南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1353-1362.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.01
• • 下一篇
常笑语1( ), 张瀚文2(
), 张瀚文2( ), 曹红亭2, 侯玲2, 孟鑫1, 陶虹2, 罗彦3(
), 曹红亭2, 侯玲2, 孟鑫1, 陶虹2, 罗彦3( ), 李光华1,2(
), 李光华1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-21
接受日期:2025-04-25
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-17
通讯作者:
罗彦,李光华
E-mail:xiaoxyyu@163.com;1912118742@qq.com;wyzxsh@hotmail.com;ghlee0404@163.com
作者简介:常笑语,博士,E-mail: xiaoxyyu@163.com基金资助:
Xiaoyu CHANG1( ), Hanwen ZHANG2(
), Hanwen ZHANG2( ), Hongting CAO2, Ling HOU2, Xin MENG1, Hong TAO2, Yan LUO3(
), Hongting CAO2, Ling HOU2, Xin MENG1, Hong TAO2, Yan LUO3( ), Guanghua LI1,2(
), Guanghua LI1,2( )
)
Received:2024-06-21
Accepted:2025-04-25
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Yan LUO, Guanghua LI
E-mail:xiaoxyyu@163.com;1912118742@qq.com;wyzxsh@hotmail.com;ghlee0404@163.com
About author:First author contact:CHANG Xiaoyu and ZHANG Hanwen contributed equally to this work
Supported by:摘要:
目的 研究热应激条件下大鼠胸主动脉结构的变化以及胸主动脉内皮细胞Bmal1和周期蛋白表达水平的变化。 方法 选取20只雄性SD大鼠,随机分为对照组和热应激组(各10只),用HE染色法观察胸主动脉的组织病理学变化,免疫组化法检测胸主动脉中Bmal1的表达。体外实验采用大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞(RTAECs),分为对照组、阴性对照组、阴性热暴露组、热暴露组(HS)、Bmal1干扰(si-Bmal1)组和 si-Bmal1+HS 组。体内和体外实验均采用 Western blotting检测 Bmal1、细胞周期蛋白 CDK1、CDK4、CDK6 和 cyclin B1 以及凋亡相关蛋白 Bax和Bcl-2 的表达。TUNEL法检测胸主动脉中的细胞凋亡,流式细胞术检测RTAECs的细胞周期分布和凋亡水平变化。 结果 与对照组相比,热应激组大鼠血压升高,心率减慢,胸主动脉出现弹力纤维断裂,Bmal1、cyclin B1 和 CDK1 表达增加。体外结果显示,与对照组相比,热应激组 RTAECs 中 Bmal1、cyclin B1 和 CDK1 蛋白表达水平升高;si-Bmal1转染逆转了热应激引起的细胞周期蛋白表达改变并抑制热应激诱导的细胞凋亡,表现为 Bax 表达降低和 Bcl-2 表达升高(P<0.05)。 结论 热应激上调大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞中生物钟基因Bmal1和细胞周期蛋白的表达,最终引发细胞凋亡。抑制Bmal1的表达可逆转热应激诱导的大鼠胸主动脉上皮细胞损伤,并在一定程度上缓解热应激引起的细胞周期变化。
常笑语, 张瀚文, 曹红亭, 侯玲, 孟鑫, 陶虹, 罗彦, 李光华. 热应激对大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞生物钟基因 Bmal1和细胞周期蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362.
Xiaoyu CHANG, Hanwen ZHANG, Hongting CAO, Ling HOU, Xin MENG, Hong TAO, Yan LUO, Guanghua LI. Heat stress affects expression levels of circadian clock gene Bmal1 and cyclins in rat thoracic aortic endothelial cells[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362.
| Gene | Sequence (5'-3') | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Bmal1 | 108 | |
| Forward | ACCCATACACAGAAGCAAACTACA | |
| Reverse | GGTCACATCCTACGACAAACAAA | |
| 140 | ||
| Forward | CCTAGACTTCGAGCAAGAGA | |
| Reverse | GGAAGGAAGGCTGGAAGA |
Tab.1 Primer sequences and the expected product sizes
| Gene | Sequence (5'-3') | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Bmal1 | 108 | |
| Forward | ACCCATACACAGAAGCAAACTACA | |
| Reverse | GGTCACATCCTACGACAAACAAA | |
| 140 | ||
| Forward | CCTAGACTTCGAGCAAGAGA | |
| Reverse | GGAAGGAAGGCTGGAAGA |
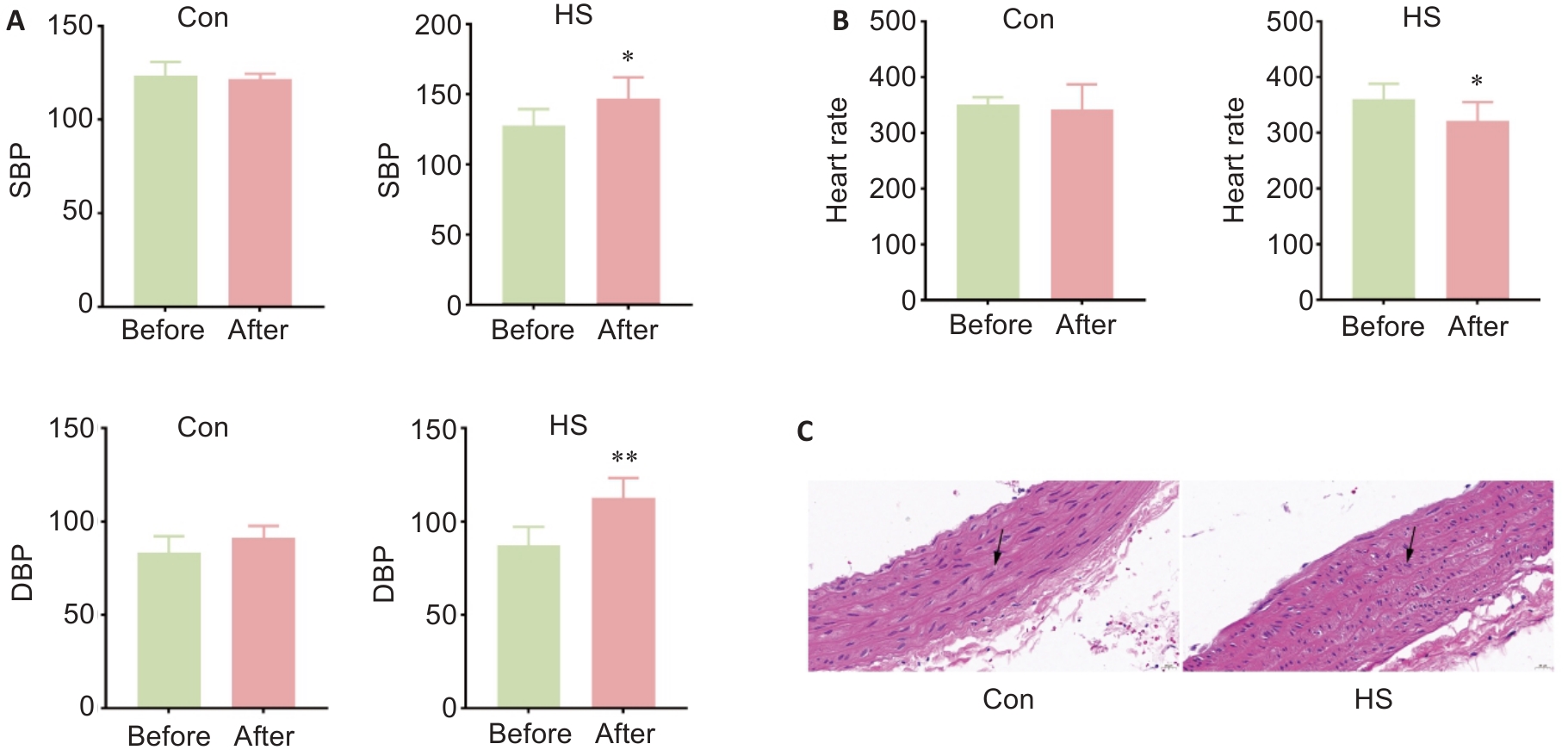
Fig.1 Effect of heat stress on blood pressure, heart rate and structure of the thoracic aorta in rats. A: Blood pressure of the rats before and after heat stress. B: Heart rate of the rats before and after heat stress. C: HE staining of the thoracic aorta of the rats (Original magnification:×40). Data are presented as Mean±SD from 8 independent measurements. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs control (Con). SBP: Systolic blood pressure; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; HS: Heat stress.
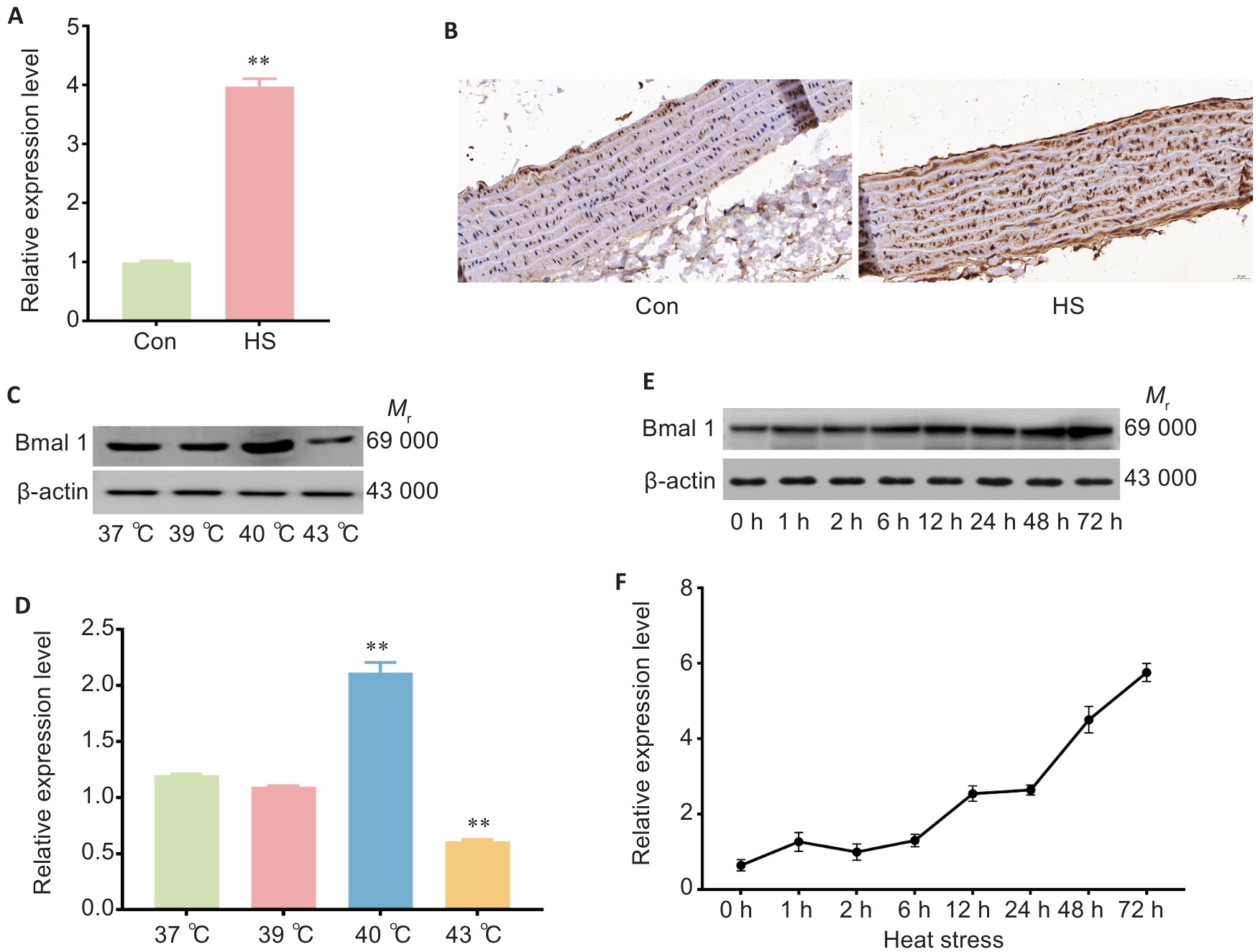
Fig.2 Heat stress increases Bmal1 expression in rat thoracic aorta and rat thoracic aortic endothelial cells (RTAECs). A: Bmal1 mRNA expression levels of in rat thoracic aorta. B: Immunohistochemical detection of Bmal1 protein in rat thoracic aorta (×40). C, D: Western blotting and quantitative analysis of Bmal1 protein expression in RTAECs with heat stress at different temperatures. E, F: Western blotting and quantitative analysis of Bmal1 protein expression in RTAECs with heat stress of different lengths. Data are presented as Mean±SD from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Con.
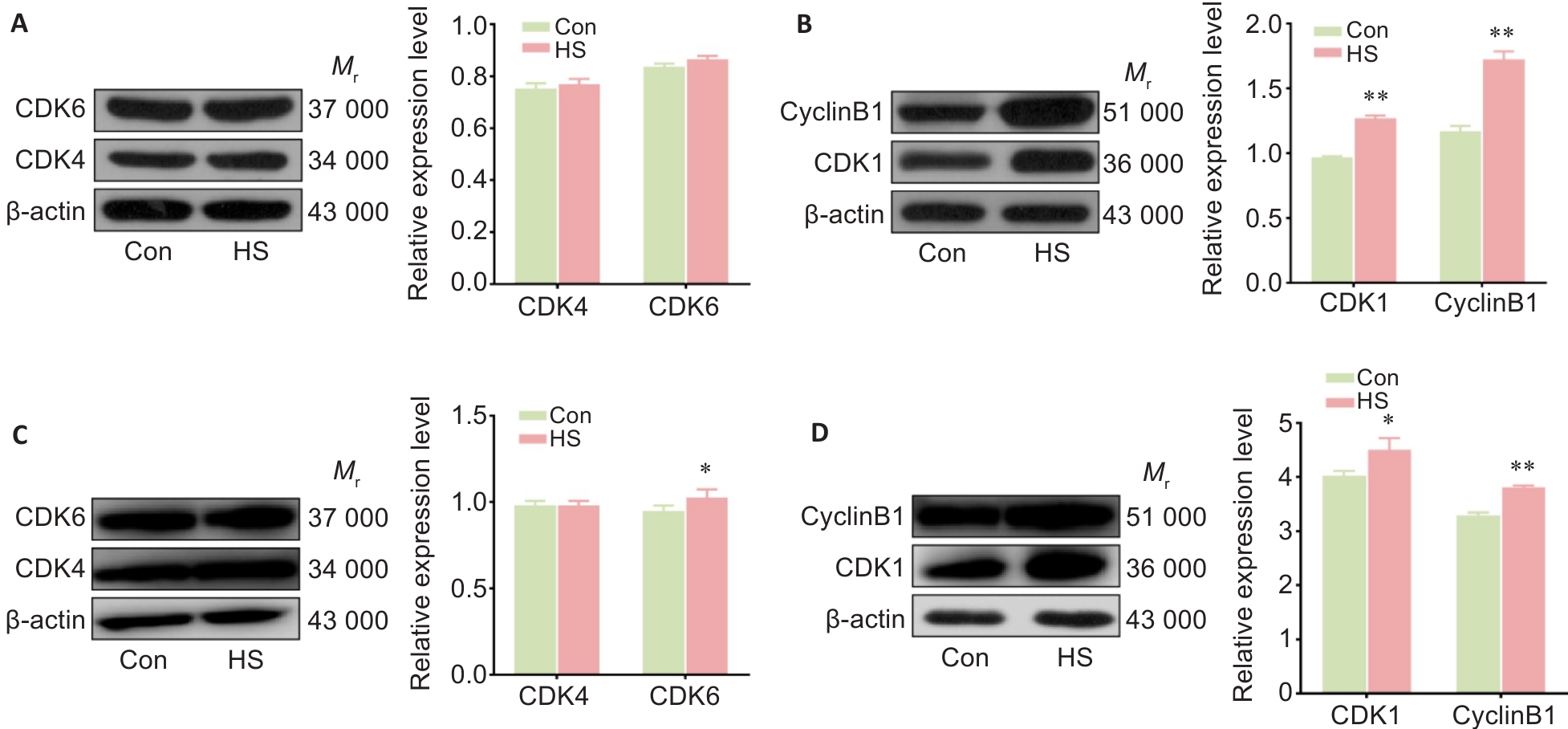
Fig.3 Heat stress causes changes in cyclin expression and cell cycle progression in rat thoracic aorta and RTAECs. A, B: Western blotting for detecting the expressions of CDK4, CDK6, cyclin B1 and CDK1 proteins in rat thoracic aorta. C, D: Western blotting for detecting CDK4, CDK6, cyclin B1 and CDK1 proteins in RTAECs. Data are presented as Mean±SD from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Con.
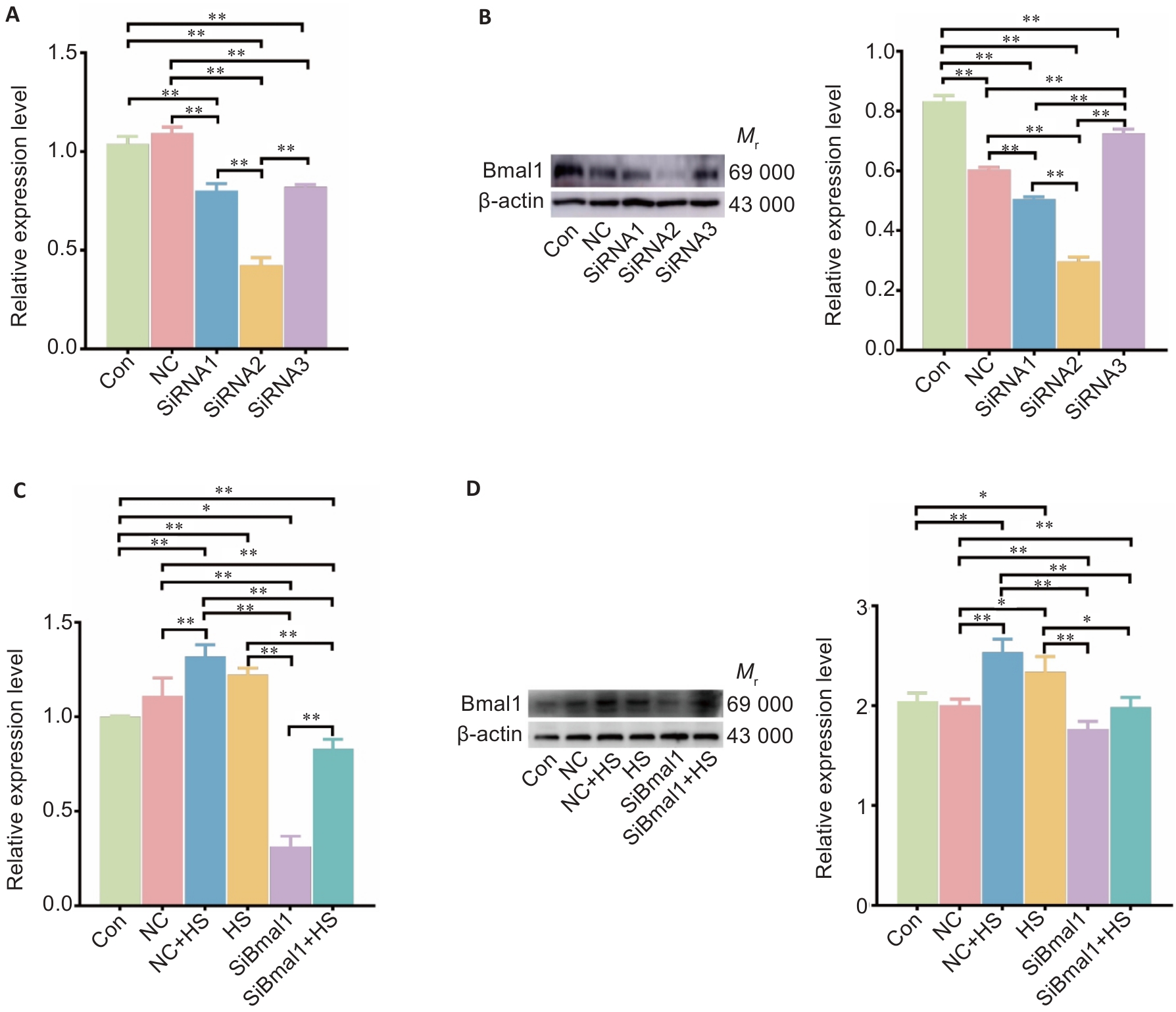
Fig.4 Efficiency of the siRNA constructs for Bmal1 knockdown and effect of siRNA2 on mRNA and protein Bmal1 expressions in RTAECs. A: Bmal1 mRNA expression levels in RTAECs transfected with different si-Bmal1 constructs. B: Western blotting for detecting Bmal1 protein expressions in the transfected cells. C: Bmal1 mRNA expression levels in RTAECs with heat stress, transfection with si-Bmal1, or both. D: Western blotting for detecting Bmal1 protein expression in different treatment groups. Data are presented as Mean±SD from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. NC: Negative control.
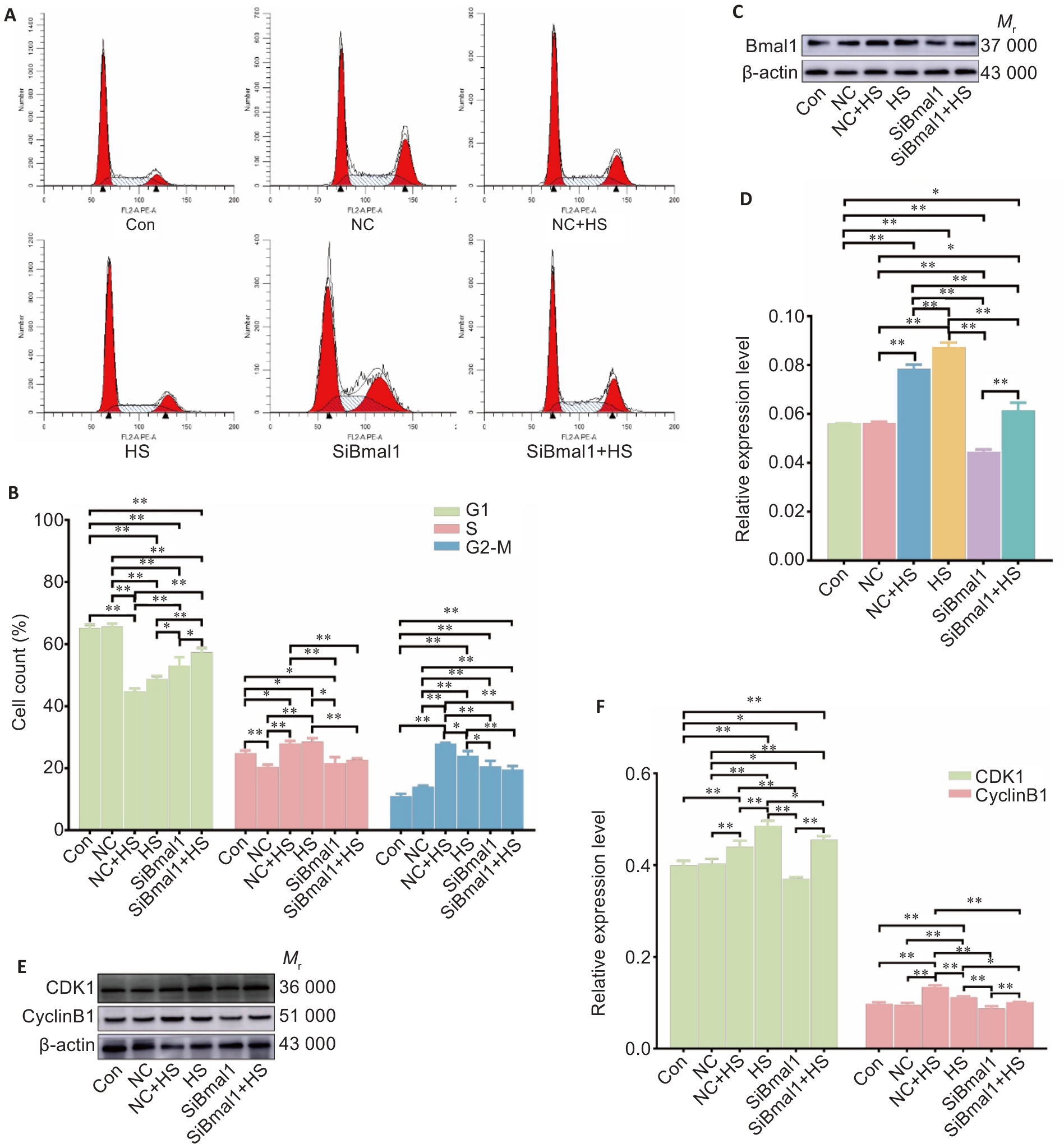
Fig.5 Bmal1 knockdown reverses heat stress-induced changes in cyclin expression and cell cycle in RTAECs. A, B: Cell cycle distribution in treated RTAECs. C-F: Western blotting for detecting CDK6, CDK1 and cyclin B1 protein expressions in the treated cells. Data are presented as Mean±SD from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
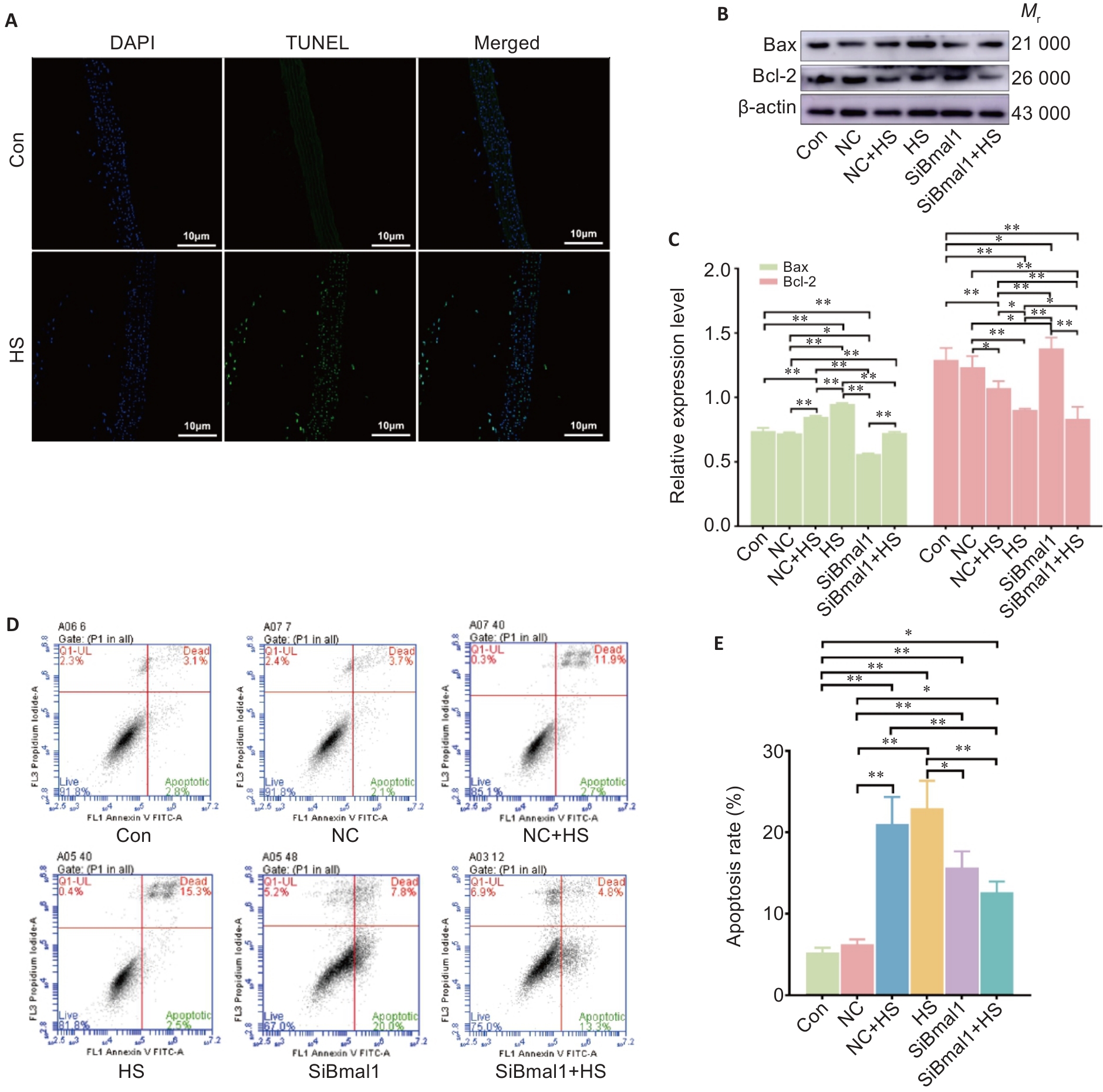
Fig.6 Bmal1 knockdown suppresses heat stress-induced apoptosis in RTAECs. A: TUNEL assay for assessing apoptosis in rat thoracic aorta. B, C: Western blotting for detecting Bax and Bcl-2 protein expressions in RTAECs. D, E: Flow cytometric analysis of apoptosis of RTAECs in different groups. Data are presented as Mean±SD from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
| [1] | Liu J, Varghese BM, Hansen A, et al. Heat exposure and cardiovascular health outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Lancet Planet Health, 2022, 6(6): e484-95. doi:10.1016/s2542-5196(22)00117-6 |
| [2] | Tang LP, Li WH, Liu YL, et al. Heat stress aggravates intestinal inflammation through TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway in Ma chickens infected with Escherichia coli O157:H7 [J]. Poult Sci, 2021, 100(5): 101030. doi:10.1016/j.psj.2021.101030 |
| [3] | Stern N, Sowers JR, McGinty D, et al. Circadian rhythm of plasma renin activity in older normal and essential hypertensive men: relation with inactive renin, aldosterone, cortisol and REM sleep[J]. J Hypertens, 1986, 4(5): 543-50. doi:10.1097/00004872-198610000-00005 |
| [4] | Minamisawa M, Izawa A, Motoki H, et al. Prognostic significance of neuroadrenergic dysfunction for cardiovascular events in patients with acute myocardial infarction [J]. Circ J, 2015, 79(10): 2238-2245. doi:10.1253/circj.cj-15-0265 |
| [5] | Welz PS, Zinna VM, Symeonidi A, et al. BMAL1-driven tissue clocks respond independently to light to maintain homeostasis[J]. Cell, 2019, 177(6): 1436-47. e12. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.009 |
| [6] | Xie M, Tang Q, Nie J, et al. BMAL1-downregulation aggravates Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced atherosclerosis by encouraging oxidative stress [J]. Circ Res, 2020, 126(6): e15-29. doi:10.1161/circresaha.119.315502 |
| [7] | Takeda N, Maemura K. Circadian clock and vascular disease [J]. Hypertens Res, 2010, 33(7): 645-51. doi:10.1038/hr.2010.68 |
| [8] | Elliott WJ. Circadian variation in the timing of stroke onset: a meta-analysis [J]. Stroke, 1998, 29(5): 992-6. doi:10.1161/01.str.29.5.992 |
| [9] | Cannon CP, McCabe CH, Stone PH, et al. Circadian variation in the onset of unstable angina and non-Q-wave acute myocardial infarction (the TIMI III Registry and TIMI IIIB) [J]. Am J Cardiol, 1997, 79(3): 253-8. doi:10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00743-1 |
| [10] | Liu L, Michowski W, Kolodziejczyk A, et al. The cell cycle in stem cell proliferation, pluripotency and differentiation [J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2019, 21(9): 1060-7. doi:10.1038/s41556-019-0384-4 |
| [11] | Tokunaga Y, Otsuyama KI, Hayashida N. Cell cycle regulation by heat shock transcription factors [J]. Cells, 2022, 11(2): 203. doi:10.3390/cells11020203 |
| [12] | Rotinen M. "Defining the independence of the liver circadian clock" & "BMAL1-driven tissue clocks respond independently to light to maintain homeostasis" [J]. Front Neurosci, 2020, 14: 107. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.00107 |
| [13] | Gallego M, Virshup DM. Post-translational modifications regulate the ticking of the circadian clock [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 8(2): 139-48. doi:10.1038/nrm2106 |
| [14] | Stojkovic K, Wing SS, Cermakian N. A central role for ubiquitination within a circadian clock protein modification code [J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2014, 7: 69. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2014.00069 |
| [15] | Trott AJ, Menet JS. Regulation of circadian clock transcriptional output by CLOCK:BMAL1 [J]. PLoS Genet, 2018, 14(1): e1007156. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1007156 |
| [16] | Balsalobre A, Damiola F, Schibler U. A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells [J]. Cell, 1998, 93(6): 929-37. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81199-x |
| [17] | Maemura K, Layne MD, Watanabe M, et al. Molecular mechanisms of morning onset of myocardial infarction [J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2001, 947: 398-402. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03972.x |
| [18] | McNamara P, Seo SB, Rudic RD, et al. Regulation of CLOCK and MOP4 by nuclear hormone receptors in the vasculature: a humoral mechanism to reset a peripheral clock [J]. Cell, 2001, 105(7): 877-89. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00401-9 |
| [19] | Nonaka H, Emoto N, Ikeda K, et al. Angiotensin II induces circadian gene expression of clock genes in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Circulation, 2001, 104(15):1746-8. doi:10.1161/hc4001.098048 |
| [20] | Bray MS, Young ME. Diurnal variations in myocardial metabolism [J]. Cardiovasc. Res., 2008, 79(2): 228-37. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvn054 |
| [21] | Deng W, Zhu S, Zeng L, et al. The circadian clock controls immune checkpoint pathway in sepsis [J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 24(2):366-78. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.026 |
| [22] | Young ME, Brewer RA, Peliciari-Garcia RA, et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific BMAL1 plays critical roles in metabolism, signaling, and maintenance of contractile function of the heart [J]. J Biol Rhythms, 2014, 29(4): 257-76. doi:10.1177/0748730414543141 |
| [23] | Morris CJ, Purvis TE, Hu K, et al. Circadian misalignment increases cardiovascular disease risk factors in humans [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016, 113(10):E1402-11. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516953113 |
| [24] | Anea CB, Zhang M, Stepp DW, et al. Vascular disease in mice with a dysfunctional circadian clock [J]. Circulation, 2009, 119(11): 1510-7. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.108.827477 |
| [25] | Kovanen L, Donner K, Kaunisto M, et al. CRY1, CRY2 and PRKCDBP genetic variants in metabolic syndrome [J]. Hypertens Res, 2015, 38(3): 186-92. doi:10.1038/hr.2014.157 |
| [26] | Anea CB, Ali MI, Osmond JM, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 dysfunction underlie vascular stiffness in circadian clock mutant mice [J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2010, 30(12): 2535-43. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.110.214379 |
| [27] | Pan X, Bradfield CA, Hussain MM. Global and hepatocyte-specific ablation of Bmal1 induces hyperlipidaemia and enhances atherosclerosis [J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 13011. doi:10.1038/ncomms13011 |
| [28] | Hsu PY, Harmer SL. Wheels within wheels: the plant circadian system [J]. Trends Plant Sci, 2014, 19(4): 240-9. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2013.11.007 |
| [29] | Wenden B, Kozma-Bognár L, Edwards KD, et al. Light inputs shape the Arabidopsis circadian system [J]. Plant J, 2011, 66(3): 480-91. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313x.2011.04505.x |
| [30] | Ki Y, Ri H, Lee H, et al. Warming up your tick-tock: temperature-dependent regulation of circadian clocks [J]. Neuroscientist, 2015, 21(5): 503-18. doi:10.1177/1073858415577083 |
| [31] | Mwimba M, Karapetyan S, Liu L, et al. Daily humidity oscillation regulates the circadian clock to influence plant physiology [J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 4290. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-06692-2 |
| [32] | Buhr ED, Yoo SH, Takahashi JS. Temperature as a universal resetting cue for mammalian circadian oscillators [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6002): 379-85. doi:10.1126/science.1195262 |
| [33] | Terman JS, Remé CE, Terman M. Rod outer segment disk shedding in rats with lesions of the suprachiasmatic nucleus [J]. Brain Res, 1993, 605(2): 256-64. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(93)91748-h |
| [34] | Collis SJ, Boulton SJ. Emerging links between the biological clock and the DNA damage response [J]. Chromosoma, 2007, 116(4): 331-9. doi:10.1007/s00412-007-0108-6 |
| [35] | Gavet O, Pines J. Progressive activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 coordinates entry to mitosis [J]. Dev Cell, 2010, 18(4): 533-43. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.02.013 |
| [36] | Fung TK, Poon RY. A roller coaster ride with the mitotic cyclins [J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2005, 16(3): 335-42. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2005.02.014 |
| [37] | Pagano M, Pepperkok R, Verde F, et al. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle [J]. EMBO J, 1992, 11(3): 961-71. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x |
| [38] | Schrader LA, Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM, Hogenesch JB, et al. Circadian disruption, clock genes, and metabolic health [J]. J Clin Invest, 2024, 134(14): e170998. doi:10.1172/jci170998 |
| [39] | Moravčík R, Olejárová S, Zlacká J, et al. Effect of miR-34a on the expression of clock and clock-controlled genes in DLD1 and Lovo human cancer cells with different backgrounds with respect to p53 functionality and 17β-estradiol-mediated regulation [J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(10): e0292880. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0292880 |
| [40] | Farshadi E, Yan J, Leclere P, et al. The positive circadian regulators CLOCK and BMAL1 control G2/M cell cycle transition through Cyclin B1 [J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(1): 16-33. doi:10.1080/15384101.2018.1558638 |
| [41] | Maemura K, de la Monte SM, Chin MT, et al. CLIF, a novel cycle-like factor, regulates the circadian oscillation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression [J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(47): 36847-51. doi:10.1074/jbc.c000629200 |
| [42] | 常笑语, 朱玲勤, 张瀚文, 等.热暴露对大鼠心脏与肝脏组织细胞凋亡及钟基因Bmal1的影响 [J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2022, 44(5): 433-7. 450. doi:10.16050/j.cnki.issn1674-6309.2022.05.001 |
| [1] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [2] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [3] | 从小凡, 陈腾, 李硕, 王媛媛, 周龙云, 李小龙, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 双氢青蒿素通过促进活性氧的产生增强鼻咽癌细胞对顺铂诱导凋亡的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1553-1560. |
| [4] | 王元国, 张鹏. 铁死亡抑制基因在食管癌中的高表达分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [5] | 任志军, 刁建新, 王奕婷. 芎归汤通过抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌凋亡减轻小鼠心梗后心衰引起的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1416-1424. |
| [6] | 陈桂玲, 廖晓凤, 孙鹏涛, 岑欢, 舒盛春, 李碧晶, 黎金华. 澳洲茄碱通过调控Bcl-2/Bax/caspase-3信号通路促进非小细胞肺癌发生凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1109-1116. |
| [7] | 王飞霞, 张政, 孙艳, 杨柳菁, 郭桐彤, 潘夜厅, 丁嵩涛, 蒋林, 刘含登. Bmal1可能介导了丁酸钠对帕金森病小鼠的神经保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 876-884. |
| [8] | 王沁智, 宋冰, 郝诗睿, 肖志远, 金连辉, 郑通, 柴芳. 基于生物信息学分析CCND2在甲状腺乳头状癌中的表达及其对免疫浸润的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 981-988. |
| [9] | 孙秀颀, 蔡静, 张安邦, 庞博, 陈春艳, 查琪琪, 全菲, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过抑制NF-kB/NLRP3信号通路介导炎症和凋亡改善大鼠脑卒中后痉挛[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| [10] | 邱建国, 邱一桐, 李国荣, 张林生, 郑雪, 姚泳江, 王熙丹, 黄海阳, 张凤敏, 苏冀彦, 郑学宝, 黄晓其. 黄芩汤通过调控内质网应激减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| [11] | 兰 玉, 王凯风, 蓝智贤, 周何琪, 孙 剑. 脱醇红酒抑制肝细胞癌的发生和发展:基于诱导细胞周期的阻滞和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1297-1305. |
| [12] | 郑庆委, 邵一丹, 郑婉婷, 邹映雪. 蛹虫草代谢产物虫草素抑制舌鳞癌裸鼠移植瘤的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 873-878. |
| [13] | 石文惠, 刘小莲, 张贵明, 叶林萱, 周润华, 李亦蕾, 余 乐. RITA体外选择性抑制BAP1缺失的皮肤黑色素瘤细胞的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 710-717. |
| [14] | 刘 芳, 彭岚竹, 席菁乐. 高表达MYH9通过激活AKT/c-Myc通路抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 527-536. |
| [15] | 吴佳明, 邓忠权, 朱 奕, 窦广健, 李 进, 黄立勇. MicroRNA-431-5p在胃癌组织中低表达:基于线粒体和Bax/Bcl-2/caspase3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 537-543. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||