南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1434-1441.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.09
收稿日期:2024-11-29
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
夏青
E-mail:tangldn@outlook.com;xiaqingcho@163.com
作者简介:唐东宁,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: tangldn@outlook.com
基金资助:
Dongning TANG1( ), Yunyun KANG1, Wenjie HE3, Qing XIA1,2(
), Yunyun KANG1, Wenjie HE3, Qing XIA1,2( )
)
Received:2024-11-29
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Qing XIA
E-mail:tangldn@outlook.com;xiaqingcho@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨针康结合对脑缺血后星形胶质细胞转分化为神经元的作用。 方法 将C57/BL6J雄性小鼠注射含有GFAP启动子的腺相关病毒后,采用电凝法制备右侧大脑中动脉缺血(dMCAO)模型。造模后小鼠随机分为模型组(14 d和21 d组)和干预组(14 d和21 d组),6只/组,模型组小鼠不做任何干预,干预组在造模后24 h(1dps)给予电针百会穴及左侧合谷、内关、足三里、阳陵泉穴位,随后置于有跑轮的鼠笼中单笼饲养,每隔24 h记录活动情况。各组小鼠分别于造模后1、14、21 d进行神经功能评分,免疫荧光双重染色观察目标脑区星形胶质细胞的转分化情况。 结果 与模型组相比,针康结合干预后14 d、21 d均可明显改善dMCAO小鼠的神经功能缺损症状(P<0.05)。2/5型腺相关病毒GFAP启动子可特异性标记局部的星形胶质细胞,与14 d模型组相比,针康结合干预14 d后腺相关病毒与神经元标志物DCX的共标阳性细胞数量增加(P<0.05),与21 d模型组相比,针康结合干预21 d后腺相关病毒与神经元标志物NeuN的共标阳性细胞数量增加(P<0.05)。 结论 针康结合可促进脑缺血局部的星形胶质细胞转分化为神经元,且转分化效率与MCAO小鼠运动功能改善情况呈正相关。
唐东宁, 康赟赟, 何文杰, 夏青. 针康结合促进C57/BL6J小鼠脑缺血后星形胶质细胞转分化为神经元[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1434-1441.
Dongning TANG, Yunyun KANG, Wenjie HE, Qing XIA. Electroacupuncture combined with rehabilitation training improves neurological function of mice with cerebral ischemia by promoting astrocyte transdifferentiation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1434-1441.
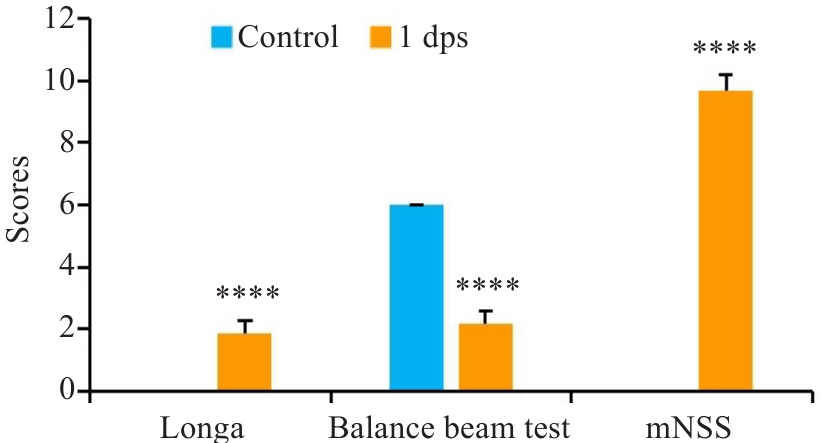
图1 dMCAO小鼠造模24 h后神经功能缺损情况
Fig.1 Neurological deficit scores of the mice 24 h after distal middle cerebral artery occlusion (dMCAO). ****P<0.0001 vs corresponding control groups.
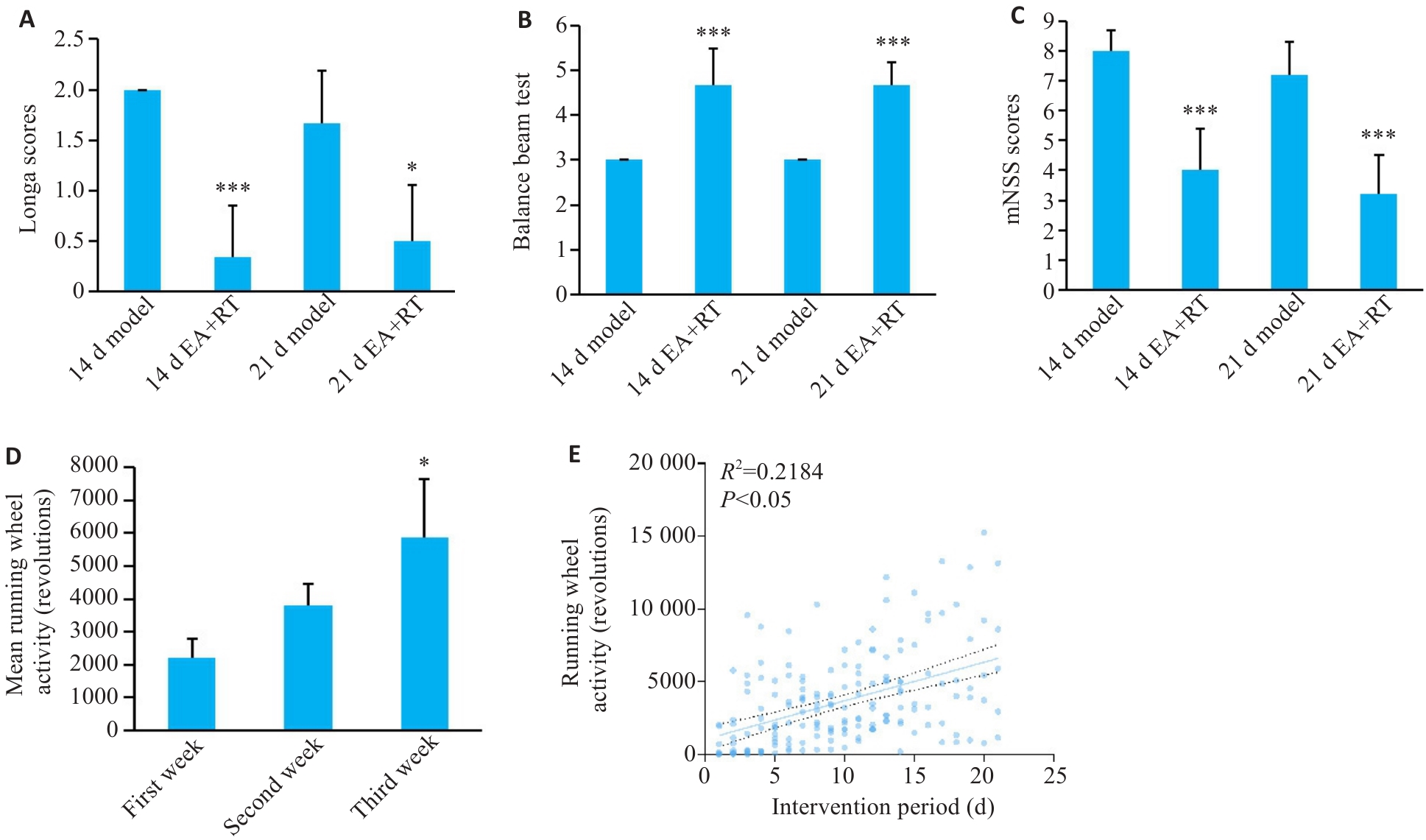
图2 针康结合对dMCAO小鼠运动功能改善情况
Fig.2 Effect of electroacupuncture and rehabilitation training on motor function improvement in dMCAO mice. A-C: Neurological deficit scores of mice in each group (*P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs corresponding model groups). D, E: Mouse activity and its correlation with the intervention period (*P<0.05 vs First Week).
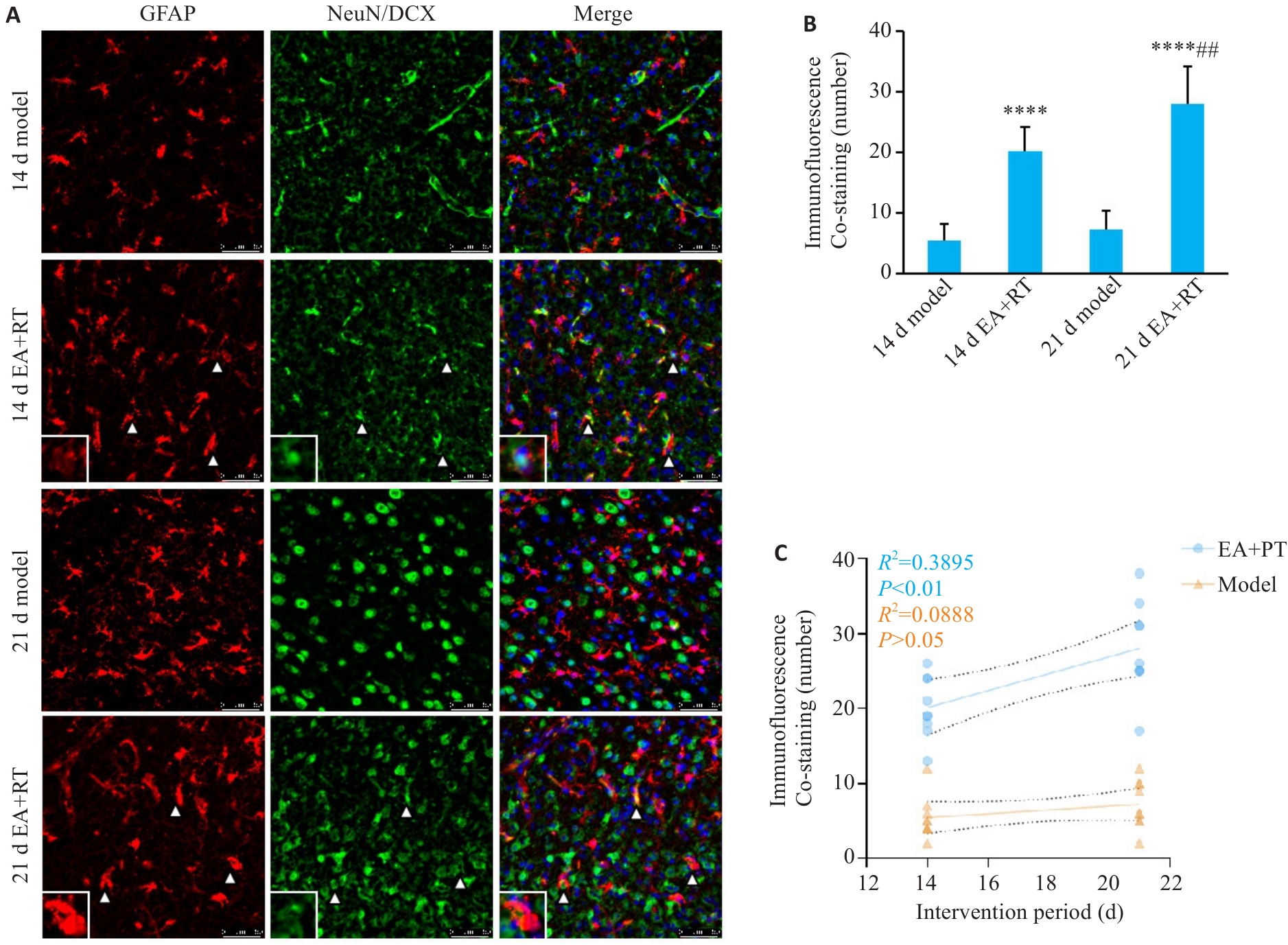
图4 腺病毒与DCX/NeuN共染情况
Fig.4 Detection of the co-localization of adenovirus with newly generated or mature neurons using immunofluorescence (scale bar=50 μm) staining for DCX and NeuN (##P<0.01 vs 14 d EA+PT, ****P<0.001 vs corresponding Model groups). A:Morphological expression of newborn neurons;B:Increased number of co-infection of cells;C:Correlation between differentiation rate and intervention time.
| [1] | Shimada IS, LeComte MD, Granger JC, et al. Self-renewal and differentiation of reactive astrocyte-derived neural stem/progenitor cells isolated from the cortical peri-infarct area after stroke[J]. J Neurosci, 2012, 32(23): 7926-40. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.4303-11.2012 |
| [2] | Hasel P, Liddelow SA. Astrocytes[J]. Curr Biol, 2021, 31(7): R326-7. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2021.01.056 |
| [3] | Filous AR, Silver J. "Targeting astrocytes in CNS injury and disease: a translational research approach"[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2016, 144: 173-87. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.03.009 |
| [4] | Okada S, Hara M, Kobayakawa K, et al. Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury[J]. Neurosci Res, 2018, 126: 39-43. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2017.10.004 |
| [5] | Magnusson JP, Göritz C, Tatarishvili J, et al. A latent neurogenic program in astrocytes regulated by Notch signaling in the mouse[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6206): 237-41. doi:10.1126/science.346.6206.237 |
| [6] | Gong SQ, Shao H, Cai XY, et al. Astrocyte-derived neuronal transdifferentiation as a therapy for ischemic stroke: advances and challenges[J]. Brain Sci, 2022, 12(9): 1175. doi:10.3390/brainsci12091175 |
| [7] | Guo ZY, Zhang L, Wu Z, et al. In vivo direct reprogramming of reactive glial cells into functional neurons after brain injury and in an Alzheimer's disease model[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 14(2): 188-202. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2013.12.001 |
| [8] | 谢小文. 电针治疗联合康复训练在缺血性脑卒中患者步行功能恢复中的应用研究[J]. 中国医学创新, 2024, 21(26): 123-7. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2024.26.028 |
| [9] | Shen Y, Hu LP, Ge J, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture treatment combined with rehabilitation care on serum sirt3 level and motor function in elderly patients with stroke hemiparesis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2023, 102(15): e33403. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000033403 |
| [10] | 张文彬, 陈媛丽. 本体感觉训练联合透刺电针疗法治疗脑卒中后偏身肢体麻木的效果及对平衡功能的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2024, 9(25): 138-42. |
| [11] | 黄 茂, 唐雨涵, 刘青松. 电针阳明经联合康复训练治疗脑卒中中后期躯体功能障碍的临床观察[J]. 实用医院临床杂志, 2024, 21(2): 87-9. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2024.02.019 |
| [12] | Zhang JY, Zhu LW, Tang Q. Electroacupuncture with rehabilitation training for limb spasticity reduction in post-stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Top Stroke Rehabil, 2021, 28(5): 340-61. doi:10.1080/10749357.2020.1812938 |
| [13] | 刘 娇, 冯晓东. 电针百会、神庭穴配合康复训练治疗脑卒中后认知障碍临床研究[J]. 中医学报, 2013, 28(4): 608-10. |
| [14] | 苏凯奇, 吕 转, 吴明莉, 等. 电针后留针联合认知训练治疗脑卒中后认知功能障碍: 多中心随机对照试验[J]. 中国针灸, 2023, 43(11): 1221-5. |
| [15] | 康赟赟, 唐东宁, 张 健, 等. 电凝法制作C57/BL6J小鼠局灶性脑缺血模型的评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 100-7. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.01.12 |
| [16] | Dong H W. Allen reference atlas: a digital color brain atlas of the C57Black/6J male mouse[M]. Hoboken, N.J: Wiley, 2008. doi:10.1354/vp.45-5-724-a |
| [17] | 中国针灸学会. 实验动物常用穴位名称与定位第3部分: 小鼠[J]. 针刺研究, 2021, 46(5): 445-6. |
| [18] | Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, et al. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination[J]. Stroke, 1986, 17(3): 472-6. doi:10.1161/01.STR.17.3.472 |
| [19] | Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats[J]. Stroke, 2001, 32(11): 2682-8. doi:10.1161/hs1101.098367 |
| [20] | Gharbawie OA, Gonzalez CLR, Whishaw IQ. Skilled reaching impairments from the lateral frontal cortex component of middle cerebral artery stroke: a qualitative and quantitative comparison to focal motor cortex lesions in rats[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2005, 156(1): 125-37. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2004.05.015 |
| [21] | 孙妍玉, 吴 晋. 神经网络重塑促进脑卒中后功能修复的研究进展[J]. 南京医科大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 43(4): 577-81. doi:10.7655/NYDXBNS20230419 |
| [22] | Wang C, Liu H, Li K, et al. Tactile modulation of memory and anxiety requires dentate granule cells along the dorsoventral axis[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 6045. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19874-8 |
| [23] | 林嘉滢, 涂舒婷, 林嘉莉, 等. 不同年龄脑卒中患者躯体感觉功能与运动功能相关性及全周期康复思考: 一项多中心横断面研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(23): 2838-45. doi:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0791 |
| [24] | 王东军, 郑 煜, 贺 民, 等. 腺病毒介导绿色荧光蛋白转染神经干细胞的实验研究[J]. 军医进修学院学报, 2007, 28(5): 330-2. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-1139.2007.05.004 |
| [25] | 付 勇, 龚树生, 刘英鹏, 等. 大鼠胚胎神经干细胞分离培养及基因感染研究[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2007, 15(5): 379-82, 386, 425. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2007.05.016 |
| [26] | Aschauer DF, Kreuz S, Rumpel S. Analysis of transduction efficiency, tropism and axonal transport of AAV serotypes 1, 2, 5, 6, 8 and 9 in the mouse brain[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e76310. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076310 |
| [27] | Ceanga M, Keiner S, Grünewald B, et al. Stroke accelerates and uncouples intrinsic and synaptic excitability maturation of mouse hippocampal DCX+ adult-born granule cells[J]. J Neurosci, 2019, 39(9): 1755-66. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3303-17.2018 |
| [28] | 郑 薏, 柳维林, 上官豪, 等. 针灸治疗脑卒中患者肢体运动功能障碍疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2016, 31(2): 217-21. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2016.02.020 |
| [29] | 岳增辉, 李 良, 常小荣, 等. 电针与手针治疗脑卒中痉挛性瘫痪效应差异研究[J]. 中国针灸, 2012, 32(7): 582-6. |
| [30] | 田 亮, 杜小正, 王金海, 等. 手针与电针治疗急性缺血性脑卒中偏瘫的对比研究[J]. 中国针灸, 2016, 36(11): 1121-5. doi:10.13703/j.0255-2930.2016.11.001 |
| [31] | 石学敏. “醒脑开窍” 针刺法治疗脑卒中[J]. 中国临床康复, 2003, 7(7): 1057-8. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1673-8225.2003.07.001 |
| [32] | 朱 丹, 白洁静, 张晓庆, 等. 电针参数定量化的研究进展[J]. 中国针灸, 2015, 35(5): 525-8. doi:10.13703/j.0255-2930.2015.05.032 |
| [33] | 张 莺, 韩德雄, 刘 喆, 等. 基于数据挖掘的脑缺血机制研究中电针参数应用规律分析[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2017, 35(3): 554-7. |
| [34] | Chang QY, Lin YW, Hsieh CL. Acupuncture and neuroregeneration in ischemic stroke[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2018, 13(4): 573-83. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.230272 |
| [35] | Robison LS, Popescu DL, Anderson ME, et al. The effects of volume versus intensity of long-term voluntary exercise on physiology and behavior in C57/Bl6 mice[J]. Physiol Behav, 2018, 194: 218-32. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.06.002 |
| [36] | Yanagita S, Amemiya S, Suzuki S, et al. Effects of spontaneous and forced running on activation of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons in rats[J]. Life Sci, 2007, 80(4): 356-63. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2006.09.027 |
| [37] | Garland T Jr, Schutz H, Chappell MA, et al. The biological control of voluntary exercise, spontaneous physical activity and daily energy expenditure in relation to obesity: human and rodent perspectives[J]. J Exp Biol, 2011, 214(Pt 2): 206-29. doi:10.1242/jeb.048397 |
| [38] | Lee DH, Cao D, Moon Y, et al. Enhancement of motor functional recovery in thoracic spinal cord injury: voluntary wheel running versus forced treadmill exercise[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2025, 20(3): 836-44. doi:10.4103/nrr.nrr-d-23-01585 |
| [39] | Manzanares G, Brito-da-Silva G, Gandra PG. Voluntary wheel running: patterns and physiological effects in mice[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2018, 52(1): e7830. doi:10.1590/1414-431x20187830 |
| [40] | Alamri FF, Al Shoyaib A, Syeara N, et al. Delayed atomoxetine or fluoxetine treatment coupled with limited voluntary running promotes motor recovery in mice after ischemic stroke[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2021, 16(7): 1244-51. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.301031 |
| [41] | Huajuan T, Xuemei C, Chenghui N, et al. Regulation of transcription factors in astrocyte-to-neuron transdifferentiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Neuromedicine, 2018, 17(10): 1059-1062. |
| [42] | Xu L, Xiang Z Q, Guo Y W, et al. Enhancing NeuroD1 Expression to Convert Lineage-Traced Astrocytes into Neurons[A]. 2022. |
| [43] | 铁金杉, 刘 垚, 陈绍春. 星形胶质细胞-神经元转化体内诱导研究进展[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2021, 42(3): 140-4. doi:10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210333 |
| [44] | 曾 鹏, 花秋红, 石昌杰, 等. 小鼠不同脑区星形胶质细胞小分子诱导转分化和基因表达差异的研究[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2020, 42(9): 1551-9. doi:10.11844/cjcb.2020.09.0006 |
| [45] | Lu JF, Bradley RA, Zhang SC. Turning reactive Glia into functional neurons in the brain[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 14(2): 133-4. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2014.01.010 |
| [46] | Talifu Z, Zhang CJ, Xu X, et al. Neuronal repair after spinal cord injury by in vivo astrocyte reprogramming mediated by the overexpression of NeuroD1 and Neurogenin-2[J]. Biol Res, 2024, 57(1): 53. doi:10.1186/s40659-024-00534-w |
| [47] | Tan ZJ, Qin SY, Yuan YM, et al. NOTCH1 signaling regulates the latent neurogenic program in adult reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(10): 4548-63. doi:10.7150/thno.71378 |
| [48] | Imayoshi I, Kageyama R. bHLH factors in self-renewal, multipotency, and fate choice of neural progenitor cells[J]. Neuron, 2014, 82(1): 9-23. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.03.018 |
| [49] | Puls B, Ding Y, Zhang FY, et al. Regeneration of functional neurons after spinal cord injury via in situ NeuroD1-mediated astrocyte-to-neuron conversion[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 591883. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.591883 |
| [50] | Livingston JM, Lee TT, Enbar T, et al. Ectopic expression of Neurod1 is sufficient for functional recovery following a sensory-motor cortical stroke[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(3): 663. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12030663 |
| [51] | Li YQ, Li PF, Tao Q, et al. Role and limitation of cell therapy in treating neurological diseases[J]. Ibrain, 2024, 10(1): 93-105. doi:10.1002/ibra.12152 |
| [52] | Li WL, Mandeville ET, Durán-Laforet V, et al. Endothelial cells regulate astrocyte to neural progenitor cell trans-differentiation in a mouse model of stroke[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 7812. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-35498-6 |
| [1] | 张安邦, 孙秀颀, 庞博, 吴远华, 时靖宇, 张宁, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过调节肠道-大脑轴及Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [2] | 浦延鹏, 王震, 储浩然. 眼针疗法通过上调METTL3介导的m6A甲基化修饰促进脑皮层血管新生进而改善脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠的神经功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 921-928. |
| [3] | 郭舒婷, 曹福羊, 郭永馨, 李言响, 郝新宇, 张倬宁, 周志康, 仝黎, 曹江北. 激活下丘脑背内侧核区星形胶质细胞可加速七氟醚麻醉小鼠觉醒[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 751-759. |
| [4] | 黄鹏伟, 陈洁, 邹金虎, 高雪锋, 曹虹. 槲皮素促进应激颗粒G3BP1解聚改善HIV-1 gp120诱导的星形胶质细胞神经毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 304-312. |
| [5] | 李丽, 汪梦哲, 刘赛赛, 张小楠, 陈洁, 陶伟婷, 李晒, 秦志文, 陶泉坊, 刘奕, 黄丽, 赵士弟. 大豆异黄酮通过抑制 Wnt/Ca2+信号通路减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注引起的钙超载[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1048-1058. |
| [6] | 陈洁, 刘晨旭, 王春, 李丽, 陶伟婷, 徐婧茹, 唐红辉, 黄丽. 外源性瘦素通过上调星形胶质细胞GLT-1和GLAST的表达减轻小鼠脑缺血再灌注引起的谷氨酸兴奋毒性损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1079-1087. |
| [7] | 满 豪, 王建伟, 吴 毛, 邵 阳, 杨俊锋, 李绍烁, 吕锦业, 周 悦. 脊髓康通过激活星形胶质细胞的YAP/PKM2信号轴促进脊髓损伤大鼠神经功能的恢复[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 636-643. |
| [8] | 刘昊铭, 林子诗, 叶 靖. CaMKIIγ和CaMKIIδ通过 PI3K/Akt/Erk 信号通路减轻小鼠神经元缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 563-570. |
| [9] | 康赟赟, 唐东宁, 张 健, 夏 青. 电凝法制作C57/BL6J小鼠局灶性脑缺血模型的评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 100-107. |
| [10] | 孙 伟, 陈 平, 唐小杭, 谷颖敏, 田雪松. 改良的四血管间断阻塞法制作大鼠全脑缺血再灌注损伤模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1194-1203. |
| [11] | 陈 兴, 王开万, 储德海, 朱 羽, 张文兵, 曹慧萍, 谢文宇, 鲁传豪, 李 侠. 连翘酯苷B抑制小鼠脑缺血/再灌注引起的氧化应激损伤:基于激活AMPK/DAF-16/FOXO3通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 199-205. |
| [12] | 李 晒, 李 丽, 闵思敏, 刘赛赛, 秦志文, 熊志尚, 徐建国, 王博文, 丁渡山, 赵士弟. 大豆异黄酮可减轻大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤:基于抑制铁死亡及炎症级联反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 323-330. |
| [13] | 曹天然, 刘青芳, 潘美民, 张雪红. LncRNA SNHG8通过抑制miR-494-3p表达减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2015-2022. |
| [14] | 王 静, 陈雪祎, 孙 丽, 陈雪梅, 李 慧, 熊彬睿, 王海华. 长链非编码RNA ZEB1-AS1通过HMGB1/TLR-4信号轴加剧大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1134-1142. |
| [15] | 文 君, 朱慧敏, 李雪梅, 黄家贵, 陈 月, 杨 琴. 抑制Sonic Hedgehog信号能抑制脑缺血性损伤后纤维瘢痕形成且不利于神经功能恢复[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 840-848. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||