南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1653-1661.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.04
陈孝华1( ), 鲁辉1, 王子良1, 王炼1, 夏勇生1, 耿志军2,4, 张小凤2,4, 宋雪2,4, 王月月3,4, 李静3,4, 胡建国3,4, 左芦根1,4(
), 鲁辉1, 王子良1, 王炼1, 夏勇生1, 耿志军2,4, 张小凤2,4, 宋雪2,4, 王月月3,4, 李静3,4, 胡建国3,4, 左芦根1,4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-22
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-09-30
通讯作者:
左芦根
E-mail:chenxiaohua9116@163.com;zuolugen@126.com
作者简介:陈孝华,硕士,E-mail: chenxiaohua9116@163.com
基金资助:
Xiaohua CHEN1( ), Hui LU1, Ziliang WANG1, Lian WANG1, Yongsheng XIA1, Zhijun GENG2,4, Xiaofeng ZHANG2,4, Xue SONG2,4, Yueyue WANG3,4, Jing LI3,4, Jianguo HU3,4, Lugen ZUO1,4(
), Hui LU1, Ziliang WANG1, Lian WANG1, Yongsheng XIA1, Zhijun GENG2,4, Xiaofeng ZHANG2,4, Xue SONG2,4, Yueyue WANG3,4, Jing LI3,4, Jianguo HU3,4, Lugen ZUO1,4( )
)
Received:2024-04-22
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-09-30
Contact:
Lugen ZUO
E-mail:chenxiaohua9116@163.com;zuolugen@126.com
摘要:
目的 探讨Abelson相互作用因子2(ABI2)在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及机制。 方法 通过TIMER2.0和GEPIA数据库分析ABI2在泛癌和胃癌中的表达,采用Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库分析ABI2表达水平与胃癌预后的关系,通过DAVID数据库预测ABI2在生物系统中的功能。纳入在我院于2016年1月~2018年10月接受胃癌根治术治疗的120例胃癌患者,检测胃癌及癌旁组织中ABI2的表达水平,分析其与疾病进展的联系,并通过Cox单因素和多因素分析影响患者预后的危险因素。构建胃癌细胞系(MGC-803)ABI2干扰及过表达模型并构建裸鼠移植瘤模型,联合CCK-8、划痕、Transwell和免疫印迹实验分析ABI2对胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响。结合体内外研究分析ABI2影响胃癌细胞恶性生物学行为的可能分子机理。 结果 生信分析和本院胃癌组织检测结果表明ABI2在胃癌组织中高表达(P<0.05)。Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库分析表明ABI2低表达患者的术后生存率优于高表达患者(P<0.0001)。本院患者的生存分析结果显示,胃癌组织中ABI2高表达患者术后5年生存率降低(P<0.0001),Cox单因素和多因素生存分析进一步表明,ABI2高表达是影响胃癌患者预后的独立危险因素(P=0.022,HR=1.887,95% CI:1.096~3.249)。富集分析提示,ABI2的作用可能与Wnt信号通路相关。上调ABI2促进裸鼠移植瘤和胃癌细胞的增殖能力(P<0.05),并增加Vimentin和N-cadherin的表达,同时降低E-cadherin的表达(P<0.05);下调ABI2则相反(P<0.05)。机制分析发现上调ABI2促进移植瘤组织和胃癌细胞中Wnt2和β-catenin的表达(P<0.05),下调ABI2则相反(P<0.05)。 结论 ABI2在胃癌中表达升高并影响疾病远期预后,其可能与调控Wnt信号通路进而促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力有关。
陈孝华, 鲁辉, 王子良, 王炼, 夏勇生, 耿志军, 张小凤, 宋雪, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国, 左芦根. ABI2在胃癌进展和预后中的作用及其调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661.
Xiaohua CHEN, Hui LU, Ziliang WANG, Lian WANG, Yongsheng XIA, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Xue SONG, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU, Lugen ZUO. Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661.
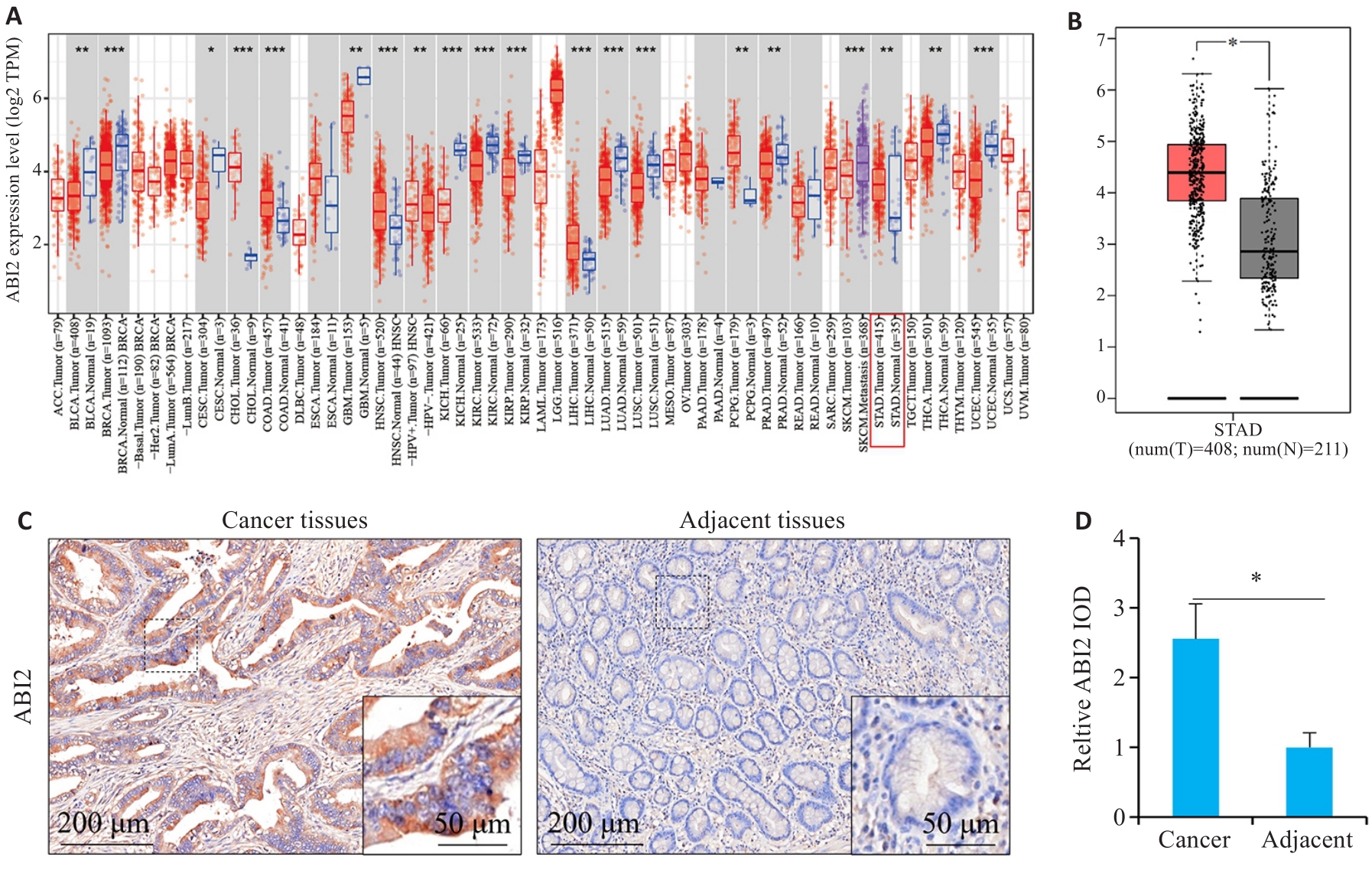
图1 ABI2在胃癌组织中表达水平升高
Fig.1 ABI2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer. A: Pan-cancer expression analysis. B: Expression of ABI2 in gastric and adjacent tissues. C, D: Immunohistochemical staining of ABI2 in gastric and adjacent tissues. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| Factors | n | ABI2 expression (n, %) | χ2 | Ρ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=60) | High (n=60) | |||||
| Gender | Male | 95 | 47 (49.47%) | 48 (50.53%) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| Female | 25 | 13 (52.00%) | 12 (48.00%) | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 49 | 27 (55.10%) | 22 (44.90%) | 0.862 | 0.353 |
| ≥60 | 71 | 33 (46.48%) | 38 (53.52%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | <5 | 57 | 35 (61.40%) | 22 (38.60%) | 5.647 | 0.017 |
| ≥5 | 63 | 25 (39.68%) | 38 (60.32%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | <37 | 67 | 44 (65.67%) | 23 (34.33%) | 14.903 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 53 | 16 (30.19%) | 37 (69.81%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | <5 | 64 | 33 (51.56%) | 31 (48.44%) | 0.134 | 0.714 |
| ≥5 | 56 | 27 (48.21%) | 29 (51.79%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 89 | 46 (51.69%) | 43 (48.31%) | 0.391 | 0.532 |
| Other | 31 | 14 (45.16%) | 17 (54.84%) | |||
| Pathological grading | G1-G2 | 66 | 41 (62.12%) | 25 (37.88%) | 8.620 | 0.003 |
| G3-G4 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 51 | 33 (64.71%) | 18 (35.29%) | 7.673 | 0.006 |
| T3-T4 | 69 | 27 (39.13%) | 42 (60.87%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 60 | 36 (60.00%) | 24 (40.00%) | 4.800 | 0.028 |
| N2-N3 | 60 | 24 (40.00%) | 36 (60.00%) | |||
表1 胃癌组织中ABI2的表达量与胃癌患者临床及病理参数间的关系
Tab.1 Correlation of ABI2 expression level with clinicopathological parameters of gastric cancer patients
| Factors | n | ABI2 expression (n, %) | χ2 | Ρ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=60) | High (n=60) | |||||
| Gender | Male | 95 | 47 (49.47%) | 48 (50.53%) | 0.051 | 0.822 |
| Female | 25 | 13 (52.00%) | 12 (48.00%) | |||
| Age (year) | <60 | 49 | 27 (55.10%) | 22 (44.90%) | 0.862 | 0.353 |
| ≥60 | 71 | 33 (46.48%) | 38 (53.52%) | |||
| CEA (μg/L) | <5 | 57 | 35 (61.40%) | 22 (38.60%) | 5.647 | 0.017 |
| ≥5 | 63 | 25 (39.68%) | 38 (60.32%) | |||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | <37 | 67 | 44 (65.67%) | 23 (34.33%) | 14.903 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 53 | 16 (30.19%) | 37 (69.81%) | |||
| Tumor size (cm) | <5 | 64 | 33 (51.56%) | 31 (48.44%) | 0.134 | 0.714 |
| ≥5 | 56 | 27 (48.21%) | 29 (51.79%) | |||
| Cancer cell type | Adenocarcinoma | 89 | 46 (51.69%) | 43 (48.31%) | 0.391 | 0.532 |
| Other | 31 | 14 (45.16%) | 17 (54.84%) | |||
| Pathological grading | G1-G2 | 66 | 41 (62.12%) | 25 (37.88%) | 8.620 | 0.003 |
| G3-G4 | 54 | 19 (35.19%) | 35 (64.81%) | |||
| T stage | T1-T2 | 51 | 33 (64.71%) | 18 (35.29%) | 7.673 | 0.006 |
| T3-T4 | 69 | 27 (39.13%) | 42 (60.87%) | |||
| N stage | N0-N1 | 60 | 36 (60.00%) | 24 (40.00%) | 4.800 | 0.028 |
| N2-N3 | 60 | 24 (40.00%) | 36 (60.00%) | |||
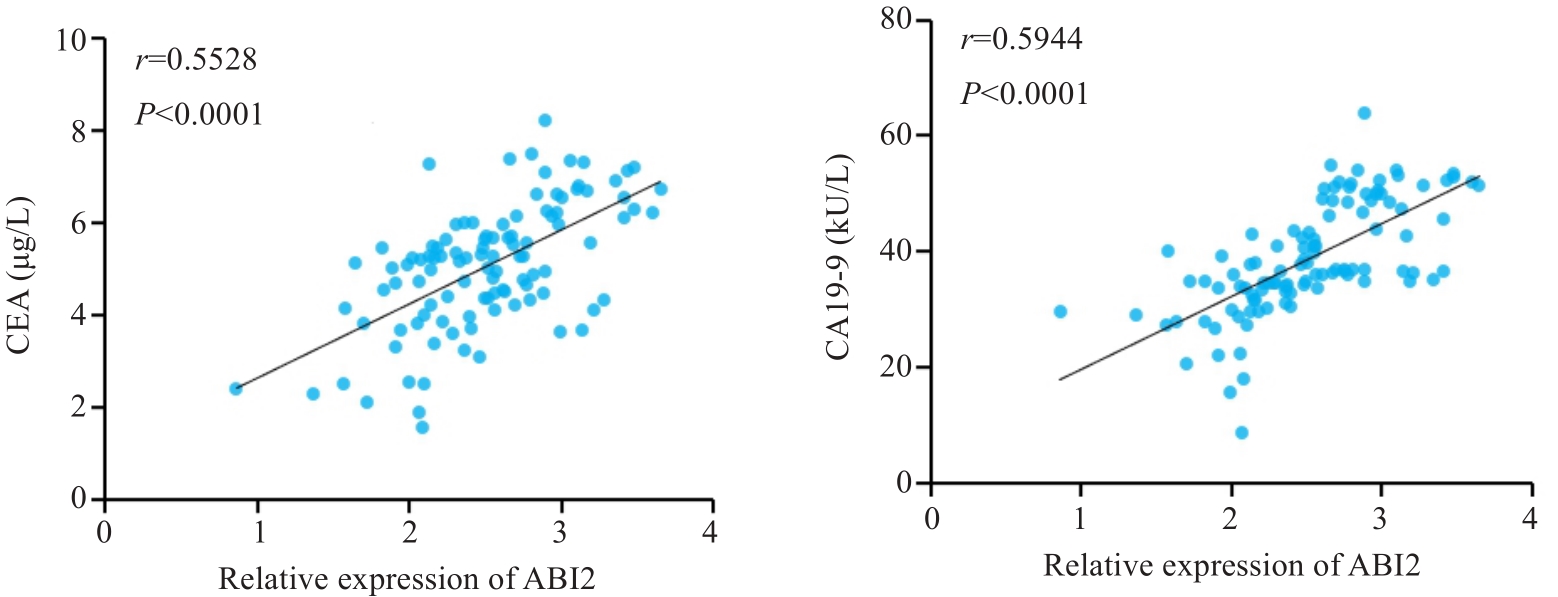
图2 胃癌组织中ABI2表达水平与外周血CEA和CA19-9水平呈正相关
Fig.2 ABI2 expression level in gastric cancer tissue is positively correlated with peripheral blood levels of CEA and CA19-9.
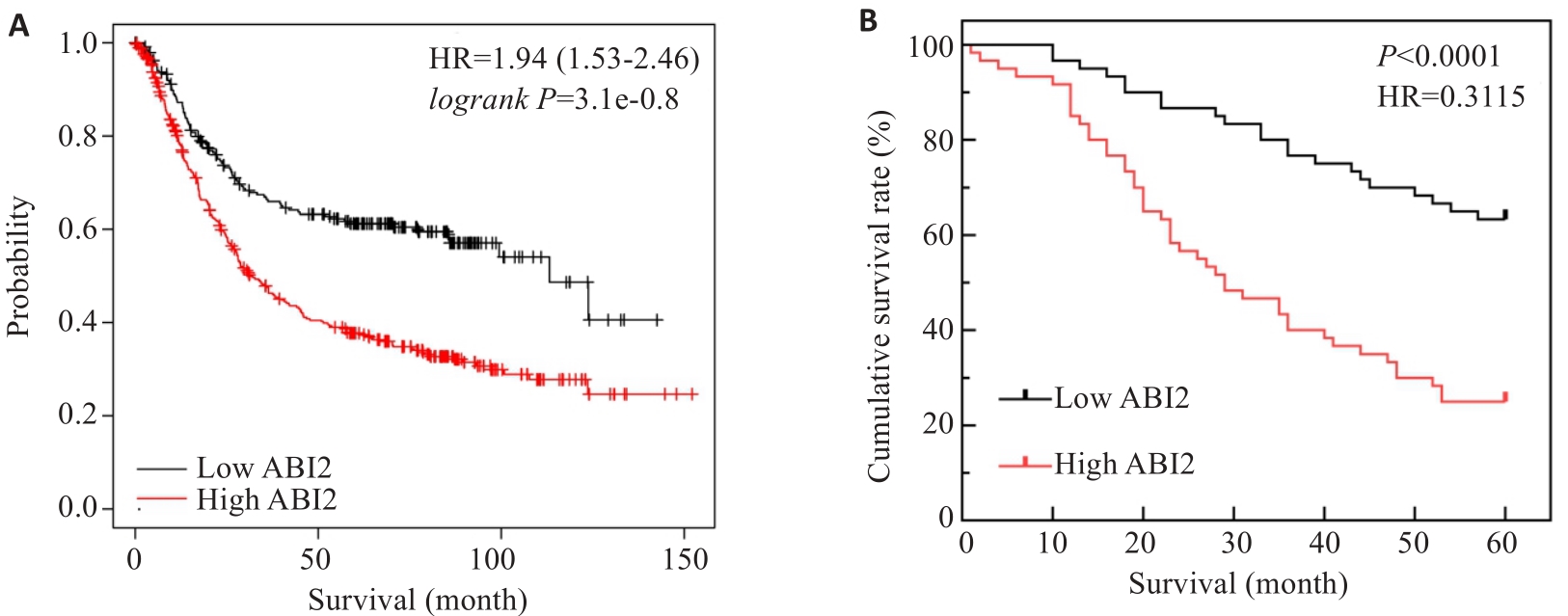
图3 胃癌组织中ABI2表达水平影响胃癌患者预后
Fig.3 ABI2 expression level in gastric cancer tissues affects prognosis of the patients. A: ABI2 expression level affects overall survival of gastric cancer patients. B: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of 5-year survival rate of the patients after radical gastrectomy.
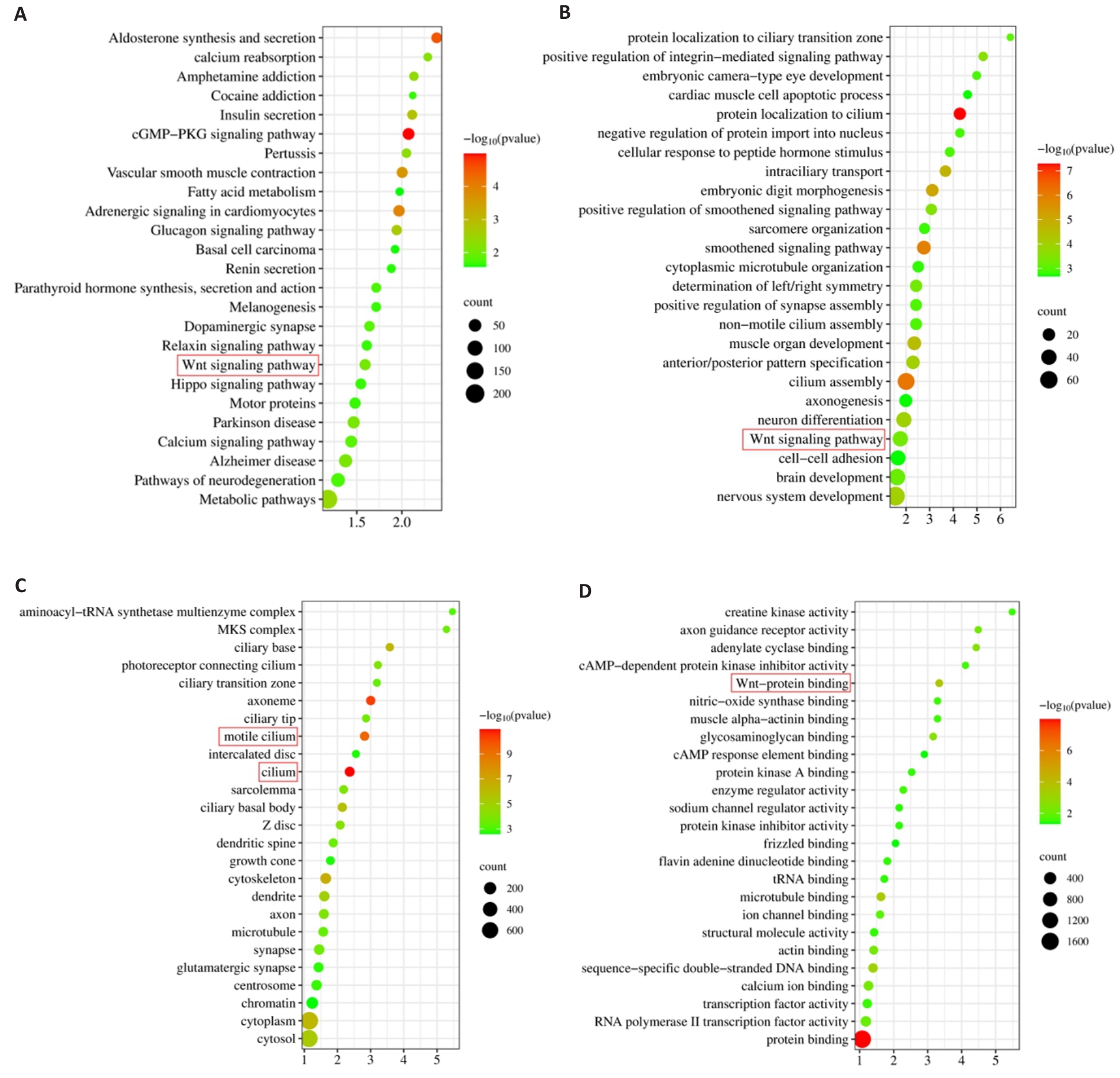
图5 ABI2的KEGG和GO富集分析结果
Fig.5 Results of KEGG and GO enrichment analysis. A: KEGG enrichment analysis. B-D: Biological processes, cellular component and molecular function in GO enrichment analysis.
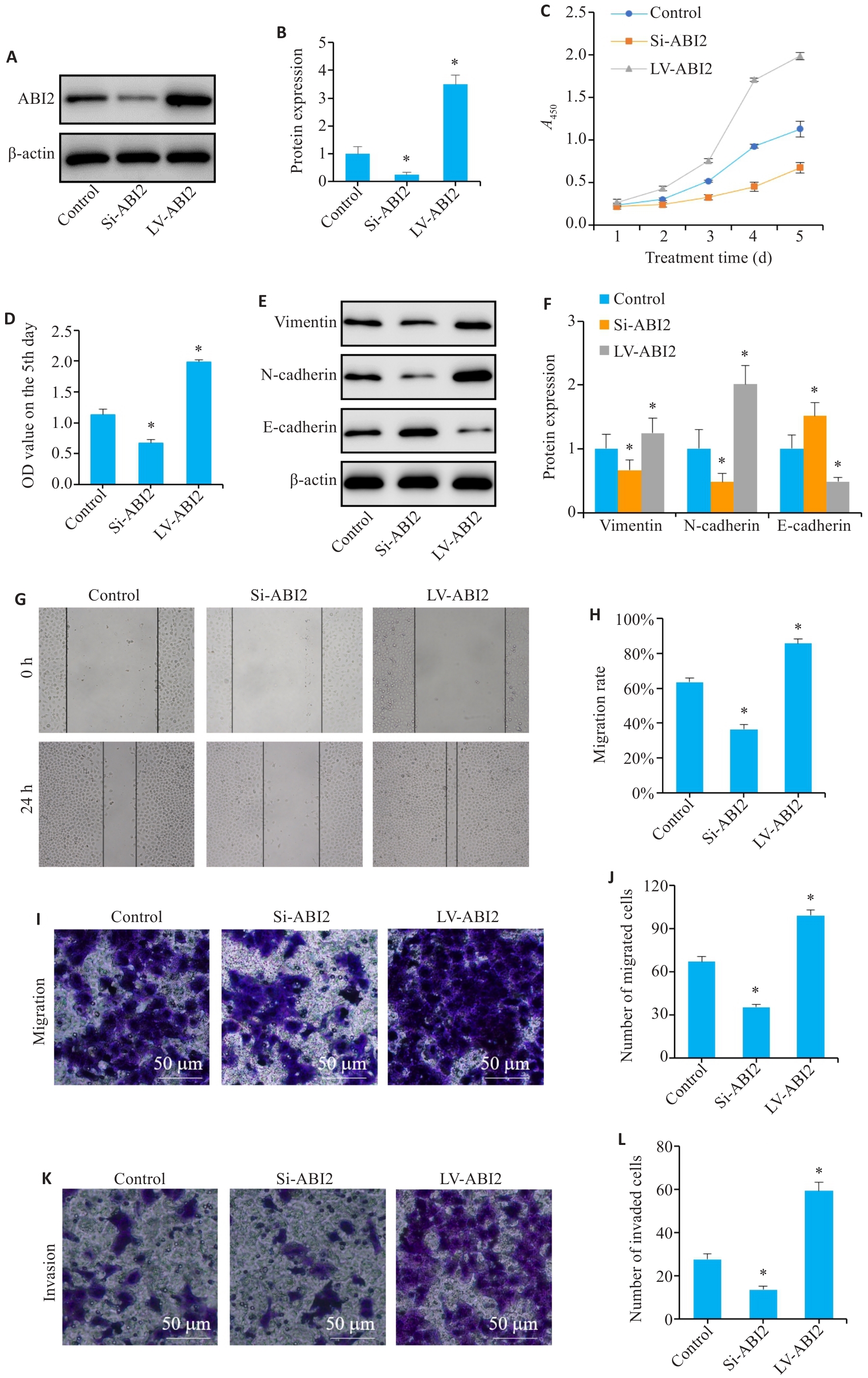
图6 ABI2在体外实验中促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和上皮间充质转化
Fig.6 ABI2 overexpression promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of gastric cancer cells in vitro. A, B: Lentiviral transfection efficiency. C, D: Results of CCK-8 assay (presented as A values) from day 1 to day 5. E, F: Expression of EMT markers in MGC803 cells. G, H: Wound-healing assay of the cells. I-L: Migration and invasion of MGC803 cells. Si: siRNA; LV: overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Control (n=3).
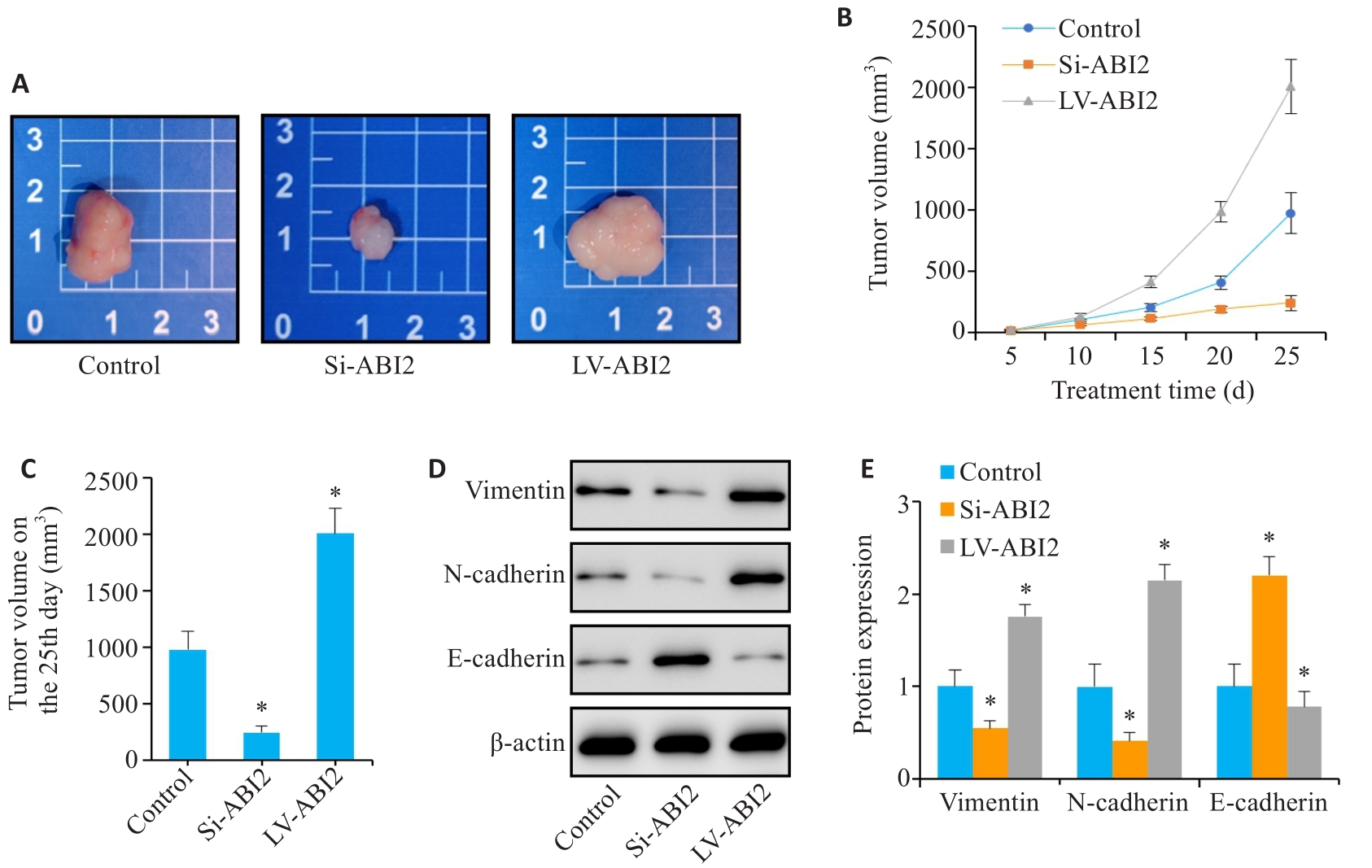
图7 ABI2在体内实验中促进胃癌细胞增殖和上皮间充质转化
Fig.7 ABI2 overexpression promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells in nude mice. A: Representative image of the transplanted tumors. B, C: Transplanted tumor volume from day 5 to day 25. D, E: Expression of EMT markers in the transplanted tumor. *P<0.05 vs Control (n=3).
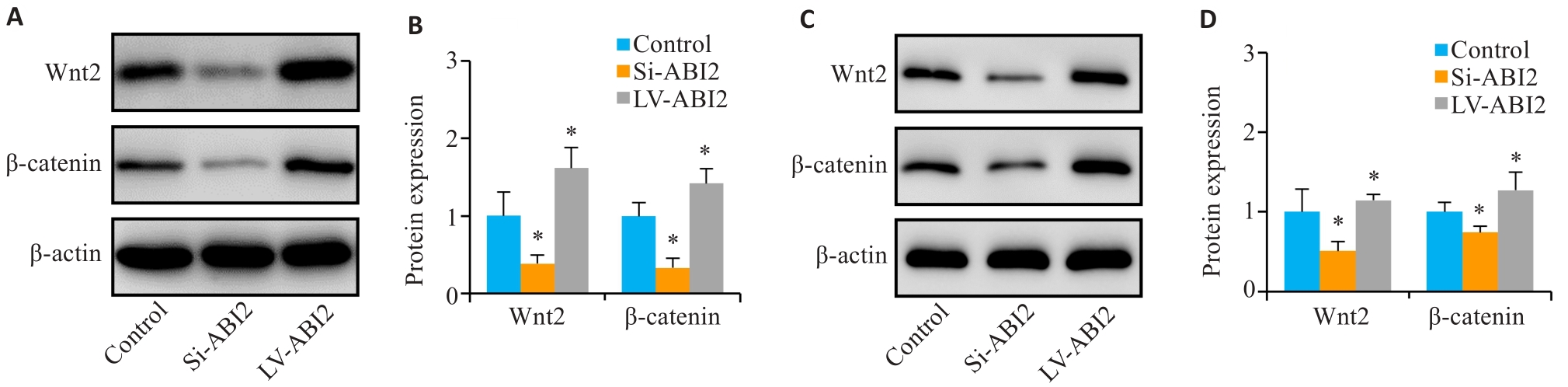
图8 ABI2对胃癌细胞恶性生物学行为的影响可能与Wnt通路相关
Fig.8 The effect of ABI2 on malignant biological behaviors of gastric cancer cells is related to the Wnt signaling pathway. A, B: Expression of Wnt2 and β-catenin in MGC803 cells. C, D: Expression of Wnt2 and β-catenin in the transplanted tumors. *P<0.05 vs Control (n=3).
| 1 | Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-48. |
| 2 | 郑荣寿, 张思维, 孙可欣, 等. 2016年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2023, 45(3): 212-20. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20220922-00647 |
| 3 | Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(3): 534-42. |
| 4 | Chia NY, Tan P. Molecular classification of gastric cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(5): 763-9. |
| 5 | Jiang PX, Tang SN, Hudgins H, et al. The Abl/Abi signaling links WAVE regulatory complex to Cbl E3 ubiquitin ligase and is essential for breast cancer cell metastasis[J]. Neoplasia, 2022, 32: 100819. |
| 6 | Ichigotani Y, Fujii K, Hamaguchi M, et al. In search of a function for the E3B1/Abi2/Argbp1/NESH family (Review)[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2002, 9(6): 591-5. |
| 7 | Zipfel PA, Bunnell SC, Witherow DS, et al. Role for the Abi/wave protein complex in T cell receptor-mediated proliferation and cytoskeletal remodeling[J]. Curr Biol, 2006, 16(1): 35-46. |
| 8 | Courtney KD, Grove M, Vandongen H, et al. Localization and phosphorylation of Abl-interactor proteins, Abi-1 and Abi-2, in the developing nervous system[J]. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2000, 16(3): 244-57. |
| 9 | Hirao N, Sato S, Gotoh T, et al. NESH (Abi-3) is present in the Abi/WAVE complex but does not promote c-Abl-mediated phosphorylation[J]. FEBS Lett, 2006, 580(27): 6464-70. |
| 10 | Li YZ, Clough N, Sun XL, et al. Bcr-Abl induces abnormal cytoskeleton remodeling, beta1 integrin clustering and increased cell adhesion to fibronectin through the Abl interactor 1 pathway[J]. J Cell Sci, 2007, 120(Pt 8): 1436-46. |
| 11 | Ryu JR, Echarri A, Li R, et al. Regulation of cell-cell adhesion by Abi/Diaphanous complexes[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2009, 29(7): 1735-48. |
| 12 | Stradal T, Courtney KD, Rottner K, et al. The Abl interactor proteins localize to sites of actin polymerization at the tips of lamellipodia and filopodia[J]. Curr Biol, 2001, 11(11): 891-5. |
| 13 | Jensen CC, Clements AN, Liou H, et al. PIM1 phosphorylates ABI2 to enhance actin dynamics and promote tumor invasion[J]. J Cell Biol, 2023, 222(6): e202208136. |
| 14 | Chen JD, Li HZ, Zhang B, et al. ABI2-mediated MEOX2/KLF4-NANOG axis promotes liver cancer stem cell and drives tumour recurrence[J]. Liver Int, 2022, 42(11): 2562-76. |
| 15 | Guan WL, He Y, Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 57. |
| 16 | Wang B, Mysliwiec T, Krainc D, et al. Identification of ArgBP1, an Arg protein tyrosine kinase binding protein that is the human homologue of a CNS-specific Xenopus gene[J]. Oncogene, 1996, 12(9): 1921-9. |
| 17 | Dai Z, Pendergast AM. Abi-2, a novel SH3-containing protein interacts with the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and modulates c-Abl transforming activity[J]. Genes Dev, 1995, 9(21): 2569-82. |
| 18 | Grove M, Demyanenko G, Echarri A, et al. ABI2-deficient mice exhibit defective cell migration, aberrant dendritic spine morphogenesis, and deficits in learning and memory[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(24): 10905-22. |
| 19 | Chen ZC, Borek D, Padrick SB, et al. Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex[J]. Nature, 2010, 468(7323): 533-8. |
| 20 | Shami Shah A, Batrouni AG, Kim D, et al. PLEKHA4/kramer attenuates dishevelled ubiquitination to modulate Wnt and planar cell polarity signaling[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 27(7): 2157-70. e8. |
| 21 | Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities[J]. Cell, 2017, 169(6): 985-99. |
| 22 | Zhao H, Ming TQ, Tang S, et al. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: pathogenic role and therapeutic target[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 144. |
| 23 | Li HJ, Ke FY, Lin CC, et al. ENO1 promotes lung cancer metastasis via HGFR and WNT signaling-driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(15): 4094-109. |
| 24 | Hiremath IS, Goel A, Warrier S, et al. The multidimensional role of the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway in human malignancies[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(1): 199-238. |
| 25 | Rim EY, Clevers H, Nusse R. The Wnt pathway: from signaling mechanisms to synthetic modulators[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2022, 91: 571-98. |
| 26 | Albrecht LV, Tejeda-Muñoz N, de Robertis EM. Cell biology of canonical Wnt signaling[J]. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 37: 369-89. |
| 27 | Cheng XX, Wang ZC, Chen XY, et al. Frequent loss of membranous E-cadherin in gastric cancers: a cross-talk with Wnt in determining the fate of beta-catenin[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2005, 22(1): 85-93. |
| 28 | Guo Q, Xu J, Huang Z, et al. ADMA mediates gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2021, 23(2): 325-34. |
| 29 | Wang J, Cai H, Liu QL, et al. Cinobufacini inhibits colon cancer invasion and metastasis via suppressing Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway and EMT[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2020, 48(3): 703-18. |
| 30 | Park JK, Song JH, He TC, et al. Overexpression of Wnt-2 in colorectal cancers[J]. Neoplasma, 2009, 56(2): 119-23. |
| 31 | Shi YH, He B, Kuchenbecker KM, et al. Inhibition of Wnt-2 and galectin-3 synergistically destabilizes beta-catenin and induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells[J]. Int J Cancer, 2007, 121(6): 1175-81. |
| 32 | Vider BZ, Zimber A, Chastre E, et al. Evidence for the involvement of the Wnt 2 gene in human colorectal cancer[J]. Oncogene, 1996, 12(1): 153-8. |
| 33 | Katoh M. WNT2 and human gastrointestinal cancer (review)[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2003, 12(5): 811-6. |
| 34 | Kramer N, Schmöllerl J, Unger C, et al. Autocrine WNT2 signaling in fibroblasts promotes colorectal cancer progression[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(39): 5460-72. |
| 35 | Lei L, Wang Y, Li ZH, et al. PHLDA3 promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and invasion via activation of the Wnt signaling pathway[J]. Lab Invest, 2021, 101(9): 1130-41. |
| 36 | Pu P, Zhang Z, Kang C, et al. Downregulation of Wnt2 and beta-catenin by siRNA suppresses malignant glioma cell growth[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2009, 16(4): 351-61. |
| [1] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | 谢婷, 王云云, 郭婷, 袁春华. 雷氏大疣蛛多肽毒素组分通过激活促凋亡通路和协同作用抑制癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1460-1470. |
| [3] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [4] | 龚秀莹, 侯顺福, 赵苗苗, 王晓娜, 张致涵, 刘清华, 尹崇高, 李洪利. LncRNA SNHG15通过miR-30b-3p调控COX6B1轴促进肺腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的分子机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1498-1505. |
| [5] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [6] | 王康, 李海宾, 余靖, 孟源, 张虹丽. ELFN1高表达是结肠癌的预后生物标志物并促进结肠癌细胞的增殖转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [7] | 李嘉豪, 冼瑞婷, 李荣. 下调ACADM介导的脂毒性抑制雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌细胞的侵袭与转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1163-1173. |
| [8] | 侯鑫睿, 张振东, 曹明远, 杜予心, 王小平. 红景天苷靶向miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB糖代谢轴抑制胃癌细胞的体内外增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [9] | 曾玉梅, 李继科, 黄仲曦, 周毅波. 绒毛样蛋白VILL通过与LMO7蛋白相互作用抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 954-961. |
| [10] | 岳雅清, 牟召霞, 王希波, 刘艳. Aurora-A过表达通过激活NF-κBp65/ARPC4信号轴促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 837-843. |
| [11] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [12] | 庆顺杰, 沈智勇. 过表达己糖激酶2通过激活JAK/STAT途径促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并调节肿瘤免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [13] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [14] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [15] | 李华莉, 宋婷, 刘嘉雯, 李永宝, 姜兆静, 窦文, 周凌宏. 预后导向的肺癌调强放疗计划优化新方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||