南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 514-521.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.09
申琳1( ), 宋翠豪1(
), 宋翠豪1( ), 王聪敏2, 高西3, 安俊红4, 李承新1(
), 王聪敏2, 高西3, 安俊红4, 李承新1( ), 梁斌5(
), 梁斌5( ), 李霞6(
), 李霞6( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-16
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
李承新,梁斌,李霞
E-mail:linlinshen1995@126.com;18110026396@163.com;chengxinderm@163.com;echo_lb666@163.com;1648248514@qq.com
作者简介:申 琳,硕士,E-mail: linlinshen1995@126.com基金资助:
Lin SHEN1( ), Cuihao SONG1(
), Cuihao SONG1( ), Congmin WANG2, Xi GAO3, Junhong AN4, Chengxin LI1(
), Congmin WANG2, Xi GAO3, Junhong AN4, Chengxin LI1( ), Bin LIANG5(
), Bin LIANG5( ), Xia LI6(
), Xia LI6( )
)
Received:2024-12-16
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Chengxin LI, Bin LIANG, Xia LI
E-mail:linlinshen1995@126.com;18110026396@163.com;chengxinderm@163.com;echo_lb666@163.com;1648248514@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探索溃疡性结肠炎伴发坏疽性脓皮病患者发生营养不良的风险因素,并建立本类患者营养风险预测模型。 方法 纳入2019~2024年277例溃疡性结肠炎伴坏疽性脓皮病患者为研究对象,根据是否发生营养不良分为不良组(n=185)和良好组(n=92)。比较两组患者一般人口学、生活饮食习惯、疾病相关资料共25项潜在相关因素的差异。采用Lasso回归筛选危险因素,建立列线图模型并验证模型预测性能。 结果 不良组与良好组间性别、年龄、文化程度、BMI指数、居住地、病程、SAS语评分等共21个指标存在差异(P<0.05)。Lasso回归分析发现溃疡性结肠炎病程、溃疡性结肠炎活动度、坏疽性脓皮病病程、合并慢性病数量、SAS评分、睡眠质量6个因素与本类患者营养不良相关性较大。基于上述6个因素建立列线图预测模型,预测该类患者营养不良AUC(95% CI)=0.992(0.984~1.000),对14例患者的应用显示准确率100%。 结论 溃疡性结肠炎病程、结肠炎活动度、坏疽性脓皮病病程、合并慢性病数量、焦虑程度、睡眠质量与溃疡性结肠炎伴发坏疽性脓皮病患者营养不良相关性较大,基于上述6个因素建立列线图预测模型有较高临床应用价值。
申琳, 宋翠豪, 王聪敏, 高西, 安俊红, 李承新, 梁斌, 李霞. 溃疡性结肠炎并发坏疽性脓皮病患者发生营养风险的因素及预测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 514-521.
Lin SHEN, Cuihao SONG, Congmin WANG, Xi GAO, Junhong AN, Chengxin LI, Bin LIANG, Xia LI. Risk factors for malnutrition in ulcerative colitis complicated with pyoderma gangrenosum and construction of a lasso regression-based prediction model[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 514-521.
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 5.988 | 0.014 | ||
| Male | 109 (58.92) | 68 (73.91) | ||
| Female | 76 (41.08) | 24 (26.09) | ||
| Age (year) | 59.63±14.62 | 52.82±13.94 | 3.165 | 0.002 |
| Education level | 6.243 | 0.044 | ||
| Elementary school or below | 99 (53.51) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| High school | 58 (31.35) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| University | 28 (15.14) | 24 (26.01) | ||
| Marital status in the past year | 6.104 | 0.047 | ||
| Unmarried | 16 (8.65) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Divorced/widowed | 34 (18.38) | 10 (10.87) | ||
| In marriage | 135 (72.97) | 79 (85.87) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.80±3.47 | 24.52±2.95 | -10.416 | <0.001 |
| Residential area in the past year | 11.457 | 0.003 | ||
| Rural area | 92 (49.73) | 33 (35.87) | ||
| Town | 37 (20.00) | 12 (13.04) | ||
| Urban area | 56 (30.27) | 47 (51.09) | ||
| Residential partner in the past year | 7.497 | 0.024 | ||
| Live alone | 41 (22.16) | 9 (9.78) | ||
| Friends/relatives | 10 (5.41) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Spouse/children | 134 (72.43) | 80 (86.96) | ||
| Economic pressure in the past year | 25.668 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 30 (16.22) | 39 (42.39) | ||
| General | 67 (36.22) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| Larger | 88 (47.56) | 22 (23.91) |
表1 两组患者一般人口学资料统计比较结果
Tab.1 Comparison of general demographic data between the two groups [Mean±SD, n(%)]
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 5.988 | 0.014 | ||
| Male | 109 (58.92) | 68 (73.91) | ||
| Female | 76 (41.08) | 24 (26.09) | ||
| Age (year) | 59.63±14.62 | 52.82±13.94 | 3.165 | 0.002 |
| Education level | 6.243 | 0.044 | ||
| Elementary school or below | 99 (53.51) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| High school | 58 (31.35) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| University | 28 (15.14) | 24 (26.01) | ||
| Marital status in the past year | 6.104 | 0.047 | ||
| Unmarried | 16 (8.65) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Divorced/widowed | 34 (18.38) | 10 (10.87) | ||
| In marriage | 135 (72.97) | 79 (85.87) | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.80±3.47 | 24.52±2.95 | -10.416 | <0.001 |
| Residential area in the past year | 11.457 | 0.003 | ||
| Rural area | 92 (49.73) | 33 (35.87) | ||
| Town | 37 (20.00) | 12 (13.04) | ||
| Urban area | 56 (30.27) | 47 (51.09) | ||
| Residential partner in the past year | 7.497 | 0.024 | ||
| Live alone | 41 (22.16) | 9 (9.78) | ||
| Friends/relatives | 10 (5.41) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Spouse/children | 134 (72.43) | 80 (86.96) | ||
| Economic pressure in the past year | 25.668 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 30 (16.22) | 39 (42.39) | ||
| General | 67 (36.22) | 31 (33.70) | ||
| Larger | 88 (47.56) | 22 (23.91) |
| Project | unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise frequency in past year | 3.714 | 0.156 | ||
| Less | 43 (23.24) | 16 (17.39) | ||
| General | 81 (43.78) | 35 (38.04) | ||
| Often | 61 (32.98) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Types of food in past year | 26.339 | <0.001 | ||
| Less | 85 (45.95) | 27 (29.35) | ||
| General | 66 (35.68) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.37) | 44 (47.82) | ||
| Dietary preference in past year | 7.407 | 0.025 | ||
| Less | 48 (25.95) | 11 (11.96) | ||
| General | 62 (33.51) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Often | 75 (40.54) | 47 (51.08) | ||
| Smoking in past year | 0.827 | 0.661 | ||
| Less | 109 (58.92) | 58 (63.04) | ||
| General | 42 (22.70) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.38) | 13 (14.13) | ||
| Drinking in the past year | 9.568 | 0.008 | ||
| Less | 95 (51.35) | 62 (67.39) | ||
| General | 48 (25.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| Often | 42 (22.70) | 8 (8.70) |
表 2 两组患者生活饮食习惯资料统计比较结果
Tab.2 Comparison of living and eating habits of the patients between the two groups [n(%)]
| Project | unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise frequency in past year | 3.714 | 0.156 | ||
| Less | 43 (23.24) | 16 (17.39) | ||
| General | 81 (43.78) | 35 (38.04) | ||
| Often | 61 (32.98) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Types of food in past year | 26.339 | <0.001 | ||
| Less | 85 (45.95) | 27 (29.35) | ||
| General | 66 (35.68) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.37) | 44 (47.82) | ||
| Dietary preference in past year | 7.407 | 0.025 | ||
| Less | 48 (25.95) | 11 (11.96) | ||
| General | 62 (33.51) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Often | 75 (40.54) | 47 (51.08) | ||
| Smoking in past year | 0.827 | 0.661 | ||
| Less | 109 (58.92) | 58 (63.04) | ||
| General | 42 (22.70) | 21 (22.83) | ||
| Often | 34 (18.38) | 13 (14.13) | ||
| Drinking in the past year | 9.568 | 0.008 | ||
| Less | 95 (51.35) | 62 (67.39) | ||
| General | 48 (25.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| Often | 42 (22.70) | 8 (8.70) |
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis (months) | 93.19±48.83 | 49.01±31.29 | 12.18 | 0.000 |
| Lesion site of colitis | 15.374 | 0.000 | ||
| Rectum | 34 (18.38) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| Colon | 151 (81.62) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Colitis activity | 48.751 | 0.000 | ||
| Mild | 41 (22.16) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Moderate | 85 (45.95) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Severe | 59 (31.89) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum (months) | 10.99±4.94 | 6.11±3.26 | 8.591 | 0.000 |
| Classification of pyoderma | 5.704 | 0.058 | ||
| Kuitang type | 78 (42.16) | 29 (31.52) | ||
| Pustular type | 42 (22.70) | 17 (18.48) | ||
| Proliferative type | 65 (35.14) | 46 (50.00) | ||
| Number of chronic diseases (types) | 4.18±2.85 | 2.89±2.02 | 6.814 | 0.000 |
| Self care ability | 14.304 | 0.001 | ||
| Unable to care on self | 11 (5.95) | 1 (1.09) | ||
| Partially self-care | 62 (33.51) | 15 (16.30) | ||
| Completely self-care | 112 (60.5) | 76 (82.61) | ||
| Sds score | 59.78±13.81 | 50.85±12.68 | 5.206 | 0.000 |
| Sas score | 62.98±12.26 | 51.83±11.33 | 6.004 | 0.000 |
| Denture or dental problems | 34 (18.38) | 5 (5.43) | 8.510 | 0.004 |
| Sleep quality in recent half a year | 47.101 | 0.000 | ||
| Poor | 85 (45.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| General | 94 (50.81) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Better | 6 (3.24) | 29 (31.52) |
表 3 两组患者疾病相关资料统计比较结果
Tab.3 Comparison of disease-related data between the two groups [Mean±SD, n(%)]
| Project | Unhealthy group (n=185) | Good group (n=92) | t/x2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis (months) | 93.19±48.83 | 49.01±31.29 | 12.18 | 0.000 |
| Lesion site of colitis | 15.374 | 0.000 | ||
| Rectum | 34 (18.38) | 37 (40.22) | ||
| Colon | 151 (81.62) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Colitis activity | 48.751 | 0.000 | ||
| Mild | 41 (22.16) | 55 (59.78) | ||
| Moderate | 85 (45.95) | 34 (36.96) | ||
| Severe | 59 (31.89) | 3 (3.26) | ||
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum (months) | 10.99±4.94 | 6.11±3.26 | 8.591 | 0.000 |
| Classification of pyoderma | 5.704 | 0.058 | ||
| Kuitang type | 78 (42.16) | 29 (31.52) | ||
| Pustular type | 42 (22.70) | 17 (18.48) | ||
| Proliferative type | 65 (35.14) | 46 (50.00) | ||
| Number of chronic diseases (types) | 4.18±2.85 | 2.89±2.02 | 6.814 | 0.000 |
| Self care ability | 14.304 | 0.001 | ||
| Unable to care on self | 11 (5.95) | 1 (1.09) | ||
| Partially self-care | 62 (33.51) | 15 (16.30) | ||
| Completely self-care | 112 (60.5) | 76 (82.61) | ||
| Sds score | 59.78±13.81 | 50.85±12.68 | 5.206 | 0.000 |
| Sas score | 62.98±12.26 | 51.83±11.33 | 6.004 | 0.000 |
| Denture or dental problems | 34 (18.38) | 5 (5.43) | 8.510 | 0.004 |
| Sleep quality in recent half a year | 47.101 | 0.000 | ||
| Poor | 85 (45.95) | 22 (23.91) | ||
| General | 94 (50.81) | 41 (44.57) | ||
| Better | 6 (3.24) | 29 (31.52) |
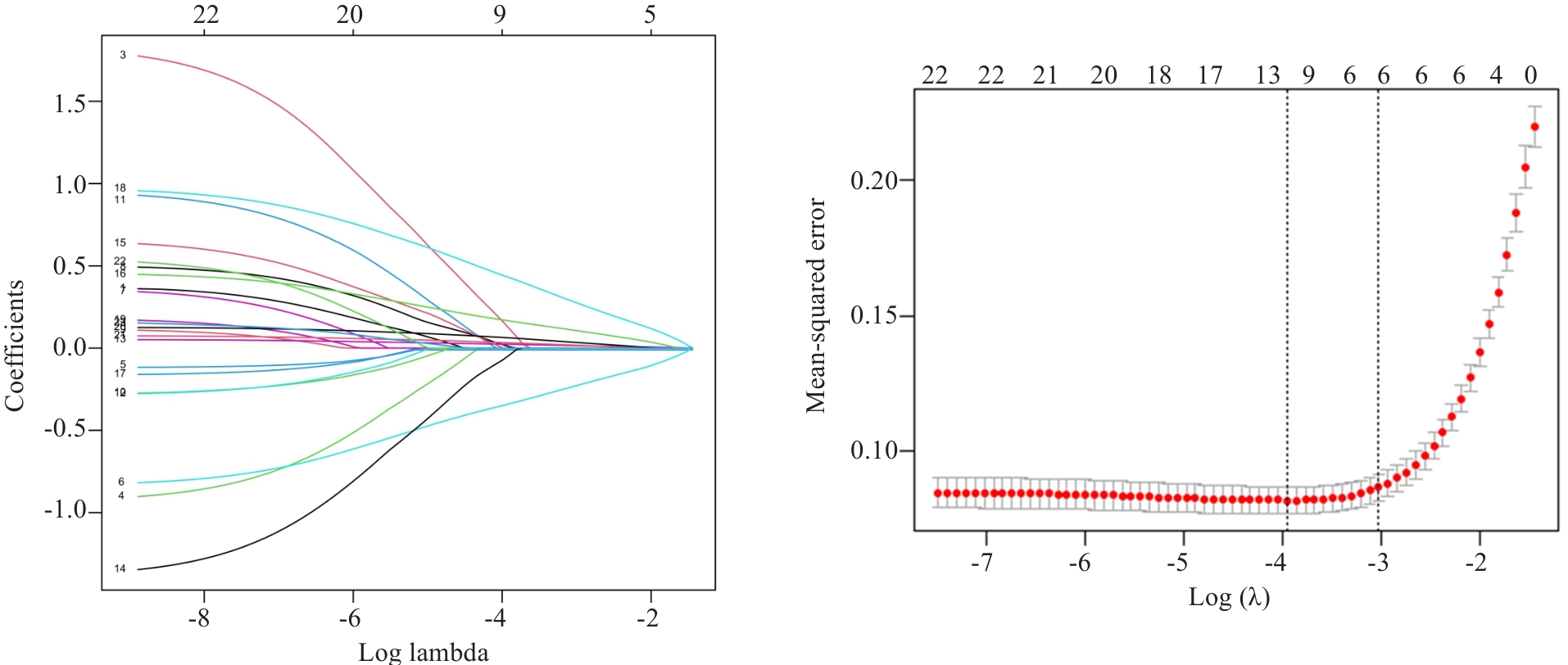
图1 Lasso回归系数图及交叉验证图
Fig.1 Lasso regression coefficient diagram and cross validation diagram. Lasso regression was used to analyze the association between each index and nutritional risk of the patients.
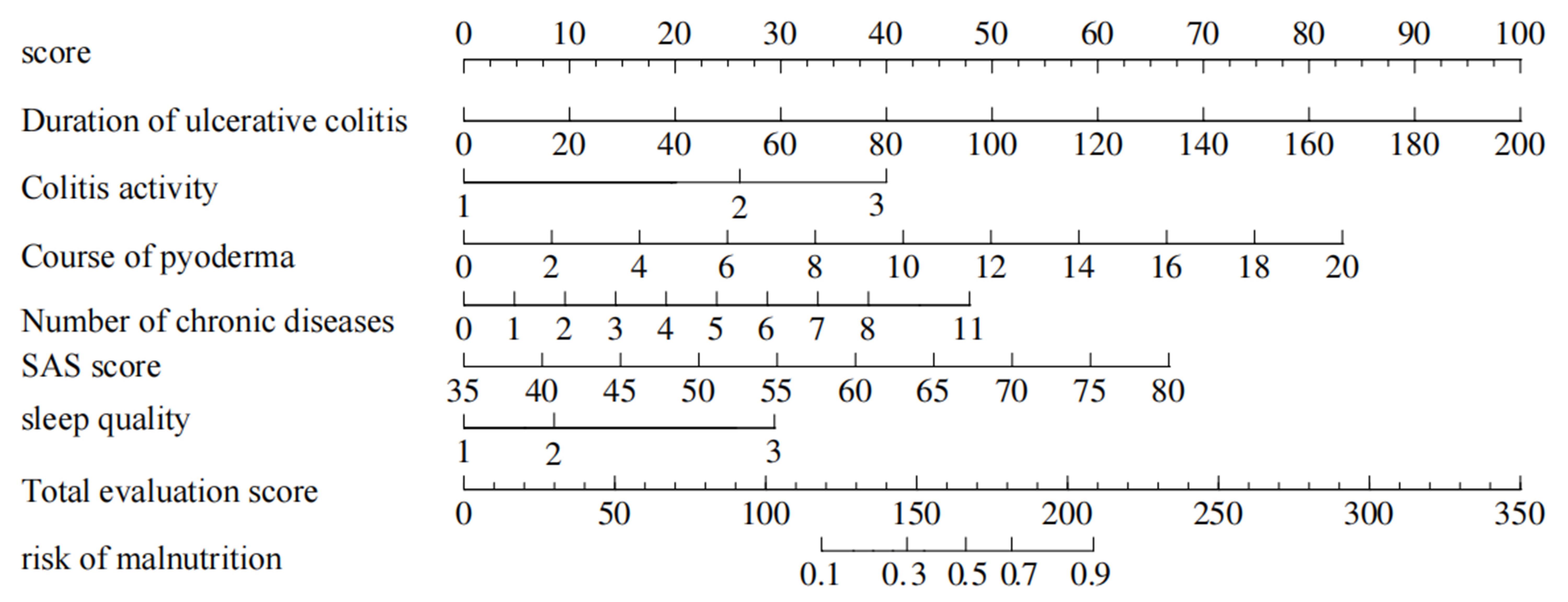
图2 溃疡性结肠炎伴发坏疽性脓皮病患者营养风险列线图预测模型
Fig.2 Nomogram prediction model of nutritional risk in patients with ulcerative colitis complicated with pyoderma gangrenosum based on the duration of ulcerative colitis, colitis activity, duration of pyoderma, number of chronic diseases, SAS score and sleep quality, showing the weighted scores of the 6 risk factors and the risk levels of the total score.
| Factors | β | S.E | Z | P | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis | 0.065 | 0.017 | 3.922 | 0.000 | 1.067 (1.033-1.102) |
| Colitis activity | |||||
| Mild | 1.000 | ||||
| Moderate | 2.541 | 1.116 | 2.277 | 0.023 | 2.694 (1.425-3.071) |
| Severe | 2.600 | 1.046 | 2.484 | 0.013 | 3.460 (1.731-4.645) |
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum | 0.539 | 0.164 | 3.280 | 0.001 | 1.715 (1.242-2.367) |
| Number of chronic diseases | 0.621 | 0.188 | 3.302 | 0.000 | 1.861 (1.287-2.690) |
| Sleep quality | |||||
| Better | 1.000 | ||||
| General | 0.742 | 0.950 | 0.781 | 0.435 | 1.101 (0.326-3.529) |
| Poor | 3.814 | 1.187 | 3.214 | 0.001 | 3.336 (1.429-6.088) |
| Sas score | 0.192 | 0.052 | 3.727 | 0.000 | 1.112 (1.025-1.341) |
表4 多因素Logistic回归分析结果
Tab.4 Results of multivariate logistic regression analysis
| Factors | β | S.E | Z | P | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of ulcerative colitis | 0.065 | 0.017 | 3.922 | 0.000 | 1.067 (1.033-1.102) |
| Colitis activity | |||||
| Mild | 1.000 | ||||
| Moderate | 2.541 | 1.116 | 2.277 | 0.023 | 2.694 (1.425-3.071) |
| Severe | 2.600 | 1.046 | 2.484 | 0.013 | 3.460 (1.731-4.645) |
| Course of pyoderma gangrenosum | 0.539 | 0.164 | 3.280 | 0.001 | 1.715 (1.242-2.367) |
| Number of chronic diseases | 0.621 | 0.188 | 3.302 | 0.000 | 1.861 (1.287-2.690) |
| Sleep quality | |||||
| Better | 1.000 | ||||
| General | 0.742 | 0.950 | 0.781 | 0.435 | 1.101 (0.326-3.529) |
| Poor | 3.814 | 1.187 | 3.214 | 0.001 | 3.336 (1.429-6.088) |
| Sas score | 0.192 | 0.052 | 3.727 | 0.000 | 1.112 (1.025-1.341) |
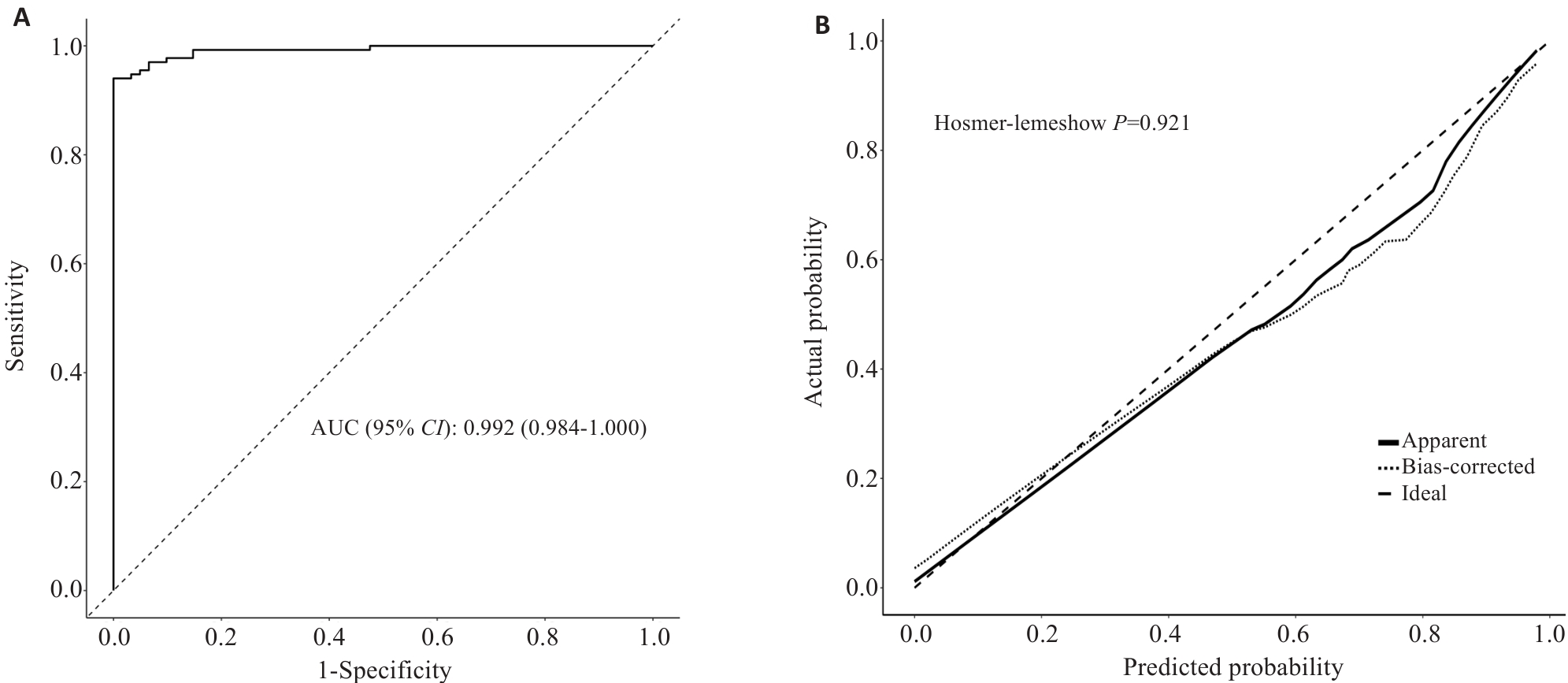
图3 列线图模型ROC曲线及校准曲线
Fig.3 Nomogram model ROC curve and the calibration curve. A: ROC curve analysis of the column chart prediction model for predicting the risk of malnutrition in patients. B: Calibration curve analysis of 1000 repeated sampling validations on the model.
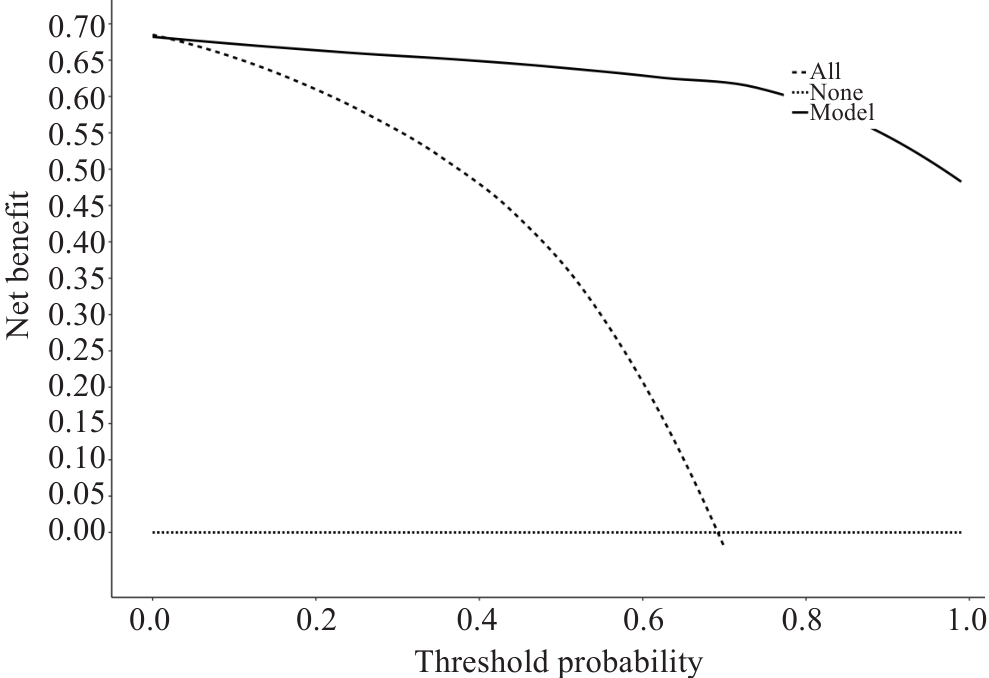
图4 列线图预测模型DCA决策曲线
Fig.4 Decision curve analysis of the nomogram model for predicting nutritional risk in the patients. The horizontal dashed line (none line) is the extreme case of all negatives, the oblique dashed line (all line) indicates the extreme case of all positives, the uppermost solid line curve (model line) indicates how the established prediction model makes decisions, and when the model line is higher than the all line, it indicates that the model prediction can be clinically beneficial.
| 1 | 中国中西医结合学会. 溃疡性结肠炎中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2023, 43(1): 5-11. |
| 2 | 宋泽军, 张明君, 任渝棠, 等. 改良Mayo内镜评分对溃疡性结肠炎有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 997-1005. |
| 3 | 焦雨竹, 杨 青. 坏疽性脓皮病治疗进展[J]. 中国麻风皮肤病杂志, 2024, 40(3): 216-20. |
| 4 | 单 玮, 雷春明, 肖 文, 等. 阙华发辨治溃疡性结肠炎并发坏疽性脓皮病经验[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2022, 49(3): 30-2. |
| 5 | Xu HM, Huang HL, Xu J, et al. Cross-talk between butyric acid and gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis following fecal microbiota transplantation[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 658292. |
| 6 | Chen QY, Fan YY, Zhang BZ, et al. Capsulized fecal microbiota transplantation induces remission in patients with ulcerative colitis by gut microbial colonization and metabolite regulation[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2023, 11(3): e0415222. |
| 7 | 袁 伟, 李 娟, 杨小娟, 等. 肠内营养对活动期溃疡性结肠炎伴营养不良患者营养状况、肠黏膜屏障功能和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2022, 22(14): 2658-62. |
| 8 | 刘仁娟, 田字彬, 王丹丹, 等. 溃疡性结肠炎病人生物电阻抗相位角与营养状况的关系研究[J]. 肠外与肠内营养, 2023, 30(6): 328-33. |
| 9 | 张文玉, 马贤纵, 谢 惠, 等. 炎症性肠病患者营养障碍的研究[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2024, 33(6): 641-5. |
| 10 | 楚俊红, 王丽敏, 樊虹雨, 等. 活动期溃疡性结肠炎住院病人营养风险研究[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(22): 4131-3. |
| 11 | Kondrup J, Rasmussen HH, Hamberg O, et al. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002): a new method based on an analysis of controlled clinical trials[J]. Clin Nutr, 2003, 22(3): 321-36. |
| 12 | 李军祥, 陈 誩. 溃疡性结肠炎中西医结合诊疗共识意见(2017年)[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2018, 26(2): 105-11, 120. |
| 13 | Jockenhöfer F, Wollina U, Salva KA, et al. The PARACELSUS score: a novel diagnostic tool for pyoderma gangrenosum[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2019, 180(3): 615-20. |
| 14 | 王征宇, 迟玉芬. 抑郁自评量表(SDS)[J]. 上海精神医学, 1984, 2: 71-2. |
| 15 | Dunstan DA, Scott N. Norms for zung's self-rating anxiety scale[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2020, 20(1): 90. |
| 16 | Sachan A, Thungapathra M, Kaur H, et al. Comprehensive assessment of nutritional and functional status of patients with ulcerative colitis and their impact on quality of life[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 2024, 43(1): 254-63. |
| 17 | Li XJ, Hu YD, Shi XD, et al. Prevalence and relevant factors of micronutrient deficiencies in hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nutrition, 2022, 99/100: 111671. |
| 18 | 刘仁娟, 田字彬, 荆 雪, 等. GLIM标准诊断的营养不良与溃疡性结肠炎住院患者疾病活动度及不良临床结局的关系[J]. 中华临床营养杂志, 2024, 32(2): 98-104. |
| 19 | Ünal NG, Oruç N, Tomey O, et al. Malnutrition and sarcopenia are prevalent among inflammatory bowel disease patients with clinical remission[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 33(11): 1367-75. |
| 20 | Kamel AY, Johnson ZD, Hernandez I, et al. Micronutrient deficiencies in inflammatory bowel disease: an incidence analysis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 36(10): 1186-92. |
| 21 | Zerouga I, Valeur J, Sommer C, et al. Dietary intake and nutritional status in patients with newly diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease: insights from the IBSEN III study[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2024, 59(6): 652-60. |
| 22 | Day AS, Davis R, Costello SP, et al. The adequacy of habitual dietary fiber intake in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review[J]. J Acad Nutr Diet, 2021, 121(4): 688-708. e3. |
| 23 | Jabłońska B, Mrowiec S. Nutritional status and its detection in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Nutrients, 2023, 15(8): 1991. |
| 24 | Whelan K, Murrells T, Morgan M, et al. Food-related quality of life is impaired in inflammatory bowel disease and associated with reduced intake of key nutrients[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2021, 113(4): 832-44. |
| 25 | Gold SL, Rabinowitz LG, Manning L, et al. High prevalence of malnutrition and micronutrient deficiencies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease early in disease course[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2023, 29(3): 423-9. |
| 26 | Dhaliwal A, Quinlan JI, Overthrow K, et al. Sarcopenia in inflammatory bowel disease: a narrative overview[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(2): 656. |
| 27 | Hashash JG, Elkins J, Lewis JD, et al. AGA clinical practice update on diet and nutritional therapies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: expert review[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 166(3): 521-32. |
| 28 | Skrzypczak D, Ratajczak AE, Szymczak-Tomczak A, et al. A vicious cycle of osteosarcopeniain inflammatory bowel diseases-aetiology, clinical implications and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(2): 293. |
| 29 | 荫士安, 董彩霞, 杨振宇. 遏制人群慢性病上升态势的全生命周期预防建议[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2024, 58(1): 107-13. |
| 30 | 王禹毅, 卜志军, 李元晞, 等. 临床预测模型变量筛选方法及比较[J]. 现代中医临床, 2024, 31(2): 6-12. |
| [1] | 赵娜, 沈梦迪, 赵睿, 奥迪, 骆泽谭, 张银亮, 徐志东, 范方田, 郑海伦. 血根碱通过调控Nrf2/NF-κB通路缓解小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1467-1475. |
| [2] | 于官正, 程炜强, 涂星, 张满, 李鸿, 聂娟. 隔山消治疗溃疡性结肠炎的机制:基于UPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及代谢组学技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1485-1496. |
| [3] | 潘甚豪, 李炎坤, 伍哲维, 毛玉玲, 王春艳. 子宫内膜异位症患者新鲜胚胎移植临床妊娠率预测模型的建立与验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1407-1415. |
| [4] | 申采玉, 王帅, 周锐盈, 汪雨贺, 高琴, 陈兴智, 杨枢. 慢性心力衰竭合并肺部感染患者院内死亡风险预测:基于可解释性机器学习方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1141-1148. |
| [5] | 戈 悦, 李建伟, 梁宏开, 侯六生, 左六二, 陈 珍, 卢剑海, 赵 新, 梁静漪, 彭 岚, 包静娜, 段佳欣, 刘 俐, 毛可晴, 曾振华, 胡鸿彬, 陈仲清. VA-ECMO患者院内死亡风险预测模型的构建及验证:一项多中心、回顾性、病例对照研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 491-498. |
| [6] | 金佳欣, 马鹏珍, 王尔玉, 谢颖桢. 急性缺血性卒中患者复发的独立影响因素及风险预测列线图模型构建:基于Lasso回归[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2375-2381. |
| [7] | 邱建国, 邱一桐, 李国荣, 张林生, 郑雪, 姚泳江, 王熙丹, 黄海阳, 张凤敏, 苏冀彦, 郑学宝, 黄晓其. 黄芩汤通过调控内质网应激减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| [8] | 宋泽军, 董海滨, 马 娜, 任渝棠, 姜 泊. 改进的MAYO内镜评分对活动期溃疡性结肠炎疗效有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1204-1213. |
| [9] | 张浩轩, 陆 进, 蒋成义, 方美芳. 基于人工智能技术的鼻咽癌风险预测模型的构建与评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [10] | 库尔班乃木·卡合曼, 赵健锋, 穆凯代斯·艾合买提, 王汉铭, 朱稷蔚, 潘文涛, 卡思木江·阿西木江. 屎肠球菌QH06能减轻溃疡性结肠炎大鼠的结肠黏膜损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 976-987. |
| [11] | 宋泽军, 张明君, 任渝棠, 姜 泊. 改良Mayo内镜评分对溃疡性结肠炎有较高的评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 997-1005. |
| [12] | 孟令飞, 朱学研, 杨立明, 李忻阳, 程思宇, 郭师正, 庄小花, 邹洪斌, 崔文鹏. 腹膜透析相关腹膜炎患者治疗失败预测模型的构建和验证:一项多中心临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(4): 546-553. |
| [13] | 邓 亚, 王春艳, 付懿铭, 李忠斌, 纪 冬. 慢性药物性肝损伤的复发风险与肝纤维化程度高度相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1655-1661. |
| [14] | 赵晨玲, 董 婷, 孙伦燕, 胡慧冰, 王 琼, 田丽伟, 江张胜. Wilson病脂代谢异常患者发生肝纤维化的列线图预测模型的建立与验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1720-1725. |
| [15] | 华 慧, 董 昕, 张雨钊, 方 凡, 张蓓蓓, 李向阳, 于 倩, 郑葵阳, 颜 超. 华支睾吸虫来源的分子伴侣rCsHscB对小鼠慢性溃疡性结肠炎有治疗作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 664-670. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||