南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2434-2442.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.20
胡玥1( ), 曾玉2(
), 曾玉2( ), 王琳婧3, 廖志伟3, 谭剑明3, 邝燕好2, 龚攀2, 齐斌3, 甄鑫1(
), 王琳婧3, 廖志伟3, 谭剑明3, 邝燕好2, 龚攀2, 齐斌3, 甄鑫1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-06
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-12-26
通讯作者:
曾玉,甄鑫
E-mail:huyue058@gmail.com;apple02180717@126.com;xinzhen@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:胡 玥,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: huyue058@gmail.com基金资助:
Yue HU1( ), Yu ZENG2(
), Yu ZENG2( ), Linjing WANG3, Zhiwei LIAO3, Jianming TAN3, Yanhao KUANG2, Pan GONG2, Bin QI3, Xin ZHEN1(
), Linjing WANG3, Zhiwei LIAO3, Jianming TAN3, Yanhao KUANG2, Pan GONG2, Bin QI3, Xin ZHEN1( )
)
Received:2024-09-06
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Yu ZENG, Xin ZHEN
E-mail:huyue058@gmail.com;apple02180717@126.com;xinzhen@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 评估不同放射性口腔黏膜炎(RIOM)预测模型的性能,对比分析分层多模态多分类器融合(H-MCF)模型的有效性。 方法 回顾性收集2022年9月~2023年2月在广州医科大学附属肿瘤医院接受观察和治疗的198例放射性口腔黏膜炎局部晚期鼻咽癌患者的数据。基于口腔放射剂量-体积参数与鼻咽癌相关的临床特征,针对不同特征选择算法和分类器两两组合得到基础分类模型。我们使用基于多准则决策的多分类器融合模型(MCF)和它的变体——H-MCF模型对基础分类模型进行融合。通过对各个模态的基础分类模型与MCF模型的性能、多模态的基础模型和MCF模型以及H-MCF模型的性能、单模态与多模态模型的性能、H-MCF与MCF以及其他集成分类器的性能进行分析比较,并通过ROC曲线下面积(AUC)、准确率(ACC)、灵敏度(SEN)和特异度(SPE)4种评价指标来评估模型的泛化性能,分析 RIOM预测模型有效性。 结果 结合多模态特征后,H-MCF模型在预测严重RIOM方面达到了最高的准确性(AUC=0.883,ACC=0.850,SEN=0.933,SPE=0.800)。 结论 相较于单个分类器的预测结果,结合临床和剂量两种模态的多分类器融合算法在预测严重RIOM发病率方面表现更优。
胡玥, 曾玉, 王琳婧, 廖志伟, 谭剑明, 邝燕好, 龚攀, 齐斌, 甄鑫. 多模态多分类器融合模型预测放射性口腔黏膜炎的性能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2434-2442.
Yue HU, Yu ZENG, Linjing WANG, Zhiwei LIAO, Jianming TAN, Yanhao KUANG, Pan GONG, Bin QI, Xin ZHEN. Performance of multi-modality and multi-classifier fusion models for predicting radiation-induced oral mucositis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2434-2442.
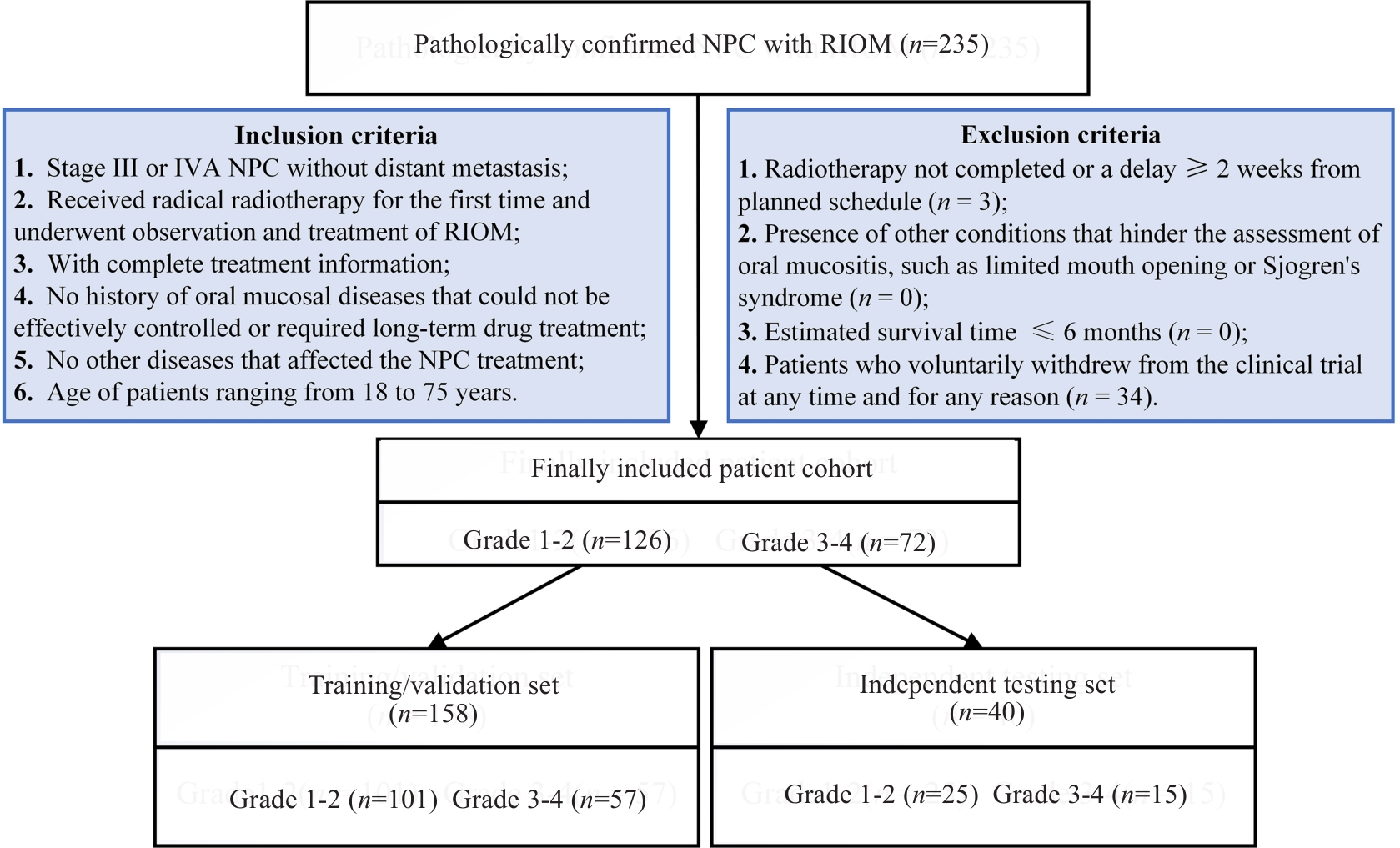
图1 患者纳入和排除标准
Fig.1 Flowchart of inclusion and exclusion of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) who experienced radiation-induced oral mucositis (RIOM) following radiotherapy.
| Characteristics | Training/validation set | Independent testing set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade (1-2) | Grade (3-4) | P | Grade (1-2) | Grade (3-4) | P | ||
| Age (year) | Median (range) | 47 (18-70) | 49 (18-75) | 0.37 | 48 (28-72) | 46 (37-67) | 0.43 |
| Height (cm) | Mean±SD | 163.66±7.36 | 164.16±8.15 | 0.58 | 163.60±8.81 | 164.00±7.68 | 0.89 |
| Weight (kg) | Mean±SD | 61.51±10.33 | 60.46±12.13 | 0.37 | 62.76±9.57 | 60.21±10.44 | 0.44 |
| Body mass index | Mean±SD | 22.91±3.22 | 22.30±3.28 | 0.16 | 23.43±2.97 | 22.24±2.74 | 0.22 |
| Gender | Female | 23 | 11 | 0.61 | 18 | 13 | 0.49 |
| Male | 78 | 46 | 7 | 2 | |||
| Tobacco use | Never | 69 | 44 | 0.46 | 16 | 10 | 0.74 |
| Former | 24 | 9 | 8 | 5 | |||
| Current | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Alcohol use | Never | 94 | 53 | 0.33 | 23 | 13 | 0.42 |
| Former | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Current | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Number of radiotherapy fractions | Mean±SD | 32.53±0.72 | 32.79±0.59 | 0.03 | 32.60±0.58 | 32.47±0.52 | 0.56 |
| Total dose (Gy) | Mean±SD | 70.23±0.97 | 70.22±1.65 | 0.54 | 70.37±0.97 | 70.04±0.19 | 0.16 |
| Cycle of induction chemotherapy | Mean±SD | 3.06±0.86 | 2.93±0.90 | 0.20 | 2.84±1.21 | 2.53±1.06 | 0.49 |
| Induced chemotherapy | No | 2 | 0 | 0.54 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 99 | 57 | 24 | 14 | |||
| Reduction of induced chemotherapy doses | No | 91 | 49 | 0.43 | 24 | 14 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 10 | 8 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Concurrent chemo-radiotherapy | No | 8 | 3 | 0.76 | 2 | 2 | 0.62 |
| Yes | 93 | 54 | 23 | 13 | |||
表1 患者临床特征
Tab.1 Demographic and clinical data of the included patients
| Characteristics | Training/validation set | Independent testing set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade (1-2) | Grade (3-4) | P | Grade (1-2) | Grade (3-4) | P | ||
| Age (year) | Median (range) | 47 (18-70) | 49 (18-75) | 0.37 | 48 (28-72) | 46 (37-67) | 0.43 |
| Height (cm) | Mean±SD | 163.66±7.36 | 164.16±8.15 | 0.58 | 163.60±8.81 | 164.00±7.68 | 0.89 |
| Weight (kg) | Mean±SD | 61.51±10.33 | 60.46±12.13 | 0.37 | 62.76±9.57 | 60.21±10.44 | 0.44 |
| Body mass index | Mean±SD | 22.91±3.22 | 22.30±3.28 | 0.16 | 23.43±2.97 | 22.24±2.74 | 0.22 |
| Gender | Female | 23 | 11 | 0.61 | 18 | 13 | 0.49 |
| Male | 78 | 46 | 7 | 2 | |||
| Tobacco use | Never | 69 | 44 | 0.46 | 16 | 10 | 0.74 |
| Former | 24 | 9 | 8 | 5 | |||
| Current | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Alcohol use | Never | 94 | 53 | 0.33 | 23 | 13 | 0.42 |
| Former | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Current | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Number of radiotherapy fractions | Mean±SD | 32.53±0.72 | 32.79±0.59 | 0.03 | 32.60±0.58 | 32.47±0.52 | 0.56 |
| Total dose (Gy) | Mean±SD | 70.23±0.97 | 70.22±1.65 | 0.54 | 70.37±0.97 | 70.04±0.19 | 0.16 |
| Cycle of induction chemotherapy | Mean±SD | 3.06±0.86 | 2.93±0.90 | 0.20 | 2.84±1.21 | 2.53±1.06 | 0.49 |
| Induced chemotherapy | No | 2 | 0 | 0.54 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 99 | 57 | 24 | 14 | |||
| Reduction of induced chemotherapy doses | No | 91 | 49 | 0.43 | 24 | 14 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 10 | 8 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Concurrent chemo-radiotherapy | No | 8 | 3 | 0.76 | 2 | 2 | 0.62 |
| Yes | 93 | 54 | 23 | 13 | |||
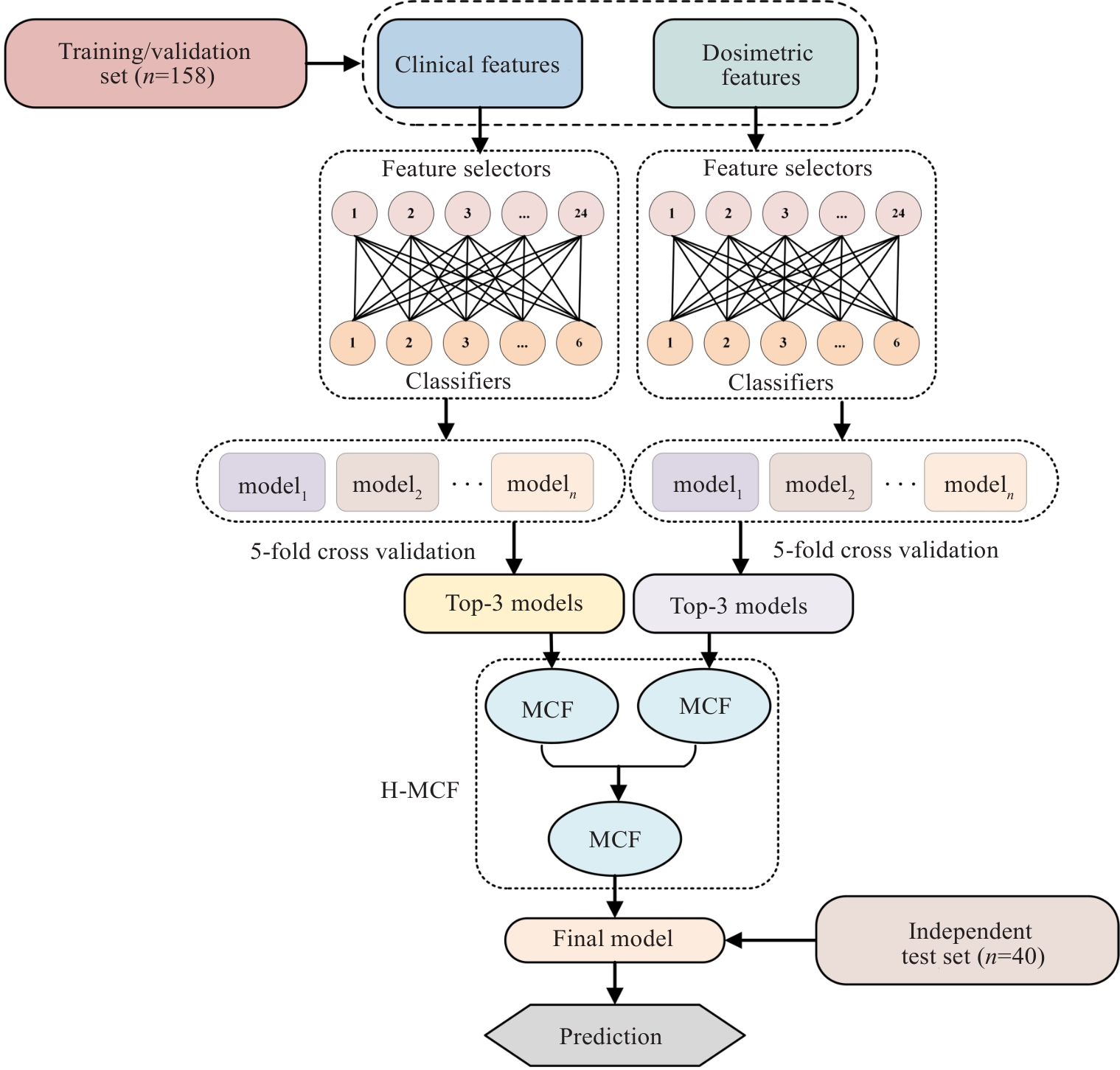
图3 H-MCF算法流程图
Fig.3 Flowchart of the H-MCF algorithm. H-MCF: Hierarchical multi-modality and multi-classifier fusion; MCF: Multi-criterion decision-making (MCDM)-based classifier fusion.
Algorithm 1 Multi-Criterion Decision-making (MCDM) Based Classifier Fusion (MCF) Pseudocode |
|---|
Input: An evaluation matrix E Process: Step 1: Normalize the evaluation matrix E column-wise: Step 2: Compute the weighted evaluation matrix: Step 3: Compute the distance of each classifier from the "worst" and "best" solutions: Step 4: Compute the fusion weight for each classifier: Step 5: Normalize the fusion weights: Step 6: Calculate the final fusion score: Output: Final prediction probability |
表2 基于多准则决策多分类器融合 (MCF) 伪代码
Tab.2 Multi-criterion decision-making (MCDM)-based classifier fusion (MCF) pseudocode
Algorithm 1 Multi-Criterion Decision-making (MCDM) Based Classifier Fusion (MCF) Pseudocode |
|---|
Input: An evaluation matrix E Process: Step 1: Normalize the evaluation matrix E column-wise: Step 2: Compute the weighted evaluation matrix: Step 3: Compute the distance of each classifier from the "worst" and "best" solutions: Step 4: Compute the fusion weight for each classifier: Step 5: Normalize the fusion weights: Step 6: Calculate the final fusion score: Output: Final prediction probability |
| Models | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOCC | LDA+MIFS | 0.568 | 0.650 | 0.533 | 0.720 |
| MLP+MIFS | 0.477 | 0.500 | 0.800 | 0.320 | |
| MLP+MRMR | 0.477 | 0.500 | 0.800 | 0.320 | |
| MCF | 0.592 | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.600 | |
| C | LR+ll_l21 | 0.779 | 0.750 | 0.600 | 0.840 |
| MLP+ll_l21 | 0.851 | 0.800 | 0.667 | 0.880 | |
| SVM+SPEC | 0.741 | 0.725 | 0.667 | 0.760 | |
| MCF | 0.864 | 0.850 | 0.800 | 0.880 | |
表3 单模态基础模型和MCF模型的预测性能
Tab.3 Predictive performance of the base models and MCF models for unimodal data
| Models | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOCC | LDA+MIFS | 0.568 | 0.650 | 0.533 | 0.720 |
| MLP+MIFS | 0.477 | 0.500 | 0.800 | 0.320 | |
| MLP+MRMR | 0.477 | 0.500 | 0.800 | 0.320 | |
| MCF | 0.592 | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.600 | |
| C | LR+ll_l21 | 0.779 | 0.750 | 0.600 | 0.840 |
| MLP+ll_l21 | 0.851 | 0.800 | 0.667 | 0.880 | |
| SVM+SPEC | 0.741 | 0.725 | 0.667 | 0.760 | |
| MCF | 0.864 | 0.850 | 0.800 | 0.880 | |
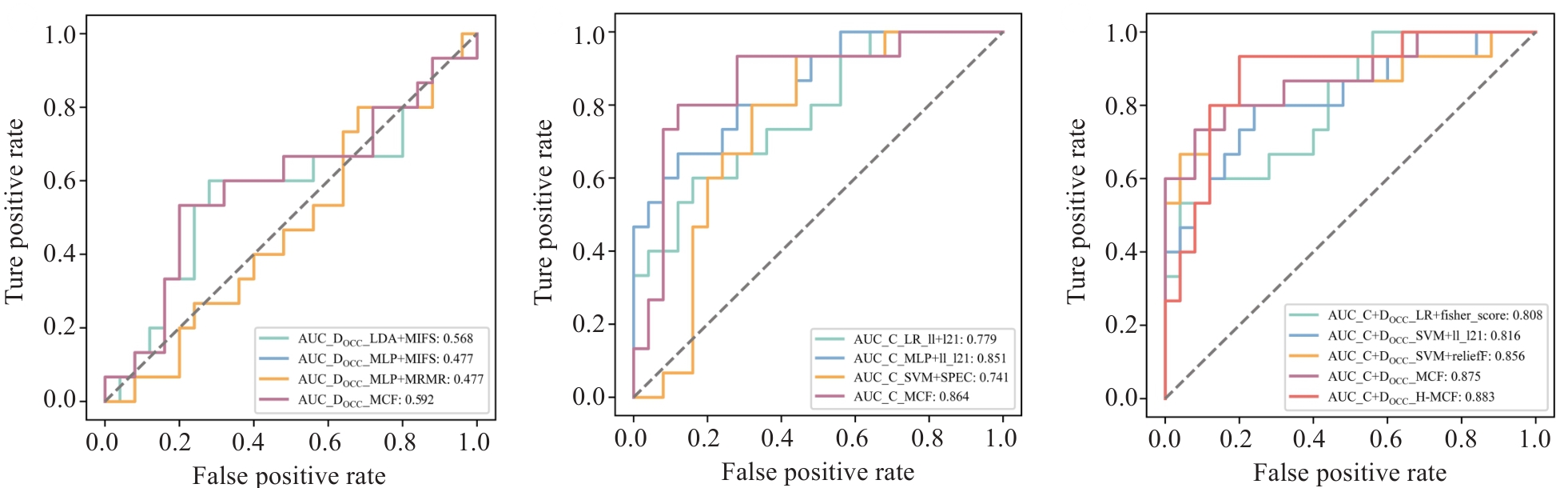
图4 各模态基础模型与MCF模型的受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线
Fig.4 Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the base models and MCF models for each modality. OCC: Oral cavity contour; DOCC: DVH parameters from OCC; C: Clinical features.
| Models | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C+DOCC | MLP+CIFE | 0.808 | 0.800 | 0.533 | 0.960 |
| MLP+t_score | 0.816 | 0.775 | 0.800 | 0.760 | |
| LR+t_score | 0.856 | 0.850 | 0.800 | 0.880 | |
| MCF | 0.875 | 0.850 | 0.733 | 0.920 | |
| H-MCF | 0.883 | 0.850 | 0.933 | 0.800 | |
表4 多模态基础模型、MCF模型和H-MCF模型的预测性能
Tab.4 Predictive performance of base models, MCF models, and H-MCF models for multimodal data
| Models | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C+DOCC | MLP+CIFE | 0.808 | 0.800 | 0.533 | 0.960 |
| MLP+t_score | 0.816 | 0.775 | 0.800 | 0.760 | |
| LR+t_score | 0.856 | 0.850 | 0.800 | 0.880 | |
| MCF | 0.875 | 0.850 | 0.733 | 0.920 | |
| H-MCF | 0.883 | 0.850 | 0.933 | 0.800 | |
| Models | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra trees+NDFS | 0.715 | 0.700 | 0.800 | 0.640 |
| Random forest+NDFS | 0.771 | 0.700 | 0.867 | 0.600 |
| Bagging+reliefF | 0.812 | 0.750 | 0.800 | 0.720 |
| AdaBoost+NDFS | 0.856 | 0.825 | 0.733 | 0.880 |
| GradientBoosting+NDFS | 0.736 | 0.725 | 0.733 | 0.720 |
| LightGBM+NDFS | 0.816 | 0.750 | 0.733 | 0.760 |
| XGBoost+NDFS | 0.749 | 0.700 | 0.600 | 0.760 |
| CatBoost+MCFS | 0.781 | 0.825 | 0.733 | 0.880 |
| MCF | 0.875 | 0.850 | 0.733 | 0.920 |
| H-MCF | 0.883 | 0.850 | 0.933 | 0.800 |
表5 H-MCF与MCF、8种集成分类器的预测性能
Tab.5 Predictive performance of H-MCF compared with MCF and eight ensemble classifiers
| Models | AUC | ACC | SEN | SPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra trees+NDFS | 0.715 | 0.700 | 0.800 | 0.640 |
| Random forest+NDFS | 0.771 | 0.700 | 0.867 | 0.600 |
| Bagging+reliefF | 0.812 | 0.750 | 0.800 | 0.720 |
| AdaBoost+NDFS | 0.856 | 0.825 | 0.733 | 0.880 |
| GradientBoosting+NDFS | 0.736 | 0.725 | 0.733 | 0.720 |
| LightGBM+NDFS | 0.816 | 0.750 | 0.733 | 0.760 |
| XGBoost+NDFS | 0.749 | 0.700 | 0.600 | 0.760 |
| CatBoost+MCFS | 0.781 | 0.825 | 0.733 | 0.880 |
| MCF | 0.875 | 0.850 | 0.733 | 0.920 |
| H-MCF | 0.883 | 0.850 | 0.933 | 0.800 |
| 1 | Global Cancer Observatory Cancer Today. Lyon, France International Agency for Research on Cancer.[EB/OL][8.28]. . |
| 2 | Zhou XT, Shao TC, Jia HJ, et al. Current state, challenges, and future perspective of adaptive radiotherapy: a narrative review of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Oral Oncol, 2024, 158: 107008. |
| 3 | Chen C, Zhang Q, Yu W, et al. Oral mucositis: an update on innate immunity and new interventional targets[J]. J Dent Res, 2020, 99(10): 1122-30. |
| 4 | Sunaga T, Nagatani A, Fujii N, et al. The association between cumulative radiation dose and the incidence of severe oral mucositis in head and neck cancers during radiotherapy[J]. Cancer Rep, 2021, 4(2): e1317. |
| 5 | Tan XJ, Liu JJ, Deng YK, et al. Analysis of factors related to radiation-induced oral mucositis in patients with head and neck tumors undergoing radiotherapy[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2024: 102042. |
| 6 | Saito N, Imai Y, Muto T, et al. Low body mass index as a risk factor of moderate to severe oral mucositis in oral cancer patients with radiotherapy[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2012, 20(12): 3373-7. |
| 7 | Wang JJ, Gu LQ, Zhi CX, et al. Risk factor and prediction model development for severe radiation-induced oral mucositis in head and neck tumors[J]. Future Oncol, 2024: 1-11. |
| 8 | Brown TJ, Gupta A. Management of cancer therapy-associated oral mucositis[J]. JCO Oncology Practice, 2020, 16(3): 103-9. |
| 9 | Manur JG, Vidyasagar N. Correlation of planning target volume with mucositis for head-and-neck cancer patients undergoing chemoradiation[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2020, 16(3): 565-8. |
| 10 | Mazzola R, Ricchetti F, Fersino S, et al. Predictors of mucositis in oropharyngeal and oral cavity cancer in patients treated with volumetric modulated radiation treatment: a dose-volume analysis[J]. Head Neck, 2016, 38(): E815-9. |
| 11 | Alsenan SA, Al-Turaiki IM, Hafez AM. Feature extraction methods in quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling: a com-parative study[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 78737-52. |
| 12 | Li PJ, Li KX, Jin T, et al. Predictive model and precaution for oral mucositis during chemo-radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 596822. |
| 13 | Hansen CR, Bertelsen A, Zukauskaite R, et al. Prediction of radiation-induced mucositis of H&N cancer patients based on a large patient cohort[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2020, 147: 15-21. |
| 14 | Dong YJ, Zhang J, Lam S, et al. Multimodal data integration to predict severe acute oral mucositis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients following radiation therapy[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(7): 2032. |
| 15 | Soutome S, Yanamoto S, Nishii M, et al. Risk factors for severe radiation-induced oral mucositis in patients with oral cancer[J]. J Dent Sci, 2021, 16(4): 1241-6. |
| 16 | Wyatt M, Radford B, Callow N, et al. Using ensemble methods to improve the robustness of deep learning for image classification in marine environments[J]. Methods Ecol Evol, 2022, 13(6): 1317-28. |
| 17 | Lertampaiporn S, Vorapreeda T, Hongsthong A, et al. Ensemble-AMPPred: robust AMP prediction and recognition using the ensemble learning method with a new hybrid feature for differentiating AMPs[J]. Genes, 2021, 12(2): 137. |
| 18 | Yu G, Li QF, Shen DG, et al. Optimal sparse linear prediction for block-missing multi-modality data without imputation[J]. J Am Stat Assoc, 2020, 115(531): 1406-19. |
| 19 | Soenksen LR, Ma Y, Zeng C, et al. Integrated multimodal artificial intelligence framework for healthcare applications[J]. NPJ Digit Med, 2022, 5(1): 149. |
| 20 | Sousa JV, Matos P, Silva F, et al. Single modality vs. multimodality: what works best for lung cancer screening[J]? Sensors, 2023, 23(12): 5597. |
| 21 | Lee N, Harris J, Garden AS, et al. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: radiation therapy oncology group phase II trial 0225[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2009, 27(22): 3684-90. |
| 22 | You R, Liu YP, Xie YL, et al. Hyperfractionation compared with standard fractionation in intensity-modulated radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2023, 401(10380): 917-27. |
| 23 | Freites-Martínez AD, Santana N, Arias-Santiago SA, et al. Using the common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE-version 5.0) to evaluate the severity of adverse events of anticancer therapies[J]. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed), 2021, 112(1): 90-2. |
| 24 | Panchal A, Keyes R. dicmplyer [EB/OL]. . |
| 25 | Bhide SA, Gulliford S, Fowler J, et al. Characteristics of response of oral and pharyngeal mucosa in patients receiving chemo-IMRT for head and neck cancer using hypofractionated accelerated radiotherapy[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2010, 97(1): 86-91. |
| Bhide SA, Gulliford S, Fowler J, et al. Characteristics of response of oral and pharyngeal mucosa in patients receiving chemo-IMRT for head and neck cancer using hypofractionated accelerated radiotherapy[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2010, 97(1): 86-91.[PubMed] | |
| 26 | He Q, Li X, Nathan Kim DW, et al. Feasibility study of a multi-criteria decision-making based hierarchical model for multi-modality feature and multi-classifier fusion: applications in medical prognosis prediction[J]. Inf Fusion, 2020, 55: 207-19. |
| He Q, Li X, Nathan Kim DW, et al. Feasibility study of a multi-criteria decision-making based hierarchical model for multi-modality feature and multi-classifier fusion: applications in medical prognosis prediction[J]. Inf Fusion, 2020, 55: 207-19.[LinkOut] | |
| 27 | Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, et al. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique[J]. J Artif Intell Res, 2002, 16: 321-57. |
| 28 | Li JD, Cheng KW, Wang SH, et al. Feature selection: a data perspective [J]. Acm Comput Surv, 2017, 50(6): 1-45. |
| 29 | Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, et al. Scikit-learn: machine learning in python[J]. J Mach Learn Res, 2011, 12: 2825-30. |
| 30 | Ye FS, Xu LX, Ren Y, et al. Predicting radiation pneumonitis in lung cancer: a EUD-based machine learning approach for volumetric modulated arc therapy patients[J]. Front Oncol, 2024, 14: 1343170. |
| 31 | Isaksson LJ, Pepa M, Zaffaroni M, et al. Machine learning-based models for prediction of toxicity outcomes in radiotherapy[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 790. |
| 32 | El-Sappagh S, Alonso JM, Islam SMR, et al. A multilayer multimodal detection and prediction model based on explainable artificial intelligence for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 2660. |
| 33 | 钟伟雄, 梁芳蓉, 杨蕊梦, 等. 基于多期动态增强CT影像组学特征和多分类器分层融合模型预测肝细胞癌的微血管侵犯[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 260-9. |
| 34 | Domingos P. A few useful things to know about machine learning[J]. Commun ACM, 2012, 55(10): 78-87. |
| 35 | Lobato-Delgado B, Priego-Torres B, Sanchez-Morillo D. Combining molecular, imaging, and clinical data analysis for predicting cancer prognosis[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(13): 3215. |
| 36 | Kline A, Wang HY, Li YK, et al. Multimodal machine learning in precision health: a scoping review[J]. NPJ Digit Med, 2022, 5(1): 171. |
| 37 | Dietterich TG. Ensemble methods in machine learning[C]//International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2000:1-15. |
| 38 | Huang KB, Gui CP, Xu YZ, et al. A multi-classifier system integrated by clinico-histology-genomic analysis for predicting recurrence of papillary renal cell carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 6215. |
| 39 | Cai GY, Huang FJ, Gao Y, et al. Artificial intelligence-based models enabling accurate diagnosis of ovarian cancer using laboratory tests in China: a multicentre, retrospective cohort study[J]. Lancet Digit Health, 2024, 6(3): e176-86. |
| [1] | 曾玉梅, 李继科, 黄仲曦, 周毅波. 绒毛样蛋白VILL通过与LMO7蛋白相互作用抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 954-961. |
| [2] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [3] | 刘瑨禹, 梁淑君, 张煜. 基于多尺度监督与残差反馈的优化算法有效提高鼻咽癌CT图像视交叉及视神经分割精度[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 632-642. |
| [4] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [5] | 王媛媛, 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 扁蒴藤素通过活性氧调控PI3K/AKT通路增强顺铂诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 904-912. |
| [6] | 钟伟雄, 梁芳蓉, 杨蕊梦, 甄 鑫. 基于多期动态增强CT影像组学特征和多分类器分层融合模型预测肝细胞癌的微血管侵犯[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 260-269. |
| [7] | 高凯绩, 王一豪, 曹海坤, 贾建光. 机器学习模型和Cox回归模型预测食管胃结合部腺癌预后的效能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 952-963. |
| [8] | 张浩轩, 陆 进, 蒋成义, 方美芳. 基于人工智能技术的鼻咽癌风险预测模型的构建与评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [9] | 胡 桐, 勾文峰, 任中昊, 刘改廷, 李祎亮, 左代英, 侯文彬. 淫羊藿素通过调控铁死亡增加鼻咽癌细胞的放射敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1665-1673. |
| [10] | 张恒毅, 庞金龙, 张语涵, 马 月, 范方田, 刘 浩. AZD9291通过抑制PI3K-AKT-mTOR通路抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 1403-1409. |
| [11] | 莫天澜, 吴煜良, 杨蕊梦, 甄 鑫. 肾细胞癌与乏脂肪肾血管平滑肌脂肪瘤的鉴别分类模型:基于随机投影的多分类器分层融合框架[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1174-1181. |
| [12] | 周兰柱, 吴 俊, 张明洁 , 赵 报 , 马士崟. PRMT1通过促进RRM2表达抑制鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1783-1790. |
| [13] | 高莉莉, 张 雄, 窦思雨, 岳小丁, 杨捷玲. 干扰长链编码RNA FOXCUT能抑制鼻咽癌细胞上皮间质转化及诱导线粒体损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(9): 1334-1341. |
| [14] | 王文忠, 周兰柱, 孙 哲, 吴 俊, 崔忆旋. TRIM59靶向调控PPM1B对鼻咽癌侵袭和迁移的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 1030-1036. |
| [15] | 王 啸, 黄 鉴, 吉 祥, 珠 珠. 人工智能在结肠息肉检测与分类中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(2): 310-312. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||