Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 1965-1975.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.15
Yumei YANG( ), Xuerou LIU, Wei LIU, Xingqi ZHOU, Zhen ZHANG, Yan HU, Peipei LIU, Xian LI, Hao LIU, Shanshan LI(
), Xuerou LIU, Wei LIU, Xingqi ZHOU, Zhen ZHANG, Yan HU, Peipei LIU, Xian LI, Hao LIU, Shanshan LI( )
)
Received:2024-04-07
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Shanshan LI
E-mail:1337781526@qq.com;lishanshan900122@163.com
Yumei YANG, Xuerou LIU, Wei LIU, Xingqi ZHOU, Zhen ZHANG, Yan HU, Peipei LIU, Xian LI, Hao LIU, Shanshan LI. Aumolertinib combined with anlotinib inhibits proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells by down-regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1965-1975.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.15
| Antibody name | Company | Dilution rate |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-beta actin | Affinity biosciences | 1:5000 |
| Anti-E-cadherin | Proteintech | 1:5000 |
| Anti-Vimentin | Proteintech | 1:1000 |
| Anti-Bax | Proteintech | 1:2000 |
| Anti-Bcl-2 | Proteintech | 1:2000 |
| Anti-MMP2 | Affinity biosciences | 1:1000 |
| Anti-MMP9 | Affinity biosciences | 1:1000 |
| Anti-PI3K | Proteintech | 1:1000 |
| Anti-AKT | Proteintech | 1:5000 |
| Anti-p-PI3K | Cell signaling technology | 1:1000 |
| Anti-p-AKT | Cell signaling technology | 1:2000 |
Tab.1 Antibodies used in this study
| Antibody name | Company | Dilution rate |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-beta actin | Affinity biosciences | 1:5000 |
| Anti-E-cadherin | Proteintech | 1:5000 |
| Anti-Vimentin | Proteintech | 1:1000 |
| Anti-Bax | Proteintech | 1:2000 |
| Anti-Bcl-2 | Proteintech | 1:2000 |
| Anti-MMP2 | Affinity biosciences | 1:1000 |
| Anti-MMP9 | Affinity biosciences | 1:1000 |
| Anti-PI3K | Proteintech | 1:1000 |
| Anti-AKT | Proteintech | 1:5000 |
| Anti-p-PI3K | Cell signaling technology | 1:1000 |
| Anti-p-AKT | Cell signaling technology | 1:2000 |
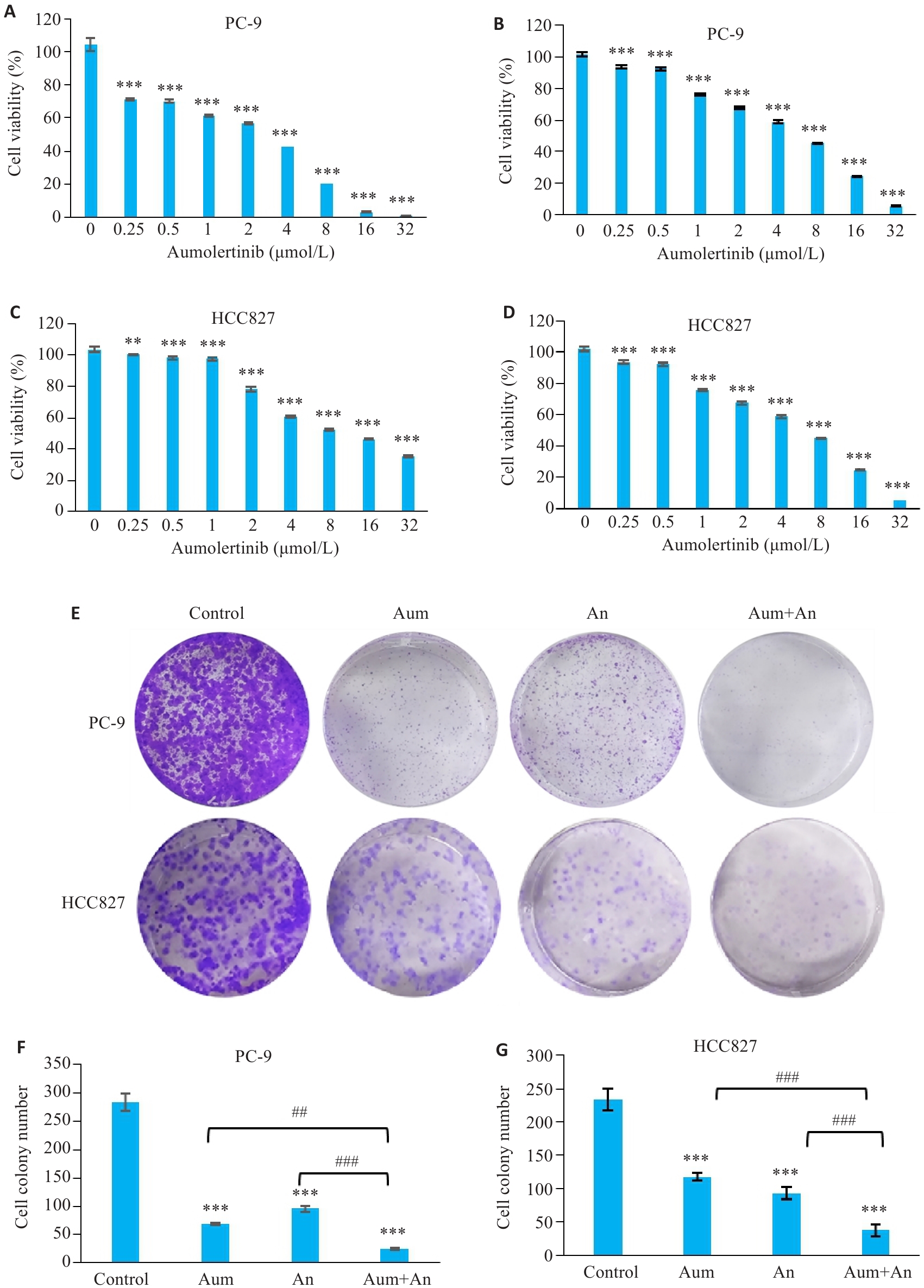
Fig.1 Aumolertinib (Aum), anlotinib (An) and their combination significantly inhibits NSCLC cell proliferation and survival. A: Effect of Aum on PC-9 cells. B: Inhibitory effect of An in PC-9 cells. C: Inhibitory effect of Aum in HCC827 cells. D. Inhibitory effect of An in HCC827 cells. E: Colony cloning. F, G: Statistics of colony formation in HCC827 cells, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs 0 μmol/L Control, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001.
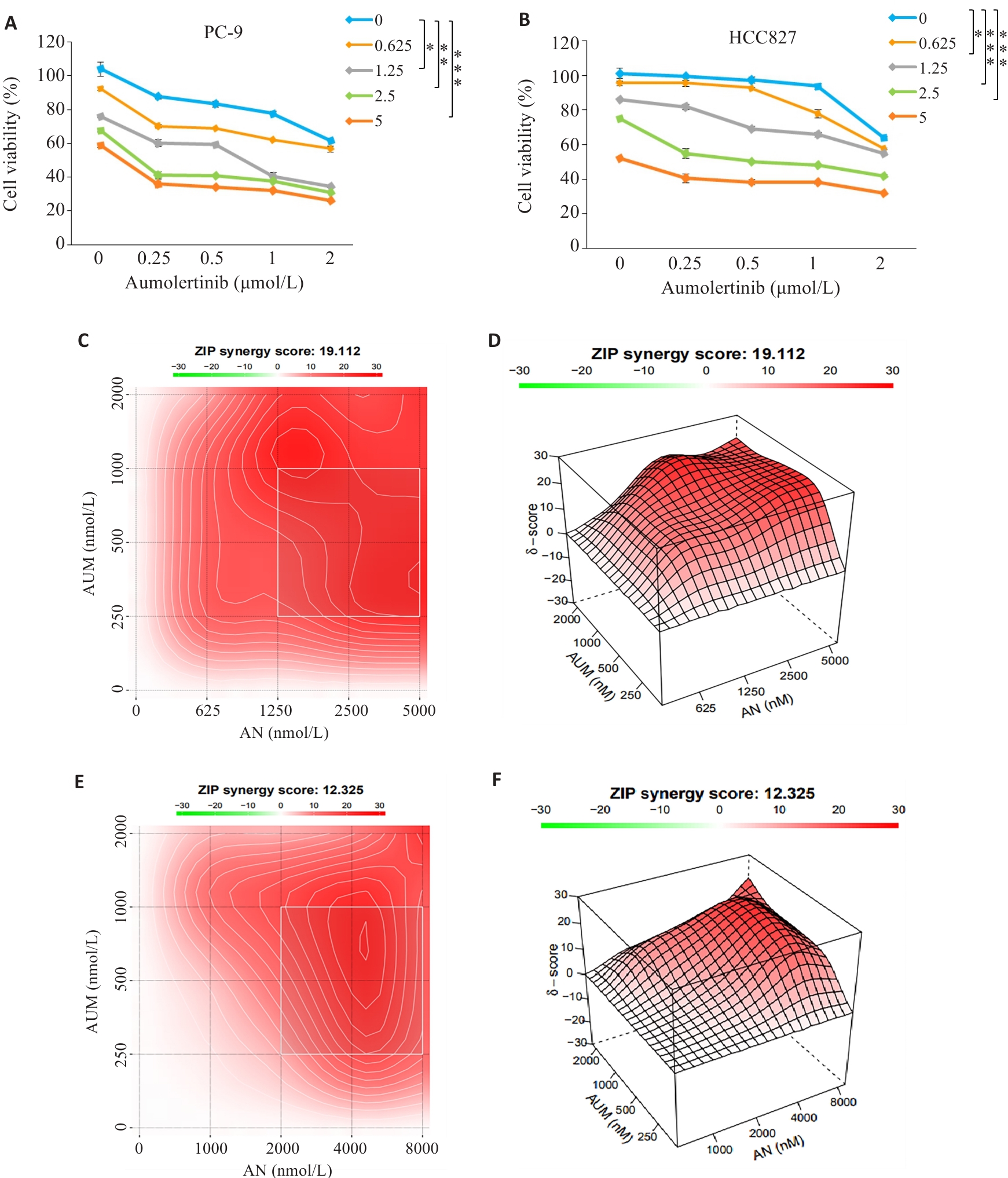
Fig.2 Aumolertinib combined with anlotinib synergistically inhibit viability of PC-9 and HCC827 cells. A, B: CCK-8 assay. C, D: Synergy scores of Aumolertinib combined with anlotinib in PC-9 cells (ZIP<0 indicates an antagonistic effect of the two drugs, 0<ZIP<10 indicates that the two drugs have antagonistic effects, and 0<ZIP<10 indicates that the two drugs have antagonistic effect, and 0<ZIP<10 indicates that the two drugs have synergy effect). ZIP<10 indicates that the two drugs have additive effect, and 10<ZIP indicates that the two drugs have synergistic effect. E,F: Synergy scores of aumolertinib combined with anlotinib in HCC827 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
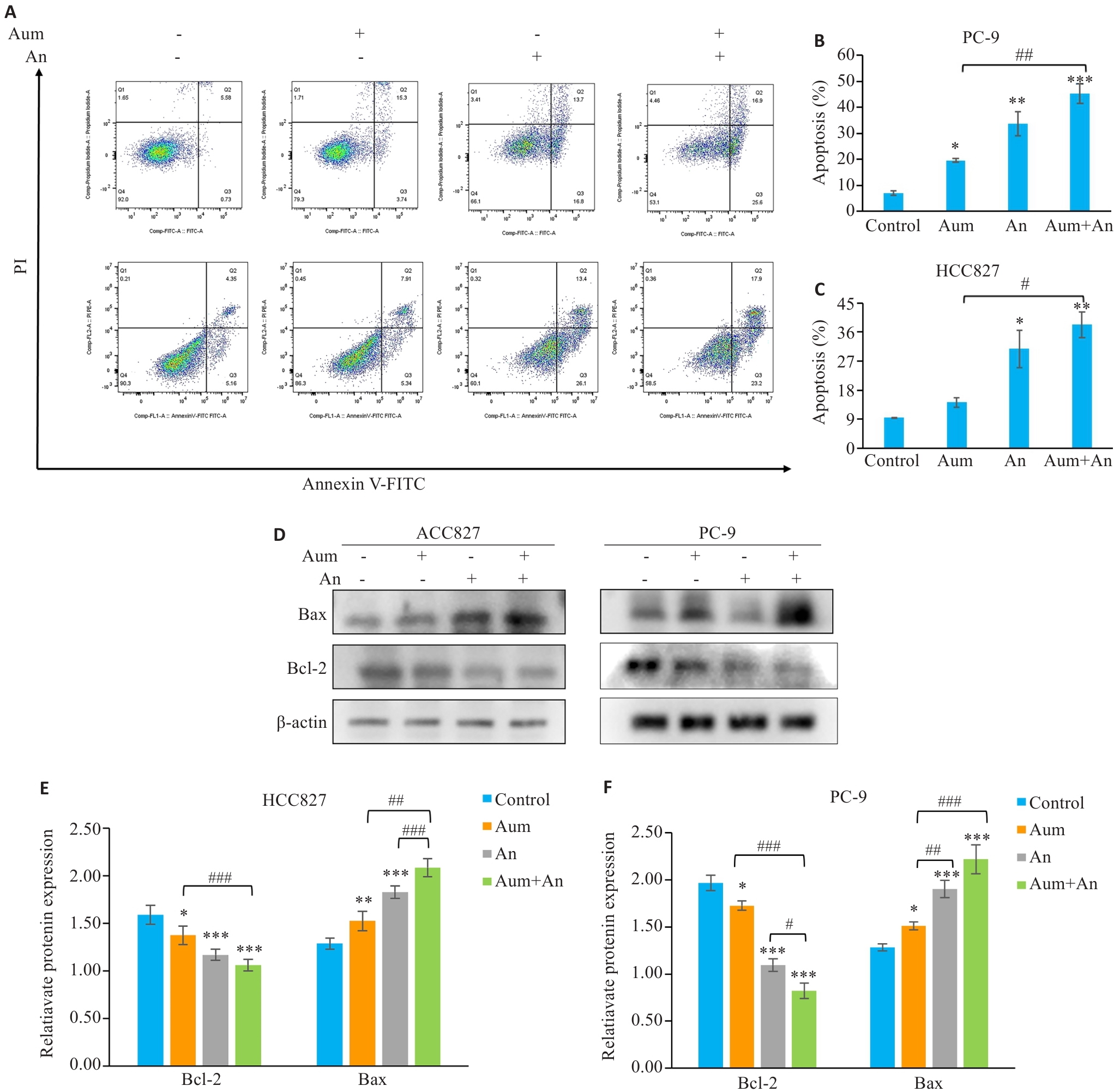
Fig.3 Aumolertinib combined with anlotinib promotes apoptosis of PC-9 cells and HCC827 cells. A: Flow cytometric analysis of apoptosis in different treatment groups. B, C: Apoptosis rates in the 4 groups. D: Apoptosis-related proteins analyzed using protein immunoblotting; E,F: Quantitative analysis of apoptotic protein expression levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001.
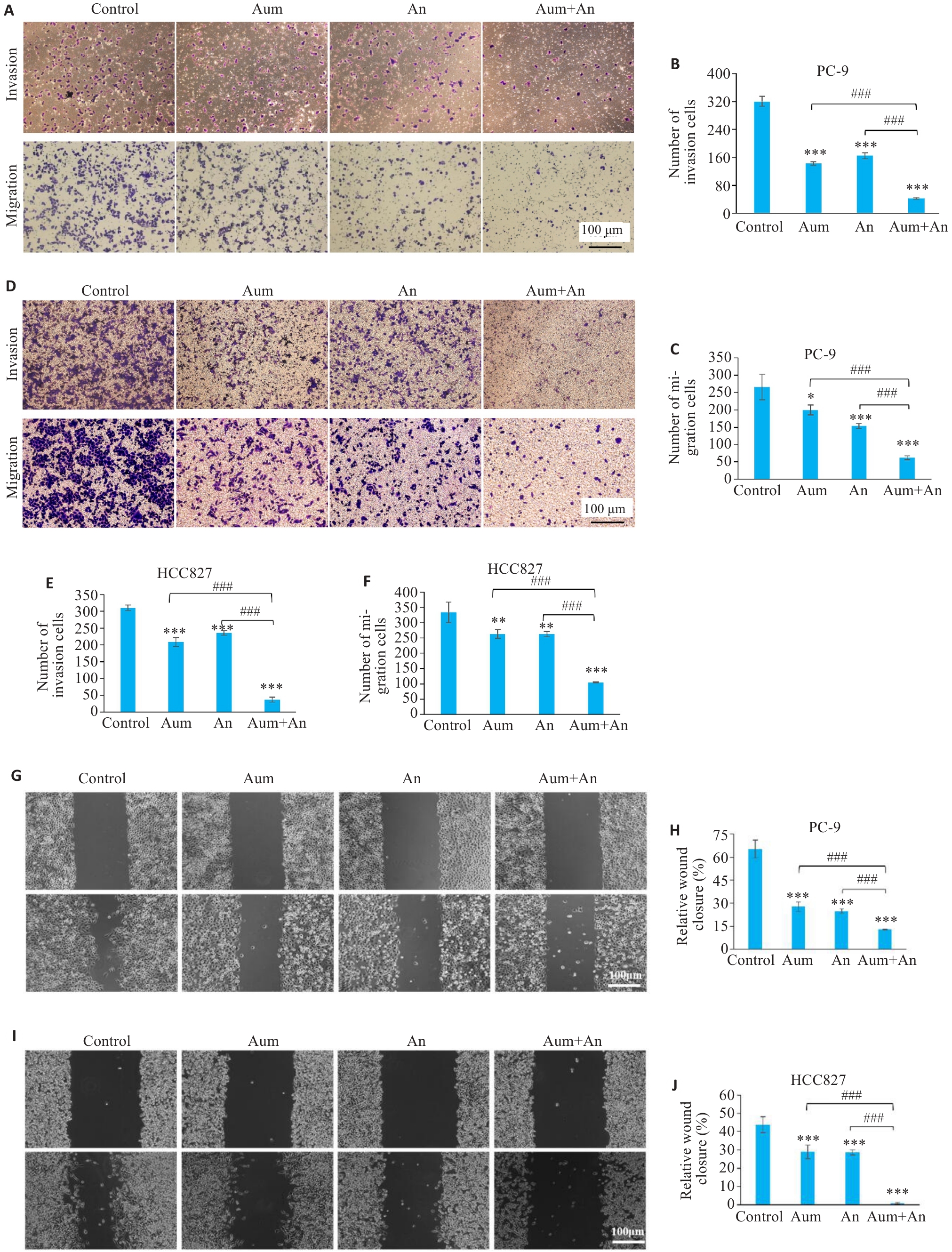
Fig.4 Aumolertinib combined with anlotinib significantly inhibits invasion and migration of PC-9 cells and HCC827 cells. A,D: Transwell assay for assessing cell invasion and migration in different groups (crystalline violet staining, original magnification: ×200). G, I: Scratch assay for assessing migration ability of the cells in different groups (×200). H,J: Quantitative analysis of PC-9 and HCC827 cell migration. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control; ###P<0.001.
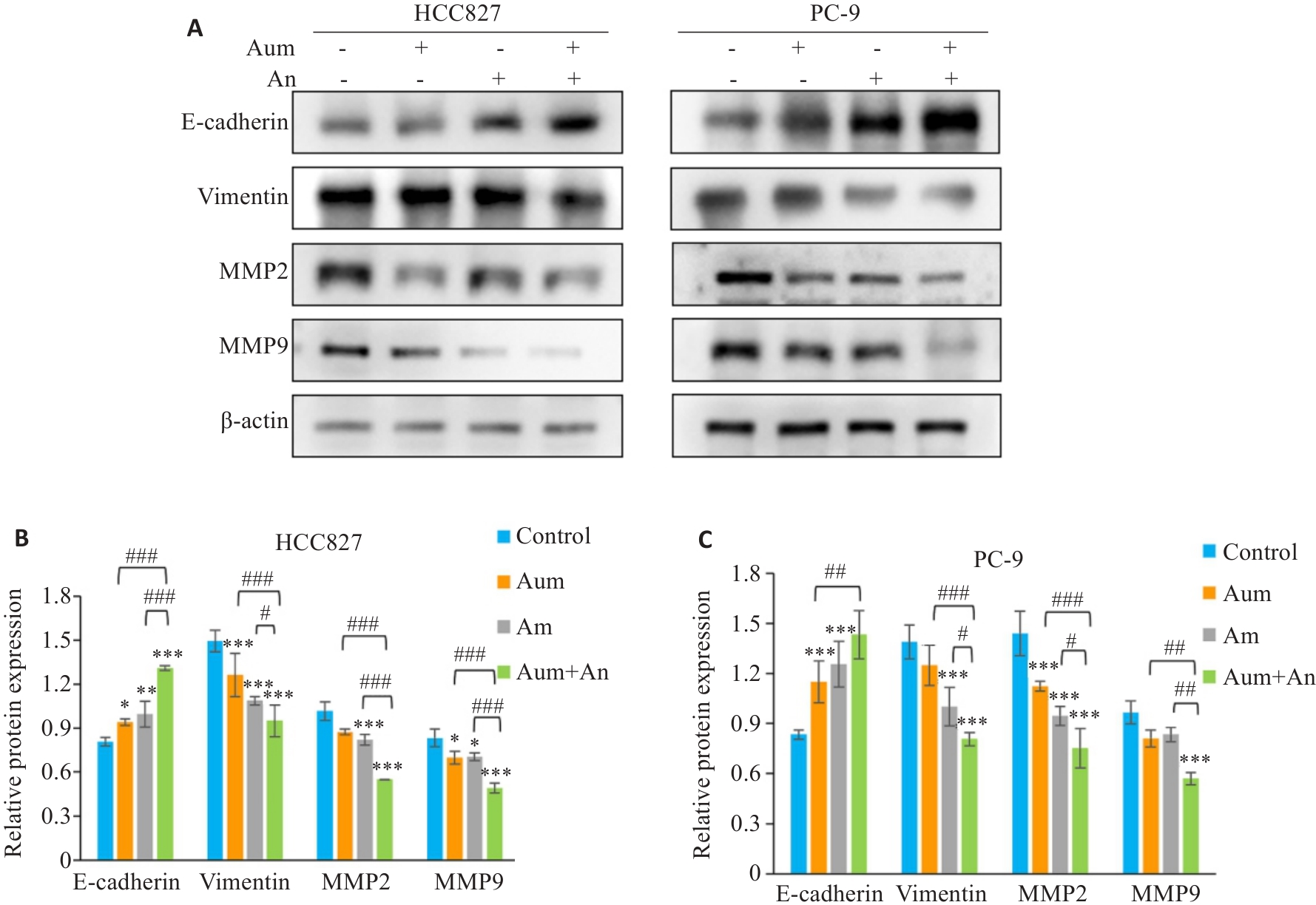
Fig.5 Western blotting for the expression of E-cadherin, vimentin, MMP2 and MMP9 in PC-9 cells or HCC827 cells (A) and their relative of protein expression levels (B, C). *P<0.05, **P<0.05,***P<0.001 vs control; #P<0.05,##P<0.01, ###P<0.001.
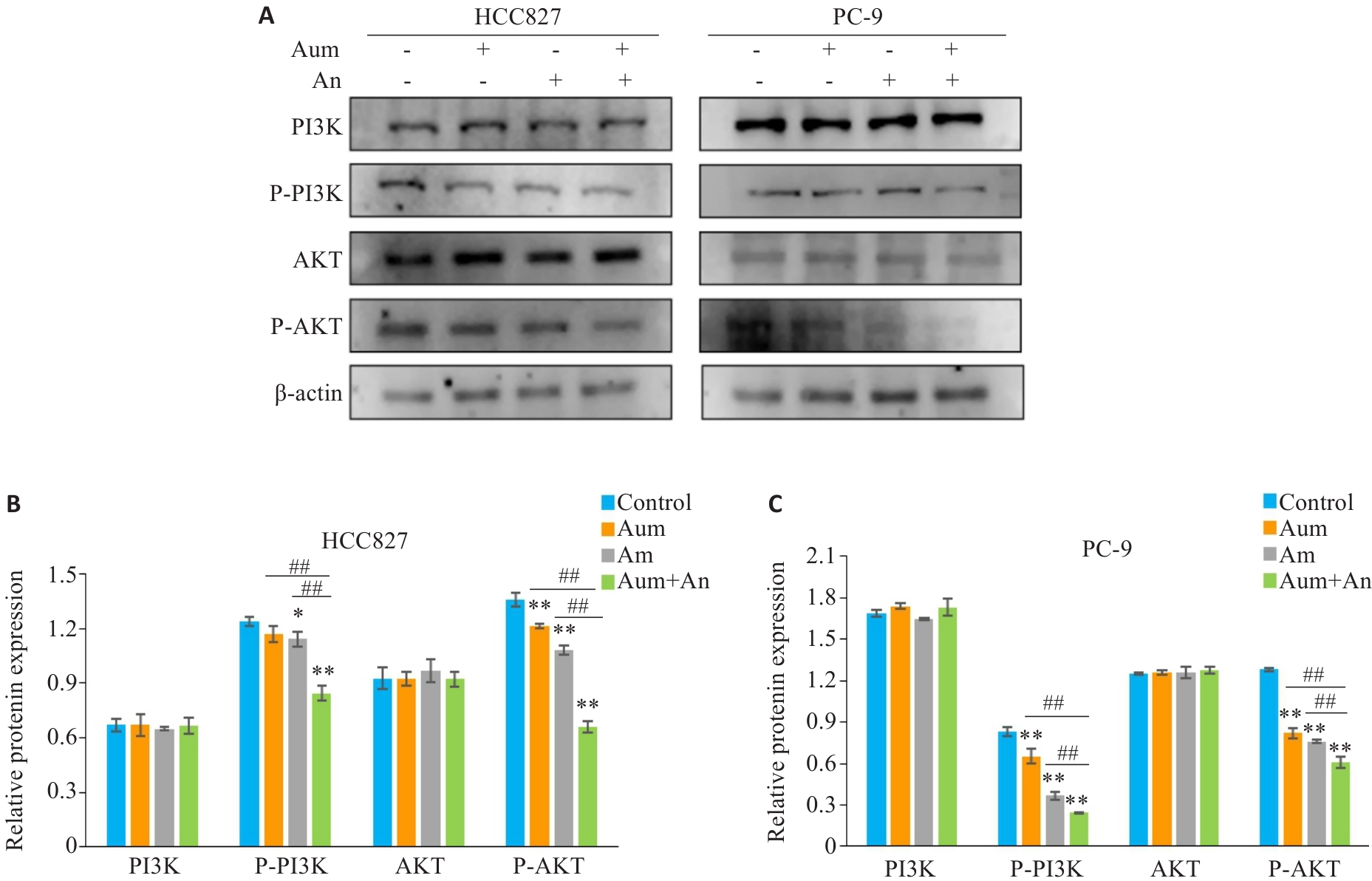
Fig.6 Aumolertinib combined with anlotinib inhibits invasion and migration of PC-9 cells and HCC827 cells by blocking phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt. A: Protein immunoblotting of PI3K-Akt pathway related proteins. B, C: Quantitative analysis of expression levels of PI3K-Akt pathway-related proteins. *P<0.05,**P<0.01 vs control,##P<0.01.
| 1 | Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-63. |
| 2 | Liang J, Guan XJ, Bao GY, et al. Molecular subtyping of small cell lung cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86(Pt 2): 450-62. |
| 3 | Succony L, Rassl DM, Barker AP, et al. Adenocarcinoma spectrum lesions of the lung: detection, pathology and treatment strategies[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2021, 99: 102237. |
| 4 | Reck M, Remon J, Hellmann MD. First-line immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(6): 586-97. |
| 5 | Zugazagoitia J, Paz-Ares L. Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: First-Line and Second-Line Treatment Options [J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(6): 671-80. |
| 6 | Chaft JE, Shyr Y, Sepesi B, et al. Preoperative and postoperative systemic therapy for operable non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(6): 546-55. |
| 7 | Ge X, Zhang Y, Huang F, et al. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor Almonertinib induces apoptosis and autophagy mediated by reactive oxygen species in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol, 2021, 40(): S49-S62. |
| 8 | Han BH, Li K, Wang QM, et al. Effect of anlotinib as a third-line or further treatment on overall survival of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: the ALTER 0303 phase 3 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2018, 4(11): 1569-75. |
| 9 | Shen GS, Zheng FC, Ren DF, et al. Anlotinib: a novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2018, 11(1): 120. |
| 10 | Syed YY. Anlotinib: first global approval[J]. Drugs, 2018, 78(10): 1057-62. |
| 11 | Hou ZW, Wu HG, Luo NN, et al. Almonertinib combined with anlotinib and temozolomide in a patient with recurrent glioblastoma with EGFR L858R mutation[J]. Oncologist, 2023, 28(5): 449-52. |
| 12 | Li T, Chang KJ, Qiu X, et al. A pilot study of anlotinib with third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in untreated EGFR-mutant patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2023, 12(6): 1256-63. |
| 13 | Chen LK, Chen J, Li MC, et al. OA03.03 aumolertinib plus anlotinib in advanced NSCLC with brain metastasis: a single-arm, phase II study[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2023, 18(11): S48-9. |
| 14 | Yang Q, Jiang W, Hou P. Emerging role of PI3K/AKT in tumor-related epigenetic regulation[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2019, 59: 112-24. |
| 15 | Xu ZR, Han X, Ou DM, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2020, 104(2): 575-87. |
| 16 | Kim SH, Seung BJ, Cho SH, et al. Dysregulation of PI3K/akt/PTEN pathway in canine mammary tumor[J]. Animals, 2021, 11(7): 2079. |
| 17 | Lu T, Wang Y, Liu F, et al. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Berberine and Low-Temperature Plasma on Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells via PI3K-AKT-Driven Signaling Axis [J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(23). |
| 18 | Moghbeli M. PI3K/AKT pathway as a pivotal regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung tumor cells[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2024, 24(1): 165. |
| 19 | Chen CL, Guo Y, Huang QS, et al. PI3K inhibitor impairs tumor progression and enhances sensitivity to anlotinib in anlotinib-resistant osteosarcoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2022, 536: 215660. |
| 20 | Zhang ZR, Zhang MX, Liu H, et al. AZD9291 promotes autophagy and inhibits PI3K/Akt pathway in NSCLC cancer cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(1): 756-67. |
| 21 | Lv YH, Du TT, Ji M, et al. A novel PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor XH002 exhibited robust antitumor activity in NSCLC[J]. J Drug Target, 2019, 27(4): 451-9. |
| 22 | Ciuffreda L, Incani UC, Steelman LS, et al. Signaling intermediates (MAPK and PI3K) as therapeutic targets in NSCLC[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2014, 20(24): 3944-57. |
| 23 | Erira A, Velandia F, Penagos J, et al. Differential regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway between low- and high-grade gliomas[J]. Brain Sci, 2021, 11(12): 1655. |
| 24 | Lin BY, Song XM, Yang DW, et al. Anlotinib inhibits angiogenesis via suppressing the activation of VEGFR2, PDGFRβ and FGFR1[J]. Gene, 2018, 654: 77-86. |
| 25 | Qin TT, Liu ZJ, Wang J, et al. Anlotinib suppresses lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in lung adeno-carcinoma through a process potentially involving VEGFR-3 signaling[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2020, 17(3): 753-67. |
| 26 | Hong C, Wei JP, Zhou T, et al. FGFR2-ERC1: a subtype of FGFR2 oncogenic fusion variant in lung adenocarcinoma and the response to anlotinib[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2022, 15: 651-7. |
| 27 | Liang LJ, Hui KY, Hu CX, et al. Autophagy inhibition potentiates the anti-angiogenic property of multikinase inhibitor anlotinib through JAK2/STAT3/VEGFA signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 71. |
| 28 | de Carlo E, Bertoli E, del Conte A, et al. Brain metastases management in oncogene-addicted non-small cell lung cancer in the targeted therapies era[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(12): 6477. |
| 29 | Sun JJ, Wu SK, Jin ZX, et al. Lymph node micrometastasis in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2022, 149: 112817. |
| 30 | Tan AC. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(3): 511-8. |
| 31 | Han D, Zhang JJ, Bao YW, et al. Anlotinib enhances the antitumor immunity of radiotherapy by activating cGAS/STING in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 468. |
| 32 | Wang J, Xu Z, Lai Y, et al. Anlotinib Inhibiting Mantle Cell Lymphoma Proliferation and Inducing Apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway [J]. Current Molecular Medicine, 2024, 24. |
| 33 | Zhang LL, Wang LC, Wang JY, et al. Anlotinib plus icotinib as a potential treatment option for EGFR-mutated advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer with concurrent mutations: final analysis of the prospective phase 2, multicenter ALTER-L004 study[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 124. |
| 34 | Zhao HY, Yao WX, Min XH, et al. Apatinib plus gefitinib as first-line treatment in advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC: the phase III ACTIVE study (CTONG1706)[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2021, 16(9): 1533-46. |
| 35 | 杜宝萍, 梁诗欣, 余 辉, 等. EGFR T790M抑制剂联合安罗替尼治疗非小细胞肺癌疗效的回顾分析[J]. 今日药学, 2023, 33(12): 922-7. |
| 36 | Zhao Y, Li SY, Yang X, et al. Overall survival benefit of osimertinib and clinical value of upfront cranial local therapy in untreated EGFR-mutant nonsmall cell lung cancer with brain metastasis[J]. Int J Cancer, 2022, 150(8): 1318-28. |
| 37 | Lu W, Kang YB. Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer progression and metastasis[J]. Dev Cell, 2019, 49(3): 361-74. |
| 38 | Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2014, 15(3): 178-96. |
| 39 | Jiang Y, Han QJ, Zhao HJ, et al. Promotion of epithelial-mesenchymal transformation by hepatocellular carcinoma-educated macrophages through Wnt2b/β‑catenin/c-Myc signaling and reprogramming glycolysis[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 13. |
| 40 | Zhang GF, Zheng G, Zhang HP, et al. MUC1 induces the accumulation of Foxp3+ Treg cells in the tumor microenvironment to promote the growth and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma through the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 118: 110091. |
| 41 | Yang SC, Liu Y, Li MY, et al. FOXP3 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16(1): 124. |
| 42 | Feng X, Xu ES. Alectinib and lorlatinib function by modulating EMT-related proteins and MMPs in NSCLC metastasis[J]. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2021, 21(3): 331-8. |
| 43 | Emery S, Fieux S, Vidal B, et al. Preclinical validation of [(18)F]2FNQ1P as a specific PET radiotracer of 5-HT(6) receptors in rat, pig, non-human primate and human brain tissue[J]. Nucl Med Biol, 2020, 82/83: 57-63. |
| 44 | Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cell, 2010, 141(1): 52-67. |
| 45 | Scheau C, Badarau I A, Costache R, et al. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma [J]. Analytical Cellular Pathology, 2019, 2019: 1-10. |
| 46 | Scheau C, Badarau IA, Costache R, et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Anal Cell Pathol, 2019, 2019: 9423907. |
| 47 | Rashid ZA, Bardaweel SK. Novel matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) inhibitors in cancer treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(15): 12133. |
| 48 | Miao Y, Bi XY, Zhao M, et al. Acetylcholine inhibits tumor necrosis factor α activated endoplasmic reticulum apoptotic pathway via EGFR-PI3K signaling in cardiomyocytes[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2015, 230(4): 767-74. |
| 49 | Tang M, Deng HD, Zheng KL, et al. Ginsenoside 3β‑O-Glc-DM (C3DM) suppressed glioma tumor growth by downregulating the EGFR/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and modulating the tumor microenvironment[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2023, 460: 116378. |
| 50 | Shirley M, Keam SJ. Aumolertinib: a review in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Drugs, 2022, 82(5): 577-84. |
| 51 | He JY, Huang ZR, Han LZ, et al. Mechanisms and management of 3rd-generation EGFR-TKI resistance in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (Review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2021, 59(5): 90. |
| 52 | Qu QH, Jiang SZ, Li XY. LncRNA TBX5-AS1 regulates the tumor progression through the PI3K/AKT pathway in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 7949-61. |
| 53 | Zhang D, Deng T, Yuan W, et al. Glaucocalyxin A induces apoptosis of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway[J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2022, 49(8): 797-804. |
| 54 | Zhou J, Peng Y, Gao YC, et al. Targeting DNAJC19 overcomes tumor growth and lung metastasis in NSCLC by regulating PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2021, 21(1): 338. |
| 55 | Cao SY, Li LF, Li J, et al. MiR-1299 impedes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer through EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 7493-502. |
| 56 | Yang F, Zheng YF, Luo Q, et al. Knockdown of NCAPD3 inhibits the tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer by regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. BMC Cancer, 2024, 24(1): 408. |
| 57 | Guan JK, Borenäs M, Xiong JF, et al. IGF1R contributes to cell proliferation in ALK-mutated neuroblastoma with preference for activating the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(17): 4252. |
| 58 | Bang J, Jun M, Lee S, et al. Targeting EGFR/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2023, 15(8): 2130. |
| 59 | Shi C, Zhang C, Fu ZW, et al. Antitumor activity of aumolertinib, a third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in non-small-cell lung cancer harboring uncommon EGFR mutations[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2023, 13(6): 2613-27. |
| 60 | Liu YL, Li F, Wang QY, et al. Anlotinib inhibits growth of human esophageal cancer TE-1 cells by negative regulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Discov Oncol, 2024, 15(1): 134. |
| 61 | Lu YF, Lin J, Duan M, et al. Anlotinib suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting the RAS protein to inhibit the PI3K/akt signalling pathway[J]. Anal Cell Pathol, 2021, 2021: 5228713. |
| 62 | Chen QL, Lai Q, Jiang YL, et al. Anlotinib exerts potent antileukemic activities in Ph chromosome negative and positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia via perturbation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Transl Oncol, 2022, 25: 101516. |
| [1] | Na ZHONG, Huijie WANG, Wenying ZHAO, Zhengui SUN, Biao GENG. High RNF7 expression enhances PD-1 resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by promoting CXCL1 expression and myeloid-derived suppressor cell recruitment via activating NF-κB signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1704-1711. |
| [2] | Shuo LIU, Jing LI, Xingwang WU. Swertiamarin ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [3] | Xiaofan CONG, Teng CHEN, Shuo LI, Yuanyuan WANG, Longyun ZHOU, Xiaolong LI, Pei ZHANG, Xiaojin SUN, Surong ZHAO. Dihydroartemisinin enhances sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma HNE1/DDP cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by promoting ROS production [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [4] | Linyu XIAO, Ting DUAN, Yongsheng XIA, Yue CHEN, Yang SUN, Yibo XU, Lei XU, Xingzhou YAN, Jianguo HU. Linarin inhibits microglia activation-mediated neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis in mouse spinal cord injury by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1589-1598. |
| [5] | Mengdong ZHENG, Yan LIU, Jiaojiao LIU, Qiaozhen KANG, Ting WANG. Effect of deletion of protein 4.1R on proliferation, apoptosis and glycolysis of hepatocyte HL-7702 cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1355-1360. |
| [6] | Yuanguo WANG, Peng ZHANG. Ferroptosis suppressor genes are highly expressed in esophageal cancer to inhibit tumor cell ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [7] | Zhijun REN, Jianxin DIAO, Yiting WANG. Xionggui Decoction alleviates heart failure in mice with myocardial infarction by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [8] | Guiling CHEN, Xiaofeng LIAO, Pengtao SUN, Huan CEN, Shengchun SHU, Bijing LI, Jinhua LI. Solasonine promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating the Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [9] | Lingjun LU, Xiaodi YANG, Huaping ZHANG, Yuan LIANG, Xiulan SHI, Xin ZHOU. Recombinant Schistosoma japonicum cystatin alleviates acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation and hepatocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [10] | Guoxin LIANG, Hongyue TANG, Chang GUO, Mingming ZHANG. MiR-224-5p overexpression inhibits oxidative stress by regulating the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 axis to attenuate hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1173-1181. |
| [11] | Feifan LI, Junxin XIANG, Jiahui LIU, Xiaojing WANG, Hao JIANG. Overexpression of lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes progression of non-small cell lung cancer via the miR-130a-5p/CCND1 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 841-850. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xiaoyan, WANG Xie, WANG Jie, SHAO Nan, CAI Biao, XIE Daojun. Huangpu Tongqiao Capsule improves cognitive impairment in rats with Wilson disease by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [13] | CHEN Guodong, LUO Suxin. Colchicine alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by activating AMPK [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 226-235. |
| [14] | HAN Qiqi, YE Mengran, JIN Qili. Demethylzeylasteral inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion and promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting the AKT/CREB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 280-288. |
| [15] | Xuerou LIU, Yumei YANG, Wei LIU, Zhen ZHANG, Xingqi ZHOU, Wenyu XIE, Lin SHEN, Mengxiao ZHANG, Xian LI, Jialan ZANG, Shanshan LI. Euphorbia helioscopia inhibits proliferation, invasion, and migration and promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1918-1925. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||