Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2199-2209.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.16
Keni¹ ZHANG1( ), Tong¹ QIAO1, Lin¹ YIN1, Ju HUANG2,3, Zhijun GENG2,3, Lugen³ ZUO3, Jianguo HU1,3, Jing LI1,3(
), Tong¹ QIAO1, Lin¹ YIN1, Ju HUANG2,3, Zhijun GENG2,3, Lugen³ ZUO3, Jianguo HU1,3, Jing LI1,3( )
)
Received:2025-05-14
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Jing LI
E-mail:kenizhang0906@163.com;lijingbyfy@bbmu.edu.cn
Keni¹ ZHANG, Tong¹ QIAO, Lin¹ YIN, Ju HUANG, Zhijun GENG, Lugen³ ZUO, Jianguo HU, Jing LI. Pinostrobin targets the PI3K/AKT/CCL2 axis in intestinal epithelial cells to inhibit intestinal macrophage infiltration and alleviate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2199-2209.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.16
| Gene name | Gene ID | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 16193 | F:TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| TNF-α | 21926 | F:CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC |
| R:CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG | ||
| CCL2 | 20296 | F:TAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAAA |
| R:GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT | ||
| CXCL10 | 15945 | F:CCAAGTGCTGCCGTCATTTTC |
| R:TCCCTATGGCCCTCATTCTCA | ||
| CX3CL1 | 20312 | F:CTGCCCTCACTAAAAATGGTGG |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| GAPDH | 14433 | F:TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC |
| R:GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene name | Gene ID | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 16193 | F:TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| TNF-α | 21926 | F:CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC |
| R:CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG | ||
| CCL2 | 20296 | F:TAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAAA |
| R:GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT | ||
| CXCL10 | 15945 | F:CCAAGTGCTGCCGTCATTTTC |
| R:TCCCTATGGCCCTCATTCTCA | ||
| CX3CL1 | 20312 | F:CTGCCCTCACTAAAAATGGTGG |
| R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT | ||
| GAPDH | 14433 | F:TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC |
| R:GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
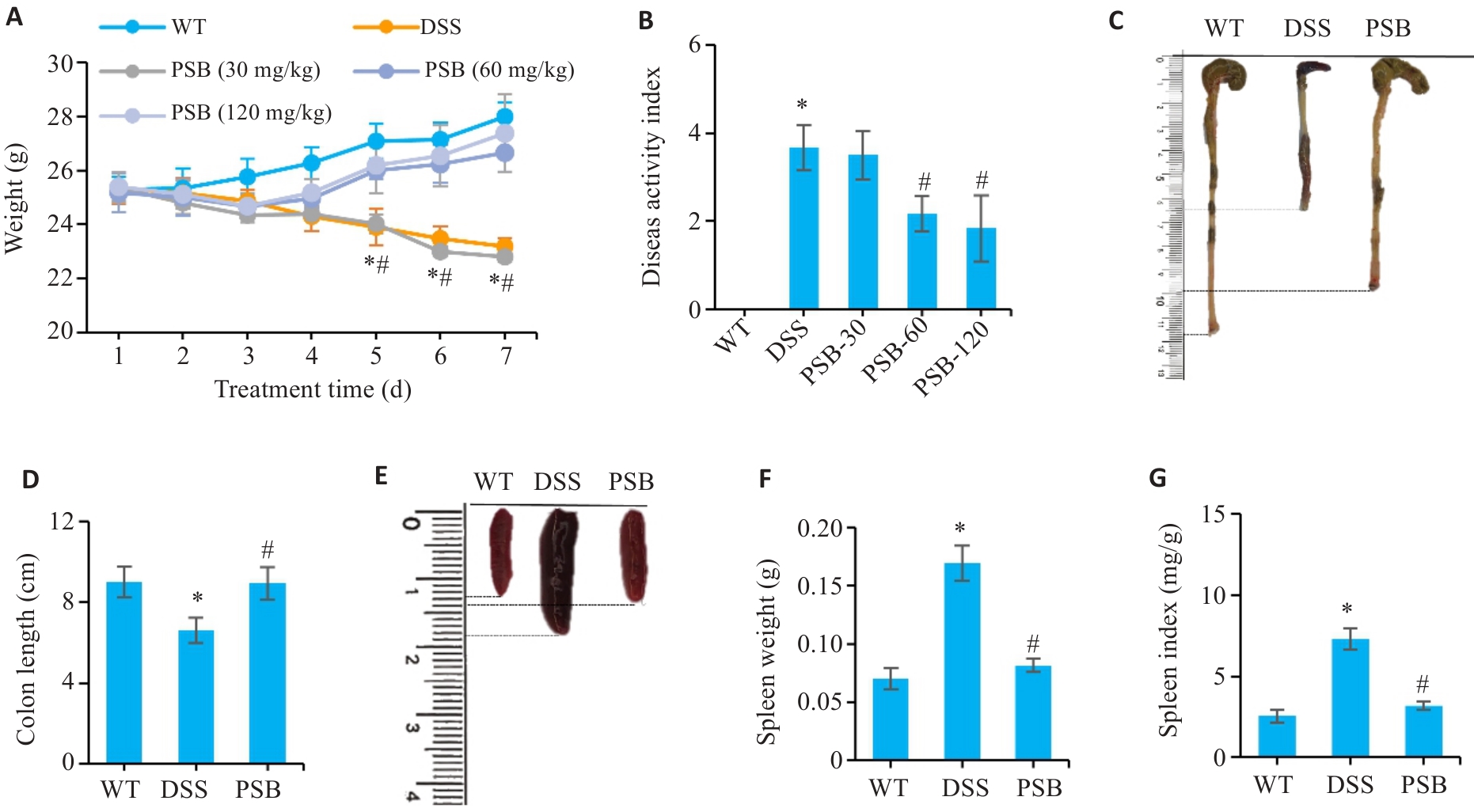
Fig.1 Effect of pinostrobin (PSB) on symptoms of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. A: Daily body weight changes in wild-type (WT), DSS, PSB-30 mg/kg, PSB-60 mg/kg and PSB-120 mg/kg groups. B: Disease activity index (DAI) scores in the 5 groups. C: Representative images of the mouse colon. D: Colon lengths of the mice. E: Representative images of mouse spleens. F: Spleen weight. G: Spleen index. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
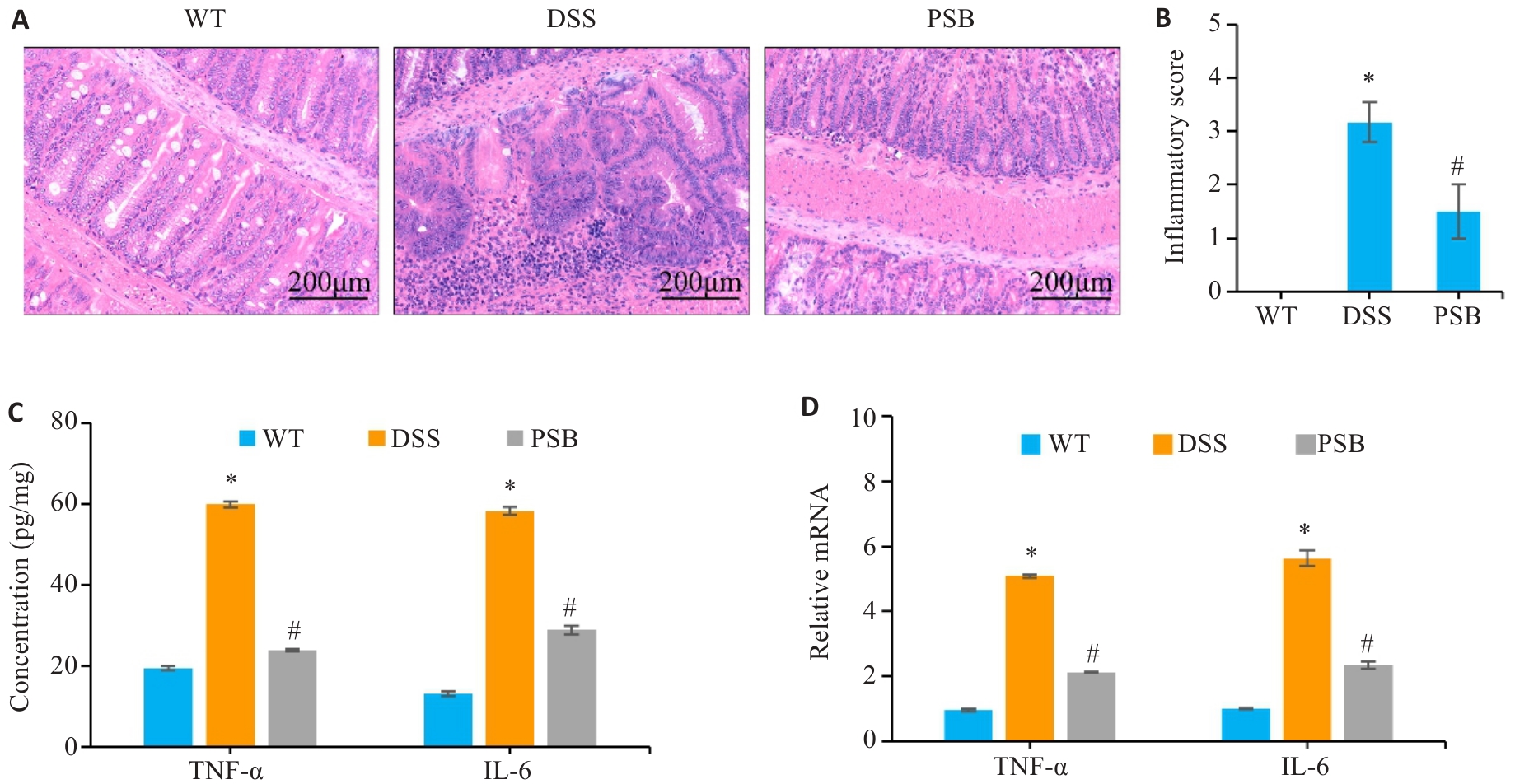
Fig.2 Effect of PSB on intestinal tissue injury and inflammation in the mouse models of colitis. A: HE staining of mouse colon tissues. B: Inflammation scores of mouse colon tissue. C: Levels of inflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-6) in the colonic mucosa detected by ELISA. D: Relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α and IL-6 in the colonic mucosa detected by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
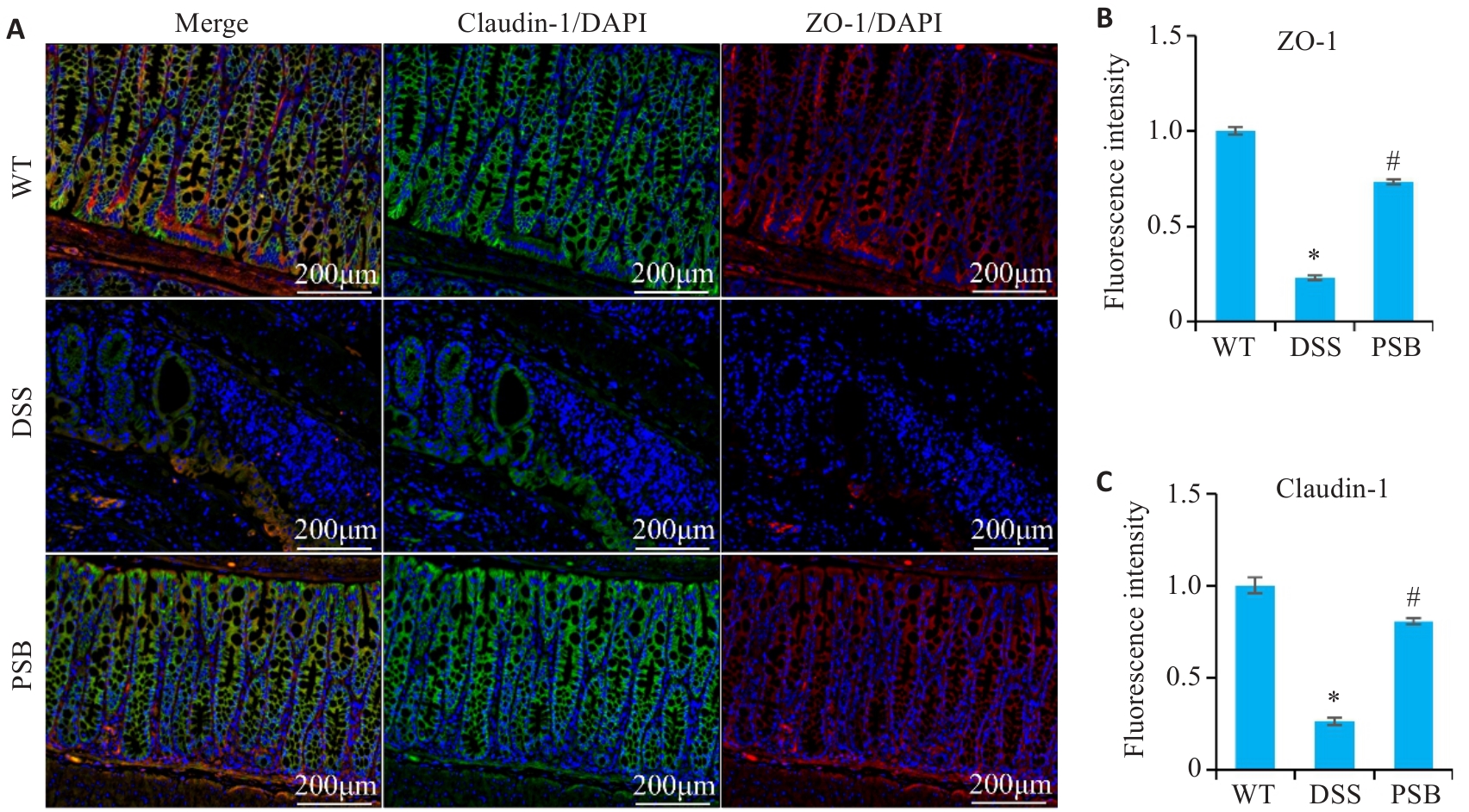
Fig.3 Effect of PSB on intestinal barrier damage in mice with DSS-induced colitis. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 and Claudin-1 in the colon of the mice. B: Fluorescence intensity of ZO-1. C: Fluorescence intensity of claudin-1. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
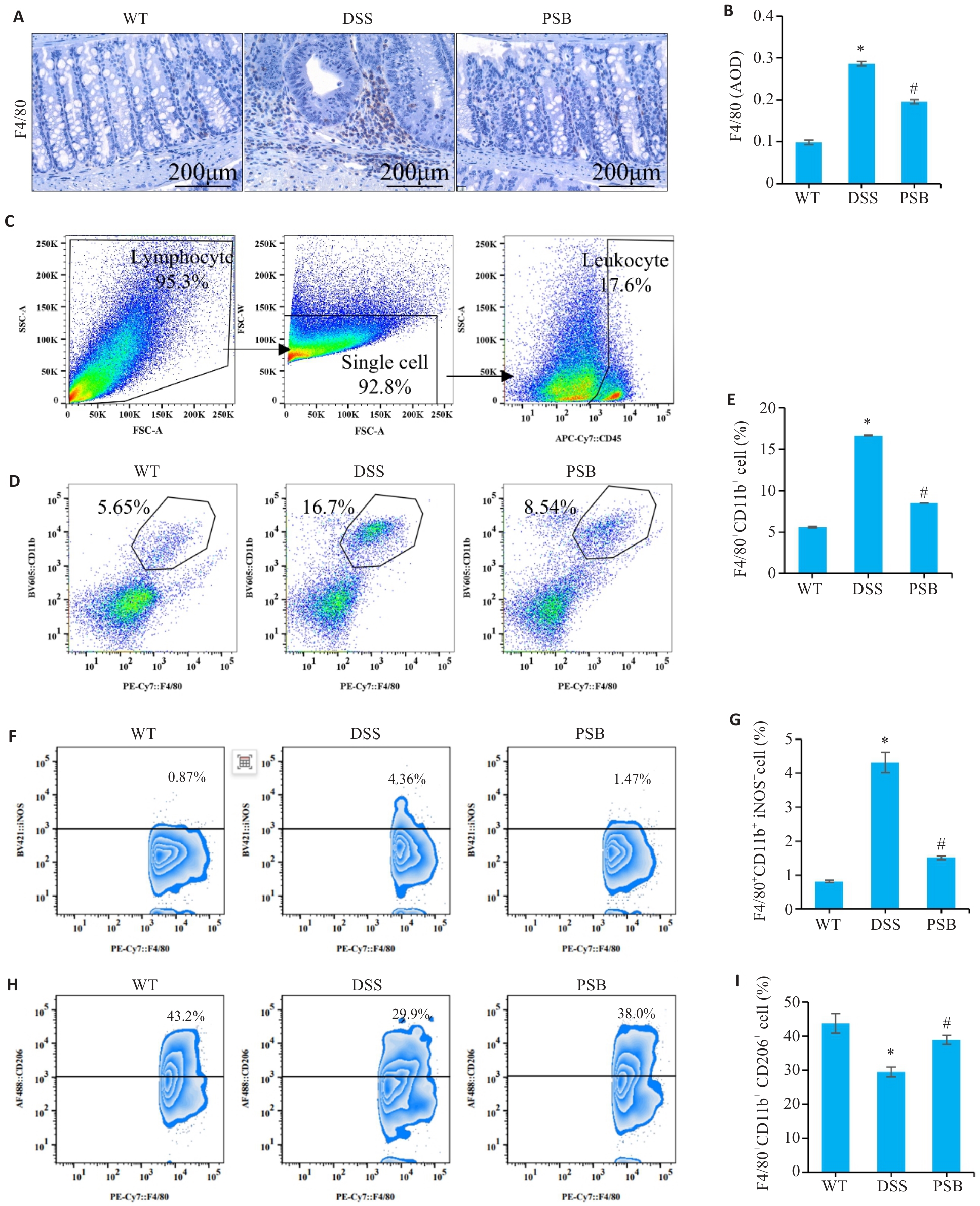
Fig.4 Effect of PSB on macrophage infiltration and polarization in the mouse models of colitis. A: Expression of F4/80 analyzed by immunohistochemical staining. B: Average optical density (AOD) of F4/80. C: Flow cytometry gating strategy. D, E: Assessment of macrophage percentage (CD45+F4/80+CD11b+ population) in mouse intestinal tissue by flow cytometry. F,G: Assessment of M1 macrophage percentage (F4/80+ CD11b+iNOS+ population) in mouse intestinal tissue by flow cytometry. H,I: Assessment of M2 Macrophage percentage (F4/80+ CD11b+CD206+ population) in mouse intestinal tissue by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
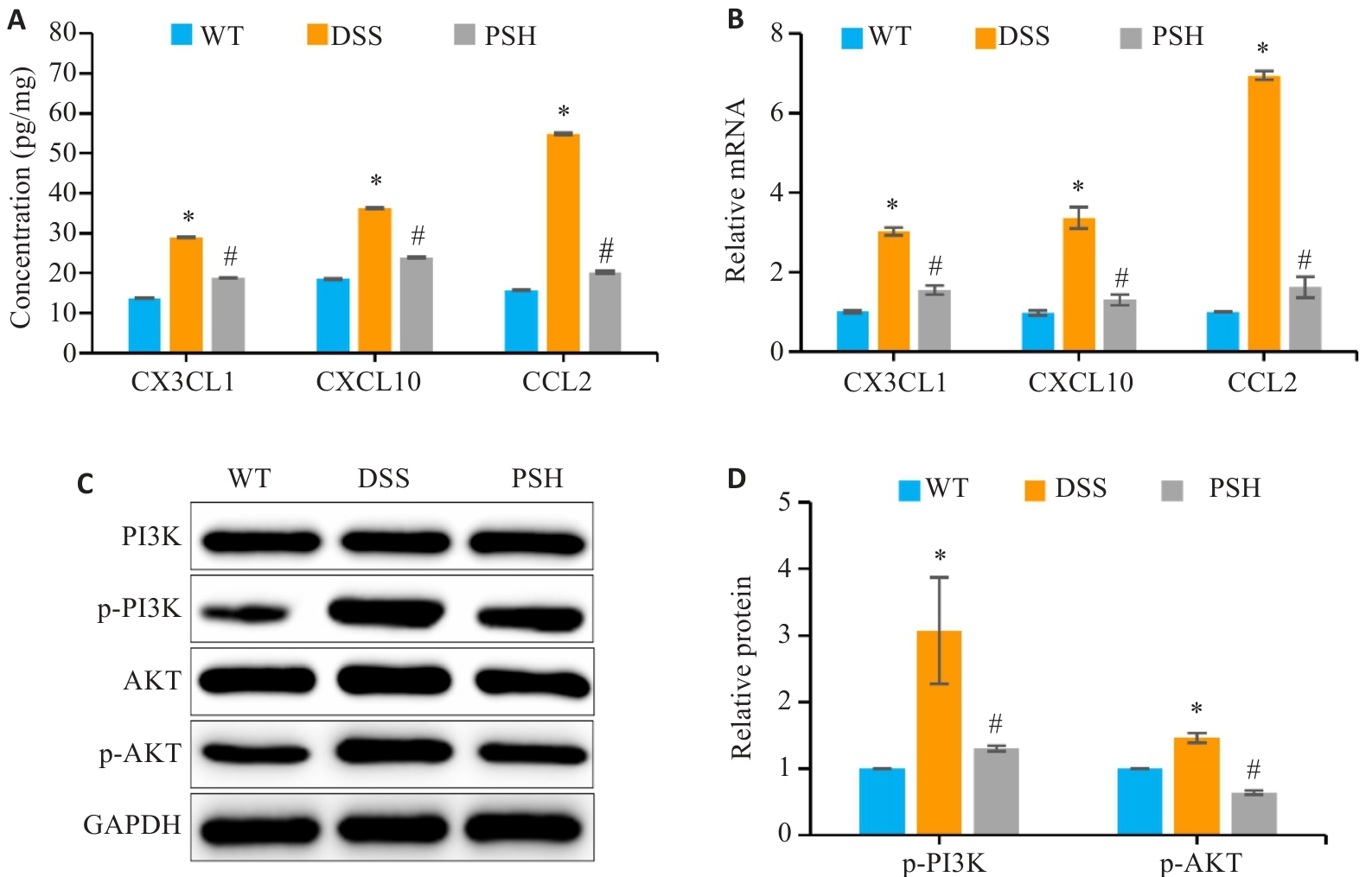
Fig.6 Effects of PSB on macrophage chemokines and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. A: Levels of chemokines (CCL2, CXCL10 and CX3CL1) in the colonic mucosa detected by ELISA. B: Relative mRNA expressions of chemokines (CCL2, CXCL10 and CX3CL1) in the colonic mucosa detected by RT-qPCR. C, D: Western blot analysis of p-PI3K and p-AKT, the key proteins of the PI3K/AKT pathway, in mouse intestinal mucosal tissues. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
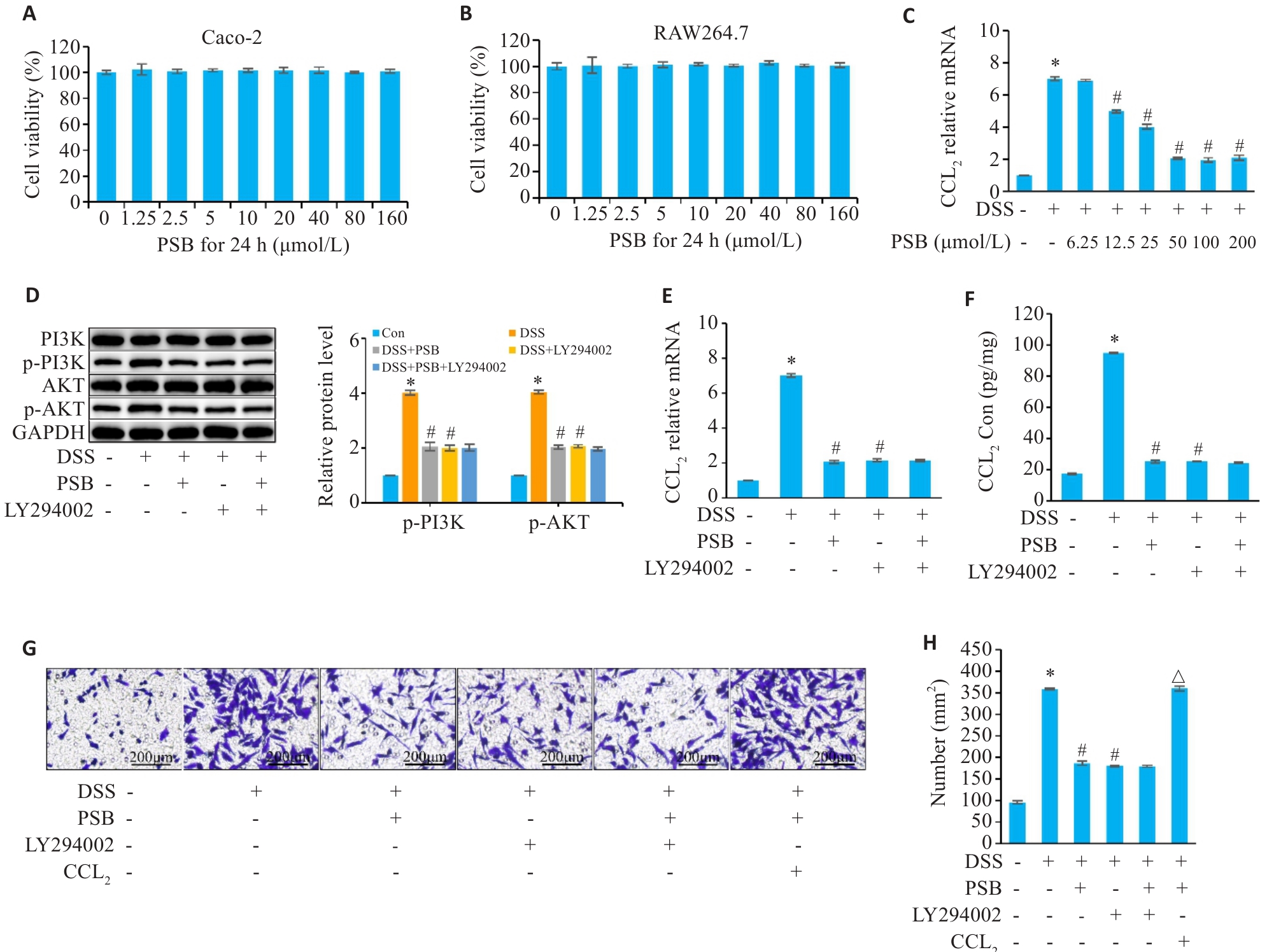
Fig.7 Effect of PSB on the chemotaxis of macrophages by regulating the PI3K/AKT/CCL2 signaling axis in intestinal epithelial cells. A, B: Determination of the cytotoxicity of PSB in Caco-2 and RAW264.7 cells by CCK-8 assay. C: Concentration-dependent inhibition of DSS-induced CCL2 mRNA expression by PSB (RT-qPCR). D: Western blot bands and quantitative analysis (p-PI3K and p-AKT). E, F: Expression levels of CCL2 mRNA (RT-qPCR) and protein (ELISA). G,H: Transwell migration images (crystal violet staining) and statistics of the number of migrated cells. *P<0.05 vs Con; #P<0.05 vs DSS; △P<0.05 vs DSS+PSB.
| [1] | Zhang YZ, Li YY. Inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenesis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(1): 91-9. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.91 |
| [2] | Kaplan GG. The global burden of IBD: from 2015 to 2025[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 12(12): 720-7. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2015.150 |
| [3] | Chen YY, Cui WW, Li X, et al. Interaction between commensal bacteria, immune response and the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 761981. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.761981 |
| [4] | 郭 琳, 耿 燕, 岳远佳, 等. 猴头菌粉与5-氨基水杨酸联用抑制小鼠急性溃疡性结肠炎并提高肠道共生菌Parabacteroides distasonis丰度[J]. 菌物学报, 2021, 40(5): 1148-59. |
| [5] | van Deventer SJ. Review article: chemokine production by intestinal epithelial cells: a therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease?[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 1997, 11(): 116-20;discussion120-1. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.1997.tb00816.x |
| [6] | Kotla NG, Rochev Y. IBD disease-modifying therapies: insights from emerging therapeutics[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2023, 29(3): 241-53. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2023.01.001 |
| [7] | Zhu YF, Yang SH, Zhao N, et al. CXCL8 chemokine in ulcerative colitis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 138: 111427. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111427 |
| [8] | Alghamdi KS, Kassar RH, Farrash WF, et al. Key disease-related genes and immune cell infiltration landscape in inflammatory bowel disease: a bioinformatics investigation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(17): 9751. doi:10.3390/ijms25179751 |
| [9] | Geng ZJ, Zuo LG, Li J, et al. Ginkgetin improved experimental colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(14): e23817. doi:10.1096/fj.202400211rr |
| [10] | Pozzi S, Satchi-Fainaro R. The role of CCL2/CCR2 axis in cancer and inflammation: The next frontier in nanomedicine[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2024, 209: 115318. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2024.115318 |
| [11] | Trivedi PJ, Adams DH. Chemokines and chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease; pitfalls and promise[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2018, 12(): S641-52. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx145 |
| [12] | Patel NK, Jaiswal G, Bhutani KK. A review on biological sources, chemistry and pharmacological activities of pinostrobin[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2016, 30(18): 2017-27. doi:10.1080/14786419.2015.1107556 |
| [13] | 朱学鑫, 庞敏霞, 黄燕芬, 等. 山核桃叶球松素制备工艺研究[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2017, 34(11): 1512-6. |
| [14] | González AS, Soto Tellini VH, Benjumea Gutiérrez DM. Study of the dermal anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and analgesic activity of pinostrobin[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(9): e10413. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10413 |
| [15] | Abdelwahab SI, Mohan S, Abdulla MA, et al. The methanolic extract of Boesenbergia rotunda (L.) Mansf. and its major compound pinostrobin induces anti-ulcerogenic property in vivo: possible involvement of indirect antioxidant action[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2011, 137(2): 963-70. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.010 |
| [16] | Shareef SH, Al-Medhtiy MH, Al Rashdi AS, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of pinostrobin against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis in rats[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2023, 30(1): 103506. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103506 |
| [17] | Murthy SN, Cooper HS, Shim H, et al. Treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 1993, 38(9): 1722-34. doi:10.1007/bf01303184 |
| [18] | 张 敏, 刘生宝, 张 诺, 等. 改进型“瑞士卷”法在小鼠肠道组织切片中的应用[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2024,53(04):393-7. |
| [19] | Le Naour J, Montégut L, Joseph A, et al. Improved Swiss-rolling method for histological analyses of colon tissue[J]. MethodsX, 2022, 9: 101630. doi:10.1016/j.mex.2022.101630 |
| [20] | Schultz M, Tonkonogy SL, Sellon RK, et al. IL-2-deficient mice raised under germfree conditions develop delayed mild focal intestinal inflammation[J]. Am J Physiol, 1999, 276(6): G1461-72. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.1999.276.6.g1461 |
| [21] | Rath HC, Herfarth HH, Ikeda JS, et al. Normal luminal bacteria, especially Bacteroides species, mediate chronic colitis, gastritis, and arthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2 microglobulin transgenic rats[J]. J Clin Invest, 1996, 98(4): 945-53. doi:10.1172/jci118878 |
| [22] | Mallawaaratchy DM, Mactier S, Kaufman KL, et al. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002, decreases aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, chaperones and glycolytic enzymes in human HT-29 colorectal cancer cells[J]. J Proteomics, 2012, 75(5): 1590-9. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2011.11.032 |
| [23] | Athapaththu AMGK, Sanjaya SS, Lee KT, et al. Pinostrobin suppresses the α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanogenic signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(1): 821. doi:10.3390/ijms24010821 |
| [24] | Gomes RN, Teixeira-Cunha MGA, Figueiredo RT, et al. Bacterial clearance in septic mice is modulated by MCP-1/CCL2 and nitric oxide[J]. Shock, 2013, 39(1): 63-9. doi:10.1097/shk.0b013e31827802b5 |
| [25] | Yu KY, Li QQ, Sun X, et al. Bacterial indole-3-lactic acid affects epithelium-macrophage crosstalk to regulate intestinal homeostasis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2023, 120(45): e2309032120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2309032120 |
| [26] | Zhang HL, Zheng YJ, Pan YD, et al. A mutation that blocks integrin α4β7 activation prevents adaptive immune-mediated colitis without increasing susceptibility to innate colitis[J]. BMC Biol, 2020, 18(1): 64. doi:10.1186/s12915-020-00784-6 |
| [27] | Hou QK, Zhu SL, Zhang CR, et al. Berberine improves intestinal epithelial tight junctions by upregulating A20 expression in IBS-D mice[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 118: 109206. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109290 |
| [28] | Borges GA, Elias ST, Amorim B, et al. Curcumin downregulates the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and inhibits growth and progression in head and neck cancer cells[J]. Phytother Res, 2020, 34(12): 3311-24. doi:10.1002/ptr.6780 |
| [29] | Mei CX, Meng FX, Wang X, et al. CD30L is involved in the regulation of the inflammatory response through inducing homing and differentiation of monocytes via CCL2/CCR2 axis and NF-κB pathway in mice with colitis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 110: 108934. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108934 |
| [30] | Gholamalizadeh H, Ensan B, Sukhorukov VN, et al. Targeting the CCL2-CCR2 signaling pathway: potential implications of statins beyond cardiovascular diseases[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2024, 76(2): 138-53. doi:10.1093/jpp/rgad112 |
| [31] | Mostafa DK, Eissa MM, Ghareeb DA, et al. Resveratrol protects against Schistosoma mansoni-induced liver fibrosis by targeting the Sirt-1/NF-κB axis[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2024, 32(1): 763-75. doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01382-y |
| [32] | Zhang H, Shan Y, Wu Y, et al. Berberine suppresses LPS-induced inflammation through modulating Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2017, 52: 93-100. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.032 |
| [33] | Zhao JJ, Guo MM, Yan YP, et al. The miR-7/EGFR axis controls the epithelial cell immunomodulation and regeneration and orchestrates the pathology in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Adv Res, 2024, 57: 119-34. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2023.04.011 |
| [34] | Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Ando M, et al. Th17 cell induction by adhesion of microbes to intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Cell, 2015, 163(2): 367-80. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.058 |
| [35] | He J, Song YJ, Li GP, et al. Fbxw7 increases CCL2/7 in CX3CR1hi macrophages to promote intestinal inflammation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129(9): 3877-93. doi:10.1172/jci123374 |
| [36] | Carson WF, Salter-Green SE, Scola MM, et al. Enhancement of macrophage inflammatory responses by CCL2 is correlated with increased miR-9 expression and downregulation of the ERK1/2 phosphatase Dusp6[J]. Cell Immunol, 2017, 314: 63-72. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.02.005 |
| [1] | Rongmao HE, Zeyang FANG, Yunyun ZHANG, Youliang WU, Shixiu LIANG, Tao JI, Kequan CHEN, Siqi WANG. Diagnostic and predictive value of ferroptosis-related genes in patients with ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937. |
| [2] | Lu RAO, Jiahe DING, Jiangping WEI, Yong YANG, Xiaomei ZHANG, Jirui WANG. Flos Sophorae improves psoriasis in mice by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1989-1996. |
| [3] | Chenfei LIU, Wei ZHANG, Yao ZENG, Yan LIANG, Mengting WANG, Mingfang ZHANG, Xinyuan LI, Fengchao WANG, Yanqing YANG. 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1654-1662. |
| [4] | Lin SHEN, Cuihao SONG, Congmin WANG, Xi GAO, Junhong AN, Chengxin LI, Bin LIANG, Xia LI. Risk factors for malnutrition in ulcerative colitis complicated with pyoderma gangrenosum and construction of a lasso regression-based prediction model [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 514-521. |
| [5] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [6] | Yuejiao PEI, Huimin LIU, Yu XIN, Bo LIU. High expression of miR-124 improves cognitive function of sleep-deprived rats by modulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 340-346. |
| [7] | Yuru ZHANG, Lei WAN, Haoxiang FANG, Fangze LI, Liwen WANG, Kefei LI, Peiwen YAN, Hui JIANG. Inhibiting miR-155-5p promotes proliferation of human submandibular gland epithelial cells in primary Sjogren's syndrome by negatively regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway via PIK3R1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 65-71. |
| [8] | Xianheng ZHANG, Jian LIU, Qi HAN, Yiming CHEN, Xiang DING, Xiaolu CHEN. Huangqin Qingrechubi Capsule alleviates inflammation and uric acid and lipid metabolism imbalance in rats with gouty arthritis by inhibiting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458. |
| [9] | Na ZHAO, Mengdi SHEN, Rui ZHAO, Di AO, Zetan LUO, Yinliang ZHANG, Zhidong XU, Fangtian FAN, Hailun ZHENG. column:Sanguinarine alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [10] | Guanzheng YU, Weiqiang CHENG, Xing TU, Man ZHANG, Hong LI, Juan NIE. Therapeutic mechanism of Cynanchum wilfordii for ulcerative colitis: an analysis using UPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology and metabolomics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [11] | Shan XIANG, Zongxing ZHANG, Lu JIANG, Daozhong LIU, Weiyi LI, Zhuoma BAO, Rui TIAN, Dan CHENG, Lin YUAN. Tujia medicine Toddalia asiatica improves synovial pannus in rats with collagen-induced arthritis through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1582-1588. |
| [12] | Yuanyuan WANG, Teng CHEN, Xiaofan CONG, Yiran LI, Rui CHEN, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO. Pristimerin enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via ROS-mediated deactivation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 904-912. |
| [13] | Jianguo QIU, Yitong QIU, Guorong LI, Linsheng ZHANG, Xue ZHENG, Yongjiang YAO, Xidan WANG, Haiyang HUANG, Fengmin ZHANG, Jiyan SU, Xuebao ZHENG, Xiaoqi HUANG. Huangqin Decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| [14] | SONG Zejun, DONG Haibin, MA Na, REN Yutang, JIANG Bo. Value of Improved Mayo Endoscopic Score for evaluating treatment efficacy for active ulcerative colitis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1204-1213. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xuefang, CHEN Yanhua, LI Zongheng, SHANG Jing, YUAN Zeting, DENG Wanli, LUO Ying, HAN Na, YIN Peihao, YIN Jun. Analysis of therapeutic mechanism of Liushen Wan against colitis-associated colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and validation in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1051-1062. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||