南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2055-2061.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.01
• •
汪一晗1( ), 张维庆2, 方婷2, 谢志敏1, 范永升1, 王新昌1(
), 张维庆2, 方婷2, 谢志敏1, 范永升1, 王新昌1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-28
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
通讯作者:
王新昌
E-mail:568398437@qq.com;ossani@126.com
作者简介:汪一晗,在站博士后,E-mail: 568398437@qq.com
基金资助:
Yihan WANG1( ), Weiqing ZHANG2, Ting FANG2, Zhimin XIE1, Yongsheng FAN1, Xinchang WANG1(
), Weiqing ZHANG2, Ting FANG2, Zhimin XIE1, Yongsheng FAN1, Xinchang WANG1( )
)
Received:2025-04-28
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Xinchang WANG
E-mail:568398437@qq.com;ossani@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 明确狼疮性肾炎(LN)患者血清中内质网应激(ERS)蛋白GRP78/CHOP含量变化,分析其诊断价值及蛋白表达改变对应的肾脏病理特征。 方法 基于系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)多中心队列研究建立样本库,随机抽取LN患者60例和无肾脏受累的SLE患者35例,ELISA法检测GRP78和CHOP在患者血清中的含量,分析其与临床特征的相关性以及对LN和LN活动期的诊断能力。以MRL/lpr小鼠为LN动物模型,检测小鼠血清GRP78和CHOP表达及肾脏中内质网凋亡相关指标。 结果 LN患者血清GRP78和CHOP高于无肾脏受累的SLE患者(P<0.05);GRP78和CHOP在LN活动期患者中也高于稳定期患者(P<0.05);关联分析提示血清GRP78和CHOP水平与SLEDAI评分、24 h尿蛋白正相关;ROC结果显示CHOP对LN(AUC=0.762)和LN活动(AUC=0.933)具有较高的诊断能力。与临床结果类似,LN小鼠GRP78和CHOP升高(P<0.05),而与该指标相关的PERK和IRE1α通路蛋白在肾脏中表达也升高(P<0.05),TUNEL染色显示LN小鼠肾脏细胞凋亡增加,凋亡相关蛋白表达升高(P<0.05)。 结论 GRP78/CHOP在狼疮性肾炎中的表达升高,可能与PERK/IRE1α双通路介导的ERS凋亡相关。
汪一晗, 张维庆, 方婷, 谢志敏, 范永升, 王新昌. PERK/IRE1α通路介导的肾细胞凋亡:GRP78/CHOP在狼疮性肾炎中的诊断价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2055-2061.
Yihan WANG, Weiqing ZHANG, Ting FANG, Zhimin XIE, Yongsheng FAN, Xinchang WANG. Elevated expressions of GRP78/CHOP in lupus nephritis: their diagnostic value and association with PERK/IRE1α pathway-mediated renal cell apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2055-2061.
| Item | LN (n=60) | SLE (n=35) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 41.31±2.08 | 38.24±2.73 | 0.28 |
| Female [n (%)] | 56 (93.33%) | 33 (94.29%) | 0.85 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.84±0.60 | 22.99±0.98 | 0.35 |
| SLEDAI | 8.14±0.74 | 5.25±0.58 | 0.05 |
| Illness duration (year) | 8.18±1.33 | 8.90±1.90 | 0.57 |
| 24 h UTP (g/d) | 1192.82±243.66 | 119.17±24.58 | 0.00 |
| Anti-dsDNA[+(%)] | 24 (40%) | 11 (31.43%) | 0.40 |
| Anti-Sm[+(%)] | 13 (21.67%) | 8 (22.86%) | 0.89 |
| Hb (g/L) | 115.25±3.04 | 123.04±5.66 | 0.10 |
| PLT (109/L) | 188.19±10.36 | 213.90±13.08 | 0.31 |
| WBC (1012/L) | 5.81±0.50 | 5.68±0.49 | 0.63 |
| C3 (g/L) | 0.70±0.04 | 0.74±0.04 | 0.80 |
| C4 (g/L) | 0.14±0.02 | 0.12±0.02 | 0.20 |
表1 LN组和SLE组间一般资料比较
Tab.1 Comparison of general clinical data between the patients in LN group and SLE group
| Item | LN (n=60) | SLE (n=35) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, Mean±SD) | 41.31±2.08 | 38.24±2.73 | 0.28 |
| Female [n (%)] | 56 (93.33%) | 33 (94.29%) | 0.85 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.84±0.60 | 22.99±0.98 | 0.35 |
| SLEDAI | 8.14±0.74 | 5.25±0.58 | 0.05 |
| Illness duration (year) | 8.18±1.33 | 8.90±1.90 | 0.57 |
| 24 h UTP (g/d) | 1192.82±243.66 | 119.17±24.58 | 0.00 |
| Anti-dsDNA[+(%)] | 24 (40%) | 11 (31.43%) | 0.40 |
| Anti-Sm[+(%)] | 13 (21.67%) | 8 (22.86%) | 0.89 |
| Hb (g/L) | 115.25±3.04 | 123.04±5.66 | 0.10 |
| PLT (109/L) | 188.19±10.36 | 213.90±13.08 | 0.31 |
| WBC (1012/L) | 5.81±0.50 | 5.68±0.49 | 0.63 |
| C3 (g/L) | 0.70±0.04 | 0.74±0.04 | 0.80 |
| C4 (g/L) | 0.14±0.02 | 0.12±0.02 | 0.20 |
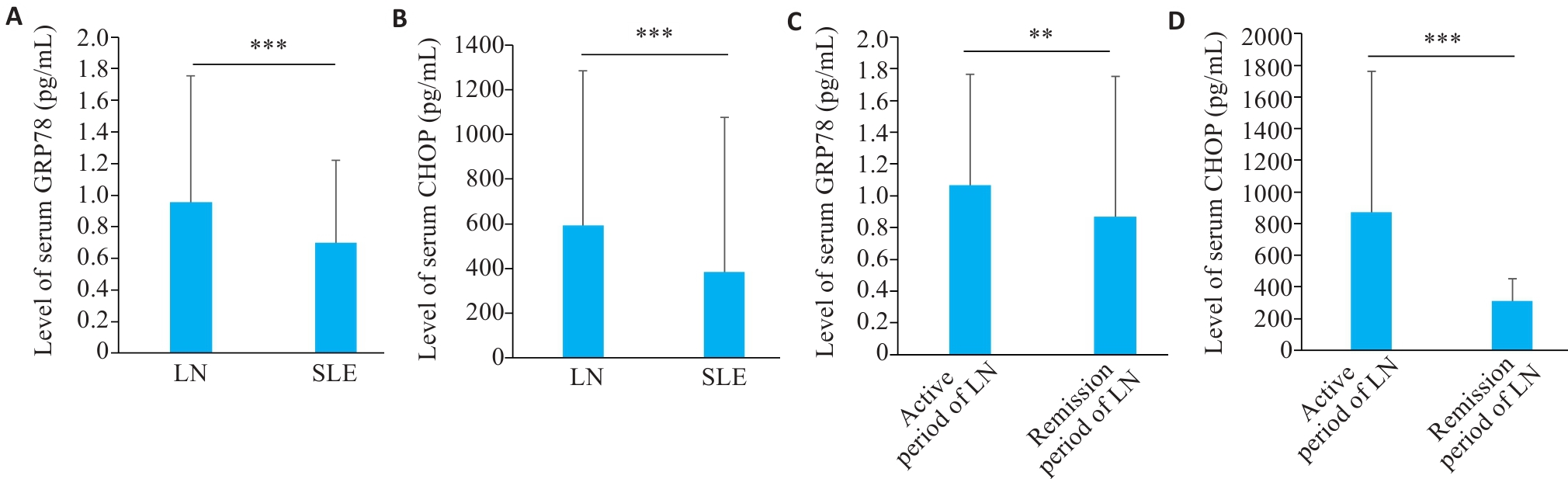
图1 LN和SLE患者血清中GRP78和CHOP水平
Fig.1 Level of serum GRP78 and CHOP in LN and SLE patients. A: Serum level of GRP78 in LN and SLE patients. B: Serum level of CHOP in LN and SLE patients. C: Serum level of GRP78 in LN patients in active and remission phase. D: Serum level of CHOP in LN patients in active and remission phase. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
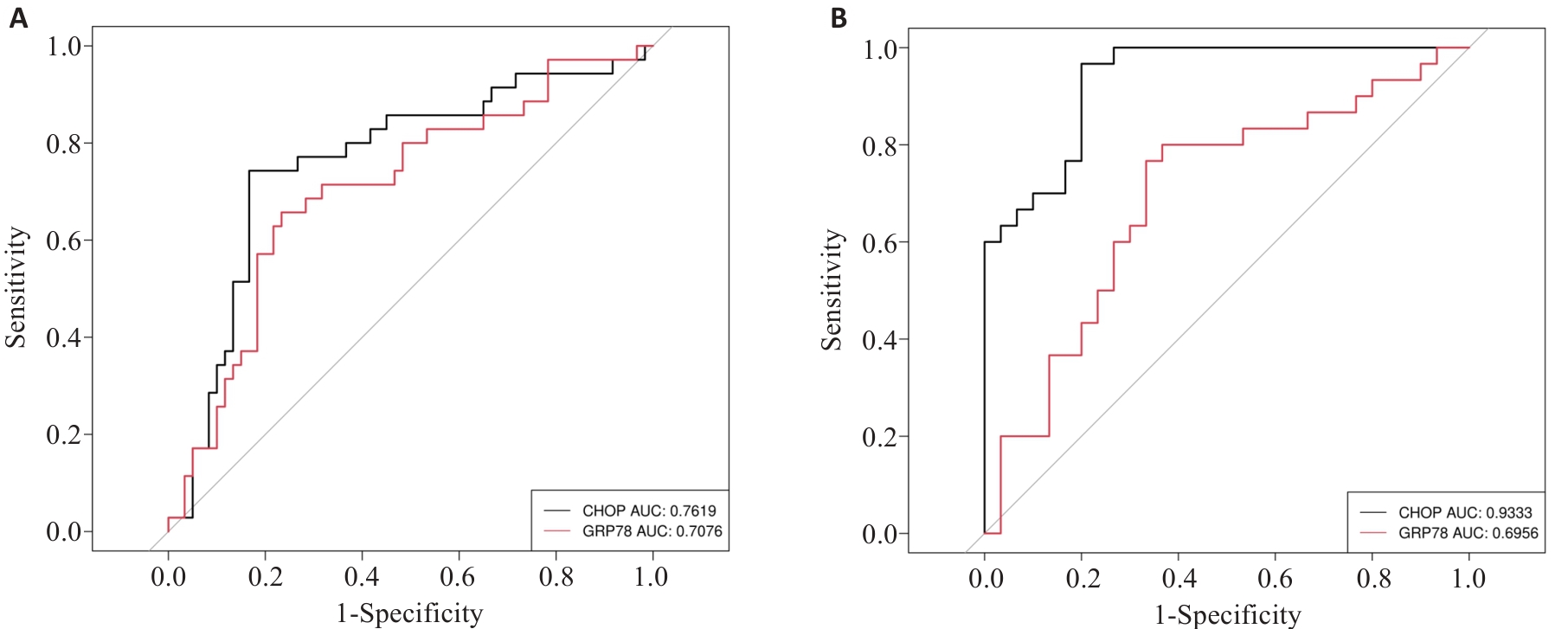
图3 GRP78和CHOP对LN的诊断能力
Fig.3 Diagnostic capabilities of GRP78 and CHOP for LN. A: ROC curves of peripheral blood GRP78 and CHOP for diagnosing LN. B: ROC curves of GRP78 and CHOP for diagnosis of LN in the active phase.
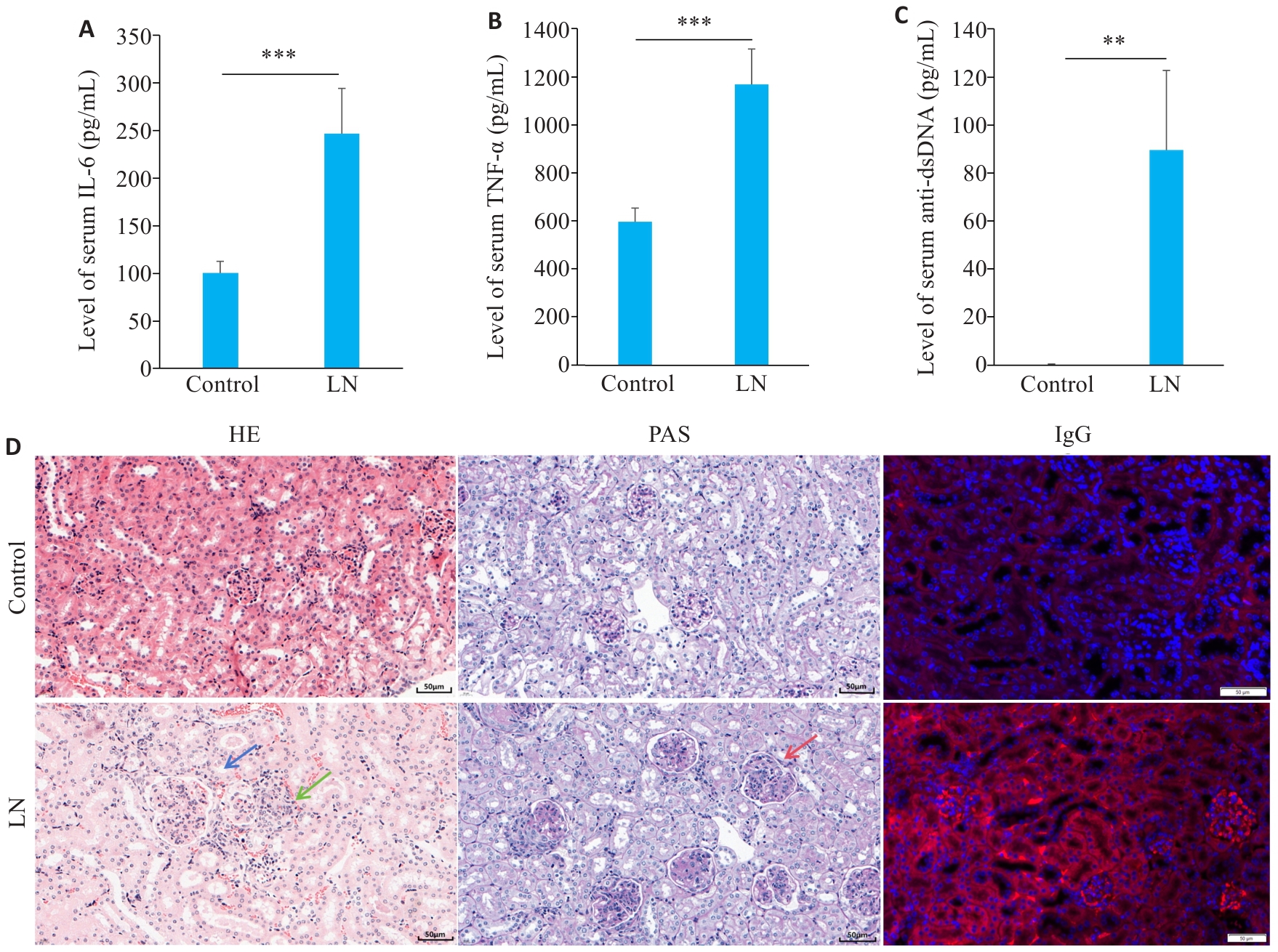
图4 LN小鼠疾病特征性表现
Fig.4 Disease characteristics in the mouse models of LN. A: Serum level of IL-6 in LN and control groups. B: Serum level of TNF-α in LN and control groups. C: Serum level of anti-dsDNA in LN and control groups. D: Renal HE staining, PAS staining and IgG staining showing mesangial cell proliferation (blue arrow), lymphocytes infiltration (green arrow), and basement membrane thickening (red arrow) (scale bar=50 μm). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
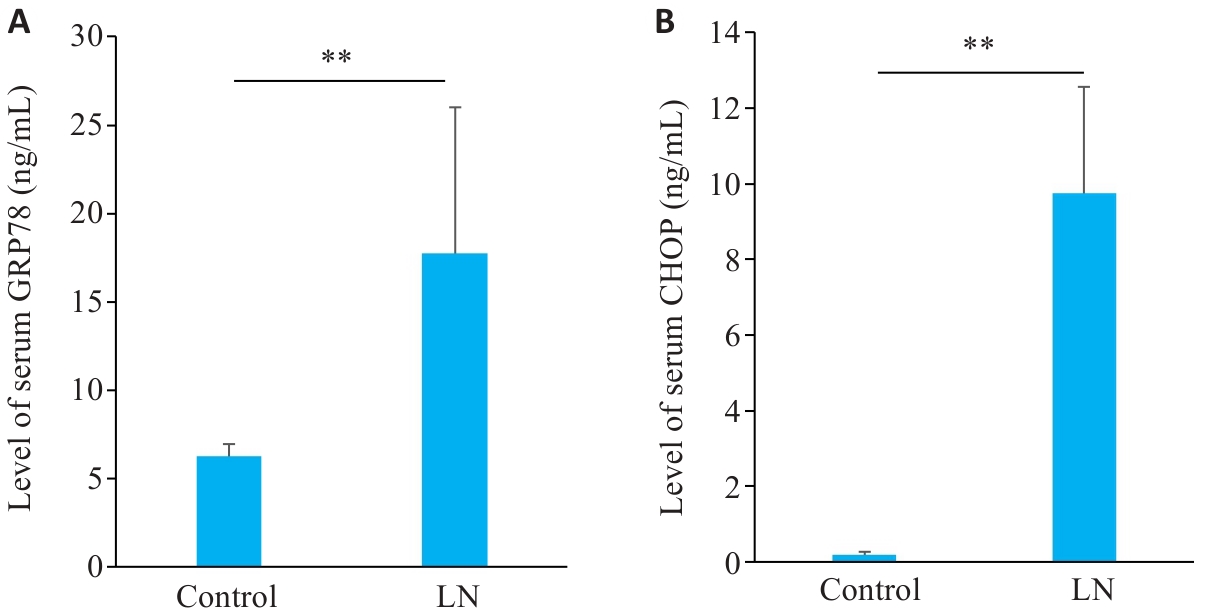
图5 LN小鼠血清GRP78和CHOP水平
Fig.5 Serum levels of GRP78 and CHOP in mouse models of LN. A: Serum levels of GRP78 in LN and control groups. B: Serum levels of CHOP in LN and control groups. **P<0.01.
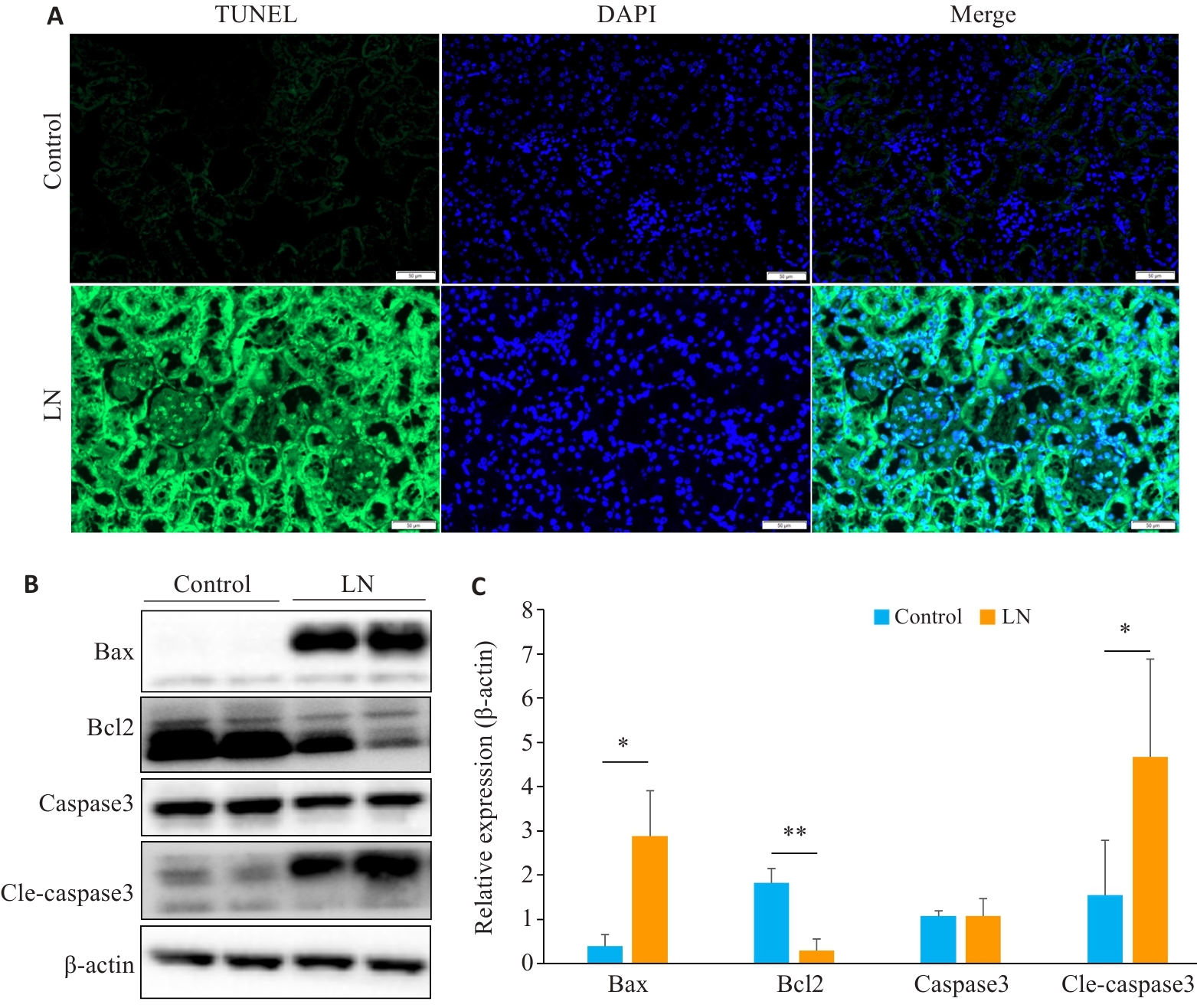
图6 LN小鼠肾脏凋亡增加
Fig.6 Renal apoptosis is increased in mouse models of LN. A: Kidney TUNEL staining in LN and control groups (scale bar=50 μm). B: Expression of apoptosis-related proteins in LN and control groups. C: Relative expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins in the two groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
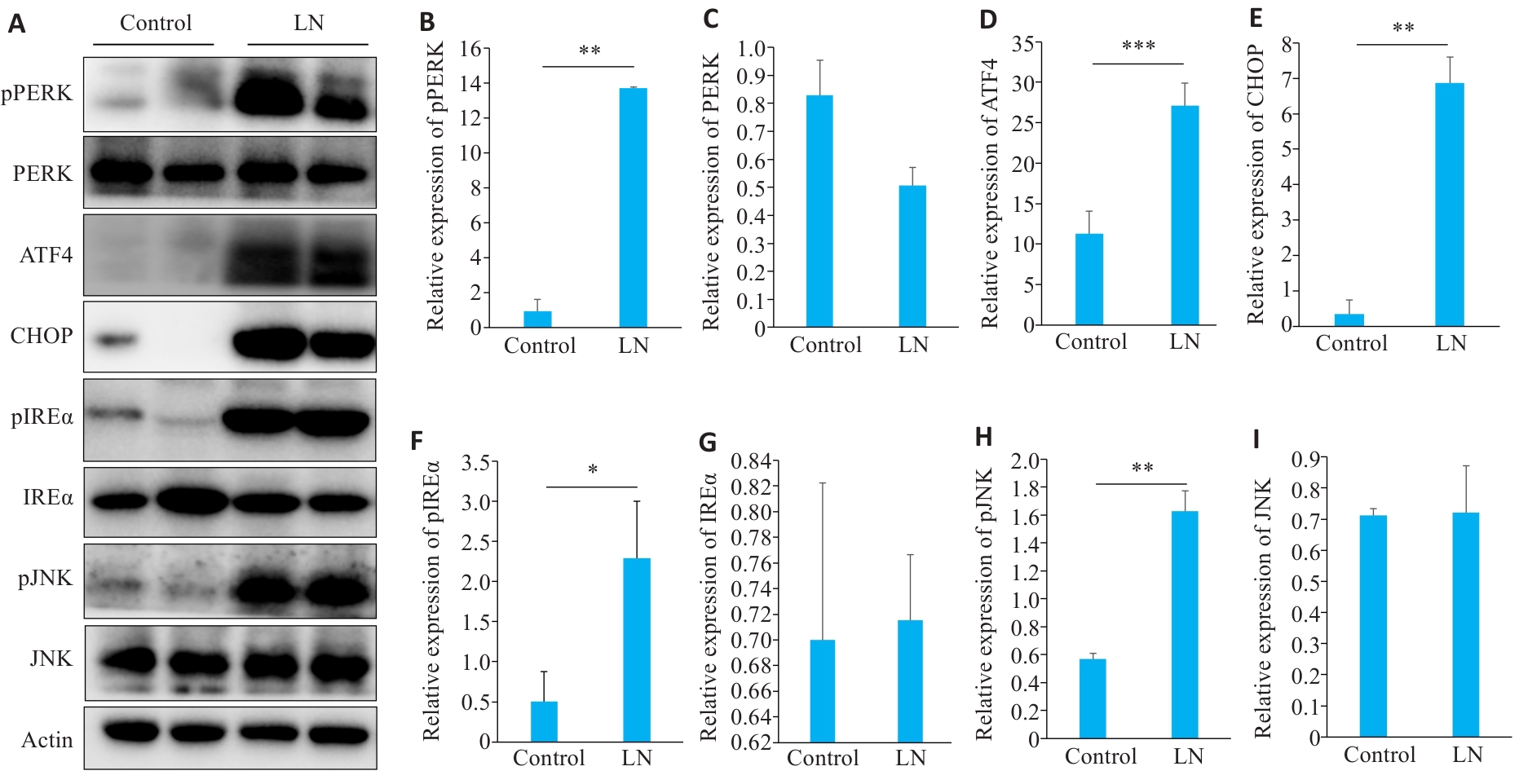
图7 LN小鼠肾脏ERS凋亡相关蛋白表达
Fig.7 Expressions of proteins related to endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis in the kidney of LN mice. A: Protein bands in Western blotting of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins. B-I: Relative PERK phosphorylation level and relative expression levels of PERK, ATF4, CHOP, IREα, IREα, phosphorylated JNK, and JNK, respectively. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| [1] | Siegel CH, Sammaritano LR. Systemic lupus erythematosus: a review[J]. JAMA, 2024, 331(17): 1480-91. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.2315 |
| [2] | Gasparotto M, Gatto M, Binda V, et al. Lupus nephritis: clinical presentations and outcomes in the 21st century[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2020, 59(): v39-51. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keaa381 |
| [3] | Anders HJ, Saxena R, Zhao M-H, et al. Lupus nephritis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6: 7. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0141-9 |
| [4] | Marciniak SJ, Chambers JE, Ron D. Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2022, 21(2): 115-40. doi:10.1038/s41573-021-00320-3 |
| [5] | Celik C, Lee SYT, Yap WS, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipids in health and diseases[J]. Prog Lipid Res, 2023, 89: 101198. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101198 |
| [6] | Ke H, Su XZ, Dong CT, et al. Sigma-1 receptor exerts protective effects on ameliorating nephrolithiasis by modulating endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrion association and inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells[J]. Redox Rep, 2024, 29(1): 2391139. doi:10.1080/13510002.2024.2391139 |
| [7] | Cybulsky AV. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, the unfolded protein response and autophagy in kidney diseases[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2017, 13(11): 681-96. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2017.129 |
| [8] | Ibrahim IM, Abdelmalek DH, Elfiky AA. GRP78: a cell’s response to stress[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 226: 156-63. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022 |
| [9] | Akinyemi AO, Simpson KE, Oyelere SF, et al. Unveiling the dark side of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) in cancers and other human pathology: a systematic review[J]. Mol Med, 2023, 29(1): 112. doi:10.1186/s10020-023-00706-6 |
| [10] | Xu ZH, Bu YW, Chitnis N, et al. miR-216b regulation of c-Jun mediates GADD153/CHOP-dependent apoptosis[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 11422. doi:10.1038/ncomms11422 |
| [11] | Gong QM, Lai TF, Liang LD, et al. Targeted inhibition of CX3CL1 limits podocytes ferroptosis to ameliorate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Mol Med, 2023, 29(1): 140. doi:10.1186/s10020-023-00733-3 |
| [12] | Sun MM, Wang FQ, Li HP, et al. Maresin-1 attenuates sepsis-associated acute kidney injury via suppressing inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis by activating the AMPK/SIRT3 pathway[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2024, 17: 1349-64. doi:10.2147/jir.s442729 |
| [13] | Andrade-Silva M, Dhillon P, Sanchez-Navarro A, et al. The critical role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway in kidney fibrosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2025, 107(2): 302-16. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2024.10.021 |
| [14] | Li HY, Huang LF, Huang XR, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis: potential therapeutic target[J]. J Immunol Res, 2023, 2023: 7625817. doi:10.1155/2023/7625817 |
| [15] | Yu F, Haas M, Glassock R, et al. Redefining lupus nephritis: clinical implications of pathophysiologic subtypes[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2017, 13(8): 483-95. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2017.85 |
| [16] | Mejia-Vilet JM, Malvar A, Arazi A, et al. The lupus nephritis management renaissance[J]. Kidney Int, 2022, 101(2): 242-55. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2021.09.012 |
| [17] | Porter AW, Brodsky JL, Buck TM. Emerging links between endoplasmic reticulum stress responses and acute kidney injury[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2022, 323(6): C1697-703. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00370.2022 |
| [18] | Chen XY, Shi CR, He MH, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: molecular mechanism and therapeutic targets[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 352. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01570-w |
| [19] | Gallazzini M, Pallet N. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and kidney dysfunction[J]. Biol Cell, 2018, 110(9): 205-16. doi:10.1111/boc.201800019 |
| [20] | Hetz C, Zhang KZ, Kaufman RJ. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(8): 421-38. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-0250-z |
| [21] | Zhang RJ, Bian C, Gao J, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic kidney disease: adaptation and apoptosis after three UPR pathways[J]. Apoptosis, 2023, 28(7/8): 977-96. doi:10.1007/s10495-023-01858-w |
| [22] | Kapuy O. Mechanism of decision making between autophagy and apoptosis induction upon endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(8): 4368. doi:10.3390/ijms25084368 |
| [23] | Verfaillie T, Rubio N, Garg AD, et al. PERK is required at the ER-mitochondrial contact sites to convey apoptosis after ROS-based ER stress[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2012, 19(11): 1880-91. doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.74 |
| [24] | Chen S, Li X, Zhang XW, et al. PCV2 and PRV coinfection induces endoplasmic reticulum stress via PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP and IRE1-XBP1-EDEM pathways[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(9): 4479. doi:10.3390/ijms23094479 |
| [25] | Cao Y, Hu LT, Chen RK, et al. Unfolded protein response-activated NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to pyroptotic and apoptotic podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease via the CHOP-TXNIP axis[J]. Cell Signal, 2025, 130: 111702. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111702 |
| [26] | Nakatsuka A, Yamaguchi S, Jun WD. GRP78 contributes to the beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitor on proximal tubular cells in DKD[J]. Diabetes, 2024, 73(5): 763-79. doi:10.2337/db23-0581 |
| [27] | Trink J, Ahmed U, O’Neil K, et al. Cell surface GRP78 regulates TGFβ1-mediated profibrotic responses via TSP1 in diabetic kidney disease[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1098321. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1098321 |
| [28] | Jin RB, Zhao AR, Han SY, et al. The interaction of S100A16 and GRP78 actives endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated through the IRE1α/XBP1 pathway in renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(10): 942. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04249-8 |
| [29] | Deng F, Zhang HP, Zhou W, et al. TRPA1 promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via regulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mitochondrial damage[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 695. doi:10.1186/s12967-023-04351-9 |
| [30] | Park SJ, Kim Y, Li C, et al. Blocking CHOP-dependent TXNIP shuttling to mitochondria attenuates albuminuria and mitigates kidney injury in nephrotic syndrome[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(35): e2116505119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2116505119 |
| [31] | Lin BB, Zhang XB, Xu XG. Nerve growth factor protects retinal ganglion cells related to inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress by inhibiting IRE1-JNK-CHOP signaling pathway[J]. Ocul Immunol Inflamm, 2022, 30(6): 1341-6. doi:10.1080/09273948.2021.1872651 |
| [1] | 王莹, 李静, 王伊迪, 华明钰, 胡玮彬, 张晓智. 原发性肝癌患者的临床结局与治疗反应预测模型:基于失巢凋亡和免疫基因[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [2] | 陈丹丹, 任乾千, 吕梦林, 张宝文, 刘醒然, 张蒙, 王阳, 寇现娟. 天麻钩藤饮通过抑制坏死性凋亡通路改善帕金森病小鼠的运动功能障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1571-1580. |
| [3] | 常笑语, 张瀚文, 曹红亭, 侯玲, 孟鑫, 陶虹, 罗彦, 李光华. 热应激对大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞生物钟基因 Bmal1和细胞周期蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [4] | 杨毓甲, 杨丽芳, 吴雅玲, 段兆达, 于春泽, 吴春云, 于建云, 杨力. 大麻二酚经PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP通路减轻多重脑震荡大鼠的神经元内质网应激和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [5] | 陈悦, 肖林雨, 任侣, 宋雪, 李静, 胡建国. 水晶兰苷通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路减少神经元凋亡改善脊髓损伤后小鼠的运动功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [6] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [7] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [8] | 陈镝, 吕莹, 郭怡欣, 张怡荣, 王蕊璇, 周小若, 陈雨欣, 武晓慧. 双氢青蒿素可显著增强阿霉素诱导的三阴性乳腺癌细胞凋亡:基于负向调控STAT3/HIF-1α通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [9] | 宾禹, 李子雯, 左素微, 孙思诺, 李敏, 宋佳茵, 林旭, 薛刚, 吴靖芳. 载脂蛋白C1高表达通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路促进甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的增殖并抑制凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [10] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [11] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [12] | 肖林雨, 段婷, 夏勇生, 陈悦, 孙洋, 许轶博, 徐磊, 闫兴洲, 胡建国. 蒙花苷通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路抑制小鼠脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞活化介导的神经炎症和神经元凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1589-1598. |
| [13] | 陶怀祥, 骆金光, 闻志远, 虞亘明, 苏萧, 王鑫玮, 关翰, 陈志军. STING高表达通过调控TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路和影响炎症与凋亡水平促进小鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1345-1354. |
| [14] | 郑孟冬, 刘妍, 刘娇娇, 康巧珍, 王婷. 蛋白4.1R对肝细胞HL-7702增殖、凋亡以及糖酵解的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1355-1360. |
| [15] | 王元国, 张鹏. 铁死亡抑制基因在食管癌中的高表达分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||