南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2598-2606.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.07
• • 上一篇
崔俊杰1( ), 赖睿茵1, 陈苏衡1, 瞿珊珊1, 廖阅1, 马雪1, 李玉兰2(
), 赖睿茵1, 陈苏衡1, 瞿珊珊1, 廖阅1, 马雪1, 李玉兰2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-27
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
李玉兰
E-mail:cuijj2023@lzu.edu.cn;liyul@lzu.edu.cn
作者简介:崔俊杰,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: cuijj2023@lzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Junjie CUI1( ), Ruiyin LAI1, Suheng CHEN1, Shanshan QU1, Yue LIAO1, Xue MA1, Yulan LI2(
), Ruiyin LAI1, Suheng CHEN1, Shanshan QU1, Yue LIAO1, Xue MA1, Yulan LI2( )
)
Received:2025-05-27
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Yulan LI
E-mail:cuijj2023@lzu.edu.cn;liyul@lzu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨过度劳累对小鼠心肌能量代谢的影响。 方法 32只C57BL/6J小鼠被随机分为4组(n=8):对照组、过劳2周(W2)组、过劳4周(W4)组和过劳6周(W6)组,W2、W4和W6组每天强迫水中站立8 h+束缚3 h,分别连续造模2周、4周和6周,每周记录小鼠体质量,并观察一般情况。造模结束后行超声心动图,并检测血脂和血糖水平,HE染色观察心肌组织病理学变化,ELISA法检测心肌甘油三酯(TG)、三磷酸腺苷(ATP)水平,免疫组化染色检测心肌组织分化簇36(CD36)和葡萄糖易化扩散转运蛋白1(GLUT1)的表达,RT-qPCR和Western blotting分析心肌脂代谢调控因子肉碱棕榈酰转移酶1B(CPT1B)和过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(PPARα),糖酵解酶磷酸果糖激酶(PFKM)和丙酮酸激酶 M2(PKM2)的mRNA表达水平和蛋白相对表达量。 结果 小鼠随着过劳时间延长逐渐表现出活动减少、毛发脱落、皮毛晦暗以及体质量增长迟缓现象,但心脏指数及心功能无显著改变(P>0.05);与CON组相比,W2和W4组血糖水平升高(P<0.001),而W6组降低(P<0.001),W4和W6组血清TG水平持续上升(P<0.001),而TC、HDL和LDL水平均降低(P<0.01);过劳导致心肌细胞肿胀、排列紊乱、疏松和空泡化,与CON组相比,W4和W6组心肌TG水平升高(P<0.001),W6组ATP水平降低(P<0.05);与CON组相比,W4和W6组CPT1B和PPARαmRNA及蛋白表达持续下调(P<0.05或P<0.01或P<0.001),W4组CD36蛋白反而表达增加(P<0.05);此外,W2组GLUT1蛋白及PFKM、PKM2mRNA和蛋白表达降低(P<0.05或P<0.01或P<0.001),但W4和W6组较W2组又有所增加(P<0.01)。 结论 过劳初期小鼠血糖水平升高,并伴有心肌糖酵解受到抑制;持续过劳导致血糖水平下降,血TG水平升高,而TC、HDL和LDL水平降低,同时心肌脂肪酸氧化能力受损、加之糖酵解供能有限,最终引起心肌结构损伤、TG堆积和ATP水平下降。
崔俊杰, 赖睿茵, 陈苏衡, 瞿珊珊, 廖阅, 马雪, 李玉兰. 过度劳累损伤小鼠心肌能量代谢稳态[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2598-2606.
Junjie CUI, Ruiyin LAI, Suheng CHEN, Shanshan QU, Yue LIAO, Xue MA, Yulan LI. Overwork damages myocardial energy metabolism homeostasis in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2598-2606.
| Gene | Sequence of primers |
|---|---|
| CPT1B | F: GCACACCAGGCAGTAGCTTT |
| R: CAGGAGTTGATTCCAGACAGGTA | |
| PPARα | F: AGAGCCCCATCTGTCCTCTC |
| R: ACTGGTAGTCTGCAAAACCAAA | |
| PFKM | F: TGTGGTCCGAGTTGGTATCTT |
| R: GCACTTCCAATCACTGTGCC | |
| PKM2 | F: GCCGCCTGGACATTGACTC |
| R: CCATGAGAGAAATTCAGCCGAG | |
| ACTB | F: GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG |
| R: CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
表1 PCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Sequence of primers |
|---|---|
| CPT1B | F: GCACACCAGGCAGTAGCTTT |
| R: CAGGAGTTGATTCCAGACAGGTA | |
| PPARα | F: AGAGCCCCATCTGTCCTCTC |
| R: ACTGGTAGTCTGCAAAACCAAA | |
| PFKM | F: TGTGGTCCGAGTTGGTATCTT |
| R: GCACTTCCAATCACTGTGCC | |
| PKM2 | F: GCCGCCTGGACATTGACTC |
| R: CCATGAGAGAAATTCAGCCGAG | |
| ACTB | F: GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG |
| R: CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| Group | Modeling time (weeks) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| CON | 20.45±0.29 | 21.13±0.23 | 22.02±0.31a | 22.54±0.47a | 23.18±0.47a | 23.96±0.37a | 24.3±0.38a |
| W2 | 20.00±0.37 | 19.94±0.50 | 20.13±0.40d | ||||
| W4 | 20.50±0.19 | 20.24±0.24 | 20.41±0.19d | 20.90±0.24b | 21.14±0.30c | ||
| W6 | 19.89±0.19 | 20.51±0.20 | 20.85±0.25c | 20.35±0.48c | 20.80±0.49d | 21.29±0.52d | 21.54±0.45d |
表2 各组小鼠体质量随造模时间变化情况
Tab.2 Changes of body weight of the mice in each group during modeling (g, Mean±SD, n=8)
| Group | Modeling time (weeks) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| CON | 20.45±0.29 | 21.13±0.23 | 22.02±0.31a | 22.54±0.47a | 23.18±0.47a | 23.96±0.37a | 24.3±0.38a |
| W2 | 20.00±0.37 | 19.94±0.50 | 20.13±0.40d | ||||
| W4 | 20.50±0.19 | 20.24±0.24 | 20.41±0.19d | 20.90±0.24b | 21.14±0.30c | ||
| W6 | 19.89±0.19 | 20.51±0.20 | 20.85±0.25c | 20.35±0.48c | 20.80±0.49d | 21.29±0.52d | 21.54±0.45d |

图1 各组心脏质量指数和超声心动图
Fig.1 Heart weight index (A) and echocardiography (B) in each group (mg/g, Mean±SD, n=8). #P>0.05 vs CON group. CON: Control group. W2: overwork for 2 weeks group; W4: overwork for 4 weeks group; W6: overwork for 6 weeks group.
| Group | LVIDs (mm) | LVIDd (mm) | EF% | FS% | LVPWd (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 2.06±0.52 | 3.03±0.02 | 65.29±0.32 | 35.01±0.50 | 0.84±0.03 |
| W2 | 2.01±0.33 | 3.06±0.03 | 65.76±0.44 | 35.14±0.79 | 0.84±0.01 |
| W4 | 2.10±0.09 | 3.11±0.06 | 64.99±0.79 | 36.26±0.21 | 0.85±0.05 |
| W6 | 2.11±0.06 | 3.18±0.01 | 64.87±0.55 | 35.28±0.43 | 0.85±0.01 |
表3 各组心功能变化
Tab.3 Cardiac function changes in each group (Mean±SD, n=3)
| Group | LVIDs (mm) | LVIDd (mm) | EF% | FS% | LVPWd (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 2.06±0.52 | 3.03±0.02 | 65.29±0.32 | 35.01±0.50 | 0.84±0.03 |
| W2 | 2.01±0.33 | 3.06±0.03 | 65.76±0.44 | 35.14±0.79 | 0.84±0.01 |
| W4 | 2.10±0.09 | 3.11±0.06 | 64.99±0.79 | 36.26±0.21 | 0.85±0.05 |
| W6 | 2.11±0.06 | 3.18±0.01 | 64.87±0.55 | 35.28±0.43 | 0.85±0.01 |
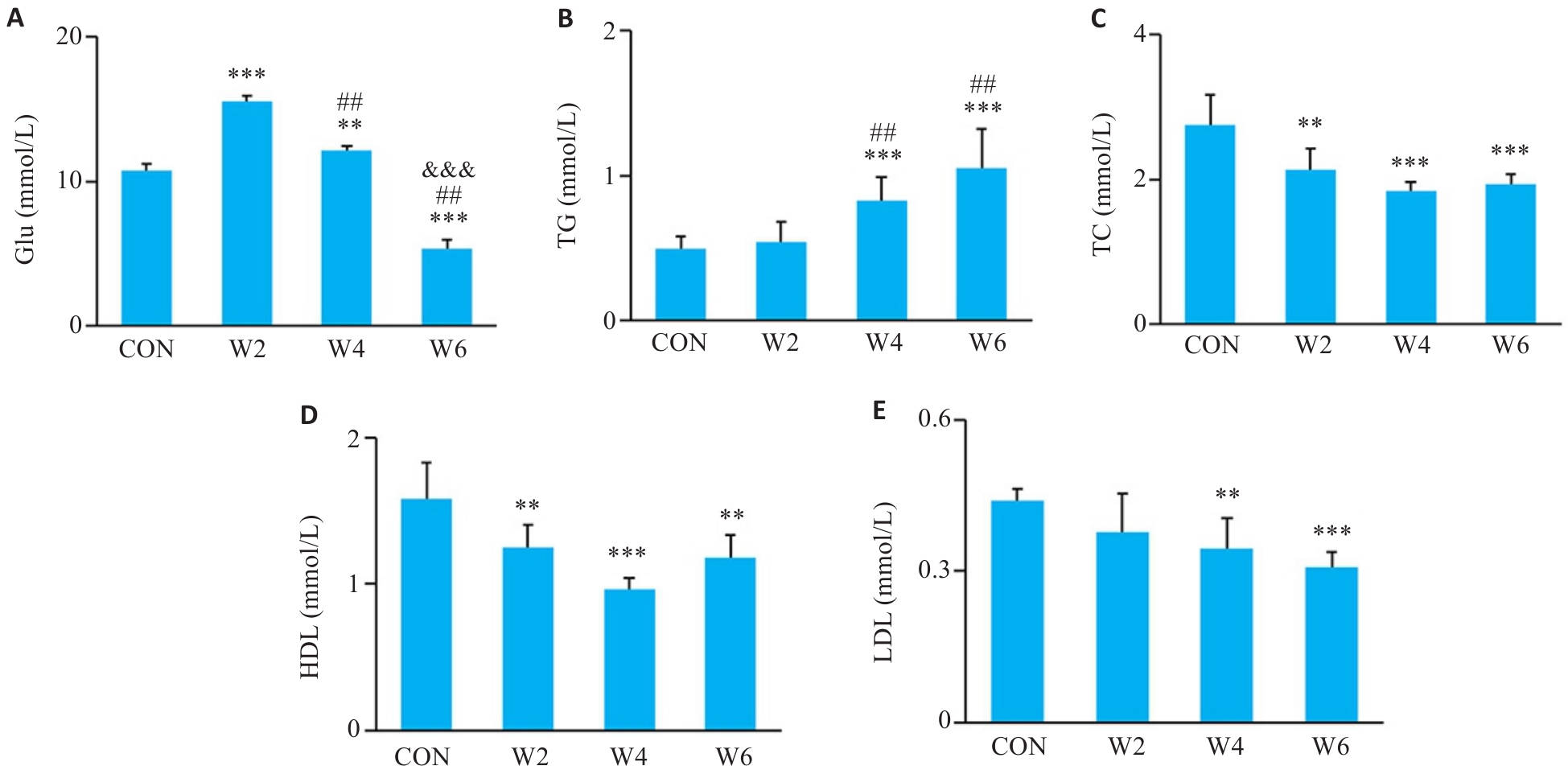
图2 各组血糖和血脂变化
Fig.2 Changes of blood glucose and blood lipids in each group (Mean±SD, n=6). A-E: Blood glucose (Glu), triglycerides (TG), cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) levels, respectively. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs CON group; ##P<0.01 vs W2 group; &&&P<0.001 vs W4 group.
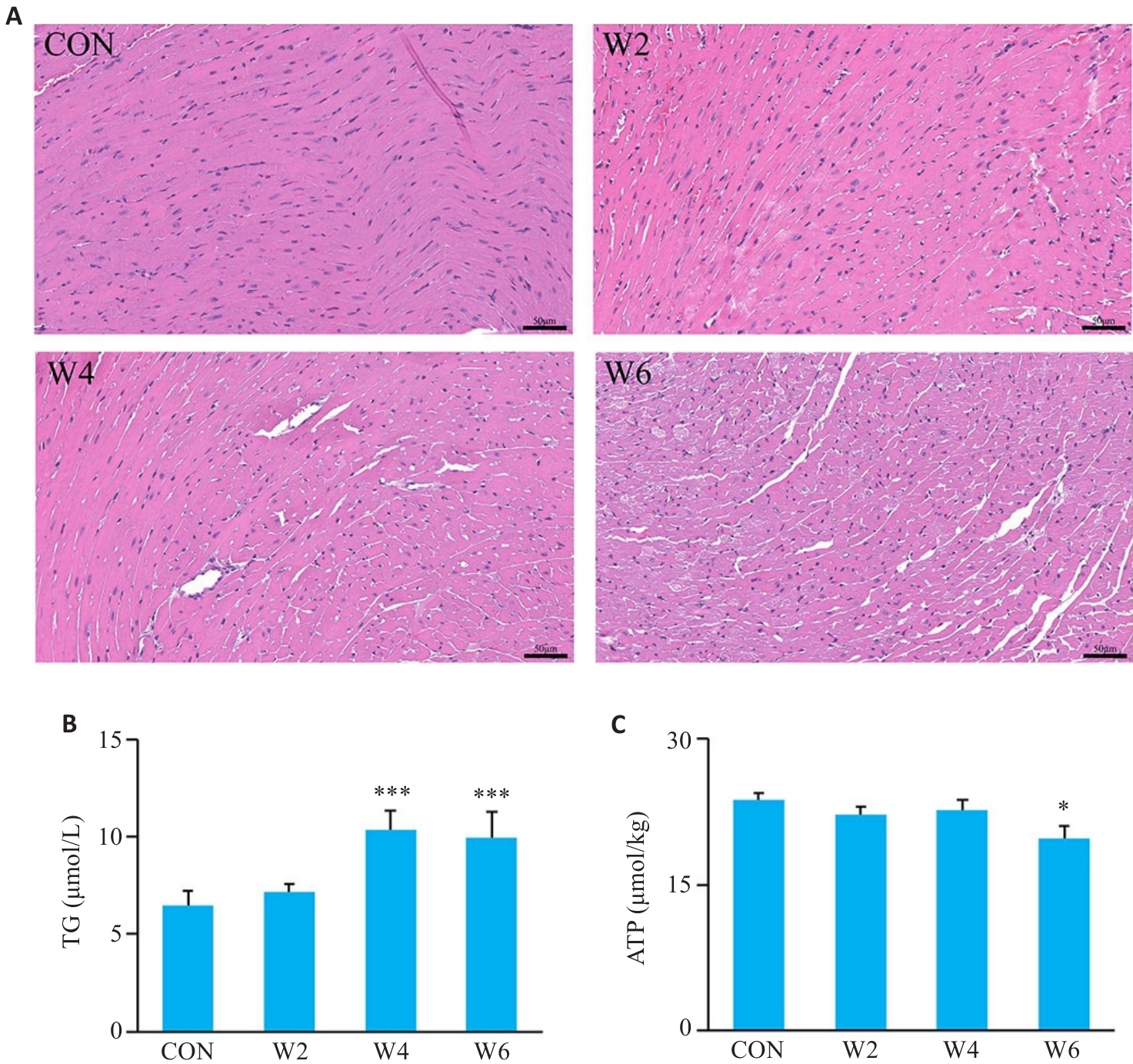
图3 各组小鼠心肌组织病理学,TG和ATP浓度变化
Fig.3 Histopathological changes of the myocardial tissues and changes in myocardial TG and ATP levels in each group. A: HE staining (Scale bar=50 μm). B: Myocardial TG level (n=6; ***P<0.001 vs CON group). C: Myocardial ATP level (n=6; *P<0.05 vs CON group).
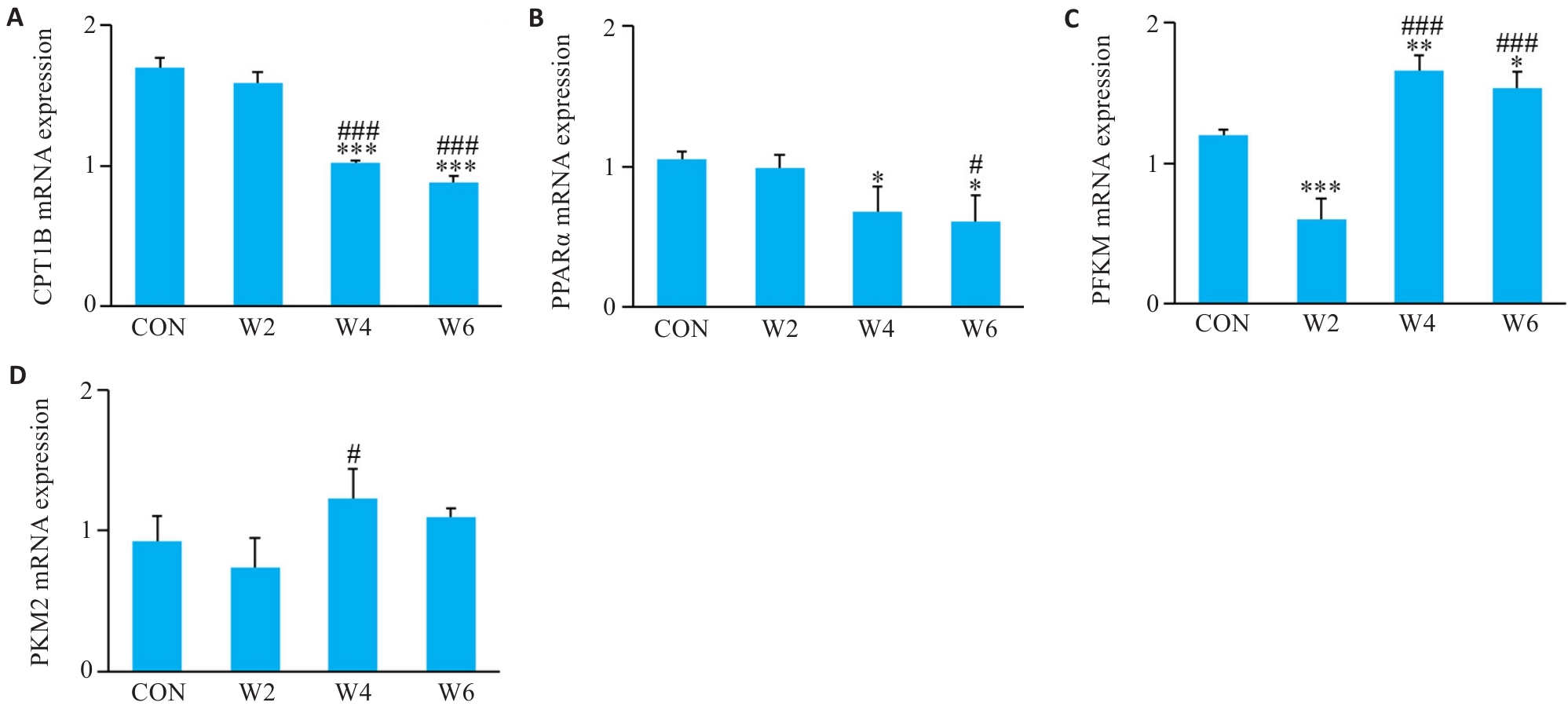
图4 各组心肌CPT1B、PPARα、PFKM、PKM2 mRNA相对表达量
Fig.4 Relative expression levels of CPT1B (A), PPARα (B), PFKM (C), and PKM2 (D) mRNA in each group (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs CON group; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs W2 group.
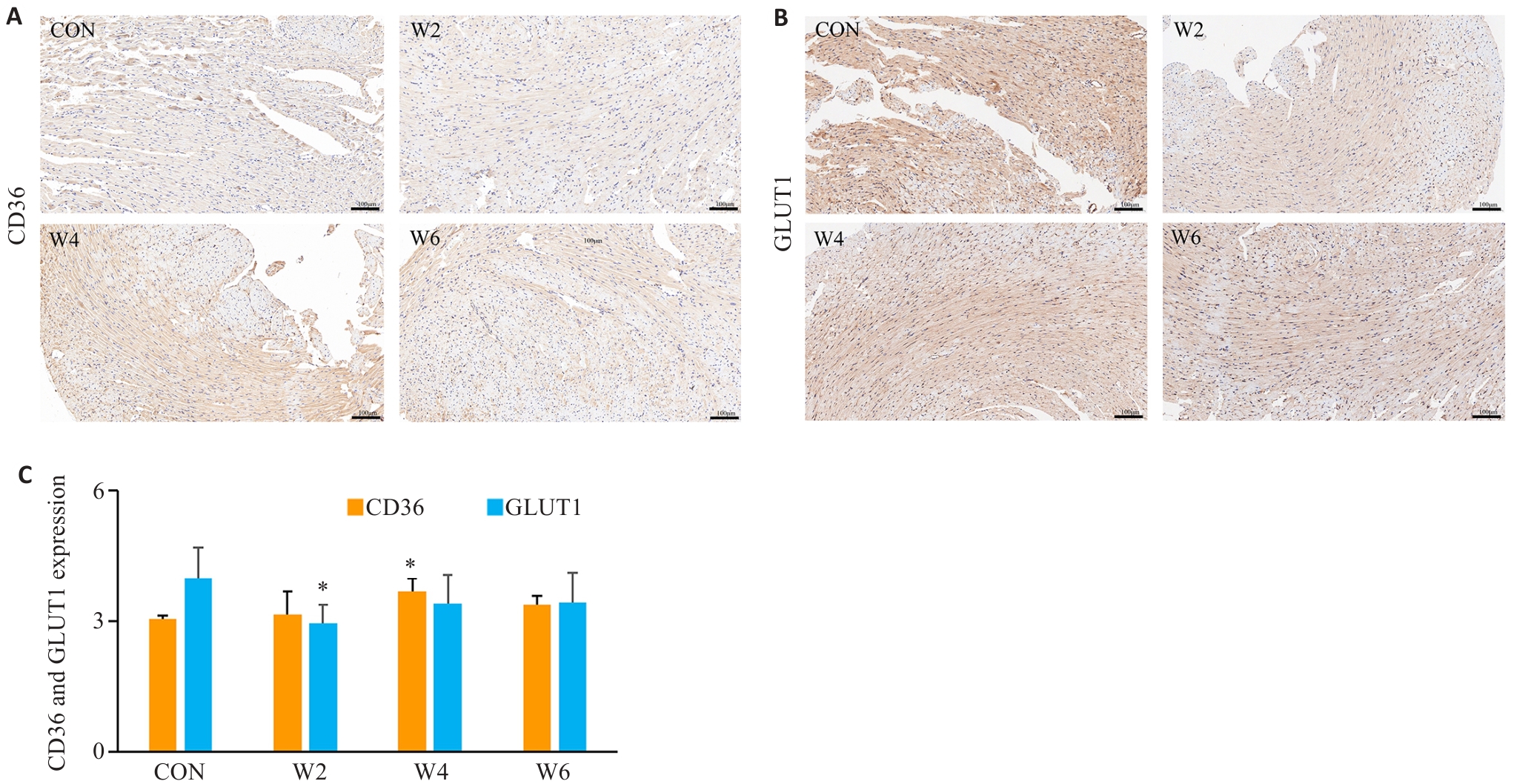
图5 各组心肌CD36、GLUT1蛋白表达及阳性细胞所占面积
Fig.5 Expression of CD36 and GLUT1 protein and the area of positive cells (%) in the myocardium in each group. A, B: Immunohistochemical staining (Scale bar=100 μm). C: CD36 and GLUT1 protein expression levels. *P<0.05 vs CON group.
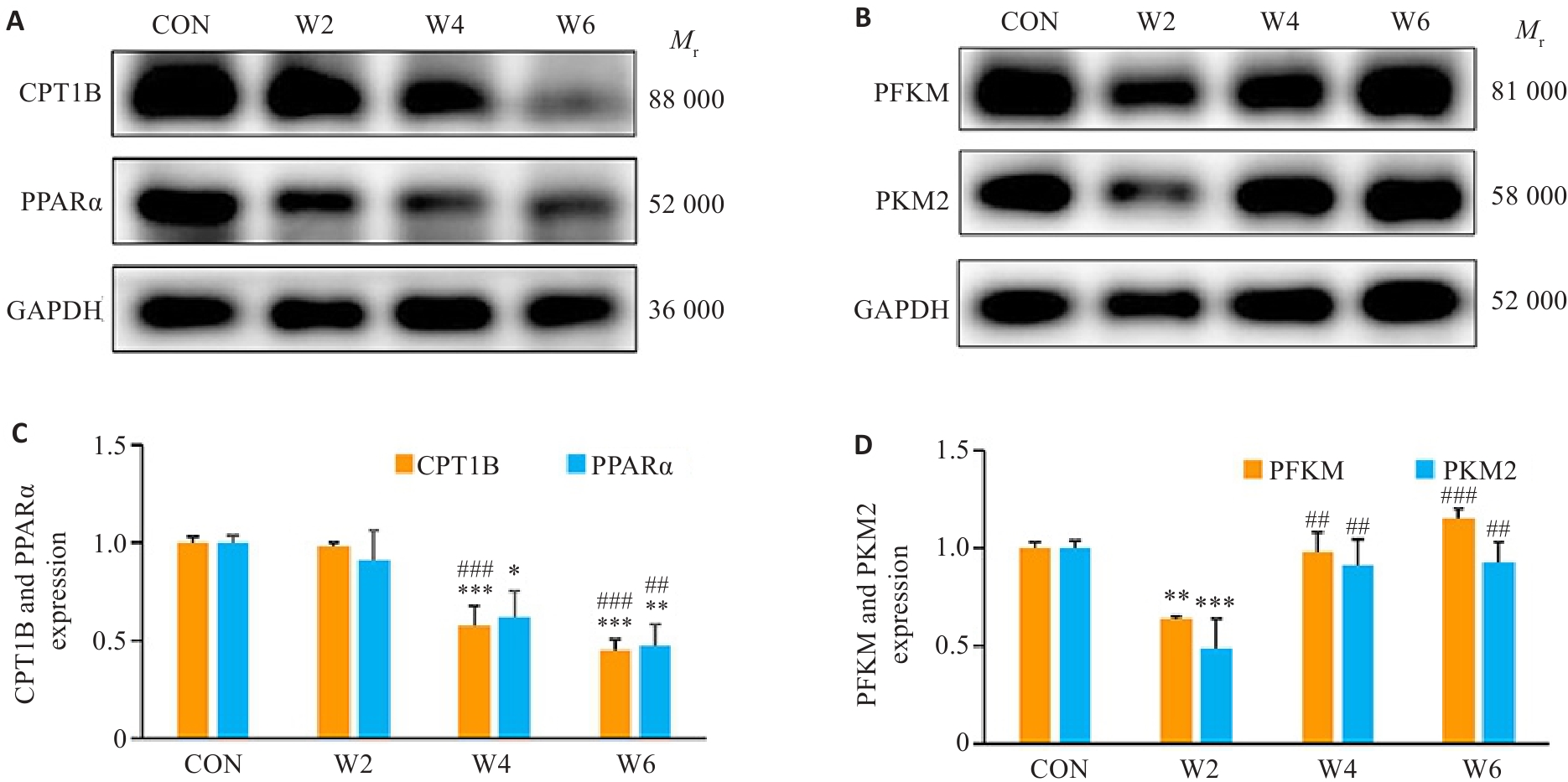
图6 各组心肌CPT1B、PPARα、PFKM、PKM2 蛋白相对表达量
Fig.6 Relative protein expressions of CPT1B, PPARα, PFKM and PKM2 in the myocardium in each group. A, B: Protein bands in Western blotting. C, D: CPT1B, PPARα, PFKM, and PKM2 protein expression levels in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs CON group; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs W2 group.
| [1] | Kivimäki M, Jokela M, Nyberg ST, et al. Long working hours and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished data for 603, 838 individuals[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(10005): 1739-46. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60295-1 |
| [2] | Pega F, Náfrádi B, Momen NC, et al. Global, regional, and national burdens of ischemic heart disease and stroke attributable to exposure to long working hours for 194 countries, 2000-2016: a systematic analysis from the WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury[J]. Environ Int, 2021, 154: 106595. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2021.106595 |
| [3] | Eguchi H, Wada K, Smith DR. Recognition, compensation, and prevention of karoshi, or death due to overwork[J]. J Occup Environ Med, 2016, 58(8): e313-4. doi:10.1097/jom.0000000000000797 |
| [4] | Al-Madhagi HA. Unveiling the global surge: unraveling the factors fueling the spread of karoshi syndrome[J]. Risk Manag Healthc Policy, 2023, 16: 2779-82. doi:10.2147/rmhp.s444900 |
| [5] | Lopaschuk GD, Karwi QG, Tian R, et al. Cardiac energy metabolism in heart failure[J]. Circ Res, 2021, 128(10): 1487-513. doi:10.1161/circresaha.121.318241 |
| [6] | Flam E, Jang C, Murashige D, et al. Integrated landscape of cardiac metabolism in end-stage human nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy[J]. Nat Cardiovasc Res, 2022, 1(9): 817-29. |
| [7] | Piché ME, Tchernof A, Després JP. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Circ Res, 2020, 126(11): 1477-500. doi:10.1161/circresaha.120.316101 |
| [8] | 李嘉敏, 苏锐冰, 于晓军, 等. 大鼠过劳死模型的建立及基于模型的能量代谢和氧化应激的蛋白质组学和代谢组学分析[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2024, 51(8): 1935-49. |
| [9] | Miao Q, Li J, Pan YP, et al. Three cases of karoshi without the typical pathomorphological features of cardiovascular/cerebrovascular disease[J]. Am J Forensic Med Pathol, 2020, 41(4): 305-8. doi:10.1097/paf.0000000000000600 |
| [10] | 刘艳艳, 程静茹, 余克强, 等. 疲劳型亚健康小鼠模型的研制[J]. 广东医学, 2012, 33(1): 21-4. |
| [11] | 邓三春, 陈苏衡, 于恺华, 等. 过度劳累对小鼠脾脏造血功能的影响[J]. 陆军军医大学学报, 2024(5): 427-33. |
| [12] | Matsui T, Ishikawa T, Ito H, et al. Brain glycogen superco-mpensation following exhaustive exercise[J]. J Physiol, 2012, 590(3): 607-16. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.217919 |
| [13] | Lee WD, Liang LF, AbuSalim J, et al. Impact of acute stress on murine metabolomics and metabolic flux[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2023, 120(21): e2301215120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2301215120 |
| [14] | Lightman SL, Birnie MT, Conway-Campbell BL. Dynamics of ACTH and Cortisol secretion and implications for disease[J]. Endocr Rev, 2020, 41(3): bnaa002. doi:10.1210/endrev/bnaa002 |
| [15] | Chen YY, Gao TH, Bai J, et al. Ren-Shen-Bu-Qi decoction alleviates exercise fatigue through activating PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 pathway in mice[J]. Chin Med, 2024, 19(1): 154. doi:10.1186/s13020-024-01027-4 |
| [16] | Flockhart M, Tischer D, Nilsson LC, et al. Reduced glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity after prolonged exercise in endurance athletes[J]. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 2023, 238(4): e13972. doi:10.1111/apha.13972 |
| [17] | Zhang QL, Shen XT, Yuan X, et al. Lipopolysaccharide binding protein resists hepatic oxidative stress by regulating lipid droplet homeostasis[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 3213. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-47553-5 |
| [18] | Geng J, Zhang XL, Guo YJ, et al. Moderate-intensity interval exercise exacerbates cardiac lipotoxicity in high-fat, high-calories diet-fed mice[J]. Nat Commun, 2025, 16(1): 613. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-55917-8 |
| [19] | 廖 阅, 马 雪, 邓三春, 等. 过劳诱导小鼠血管内皮屏障功能障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1814-20. |
| [20] | Kim HG, Lee JS, Lee JS, et al. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Myelophil on restraint stress-induced liver injury in BALB/c mice[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2012, 142(1): 113-20. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.04.023 |
| [21] | Raposeiras-Roubin S, Rosselló X, Oliva B, et al. Triglycerides and residual atherosclerotic risk[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2021, 77(24): 3031-41. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.059 |
| [22] | Nordestgaard BG. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: new insights from epidemiology, genetics, and biology[J]. Circ Res, 2016, 118(4): 547-63. doi:10.1161/circresaha.115.306249 |
| [23] | Miller M, Stone NJ, Ballantyne C, et al. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2011, 123(20): 2292-333. doi:10.1161/cir.0b013e3182160726 |
| [24] | 陈苏衡, 甘 露, 庄 苗, 等. 过度劳累对大鼠动脉血管壁细胞外基质的影响[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2022, 44(2): 262-9. |
| [25] | Zhang YF, Yu MY, Chen Y, et al. High-density lipoprotein in cardiovascular diseases: From high quantity to high quality[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2026, 578: 120574. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2025.120574 |
| [26] | Ljones K, Ness HO, Solvang-Garten K, et al. Acute exhaustive aerobic exercise training impair cardiomyocyte function and calcium handling in Sprague-Dawley rats[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(3): e0173449. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0173449 |
| [27] | Oláh A, Németh BT, Mátyás C, et al. Cardiac effects of acute exhaustive exercise in a rat model[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2015, 182: 258-66. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.12.045 |
| [28] | 马 雪, 廖阅, 邓三春, 等.过劳不同时间对小鼠心肌细胞焦亡的影响[J], 解放军医学杂志, 2025, 50(6): 756-761. |
| [29] | Haynie KR, Vandanmagsar B, Wicks SE, et al. Inhibition of carnitine palymitoyltransferase1b induces cardiac hypertrophy and mortality in mice[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2014, 16(8): 757-60. doi:10.1111/dom.12248 |
| [30] | He L, Kim T, Long QQ, et al. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1b deficiency aggravates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy caused by lipotoxicity[J]. Circulation, 2012, 126(14): 1705-16. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.111.075978 |
| [31] | 高瑞芳, 常 芸, 刘云清, 等. 力竭运动后大鼠心肌组织结构改变及不同时相PPARα表达的变化[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2009, 28(3): 264-8. |
| [32] | O’Connell RP, Musa H, Gomez MSM, et al. Free fatty acid effects on the atrial myocardium: membrane ionic currents are remodeled by the disruption of T-tubular architecture[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0133052. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0133052 |
| [33] | Schulze PC, Drosatos K, Goldberg IJ. Lipid use and misuse by the heart[J]. Circ Res, 2016, 118(11): 1736-51. doi:10.1161/circresaha.116.306842 |
| [34] | Gibb AA, Hill BG. Metabolic coordination of physiological and pathological cardiac remodeling[J]. Circ Res, 2018, 123(1): 107-28. doi:10.1161/circresaha.118.312017 |
| [35] | Kemppainen J, Fujimoto T, Kalliokoski KK, et al. Myocardial and skeletal muscle glucose uptake during exercise in humans[J]. J Physiol, 2002, 542(Pt 2): 403-12. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.018135 |
| [36] | Wang X, Zhu XX, Jiao SY, et al. Cardiomyocyte peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α is essential for energy metabolism and extracellular matrix homeostasis during pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2022, 43(5): 1231-42. doi:10.1038/s41401-021-00743-z |
| [37] | Gibb AA, Epstein PN, Uchida S, et al. Exercise-induced changes in glucose metabolism promote physiological cardiac growth[J]. Circulation, 2017, 136(22): 2144-57. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.117.028274 |
| [1] | 云琦, 杜若丽, 贺玉莹, 张贻欣, 王佳慧, 叶红伟, 李正红, 高琴. 肉桂酸通过抑制TLR4减轻阿霉素诱导的小鼠心肌损伤铁死亡的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1946-1958. |
| [2] | 王堃, 左海燕, 张娇娇, 吴欣, 王文慧, 吴生兵, 周美启. 电针通过调控海马谷氨酸释放抑制HPA轴亢进从而改善急性心肌缺血大鼠的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1599-1607. |
| [3] | 薄海美, 曹新营, 邢平川, 王志军. 外泌体来源的miR-1275通过上调淋巴细胞中IL-38的表达抑制脓毒症心肌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1608-1615. |
| [4] | 吴秋岑, 卢学麒, 温耀棋, 洪永, 吴煜良, 陈超敏. II导联心电图中心肌梗死检测与定位:基于多尺度残差模块融合改进通道注意力模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1777-1790. |
| [5] | 卞芬兰, 倪诗垚, 赵鹏, 戚毛男星, 唐碧, 王洪巨, 康品方, 刘进军. 积雪草苷通过抑制NLRP3炎症体介导的细胞焦亡减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 977-985. |
| [6] | 马振岩, 阿鑫, 赵蕾, 张洪博, 刘科, 赵依晴, 钱赓. 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死经皮冠状动脉介入术后左心室不良重构的新型风险预测模型:基于心脏磁共振的多中心前瞻性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 669-683. |
| [7] | 孙红燕, 卢国庆, 付程文, 徐梦文, 朱小翌, 邢国权, 刘乐强, 柯雨菲, 崔乐妹, 陈睿旸, 王磊, 康品方, 唐碧. 槲皮素通过调控L型钙通道改善糖尿病大鼠心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 531-541. |
| [8] | 蔡蕊, 黄卓, 贺文霞, 艾添红, 宋晓伟, 胡淑婷. 剪接因子HNRNPH1通过调控Circ-MYOCD的反向剪接影响心肌肥厚的发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 587-594. |
| [9] | 付长龙, 陈若岚, 徐诗淇, 游锦欣, 林晴, 黄艳峰. 巴戟天多糖通过靶向lncRNA XIST调控糖酵解-焦亡延缓小鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞退变[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2541-2550. |
| [10] | 李思蒙, 陈建宁, 申思满, 刘望龙, 于丽丽, 张良清. 丹酚酸B通过抑制Sirt1蛋白降解促进心肌细胞线粒体功能稳态和改善缺血再灌注小鼠的心脏功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2062-2070. |
| [11] | 鲁辉, 宋博文, 施金冉, 王舜印, 陈孝华, 杨晶晶, 葛思堂, 左芦根. 高表达SF3B3促进胃癌细胞恶性增殖并与患者不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2240-2249. |
| [12] | 贺松其, 刘洋, 秦梦晨, 何春雨, 江稳滔, 王一钦, 谭思蕊, 孙海燕, 孙海涛. 中医药调控糖酵解重塑肿瘤免疫微环境的研究进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2277-2284. |
| [13] | 石情, 冉苏叶, 宋铃榆, 杨红, 王文娟, 刘晗琳, 刘琦. NLRP6过表达通过AMPK/CPT1A/PGC1A通路促进肝细胞脂肪氧化分解改善非酒精性脂肪肝[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 118-125. |
| [14] | 季春斐, 左宗超, 王钧, 李妙男. N-乙酰神经氨酸中通过抑制Nrf2轴促进缺氧/复氧损伤的H9C2心肌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 72-79. |
| [15] | 温小慧, 黄诗雅, 刘学红, 李坤寅, 关永格. Notch1信号通过调控细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和糖酵解参与子宫腺肌病的发生及发展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1599-1604. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||