Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2690-2698.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.16
Meng QIN1,2( ), Siyu SUN2,3, Jiaqi LIU2, Yujiao GAO1,2, Hao WANG2,3, Youkun WANG2, Ao SUN2, Jiachun YAN2, Jinbao WANG2, Ying YU1,2(
), Siyu SUN2,3, Jiaqi LIU2, Yujiao GAO1,2, Hao WANG2,3, Youkun WANG2, Ao SUN2, Jiachun YAN2, Jinbao WANG2, Ying YU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-04-14
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Ying YU
E-mail:13017518983@163.com;yuying2011@126.com
Meng QIN, Siyu SUN, Jiaqi LIU, Yujiao GAO, Hao WANG, Youkun WANG, Ao SUN, Jiachun YAN, Jinbao WANG, Ying YU. Resveratrol protects barrier function of mouse brain microvascular endothelial cell monolayers with oxygen/glucose deprivation and PM2.5 exposure by maintaining mitochondrial dynamics balance[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2690-2698.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.16
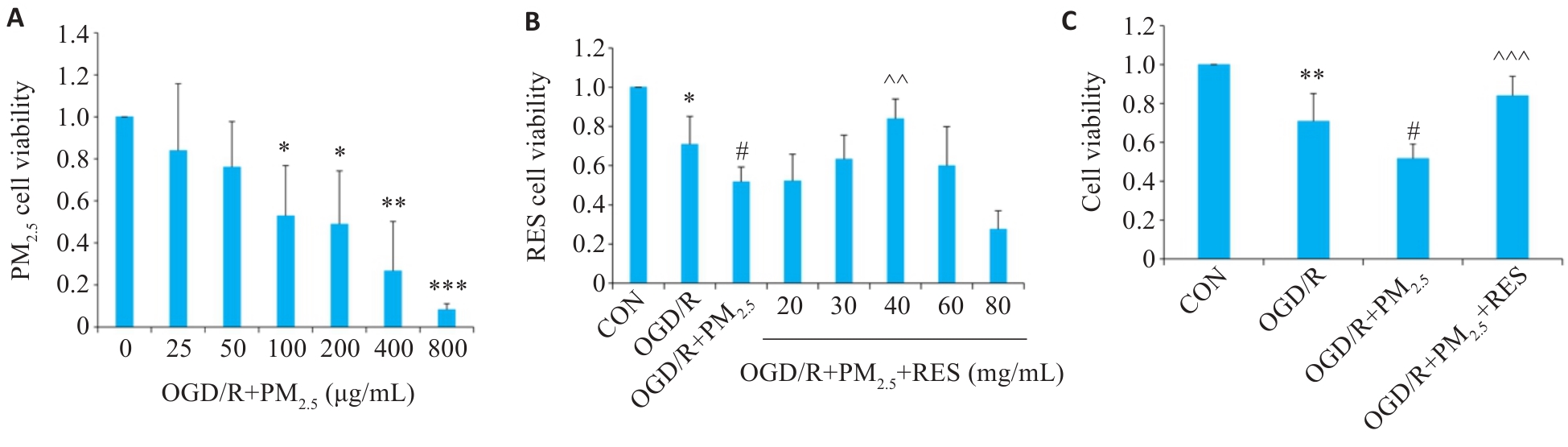
Fig.1 Viability of brain microvascular endothelial cells exposed to oxygen/glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) and different concentrations of PM2.5 (A), pretreated with RES (B), and both (C) (Mean±SD, n=5). Data normalized to control (set as 1) and statistical comparisons are conducted on normalized data. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs CON group; #P<0.05 vs OGD/R group; ^^P<0.01, ^^^P<0.001 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.
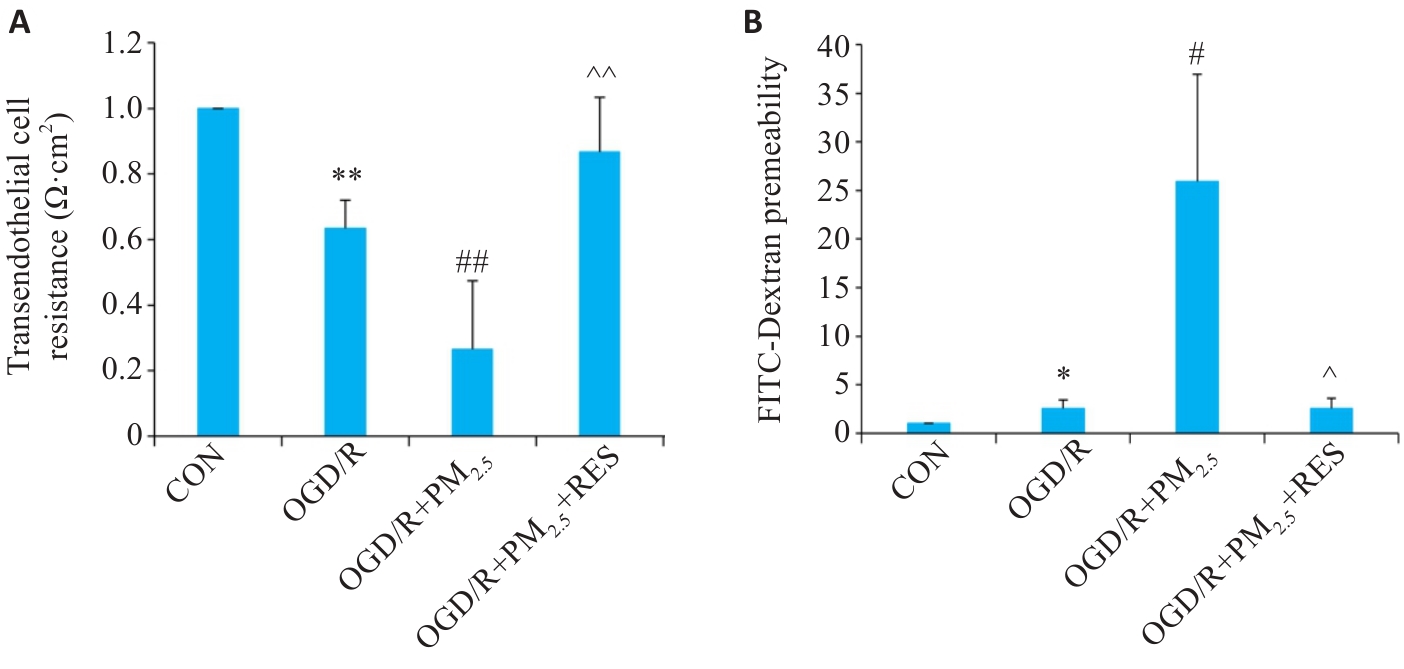
Fig.2 Effect of PM2.5 on TEER (A) and FITC-dextran permeability (B) of mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells with OGD/R (Mean±SD, n=5). Data normalized to control (set as 1) and statistical comparisons are conducted on normalized data. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CON group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs OGD/R group; ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.01 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.
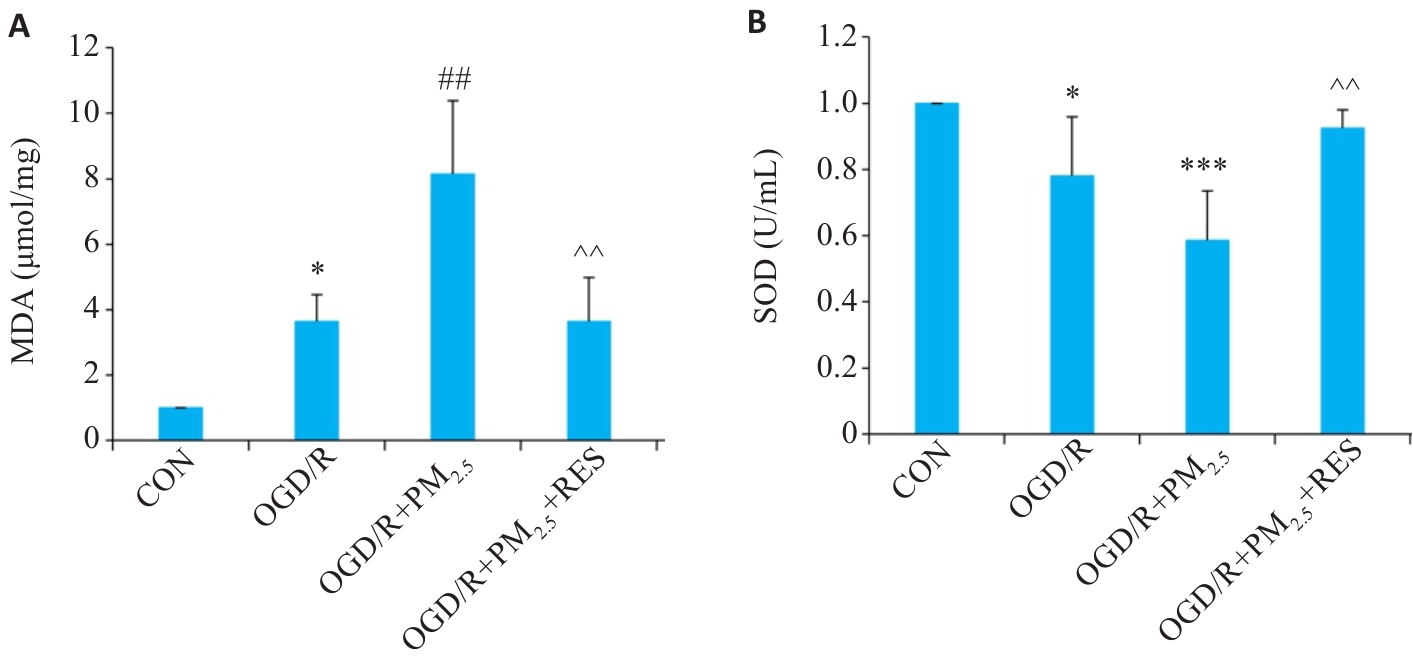
Fig.3 Comparison of MDA (A) and SOD (B) levels in the cells in different groups (Mean±SD, n=5). Data normalized to control (set as 1) and statistical comparisons are conducted on normalized data. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs CON group; ##P<0.01 vs OGD/R group; ^^P<0.01 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.

Fig.4 Immunofluorescence staining of ROS in the cells in different groups. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ROS and DAPI (Scale bar=100 μm). B: Quantitative analysis of ROS fluorescence intensity (Mean±SD, n=5). ***P<0.001 vs CON group; ##P<0.01 vs OGD/R group; ^^P<0.01 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.
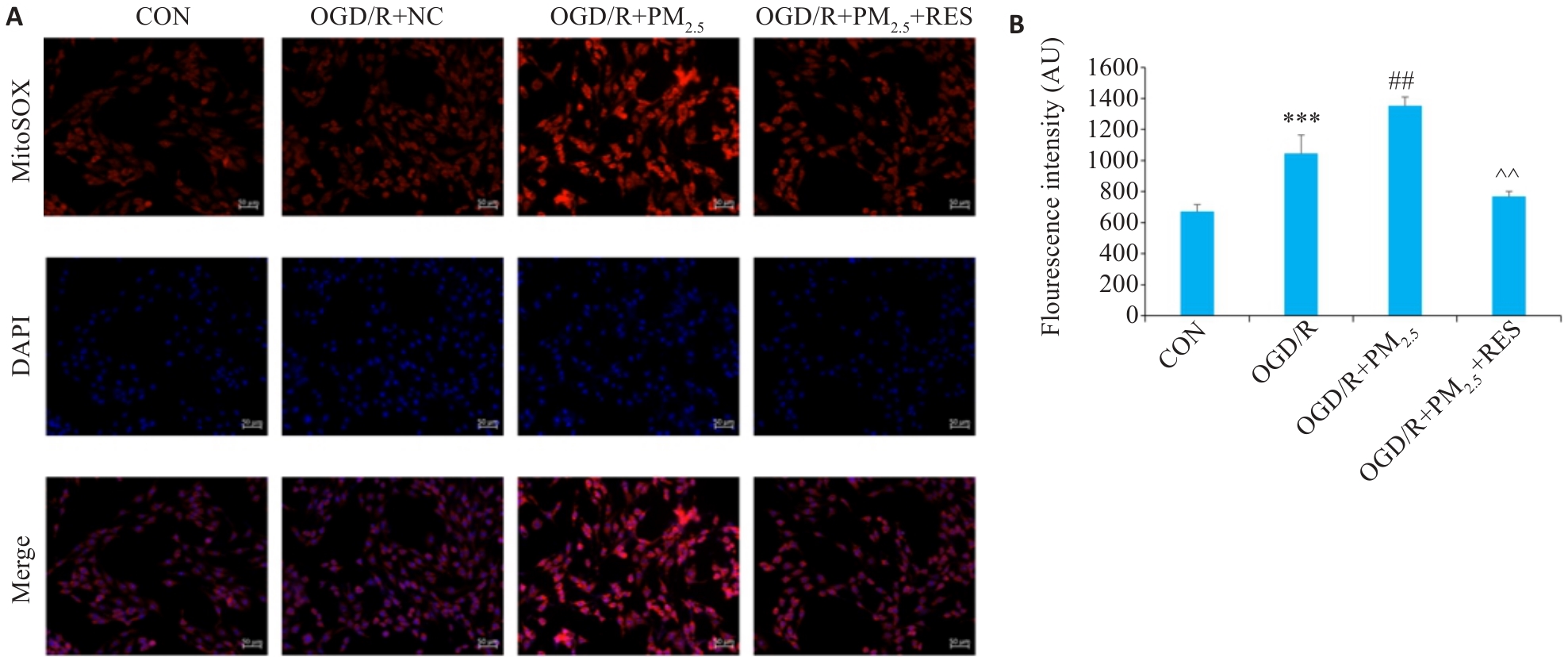
Fig.5 Immunofluorescence staining for detecting mitochondrial ROS in different groups. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ROS and DAPI (Scale bar=100 μm). B: Quantitative analysis of ROS fluorescence intensity (Mean±SD, n=5). ***P<0.001 vs CON group; ##P<0.01 vs OGD/R group; ^^P<0.01 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.

Fig.6 Immunofluorescence staining for evaluating mitochondrial membrane potential in different groups. A: Immunofluorescence staining of aggregates (red) and monomers (green) (scale bar=20 μm). B, C: Quantitative analysis of membrane potential fluorescence intensity (Mean±SD, n=5). **P<0.01 vs CON group; #P<0.05 vs OGD/R group; ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.01 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.
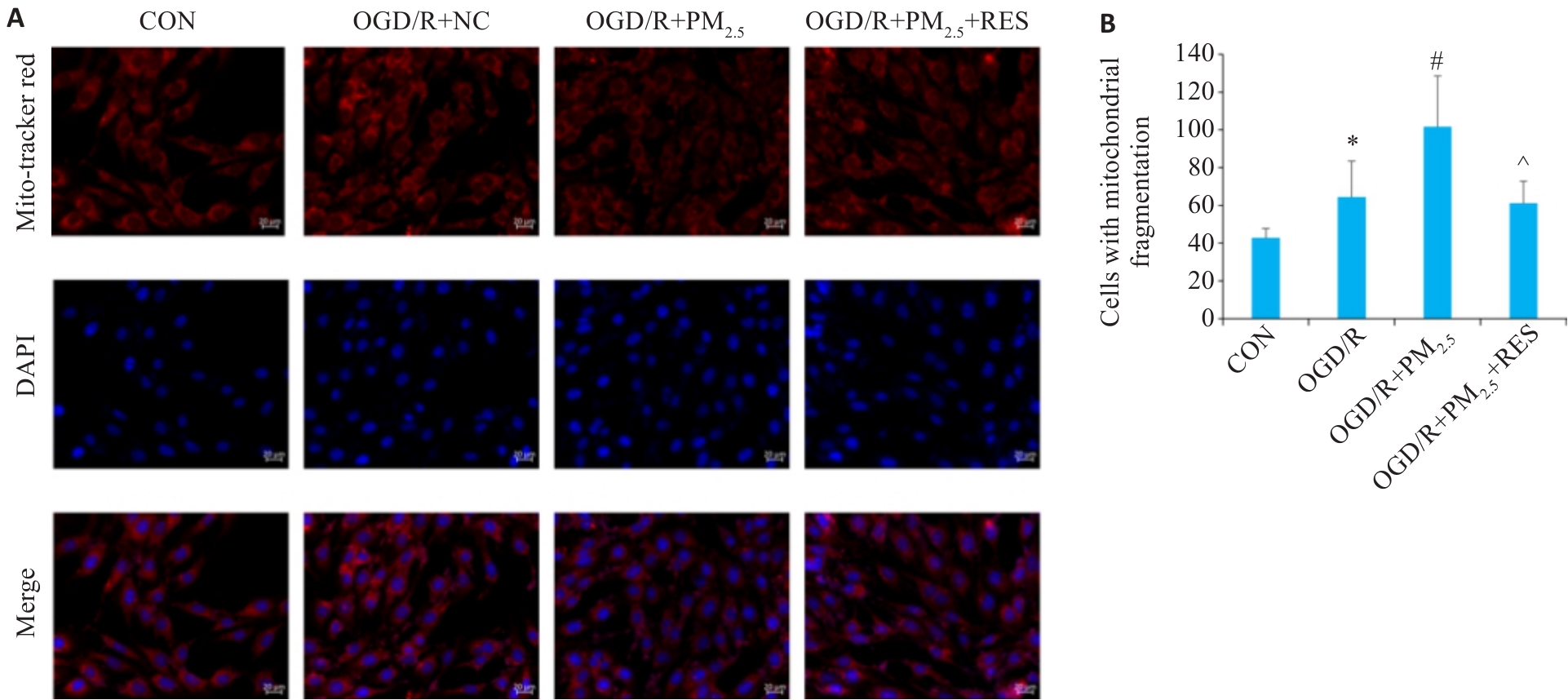
Fig.7 Immunofluorescence staining for observing mitochondrial morphology in different groups. A: Immunofluorescence staining with Mito-Tracker Red and DAPI (scale bar=20 μm). B: Comparison of mitochondrial fragmentation in each group (Mean±SD, n=5). *P<0.05 vs CON group; #P<0.05 vs OGD/R group; ^P<0.05 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.
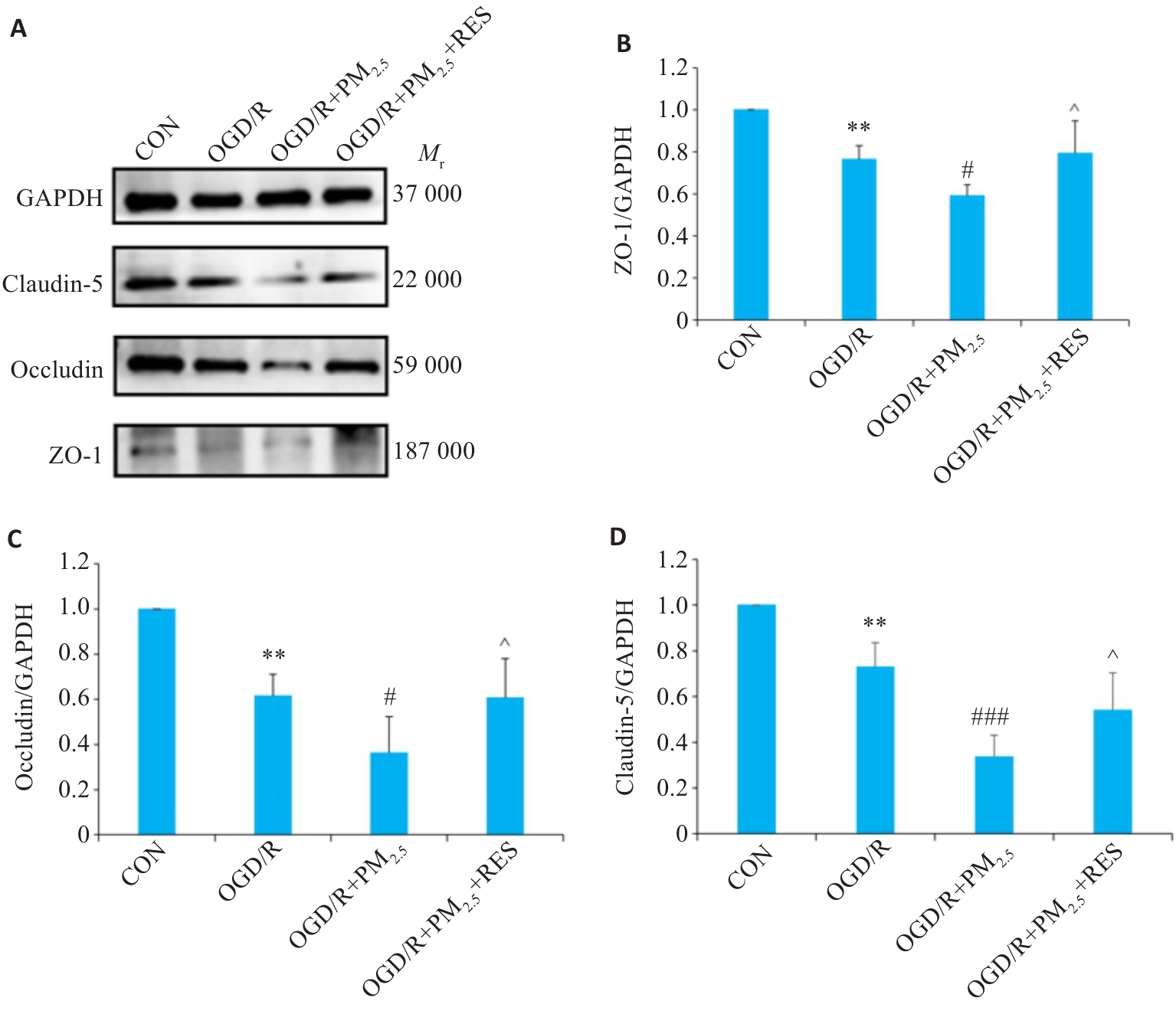
Fig.8 Expression of ZO-1, occludin, claudin-5 proteins in each group detected by Western blotting. A: Western blots of ZO-1, occludin, claudin-5 and GAPDH. B-D: Expression levels of ZO-1 (B), occludin (C), and claudin-5 (D) proteins normalized by GAPDH levels (Mean±SD, n=5). Data normalized to control (set as 1) and statistical comparisons are conducted on normalized data.**P<0.01 vs CON group; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs OGD/R group; ^P<0.05 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.
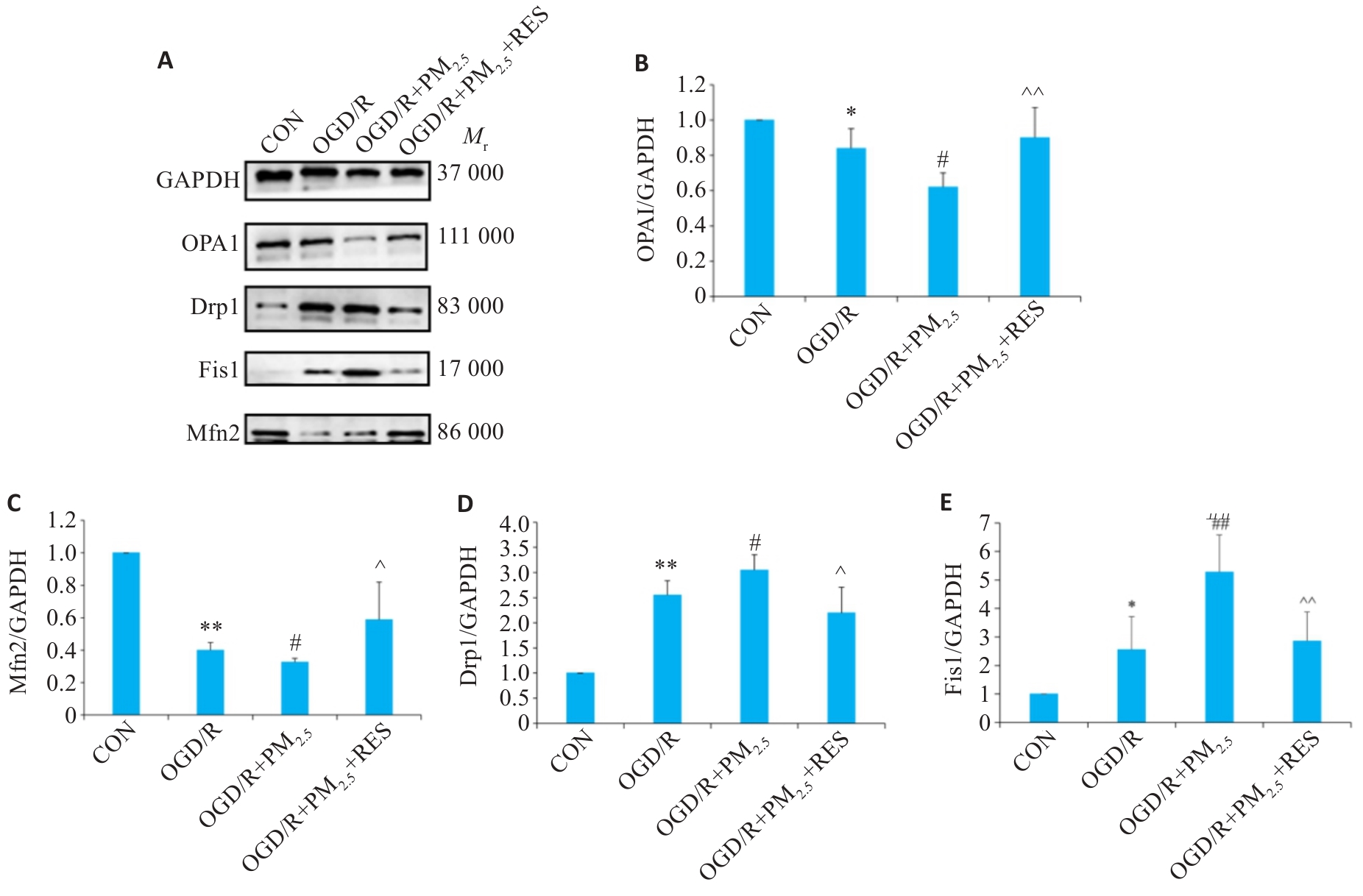
Fig.9 Expressions of OPA1, Mfn2, Drp1and Fis1 proteins in each group detected by Western blotting. A: Western blots of OPA1, Mfn2, Drp1, Fis1 and GAPDH. B-E: Expression levels of OPA1, Mfn2, Drp1 and Fis1 proteins normalized by GAPDH levels (Mean±SD, n=5). Data normalized to control (set as 1) and statistical comparisons are conducted on normalized data. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs CON group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs OGD/R group; ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.01 vs OGD/R+PM2.5 group.
| [1] | Hendriks S, Ranson JM, Peetoom K, et al. Risk factors for young-onset dementia in the UK biobank[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2024, 81(2): 134-42. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.4929 |
| [2] | Bennett EE, Song ZW, Lynch KM, et al. The association of long-term exposure to criteria air pollutants, fine particulate matter components, and airborne trace metals with late-life brain amyloid burden in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study[J]. Environ Int, 2023, 180: 108200. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2023.108200 |
| [3] | Stinear CM, Lang CE, Zeiler S, et al. Advances and challenges in stroke rehabilitation[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2020, 19(4): 348-60. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30415-6 |
| [4] | Li C, van Donkelaar A, Hammer MS, et al. Reversal of trends in global fine particulate matter air pollution[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 5349. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-41086-z |
| [5] | Huang KY, Liang FC, Yang XL, et al. Long term exposure to ambient fine particulate matter and incidence of stroke: prospective cohort study from the China-PAR project[J]. BMJ, 2019, 367: l6720. doi:10.1136/bmj.l6720 |
| [6] | Cao JJ, Shen ZX, Chow JC, et al. Winter and summer PM2.5 chemical compositions in fourteen Chinese cities[J]. J Air Waste Manag Assoc, 2012, 62(10): 1214-26. doi:10.1080/10962247.2012.701193 |
| [7] | Paul S, Candelario-Jalil E. Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: an overview of clinical and preclinical studies[J]. Exp Neurol, 2021, 335: 113518. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113518 |
| [8] | Koton S, Pike JR, Johansen M, et al. Association of ischemic stroke incidence, severity, and recurrence with dementia in the athero-sclerosis risk in communities cohort study[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2022, 79(3): 271-80. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.5080 |
| [9] | GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10258): 1223-49. |
| [10] | Chen ZZ, Liu PL, Xia XS, et al. The underlying mechanism of PM2.5-induced ischemic stroke[J]. Environ Pollut, 2022, 310: 119827. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119827 |
| [11] | Sekerdag E, Solaroglu I, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y. Cell death mechanisms in stroke and novel molecular and cellular treatment options[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2018, 16(9): 1396-415. doi:10.2174/1570159x16666180302115544 |
| [12] | Block ML, Calderón-Garcidueñas L. Air pollution: mechanisms of neuroinflammation and CNS disease[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2009, 32(9): 506-16. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2009.05.009 |
| [13] | MohanKumar SMJ, Campbell A, Block M, et al. Particulate matter, oxidative stress and neurotoxicity[J]. Neurotoxicology, 2008, 29(3): 479-88. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2007.12.004 |
| [14] | Rovira-Llopis S, Bañuls C, Diaz-Morales N, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics in type 2 diabetes: pathophysiological implications[J]. Redox Biol, 2017, 11: 637-45. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.013 |
| [15] | Li XL, Klaus JA, Zhang J, et al. Contributions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and-2 to nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor and injury from focal cerebral ischemia[J]. J Neurochem, 2010, 113(4): 1012-22. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06667.x |
| [16] | Owjfard M, Rahimian Z, Karimi F, et al. A comprehensive review on the neuroprotective potential of resveratrol in ischemic stroke[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(14): e34121. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34121 |
| [17] | Wang J, Zhu Q, Wang Y, et al. Irisin protects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy by suppressing ferroptosis via activation of the Nrf2/GPX4 signal axis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 187: 171-84. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.11.024 |
| [18] | Yadav E, Yadav P, Khan MMU, et al. Resveratrol: a potential therapeutic natural polyphenol for neurodegenerative diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 922232. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.922232 |
| [19] | Wang N, Luo ZW, Jin M, et al. Exploration of age-related mitochondrial dysfunction and the anti-aging effects of resveratrol in zebrafish retina[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2019, 11(10): 3117-37. doi:10.18632/aging.101966 |
| [20] | Yin Y, Lv GG, Zhang W, et al. Resveratrol glycoside mediates microglial endoplasmic reticulum stress to mitigate LPS-induced sepsis-associated cognitive dysfunction[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2023, 443: 114326. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114326 |
| [21] | Çetin R, Bahadir S, Basar İ, et al. Neuroprotective effects of the combined treatment of resveratrol and urapidil in experimental cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats[J]. Acta Cir Bras, 2024, 39: e395329. doi:10.1590/acb395329 |
| [22] | Sonneville R, Verdonk F, Rauturier C, et al. Understanding brain dysfunction in sepsis[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2013, 3(1): 15. doi:10.1186/2110-5820-3-15 |
| [23] | Xiao MJ, Xiao ZJ, Yang BB, et al. Blood-brain barrier: more contributor to disruption of central nervous system homeostasis than victim in neurological disorders[J]. Front Neurosci, 2020, 14: 764. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.00764 |
| [24] | RONALDSON P T, DAVIS T P. Regulation of blood-brain barrier integrity by microglia in health and disease: A therapeutic opportunity [J]. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 2020, 40(): S6-s24. doi:10.1177/0271678x20951995 |
| [25] | Haupt M, Zechmeister B, Bosche B, et al. Lithium enhances post-stroke blood-brain barrier integrity, activates the MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway and alters immune cell migration in mice[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2020, 181: 108357. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108357 |
| [26] | Ni HZ, Li JX, Zheng JY, et al. Cardamonin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway[J]. Phytother Res, 2022, 36(4): 1736-47. doi:10.1002/ptr.7409 |
| [27] | Wu Q, Liu J, Mao ZG, et al. Ligustilide attenuates ischemic stroke injury by promoting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission via activation of AMPK[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 95: 153884. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153884 |
| [28] | Murata D, Arai K, Iijima M, et al. Mitochondrial division, fusion and degradation[J]. J Biochem, 2020, 167(3): 233-41. doi:10.1093/jb/mvz106 |
| [29] | Zou GP, Yu CX, Shi SL, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics mediated by DRP1 and MFN2 contributes to cisplatin chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(24): 7358-73. doi:10.7150/jca.61379 |
| [30] | Fu PF, Epshtein Y, Ramchandran R, et al. Essential role for paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation in LPS-induced mitochondrial fission, ROS generation and lung endothelial barrier loss[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 17546. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-97006-y |
| [31] | Lai YX, Lin PQ, Chen ML, et al. Retraction notice to “Restoration of L-OPA1 alleviates acute ischemic stroke injury in rats via inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and preserving mitochondrial function” [Redox Biol. 34 (2020) 101503[J]. Redox Biol, 2024, 75: 103271. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2024.103271 |
| [32] | Fan LF, He PY, Peng YC, et al. Mdivi-1 ameliorates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via the suppression of inflammation-related blood-brain barrier disruption and endoplasmic reticulum stress-based apoptosis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2017, 112: 336-49. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.08.003 |
| [33] | Wang SS, Liu ZY, Li R, et al. Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial barrier damage by inhibiting mitochondrial fission in sepsis-associated encephalo-pathy[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2025, 997: 177468. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177468 |
| [34] | Chen CH, Budas GR, Churchill EN, et al. Activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 reduces ischemic damage to the heart[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5895): 1493-5. doi:10.1126/science.1158554 |
| [35] | Haileselassie B, Joshi AU, Minhas PS, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic encephalopathy[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 36. doi:10.1186/s12974-019-1689-8 |
| [36] | Gherardi G, Corbioli G, Ruzza F, et al. CoQ10 and resveratrol effects to ameliorate aged-related mitochondrial dysfunctions[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(20): 4326. doi:10.3390/nu14204326 |
| [37] | Chang HC, Tai YT, Cherng YG, et al. Resveratrol attenuates high-fat diet-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier and protects brain neurons from apoptotic insults[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2014, 62(15): 3466-75. doi:10.1021/jf403286w |
| [1] | Jingxian WANG, Zijing REN, Peiyang ZHOU. S1PR5 activation or overexpression enhances barrier function of mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells against OGD/R injury by modulating oxidative stress [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1451-1459. |
| [2] | Anbang ZHANG, Xiuqi SUN, Bo PANG, Yuanhua WU, Jingyu SHI, Ning ZHANG, Tao YE. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis through the gut-brain axis and the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [3] | Zehan LI, Meng LIANG, Gencheng HAN, Xuewu ZHANG. Therapeutic effects of inulin-type oligosaccharides of Morinda officinalis on Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 577-586. |
| [4] | Jie CHEN, Chenxu LIU, Chun WANG, Li LI, Weiting TAO, Jingru XUN, Honghui TANG, Li HUANG. Exogenous leptin improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced glutamate excitotoxic injury in mice by up-regulating GLT-1 and GLAST expression in astrocytes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1079-1087. |
| [5] | Qian ZHAO, Zhen ZHANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Xiangyu RONG, Xuerou LIU, Xinli ZHAO, Haojie WANG, Jinlong PANG, Shanshan LI, Xian LI. Aqueous extract of Chuan Xiong Rhizoma enhances inhibitory effect of temozolomide against brain metastasis of melanoma in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1088-1097. |
| [6] | XU Guangming, GAO Andi, CONG Bin. Restraint stress induces blood-brain barrier injury in rat amygdala by activating the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 411-419. |
| [7] | GUI Jianjun, SUN Xiaodong, WEN Shu, LIU Xin, QIN Bingqing, SANG Ming. Resveratrol protects dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease by regulating the gut-brain axis via inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 270-279. |
| [8] | LI Xinyi, LIU Yujie, DENG Kechong, HU Yikui. Modulating gut microbiota improves neurological function and depressive symptoms in rats with post-stroke depression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 405-410. |
| [9] | Ruhui LIN, Jinyan XIA, Xiaohan MA, Zuanfang LI. Electroacupuncture improves learning and memory function and promotes hippocampal synaptic regeneration in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2317-2326. |
| [10] | YE Hongwei, ZHANG Yuming, YUN Qi, DU Ruoli, LI Lu, LI Yuping, GAO Qin. Resveratrol alleviates hyperglycemia-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis via enhancing SIRT1 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 45-51. |
| [11] | SUN Wei, CHEN Ping, TANG Xiaohang, GU Yingmin, TIAN Xuesong. An improved 4-vessel intermittent occlusion method for establishing rat models of global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1194-1203. |
| [12] | NIU Wenwen, RONG Xiangyu, ZHAO Qian, LIU Xuerou, XU Liansong, LI Shanshan, LI Xian. Wine-processed Chuanxiong Rhizoma enhances efficacy of aumolertinib against EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer xenografts in nude mouse brain [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(3): 375-382. |
| [13] | LI Shai, LI Li, MIN Simin, LIU Saisai, QIN Zhiwen, XIONG Zhishang, XU Jianguo, WANG Bowen, DING Dushan, ZHAO Shidi. Soybean isoflavones alleviate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis and inflammatory cascade reaction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 323-330. |
| [14] | CAO Tianran, LIU Qingfang, PAN Meimin, ZHANG Xuehong. LncRNA SNHG8 inhibits miR-494-3p expression to alleviate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2015-2022. |
| [15] | LI Fan, ZHU Yanyan, SUN Xiaoming, HU Huijuan, ZHOU Miaomaio, BAI Yixue, HU Hao. Diethylhexyl phthalate induces anxiety-like behavior and learning and memory impairment in mice probably by damaging blood-brain barrier [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(8): 1237-1243. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||