南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1212-1219.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.10
张骁翔( ), 田颖, 傅丽兰, 张胤, 董烨, 谢飞, 陈莉, 黄衍超, 吴湖炳(
), 田颖, 傅丽兰, 张胤, 董烨, 谢飞, 陈莉, 黄衍超, 吴湖炳( ), 谭建儿(
), 谭建儿( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-06
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
吴湖炳,谭建儿
E-mail:xxzhang23@163.com;wuhbym@163.com;Jianer.tan@foxmail.com
作者简介:张骁翔,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: xxzhang23@163.com
基金资助:
Xiaoxiang ZHANG( ), Ying TIAN, Lilan FU, Yin ZHANG, Ye DONG, Fei XIE, Li CHEN, Yanchao HUANG, Hubing WU(
), Ying TIAN, Lilan FU, Yin ZHANG, Ye DONG, Fei XIE, Li CHEN, Yanchao HUANG, Hubing WU( ), Jianer TAN(
), Jianer TAN( )
)
Received:2025-01-06
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Hubing WU, Jianer TAN
E-mail:xxzhang23@163.com;wuhbym@163.com;Jianer.tan@foxmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨68Ga-DOTATATE与18F-FDG PET/CT显像在不同级别胃肠胰神经内分泌肿瘤(GEP-NEN)分期及治疗决策中的价值。 方法 回顾性分析2020年8月~2023年3月在南方医科大学南方医院行18F-FDG和68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT显像的GEP-NEN患者49例,包括初诊患者34例,治疗后复发、转移患者15例。按病理分型将GEP-NEN分为G1、G2、G3神经内分泌瘤(NET)及神经内分泌癌(NEC)。依据同一患者双示踪剂阳性肿瘤病灶检出效能分为4种模式:68Ga-DOTATATE>18F-FDG(A);68Ga-DOTATATE=18F-FDG(B);68Ga-DOTATATE<18F-FDG(C);互补(D)。分析评价双示踪联合显像在分期及治疗决策中的价值。 结果 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT对全身肿瘤病灶检出优于18F-FDG PET/CT(P<0.001); 68Ga-DOTATATE显像在原发灶/复发灶、淋巴结转移、肝转移及骨转移的检出率更高(P<0.05),而18F-FDG PET/CT在肺转移和腹膜转移的检出率更高(P<0.05)。49例患者双示踪剂检出模式的比例为:模式A占46.9%(23/49),模式B占38.8%(19/49),模式C占12.2%(6/49),模式D占2.0%(1/49)。不同级别GEP-NEN患者18F-FDG PET/CT对68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT的补充价值为:G1 NET患者为0%(0/13)、G2 NET患者为8.3%(2/24)、G3 NET患者为50%(3/6)及NEC患者为33.3%(2/6)。12.2%(6/49)患者因联合18F-FDG PET/CT显像额外发现病灶而确定或改变分期,从而确定或改变治疗方案。 结论 GEP-NEN患者应首选68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT显像。对于G1 NET患者,联合18F-FDG PET/CT显像对分期及治疗决策无帮助,对G2、G3、NEC患者,联合18F-FDG PET/CT显像提高了部分患者分期及治疗决策精准度。
张骁翔, 田颖, 傅丽兰, 张胤, 董烨, 谢飞, 陈莉, 黄衍超, 吴湖炳, 谭建儿. 68Ga-DOTATATE、18F-FDG PET/CT双显像模式在胃肠胰神经内分泌肿瘤的分期及治疗中的价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1212-1219.
Xiaoxiang ZHANG, Ying TIAN, Lilan FU, Yin ZHANG, Ye DONG, Fei XIE, Li CHEN, Yanchao HUANG, Hubing WU, Jianer TAN. 68Ga-DOTATATE and 18F-FDG PET/CT dual-modality imaging enhances precision of staging and treatment decision for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1212-1219.
| Characteristics | Value | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender (n) | ||
| Male | 29 | 59.2 |
| Female | 20 | 40.8 |
| Age [year, M(P25,P75)] | 55 (45.5-60) | - |
| Diagnosis (n) | ||
| Newly diagnosed | 34 | 69.4 |
| Recurrence or metastasis after treatment | 15 | 30.6 |
| Primary tumor (n) | ||
| Gastric | 6 | 12.2 |
| Colorectal | 18 | 36.7 |
| Pancreatic | 25 | 51.0 |
| Histopathology (n) | ||
| G1 NET | 13 | 26.5 |
| G2 NET | 24 | 49.0 |
| G3 NET | 6 | 12.2 |
| NEC | 6 | 12.2 |
| Patient with metastasis (n) | ||
| Yes | 30 | 61.2 |
| No | 19 | 38.8 |
表1 49例GEP-NEN患者特征
Tab.1 Characteristics of 49 patients with GEP-NEN
| Characteristics | Value | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender (n) | ||
| Male | 29 | 59.2 |
| Female | 20 | 40.8 |
| Age [year, M(P25,P75)] | 55 (45.5-60) | - |
| Diagnosis (n) | ||
| Newly diagnosed | 34 | 69.4 |
| Recurrence or metastasis after treatment | 15 | 30.6 |
| Primary tumor (n) | ||
| Gastric | 6 | 12.2 |
| Colorectal | 18 | 36.7 |
| Pancreatic | 25 | 51.0 |
| Histopathology (n) | ||
| G1 NET | 13 | 26.5 |
| G2 NET | 24 | 49.0 |
| G3 NET | 6 | 12.2 |
| NEC | 6 | 12.2 |
| Patient with metastasis (n) | ||
| Yes | 30 | 61.2 |
| No | 19 | 38.8 |
| Lesion | Number of patients (n) | Number of lesions (n) | 18F-FDG positive lesion detection [n(%)] | 68Ga-DOTATATE positive lesion detection [n(%)] | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 49 | 539 | 347 (64.4) | 447 (82.9) | <0.001 |
| Primary/recurrent | 45 | 45 | 32 (71.1) | 42 (93.3) | 0.011 |
| Lymph nodes | 29 | 109 | 89 (81.7) | 107 (98.2) | <0.001 |
| Liver | 1 | 277 | 193 (69.7) | 220 (79.4) | 0.011 |
| Bone | 9 | 65 | 11 (16.9) | 62 (95.4) | <0.001 |
| Lung | 3 | 23 | 9 (39.1) | 2 (8.7) | 0.035 |
| Peritoneum | 2 | 6 | 6 (100) | 1 (16.7) | 0.015 |
| Adrenal | 2 | 3 | 3 (100) | 3 (100) | >0.999 |
| Brain | 1 | 3 | 2 (66.7) | 3 (100) | >0.999 |
| Kidney | 1 | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | >0.999 |
| Spleen | 1 | 2 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (100) | 0.333 |
| Pancreas | 1 | 1 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (100) | >0.999 |
| Ovary | 1 | 1 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (100) | >0.999 |
| Soft tissue | 2 | 3 | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | >0.999 |
表2 18F-FDG和68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT对原发/复发灶及转移灶阳性检出的比较
Tab.2 Comparison of 18F-FDG and 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT for detection of primary/recurrent and metastatic lesion
| Lesion | Number of patients (n) | Number of lesions (n) | 18F-FDG positive lesion detection [n(%)] | 68Ga-DOTATATE positive lesion detection [n(%)] | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 49 | 539 | 347 (64.4) | 447 (82.9) | <0.001 |
| Primary/recurrent | 45 | 45 | 32 (71.1) | 42 (93.3) | 0.011 |
| Lymph nodes | 29 | 109 | 89 (81.7) | 107 (98.2) | <0.001 |
| Liver | 1 | 277 | 193 (69.7) | 220 (79.4) | 0.011 |
| Bone | 9 | 65 | 11 (16.9) | 62 (95.4) | <0.001 |
| Lung | 3 | 23 | 9 (39.1) | 2 (8.7) | 0.035 |
| Peritoneum | 2 | 6 | 6 (100) | 1 (16.7) | 0.015 |
| Adrenal | 2 | 3 | 3 (100) | 3 (100) | >0.999 |
| Brain | 1 | 3 | 2 (66.7) | 3 (100) | >0.999 |
| Kidney | 1 | 1 | 1 (100) | 1 (100) | >0.999 |
| Spleen | 1 | 2 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (100) | 0.333 |
| Pancreas | 1 | 1 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (100) | >0.999 |
| Ovary | 1 | 1 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (100) | >0.999 |
| Soft tissue | 2 | 3 | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | >0.999 |
| Grades | Patterns A | Patterns B | Patterns C | Patterns D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 23 (46.9) | 19 (38.8) | 6 (12.2) | 1 (2.0) |
| G1 NET | 6 (12.2) | 7 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| G2 NET | 14 (28.6) | 8 (16.3) | 2 (4.1) | 0 (0.0) |
| G3 NET | 2 (4.1) | 1 (2.0) | 2 (4.1) | 1 (2.0) |
| NEC | 1 (2.0) | 3 (6.1) | 2 (4.1) | 0 (0.0) |
表3 18F-FDG和68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT对不同级别GEP-NEN的检出比较
Tab.3 Comparison of 18F-FDG and 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT for detecting different grades of GEP-NEN [n(%)]
| Grades | Patterns A | Patterns B | Patterns C | Patterns D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 23 (46.9) | 19 (38.8) | 6 (12.2) | 1 (2.0) |
| G1 NET | 6 (12.2) | 7 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| G2 NET | 14 (28.6) | 8 (16.3) | 2 (4.1) | 0 (0.0) |
| G3 NET | 2 (4.1) | 1 (2.0) | 2 (4.1) | 1 (2.0) |
| NEC | 1 (2.0) | 3 (6.1) | 2 (4.1) | 0 (0.0) |
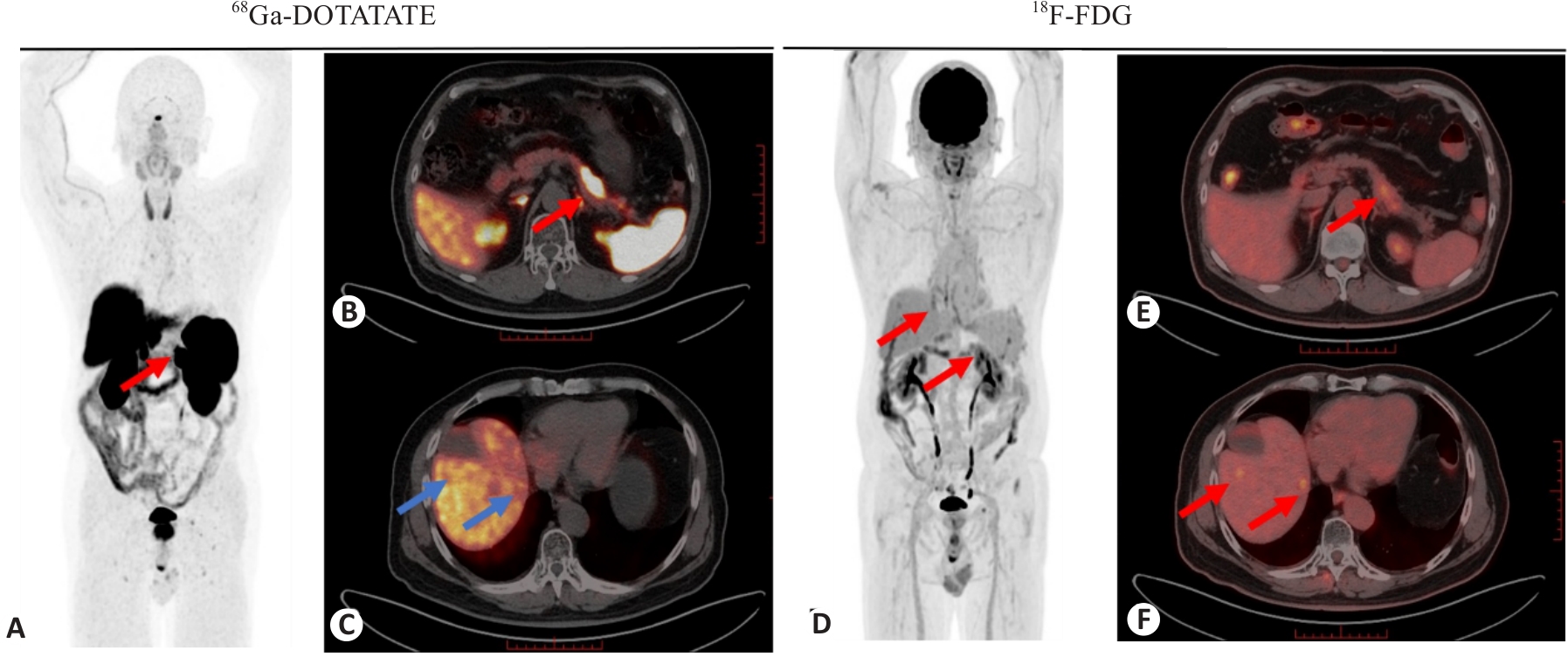
图2 G2 NET患者行双示踪剂联合显像, 因联合18F-FDG PET/CT显像额外发现多发肝脏转移灶而改变分期
Fig.2 A G2 NET patient underwent dual tracer PET/CT scans, and the staging was changed due to additional detection of multiple liver metastases by 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging. The 66-year-old male patient was diagnosed with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (G2 NET) with multiple liver metastases. 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT showed a high uptake lesion in the tail of the pancreas (A, B, red arrows, SUVmax: 35.2), while 18F-FDG PET/CT showed a mild hypermetabolic lesion in the tail of the pancreas (D, E, red arrows, SUVmax: 4.2). 18F-FDG PET/CT displayed multiple hypermetabolic lesions in the liver (D, F, red arrows, SUVmax: 4.0 and 3.6, respectively), while 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT did not show abnormal uptake at the corresponding site (C, blue arrows).
| 1 | Pavel M, Öberg K, Falconi M, et al. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31(7): 844-60. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.304 |
| 2 | Oronsky B, Ma PC, Morgensztern D, et al. Nothing but NET: a review of neuroendocrine tumors and carcinomas[J]. Neoplasia, 2017, 19(12): 991-1002. doi:10.1016/j.neo.2017.09.002 |
| 3 | Christofer Juhlin C, Mete O, Baloch ZW. The 2022 WHO classification of thyroid tumors: novel concepts in nomenclature and grading[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2022, 30(2): e220293. doi:10.1530/erc-22-0293 |
| 4 | Rindi G, Klimstra DS, Abedi-Ardekani B, et al. A common classification framework for neuroendocrine neoplasms: an International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and World Health Organization (WHO) expert consensus proposal[J]. Mod Pathol, 2018, 31(12): 1770-86. doi:10.1038/s41379-018-0110-y |
| 5 | Zhang XB, Fan YB, Jing R, et al. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: current development, challenges, and clinical perspectives[J]. Mil Med Res, 2024, 11(1): 35. doi:10.1186/s40779-024-00535-6 |
| 6 | Zhang PP, Yu JY, Li J, et al. Clinical and prognostic value of PET/CT imaging with combination of 68Ga-DOTATATE and 18F-FDG in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Contrast Media Mol Imaging, 2018, 2018: 2340389. doi:10.1155/2018/2340389 |
| 7 | 张青菊, 杨卫东, 王胜军, 等. Ga-DOTANOC PET/CT显像在胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤诊断及分期中的应用价值[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2019, 39(8): 453-7. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-2848.2019.08.002 |
| 8 | Panzuto F, Ramage J, Pritchard DM, et al. European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society (ENETS) 2023 guidance paper for gastroduodenal neuroendocrine tumours (NETs) G1-G3[J]. J Neuroendocrinol, 2023, 35(8): e13306. doi:10.1111/jne.13306 |
| 9 | You H, Kandathil A, Beg M, et al. Ga-68 DOTATATE PET/CT and F-18 FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of low and intermediate versus high-grade neuroendocrine tumors[J]. Nucl Med Commun, 2020, 41(10): 1060-5. doi:10.1097/mnm.0000000000001255 |
| 10 | Chan DL, Pavlakis N, Schembri GP, et al. Dual somatostatin receptor/FDG PET/CT imaging in metastatic neuroendocrine tumours: proposal for a novel grading scheme with prognostic significance[J]. Theranostics, 2017, 7(5): 1149-58. doi:10.7150/thno.18068 |
| 11 | Naswa N, Sharma P, Gupta SK, et al. Dual tracer functional imaging of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors using 68Ga-DOTA-NOC PET-CT and 18F-FDG PET-CT: competitive or complimentary?[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2014, 39(1): e27-34. doi:10.1097/rlu.0b013e31827a216b |
| 12 | Kaewput C, Vinjamuri S. Role of combined 68Ga DOTA-Peptides and 18F FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Diagnostics, 2022, 12(2): 280. doi:10.3390/diagnostics12020280 |
| 13 | Carideo L, Prosperi D, Panzuto F, et al. Role of combined 68Ga Ga-DOTA-SST analogues and 18F FDG PET/CT in the management of GEP-NENs: a systematic review[J]. J Clin Med, 2019, 8(7): 1032. doi:10.3390/jcm8071032 |
| 14 | Partelli S, Rinzivillo M, Maurizi A, et al. The role of combined Ga-DOTANOC and 18FDG PET/CT in the management of patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors[J]. Neuroendocrinology, 2014, 100(4): 293-9. doi:10.1159/000368609 |
| 15 | Has Simsek D, Kuyumcu S, Turkmen C, et al. Can complementary 68Ga-DOTATATE and 18F-FDG PET/CT establish the missing link between histopathology and therapeutic approach in gastro-enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors[J]? J Nucl Med, 2014, 55(11): 1811-7. doi:10.2967/jnumed.114.142224 |
| 16 | Chauhan A, Chan K, Halfdanarson TR, et al. Critical updates in neuroendocrine tumors: version 9 American joint committee on cancer staging system for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(4): 359-67. doi:10.3322/caac.21840 |
| 17 | Kryza D, Tadino V, Filannino MA, et al. Fully automated 18F fluorocholine synthesis in the TracerLab MX FDG Coincidence synthesizer[J]. Nucl Med Biol, 2008, 35(2): 255-60. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.11.008 |
| 18 | He Q, Zhang ZK, Zhang LQ, et al. Head-to-head comparison between 68Ga Ga-DOTA-NOC and 18F DOPA PET/CT in a diverse cohort of patients with pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2024, 51(7): 1989-2001. doi:10.1007/s00259-024-06622-z |
| 19 | Velikyan I. 68Ga-Based radiopharmaceuticals: production and application relationship[J]. Molecules, 2015, 20(7): 12913-43. doi:10.3390/molecules200712913 |
| 20 | Hope TA, Allen-Auerbach M, Bodei LS, et al. SNMMI procedure standard/EANM practice guideline for SSTR PET: imaging neuroendocrine tumors[J]. J Nucl Med, 2023, 64(2): 204-10. doi:10.2967/jnumed.122.264860 |
| 21 | 余浩军, 顾宇参, 杨 志, 等. 神经内分泌肿瘤68Ga-DOTATATE联合18F-FDG两日法全身PET/CT显像操作规范专家共识[EB/OL]. [2025-01-21]. . |
| 22 | Wang LJ, Tang GH, Hu KZ, et al. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of advanced lung cancer[J]. Radiology, 2022, 303(1): 191-9. doi:10.1148/radiol.211424 |
| 23 | Zamora V, Cabanne A, Salanova R, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of somatostatin receptors in digestive endocrine tumours[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2010, 42(3): 220-5. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2009.07.018 |
| 24 | Virgolini I, Ambrosini V, Bomanji JB, et al. Procedure guidelines for PET/CT tumour imaging with 68Ga-DOTA-conjugated peptides: 68Ga-DOTA-TOC, 68Ga-DOTA-NOC, 68Ga-DOTA-TATE[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2010, 37(10): 2004-10. doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1512-3 |
| 25 | Hofman MS, Eddie Lau WF, Hicks RJ. Somatostatin receptor imaging with 68Ga DOTATATE PET/CT: clinical utility, normal patterns, pearls, and pitfalls in interpretation[J]. Radiographics, 2015, 35(2): 500-16. doi:10.1148/rg.352140164 |
| 26 | Putzer D, Gabriel M, Henninger B, et al. Bone metastases in patients with neuroendocrine tumor: 68Ga-DOTA-Tyr3-octreotide PET in comparison to CT and bone scintigraphy[J]. J Nucl Med, 2009, 50(8): 1214-21. doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.060236 |
| 27 | 唐文鑫, 王琦新, 杨松松, 等. 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT与18F-FDG PET/CT对分化良好和分化不良的胃肠胰神经内分泌肿瘤显像的对比研究[J]. 肿瘤影像学, 2022, 31(3): 230-5. doi:10.19732/j.cnki.2096-6210.2022.03.003 |
| 28 | Muffatti F, Partelli S, Cirocchi R, et al. Combined 68Ga-DOTA-peptides and 18F-FDG PET in the diagnostic work-up of neuroendocrine neoplasms (NEN)[J]. Clin Transl Imag, 2019, 7(3): 181-8. doi:10.1007/s40336-019-00328-1 |
| 29 | 赵 帅, 程 超, 左长京. Ga-SSA/F-FDG PET/CT联合显像在神经内分泌肿瘤诊治中的应用价值[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2020, 40(1): 47-51. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-2848.2020.01.012 |
| 30 | 中国抗癌协会神经内分泌肿瘤专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会神经内分泌肿瘤诊治指南(2022年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2022, 32(6): 545-79. doi:10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2022.06.010 |
| 31 | Yang ZH, Tang LH, Klimstra DS. Effect of tumor heterogeneity on the assessment of Ki67 labeling index in well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors metastatic to the liver: implications for prognostic stratification[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2011, 35(6): 853-60. doi:10.1097/pas.0b013e31821a0696 |
| 32 | Kayani I, Bomanji JB, Groves A, et al. Functional imaging of neuroendocrine tumors with combined PET/CT using 68Ga-DOTATATE (DOTA-DPhe1, Tyr3-octreotate) and 18F-FDG[J]. Cancer, 2008, 112(11): 2447-55. doi:10.1002/cncr.23469 |
| 33 | Abgral R, Leboulleux S, Déandreis D, et al. Performance of 18Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography and somatostatin receptor scintigraphy for high Ki67 (≥10%) well-differentiated endocrine carcinoma staging[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2011, 96(3): 665-71. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-2022 |
| 34 | Centonze G, Maisonneuve P, Simbolo M, et al. Lung carcinoid tumours: histology and Ki-67, the eternal rivalry[J]. Histopathology, 2023, 82(2): 324-39. doi:10.1111/his.14819 |
| 35 | Reubi JC, Waser B. Concomitant expression of several peptide receptors in neuroendocrine tumours: molecular basis for in vivo multireceptor tumour targeting[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2003, 30(5): 781-93. doi:10.1007/s00259-003-1184-3 |
| 36 | Vesterinen T, Leijon H, Mustonen H, et al. Somatostatin receptor expression is associated with metastasis and patient outcome in pulmonary carcinoid tumors[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 104(6): 2083-93. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01931 |
| 37 | Ivanidze J, Roytman M, Sasson A, et al. Molecular imaging and therapy of somatostatin receptor positive tumors[J]. Clin Imaging, 2019, 56: 146-54. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2019.04.006 |
| 38 | Hu XW, Li DD, Wang R, et al. Comparison of the application of 18F-FDG and 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in neuroendocrine tumors: a retrospective study[J]. Medicine, 2023, 102(19): e33726. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000033726 |
| 39 | 杜长治, 谢 卿, 翟士桢, 等. Ga-DOTATATE与F-FDG PET/CT显像探测神经内分泌肿瘤骨转移的对比研究[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2021, 41(9): 520-4. |
| 40 | Shen ZH, Zhang XJ, Li QX, et al. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT and 18F-DOTATATE PET/CT in the diagnosis of multiple metastases in rectal neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Radiol Case Rep, 2024, 19(9): 3757-62. doi:10.1016/j.radcr.2024.03.051 |
| 41 | 王 玲, 胡桂兰, 乔 真, 等. 神经内分泌肿瘤转移灶PET/CT生长抑素受体显像特点分析[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2017, 37(3): 132-6. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-2848.2017.03.002 |
| 42 | Shastry M, Kayani I, Wild D, et al. Distribution pattern of 68Ga-DOTATATE in disease-free patients[J]. Nucl Med Commun, 2010, 31(12): 1025-32. doi:10.1097/mnm.0b013e32833f635e |
| 43 | Yi CA, Shin KM, Lee KS, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer staging: efficacy comparison of integrated PET/CT versus 3.0-T whole-body MR imaging[J]. Radiology, 2008, 248(2): 632-42. doi:10.1148/radiol.2482071822 |
| 44 | Zhou Y, Li L, Wang H, et al. Heterogeneous uptake of 68Ga-DOTATATE and 18F-FDG in initial diagnosed neuroendocrine tumors patients: which patients are suitable for dual-tracer PET imaging[J]? Clin Nucl Med, 2024, 49(6): 516-20. doi:10.1097/rlu.0000000000005231 |
| 45 | Adams S, Baum R, Rink T, et al. Limited value of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for the imaging of neuroendocrine tumours[J]. Eur J Nucl Med, 1998, 25(1): 79-83. doi:10.1007/s002590050197 |
| 46 | Fang JM, Li J, Shi JQ. An update on the diagnosis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(10): 1009-23. doi:10.3748/wjg.v28.i10.1009 |
| 47 | Skoura E, Michopoulou S, Mohmaduvesh M, et al. The impact of 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT imaging on management of patients with neuroendocrine tumors: experience from a national referral center in the United Kingdom[J]. J Nucl Med, 2016, 57(1): 34-40. doi:10.2967/jnumed.115.166017 |
| 48 | Tierney JF, Kosche C, Schadde E, et al. 68Gallium-DOTATATE positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET CT) changes management in a majority of patients with neuroendocrine tumors[J]. Surgery, 2019, 165(1): 178-85. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2018.03.030 |
| 49 | Ghobrial SN, Menda Y, Zamba GK, et al. Prospective analysis of the impact of 68Ga-DOTATOC positron emission tomography-computerized axial tomography on management of pancreatic and small bowel neuroendocrine tumors[J]. Pancreas, 2020, 49(8): 1033-6. doi:10.1097/mpa.0000000000001625 |
| [1] | 张奔龙, 鲁意迅, 李 力, 高云鹤, 梁文全, 郗洪庆, 王鑫鑫, 张珂诚, 陈 凛. 基于单中心490例胃神经内分泌肿瘤建立的列线图具有良好的预后预测性能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 183-190. |
| [2] | 戴戈扬, 陈高文, 李肖璇, 郑友红, 王 袁, 李兴嵩, 李 菁, 周 璟, 谢 郁, 王沂峰. 罕见宫颈大细胞神经内分泌癌患者的维持妊娠与母婴管理[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 1-9. |
| [3] | 郭 飞,朱 林,许 红,秦 雷,梁啸寒,邓雪飞. COVID-19临床分型与MSCT容积扫描间的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(03): 321-326. |
| [4] | 向 颖,杨全新,孙泓泓,秦幸茹,李晓会,张秋娟. COVID-19患者胸部CT表现及动态演变[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(03): 327-332. |
| [5] | 古嘉媚,任云燕,陈小慧,蒋燕萍,周文兰,王丽娟,韩彦江,王巧愚,吴湖炳. 肿块型活动性肺结核的18F-FDG PET/CT影像表现及其与肺癌的鉴别[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(01): 49-55. |
| [6] | 任云燕,李友财,吴湖炳,王全师,韩彦江,周文兰,李洪生,王珍,MOHAMMED Shah Alam. 薄层CT与18F-FDG PET/CT 联合运用可提高肺孤立性结节定性诊断的准确性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(03): 283-. |
| [7] | 关炜,王全师,吴湖炳,周文兰. 原发性肠淋巴瘤的18F-FDG PET/CT影像学表现[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(09): 1175-. |
| [8] | 李雯霞,黄业恩,石晓欣,林佩欣,邹振宁,张耀忠,申洪. YY1 在胰岛素瘤中的表达及意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(03): 361-. |
| [9] | 贾茜,薛建军,高蕊,邓惠兴,张芬茹,杨爱民. 99Tcm-MIBI SPECT/CT及18F-FDG SPECT/CT对孤立性肺结节的诊断效能比较[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(03): 386-. |
| [10] | 李蕙旨,吴湖炳,王全师,李洪生,周文兰,田颖,董烨. 弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤化疗中后期用18F-FDG PET/CT显像预测预后是否优于化疗中期?[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(02): 208-. |
| [11] | 田树平,吴芳,李春平,宋翔,李颖娜,陈敏,肖华锋,杨立. 糖尿病患者前降支心肌桥与桥前血管冠状动脉粥样硬化的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(12): 1772-. |
| [12] | 李洪生,吴湖炳,王巧愚,韩彦江,王全师. 18F-FDG PET/CT双时相显像在膀胱癌术前分期中的临床价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(04): 500-. |
| [13] | 杨晓波,杨俊杰,田峰,周迎,汪奇,张华巍,杜洛山,陈韵岱. 双源CT大螺距前瞻性双次扫描模式在冠心病诊断中的价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(11): 1605-. |
| [14] | 吕茵,郑航,王全师,吴湖炳,李洪生,周文兰,田颖. 18F-FDG PET/CT对喉癌的诊断价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2012, 32(10): 1486-. |
| [15] | 李娟,刘宏斌,智光,尹大一,王晶,盖泾兢,谢雷星,刘家金,张雄伟. 超声造影与PET/CT技术对颈动脉粥样斑块稳定性的整体评估[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2012, 32(07): 981-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||