南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 191-199.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.21
张淑芬1( ), 黄添容2(
), 黄添容2( ), 杨灿洪2, 陈家镒2, 吕田明2, 张嘉发2(
), 杨灿洪2, 陈家镒2, 吕田明2, 张嘉发2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-09-15
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
张嘉发
E-mail:252300534@qq.com;120064577@qq.com;596471200@qq.com
作者简介:张淑芬,主治医师,E-mail: 252300534@qq.com基金资助:
Shufen ZHANG1( ), Tianrong HUANG2(
), Tianrong HUANG2( ), Canhong YANG2, Jiayi CHEN2, Tianming LÜ2, Jiafa ZHANG2(
), Canhong YANG2, Jiayi CHEN2, Tianming LÜ2, Jiafa ZHANG2( )
)
Received:2025-09-15
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Jiafa ZHANG
E-mail:252300534@qq.com;120064577@qq.com;596471200@qq.com
摘要:
目的 探讨莱菔硫烷(SFN)和Aβ42寡聚体对U87细胞的影响,及其通过下调MAPK/NF-κB信号通路逆转神经炎症介导的SH-SY5Y神经元凋亡。 方法 以不同浓度Aβ42和SFN对U87细胞作用48 h,使用CCK-8试剂盒检测各组细胞活性。实验分组:溶媒对照组、Aβ组、Aβ+SFN组、Aβ+SB203580组。使用RT-qPCR检测U87细胞中IL-6及TNF‑α mRNA水平,采用ELISA检测细胞上清液中IL-6及TNF-α水平,Western blotting检测各组U87细胞蛋白中p-p38、p-p65和GFAP蛋白表达水平;U87与SH-SY5Y共培养后提取SH-SY5Y蛋白,使用Western blotting检测SH-SY5Y细胞蛋白中Bax蛋白表达水平。星形胶质细胞和原代细神经元培养及鉴定。以不同浓度Aβ42和SFN对星形胶质细胞作用48 h后使用CCK-8试剂盒检测各组细胞活性。星形胶质细胞和原代细神经元共培养后,检测神经元细胞活性。 结果 CCK-8结果显示,与溶媒对照组相比,1.25 μmol/L浓度Aβ42导致U87细胞活力增加(P<0.05),≥5 μmol/L浓度活力降低(P<0.05)。SFN在0~5 μmol/L,对U87细胞作用24 h后,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。RT-qPCR、ELISA以及Western blotting结果显示,在U87细胞中,Aβ组与其他3组相比,p-p38、p-p65和GFAP表达升高(P<0.05)、IL-6和TNF‑α mRNA表达升高(P<0.05)及上清中IL-6、TNF-α浓度升高(P<0.001)。在SH-SY5Y细胞中,Aβ组与其他3组相比Bax表达升高(P<0.05)。CCK-8结果显示,与溶媒对照组相比,Aβ42 ≥10 μmol/L浓度的活力降低(P<0.05)。SFN在0~5 μmol/L对星形胶质细胞作用24 h后,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与溶媒对照组、Aβ+SFN组和Aβ+SB203580组相比,Aβ组原代神经元细胞活性降低(P<0.05)。 结论 SFN通过在Aβ42寡聚体激活的U87细胞中下调MAPK/NF-κB信号通路以降低星形胶质细胞介导的SH-SY5Y凋亡。
张淑芬, 黄添容, 杨灿洪, 陈家镒, 吕田明, 张嘉发. 莱菔硫烷通过抑制Aβ42寡聚体激活的U87细胞中MAPK/NF-κB信号通路降低反应性星形胶质细胞介导的SH-SY5Y凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 191-199.
Shufen ZHANG, Tianrong HUANG, Canhong YANG, Jiayi CHEN, Tianming LÜ, Jiafa ZHANG. Sulforaphane reduces reactive astrocyte-mediated neuron apoptosis in vitro by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in Aβ42 oligomer-activated astrocytes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 191-199.
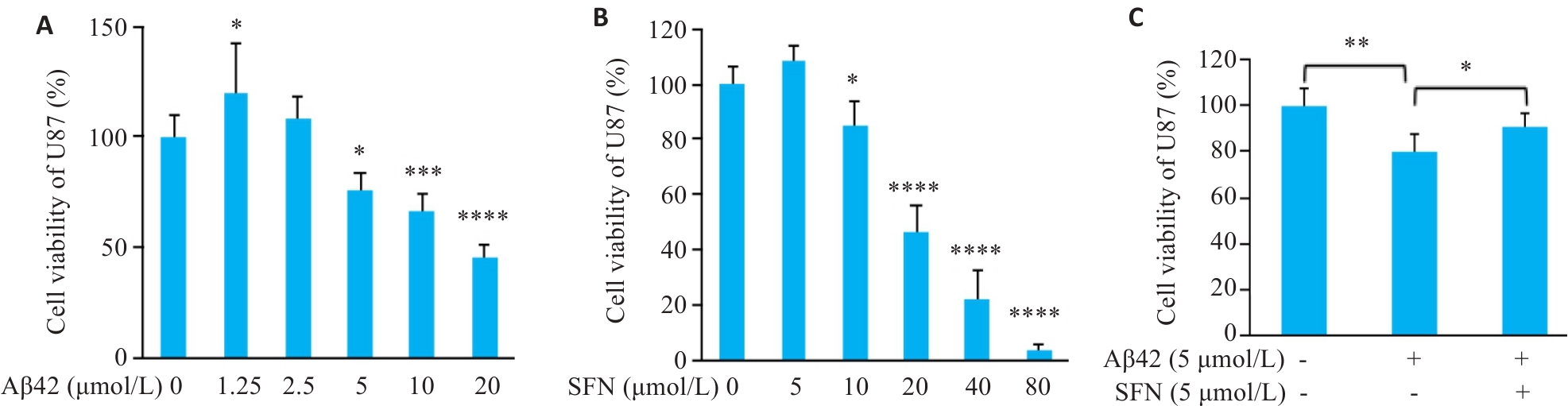
图1 CCK-8法检测Aβ42与SFN对U87细胞活性的影响
Fig.1 CCK-8 assay for assessing viability of U87 cells treated with different concentration of Aβ42, sulforaphane (SFN) and both. A: Viability of U87 cells treated with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 μmol/L Aβ42 for 48 h (*P˂0.05, ***P˂0.001, ****P˂0.0001 vs 0 μmol/L group). B: Viability of U87 cells treated with 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μmol/L SFN for 24 h (*P˂0.05, ****P˂0.0001 vs 0 μmol/L group). C: Viability of U87 cells treated with vehicle, Aβ42 (5 μmol/L), and Aβ42 (5 μmol/L)+SFN (5 μmol/L) (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01).
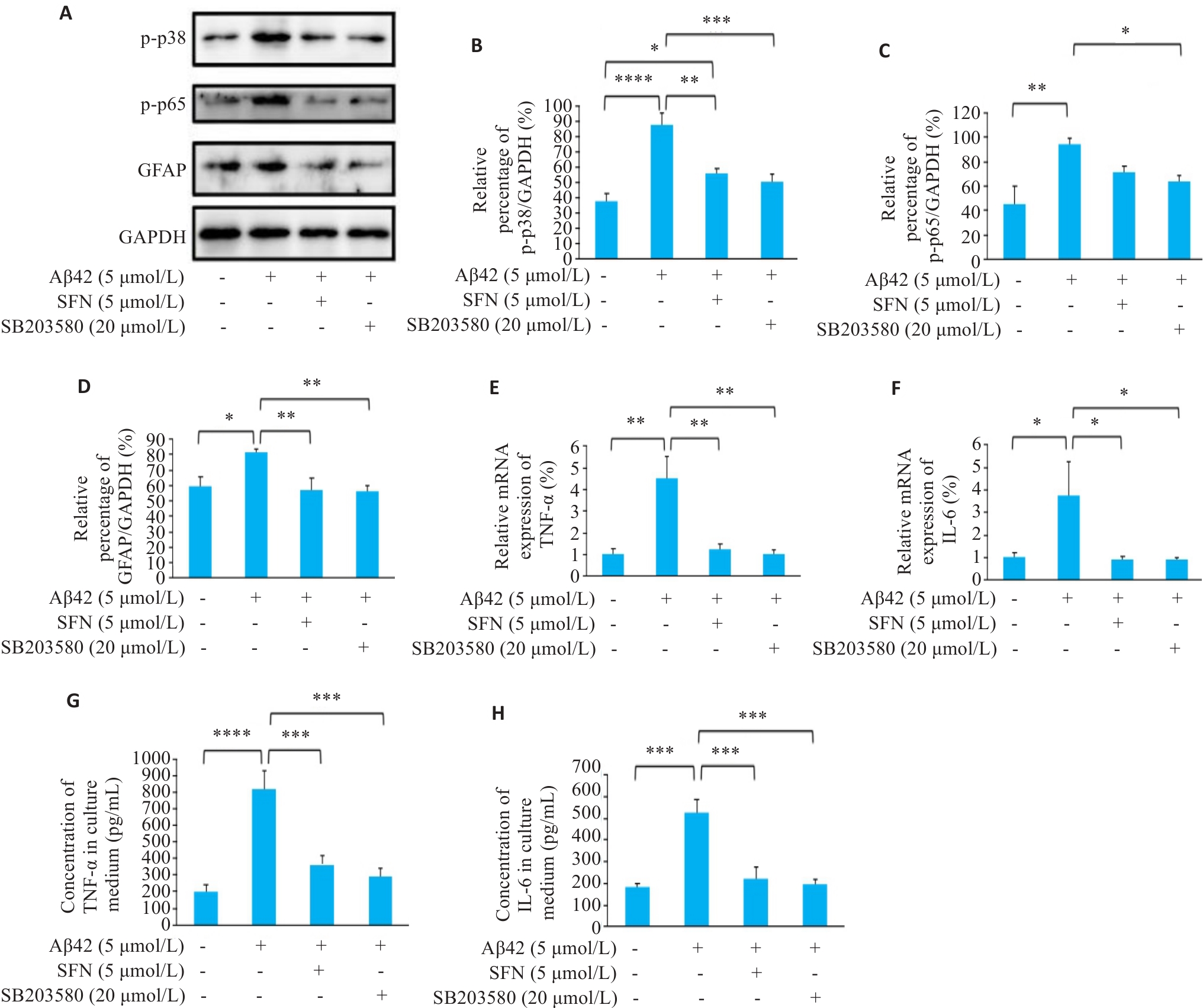
图2 Aβ42、SFN和p38抑制剂SB203580对U87细胞的影响
Fig.2 Effects of Aβ42 (5 μmol/L), SFN (5 μmol/L) and SB203580 (20 μmol/L) on protein expressions of p-p38, p-p65 and GFAP, mRNA expressions of TNF‑α and IL-6, and TNF‑α and IL-6 levels in culture supernatant of U87 cells. A-D: Protein expression levels of p-p38, p-p65 and GFAP in U87 cells treated with vehicle, Aβ42, Aβ42+SFN, and Aβ42+ SB203580 detected by Western blotting (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01, ***P˂0.001, ****P˂0.0001). E, F: Expression levels of TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA in treated U87 cells detected by RT-qPCR (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01). G-H: TNF-α and IL-6 levels in culture supernatant of the treated U87 cells (***P˂0.001, ****P˂0.0001).
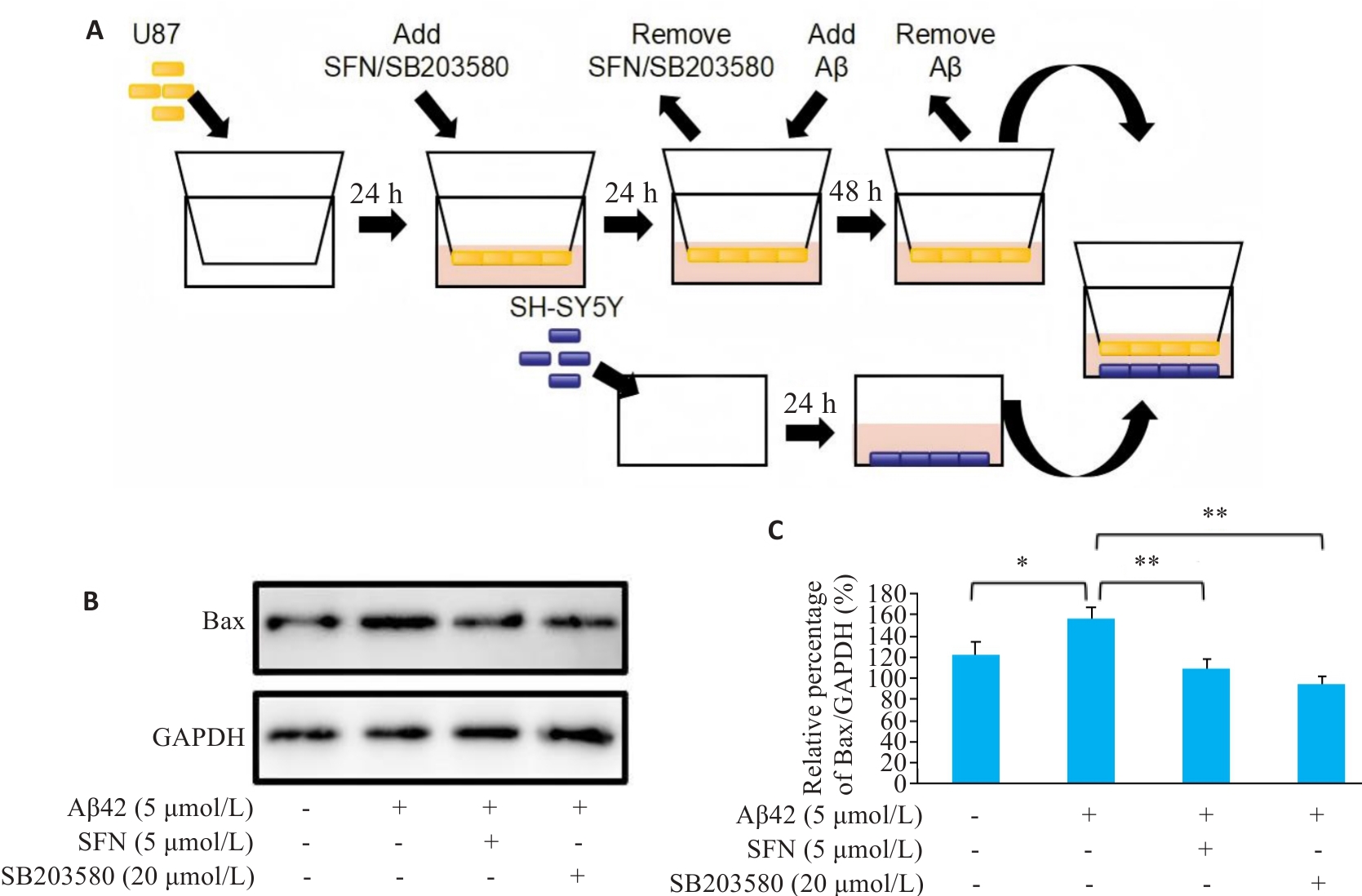
图3 Aβ42、SFN和p38抑制剂SB203580通过U87细胞对SH-SY5Y的间接作用
Fig.3 Indirect effects of Aβ42, SFN and SB203580 treatment of U87 cells on co-cultured SH-SY5Y neurons. A: Transwell co-culture scheme of U87 and SH-SY5Y Cells. B: Protein expression of Bax in SH-SY5Y cells co-cultured with U87 cells treated with vehicle, Aβ42, Aβ42+SFN, and Aβ42+SB203580. C: Quantification of Bax expression levels. *P˂0.05, **P˂0.01.
| Primer | Sequuence (5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-F | CTA GGC CAC AGA ATT GAA AGA TCT |
| GAPDH-R | GTA GGT GGA AAT TCT AGC ATC ATC C |
| TNF-α-F | CTG TGA AGG GAA TGG GTG TT |
| TNF-α-R | CAG GGA AGA ATC TGG AAA GGT C |
| IL-6-F | GAG AGC ATT GGA AGT TGG GG |
| IL-6-R | CTT CCA GCC AGT TGC CTT CT |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primers sequences for qRT-PCR
| Primer | Sequuence (5' to 3') |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-F | CTA GGC CAC AGA ATT GAA AGA TCT |
| GAPDH-R | GTA GGT GGA AAT TCT AGC ATC ATC C |
| TNF-α-F | CTG TGA AGG GAA TGG GTG TT |
| TNF-α-R | CAG GGA AGA ATC TGG AAA GGT C |
| IL-6-F | GAG AGC ATT GGA AGT TGG GG |
| IL-6-R | CTT CCA GCC AGT TGC CTT CT |
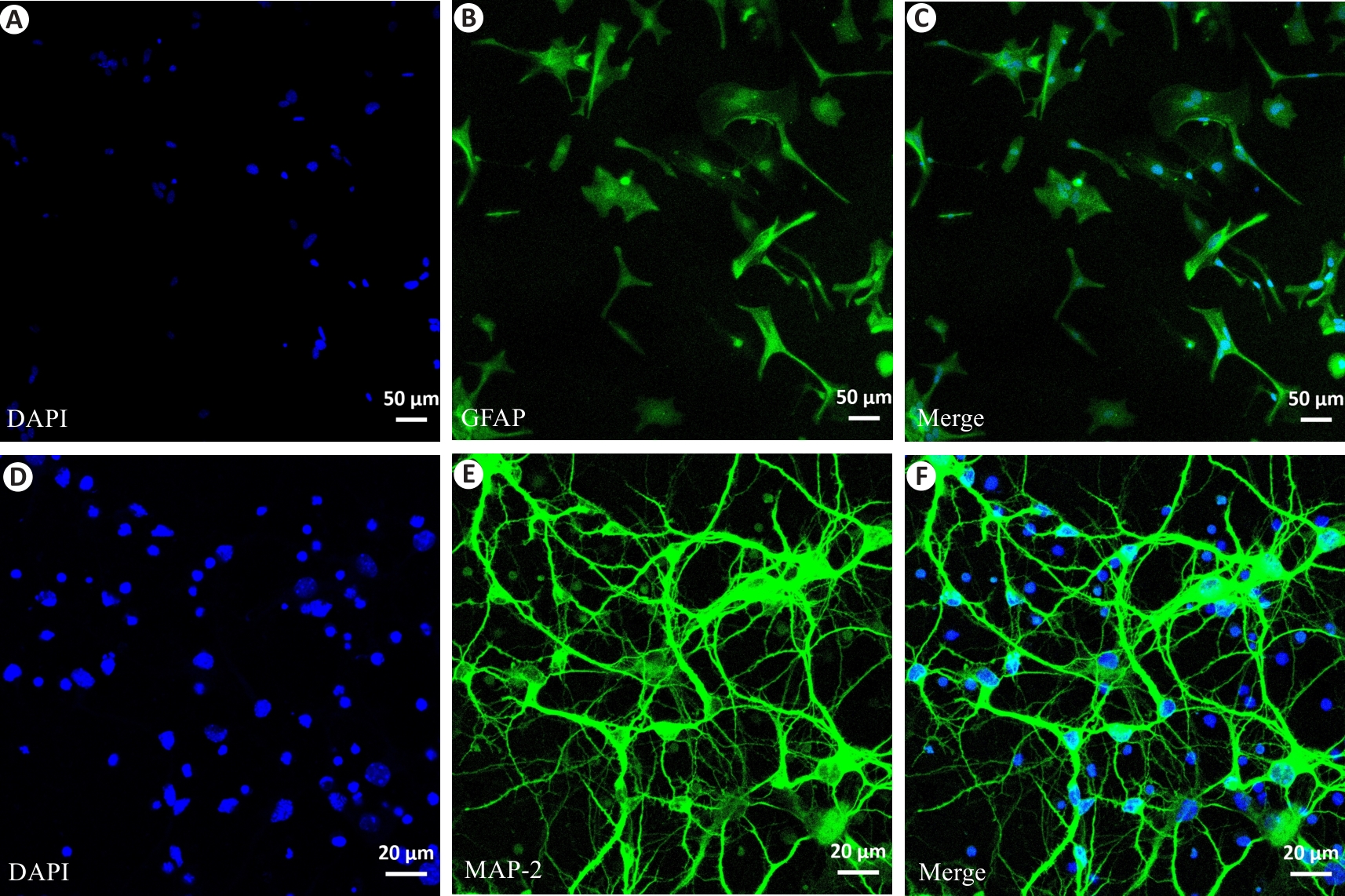
图4 星形胶质细胞和原代神经元细胞纯度鉴定
Fig.4 Purity identification of astrocytes and primary neurons isolated from mouse brain tissues. A-C: Immunofluorescence staining for assessing purity of the astrocytes labeled with GFAP (green). DAPI (blue) was used to label the cell nuclei (Scale bar=50 μm). D-F: Immunofluorescence staining for assessing purity of the primary neurons labeled with MAP-2 (green). DAPI (blue) was used to label the cell nuclei (Scale bar=20 μm).
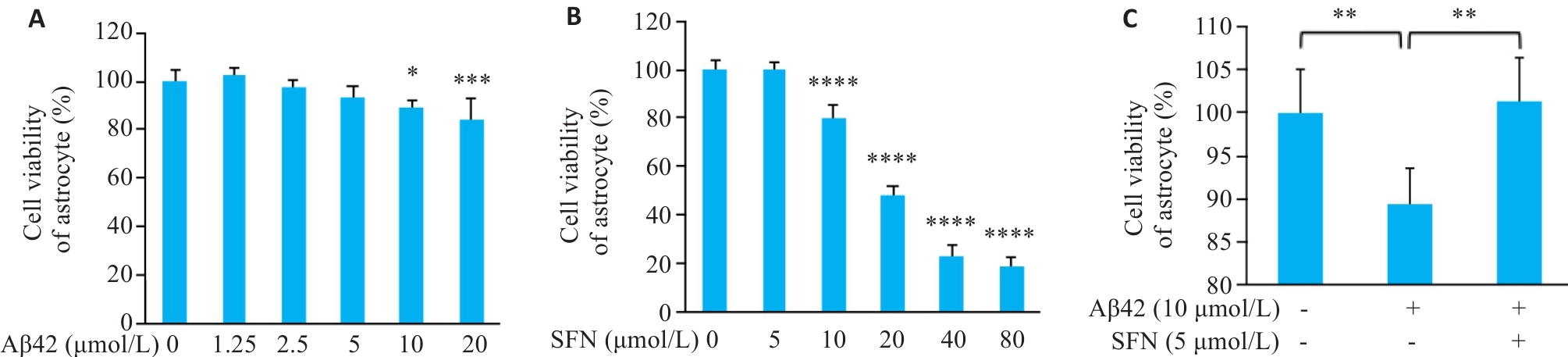
图5 CCK-8法检测Aβ42与SFN对星形胶质细胞活性的影响
Fig.5 CCK-8 assay for assessing the effect of different concentrations of Aβ42, SFN and their combination on viability of isolated mouse astrocytes. A: Viability of mouse astrocytes treated with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 μmol/L Aβ42 for 48 h (*P˂0.05, ***P˂0.001 vs control group). B: Viability of mouse astrocytes treated with 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μmol/L SFN for 24 h (****P˂0.0001 vs control group). C: Viability of mouse astrocytes treated with vehicle, Aβ42 (10 μmol/L), and Aβ42 (10 μmol/L) + SFN (5 μmol/L) (*P˂0.05, **P˂0.01).
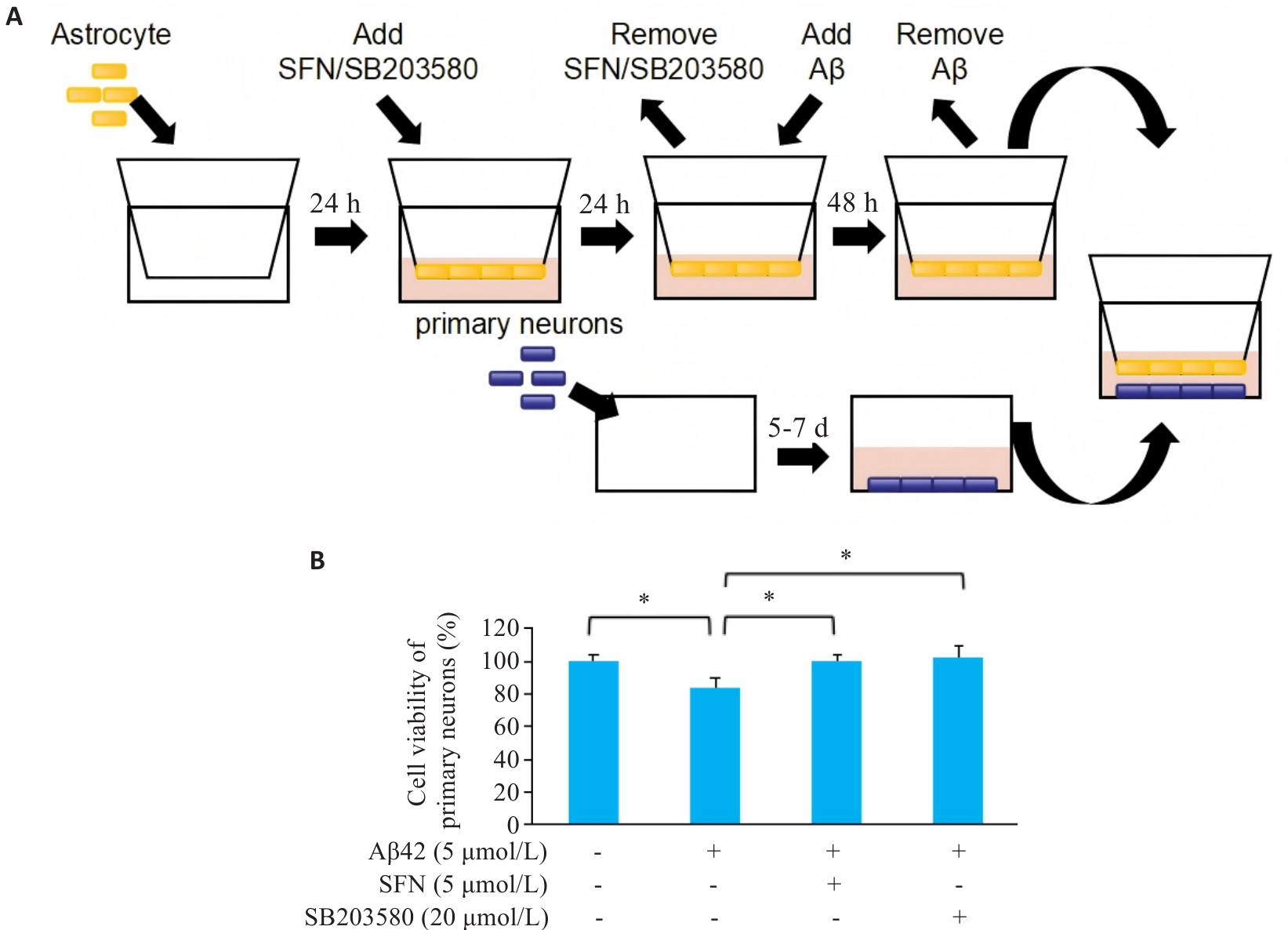
图6 Aβ42、SFN和p38抑制剂SB203580通过星形胶质细胞对原代神经元细胞的间接作用
Fig.6 Indirect effects of Aβ42, SFN and SB203580 treatment of isolated mouse astrocytes on the primary neurons. A: Transwell co-culture scheme for mouse astrocytes and primary neurons. B: Viability of primary neurons co-cultured with mouse astrocytes treated with vehicle, Aβ42 (10 μmol/L), Aβ42 (10 μmol/L)+SFN (5 μmol/L), and Aβ42 (10 μmol/L)+SB203580 (20 μmol/L). *P˂0.05.
| [1] | Ji QQ, Chen JQ, Li YF, et al. Incidence and prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2024, 39(7): 701-14. doi:10.1007/s10654-024-01144-2 |
| [2] | Jorfi M, Maaser-Hecker A, Tanzi RE. The neuroimmune axis of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Genome Med, 2023, 15(1): 6. doi:10.1186/s13073-023-01155-w |
| [3] | Kim J, Lee HJ, Park SK, et al. Donepezil regulates LPS and aβ-stimulated neuroinflammation through MAPK/NLRP3 inflammas ome/STAT3 signaling[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10637. doi:10.3390/ijms221910637 |
| [4] | Qiu S, Palavicini JP, Wang J, et al. Adult-onset CNS myelin sulfatide deficiency is sufficient to cause Alzheimer's disease-like neuroinflam -mation and cognitive impairment[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2021, 16(1): 64. doi:10.1186/s13024-021-00488-7 |
| [5] | Du Z, Li M, Ren J, et al. Current strategies for modulating aβ aggregation with multifunctional agents[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2021, 54(9): 2172-84. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00055 |
| [6] | Ding B, Lin C, Liu Q, et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates neuroinflammation via inhibiting RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro [J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 302. doi:10.1186/s12974-020-01981-4 |
| [7] | Bernabeu-Zornoza A, Coronel R, Palmer C, et al. Oligomeric and fibrillar species of Aβ42 diversely affect human neural stem cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9537. doi:10.3390/ijms22179537 |
| [8] | Calabrese EJ, Kozumbo WJ. The phytoprotective agent sulforaphane prevents inflammatory degenerative diseases and age-related pathologies via Nrf2-mediated hormesis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 163: 105283. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105283 |
| [9] | Kim J. Pre-clinical neuroprotective evidences and plausible mechanisms of sulforaphane in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(6): 2929. doi:10.3390/ijms22062929 |
| [10] | Allen NJ, Lyons DA. Glia as architects of central nervous system formation and function[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6411): 181-5. doi:10.1126/science.aat0473 |
| [11] | Endo F, Kasai A, Soto JS, et al. Molecular basis of astrocyte diversity and morphology across the CNS in health and disease[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6619): eadc9020. doi:10.1126/science.adc9020 |
| [12] | Yu X, Nagai J, Khakh BS. Improved tools to study astrocytes[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2020, 21(3): 121-38. doi:10.1038/s41583-020-0264-8 |
| [13] | Nagai J, Yu X, Papouin T, et al. Behaviorally consequential astrocytic regulation of neural circuits[J]. Neuron, 2021, 109(4): 576-96. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2020.12.008 |
| [14] | Lee HG, Wheeler MA, Quintana FJ. Function and therapeutic value of astrocytes in neurological diseases[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2022, 21(5): 339-58. doi:10.1038/s41573-022-00390-x |
| [15] | Jung E, Koh SH, Yoo M, et al. Regenerative potential of carbon monoxide in adult neural circuits of the central nervous system[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(7): E2273. doi:10.3390/ijms21072273 |
| [16] | Qin SS, Yang CH, Huang WH, et al. Sulforaphane attenuates microglia-mediated neuronal necroptosis through down-regulation of MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in LPS-activated BV-2 microglia[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2018, 133: 218-35. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.01.014 |
| [17] | Wang H, Ma J, Tan Y, et al. Amyloid-beta1-42 induces reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagic cell death in U87 and SH-SY5Y cells[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2010, 21(2): 597-610. doi:10.3233/jad-2010-091207 |
| [18] | Lopez-Suarez L, Al Awabdh S, Coumoul X, et al. The SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line, a relevant in vitro cell model for investigating neurotoxicology in human: Focus on organic pollutants[J]. NeuroToxicology, 2022, 92: 131-55. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2022.07.008 |
| [19] | Ozbolat G, Alizade A. Investigation of the protective effect of thymoquinone of U87 cells induced by beta-amyloid[J]. Bratisl Lek Listy, 2021, 122(10): 748-52. doi:10.4149/bll_2021_120 |
| [20] | Pandey M, Karmakar V, Majie A, et al. The SH-SY5Y cell line: a valuable tool for Parkinson's disease drug discovery[J]. Expert Opin Drug Discov, 2024, 19(3): 303-16. doi:10.1080/17460441.2023.2293158 |
| [21] | Saeed Y, Xie B, Xu J, et al. Glial U87 cells protect neuronal SH-SY5Y cells from indirect effect of radiation by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin: Shanghai, 2015, 47(4): 250-7. doi:10.1093/abbs/gmv004 |
| [22] | Fu Y, Zhang J, Yang C, et al. Effects of solvent dimethyl sulfoxide invites a rethink of its application in amyloid beta cytotoxicity[J]. Int J Toxicol, 2025, 44(4): 297-313. doi:10.1177/10915818251338235 |
| [23] | Liu T, Guo WH, Gong M, et al. Pericyte loss: a key factor inducing brain Aβ40 accumulation and neuronal degeneration in cerebral amyloid angiopathy[J]. Exp Brain Res, 2025, 243(8): 191. doi:10.1007/s00221-025-07134-4 |
| [24] | White JA, Manelli AM, Holmberg KH, et al. Differential effects of oligomeric and fibrillar amyloid-β1-42 on astrocyte-mediated inflammation[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2005, 18(3): 459-65. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2004.12.013 |
| [25] | Kim S, Chun H, Kim Y, et al. Astrocytic autophagy plasticity modulates Aβ clearance and cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2024, 19(1): 55. doi:10.1186/s13024-024-00740-w |
| [26] | Huo SM, Li B, Du JY, et al. Dibutyl phthalate induces liver fibrosis via p38MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2023, 897: 165500. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.165500 |
| [27] | Kim KM, Yoo GD, Heo W, et al. TAZ stimulates exercise-induced muscle satellite cell activation via Pard3-p38 MAPK-TAZ signalling axis[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2023, 14(6): 2733-46. doi:10.1002/jcsm.13348 |
| [28] | Dey P, Biswas S, Das R, et al. p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 enhances anticancer activity of PARP inhibitor olaparib in a synergistic way on non-small cell lung carcinoma A549 cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2023, 670: 55-62. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.05.116 |
| [29] | Bahattab S, Assiri A, Alhaidan Y, et al. Pharmacological p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 enhances AML stem cell line KG1a chemosensitivity to daunorubicin by promoting late apoptosis, cell growth arrest in S-phase, and miR-328-3p upregulation[J]. Saudi Pharm J, 2024, 32(6): 102055. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102055 |
| [30] | Santoro A, Martucci M, Conte M, et al. Inflammaging, hormesis and the rationale for anti-aging strategies[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2020, 64: 101142. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2020.101142 |
| [31] | Balusu S, De Strooper B. The necroptosis cell death pathway drives neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2024, 147(1): 96. doi:10.1007/s00401-024-02747-5 |
| [32] | Lou S, Gong D, Yang M, et al. Curcumin improves neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease mice via the upregulation of Wnt/β-catenin and BDNF[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(10): 5123. doi:10.3390/ijms25105123 |
| [33] | Huang JH, Xu ZW, Yu CS, et al. The volatile oil of Acorus tatarinowii Schott ameliorates Alzheimer's disease through improving insulin resistance via activating the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 135: 156168. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156168 |
| [34] | Li Q, Yuan Y, Huang S, et al. Excess ub-K48 induces neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Integr Neurosci, 2024, 23(12): 223. doi:10.31083/j.jin2312223 |
| [1] | 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 牛民主, 黄菊, 耿志军, 李静, 胡建国. 茯苓新酸A通过调节AMPK/mTOR介导的自噬来减轻葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 131-140. |
| [2] | 赵锦燕, 彭娇, 林明和, 朱晓勤, 黄彬, 林久茂. 清解扶正颗粒通过抑制线粒体依赖的凋亡、激活AMPK-PGC-1α通路缓解5-氟尿嘧啶引起的骨骼肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 94-103. |
| [3] | 王莹, 李静, 王伊迪, 华明钰, 胡玮彬, 张晓智. 原发性肝癌患者的临床结局与治疗反应预测模型:基于失巢凋亡和免疫基因[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [4] | 陈丹丹, 任乾千, 吕梦林, 张宝文, 刘醒然, 张蒙, 王阳, 寇现娟. 天麻钩藤饮通过抑制坏死性凋亡通路改善帕金森病小鼠的运动功能障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1571-1580. |
| [5] | 汤忠富, 黄传兵, 李明, 程丽丽, 陈君洁, 尚双双, 刘思娣. 芪黄健脾滋肾颗粒通过抑制MyD88/NF-κB通路减轻MRL/lpr小鼠肾损害[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1625-1632. |
| [6] | 常笑语, 张瀚文, 曹红亭, 侯玲, 孟鑫, 陶虹, 罗彦, 李光华. 热应激对大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞生物钟基因 Bmal1和细胞周期蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [7] | 范正媛, 沈子涵, 李亚, 沈婷婷, 李高峰, 李素云. 补肺益肾方对香烟烟雾提取物诱导的人支气管上皮细胞损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1372-1379. |
| [8] | 唐东宁, 康赟赟, 何文杰, 夏青. 针康结合促进C57/BL6J小鼠脑缺血后星形胶质细胞转分化为神经元[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1434-1441. |
| [9] | 夏冰, 彭进, 丁九阳, 王杰, 唐国伟, 刘国杰, 王沄, 万昌武, 乐翠云. ATF3通过NF-κB信号通路调控动脉粥样硬化斑块内的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [10] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [11] | 杨毓甲, 杨丽芳, 吴雅玲, 段兆达, 于春泽, 吴春云, 于建云, 杨力. 大麻二酚经PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP通路减轻多重脑震荡大鼠的神经元内质网应激和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [12] | 梁晓涛, 熊一凡, 刘雪琪, 梁小珊, 朱晓煜, 谢炜. 活血疏风颗粒通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路改善慢性偏头痛小鼠的中枢敏化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [13] | 杨洋, 王凯, 柳鉴修, 周志谟, 贾雯, 吴思谋, 李金星, 何方, 程如越. 生命早期两歧双歧杆菌BD-1干预可缓解注意缺陷多动障碍雌性大鼠幼年期的多动行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 702-710. |
| [14] | 郭舒婷, 曹福羊, 郭永馨, 李言响, 郝新宇, 张倬宁, 周志康, 仝黎, 曹江北. 激活下丘脑背内侧核区星形胶质细胞可加速七氟醚麻醉小鼠觉醒[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 751-759. |
| [15] | 陈悦, 肖林雨, 任侣, 宋雪, 李静, 胡建国. 水晶兰苷通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路减少神经元凋亡改善脊髓损伤后小鼠的运动功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||