Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 461-469.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.03
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yanyan DONG1,3( ), Kejing ZHANG1, Jun CHU1,2,3, Quangen CHU1,2,3(
), Kejing ZHANG1, Jun CHU1,2,3, Quangen CHU1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-12-04
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Quangen CHU
E-mail:yytung@ahtcm.edu.cn;286428483@qq.com
Supported by:Yanyan DONG, Kejing ZHANG, Jun CHU, Quangen CHU. Didang Decoction-medicated serum enhances autophagy in high glucose-induced rat glomerular endothelial cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 461-469.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.03
| Primer | Length (bp) | Forward (5'→3') | Reverse (3'→5') |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | 150 | CCCATCTATGAGGGTTACGC | TTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC |
| Beclin-1 | 86 | CAGCCTCTGAAACTGGACAC | TGGGCTGTGGTAAGTAATGG |
| P62 | 173 | CGAAAGCTGACGCTGTTCAT | GGAGGACGGTACAAATCCATTA |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Primer | Length (bp) | Forward (5'→3') | Reverse (3'→5') |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | 150 | CCCATCTATGAGGGTTACGC | TTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC |
| Beclin-1 | 86 | CAGCCTCTGAAACTGGACAC | TGGGCTGTGGTAAGTAATGG |
| P62 | 173 | CGAAAGCTGACGCTGTTCAT | GGAGGACGGTACAAATCCATTA |
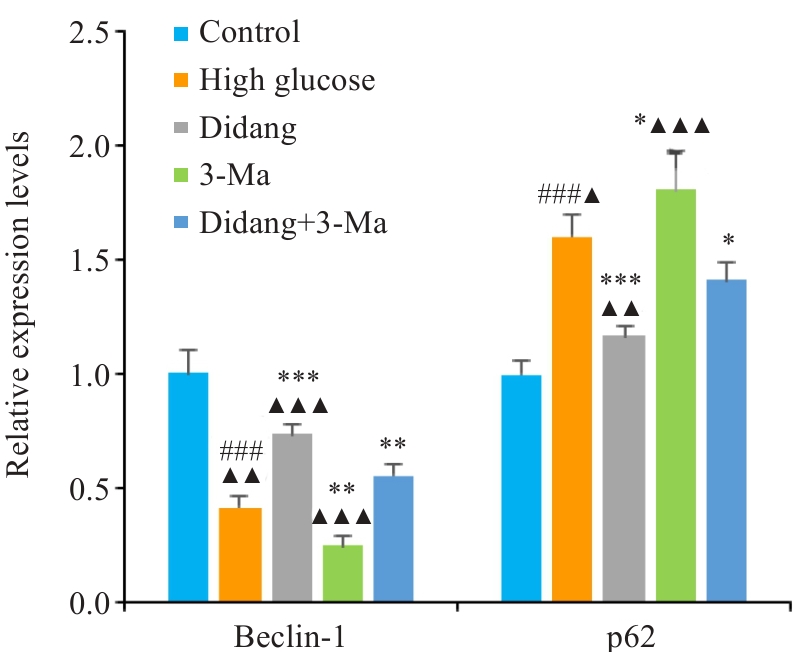
Fig.8 Transcriptional levels of autophagy-related genes (Beclin-1 and p62) in each group. ###P<0.001 vs Control. ***P<0.001,**P<0.01, *P<0.05 vs High Glucose.▲▲▲P<0.001, ▲▲P<0.01, ▲P<0.05 vs Didang+3-Ma.
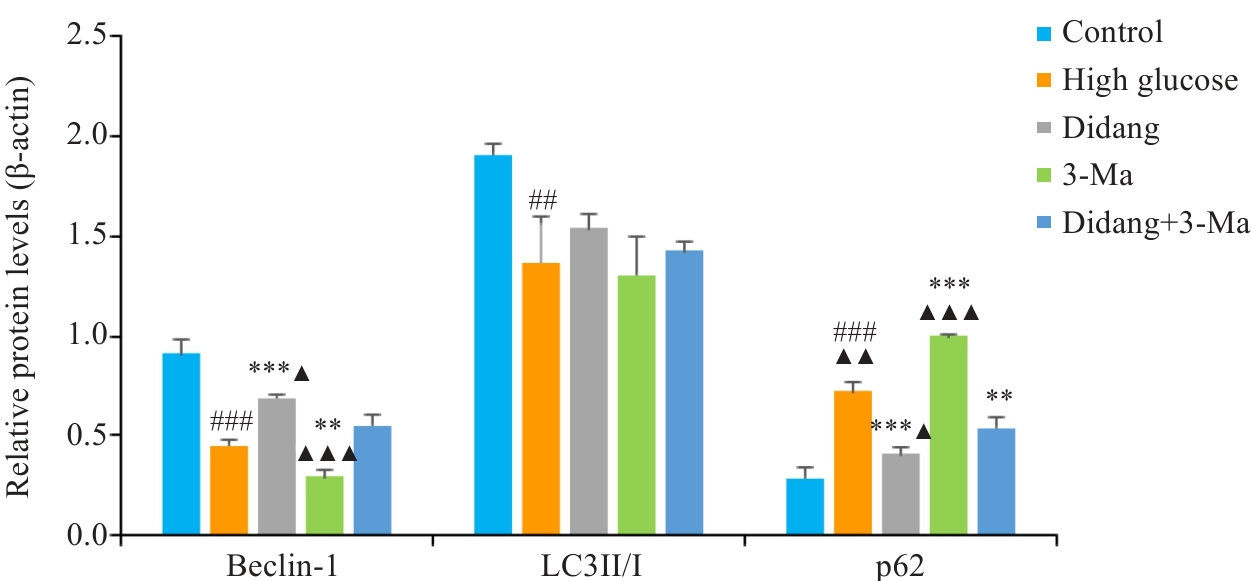
Fig.10 Expressions of autophagy-related proteins in each group of RGECs. ###P<0.001, ##P<0.01 vs Control. ***P<0.001,**P<0.01 vs High Glucose.▲▲▲P<0.001, ▲▲P<0.01, ▲P<0.05 vs Didang+3-Ma.
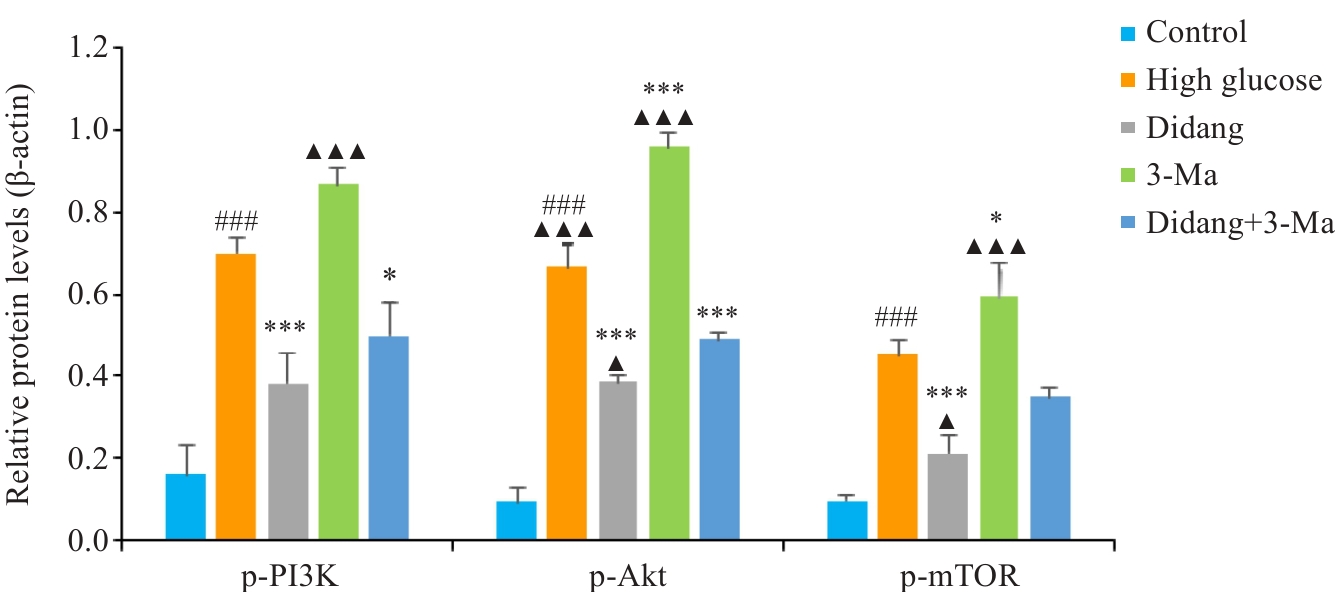
Fig.12 Expression levels of p-PI3K, p-Akt and p-mTOR proteins in each group of RGECs. ###P<0.001 vs Control. ***P<0.001,*P<0.05 vs High Glucose.▲▲▲P<0.001, ▲P<0.05 vs Didang+3-Ma.
| 1 | Raval N, Kumawat A, Kalyane D, et al. Understanding molecular upsets in diabetic nephropathy to identify novel targets and treatment opportunities[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2020, 25(5): 862-78. |
| 2 | Xu L, Shao FM. Sitagliptin protects renal glomerular endothelial cells against high glucose-induced dysfunction and injury[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(1): 655-66. |
| 3 | Li QQ, Xin YL, Liu PL, et al. Deciphering the therapeutic mechanisms of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi on diabetic nephropathy via bioinformatics analysis[J]. J Chin Pharmaceut Sci, 2024, 33(11): 1025-39. |
| 4 | Huang JH, Wang JZ. Selective protein degradation through chaperone-mediated autophagy: Implications for cellular homeo-stasis and disease (Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2024, 31: 13. |
| 5 | Yu L, Wei J, Liu PD. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment in human cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 85: 69-94. |
| 6 | 杨 继, 江宗岳, 周婧雅. 从微型癥瘕理论探讨糖尿病血管并发症的病机转变[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2024, 39(3): 1270-4. |
| 7 | 储全根, 王 玲, 张 凯, 等. 抵当汤调控NF-κB通路干预DM大鼠心肌炎症反应的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2018, 24(1): 109-13. |
| 8 | 王 玲, 储全根, 张 凯, 等. 抵当汤对糖尿病大鼠心肌微血管病变的影响[J]. 江西中医药, 2017, 48(12): 27-9. |
| 9 | 许笑雯, 储全根, 储 俊, 等. 痰瘀同治法对糖尿病大鼠心肌微血管病变AGEs/RAGE轴及氧化应激的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(10): 1527-33. |
| 10 | 张 凯, 储全根, 毕华剑, 等. 抵当汤对糖尿病大鼠心肌组织JAK2/STAT3信号通路的影响[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报, 2016, 35(2): 65-9. |
| 11 | 蔡正银, 储 俊, 储全根, 等. 抵当陷胸汤对糖尿病大鼠心肌超微结构和CTGF及其受体LRP蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(22): 100-5. |
| 12 | 陈 静, 储全根, 储 俊, 等. 基于JAK/STAT信号通路探讨痰瘀同治法对糖尿病大鼠心肌病变的影响[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报, 2023, 42(5): 88-93. |
| 13 | 罗宝璐, 储全根, 储 俊, 等. 抵当汤含药血清对高糖诱导大鼠肾小球内皮细胞损伤的影响[J]. 中成药, 2024, 46(9): 2930-5. |
| 14 | 储全根, 蔡正银, 储 俊, 等. 痰瘀同治法对糖尿病大鼠肾脏TGF-β1/Smad3信号通路的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(5): 708-12. |
| 15 | 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典-一部: 2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 24-220. |
| 16 | 王 群, 唐甜甜, 韩 伟, 等. 基于网络药理学和实验验证的黄芪六一汤药效组分促肾小管上皮细胞自噬抗糖尿病肾病的机制研究[J]. 药物评价研究, 2024, 47(6): 1187-98. |
| 17 | 范永升, 姜德友. 金匮要略[M]. 5版. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2021: 95. |
| 18 | 唐容川. 血证论[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2007: 113. |
| 19 | 吴以岭, 魏 聪, 贾振华, 等. 从络病学说探讨糖尿病肾病的病机[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2007, 13(9): 659-60. |
| 20 | 王新苗, 杨浩宇, 顾成娟, 等. 黄芪、水蛭粉、大黄治疗糖尿病肾病经验: 仝小林三味小方撷萃[J]. 吉林中医药, 2020, 40(1): 5-7. |
| 21 | 傅 强, 王世东, 肖永华, 等. 吕仁和教授分期辨治糖尿病学术思想探微[J]. 世界中医药, 2017, 12(1): 21-4. |
| 22 | Lassén E, Daehn IS. Molecular mechanisms in early diabetic kidney disease: glomerular endothelial cell dysfunction[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(24): 9456. |
| 23 | Jennifer Weil E, Lemley KV, Mason CC, et al. Podocyte detachment and reduced glomerular capillary endothelial fenestration promote kidney disease in type 2 diabetic nephropathy[J]. Kidney Int, 2012, 82(9): 1010-7. |
| 24 | 马华根, 刘海琴, 刘昭德, 等. 原代大鼠肾小球微血管内皮细胞的培养与鉴定[J]. 生理学报, 2021, 73(6): 926-30. |
| 25 | Rops AL, van der Vlag J, Jacobs CW, et al. Isolation and characterization of conditionally immortalized mouse glomerular endothelial cell lines[J]. Kidney Int, 2004, 66(6): 2193-201. |
| 26 | Dylewski JF, Wilson N, Lu SZ, et al. Isolation, purification, and conditional immortalization of murine glomerular endothelial cells of microvascular phenotype[J]. MethodsX, 2020, 7: 101048. |
| 27 | Yang DY, Livingston MJ, Liu ZW, et al. Autophagy in diabetic kidney disease: regulation, pathological role and therapeutic potential[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2018, 75(4): 669-88. |
| 28 | Levine B, Kroemer G. Biological functions of autophagy genes: a disease perspective[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(1/2): 11-42. |
| 29 | Huang JD, Chen LY, Wu JX, et al. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in the treatment of human diseases: current status, trends, and solutions[J]. J Med Chem, 2022, 65(24): 16033-61. |
| 30 | Kim YC, Guan KL. mTOR: a pharmacologic target for autophagy regulation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2015, 125(1): 25-32. |
| 31 | Dong RX, Zhang X, Liu YD, et al. Rutin alleviates EndMT by restoring autophagy through inhibiting HDAC1 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in diabetic kidney disease[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 112: 154700. |
| [1] | Weiyi LI, Lu JIANG, Zongxing ZHANG, Dan CHEN, Zhuoma BAO, Li HUANG, Lin YUAN. Qianggu Kangshu Formula attenuates osteoclast differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting the HIF-1α/BNIP3 autophagy signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1389-1396. |
| [2] | Xinheng WANG, Xiaohan SHAO, Tongtong LI, Lu ZHANG, Qinjun YANG, Weidong YE, Jiabing TONG, Zegeng LI, Xiangming FANG. Pingchuanning Formula suppresses airway inflammation in a rat model of asthmatic cold syndrome by regulating the HMGB1/Beclin-1 axis-mediated autophagy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1153-1162. |
| [3] | Ming LIAO, Wenhua ZHONG, Ran ZHANG, Juan LIANG, Wentaorui XU, Wenjun WAN, Chao LI Shu WU. Protein C activator derived from snake venom protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by suppressing ROS via upregulating HIF-1α and BNIP3 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 614-621. |
| [4] | Kelei GUO, Yingli LI, Chenguang XUAN, Zijun HOU, Songshan YE, Linyun LI, Liping CHEN, Li HAN, Hua BIAN. Yiqi Yangyin Huazhuo Tongluo Formula alleviates diabetic podocyte injury by regulating miR-21a-5p/FoxO1/PINK1-mediated mitochondrial autophagy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [5] | Junping ZHAN, Shuo HUANG, Qingliang MENG, Wei FAN, Huimin GU, Jiakang CUI, Huilian WANG. Buyang Huanwu Decoction reduces mitochondrial autophagy in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts in hypoxic culture by inhibiting the BNIP3-PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 35-42. |
| [6] | Zhiliang CHEN, Yonggang YANG, Xia HUANG, Yan CHENG, Yuan QU, Qiqi HENG, Yujia FU, Kewei LI, Ning GU. Differential expressions of exosomal miRNAs in patients with chronic heart failure and hyperuricemia: diagnostic values of miR-27a-5p and miR-139-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 43-51. |
| [7] | Yifan JIANG, Xiaorong LI, Jiayi GENG, Yongfeng CHEN, Bi TANG, Pinfang KANG. Quercetin ameliorates diabetic kidney injury in rats by inhibiting the HMGB1/RAGE/ NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1769-1775. |
| [8] | Yao CHENG, Yuanying WANG, Feiyang YAO, Pan HU, Mingxian CHEN, Ning WU. Baicalin suppresses type 2 dengue virus-induced autophagy of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1272-1283. |
| [9] | Yeming ZHANG, Yuanxiang ZHANG, Xuebin SHEN, Guodong WANG, Lei ZHU. MiRNA-103-3p promotes neural cell autophagy by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling via targeting rab10 in a rat model of depression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1315-1326. |
| [10] | Qianyi CHEN, Shuhan SHANG, Huan LU, Sisi LI, Zhimian SUN, Xirui FAN, Zhilin QI. Calenduloside E inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by down-regulating GPX4 and SLC7A11 expression through the autophagy pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1327-1335. |
| [11] | ZHOU Fengmin, GUO Yanju, CHEN Ning. Exercise promotes irisin expression to ameliorate renal injury in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 675-681. |
| [12] | CHEN Junjie, HUANG Chuanbing, LI Ming. Jianpi Zishen granule inhibits podocyte autophagy in systemic lupus erythematosus: a network pharmacology and clinical study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [13] | XIAO Hongmin, HAN Baosong, GUO Jiacheng, WU Chao, WU Jingyi. HTD4010 attenuates myocardial injury in mice with septic cardiomyopathy by promoting autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 507-514. |
| [14] | Yunfei LI, Lijun PANG, Longwu SHU, Ming LI, Chuanbing HUANG. Qihuang Jianpi Zishen Granules improves thrombocytopenia in mice with systemic lupus erythematosus by suppressing platelet autophagy via the Ca2+/CaMKK2/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2327-2334. |
| [15] | Chengcheng JIANG, Yangyang LI, Kexin DUAN, Tingting ZHAN, Zilong CHEN, Yongxue WANG, Rui ZHAO, Caiyun MA, Yu GUO, Changqing LIU. Parkin deletion affects PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy to exacerbate neuroinflammation and accelerate progression of Parkinson's disease in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2359-2366. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||