南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1200-1211.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.09
莫艳秀1( ), 舒洋2, 莫钰兰3, 刘峻彤1, 徐欧欧1, 邓华菲1, 王岐本1(
), 舒洋2, 莫钰兰3, 刘峻彤1, 徐欧欧1, 邓华菲1, 王岐本1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-24
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
王岐本
E-mail:moyanxiu@163.com;wangqiben@163.com
作者简介:莫艳秀,博士,副教授,E-mail: moyanxiu@163.com
基金资助:
Yanxiu MO1( ), Yang SHU2, Yulan MO3, Juntong LIU1, Ouou XU1, Huafei DENG1, Qiben WANG1(
), Yang SHU2, Yulan MO3, Juntong LIU1, Ouou XU1, Huafei DENG1, Qiben WANG1( )
)
Received:2024-10-24
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Qiben WANG
E-mail:moyanxiu@163.com;wangqiben@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨细胞分裂周期蛋白20(CDC20)在宫颈癌中的功能及其对宫颈癌C33A细胞增殖、迁移以及侵袭的影响和作用机制。 方法 TCGA数据库分析CDC20在宫颈癌组织中的表达情况,免疫组化(IHC)检测宫颈癌组织与癌旁组织中的CDC20和β-Catenin蛋白表达水平。利用CRISPR/Cas9设计CDC20基因双靶点的sgRNA2&7序列,构建重组质粒并测序验证。将宫颈癌细胞C33A按转染的质粒不同分为sgRNA-NC组和sgRNA-CDC20组,通过qRT-PCR和Western blotting检测CDC20的mRNA和蛋白表达水平,平板克隆检测其增殖能力,流式细胞术检测细胞周期和凋亡水平;Transwell小室法检测细胞迁移和侵袭能力。将2组C33A细胞分别接种于裸鼠(5只/组)双侧腋下左、右两侧,定期监测肿瘤体积并绘制其生长曲线,称取裸鼠体质量并脱臼处死。Western blotting分别检测细胞和瘤体组织中的CDC20和 β-Catenin蛋白的表达水平;免疫共沉淀(CoIP)和免疫荧光共定位验证CDC20与β-Catenin的相互作用。 结果 CDC20和β-Catenin在宫颈癌组织中的表达高于癌旁组织(P<0.001)。体外细胞实验结果显示:与sgRNA-NC组细胞比较,sgRNA-CDC20敲除株的细胞增殖能力下降(P<0.001)且细胞凋亡显著升高(P<0.01);迁移和侵袭能力受到明显抑制(P<0.05)。体内动物实验结果显示:与sgRNA-NC组比较,sgRNA-CDC20组的瘤体体积生长曲线明显减小(P<0.05),但裸鼠体质量无明显变化(P>0.05);sgRNA-CDC20组中的细胞和组织中的CDC20和β-Catenin的蛋白水平明显降低(P<0.05),免疫共沉淀(CoIP)和免疫荧光验证CDC20和β-Catenin存在相关性。 结论 CDC20在宫颈癌组织、细胞以及瘤体中的表达明显升高,敲除CDC20可明显抑制C33A细胞的增殖和侵袭转移能力,并促进凋亡,其机制可能与Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路密切相关。
莫艳秀, 舒洋, 莫钰兰, 刘峻彤, 徐欧欧, 邓华菲, 王岐本. 敲除CDC20可明显抑制宫颈癌细胞的增殖及侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1200-1211.
Yanxiu MO, Yang SHU, Yulan MO, Juntong LIU, Ouou XU, Huafei DENG, Qiben WANG. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated CDC20 gene knockout inhibits cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1200-1211.
| Sequence name | Target sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| sgRNA2 target sequence | 5' GTAACGGCAGGTCTTCCGGC 3' | |
| sgRNA7 target sequence | 5' GTGGCCAGAACGTGAACCAC 3' |
表1 sgRNA靶序列扩增引物
Tab.1 Target sequence of sgRNA of CDC20
| Sequence name | Target sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| sgRNA2 target sequence | 5' GTAACGGCAGGTCTTCCGGC 3' | |
| sgRNA7 target sequence | 5' GTGGCCAGAACGTGAACCAC 3' |
| Sequence name | Sequences (5'→3') | |
|---|---|---|
| CDC20 | CDC20-F | ATGCGCCAGAGGGTTATCAG |
| CDC20-R | AGGATGTCACCAGAGCTTGC | |
| GAPDH | GAPDH-F | GCTGTAGCCAAATCGTTGT |
| GAPDH-R | CCAGGTGGTCTCCTCTGA | |
表2 CDC20引物序列
Tab.2 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR of CDC20
| Sequence name | Sequences (5'→3') | |
|---|---|---|
| CDC20 | CDC20-F | ATGCGCCAGAGGGTTATCAG |
| CDC20-R | AGGATGTCACCAGAGCTTGC | |
| GAPDH | GAPDH-F | GCTGTAGCCAAATCGTTGT |
| GAPDH-R | CCAGGTGGTCTCCTCTGA | |
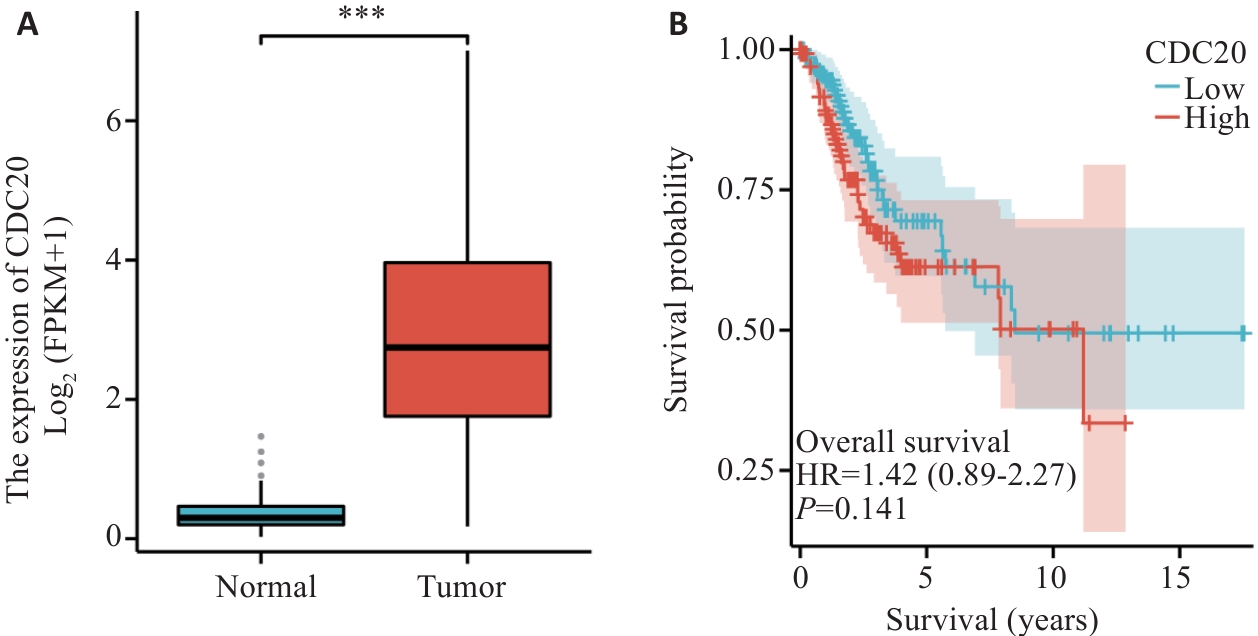
图1 CDC20在宫颈癌和癌旁组织中的差异表达以及患者生存预后的关系
Fig.1 Analysis of CDC20 expression in cervical cancer vs normal tissues and its impact on patient survival. A: Analysis of CDC20 levels in cancer (red) vs normal (green) tissues based on TCGA data. B: CDC20 expression level is correlated with survival of cervical cancer patients (red: high expression; green: low expression). ***P<0.001.
| Patients' age (year) | Number | Percentage of the age distribution | Adenocarcinoma type | Squamous cell carcinoma type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-30 | 3 | 1.38% | 1 | 1 |
| 30-40 | 17 | 7.80% | 2 | 3 |
| 40-50 | 66 | 30.28% | 18 | 33 |
| 50-60 | 74 | 33.94% | 23 | 31 |
| 60-70 | 45 | 20.64% | 10 | 22 |
| 70-80 | 8 | 3.67% | 3 | 1 |
| 80+ | 4 | 1.83% | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 218 | 100% | 59 | 93 |
表3 宫颈癌患者的年龄
Tab.3 Age distribution of cervical cancer patients with different histopathological types
| Patients' age (year) | Number | Percentage of the age distribution | Adenocarcinoma type | Squamous cell carcinoma type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-30 | 3 | 1.38% | 1 | 1 |
| 30-40 | 17 | 7.80% | 2 | 3 |
| 40-50 | 66 | 30.28% | 18 | 33 |
| 50-60 | 74 | 33.94% | 23 | 31 |
| 60-70 | 45 | 20.64% | 10 | 22 |
| 70-80 | 8 | 3.67% | 3 | 1 |
| 80+ | 4 | 1.83% | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 218 | 100% | 59 | 93 |
| CDC20 expression | Pathological type | Degree of differentiation | Clinical staging | Lymph node metastasis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Adenocarcinoma | Medium and low differentiation | High differentiation | I、II stage | III stage | No exist | Exist | |
| Positive | 93 (42.7%) | 59 (27.1%) | 159 (72.9%) | 188 (86.2%) | 46 (21.1%) | 191 (87.6%) | 12 (26.1%) | 24 (52.2%) |
| Negative | 125 (57.3%) | 159 (72.1%) | 59 (27.1%) | 30 (13.8%) | 172 (78.9%) | 27 (12.4%) | 9 (19.6%) | 1 (2.2%) |
| P | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | ||||
表4 CDC20在不同临床病理特征的患者中表达情况分析(218例)
Tab.4 Analysis of CDC20 expression in patients with different clinicopathological characteristics (218 Cases)
| CDC20 expression | Pathological type | Degree of differentiation | Clinical staging | Lymph node metastasis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Adenocarcinoma | Medium and low differentiation | High differentiation | I、II stage | III stage | No exist | Exist | |
| Positive | 93 (42.7%) | 59 (27.1%) | 159 (72.9%) | 188 (86.2%) | 46 (21.1%) | 191 (87.6%) | 12 (26.1%) | 24 (52.2%) |
| Negative | 125 (57.3%) | 159 (72.1%) | 59 (27.1%) | 30 (13.8%) | 172 (78.9%) | 27 (12.4%) | 9 (19.6%) | 1 (2.2%) |
| P | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | ||||
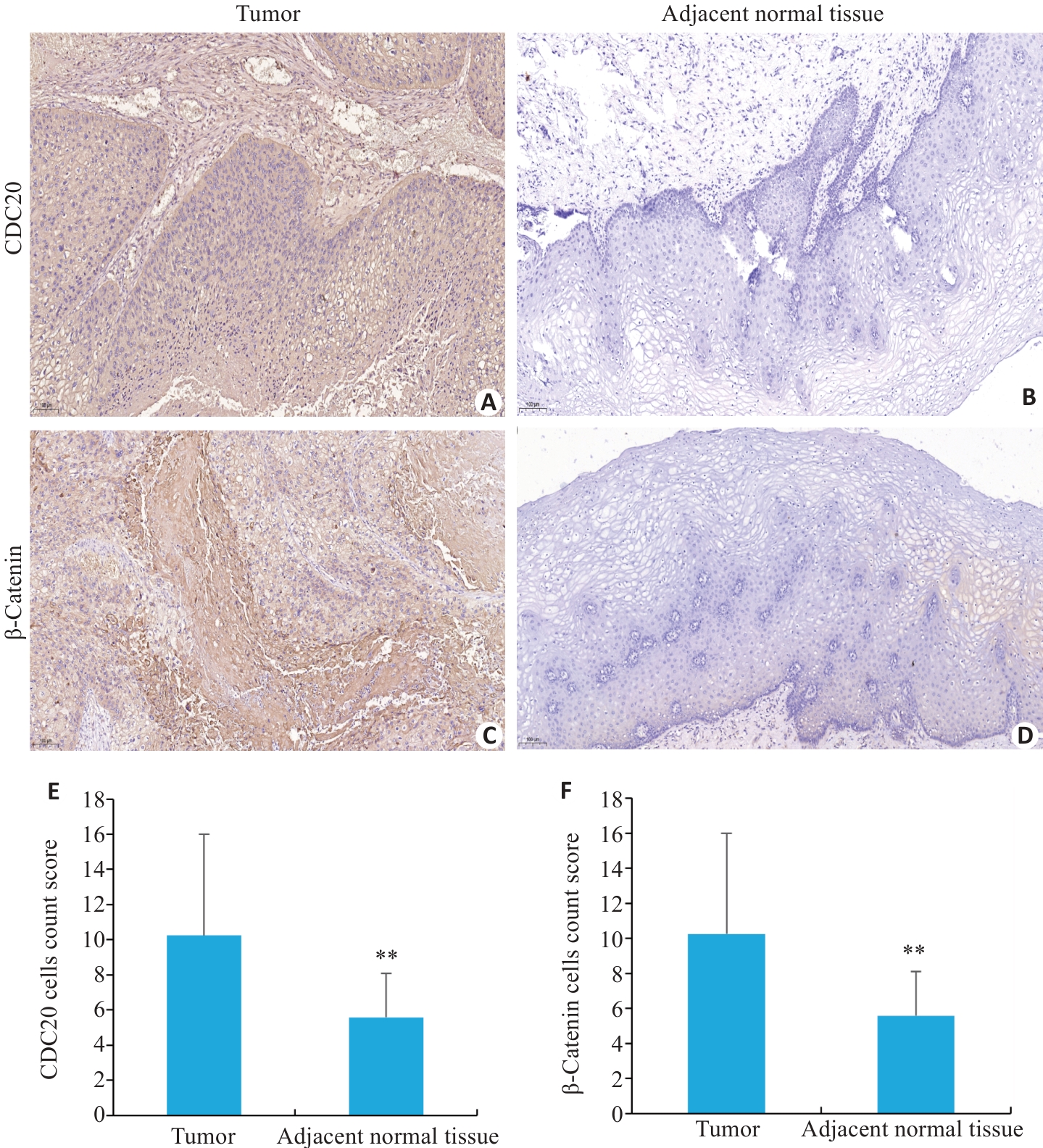
图2 免疫组化检测(IHC)CDC20和β-Catenin在宫颈癌组织与癌旁组织中的表达情况
Fig.2 Immunohistochemical analysis of CDC20 and β-Catenin in cervical cancer and normal tissues (Original magnification: ×100). A, B: CDC20 expression in cervical cancer and adjacent tissues. C, D: β-Catenin expression in cervical cancer and adjacent tissues. E, F: Comparison of CDC20 and β-Catenin expression levels between cervical cancer and adjacent tissues (5 fields per section). Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). **P<0.01 vs Tumor.
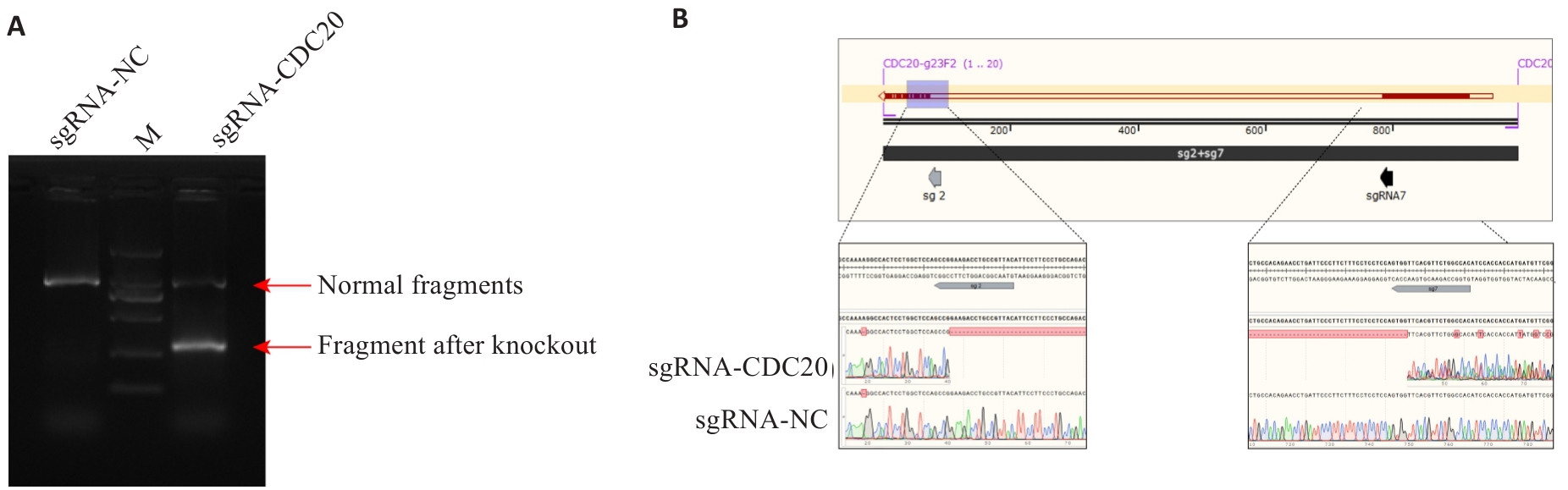
图3 C33A-CRISPR-CDC20 sgRNA 基因组PCR及测序结果
Fig.3 Results of C33A-CRISPR-CDC20 sgRNA genome PCR and sequencing. A: Agarose gel of PCR products. B: Sequencing results of the C33A-CRISPR-CDC20 sgRNA cells and sgRNA-NC cells.
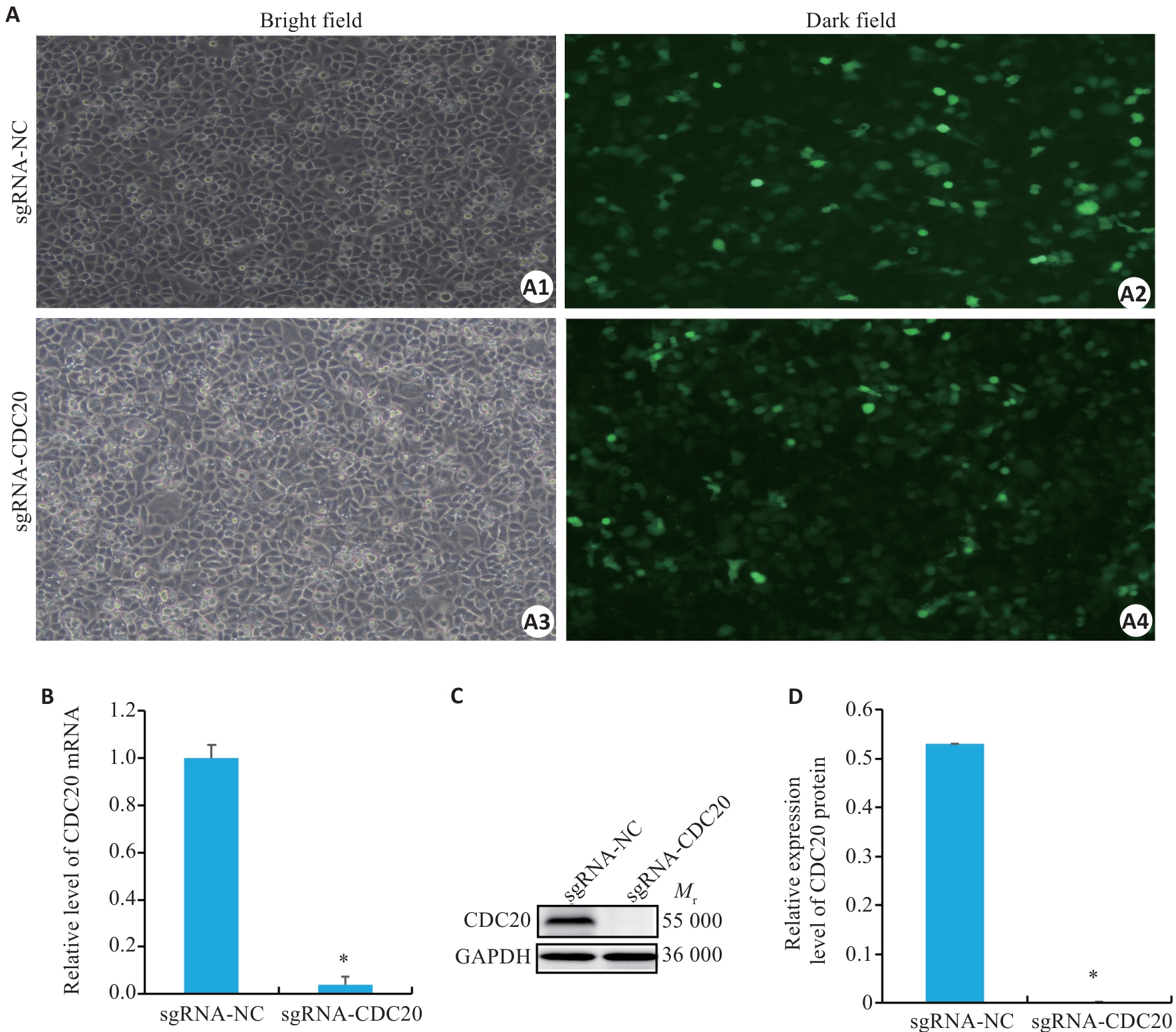
图4 CDC20 基因敲除效果验证
Fig.4 Validation of CDC20 gene knockdown (Mean±SD, n=3). A: Fluorescent transfection using sgRNA-CDC20 (×100). B: CDC20 knockout confirmed by qRT-PCR. C: sgRNA-CDC20 knockdown shown by Western blotting. D: Quantification of CDC20 expression levels. *P<0.05 vs sgRNA-NC group.
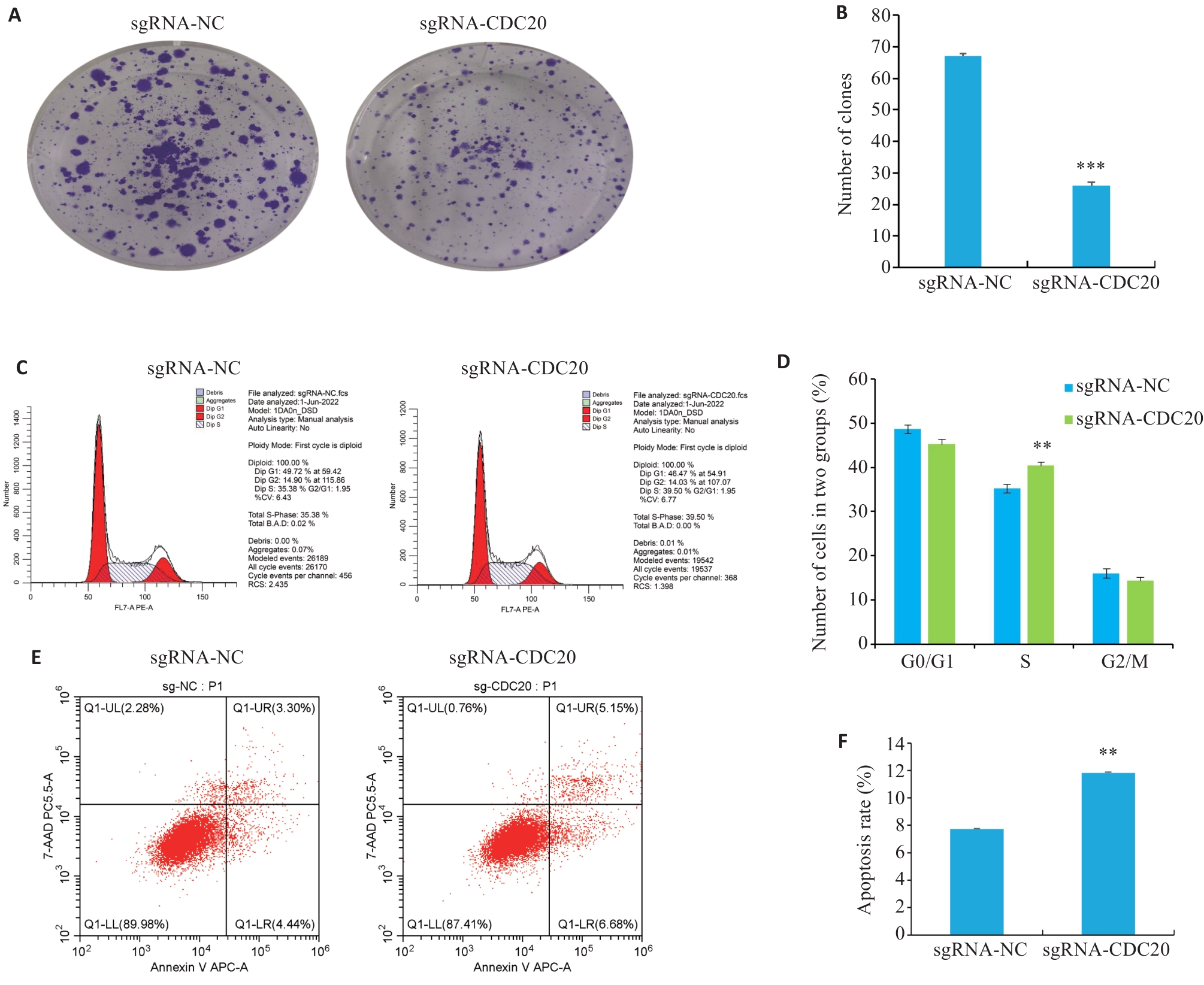
图5 CDC20敲除对细胞克隆、周期与凋亡的影响
Fig.5 Impact of CDC20 knockdown on clone formation (A, B), cell cycle (C, D) and apoptosis (E, F) in cervical cancer C33A cells (Mean±SD, n=3). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs sgRNA-NC group.
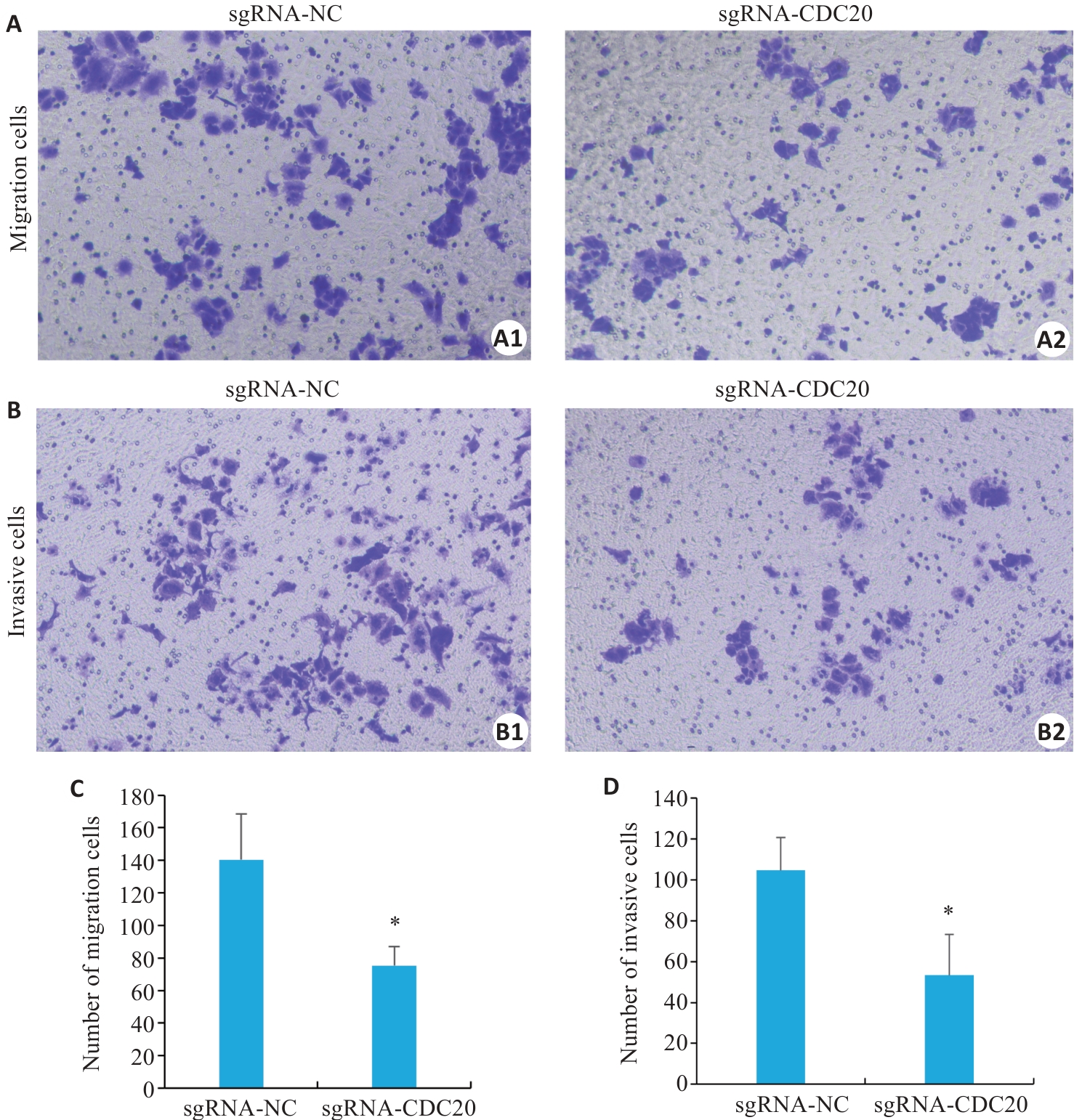
图6 敲除CDC20抑制宫颈癌细胞的迁移和侵袭能力
Fig.6 CDC20 knockdown inhibits migration and invasion of cervical cancer C33A cells (Mean±SD, n=3). A, B: Impact of CDC20 knockdown on migration and invasion of C33A cells (×100). C, D: Quantitative analysis of cell migration and invasion data. *P<0.05 vs sgRNA-NC group.
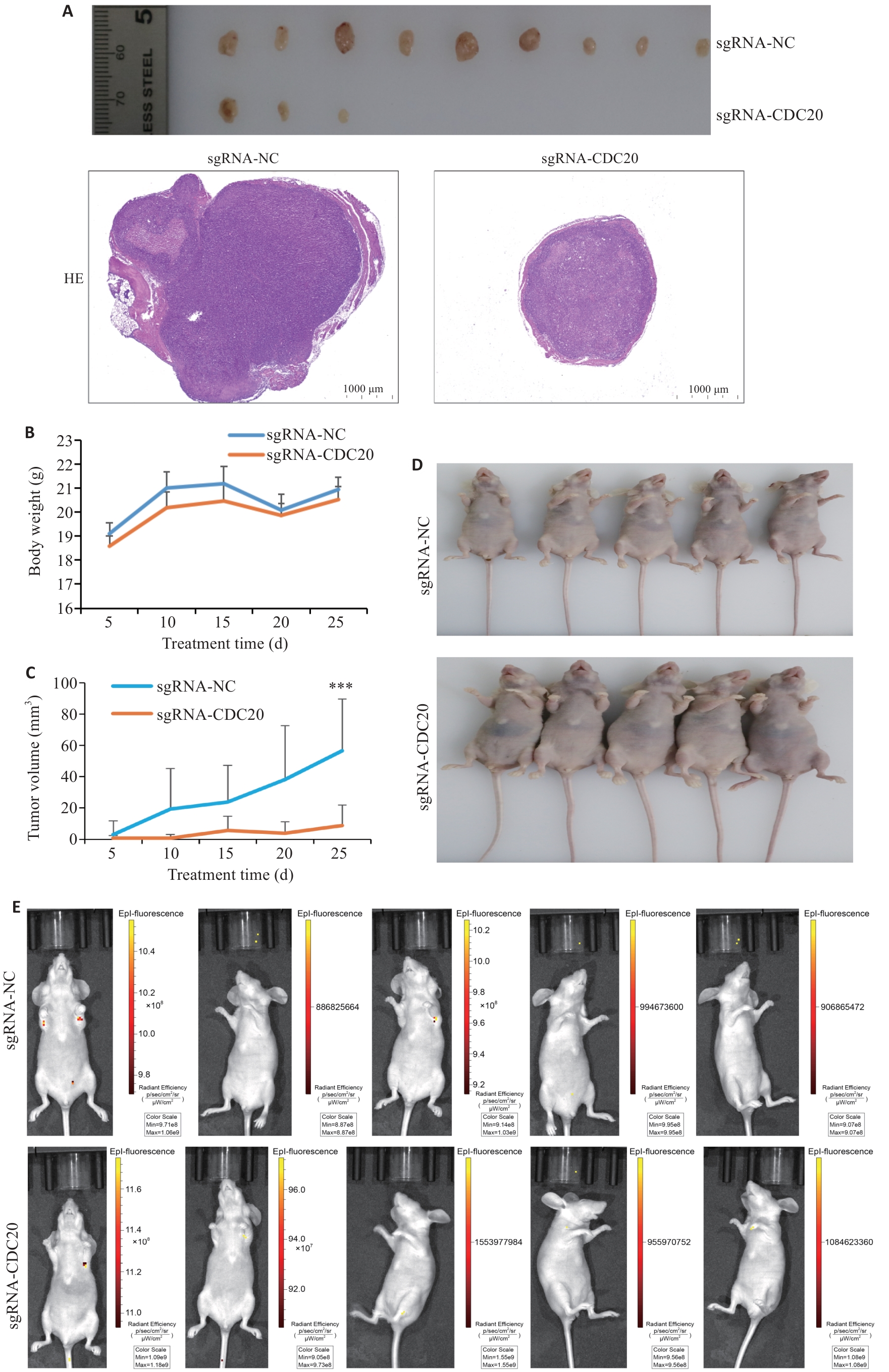
图7 CDC20敲除抑制裸鼠移植瘤生长
Fig.7 CDC20 knockdown suppresses xenograft tumor growth in nude mice (Mean±SD, n=3). A: Sizes and HE staining of the dissected tumors (×100). B: Body mass changes of the nude mice in the two groups. C: Tumor growth curves in the two groups. D: Observation of the tumor-bearing nude mice in the two groups. E: In vivo imaging of nude mice in the two groups. **P<0.001 vs sgRNA-NC group.
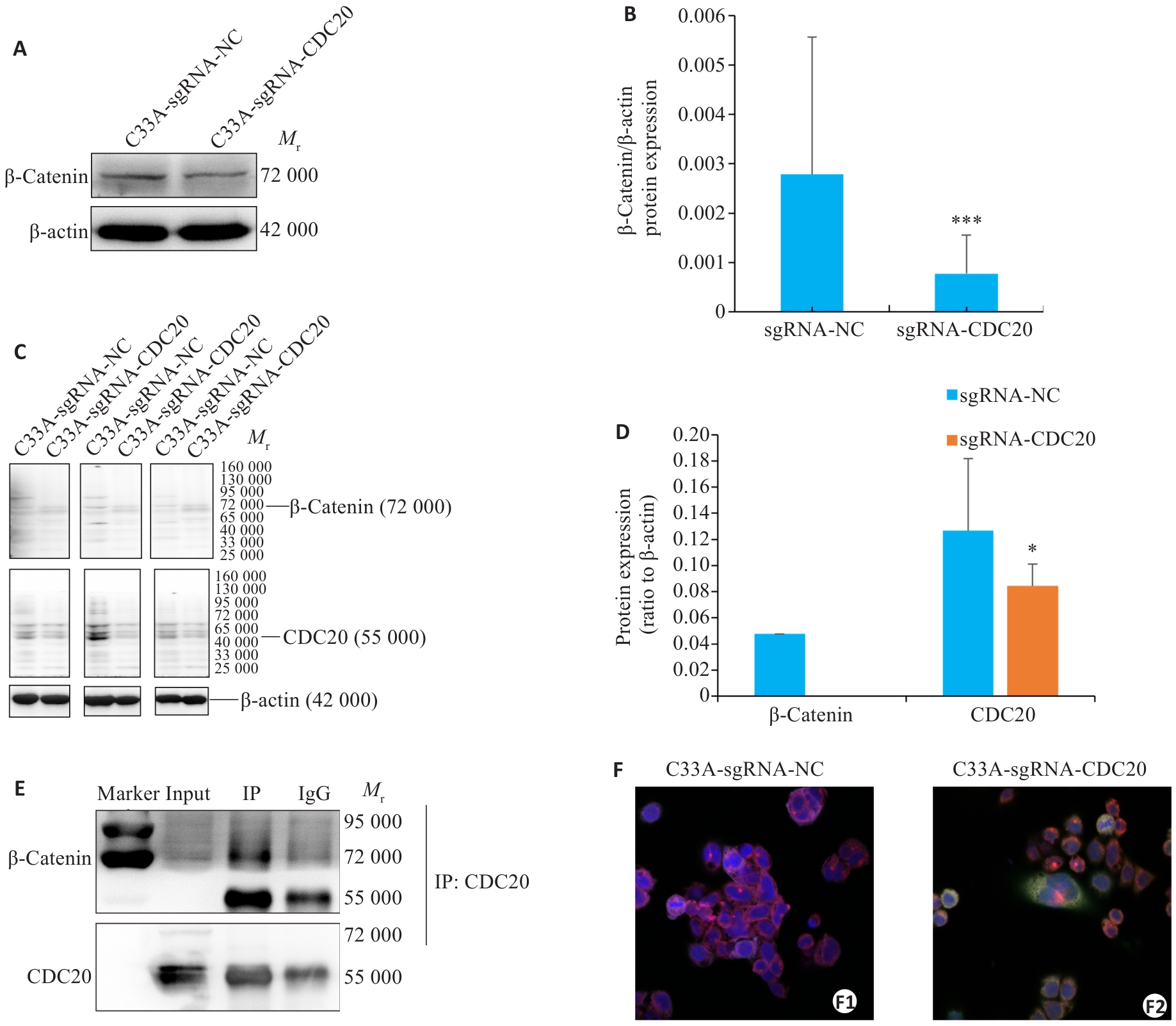
图8 敲除CDC20通过β-Catenin信号通路抑制宫颈癌细胞迁移和侵袭
Fig.8 CDC20 knockdown suppresses cervical cancer cell migration and invasion via the β-Catenin pathway. A, B: Western blotting for detecting β-Catenin levels in C33A cells (Mean±SD, n=3; ***P<0.001 vs sgRNA-NC group). C, D: Western blotting for detecting CDC20 and β‑Catenin expressions in tumor tissues from nude mic (Mean±SD, n=5; *P<0.05 vs sgRNA-NC group). E: Co-IP confirms CDC20 and β-Catenin interaction in mouse tissues. F: Immunofluorescence co-localization assay showing CDC20 and β-Catenin co-expression in C33A cells (×100).
| 1 | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| 2 | Lin M, Ye MM, Zhou JH, et al. Recent advances on the molecular mechanism of cervical carcinogenesis based on systems biology technologies[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2019, 17: 241-50. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2019.02.001 |
| 3 | Bruni L, Serrano B, Roura E, et al. Cervical cancer screening programmes and age-specific coverage estimates for 202 countries and territories worldwide: a review and synthetic analysis[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2022, 10(8): e1115-27. doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(22)00241-8 |
| 4 | Wang S, Chen B, Zhu Z, et al. CDC20 overexpression leads to poor prognosis in solid tumors: a system review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine: Baltimore, 2018, 97(52): e13832. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000013832 |
| 5 | Gayyed MF, El-Maqsoud NMRA, Tawfiek ER, et al. A comprehensive analysis of CDC20 overexpression in common malignant tumors from multiple organs: its correlation with tumor grade and stage[J]. Tumor Biol, 2016, 37(1): 749-62. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3808-1 |
| 6 | Song C, Lowe VJ, Lee S. Inhibition of Cdc20 suppresses the metastasis in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC)[J]. Breast Cancer, 2021, 28(5): 1073-86. doi:10.1007/s12282-021-01242-z |
| 7 | Xi X, Cao T, Qian Y, et al. CDC20 is a novel biomarker for improved clinical predictions in epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2022, 12(7): 3303-17. |
| 8 | Liu Y, Zou SH, Gao X. Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation reveal that CDC20 overexpression promotes bladder cancer progression and potential underlying mechanisms[J]. Genes Genom, 2024, 46(4): 437-49. doi:10.1007/s13258-024-01505-x |
| 9 | Zhang Q, Huang H, Liu A, et al. Cell division cycle 20 (CDC20) drives prostate cancer progression via stabilization of β-catenin in cancer stem-like cells[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 42: 397-407. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.032 |
| 10 | Chu Z, Zhang X, Li Q, et al. CDC20 contributes to the development of human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2019, 54(5): 1534-44. |
| 11 | Pang F, Shi D, Yuan L. Screening and identification of key genes for cervical cancer, Ovarian Cancer and endometrial cancer by combinational bioinformatic analysis[J]. Curr Bioinform, 2023, 18(8): 647-57. doi:10.2174/1574893618666230428095114 |
| 12 | Lin Y, Kong LL, Zhao YT, et al. The oncogenic role of EIF4A3/CDC20 axis in the endometrial cancer[J]. J Mol Med, 2024, 102(11): 1395-410. doi:10.1007/s00109-024-02486-w |
| 13 | Yu SJ, Zhao RR, Zhang BC, et al. Research progress and application of the CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology based on hepato-cellular carcinoma[J]. Asian J Pharm Sci, 2023, 18(4): 100828. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100828 |
| 14 | Chunjing L, Yujie Y, Wei Z, et al. Effect of silencing CDC20 on proliferation and cell cycle of endometrial cancer cells by inhibiting Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1305-12. |
| 15 | Wang BQ, Li XP, Liu L, et al. β‑Catenin: oncogenic role and therapeutic target in cervical cancer[J]. Biol Res, 2020, 53(1): 33. doi:10.1186/s40659-020-00301-7 |
| 16 | 许晓燕, 冯 群, 夏 嫱. Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在宫颈癌发生发展中的研究进展[J]. 医学信息, 2021, 34(5): 1-5. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2021.05.001 |
| 17 | 莫艳秀, 徐欧欧, 李梁政, 等.基于TCGA数据库探讨CDC20在宫颈癌组织中的表达及其对癌细胞自噬的影响[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2025,33(3): 375-87. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2025.03.004 |
| 18 | 莫艳秀, 陈淑娟, 范云鹏, 等. 顺铂作用于人恶性睾丸生殖细胞瘤NT2细胞后对肿瘤干细胞标志物的影响[J]. 生命科学研究, 2018, 22(5): 390-6. doi:10.16605/j.cnki.1007-7847.2018.05.008 |
| 19 | 莫艳秀, 姚飞虹, 刘峻彤, 等. SP600125对人宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖和侵袭的影响[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2022, 49(4): 304-13. doi:10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2022.21.0807 |
| 20 | Mo YX, Fan YP, Fu W, et al. Acute immune stress improves cell resistance to chemical poison damage in SP600125-induced pol-yploidy of fish cells in vitro [J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2019, 84: 656-63. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.063 |
| 21 | Burmeister CA, Khan SF, Schäfer G, et al. Cervical cancer therapies: Current challenges and future perspectives[J]. Tumour Virus Res, 2022, 13: 200238. doi:10.1016/j.tvr.2022.200238 |
| 22 | Mondal G, Sengupta S, Panda CK, et al. Overexpression of Cdc20 leads to impairment of the spindle assembly checkpoint and aneuplo-idization in oral cancer[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2007, 28(1): 81-92. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl100 |
| 23 | Ni K, Hong L. Current progress and perspectives of CDC20 in female reproductive cancers[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2023, 23(3): 193-9. doi:10.2174/1573405618666220321130102 |
| 24 | Tang J, Lu M, Cui Q, et al. Overexpression of ASPM CDC20 and TTK confer a poorer prognosis in breast cancer identified by gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 310. doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.00310 |
| 25 | 严龙君, 夏 萌, 李 明, 等. CDC20、TOP2A、NEK2的表达特征以及对食管鳞状细胞癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21(21): 2273-7. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.21.009 |
| 26 | 石 峰, 孙文功, 刘增振, 等. CDC20基因的表达对前列腺癌患者临床病理特征及预后的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2021, 46(11): 1092-7. |
| 27 | Gu Q, Li F, Ge S, et al. CDC20 knockdown and acidic microenvironment collaboratively promote tumorigenesis through inhibiting autophagy and apoptosis[J]. Molecular Therapy-Oncolytics, 2020, 17: 94-106. doi:10.1016/j.omto.2020.03.015 |
| 28 | Shang G, Ma X, Lv G. Cell division cycle 20 promotes cell proliferation and invasion and inhibits apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells[J]. Cell Cycle, 2018, 17(1): 43-52. doi:10.1080/15384101.2017.1387700 |
| 29 | Cheng S, Castillo V, Sliva D. CDC20 associated with cancer metastasis and novel mushroom-derived CDC20 inhibitors with antimetastatic activity[J]. Int J Oncol, 2019, 54(6): 2250-6. |
| 30 | Gao Y, Zhang B, Wang Y, et al. Cdc20 inhibitor apcin inhibits the growth and invasion of osteosarcoma cells[J]. Oncology reports, 2018, 40(2): 841-8. |
| 31 | Wang B, Wang M, Li X, et al. Variations in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway key genes as predictors of cervical cancer susceptibility[J]. Pharmgenomics Pers Med, 2020, 13: 157-65. doi:10.2147/pgpm.s248548 |
| 32 | Song P, Gao ZR, Bao YG, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in carcinogenesis and cancer therapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2024, 17(1): 46. doi:10.1186/s13045-024-01563-4 |
| 33 | Deng Q, Wu L, Li Y, et al. MYBL2 in synergy with CDC20 promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of gastric cancer cells[J]. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 2021, 30(9): 957-66. doi:10.17219/acem/135938 |
| 34 | Li K, Mao Y, Lu L, et al. Silencing of CDC20 suppresses metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer growth and enhances chemo-sensitivity to docetaxel[J]. International Journal of Oncology, 2016, 49(4): 1679-85. doi:info:doi/10.3892/ijo.2016.3671 |
| [1] | 朱胤福, 李怡燃, 王奕, 黄颖而, 龚昆翔, 郝文波, 孙玲玲. 桂枝茯苓丸活性成分常春藤皂苷元通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [2] | 岳雅清, 牟召霞, 王希波, 刘艳. Aurora-A过表达通过激活NF-κBp65/ARPC4信号轴促进宫颈癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 837-843. |
| [3] | 张文静, 张 诺, 杨 子, 张小凤, 孙奥飞, 王 炼, 宋 雪, 耿志军, 李 静, 胡建国. BZW1 高表达促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移:基于调控Wnt//β-catenin通路和促进上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 354-362. |
| [4] | 刘 欢, 饶 阳, 孙传铸, 王洋涛, 齐 顺, 李 想, 田 萌, 禹 汛, 穆允凤. 宫颈癌放疗后癌因性失眠患者的大脑功能网络与个体-经颅磁刺激干预的相关性:基于图论分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1629-1635. |
| [5] | 郭雨军, 李 婷, 杨 鑫, 祁振宇, 陈 利, 黄思娟. 放疗计划定量评估在宫颈癌外照射精准放疗流程管理中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 1035-1040. |
| [6] | 毛建英, 杨文静, 郭 和, 董瑞丽, 任丽芳, 李树斌. 体外重建宫颈癌的三维培养模型:基于人宫颈癌组织的去细胞支架[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 157-165. |
| [7] | 肖姝喆, 成燕玲, 朱 云, 唐 芮, 古建标, 兰 林, 何志华, 刘丹琼, 耿岚岚, 程 旸, 龚四堂. WNT2b高表达的成纤维细胞破坏肠道黏膜屏障[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 206-212. |
| [8] | 梁 健, 余凤姿, 朱金汉, 宋 婷. 准直器叶片到位精度对宫颈癌容积调强计划验证的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 1089-1094. |
| [9] | 赵行宇, 杨 昆, 宋梓桐, 何 涵, 张 巍. 胡桃醌通过促进c-Myc泛素化降解抑制宫颈癌细胞的生长和促进凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 1026-1031. |
| [10] | 霍叶琳, 王 月, 安 娜, 杜 雪. TIM-3 基因在上皮性卵巢癌中高表达并促进癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 190-200. |
| [11] | 林小丽, 何金梅, 卢佳蕴, 黄承颖, 刘 楠. 纳米炭示踪前哨淋巴结在宫颈癌诊治中的应用价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1896-1901. |
| [12] | 孙子久, 胡 静, 胡 凯, 唐 敏, 孙恃雷, 方玉婷, 余伙梅, 张 彦. LncRNA SNHG3对宫颈癌细胞SiHa增殖、迁移及侵袭的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(6): 931-936. |
| [13] | 朱梦云, 崔双慧, 郝泽宇, 王文锐, 杨清玲, 陈昌杰, 王剑锋, 周 琦. 姜黄素通过 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路诱导人晶状体上皮细胞的凋亡和细胞周期阻滞[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 722-728. |
| [14] | 张 涛, 李维丽, 邱晓拂, 刘百川, 李高远, 冯才鑫, 廖俊发, 林康健. TEAD1基因敲除对糖尿病性ED大鼠阴茎海绵体平滑肌细胞表型转化的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(4): 567-573. |
| [15] | 周丽婷, 叶 颖, 原海波, 吴超逸, 吴淑燕. gsdmd基因敲除巨噬细胞RAW 264.7的构建:基于CRISPR/Cas9 系统[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 116-122. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||