. |
| 9 | Hagberg H, Mallard C, Ferriero DM, et al. The role of inflammation in perinatal brain injury[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2015, 11(4): 192-208. |
| 10 | Deng WB. Neurobiology of injury to the developing brain[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2010, 6(6): 328-36. |
| 11 | Zhou DD, Ji L, Chen YG. TSPO modulates IL-4-induced microglia/macrophage M2 polarization via PPAR‑γ pathway[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2020, 70(4): 542-9. |
| 12 | Kim HJ, Moon KD, Lee DS, et al. Ethyl ether fraction of Gastrodia elata Blume protects amyloid beta peptide-induced cell death[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2003, 84(1): 95-8. |
| 13 | Kim HJ, Moon KD, Oh SY, et al. Ether fraction of methanol extracts of Gastrodia elata, a traditional medicinal herb, protects against kainic acid-induced neuronal damage in the mouse hippocampus[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2001, 314(1/2): 65-8. |
| 14 | Zeng XH, Zhang SM, Zhang L, et al. A study of the neuroprotective effect of the phenolic glucoside gastrodin during cerebral ischemia in vivo and in vitro [J]. Planta Med, 2006, 72(15): 1359-65. |
| 15 | Deng CJ, Chen HZ, Meng ZY, et al. Gastrodin and vascular dementia: advances and current perspectives[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022: 2563934. |
| 16 | Liu Y, Gao JL, Peng M, et al. A review on central nervous system effects of gastrodin[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 24. |
| 17 | Zhang JQ, Li LY, Liu Q, et al. Gastrodin programs an Arg-1+ microglial phenotype in hippocampus to ameliorate depression- and anxiety-like behaviors via the Nrf2 pathway in mice[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 113: 154725. |
| 18 | Guo J, Zhang XL, Bao ZR, et al. Gastrodin regulates the Notch signaling pathway and Sirt3 in activated microglia in cerebral hypoxic-ischemia neonatal rats and in activated BV-2 microglia[J]. Neuromolecular Med, 2021, 23(3): 348-62. |
| 19 | Zhu M, Li D, Wu Y, et al. TREM-2 promotes macrophage-mediated eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via a PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2014, 79(3): 187-96. |
| 20 | Lv MR, Li B, Wang MG, et al. RETRACTED: activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway promotes neuroprotection of the δ‑opioid receptor agonist against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat models[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2017, 93: 230-7. |
| 21 | Tu XK, Zhang HB, Shi SS, et al. 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton reduces inflammatory reaction and ischemic brain damage through the activation of PI3K/akt signaling pathway[J]. Neurochem Res, 2016, 41(10): 2779-87. |
| 22 | Liu SJ, Liu XY, Li JH, et al. Gastrodin attenuates microglia activation through renin-angiotensin system and Sirtuin3 pathway[J]. Neurochem Int, 2018, 120: 49-63. |
| 23 | Chen Z, Hu Y, Lu RF, et al. MicroRNA-374a-5p inhibits neuroinflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome targeted Smad6[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 252: 117664. |
| 24 | Karve IP, Taylor JM, Crack PJ. The contribution of astrocytes and microglia to traumatic brain injury[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2016, 173(4): 692-702. |
| 25 | Shrivastava SK, Dalko E, Delcroix-Genete D, et al. Uptake of parasite-derived vesicles by astrocytes and microglial phagocytosis of infected erythrocytes may drive neuroinflammation in cerebral malaria[J]. Glia, 2017, 65(1): 75-92. |
| 26 | Nayak D, Roth TL, McGavern DB. Microglia development and function[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2014, 32: 367-402. |
| 27 | Lalancette-Hébert M, Gowing G, Simard A, et al. Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain[J]. J Neurosci, 2007, 27(10): 2596-605. |
| 28 | Tsuji S, di Martino E, Mukai T, et al. Aggravated brain injury after neonatal hypoxic ischemia in microglia-depleted mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 111. |
| 29 | Serdar M, Kempe K, Rizazad M, et al. Early pro-inflammatory microglia activation after inflammation-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2019, 13: 237. |
| 30 | Dai JN, Zong Y, Zhong LM, et al. Gastrodin inhibits expression of inducible NO synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and proinflammatory cytokines in cultured LPS-stimulated microglia via MAPK pathways[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(7): e21891. |
| 31 | Peng Z, Wang H, Zhang R, et al. Gastrodin ameliorates anxiety-like behaviors and inhibits IL-1beta level and p38 MAPK phosphorylation of hippocampus in the rat model of posttraumatic stress disorder[J]. Physiol Res, 2013, 62(5): 537-45. |
| 32 | Jafari M, Ghadami E, Dadkhah T, et al. PI3k/AKT signaling pathway: erythropoiesis and beyond[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(3): 2373-85. |
| 33 | Wang JT, Ma WM, Liu YD. Long non-coding RNA HULC promotes bladder cancer cells proliferation but inhibits apoptosis via regulation of ZIC2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2017, 20(4): 425-34. |
| 34 | Choudhury R, Bonacci T, Wang XX, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF(cyclin F) transmits AKT signaling to the cell-cycle machinery[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 20(13): 3212-22. |
| 35 | Xian MH, Cai JL, Zheng KN, et al. Aloe-emodin prevents nerve injury and neuroinflammation caused by ischemic stroke via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and NF-κB pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(17): 8056-67. |
| 36 | Wang XS, Tian Z, Zhang N, et al. Protective effects of gastrodin against autophagy-mediated astrocyte death[J]. Phytother Res, 2016, 30(3): 386-96. |
| [1] | 范正媛, 沈子涵, 李亚, 沈婷婷, 李高峰, 李素云. 补肺益肾方对香烟烟雾提取物诱导的人支气管上皮细胞损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1372-1379. |
| [2] | 王静娴, 任自敬, 周佩洋. S1PR5激动与过表达通过调控氧化应激增强脑微血管内皮细胞屏障功能抵抗氧糖剥夺/复氧复糖损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1451-1459. |
| [3] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [4] | 夏冰, 彭进, 丁九阳, 王杰, 唐国伟, 刘国杰, 王沄, 万昌武, 乐翠云. ATF3通过NF-κB信号通路调控动脉粥样硬化斑块内的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [5] | 陈悦, 肖林雨, 任侣, 宋雪, 李静, 胡建国. 水晶兰苷通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路减少神经元凋亡改善脊髓损伤后小鼠的运动功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [6] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [7] | 董妍妍, 张可敬, 储俊, 储全根. 抵当汤含药血清通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路增强高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [8] | 廖茗, 钟文华, 张冉, 梁娟, 徐文陶睿, 万文珺, 吴超, 李曙. 源自蛇毒的蛋白C激活剂通过调控HIF-1α抑制BNIP3活性氧生成保护人脐静脉内皮细胞免受缺氧-复氧损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 614-621. |
| [9] | 黄菊, 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 耿志军, 左芦根, 李静, 胡建国. 紫花前胡苷通过抑制肠上皮细胞焦亡改善2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [10] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | 裴月娇, 刘慧敏, 昕宇, 刘波. miR-124通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路改善睡眠剥夺大鼠认知功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 340-346. |
| [12] | 展俊平, 黄硕, 孟庆良, 范围, 谷慧敏, 崔家康, 王慧莲. 缺氧微环境下补阳还五汤通过抑制BNIP3-PI3K/Akt通路抑制类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞的线粒体自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 35-42. |
| [13] | 张玉如, 万磊, 方昊翔, 李方泽, 王丽文, 李柯霏, 闫佩文, 姜辉. miR-155-5p介导PIK3R1负调控PI3K/AKT信号通路促进原发性干燥综合征人唾液腺上皮细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 65-71. |
| [14] | 周雪利, 李华, 陈青宇, 靳美娜, 李海波, 白炜, 贾楚璇, 魏翠英. 慢性间歇低氧和复氧对大鼠胰岛素抵抗及骨骼肌miR-27a-3p/PPARγ/IRS1/PI3K/AKT表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1729-1737. |
| [15] | 张先恒, 刘健, 韩琦, 陈一鸣, 丁香, 陈晓露. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路改善痛风性关节炎大鼠的炎症反应及尿酸、脂质代谢失衡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||